The Relationship between Environmental Quality, Sustainable Health, and the Coronavirus Pandemic in European Countries
Abstract
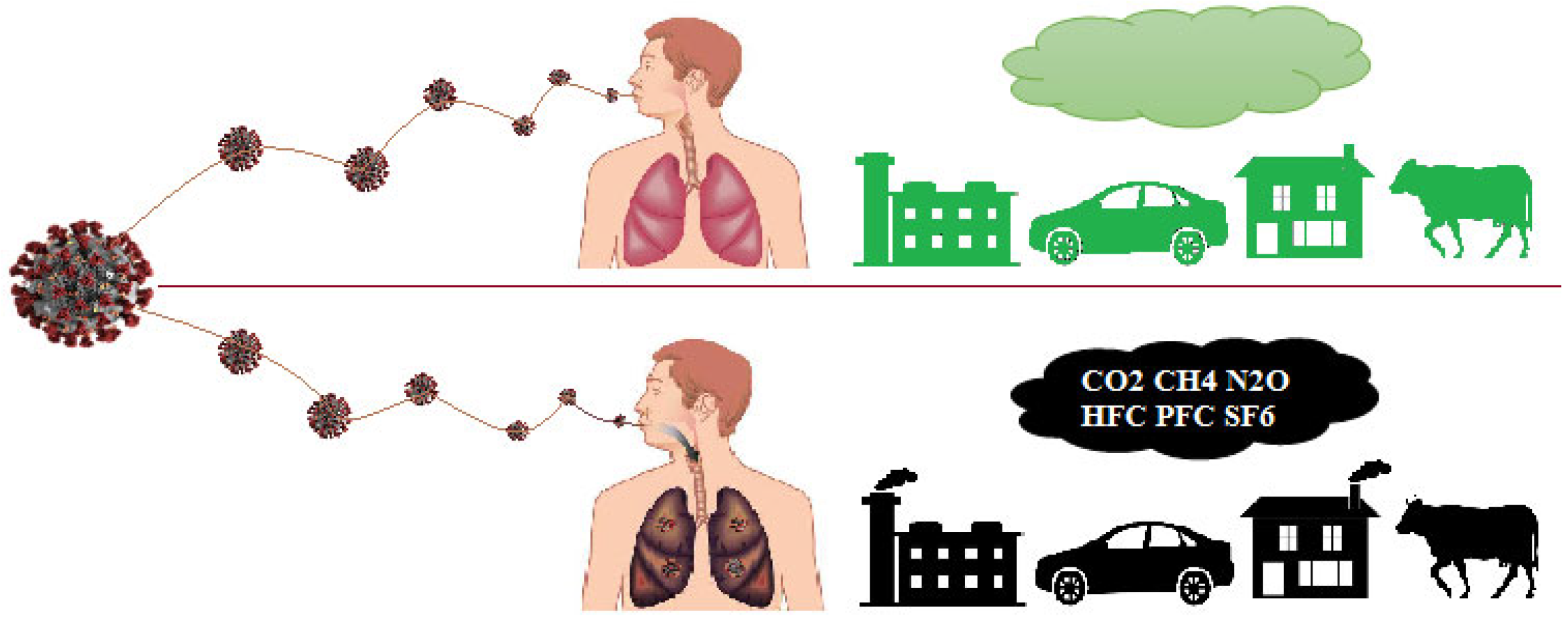
1. Introduction
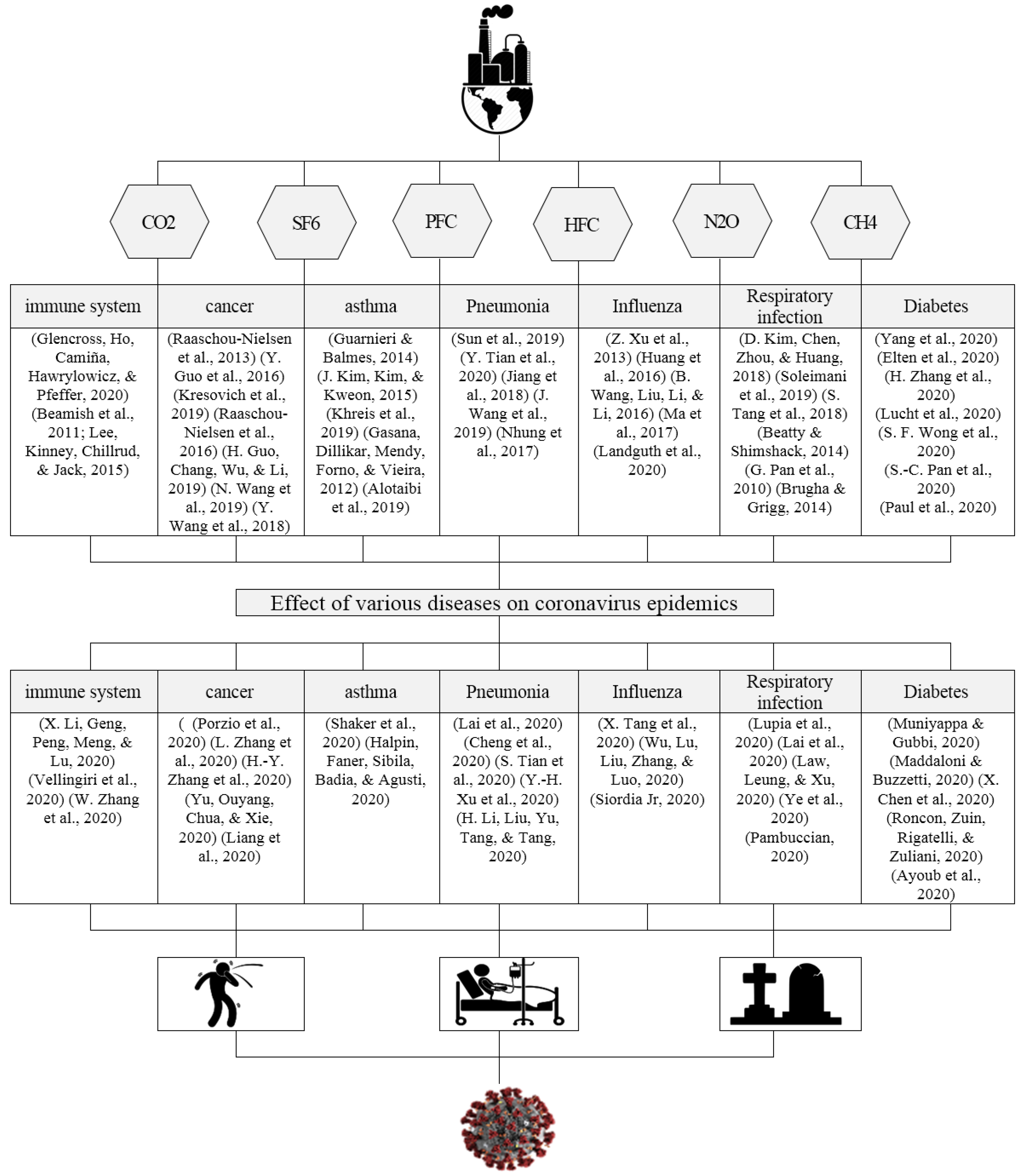
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Variables and Data Source
3.1.1. Environmental Pollutant Gases in the European Countries
3.1.2. Coronavirus Cases in the European Countries
3.2. Statistical Methods
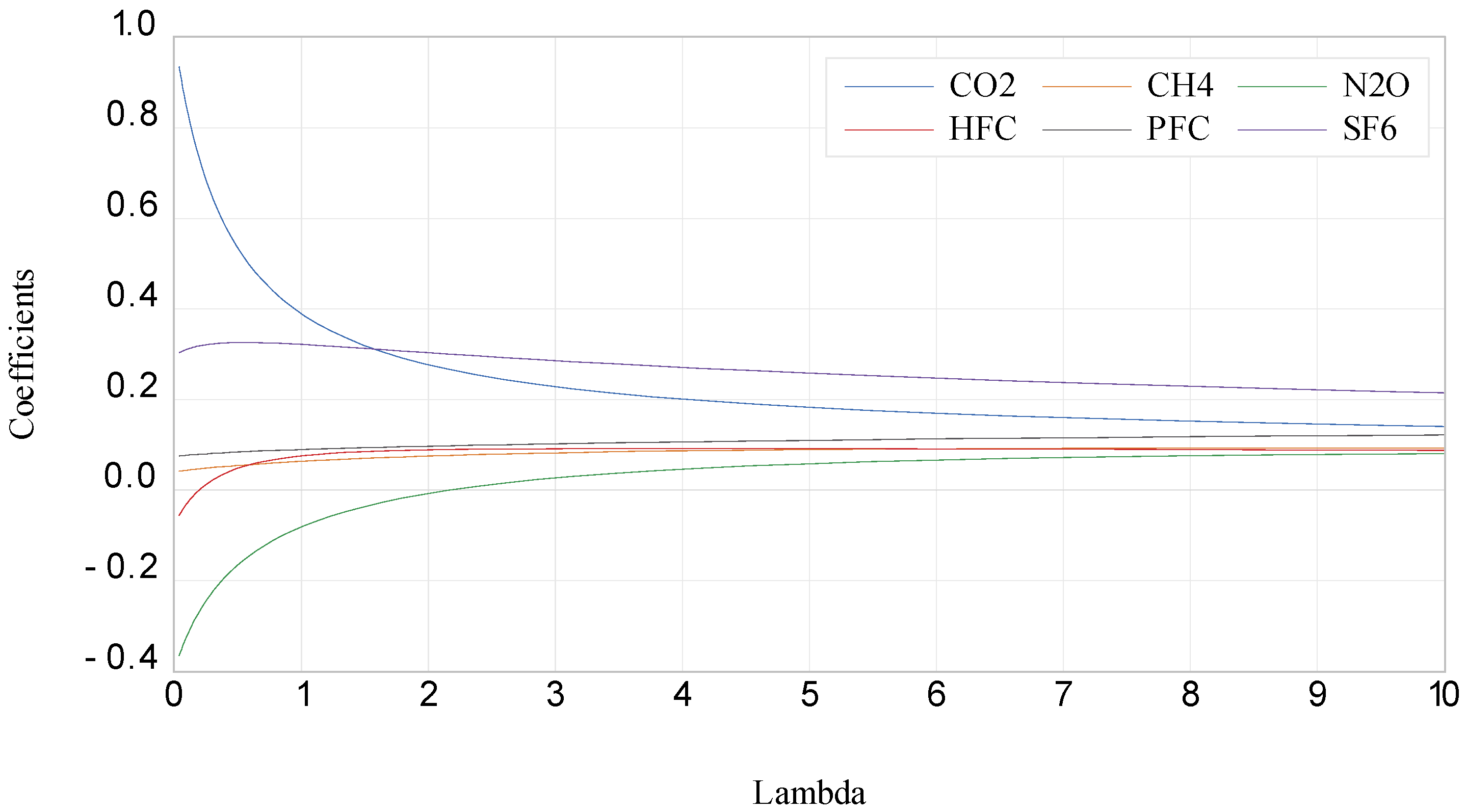
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research Directions
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Limitations
6.3. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayat, R.; Ashrafi, K.; Motlagh, M.S.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Daroudi, R.; Fink, G.; Künzli, N. Health impact and related cost of ambient air pollution in Tehran. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schikowski, T.; Altug, H. The role of air pollution in cognitive impairment and decline. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 136, 104708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, L.A.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Wine, E. Air pollution: An environmental factor contributing to intestinal disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2011, 5, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Kinney, P.; Chillrud, S.; Jack, D. A systematic review of innate immunomodulatory effects of household air pollution secondary to the burning of biomass fuels. Ann. Glob. Health 2015, 81, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, D.A.; Ho, T.-R.; Camiña, N.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; Pfeffer, P.E. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tian, L.; Cao, W.; Lai, P.-C.; Wong, P.P.Y.; Lee, R.S.-y.; Mason, T.G.; Krämer, A.; Wong, C.-M. Urban climate modified short-term association of air pollution with pneumonia mortality in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, W.; Williams, G.; Clements, A.C.; Kan, H.; Tong, S. Air pollution, temperature and pediatric influenza in Brisbane, Australia. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.-F.; Huang, S.-X. Air pollutants and early origins of respiratory diseases. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cheng, H.; Shen, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Ding, R. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellingiri, B.; Jayaramayya, K.; Iyer, M.; Narayanasamy, A.; Govindasamy, V.; Giridharan, B.; Ganesan, S.; Venugopal, A.; Venkatesan, D.; Ganesan, H. COVID-19: A promising cure for the global panic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, F.; Xie, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Jia, P.; Guan, H.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19-infected cancer patients: A retrospective case study in three hospitals within Wuhan, China. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Yen, M.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Du, R.; Wang, R.; Cao, T.; Guan, L.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Comparison of Hospitalized Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Caused by COVID-19 and H1N1. Chest 2020, 158, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, B.M.; Ramadan, E.; Ashoush, N.; Tadros, M.M.; Hendy, M.S.; Elmazar, M.M.; Mousa, S.A. Avoiding COVID-19 Complications with Diabetic Patients Could Be Achieved by Multi-Dose Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Vaccine: A Case Study of Beta Cells Regeneration by Serendipity. Die Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 75, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajirahimova, M.S.; Aliyeva, A.S. Analyzing the Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Confirmed Cases and Deaths in Azerbaijan Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Adigun, J.O.; Irunokhai, E.A.; Adeniji, O.A.; Areo, Y.M.; Onihunwa, J.O.; Sada, Y.A.; Jeje, C.A. Role of Coronavirus Outbreak on Adoption of Electronic Education in New Bussa, Niger State, Nigeria. Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng. 2021, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Sunwoo, Y. Impact of Aviation Emissions and its Changes Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic on Air Quality in South Korea. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Vissa, N.K.; Ghude, S.D. Evolution of Pollution Levels from COVID-19 Lockdown to Post-Lockdown over India. Toxics 2022, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapungu, L.; Nhamo, G.; Chikodzi, D.; Maoela, M.A. BRICS and the Race to Net-Zero Emissions by 2050: Is COVID-19 a Barrier or an Opportunity? J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderipour, A.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Ahmad, N.A.; Kamyab, H.; Ashokkumar, V.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C.; Chelliapan, S. Effect of COVID-19 virus on reducing GHG emission and increasing energy generated by renewable energy sources: A brief study in Malaysian context. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedushko, S.; Ustyianovych, T. Medical card data imputation and patient psychological and behavioral profile construction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 160, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannarini, G.; Salinas, M.L.; Carelli, L.; Fassò, A. How COVID-19 Affected GHG Emissions of Ferries in Europe. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Darzi, A.; Kabiri, A.; Zhao, G.; Luo, W.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, L. Quantifying human mobility behaviour changes during the COVID-19 outbreak in the United States. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Deng, Z.; Lei, R.; Davis, S.J.; Feng, S.; Zheng, B.; Cui, D.; Dou, X.; Zhu, B.; et al. Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, V.; Sarah, S.; Deborah, N. Long-Term Effects of COVID-19, and Its Impact on Business, Employees, and CO2 Emissions, a Study Using Arc-GIS Survey 123 and Arc-GIS Mapping. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, R.; Pavlovic, R.; Racine, J.; Moran, M.D.; Manseau, P.M.; Duhamel, A.; Katal, A.; Miville, J.; Niemi, D.; Peng, S.J.; et al. Isolating the impact of COVID-19 lockdown measures on Urban Air Quality in Canada. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1549–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroń, A.; Borucka, A.; Parczewski, R. Analysis of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Value of CO2 Emissions from Electricity Generation. Energies 2022, 15, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Fernández, A.; Cerezo-Narváez, A.; Montero-Gutiérrez, P.; Ballesteros-Pérez, P.; Otero-Mateo, M. Use of Low-Cost Devices for the Control and Monitoring of CO2 Concentration in Existing Buildings after the COVID Era. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Cao, Y. Forest Area, CO2 Emission, and COVID-19 Case-Fatality Rate: A Worldwide Ecological Study Using Spatial Regression Analysis. Forests 2022, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, M. Ambient air pollutants and their effect on COVID-19 mortality in the United States of America. Pan Am. J. Public Health 2020, 44, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, R.; Fornacca, D. COVID-19 Higher Mortality in Chinese Regions with Chronic Exposure to Lower Air Quality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 597753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijheid, M.; Casas, M.; Gascon, M.; Valvi, D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Environmental pollutants and child health—A review of recent concerns. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, D.; Kaali, S.; Kinney, P.L.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Chillrud, S.; Yawson, A.K.; Quinn, A.; Wylie, B.; Ae-Ngibise, K.; Lee, A.G. Examining the relationship between household air pollution and infant microbial nasal carriage in a Ghanaian cohort. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wan, X.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of PM2. 5 and pancreatic cancer mortality in China. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticini, E.; Frediani, B.; Caro, D. Can atmospheric pollution be considered a co-factor in extremely high level of SARS-CoV-2 lethality in Northern Italy? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegolon, L. Investigating hypothiocyanite against SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 227, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Consensus Document on the Epidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C. Severe acute respiratory syndrome and biology, air quality, physics, and mechanical engineering. Hong Kong Med. J. Xianggang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2003, 9, 304–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.-C.; Lu, J.; Xu, Q.-F.; Guo, Q.; Xu, D.-Z.; Sun, Q.-W.; Yang, H.; Zhao, G.-M.; Jiang, Q.-W. Influence of meteorological factors and air pollution on the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Public Health 2007, 121, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Hoek, G.; Van Vliet, P.; Meliefste, K.; Fischer, P.H.; Wijga, A.; Koopman, L.P.; Neijens, H.J.; Gerritsen, J.; Kerkhof, M. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, E.A.; Gehring, U.; Mölter, A.; Fuertes, E.; Klümper, C.; Krämer, U.; Quass, U.; Hoffmann, B.; Gascon, M.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution and respiratory infections during early childhood: An analysis of 10 European birth cohorts within the ESCAPE Project. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Samet, J.M.; Smith, K.R.; Bruce, N. Outdoor air pollution and acute respiratory infections among children in developing countries. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 44, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeger, C.; Forouzanfar, M.; Rao, P.C.; Khalil, I.; Brown, A.; Swartz, S.; Fullman, N.; Mosser, J.; Thompson, R.L.; Reiner, R.C., Jr. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1133–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, L.; Ghilardi, L.; Arnoldi, E.; Tondini, C.A.; Bettini, A.C. A rapid fatal evolution of Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) in an advanced lung cancer patient with a long time response to nivolumab. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, e83–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M.S.; Oppenheimer, J.; Grayson, M.; Stukus, D.; Hartog, N.; Hsieh, E.W.; Rider, N.; Dutmer, C.M.; Vander Leek, T.K.; Kim, H. COVID-19: Pandemic Contingency Planning for the Allergy and Immunology Clinic. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1477–1488.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Pan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Clinical characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reactivation. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e14–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Gubbi, S. COVID-19 Pandemic, Corona Viruses, and Diabetes Mellitus; American Physiological Society: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Li, S.; Barnett, A.G.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Huxley, R.; Chen, W.; Williams, G. The association between lung cancer incidence and ambient air pollution in China: A spatiotemporal analysis. Environ. Res. 2016, 144, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresovich, J.K.; Erdal, S.; Chen, H.Y.; Gann, P.H.; Argos, M.; Rauscher, G.H. Metallic air pollutants and breast cancer heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Beelen, R.; Wang, M.; Hoek, G.; Andersen, Z.J.; Hoffmann, B.; Stafoggia, M.; Samoli, E.; Weinmayr, G.; Dimakopoulou, K. Particulate matter air pollution components and risk for lung cancer. Environ. Int. 2016, 87, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chang, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in China: Who are faced with a greater effect? Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Mengersen, K.; Tong, S.; Kimlin, M.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Yin, P.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y. Short-term association between ambient air pollution and lung cancer mortality. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kweon, J. Hourly differences in air pollution on the risk of asthma exacerbation. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Ramani, T.; de Hoogh, K.; Mueller, N.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Zietsman, J.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Traffic-related air pollution and the local burden of childhood asthma in Bradford, UK. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasana, J.; Dillikar, D.; Mendy, A.; Forno, E.; Vieira, E.R. Motor vehicle air pollution and asthma in children: A meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2012, 117, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, R.; Bechle, M.; Marshall, J.D.; Ramani, T.; Zietsman, J.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Khreis, H. Traffic related air pollution and the burden of childhood asthma in the contiguous United States in 2000 and 2010. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lu, C.; Miao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Deng, Q. Outdoor particulate air pollution and indoor renovation associated with childhood pneumonia in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, H.; Sun, D.; Qi, Z.; Guo, C.; Peng, W.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, B. Associations between ambient air pollution and mortality from all causes, pneumonia, and congenital heart diseases among children aged under 5 years in Beijing, China: A population-based time series study. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhung, N.T.T.; Amini, H.; Schindler, C.; Joss, M.K.; Dien, T.M.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Perez, L.; Künzli, N. Short-term association between ambient air pollution and pneumonia in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of time-series and case-crossover studies. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, F. Acute effects of air pollution on influenza-like illness in Nanjing, China: A population-based study. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z. Association of indoor air pollution from coal combustion with influenza-like illness in housewives. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Guo, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Peng, L.; Fu, Z.-R. Long-term exposure to PM2. 5 lowers influenza virus resistance via down-regulating pulmonary macrophage Kdm6a and mediates histones modification in IL-6 and IFN-β promoter regions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landguth, E.L.; Holden, Z.A.; Graham, J.; Stark, B.; Mokhtari, E.B.; Kaleczyc, E.; Anderson, S.; Urbanski, S.; Jolly, M.; Semmens, E.O. The delayed effect of wildfire season particulate matter on subsequent influenza season in a mountain west region of the USA. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, Z.; Boloorani, A.D.; Khalifeh, R.; Teymouri, P.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Griffin, D.W. Air pollution and respiratory hospital admissions in Shiraz, Iran, 2009 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yan, Q.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, P.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Y. Measuring the impact of air pollution on respiratory infection risk in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, T.K.; Shimshack, J.P. Air pollution and children’s respiratory health: A cohort analysis. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 67, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kagawa, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Hou, S. Air pollution and children’s respiratory symptoms in six cities of Northern China. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugha, R.; Grigg, J. Urban air pollution and respiratory infections. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elten, M.; Donelle, J.; Lima, I.; Burnett, R.T.; Weichenthal, S.; Stieb, D.M.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Chen, H.; Paul, L.A. Ambient air pollution and incidence of early-onset paediatric type 1 diabetes: A retrospective population-based cohort study. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, H.; Ren, M.; Liang, Q.; Shen, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Luo, Q.; Chen, W. Ambient air pollution exposure and gestational diabetes mellitus in Guangzhou, China: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, S.; Hennig, F.; Moebus, S.; Ohlwein, S.; Herder, C.; Kowall, B.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Hoffmann, B. All-source and source-specific air pollution and 10-year diabetes Incidence: Total effect and mediation analyses in the Heinz Nixdorf recall study. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.F.; Yap, P.S.; Mak, J.W.; Chan, W.L.E.; Khor, G.L.; Ambu, S.; Chu, W.L.; Mohamad, M.S.; Wong, N.I.; Majid, N.L.A. Association between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Malaysian adults. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chin, W.-S.; Chen, B.-Y.; Chan, C.-C.; Guo, Y.L. Association between air pollution exposure and diabetic retinopathy among diabetics. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Kwong, J.C.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Bai, L.; Goldberg, M.S.; Lavigne, E.; Copes, R.; Martin, R.V. The impact of air pollution on the incidence of diabetes and survival among prevalent diabetes cases. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The experience of clinical immunologists from China. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 214, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzio, G.; Cortellini, A.; Bruera, E.; Verna, L.; Ravoni, G.; Peris, F.; Spinelli, G. Home care for cancer patients during COVID-19 pandemic: The “double triage” protocol. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2020, 60, e5–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, L.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Shen, X.-K.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.-Q.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.-H. A Multicentre Study of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease Outcomes of Cancer Patients in Wuhan, China. medRxiv 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ouyang, W.; Chua, M.L.; Xie, C. SARS-CoV-2 transmission in patients with cancer at a tertiary care hospital in Wuhan, China. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Guan, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Li, C.; Ai, Q.; Lu, W.; Liang, H. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, D.M.; Faner, R.; Sibila, O.; Badia, J.R.; Agusti, A. Do chronic respiratory diseases or their treatment affect the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Hu, W.; Niu, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, S.-Y. Pulmonary pathology of early phase 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia in two patients with lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-H.; Dong, J.-H.; An, W.-M.; Lv, X.-Y.; Yin, X.-P.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Dong, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.-J.; Gao, B.-L. Clinical and computed tomographic imaging features of novel coronavirus pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.-M.; Yu, X.-H.; Tang, S.-L.; Tang, C.-K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current status and future perspective. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, L. Positive effects of COVID-19 control measures on influenza prevention. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 95, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siordia, J.A., Jr. Epidemiology and Clinical Features of COVID-19: A Review of Current Literature. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupia, T.; Scabini, S.; Pinna, S.M.; Di Perri, G.; De Rosa, F.G.; Corcione, S. 2019-novel coronavirus outbreak: A new challenge. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Leung, A.W.; Xu, C. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) and Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): From Causes to Preventions in Hong Kong. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambuccian, S.E. The COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for the cytology laboratory. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2020, 9, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, E.; Buzzetti, R. Covid-19 and diabetes mellitus: Unveiling the interaction of two pandemics. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2020, 36, e33213321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, W.; Ling, J.; Mo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Cao, Q.; Deng, L.; Song, S. Hypertension and Diabetes Delay the Viral Clearance in COVID-19 Patients. medRxiv 2020, 22, 20040774. [Google Scholar]
- Roncon, L.; Zuin, M.; Rigatelli, G.; Zuliani, G. Diabetic patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk of ICU admission and poor short-term outcome. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chiang, Y.-L.F.; Chien, Y.-C.; Cheng, M.; Yang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-N. First case of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Alam, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Yuan, W. Optimal intensity measures for probabilistic seismic demand models of a cable-stayed bridge based on generalized linear regression models. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 131, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Lambda | 6.582 | (+1 SE):38.55 | (+2 SE):67.36 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | |
| C | −0.579 | 0.1774 | −3.263 | 0.701 | 0.2198 | 3.189 | 1.247 | 0.4147 | 3.007 |
| CO2 | 0.164 | 0.0513 | 3.199 | 0.084 | 0.0239 | 3.521 | 0.065 | 0.0196 | 3.32 |
| CH4 | 0.091 | 0.013 | 7.002 | 0.074 | 0.0079 | 9.347 | 0.06 | 0.0062 | 9.652 |
| N2O | 0.069 | 0.002 | 34.023 | 0.073 | 0.0019 | 37.881 | 0.061 | 0.0015 | 39.74 |
| HFC | 0.09 | 0.0034 | 26.609 | 0.067 | 0.0025 | 27.146 | 0.056 | 0.002 | 27.89 |
| PFC | 0.114 | 0.0265 | 4.305 | 0.136 | 0.0184 | 7.379 | 0.13 | 0.0144 | 9.01 |
| SF6 | 0.241 | 0.0178 | 13.522 | 0.131 | 0.0109 | 12.047 | 0.101 | 0.0093 | 10.85 |
| R2 | 0.763 | 0.705 | 0.659 | ||||||
| Lambda | 6.769 | (+1 SE):39.64 | (+2 SE):63.13 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | |
| C | −0.8666 | 0.2545 | −3.405 | 0.6034 | 0.1539 | 3.921 | 1.0766 | 0.2558 | 4.209 |
| CO2 | 0.1666 | 0.0514 | 3.239 | 0.0836 | 0.0243 | 3.441 | 0.0675 | 0.017 | 3.962 |
| CH4 | 0.1174 | 0.0166 | 7.067 | 0.0785 | 0.0092 | 8.507 | 0.0653 | 0.0071 | 9.146 |
| N2O | 0.0827 | 0.0028 | 29.64 | 0.0754 | 0.0022 | 34.712 | 0.0637 | 0.0017 | 37.003 |
| HFC | 0.1103 | 0.0046 | 24.241 | 0.0716 | 0.0027 | 26.58 | 0.0598 | 0.0022 | 27.073 |
| PFC | 0.0982 | 0.0188 | 5.218 | 0.124 | 0.0166 | 7.452 | 0.1205 | 0.0145 | 8.305 |
| SF6 | 0.1969 | 0.0172 | 11.427 | 0.1168 | 0.0114 | 10.229 | 0.0956 | 0.0095 | 10.046 |
| R2 | 0.74 | 0.681 | 0.644 | ||||||
| Lambda | 6.191 | (+1 SE):39.800 | (+2 SE):76.330 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | Coef | Std | t-Stat | |
| C | −4.4341 | 0.7757 | −5.716 | −2.1678 | 0.6768 | −3.203 | −1.1779 | 0.2455 | −4.799 |
| CO2 | 0.2447 | 0.0451 | 5.428 | 0.1222 | 0.0176 | 6.934 | 0.0901 | 0.0118 | 7.642 |
| CH4 | 0.16 | 0.0169 | 9.442 | 0.1142 | 0.0108 | 10.563 | 0.0877 | 0.0072 | 12.158 |
| N2O | 0.1591 | 0.0042 | 38.195 | 0.1192 | 0.0028 | 42.522 | 0.091 | 0.002 | 45.076 |
| HFC | 0.1566 | 0.0054 | 29.163 | 0.104 | 0.0031 | 33.181 | 0.0804 | 0.0021 | 37.909 |
| PFC | 0.1357 | 0.0185 | 7.322 | 0.1782 | 0.0197 | 9.071 | 0.1691 | 0.0149 | 11.338 |
| SF6 | 0.2982 | 0.0228 | 13.056 | 0.1737 | 0.0113 | 15.374 | 0.1297 | 0.0071 | 18.169 |
| R2 | 0.769 | 0.705 | 0.645 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ansarinasab, M.; Saghaian, S. The Relationship between Environmental Quality, Sustainable Health, and the Coronavirus Pandemic in European Countries. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511683
Ansarinasab M, Saghaian S. The Relationship between Environmental Quality, Sustainable Health, and the Coronavirus Pandemic in European Countries. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511683
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnsarinasab, Moslem, and Sayed Saghaian. 2023. "The Relationship between Environmental Quality, Sustainable Health, and the Coronavirus Pandemic in European Countries" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511683
APA StyleAnsarinasab, M., & Saghaian, S. (2023). The Relationship between Environmental Quality, Sustainable Health, and the Coronavirus Pandemic in European Countries. Sustainability, 15(15), 11683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511683






