Discovering the Sustainable Innovation Service Process of Organizational Environment, Information Sharing and Satisfaction: The Moderating Roles of Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- What factors may help to enhance sustainable innovation service?
- (2)
- What direct and indirect effects may exist in the relationship between the organizational environment and sustainable innovation services.
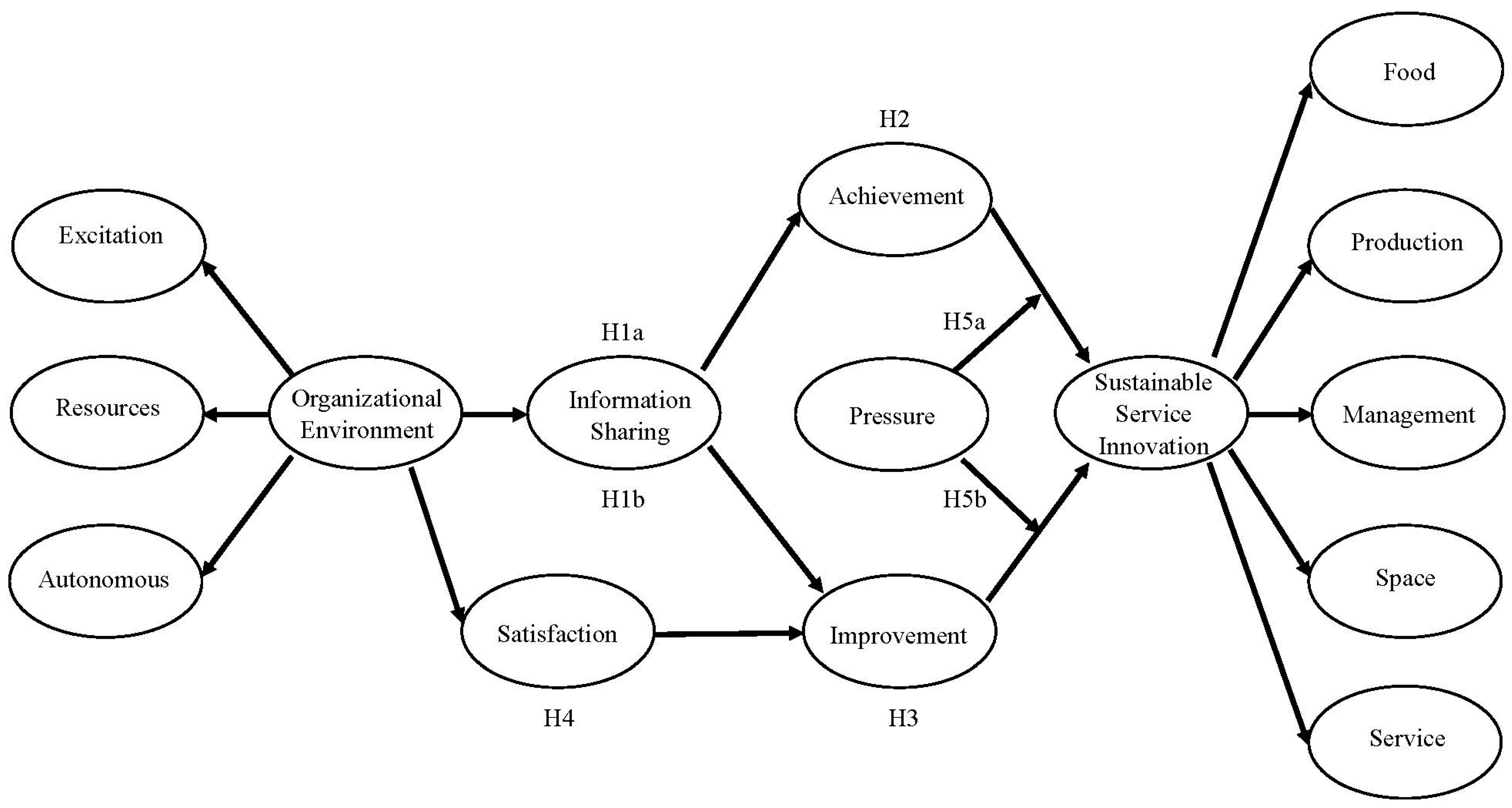
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Organizational Environment
2.2. Information Sharing
2.3. Sustainable Innovation Service
2.4. Achievement
2.5. Improvement
2.6. Satisfaction
2.7. Pressures
2.8. Innovation Diffusion Theory
2.9. Organizational Environment, Information Sharing, and Achievement
2.10. Information Sharing, Achievement, Improvement, and Sustainable Innovation Service
2.11. Mediating Role of Satisfaction
2.12. Moderating Role of Pressure
3. Methodology
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection
3.2. Variable Measurements
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Contribution
5.2. Managerial Contribution
5.3. Limitations and Future Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.-H.; Horng, J.-S.; Chou, S.-F.; Yu, T.-Y.; Lee, M.-T.; Lapuz, M.C.B. Discovery sustainable servicescape on behavioural intention practices and nationality: The moderating role of parasocial interaction. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2023, 71, 103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, C.; Luo, G.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Li, K.; Jiang, T.; Xiong, Q. User-Centered Software Design: User Interface Redesign for Blockly–Electron, Artificial Intelligence Educational Software for Primary and Secondary Schools. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Costa, R.; Ghiron, N.L.; Tiburzi, L.; Pedersen, E.R.G. How sustainable-orientated service innovation strategies are contributing to the sustainable development goals. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 169, 120816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hertog, P.; van der Aa, W.; de Jong, M.W. Capabilities for managing service innovation: Towards a conceptual framework. J. Serv. Manag. 2010, 21, 490–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Pung, J.M.; Del Chiappa, G. Exploring the nexus of tradition, modernity, and innovation in restaurant SMEs. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 100, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, S.J.S. Food Service Industry: Global Market Size 2020–2027. Statista 2021, 18, 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1095667/global-food-serErişimTarihi (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; She, B.; Li, Z. Diverged landscape of restaurant recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. iScience 2023, 26, 106811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hua, N. Transcending the COVID-19 crisis: Business resilience and innovation of the restaurant industry in China. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 49, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.T.; Wang, J. Building competitive advantage for hospitality companies: The roles of green innovation strategic orientation and green intellectual capital. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 102, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Horng, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Gan, B. Explicating restaurant performance: The nature and foundations of sustainable service and organizational environment. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 72, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabile, T.M. Creativity and Innovation in Organizations; Harvard Business School: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Horng, J.-S.; Chou, S.-F.; Liu, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-Y. Creativity, aesthetics and eco-friendliness: A physical dining environment design synthetic assessment model of innovative restaurants. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Tseng, T.-W. The multiple effects of service innovation and quality on transitional and electronic word-of-mouth in predicting customer behaviour. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 64, 102791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.J.; Ul Hameed, W.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, A.A.; Tariq, M.A.; Ahmed, S. Adoption of Sustainability Innovations and Environmental Opinion Leadership: A Way to Foster Environmental Sustainability through Diffusion of Innovation Theory. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Innovation Diffusion of Mobile Applications in Social Networks: A Multi-Agent System. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiau, S.J.H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-L.; Juang, J.-N. A Derivation of Factors Influencing the Innovation Diffusion of the OpenStreetMap in STEM Education. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, S.-F.; Horng, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chung, Y.-C. Expert Concepts of Sustainable Service Innovation in Restaurants in Taiwan. Sustainability 2016, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horng, J.-S.; Wang, C.-J.; Liu, C.-H.; Chou, S.-F.; Tsai, C.-Y. The Role of Sustainable Service Innovation in Crafting the Vision of the Hospitality Industry. Sustainability 2016, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afsar, B.; Masood, M.; Umrani, W.A. The role of job crafting and knowledge sharing on the effect of transformational leadership on innovative work behavior. Pers. Rev. 2019, 48, 1186–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikhamn, W. Innovation, sustainable HRM and customer satisfaction. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 76, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, A.X.; Zhou, K.Z.; Jiang, W. Environmental Strategy, Institutional Force, and Innovation Capability: A Managerial Cognition Perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 159, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, R. Innovating for sustainability: A framework for sustainable innovations and a model of sustainable innovations orientation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2017, 45, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberoglu, A. Impact of organizational climate on organizational commitment and perceived organizational performance: Empirical evidence from public hospitals. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robbins, S.P. Organizational Behavior: Concepts, Controversies, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, G.A.; Ford, N.M.; Walker, O.C. Organizational Climate and Job Satisfaction in the Salesforce. J. Mark. Res. 1976, 13, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, T.C.; Tajeddini, K. A multi-layer organizational culture framework for enhancing the financial performance in tourism and hospitality family firms. Tour. Manag. 2022, 91, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.-H.; Kang, H.-y. Effect of leadership style and organizational climate on employees’ food safety and hygiene behaviors in the institutional food service of schools. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryani Dhyan, P.; Mochammad, F.; Muhamad, E.; Acep, H. The Influence of Work Environment and Competence on Motivation and Its Impact on Employee Performance in Health Sector. In Proceedings of the 3rd Asia Pacific International Conference of Management and Business Science (AICMBS 2019), Batu, Indonesia, 30 October–1 November 2019; pp. 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ramasubbu, N.; Bardhan, I.R. Reconfiguring for agility: Examining the performance implications of project team autonomy through an organizational policy experiment. MIS Q. 2021, 45, 2261–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmann, J.; Guenther, E. Organizational Resilience: A Valuable Construct for Management Research? Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2021, 23, 7–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, H.M.; Yanamandra, R.J.U.S.C.M. Investigating the mediating role of information sharing strategy on agile supply chain. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 8, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Talja, S.; Hansen, P. Information Sharing. In New Directions in Human Information Behavior; Spink, A., Cole, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.C.H. Paternalistic leadership and employee voice: Does information sharing matter? Hum. Relat. 2013, 67, 667–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bonn, M.A.; Ye, B.H. Hotel employee’s artificial intelligence and robotics awareness and its impact on turnover intention: The moderating roles of perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate. Tour. Manag. 2019, 73, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kervenoael, R.; Hasan, R.; Schwob, A.; Goh, E. Leveraging human-robot interaction in hospitality services: Incorporating the role of perceived value, empathy, and information sharing into visitors’ intentions to use social robots. Tour. Manag. 2020, 78, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presenza, A.; Messeni Petruzzelli, A.; Sheehan, L. Innovation through tradition in hospitality. The Italian case of Albergo Diffuso. Tour. Manag. 2019, 72, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillo, V.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Ardito, L.; Del Giudice, M. Understanding sustainable innovation: A systematic literature review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shils Edward, A. Deference. In The Logic of Social Hierarchies; Laumann, E.O., Siegel, P.M., Hodge, R.W., Eds.; Markham: Chicago, IL, USA, 1970; pp. 420–448. [Google Scholar]
- Spenner, K.I.; Featherman, D.L. Achievement Ambitions. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1978, 4, 373–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.H. Are There Universal Aspects in the Structure and Contents of Human Values? J. Soc. Issues 1994, 50, 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lee, T.J.; Hyun, S.S. How does a global coffeehouse chain operate strategically in a traditional tea-drinking country? The influence of brand authenticity and self-enhancement. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 51, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, R. Improving Product Quality and Satisfaction as Fundamental Strategies in Strengthening Customer Loyalty. AKADEMIK J. Mhs. Ekon. Bisnis 2022, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, L.; Cabiddu, F. An agile marketing capability maturity framework. Tour. Manag. 2021, 86, 104347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, H. Continuous improvement philosophy—Literature review and directions. Benchmarking Int. J. 2015, 22, 75–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatulli, C.; De Angelis, M.; Stoppani, A. The appeal of sustainability in luxury hospitality: An investigation on the role of perceived integrity. Tour. Manag. 2021, 83, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersberger, B.; Herstad, S.J.; Nordli, A. Hospitality innovation strategies: Robustness analysis of paths to firm performance. Tour. Manag. 2021, 85, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.-W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z.-P.; Zhang, J. Exploring asymmetric effects of attribute performance on customer satisfaction in the hotel industry. Tour. Manag. 2020, 77, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshami, W.; Taha, M.H.; Abuzaid, M.; Saravanan, C.; Al Kawas, S.; Abdalla, M.E. Satisfaction with online learning in the new normal: Perspective of students and faculty at medical and health sciences colleges. Med. Educ. Online 2021, 26, 1920090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnawi, A.; Awang, Z.; Afthanorhan, A.; Mohamad, M.; Karim, F.J.M.S.L. The influence of hospital image and service quality on patients’ satisfaction and loyalty. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2019, 9, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- Gerdt, S.-O.; Wagner, E.; Schewe, G. The relationship between sustainability and customer satisfaction in hospitality: An explorative investigation using eWOM as a data source. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, R.; Zijlstra, F. Work Pressure. Results of a Conceptual and Empirical Analysis. 2000, pp. 29–45. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230627007_Work_pressure_Results_of_a_conceptual_and_empirical_analysis (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Shao, Y.; Nijstad, B.A.; Täuber, S. Creativity under workload pressure and integrative complexity: The double-edged sword of paradoxical leadership. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2019, 155, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijtendijk, H.; van Heiningen, J.; Duineveld, M. The productive role of innovation in a large tourism organisation (TUI). Tour. Manag. 2021, 85, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divisekera, S.; Nguyen, V.K. Determinants of innovation in tourism evidence from Australia. Tour. Manag. 2018, 67, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-C.; Chen, C.-H. Exploring the Innovation Diffusion of Big Data Robo-Advisor. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, W.; Meng, J.; Shi, J.; Zhu, J. A Study on the Impact Mechanism of Digitalization on Corporate Green Innovation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, C. Does Environmental Information Disclosure Affect the Sustainable Development of Enterprises: The Role of Green Innovation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, Y. A Study on the Impact of Digital Transformation on Corporate ESG Performance: The Mediating Role of Green Innovation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Qun, W.; Hui, L.; Shafi, A. Influence of Social Exchange Relationships on Affective Commitment and Innovative Behavior: Role of Perceived Organizational Support. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Chen, C.-C.; Suanpong, K.; Ruangkanjanases, A.; Kittikowit, S.; Chen, S.-C. The Impact of CSR on Sustainable Innovation Ambidexterity: The Mediating Role of Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Second-Order Social Capital. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, P.M.J.N.Y. Exchange and Power in Social Life; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1964; pp. 93–94. [Google Scholar]
- Roch, S.G.; Shannon, C.E.; Martin, J.J.; Swiderski, D.; Agosta, J.P.; Shanock, L.R. Role of employee felt obligation and endorsement of the just world hypothesis: A social exchange theory investigation in an organizational justice context. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2019, 49, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J. The Effectiveness of Augmented Reality in Physical Sustainable Education on Learning Behaviour and Motivation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Taeihagh, A.; Pande, D. Data Sharing in Disruptive Technologies: Lessons from Adoption of Autonomous Systems in Singapore. Policy Des. Pract. 2023, 6, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.M.; Veile, J.W.; Voigt, K.-I. Prerequisites and incentives for digital information sharing in Industry 4.0—An international comparison across data types. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 148, 106733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, C.W.; Sumaji, Y.M.P.; Susanto, H.; Septina, F.; Pratama, I. Effect of Supply Chain Management Practices on Financial and Economic Sustainable Performance of Indonesian SMEs. 2019. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337562303_Effect_of_Supply_Chain_Management_Practices_on_Financial_and_Economic_Sustainable_Performance_of_Indonesian_SMEs (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Wang, M.-H.; Yang, T.-Y. Investigating the success of knowledge management: An empirical study of small- and medium-sized enterprises. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2016, 21, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicchia, C.; Creazza, A.; Noè, C.; Strozzi, F. Information sharing in supply chains: A review of risks and opportunities using the systematic literature network analysis (SLNA). Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2019, 24, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.H.; Masoud, N.; Krishnan, M.S.; Li, V.C. Integrated digital twin and blockchain framework to support accountable information sharing in construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meihami, B.; Meihami, H. Knowledge Management a Way to Gain a Competitive Advantage in Firms (Evidence of Manufacturing Companies). Int. Lett. Soc. Humanist. Sci. 2012, 14, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Bahadur, W.; Wang, N.; Luqman, A.; Khan, A.N. Improving team innovation performance: Role of social media and team knowledge management capabilities. Technol. Soc. 2020, 61, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Talukdar, A.; Chatterjee, D. Evaluating the role of social capital, tacit knowledge sharing, knowledge quality and reciprocity in determining innovation capability of an organization. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 23, 1105–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.K.; Kang, S.; Jeong, H.Y. The Effect of Market Orientation on Performance of Sharing Economy Business: Focusing on Marketing Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage. Sustainability 2019, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imam, S.i.; Tarmini, W.; Hikmat, A.; Gusti Yanti, P. Competency achievement indicators in Indonesian high school electronic school books: Overview of the development of creative-innovative thinking aspects. KEMBARA J. Keilmuan Bhs. Sastra Dan Pengajarannya 2022, 8, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, R.; Nazeer, M.T.; Tabassum, F.; Atta, H.; Wahid, A.U.H. Relationship of sports participation with achievement, motivation, and innovation traits of the university students. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2021, 9, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Fatorachian, H.; Kazemi, H. Impact of Industry 4.0 on supply chain performance. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, C.M.; Ruiz-Eugenio, L.; Redondo-Sama, G.; Villarejo-Carballido, B. A New Application of Social Impact in Social Media for Overcoming Fake News in Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Could environmental regulation and R&D tax incentives affect green product innovation? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A.; Fernandes, F.A.P. Innovations in Teaching and Learning: Exploring the Perceptions of the Education Sector on the 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR). J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Whaley, J.E. Determinants of dining satisfaction. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2019, 28, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Li, X. Effects of corporate social responsibility on customer satisfaction and organizational attractiveness: A signaling perspective. Bus. Ethics Eur. Rev. 2020, 29, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, Z.; Alomari, K.; Aljawarneh, N. The role of empowerment in improving internal process, customer satisfaction, learning and growth. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2019, 10, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, B.; Spasojevic Brkic, V.K. Customer satisfaction and ISO 9001 improvement requirements in the supply chain. TQM J. 2019, 31, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.S.; Szymanski, D.M.; Varadarajan, R. Customer satisfaction and firm performance: Insights from over a quarter century of empirical research. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-A.; Kim, D.-Y. Does customer satisfaction increase firm performance? An application of American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI). Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 35, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Fang, H.; Jacoby, G.; Li, G.; Wu, Z. Environmental regulations and innovation for sustainability? Moderating effect of political connections. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2022, 50, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, M. Analysis on China’s eco-innovations: Regulation context, intertemporal change and regional differences. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 247, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, B. Environmental regulation and firm eco-innovation: Evidence of moderating effects of fiscal decentralization and political competition from listed Chinese industrial companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-P.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-T. Developing green management standards for restaurants: An application of green supply chain management. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 34, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Horng, J.-S.; Sam Liu, C.-H.; Lin, J.-Y. Identifying the critical factors of customer behavior: An integration perspective of marketing strategy and components of attitudes. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 55, 102113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sajjad, N.; Wang, Q.; Muhammad Ali, A.; Khaqan, Z.; Amina, S. Influence of Transformational Leadership on Employees’ Innovative Work Behavior in Sustainable Organizations: Test of Mediation and Moderation Processes. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistilis, N.; Buhalis, D.; Gretzel, U. Future eDestination Marketing: Perspective of an Australian Tourism Stakeholder Network. J. Travel Res. 2014, 53, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Chou, S.-F.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chung, Y.-C. From innovation to sustainability: Sustainability innovations of eco-friendly hotels in Taiwan. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 63, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.A. Education Reform, Redistribution, and Student Achievement: Evidence from the Kentucky Education Reform Act. Ph.D. Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Horng, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.S.; Chou, S.-F.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Hu, D.-C. Developing a sustainable service innovation framework for the hospitality industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Aen, M.; Amit, N.; Said, Z.; Siau, C.S. Victimisation, Depression and Suicidal Ideation among Lesbian, Gay and Bisexual Adults in Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. MJMS 2022, 29, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N. Factor Analysis as a Tool for Survey Analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 9, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.C.; Scott, N. Food experience, place attachment, destination image and the role of food-related personality traits. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2020, 44, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Q.; Ahmad, N.H.; Li, Y. Sustainable Leadership in Frontier Asia Region: Managerial Discretion and Environmental Innovation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Multifaceted trust in tourism service robots. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbongli, K.; Xu, Y.; Amedjonekou, K.M. Extended Technology Acceptance Model to Predict Mobile-Based Money Acceptance and Sustainability: A Multi-Analytical Structural Equation Modeling and Neural Network Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornell, C.; Bookstein, F.L. Two Structural Equation Models: LISREL and PLS Applied to Consumer Exit-Voice Theory. J. Mark. Res. 1982, 19, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dedeoğlu, B.B.; Bilgihan, A.; Ye, B.H.; Wang, Y.; Okumus, F. The role of elaboration likelihood routes in relationships between user-generated content and willingness to pay more. Tour. Rev. 2021, 76, 614–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, E.; Del Chiappa, G.; Coudounaris, D.N.; Björk, P. Tourism experiences, memorability and behavioural intentions: A study of tourists in Sardinia, Italy. Tour. Rev. 2020, 75, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W.J.P.b. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 103, 411. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, N. Detecting Multicollinearity in Regression Analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2020, 8, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Dash, S. Marketing Research An Applied Orientation (Seventh); Pearson Education: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.; Black, W.; Babin, B.; Anderson, R.J.H. Multivariate Data Analysis; Cengage Learning: Hampshire, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Shim, C. Social capital, knowledge sharing and innovation of small- and medium-sized enterprises in a tourism cluster. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 2417–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J.E. Applied Structural Equation Modeling Using AMOS: Basic to Advanced Techniques; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-H.S. Examining social capital, organizational learning and knowledge transfer in cultural and creative industries of practice. Tour. Manag. 2018, 64, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokols, D.; Clitheroe, C.; Zmuidzinas, M. Qualities of Work Environments That Promote Perceived Support for Creativity. Creat. Res. J. 2002, 14, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Horng, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, D.-C. Work environment and atmosphere: The role of organizational support in the creativity performance of tourism and hospitality organizations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 46, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ok, C.M. Knowledge sharing in hospitality organizations: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 95, 102940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.T. Knowledge sharing in the hospitality context: The roles of leader humility, job crafting, and promotion focus. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 94, 102848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.-J.; Yang, D.-Y. National innovation systems and the achievement of sustainable development goals: Effect of knowledge-based dynamic capability. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontis, N.; Richards, D.; Serenko, A. Improving service delivery: Investigating the role of information sharing, job characteristics, and employee satisfaction. Learn. Organ. 2011, 18, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paais, M.; Pattiruhu, J. Effect of Motivation, Leadership, and Organizational Culture on Satisfaction and Employee Performance. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2020, 7, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, O.I. Employee motivation and organizational performance. Rev. Appl. Socio-Econ. Res. 2013, 5, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Hallak, R.; Sardeshmukh, S.R. Creativity and innovation in the restaurant sector: Supply-side processes and barriers to implementation. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2019, 31, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, Q.B.; Maher, S.; Iqbal, N.; Shah, S.N.; Sheeraz, M.; Raheem, F.; Khan, K.I. Role of organizational environment in sustained organizational economic performance. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2022, 28, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, E.; Hidalgo, A.; Nuur, C. Diffusion of eco-innovations: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) | Accumulate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 191 | 42.07 | 42.07 |
| Female | 263 | 57.93 | 100.00 |
| Age | |||
| Younger than 20 years old | 108 | 23.79 | 23.79 |
| 21–30 years old | 254 | 55.95 | 79.74 |
| 31–40 years old | 59 | 13.00 | 92.73 |
| 41–50 years old | 23 | 5.07 | 97.80 |
| 51–60 years old | 10 | 2.20 | 100.00 |
| Education level | |||
| Senior high school | 73 | 16.08 | 16.08 |
| College | 70 | 15.42 | 31.50 |
| University | 310 | 68.28 | 99.78 |
| Graduate school | 1 | 0.22 | 100.00 |
| Work experience | |||
| Fewer than 5 years | 383 | 84.36 | 84.36 |
| 6–10 years | 43 | 9.47 | 93.83 |
| 11–20 years | 22 | 4.85 | 98.68 |
| 21–30 years | 5 | 1.10 | 99.78 |
| More than 30 years | 1 | 0.22 | 100.00 |
| Job level | |||
| Grassroots employee | 365 | 80.40 | 80.40 |
| Supervisor | 41 | 9.03 | 89.43 |
| Manager | 41 | 9.03 | 98.46 |
| Senior executive | 7 | 1.54 | 100.00 |
| Residence | |||
| Northern Taiwan | 353 | 77.75 | 77.75 |
| Central Taiwan | 48 | 10.57 | 88.33 |
| Southern Taiwan | 38 | 8.37 | 96.70 |
| Eastern Taiwan | 15 | 3.30 | 100.00 |
| Other | |||
| Restaurant type | |||
| Hotel restaurant | 126 | 27.75 | 27.75 |
| Restaurant | 230 | 50.66 | 78.41 |
| Fast food restaurant | 80 | 17.62 | 96.04 |
| Snack shop | 4 | 0.88 | 96.92 |
| Beverage shop | 11 | 2.42 | 99.34 |
| Other | 3 | 0.66 | 100.00 |
| Department | |||
| Kitchen | 116 | 25.55 | 25.55 |
| Service | 306 | 67.40 | 92.95 |
| Other | 32 | 7.05 | 100.00 |
| Measurement Variables | Mean | Standard Deviation | Factor Loading | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Environment | |||||
| Excitation (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8431) | 0.845 | 0.731 | |||
| The company has a sound internal mechanism that encourages employees to develop new ideas. | 5.12 | 1.235 | 0.821 | ||
| The company highly values the cultivation and retention of related technical talents. | 5.13 | 1.222 | 0.888 | ||
| Resources (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8545) | 0.858 | 0.670 | |||
| The company can fully supply the necessary funds or budgets for innovation. | 5.13 | 1.148 | 0.808 | ||
| The company can provide human resource support for innovation. | 5.09 | 1.179 | 0.888 | ||
| The company can fully provide the required equipment. | 5.19 | 1.142 | 0.754 | ||
| Autonomous (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8952) | 0.899 | 0.692 | |||
| Employees are free to choose what work they want to do. | 4.64 | 1.378 | 0.728 | ||
| Employees are free to decide how to implement their own plans. | 4.72 | 1.371 | 0.867 | ||
| Employees can independently decide on the content of their work. | 4.63 | 1.390 | 0.918 | ||
| Employees can independently control their own work progress. | 4.66 | 1.410 | 0.802 | ||
| Information Sharing (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8745) | 0.875 | 0.701 | |||
| Companies provide us with opportunities to share unique life experiences. | 4.91 | 1.324 | 0.783 | ||
| The company encourages its members to share work experiences. | 5.04 | 1.260 | 0.854 | ||
| The company encourages its members to share learning experiences. | 5.11 | 1.209 | 0.872 | ||
| Achievement (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.9109) | 0.913 | 0.723 | |||
| Company members set goals for themselves and are willing to achieve them. | 5.38 | 1.167 | 0.825 | ||
| Company members are willing to accept more difficult but achievable tasks. | 5.29 | 1.182 | 0.901 | ||
| Company members are willing to face challenges. | 5.34 | 1.149 | 0.879 | ||
| Company members have a strong will and are willing to pursue higher achievements. | 5.28 | 1.172 | 0.793 | ||
| Improvement (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8272) | 0.841 | 0.729 | |||
| Company members actively seek ways to improve organizational operations. | 5.15 | 1.218 | 0.953 | ||
| Most company members are willing to challenge new operating methods. | 5.12 | 1.160 | 0.741 | ||
| Sustainable Innovation Service | |||||
| Food (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8727) | 0.878 | 0.707 | |||
| The restaurant actively seeks and uses local ingredients for sustainable innovation. | 5.11 | 1.226 | 0.817 | ||
| The restaurant uses seasonal ingredients to develop innovative products. | 5.30 | 1.185 | 0.917 | ||
| The restaurant encourages the use of natural ingredients for new product development. | 5.34 | 1.212 | 0.783 | ||
| Production (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.7325) | 0.733 | 0.578 | |||
| The restaurant encourages customers to bring their own utensils and bags to reduce disposable waste. | 5.12 | 1.152 | 0.763 | ||
| The restaurant uses energy-saving and water-saving innovative cooking equipment. | 5.31 | 1.169 | 0.758 | ||
| Management (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8789) | 0.882 | 0.653 | |||
| Sustainable innovation is included in the restaurant’s management policy. | 5.32 | 1.215 | 0.791 | ||
| Innovative management is used to reduce waste and costs. | 5.19 | 1.138 | 0.847 | ||
| The company provides employees with new concepts of pollution prevention and control management. | 5.20 | 1.226 | 0.863 | ||
| The company uses a new management system to improve efficiency and reduce waste. | 5.27 | 1.125 | 0.724 | ||
| Space (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.7918) | 0.797 | 0.569 | |||
| Most of my restaurant uses green building materials. | 4.85 | 1.364 | 0.847 | ||
| The restaurant’s space uses innovative energy-saving designs for ventilation, lighting, and insulation. | 5.07 | 1.226 | 0.758 | ||
| Recyclable or second-hand furniture is used in the restaurant’s decor as much as possible. | 4.88 | 1.341 | 0.645 | ||
| Service (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.7735) | 0.781 | 0.476 | |||
| We use online marketing as much as possible to reduce printing waste. | 5.12 | 1.211 | 0.688 | ||
| The restaurant’s service process understands the production history of ingredients through information systems. | 5.10 | 1.290 | 0.520 | ||
| The restaurant’s service uses more environmentally friendly ordering methods, such as barcodes, PDAs, or online tools. | 5.10 | 1.421 | 0.749 | ||
| We promote more environmentally friendly service methods (such as bringing one’s own utensils) to customers during the service process. | 4.92 | 1.532 | 0.775 | ||
| Pressure (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.9206) | 0.923 | 0.799 | |||
| The company gives employees a heavy workload, making it impossible for them to innovate. | 4.43 | 1.548 | 0.843 | ||
| The company usually does not give us enough time when we are innovating. | 4.35 | 1.542 | 0.944 | ||
| Company policies often hinder our ability to innovate. | 4.37 | 1.585 | 0.892 | ||
| Satisfaction (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.8883) | 0.891 | 0.732 | |||
| Sustainable innovation services can increase customer satisfaction. | 5.42 | 1.080 | 0.804 | ||
| Sustainable innovation services bring more new customers to the restaurant. | 5.46 | 1.083 | 0.919 | ||
| Sustainable innovation services can increase customer willingness to spend. | 5.52 | 1.115 | 0.840 |
| Construct | E | R | Au | IS | S | Ac | I | P | F | Pr | M | Sp | Se | Variance Inflation Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization Environment (OE) | ||||||||||||||
| Excitation (E) | (0.8431) | 1.94 | ||||||||||||
| Resources (R) | 0.5626 *** | (0.8545) | 1.87 | |||||||||||
| Autonomous (Au) | 0.1681 *** | 0.2805 *** | (0.8952) | 1.51 | ||||||||||
| Information Sharing (IS) | 0.4629 *** | 0.4021 *** | 0.1989 *** | (0.8745) | 2.01 | |||||||||
| Satisfaction (S) | 0.3533 *** | 0.3425 *** | 0.0149 | 0.3070 *** | (0.8883) | 1.30 | ||||||||
| Achievement (Ac) | 0.3923 *** | 0.3638 *** | 0.0627 | 0.3694 *** | 0.3576 *** | (0.9109) | 1.53 | |||||||
| Improvement (I) | 0.3961 *** | 0.3970 *** | 0.1543 *** | 0.6575 *** | 0.3120 *** | 0.4508 *** | (0.8272) | 1.99 | ||||||
| Pressure(P) | −0.0158 | 0.0030 | 0.4836 *** | 0.0527 | −0.0762 | −0.1395** | −0.0037 | (0.9206) | 1.41 | |||||
| Sustainable Innovation Service (SIS) | ||||||||||||||
| Food (F) | 0.3054 *** | 0.3702 *** | 0.1336 ** | 0.2953 *** | 0.2822 *** | 0.3123 *** | 0.2892 *** | 0.0145 | (0.8727) | 1.53 | ||||
| Production (Pr) | 0.3603 *** | 0.4210 *** | 0.2000 *** | 0.3277 *** | 0.2685 *** | 0.3347 *** | 0.3119 *** | −0.0011 | 0.5171 *** | (0.7325) | 1.88 | |||
| Management (M) | 0.4546 *** | 0.4522 *** | 0.1163 *** | 0.3912 *** | 0.3367 *** | 0.4410 *** | 0.3896 *** | −0.0865 * | 0.5040 *** | 0.6152 *** | (0.8789) | 2.27 | ||
| Space (Sp) | 0.3757 *** | 0.4783 *** | 0.3068 *** | 0.3945 *** | 0.1992 *** | 0.2361 *** | 0.3496 *** | 0.1409 ** | 0.3603 *** | 0.4764 *** | 0.5444 *** | (0.7918) | 1.89 | |
| Service (Se) | 0.5445 *** | 0.4397 *** | 0.1668 *** | 0.3773 *** | 0.2740 *** | 0.2757 *** | 0.3492 *** | 0.0657 | 0.2964 *** | 0.3697 *** | 0.4363 *** | 0.4930 *** | (0.7735) | 1.70 |
| Mean | 5.129 | 5.137 | 4.663 | 5.020 | 5.470 | 5.322 | 5.134 | 4.384 | 5.252 | 5.217 | 5.245 | 4.933 | 5.060 | |
| S.D. | 1.142 | 1.018 | 1.210 | 1.131 | 0.988 | 1.037 | 1.098 | 1.448 | 1.078 | 1.031 | 1.008 | 1.102 | 1.057 |
| No | Constructs | Indirect Effect | Percentile 95% CI | Bias-corrected 95% CI | p-Value | Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| 1 | Organization Environment > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.316 | 0.223 | 0.443 | 0.221 | 0.440 | *** | Support |
| 2 | Organization Environment > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.650 | 0.509 | 0.838 | 0.507 | 0.834 | *** | Support |
| 3 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Sustainable Innovation Service | 0.078 | 0.038 | 0.131 | 0.038 | 0.132 | *** | Support |
| 4 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Sustainable Innovation Service | 0.206 | 0.128 | 0.295 | 0.131 | 0.298 | *** | Support |
| 5 | Organization Environment > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.056 | 0.001 | 0.110 | 0.004 | 0.113 | * | Support |
| (a) Analysis of Mediation Effects in Alternative Model 1 | ||||||||
| No | Constructs | Indirect Effect | Percentile 95% CI | Bias-Corrected 95% CI | p-Value | Results | ||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| 1 | Excitation > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.165 | 0.107 | 0.236 | 0.109 | 0.238 | *** | Support |
| 2 | Excitation > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.339 | 0.233 | 0.449 | 0.233 | 0.449 | *** | Support |
| 3 | Resources > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.119 | 0.051 | 0.203 | 0.051 | 0.204 | *** | Support |
| 4 | Resources > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.245 | 0.115 | 0.380 | 0.111 | 0.375 | *** | Support |
| 5 | Autonomous > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.037 | −0.004 | 0.077 | −0.006 | 0.074 | insignificant | Not support |
| 6 | Autonomous > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.075 | −0.008 | 0.164 | −0.015 | 0.159 | insignificant | Not support |
| 7 | Excitation > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.034 | 0.004 | 0.067 | 0.007 | 0.073 | * | Support |
| 8 | Resources > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.028 | 0.002 | 0.065 | 0.005 | 0.070 | * | Support |
| 9 | Autonomous > Satisfaction > Improvement | −0.009 | −0.025 | 0.003 | −0.028 | 0.001 | insignificant | Not support |
| 10 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Sustainable Innovation Service | 0.078 | 0.038 | 0.130 | 0.038 | 0.131 | *** | Support |
| 11 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Sustainable Innovation Service | 0.206 | 0.128 | 0.294 | 0.131 | 0.299 | *** | Support |
| 12 | Satisfaction > Improvement > Sustainable Innovation Service | 0.031 | 0.004 | 0.071 | 0.006 | 0.078 | * | Support |
| (b) Analysis of Mediation Effects in Alternative Model 2 | ||||||||
| No | Constructs | Indirect Effect | Percentile 95% CI | Bias-Corrected 95% CI | p-Value | Results | ||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| 1 | Organizational Environment > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.332 | 0.229 | 0.466 | 0.232 | 0.474 | *** | Support |
| 2 | Organizational Environment > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.557 | 0.300 | 0.797 | 0.280 | 0.766 | ** | Support |
| 3 | Organizational Environment > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.092 | 0.033 | 0.148 | 0.043 | 0.160 | *** | Support |
| 4 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Food | 0.044 | −0.034 | 0.135 | −0.035 | 0.131 | insignificant | Not support |
| 5 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Production | 0.039 | −0.036 | 0.143 | −0.039 | 0.138 | insignificant | Not support |
| 6 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Management | 0.067 | −0.010 | 0.171 | −0.010 | 0.171 | insignificant | Not support |
| 7 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Space | −0.032 | −0.123 | 0.074 | −0.138 | 0.060 | insignificant | Not support |
| 8 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Service | 0.012 | −0.059 | 0.109 | −0.070 | 0.100 | insignificant | Not support |
| 9 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Food | 0.355 | 0.167 | 0.488 | 0.194 | 0.514 | *** | Support |
| 10 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Production | 0.396 | 0.180 | 0.536 | 0.203 | 0.557 | *** | Support |
| 11 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Management | 0.442 | 0.227 | 0.577 | 0.255 | 0.597 | *** | Support |
| 12 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Space | 0.605 | 0.361 | 0.755 | 0.429 | 0.807 | *** | Support |
| 13 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Service | 0.521 | 0.306 | 0.665 | 0.371 | 0.726 | *** | Support |
| (c) Analysis of Mediation Effects in Alternative Model 3 | ||||||||
| No | Constructs | Indirect Effect | Percentile 95% CI | Bias-Corrected 95% CI | p-Value | Results | ||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| 1 | Excitation > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.172 | 0.112 | 0.243 | 0.115 | 0.247 | *** | Support |
| 2 | Excitation > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.288 | 0.153 | 0.421 | 0.151 | 0.417 | *** | Support |
| 3 | Resources > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.126 | 0.054 | 0.214 | 0.059 | 0.221 | *** | Support |
| 4 | Resources > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.211 | 0.081 | 0.350 | 0.083 | 0.354 | *** | Support |
| 5 | Autonomous > Information Sharing > Achievement | 0.042 | 0.002 | 0.082 | 0.001 | 0.082 | * | Support |
| 6 | Autonomous > Information Sharing > Improvement | 0.070 | 0.003 | 0.144 | 0.003 | 0.145 | * | Support |
| 7 | Excitation > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.054 | 0.020 | 0.087 | 0.026 | 0.098 | *** | Support |
| 8 | Resources > Satisfaction > Improvement | 0.046 | 0.011 | 0.087 | 0.015 | 0.097 | *** | Support |
| 9 | Autonomous > Satisfaction > Improvement | −0.014 | −0.032 | 0.004 | −036 | 0.001 | insignificant | Not support |
| 10 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Food | 0.043 | −0.034 | 0.133 | −0.035 | 0.130 | insignificant | Not support |
| 11 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Production | 0.038 | −0.036 | 0.142 | −0.040 | 0.135 | insignificant | Not support |
| 12 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Management | 0.066 | −0.010 | 0.169 | −0.010 | 0.169 | insignificant | Not support |
| 13 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Space | −0.032 | −0.122 | 0.073 | −0.137 | 0.059 | insignificant | Not support |
| 14 | Information Sharing > Achievement > Service | 0.011 | −0.059 | 0.107 | −0.069 | 0.098 | insignificant | Not support |
| 15 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Food | 0.355 | 0.168 | 0.486 | 0.193 | 0.509 | *** | Support |
| 16 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Production | 0.396 | 0.180 | 0.533 | 0.204 | 0.551 | *** | Support |
| 17 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Management | 0.442 | 0.227 | 0.573 | 0.256 | 0.594 | *** | Support |
| 18 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Space | 0.605 | 0.361 | 0.751 | 0.430 | 0.803 | *** | Support |
| 19 | Information Sharing > Improvement > Service | 0.521 | 0.306 | 0.660 | 0.373 | 0.724 | *** | Support |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-H.; La, Q.P.; Ng, Y.-L.; Mamengko, R.P. Discovering the Sustainable Innovation Service Process of Organizational Environment, Information Sharing and Satisfaction: The Moderating Roles of Pressure. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411445
Liu C-H, La QP, Ng Y-L, Mamengko RP. Discovering the Sustainable Innovation Service Process of Organizational Environment, Information Sharing and Satisfaction: The Moderating Roles of Pressure. Sustainability. 2023; 15(14):11445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411445
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chih-Hsing, Quoc Phong La, Yen-Ling Ng, and Rullyana Puspitaningrum Mamengko. 2023. "Discovering the Sustainable Innovation Service Process of Organizational Environment, Information Sharing and Satisfaction: The Moderating Roles of Pressure" Sustainability 15, no. 14: 11445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411445
APA StyleLiu, C.-H., La, Q. P., Ng, Y.-L., & Mamengko, R. P. (2023). Discovering the Sustainable Innovation Service Process of Organizational Environment, Information Sharing and Satisfaction: The Moderating Roles of Pressure. Sustainability, 15(14), 11445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411445


_Li.png)






