Selective Mechanisms of WO3 Catalyzing CO2 Desorption and Inhibiting NH3 Escape
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Reactions and Experiment
2.1. Reactions
2.2. Materials
2.3. Apparatus and Methods
2.4. Order Independence Validation of Addition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Catalyst on CO2 Desorption
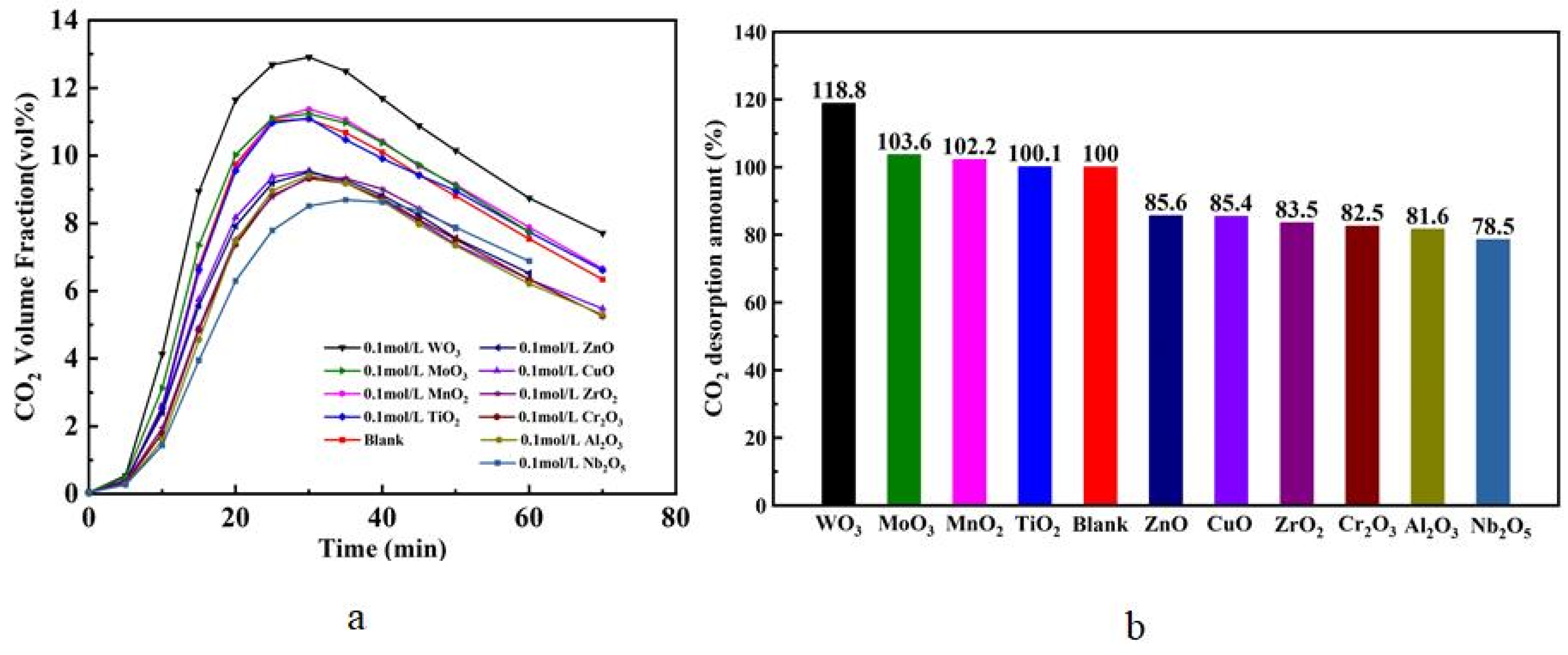
3.1.1. Ten Kinds of Metal Oxides
3.1.2. WO3 Concentration Effects
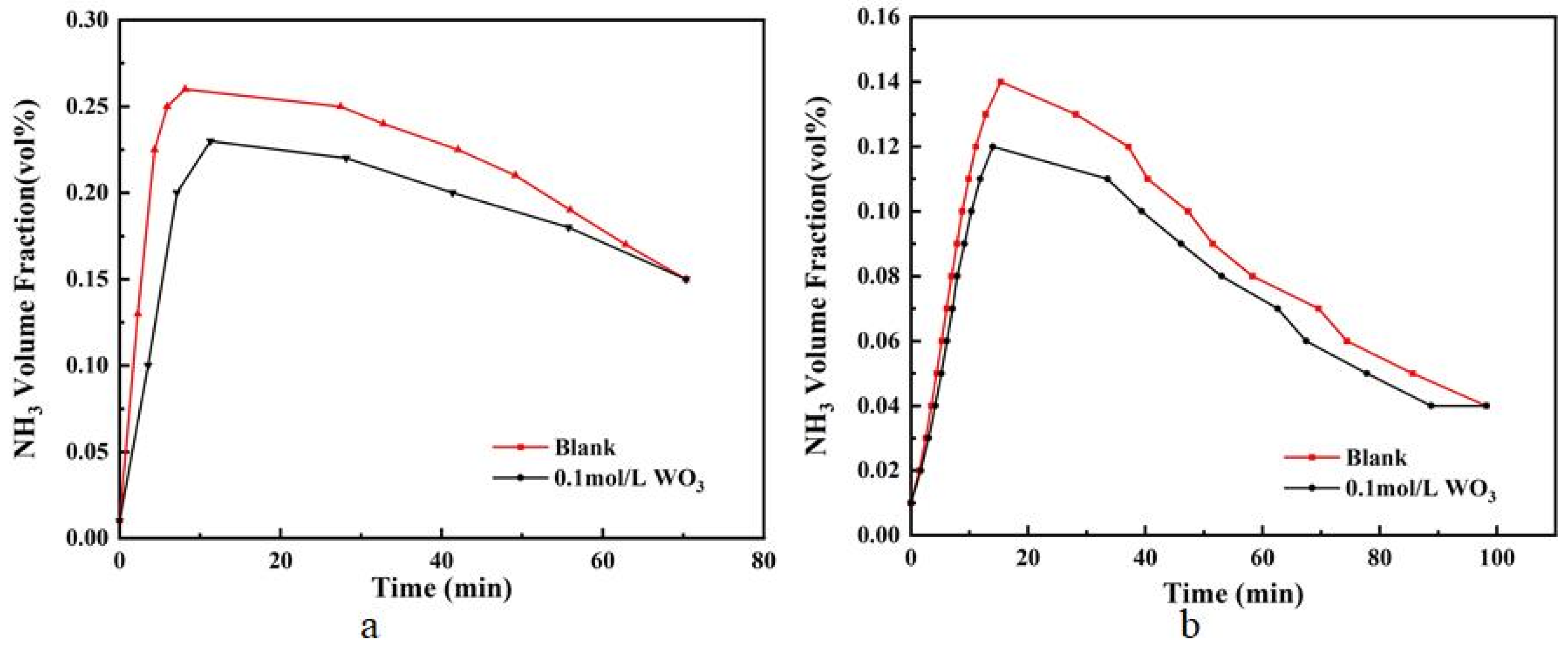
3.2. Effect of Inhibiting Ammonia Escape
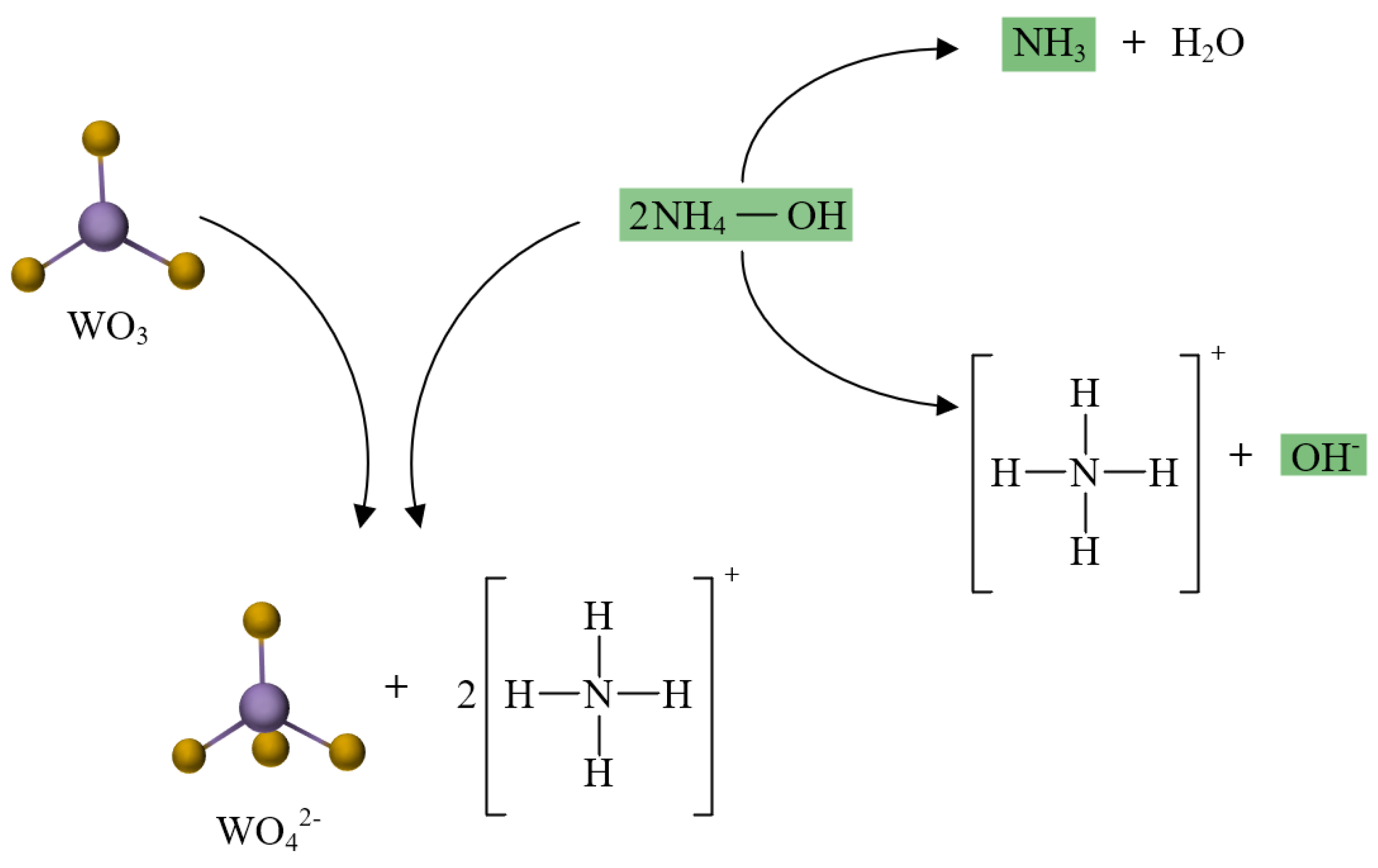
3.3. Analysis and Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mora, C.; Spirandelli, D.; Franklin, E.C.; Lynham, J.; Kantar, M.B.; Miles, W.; Smith, C.Z.; Freel, K.; Moy, J.; Louis, L.V.; et al. Broad threat to humanity from cumulative climate hazards intensified by greenhouse gas emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Kang, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, W.-F. A strategy for CO2 capture and utilization towards methanol production at industrial scale: An integrated highly efficient process based on multi-criteria assessment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 293, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Li, K.; Yu, H.; Jiang, K.; Chen, J.; Feron, P. Amine-based post-combustion CO2 capture mediated by metal ions: Advancement of CO2 desorption using copper ions. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Conway, W.; Burns, R.; Maeder, M.; Puxty, G.; Clifford, S.; Yu, H. Investigation of metal ion additives on the suppression of ammonia loss and CO2 absorption kinetics of aqueous ammonia-based CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 56, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voice, A. Amine Oxidation in Carbon Dioxide Capture by Aqueous Scrubbing. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Qi, G.; Chen, C. Study on mass transfer and kinetics of CO2 absorption into aqueous ammonia and piperazine blended solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 75, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, U.H.; Shah, A.K.; Kim, J.N.; You, J.K.; Choi, S.H.; Lim, D.H.; Nam, S.; Park, Y.H.; Baek, I.H. Effects of Transition Metal Oxide Catalysts on MEA Solvent Regeneration for the Post-Combustion Carbon Capture Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5862–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, H.; Tade, M.; Feron, P. Theoretical and experimental study of NH3 suppression by addition of Me(II) ions (Ni, Cu and Zn) in an ammonia-based CO2 capture process. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 24, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachitsas, S.; Bonalumi, D. Parametric investigation of CO2 capture from industrial flue gases using aqueous mixtures of ammonia (NH3) and potassium carbonate (K2CO3). Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 114, 103567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.N.; Qiao, K.; Chu, F.M.; Yang, L.J.; Du, X.Z. Experimental study of divalent metal ion effects on ammonia escape and carbon dioxide desorption in regeneration process of ammonia decarbonization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, G.; Zhu, S.; Han, T.; Yu, W. Mass transfer of ammonia escape and CO2 absorption in CO2 capture using ammonia solution in bubbling reactor. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, S.-R.; Park, J.M. The effects of Cu(II) ion as an additive on NH3 loss and CO2 absorption in ammonia-based CO2 capture processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, F.; Peruzzini, M.; Barzagli, F. The role of zinc(II) in the absorption-desorption of CO2 by aqueous NH3, a potentially cost-effective method for CO2 capture and recycling. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Chen, G.; Ma, X.; Guo, M.; Han, T.; Song, H. Ammonia escape control in carbon dioxide capture using ammonia method. Huagong Xuebao/CIESC J. 2014, 65, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Song, H.; Zang, B.; Chen, G.; Zhu, S. Experimental study of Co(II) additive on ammonia escape in carbon capture using renewable ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Resnik, K.P.; Garber, W.; Hreha, D.C.; Yeh, J.T.; Pennline, H.W. A parametric scan for regenerative ammonia-based scrubbing for the capture of CO2. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Pittsburgh Coal Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.C.; Song, H.H.; Sun, Y.X. Ammonia escape inhibited by NHD in the process of carbon capture using ammonia solution. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 610, 1901–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazuki, G.R.; Pahlevanzadeh, H.; Mohseni Ahooei, A. Solubility of CO2 in aqueous ammonia solution at low temperature. Calphad 2006, 30, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekunova, T.O.; Baranchikov, A.E.; Yapryntsev, A.D.; Rudakovskaya, P.G.; Ivanova, O.S.; Karavanova, Y.A.; Kalinina, M.A.; Rumyantseva, M.N.; Dorofeev, S.G.; Ivanov, V.K. Ultrasonic disintegration of tungsten trioxide pseudomorphs after ammonium paratungstate as a route for stable aqueous sols of nanocrystalline WO3. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Zhou, K.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z. Equilibrium WO3 concentration in the Ca2+-(NH4)2CO3-(NH4)2WO4-NH3-H2O system. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 206, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, G.; Han, T.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J. Experimental study on the effect of Ni(II) additive on ammonia escape in CO2 capture using ammonia solution. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 37, 249–255. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, F.; Liu, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhong, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, Q. Selective Mechanisms of WO3 Catalyzing CO2 Desorption and Inhibiting NH3 Escape. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13044. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713044
Chu F, Liu X, Gao Q, Zhong L, Xiao G, Wang Q. Selective Mechanisms of WO3 Catalyzing CO2 Desorption and Inhibiting NH3 Escape. Sustainability. 2023; 15(17):13044. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713044
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Fengming, Xi Liu, Qianhong Gao, Longchun Zhong, Guozhen Xiao, and Qianlin Wang. 2023. "Selective Mechanisms of WO3 Catalyzing CO2 Desorption and Inhibiting NH3 Escape" Sustainability 15, no. 17: 13044. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713044
APA StyleChu, F., Liu, X., Gao, Q., Zhong, L., Xiao, G., & Wang, Q. (2023). Selective Mechanisms of WO3 Catalyzing CO2 Desorption and Inhibiting NH3 Escape. Sustainability, 15(17), 13044. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713044






