Characteristics of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier and Its Effect on the Performance of Asphalt Mixture
Abstract
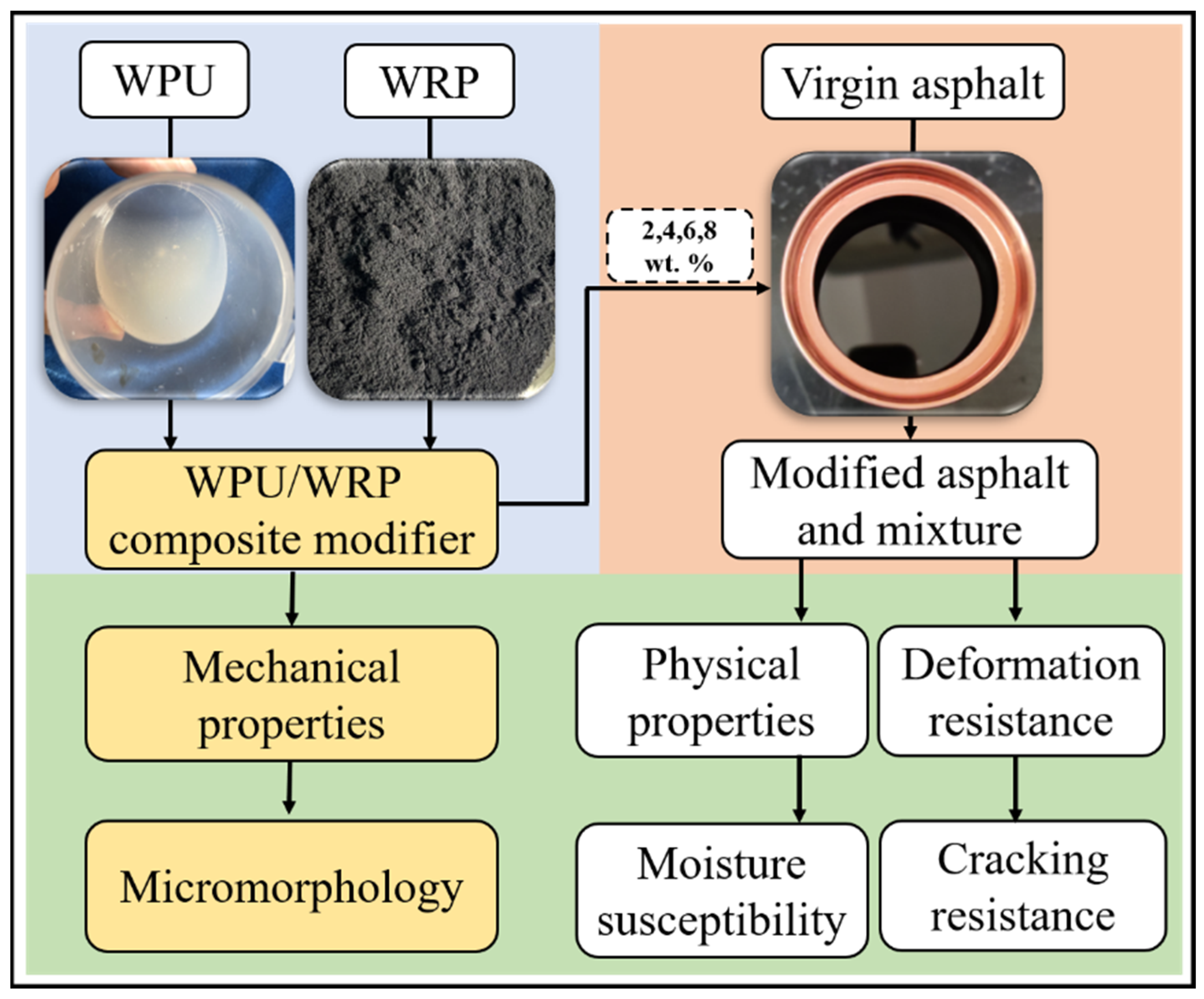
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Samples Preparation
2.2.1. Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier
2.2.2. Modified Asphalt Binder
2.2.3. Modified Asphalt Mixture
2.3. Measurement and Characterization
2.3.1. Tensile Strength Test of Composite Modifier
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Test of Modified Modifier
2.3.3. Basic Properties Test of Modified Asphalt Binders
2.3.4. Deformation Resistance of Modified Asphalt Mixture
2.3.5. Cracking Resistance of Modified Asphalt Mixture
2.3.6. Moisture Susceptibility of Modified Asphalt Mixture
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier
3.1.1. Tensile Strength
3.1.2. Microscopic Morphology
3.2. Physical Properties of Modified Asphalt Binders
3.3. Engineering Performance of Modified Asphalt Mixtures
3.3.1. Rutting Resistance
3.3.2. Cracking Resistance
3.3.3. Moisture Susceptibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Y. Effects of waterborne polyurethane on storage stability, rheological properties, and VOCs emission of crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Bulletin of the People’s Republic of China on National Economic and Social Development for 2022. 2023. Available online: www.stats.gov.cn/xxgk/sjfb/zxfb2020/202302/t20230228_1919001.html (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Cui, P.; Amirkhanian, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, M.; Zhou, X.; Xie, J. Performance characterization and enhancement mechanism of recycled asphalt mixtures involving high RAP content and steel slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Dong, H.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, P.; Sun, C. Reinforcing behavior of reclaimed rubber filled natural rubber composites. Polym. Int. 2023, 72, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, M.; Falck, K.; Maki-Paakkanen, J.; Vainio, H. Genotoxic hazards in the rubber industry. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1983, 9, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, R.; Yang, T. Environmental performance and functional analysis of chip seals with recycled basic oxygen furnace slag as aggregate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y. Research progress and performance evaluation of crumb-rubber-modified asphalts and their mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D. Recycled Tyre Rubber Modified Bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.J.; Partal, P.; Martınez-Boza, F.; Gallegos, C. Thermo-rheological behaviour and storage stability of ground tire rubber-modified bitumens. Fuel 2004, 83, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohayzi, N.F.; Katman, H.Y.B.; Ibrahim, M.R.; Norhisham, S.; Rahman, N.A. Potential Additives in Natural Rubber-Modified Bitumen: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S. Investigation on rheological characteristics of low-emissions crumb rubber modified asphalt. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2164891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, S.B.; Peng, A.; Xuan, W.; Li, W. Analysis of the performance and mechanism of desulfurized rubber and low-density polyethylene compound-modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-N.; Le, T.H.M. Durability of Polymer-Modified Asphalt Mixture with Wasted Tire Powder and Epoxy Resin under Tropical Climate Curing Conditions. Polymers 2023, 15, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Leng, Z.; Zou, F.; Yu, H. Effects of rubber absorption on the aging resistance of hot and warm asphalt rubber binders prepared with waste tire rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, C. Laboratory evaluation of the performance of reclaimed asphalt mixed with composite crumb rubber-modified asphalt: Reconciling relatively high content of RAP and virgin asphalt. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2217320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hong, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Jia, D. Grafting waste rubber powder and its application in asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, A.; Cui, H.; Dai, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of Crumb Rubber Particles on Antisliding and Noise-Reduction Performance of Asphalt Pavement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, H.; Hu, M.; Sun, D. Optimization design of rubberized porous asphalt mixture based on noise reduction and pavement performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, H.; Wan, P.; Zhang, J. Preparation and characterization of phase change capsules containing waste cooking oil for asphalt binder thermoregulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 395, 132311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A. Production of a sustainable paving material through chemical recycling of waste PET into crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Z.; Liu, H.; Ahmed, A.T.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P.; Sheng, Y. Performance and inorganic fume emission reduction of desulfurized rubber powder/styrene–butadiene–styrene composite modified asphalt and its mixture. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Flue gas composition of waste rubber modified asphalt (WRMA) and effect of deodorants on hazardous constituents and WRMA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.-J. Laboratory Investigation of Different Standards of Phase Separation in Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Gao, J.; Pei, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, R. Research on highly dissolved rubber asphalt prepared using a composite waste engine oil addition and microwave desulfurization method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Hu, W.; Polaczyk, P.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Compatibility and rheological characterization of asphalt modified with recycled rubber-plastic blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Dong, R. Reaction mechanism and rheological properties of waste cooking oil pre-desulfurized crumb tire rubber/SBS composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 122083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wan, P.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, S. Synthesis of environmental-curable CO2-based polyurethane and its enhancement on properties of asphalt binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG-E20; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Highway Science Research Institute of the Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2011.
- G.T. 528-1998; Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determinaion of Tensile Stress-Strain Properties. Ministry of Chemical Industry of The People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1998.
- Hong, B.; Lu, G.; Gao, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, D. Green tunnel pavement: Polyurethane ultra-thin friction course and its performance characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Properties | Test Values | Test Method (JTG E20-2011 [29]) |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration | 67 (0.1 mm) | T 0604 |
| Softening point | 49.7 (°C) | T 0606 |
| Ductility | >100 (cm) | T 0605 |
| Density | 1.022 (g/cm3) | T 0603 |
| Items | Grain Size (mm) | Results | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent specific gravity | 9.5~16 | 3.032 | ≥2.6 |
| 4.75~9.5 | 2.998 | ||
| 2.36~4.75 | 3.009 | ||
| <2.36 | 2.987 | ||
| Water absorption (%) | 9.5~16 | 0.53 | ≤3 |
| 4.75~9.5 | 0.62 | ||
| 2.36~4.75 | 0.98 | ||
| Los Angeles abrasion (%) | 14.2 | ≤28 | |
| Crushed value (%) | 15.1 | ≤26 |
| Samples | PR11 | PR10 | PR23 | PR32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fracture energy | 20,156 J/mm2 | 19,262 J/mm2 | 13,902 J/mm2 | 25,122 J/mm2 |
| Modifier Content | MS0 (Kn)/ Std. Dev | MS1 (kN)/ Std. Dev | RMS (%) | TS0 (MPa)/ Std. Dev | TS1 (MPa)/ Std. Dev | ITSR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt% | 14.25/2.61 | 12.73/2.14 | 88.0 | 0.981/0.054 | 0.837/0.037 | 85.3 |
| 2 wt% | 14.71/2.35 | 13.11/2.53 | 89.1 | 1.067/0.038 | 0.917/0.029 | 85.9 |
| 4 wt% | 17.95/2.87 | 16.16/2.77 | 90.0 | 1.090/0.042 | 0.943/0.036 | 86.5 |
| 6 wt% | 18.01/3.01 | 16.47/3.12 | 91.4 | 1.117/0.053 | 0.976/0.043 | 87.4 |
| 8 wt% | 18.92/2.93 | 17.35/3.02 | 91.7 | 1.132/0.049 | 1.015/0.051 | 89.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z. Characteristics of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier and Its Effect on the Performance of Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712703
Gao B, Zhao Y, Zhao Z. Characteristics of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier and Its Effect on the Performance of Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability. 2023; 15(17):12703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712703
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Bo, Yuechao Zhao, and Zenggang Zhao. 2023. "Characteristics of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier and Its Effect on the Performance of Asphalt Mixture" Sustainability 15, no. 17: 12703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712703
APA StyleGao, B., Zhao, Y., & Zhao, Z. (2023). Characteristics of Polyurethane/Waste Rubber Powder Composite Modifier and Its Effect on the Performance of Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability, 15(17), 12703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712703







