SCHEMA: A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games—A Systematic Review towards Sustainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Theoretical Framework
1.1.1. Serious Games: An Educational Tool for Digital Generations
1.1.2. The Need to Find a Complete Model for Designing, Creating, and Evaluating Educational Video Games
2. Materials and Methods
- To systematise the scientific production around serious games by studying methodological models and processes to create and evaluate educational video games.
- To explore the stages proposed in the existing literature obtained from the studies analysed.
- To investigate the methodological models’ underlying characteristics to understand their context and see if they incorporate the necessary components for a consistent and complete process.
- To find similar patterns in the methodologies reviewed to outline a standard, versatile, straightforward process.
- To determine if there are complete and adequate models that contemplate the design process of a serious game from all its variables to rescue and value this quality content to be used in future developments, promoting the use and sustainability of already available resources.
2.1. Procedure
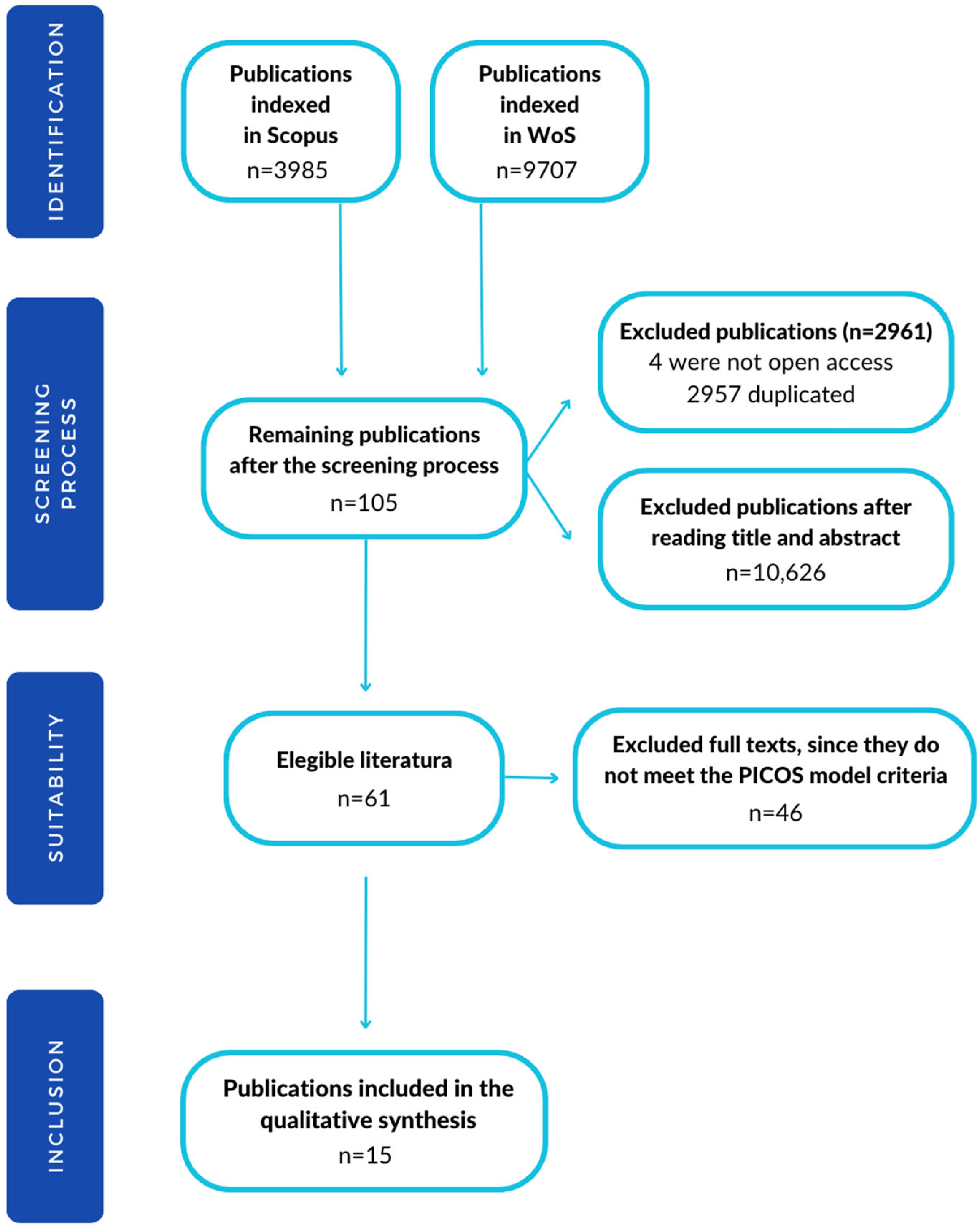
2.1.1. Systematic Literature Review
2.1.2. Qualitative Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Methodologies for the Design and Development of Serious Games: Articles Included in the Review
3.1.1. Article 01
3.1.2. Article 02
3.1.3. Article 03
3.1.4. Article 04
3.1.5. Article 05
3.1.6. Article 06
3.1.7. Article 07
3.1.8. Article 08
3.1.9. Article 09
3.1.10. Article 10
3.1.11. Article 11
3.1.12. Article 12
3.1.13. Article 13
3.1.14. Article 14
3.1.15. Article 15
3.2. Main Dimensions Drawn from the Literature
3.3. A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games: SCHEMA
4. Discussion
4.1. The Dimensions Mined from Literature
4.2. Methodologies Weaknesses to Be Improved in Future Research
4.3. SCHEMA: A First Step towards Improving Serious Games Methodologies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrero, B. Innovación Social, Tecnología y ODS. Fórmula Magistral Para Un Mundo Mejor En La Era Del COVID-19. Rev. Iberoam. Econ. Solidar. Innovación Socioecol. 2021, 4, 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.F.; Mira, Y.M. La Globalización y La Importancia de Las TIC En El Desarrollo Social. Rev. Reflex. Saberes 2019, 11, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, F.; Simoes, J. The Role of Serious Games, Gamification and Industry 4.0 Tools in the Education 4.0 Paradigm. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2019, 10, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L. Necesidad de Una Educación Digital En Un Mundo Digital. RIED. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. A Distancia 2019, 22, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Enciso, E.M.; Arias, J.; Arias, A. El Papel de Las Narrativas Digitales Como Nueva Estrategia Educativa: Resultados Desde Un Análisis Bibliométrico. Kepes 2016, 13, 197–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A. Innovación, Tecnologías y Educación: Las Narrativas Digitales Como Estrategias Didácticas. Kill. Soc. Rev. Investig. Científica 2018, 2, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A. Las Narrativas Digitales En Educación Infantil: Una Experiencia de Investigación e Innovación Con Booktrailer, Cuentos Interactivos Digitales y Realidad Aumentada. Diablotexto Digit. 2018, 3, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Chóez, J.S. Narrativas Digitales Como Didáctica Educativa. PoloConoc. Rev. Científico-Prof. 2021, 6, 846–859. [Google Scholar]
- Scolari, C.A. Adolescentes, Medios de Comunicación y Culturas Colaborativas. Aprovechando las Competencias Transmedia de los Jóvenes En El Aula; EC|H2020|Research and Innovation Actions: Barcelona, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Echauri, G.; Figueras-Maz, M. El Acercamiento de Estudiantes Universitarios Internacionales a Plataformas de Streaming. Virtualis Rev. Cult. Digit. 2021, 12, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, G.; Muzellec, L.; Johnson, D. Message Content Features and Social Media Engagement: Evidence from the Media Industry. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2019, 29, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-de-Cózar, S.; Ramírez-Moreno, C.; Barroso-Tristán, J.M. A Qualitative Analysis of the Educational Value of Commercial Video Games. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, C.D.; Capafons, J.I.; Pérez-Correa, S.M.; Hernández-Zamora, G.L.; Capafons, J.I.; Prieto, P. El Uso de Las Nuevas Tecnologías (Internet, Redes Sociales, Videojuegos) en Jóvenes: Un Estudio Con Población Canaria. Rev. Española Drogodepend. 2019, 44, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Felicia, P. Using Educational Games in the Classroom: Guidelines for Successful Learning Outcomes; Herzt, B., Pinzi, V., Sefen, M., Eds.; European Schoolnet & Interactive Software Federation of Europe (ISFE): Brussels, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 9789492913951. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, F.; Helms, N.H. Creating Evaluation Profiles for Games Designed to Be Fun: An Interpretive Framework for Serious Game Mechanics. Simul. Gaming 2017, 48, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosalanejad, L.; Abdollahifard, S. Gamification in Psychiatry: Design and Development of Native Model and the Innovate Strategy in Medical Education as a Funny and Exciting Learning. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2018, 12, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalodeen, V.J.; Ramsawak-Jodha, N.; Figaro-Henry, S.; Jaggernauth, S.J.; Dedovets, Z. Designing Gamification for Geometry in Elementary Schools: Insights from the Designers. Smart Learn. Environ. 2021, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, A.; Yedri, O.B.; Elouaai, F.; Bouhorma, M. Towards a Design Approach for Serious Games. Int. J. Knowl. Learn. 2016, 11, 58–81. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, M.A.; Camilleri, A.C. Student Centred Learning Through Serious Games. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual International Technology, Education and Development Conference, Valencia, Spain, 11–13 March 2018; International Academy of Technology, Education and Development (IATED): Valencia, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Anastasiadis, T.; Siakas, K. Digital Game-Based Learning in Education: Significance of Motivating, Engaging and Interactive Learning Environments. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Software Process Improvement-Research into Education and Training (INSPIRE 2019), Southampton, UK, 25–26 May 2019; pp. 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Asociación Española del Videojuego (AEVI). La Industria del Videojuego en España En 2021; AEVI: Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mieres, R. Los Videojuegos Como Producto Cultural. Available online: http://bit.ly/3Rp0pLN (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Oo, A.M.; Vallabhajosyula, R. Perceived Effectiveness of an Innovative Mobile-based Serious Game on the Improvement of Soft Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgical Training. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2023, 16, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisford, C.J.; Blackburn, L.; Ollett, J.M.; Tonner, T.B.; Yuen, C.S.H.; Walton, R.; Olayinka, O. Can Gamification Help to Teach Cybersecurity? In Proceedings of the 2022 20th International Conference on Information Technology Based Higher Education and Training (ITHET), Antalya, Turkey, 7–9 November 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, S.R.Z.; Fadzilah, S.; Sahari, N. Low-Fidelity Prototype Design for Serious Game for Slow-Reading Students. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Arroum, F.-Z.; Hanoune, M.; Zidoun, Y. Serious Game Design: Presenting a New Generic Creative Reflection Framework. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (IJET) 2020, 15, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Spek, E.V.D.; Hu, J.; Feijs, L. Extracting Design Guidelines for Augmented Reality Serious Games for Children. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66660–66671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravyse, W.S.; Seugnet Blignaut, A.; Leendertz, V.; Woolner, A. Success Factors for Serious Games to Enhance Learning: A Systematic Review. Virtual Real 2017, 21, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Shangguan, D. Researching and Designing Educational Games on the Basis of “Self-Regulated Learning Theory”. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 996403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsaounidou, A.; Vrysis, L.; Kotsakis, R.; Dimoulas, C.; Veglis, A. MAthE the Game: A Serious Game for Education and Training in News Verification. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegog, R.; Brown, K.; Bull, S.; Christensen, J.L.; Hieftje, K.; Jozkowski, K.N.; Ybarra, M.L. Serious Games for Sexual Health. Games Health J. 2015, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovreglio, R.; Gonzalez, V.; Feng, Z.; Amor, R.; Spearpoint, M.; Thomas, J.; Trotter, M.; Sacks, R. Prototyping Virtual Reality Serious Games for Building Earthquake Preparedness: The Auckland City Hospital Case Study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 38, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnechère, B. Serious Games in Physical Rehabilitation: From Theory to Practice; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-66121-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga-Varela, F.; Vila-Couñago, E.; Martínez-Piñeiro, E. The Impact of Serious Games in Mathematics Fluency: A Study in Primary Education. Comunicar 2021, 29, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhonggen, Y. A Meta-Analysis of Use of Serious Games in Education over a Decade. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2019, 2019, 4797032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-de-Lope, R.; Medina-Medina, N. A Comprehensive Taxonomy for Serious Games. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2017, 55, 629–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barianos, A.K.; Papadakis, A.; Vidakis, N. Content Manager for Serious Games: Theoretical Framework and Digital Platform. Adv. Mob. Learn. Educ. Res. 2022, 2, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekleves, E.; Cosmas, J.; Aggoun, A. Benefits, Barriers and Guideline Recommendations for the Implementation of Serious Games in Education for Stakeholders and Policymakers. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2016, 47, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.G.M. Practical Methodology for the Design of Educational Serious Games. Information 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Xie, T.; Liu, G. A Learning Engagement Model of Educational Games Based on Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Information, Media and Engineering (ICIME), Osaka, Japan, 12–14 December 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yuxuan, C.; Souza, R.C.G.; Contessoto, A.G.; Amorim, A.R. Guidelines for the Development of Educational Games to Motivate the Learning of Theoretical Concepts in Engineering and Computing Courses. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2021, 29, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Vivancos, A.; Arias-Ferrer, L. Principles for the Design of a History and Heritage Game Based on the Evaluation of Immersive Virtual Reality Video Games. E-Learn. Digit. Media 2021, 18, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, J.-M.; Haavisto, E.; Niemi, H.; Haho, P.; Nylund, S.; Multisilta, J. Design Principles for Simulation Games for Learning Clinical Reasoning: A Design-Based Research Approach. Nurse Educ. Today 2018, 60, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Almeida, J.L.; Machado, L. dos S. Design Requirements for Educational Serious Games with Focus on Player Enjoyment. Entertain. Comput. 2021, 38, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarraonandia, T.; Diaz, P.; Aedo, I.; Ruiz, M.R. Designing Educational Games through a Conceptual Model Based on Rules and Scenarios. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 4535–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breien, F.; Wasson, B. ELuna: A Co-Design Framework for Narrative Digital Game-Based Learning That Support STEAM. Front. Educ. 2022, 6, 775746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.B.; Bellotti, F.; Berta, R.; De Gloria, A.; Sedano, C.I.; Hauge, J.B.; Hu, J.; Rauterberg, M. An Activity Theory-Based Model for Serious Games Analysis and Conceptual Design. Comput. Educ. 2015, 87, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma, M.R.; Simini, F. Serious Game Design by Unified Block Interactions to Support Educational Transformations. Int. J. Comput. 2021, 20, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Laguna, Á.; Manero, B.; Freire, M.; Fernández-Manjón, B. A Methodology for Assessing the Effectiveness of Serious Games and for Inferring Player Learning Outcomes. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 2849–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Catalá-López, F.; Moher, D. La Extensión de la Declaración PRISMA Para Revisiones Sistemáticas Que Incorporan Metaanálisis en Red: PRISMA-NMA. Med. Clin. 2016, 147, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-de-Cózar, S.; Pérez-Escolar, M.; Navazo-Ostúa, P. Digital Competencies for New Journalistic Work in Media Outlets: A Systematic Review. Media Commun. 2022, 10, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappur, R.F.; Forcellini, F.A.; Spanhol, F.J. Modelo conceitual para jogos educativos digitais. AtoZ Novas Práticas Informação Conhecimento 2014, 3, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Zea, N.; Medina-Medina, N.; Gutiérrez-Vela, F.L.; López-Arcos, J.R.; Paderewski, P.; González-González, C.S. A design process for balanced educational video games with collaborative activities. DYNA 2015, 82, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, R.; Corolla, A.; Faggiano, A.; Malandrino, D.; Pirozzi, D.; Ranaldi, M.; Santangelo, G.; Scarano, V. A Framework to Design, Develop, and Evaluate Immersive and Collaborative Serious Games in Cultural Heritage. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2018, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaouti, D. DICE: A Generic Model for the Design Process of Serious Games. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2020, 10, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, R.W.C.; Au, C.H. Establishing an educational game development model: From the experience of teaching search engine optimization. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2018, 8, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.; Mateus, A.; Leonor, S.; Sequeira, M.; Gaio, R. Game-thinking: A roadmap to a Design Thinking-based model for Game Development education. Rev. Lusófona Educ. 2018, 40, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño, L.M.; Rojas, M.D. Determinación de criterios generales para el diseño de juegos serios: Modelo metodológico integrador. Inf. Tecnol. 2021, 32, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Toro, M.; Santorum, M.; Acosta-Vargas, P.; Aguilar, J.; Pérez, M. iPlus a User-Centered Methodology for Serious Games Design. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual Alcover, E.; Jaume-i-Capó, A.; Moyà-Alcover, B. PRO-Game: A process framework for serious game development for motor rehabilitation therapy. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Pesantez, D.; Delgadillo, R.; Rivera, L.A. Proposal of a Conceptual Model for Serious Games Design: A Case Study in Children with Learning Disabilities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 161017–161033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedavan, R.; Pudjoatmodjo, B.; Siradj, Y.; Salam, S.; Hardianti, B.D. Serious Game Development Model Based on the Game-Based Learning Foundation. J. ICT Res. Appl. 2021, 15, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipe, M.A. Modelo de serious game para mejorar la atención en niños con trastorno por déficit de atención e hiperactividad (TDAH). Rev. Ibérica Sist. Tecnol. Inform. 2019, 17, 936–946. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, S.; Munoz Arteaga, J.; Collazos, C.A.; Gonzalez, C.S.; Zapata, S. Toward a methodology for serious games design for children with auditory impairments. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, S. Are Games Effective Learning Tools? A Review of Educational Games. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, S.V.; Gauthier, A.; L’Estrade Ehrstrom, B.; Wortley, D.; Lilienthal, A.; Tudor Car, L.; Dauwels-Okutsu, S.; Nikolaou, C.K.; Zary, N.; Campbell, J.; et al. Serious Gaming and Gamification Education in Health Professions: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Klerk, S.; Kato, P.M. The Future Value of Serious Games for Assessment: Where Do We Go Now? J. Appl. Test. Technol. 2017, 18, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero-Hernández, J.A.; Palomo-Duarte, M.; Dodero, J.M.; Person, T. Evaluación de Competencias En Serious Games Mediante Analítica de Aprendizaje Con Process Mining. In Proceedings of the Aprendizaje, Innovación y Cooperación Como Impulsores del Cambio Metodológico, Madrid, Spain, 9–11 October 2019; Servicio de Publicaciones Universidad: Zaragoza, Spain, 2019; pp. 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Schickler, M.; Pryss, R.; Reichert, M.; Schobel, J.; Langguth, B.; Schlee, W. Using Mobile Serious Games in the Context of Chronic Disorders: A Mobile Game Concept for the Treatment of Tinnitus. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Belfast and Dublin, Ireland, 20–24 June 2016; IEEE: Belfast/Dublin, Ireland; pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo-Alcázar, A.; Luján-Mora, S. Mobile Serious Games. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality, Cádiz, Spain, 18–20 October 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, S.K.; Krishna, S.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Bhavani, R.R. Virtual Reality Learning Environments for Vocational Education: A Comparison Study with Conventional Instructional Media on Knowledge Retention. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 18th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Mumbai, India, 9–13 July 2018; IEEE: Mumbai, India, 2018; pp. 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, F.; Barbieri, L.; Lagudi, A.; Cozza, M.; Cozza, A.; Peluso, R.; Muzzupappa, M. Virtual Dives into the Underwater Archaeological Treasures of South Italy. Virtual Real 2018, 22, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjorlu, A.; Serafin, S. Head-Mounted Display-Based Virtual Reality as a Tool to Teach Money Skills to Adolescents Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 265, pp. 450–461. [Google Scholar]
- Gros, B. Game Dimensions and Pedagogical Dimension in Serious Games. In Handbook of Research on Serious Games for Educational Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 402–417. [Google Scholar]
- Viudes-Carbonell, S.J.; Gallego-Durán, F.J.; Llorens-Largo, F.; Molina-Carmona, R. Towards an Iterative Design for Serious Games. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, M.; Koskinen, A.; Krokfors, L. A Qualitative Literature Review of Educational Games in the Classroom: The Teacher’s Pedagogical Activities. Teach. Teach. 2016, 23, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameras, P.; Arnab, S.; Dunwell, I.; Stewart, C.; Clarke, S.; Petridis, P. Essential Features of Serious Games Design in Higher Education: Linking Learning Attributes to Game Mechanics. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2017, 48, 972–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | Any | None |
| Intervention | Any | None |
| Context 1 | Published between 2014–2023 Articles Final stage | Others Books, chapters, proceedings, and others In press and others |
| Outcomes | Focused on processes or methodologies to design, develop and/or evaluate SG Educational video games | Focus on guidelines, recommendations, principles, or models Commercial video games |
| Nomenclature in the Study | Authors (Year) | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| [53] | Jappur, Forcellini y Spanhol (2014) | Literature review |
| [54] | Padilla-Zea et al. (2015) | Literature review |
| [55] | Andreoli et al. (2017) | Not specified |
| [56] | Djaouti (2020) | Literature review |
| [47] | Breien y Wasson (2022) | Not specified |
| [57] | Lui y Au (2018) | Literature review |
| [58] | Fernandes et al. (2018) | Literature review |
| [59] | Londoño y Rojas (2021) | Literature review |
| [60] | Carrión-Toro et al. (2020) | Not specified |
| [61] | Amengual, Jaume-i-Capo y Moyà-Alcover (2018) | Not specified |
| [62] | Avila-Pesantez, Delgadillo y Rivera (2019) | Not specified |
| [63] | Roedavan et al. (2021) | Not specified |
| [64] | Taipe (2019) | Literature review |
| [19] | Slimani et al. (2016) | Interviews with experts in game design (non-Delphi) |
| [65] | Cano et al. (2016) | Literature review |
| ID | Focus/Base | Scope | Use | Phases Iteration | Format | Approach | Practical Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53] | Learning about the culture of sustainability in the residential and home environment | General | Design Development | No | Computer game | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [54] | Collaborative aspect | General | Design Development Evaluation | No | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [55] | Collaborative and cultural aspect | General | Design Development Evaluation | Yes | Not specified | Playful | Yes |
| [56] | None | General | Design | Yes | Not specified | Mostly playful | No |
| [47] | Learning based on digital and narrative games Co-design (teachers and designers) | STEAM (Learning) | Design Development | No | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [57] | Teaching SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) | Marketing (SEO) | Design Development | Yes | Not specified | Mostly pedagogical | Yes |
| [58] | Design Thinking | Design Thinking | Development | No | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | No |
| [59] | None | General | Design Development | Not at all | Not specified | Playful | No |
| [60] | User-centred design | General | Design | No | Not specified | Mostly playful | Yes |
| [61] | Motor rehabilitation | Therapy (Health) | Development | Yes | Not specified | Playful | Yes |
| [62] | Learning disabilities | Learning | Design | No | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [63] | Game-based learning foundation | General | Development | Not at all | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [64] | Improving attention of children with ADHD | ADHD (Health) | Design Development | No | Augmented Reality | Mostly playful | No |
| [19] | Collaborative design Multi-layered model | General | Design Evaluation | Yes | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| [65] | Children with disabilities hearing impairment | Disabilities (Health) | Design Development | No | Not specified | Playful and pedagogical balance | Yes |
| Steps | Definition | In Literature | Playful vs. Pedagogical |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | This is the initial point at which the need for creating a serious game, the target audience, and the objectives to be achieved are identified | [55] Preliminary phase [59] Pre-design phase [60] Identification phase [61] Project initiation | Playful |
| [56] Define [47] Preparation [64] Enquiry [19] Learning layer | Pedagogical | ||
| [58] Involvement [62] Analysis | Playful and pedagogical balance | ||
| Content Hierarchy | The aim will be to give shape to all the material to be included in the educational video game, both educational-pedagogical content, as well as all the considerations at the level of mechanics, dynamics, and aesthetics of the game | [54] Entertaining content design [55] Conceptual phase [56] Imagine [59] Design phase (writing sub-phase) [60] Ludic game script phase [61] Planning and control Modelling [62] Design [19] Gameplay layer [65] Pre-production | Playful |
| [54] Educational content design [58] Ideation [60] Pedagogical objectives phase [63] Analysis [64] Modelling | Pedagogical | ||
| [53] Creation stage [47] Co-design and co-specification [57] Conceptual design Game design [58] Inspiration [62] Analysis [19] Story layer [65] Analysis | Playful and pedagogical balance | ||
| Engineering | The serious game is implemented, the previous design is put into practice and the game is created | [54] User modelling [55] Development phase [56] Create [47] Development [57] Prototyping [59] Design phase (construction sub-phase) [60] Gameplay phase [61] Construction [62] Development [63] Production [64] Design [19] Experimentation layer [65] Production | Playful |
| [53] Application stage | Pedagogical | ||
| [54] Relating educational and entertaining content [58] Integration | Playful and pedagogical balance | ||
| Monitoring and Assessment | The aim is to correct possible errors. The game is tested with the sample to detect problems and fix them. | [55] Evaluation phase [56] Evaluate [57] Evaluation Identification [58] Implementation Interaction [59] Testing phase [60] Refine phase [61] Evaluation [63] Testing [64] Evaluation | Playful |
| [63] Release [65] Post-production | Pedagogical | ||
| [53] Evaluation stage [62] Evaluation [19] Debriefing layer | Playful and pedagogical balance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merino-Cajaraville, A.; Reyes-de-Cózar, S.; Navazo-Ostúa, P. SCHEMA: A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games—A Systematic Review towards Sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612351
Merino-Cajaraville A, Reyes-de-Cózar S, Navazo-Ostúa P. SCHEMA: A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games—A Systematic Review towards Sustainability. Sustainability. 2023; 15(16):12351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612351
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerino-Cajaraville, Alba, Salvador Reyes-de-Cózar, and Pablo Navazo-Ostúa. 2023. "SCHEMA: A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games—A Systematic Review towards Sustainability" Sustainability 15, no. 16: 12351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612351
APA StyleMerino-Cajaraville, A., Reyes-de-Cózar, S., & Navazo-Ostúa, P. (2023). SCHEMA: A Process for the Creation and Evaluation of Serious Games—A Systematic Review towards Sustainability. Sustainability, 15(16), 12351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612351








