Air Traffic Sector Network: Motif Identification and Resilience Evaluation Based on Subgraphs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We use a technique for detecting micro subgraph patterns to reveal how small, closely interconnected components are constructed in order to link and integrate the ATSN.
- (2)
- This paper explores network subgraphs as a means of understanding resilience in the ATSN, and can be generalized to other relevant studies in network science and sustainability.
2. Methodology
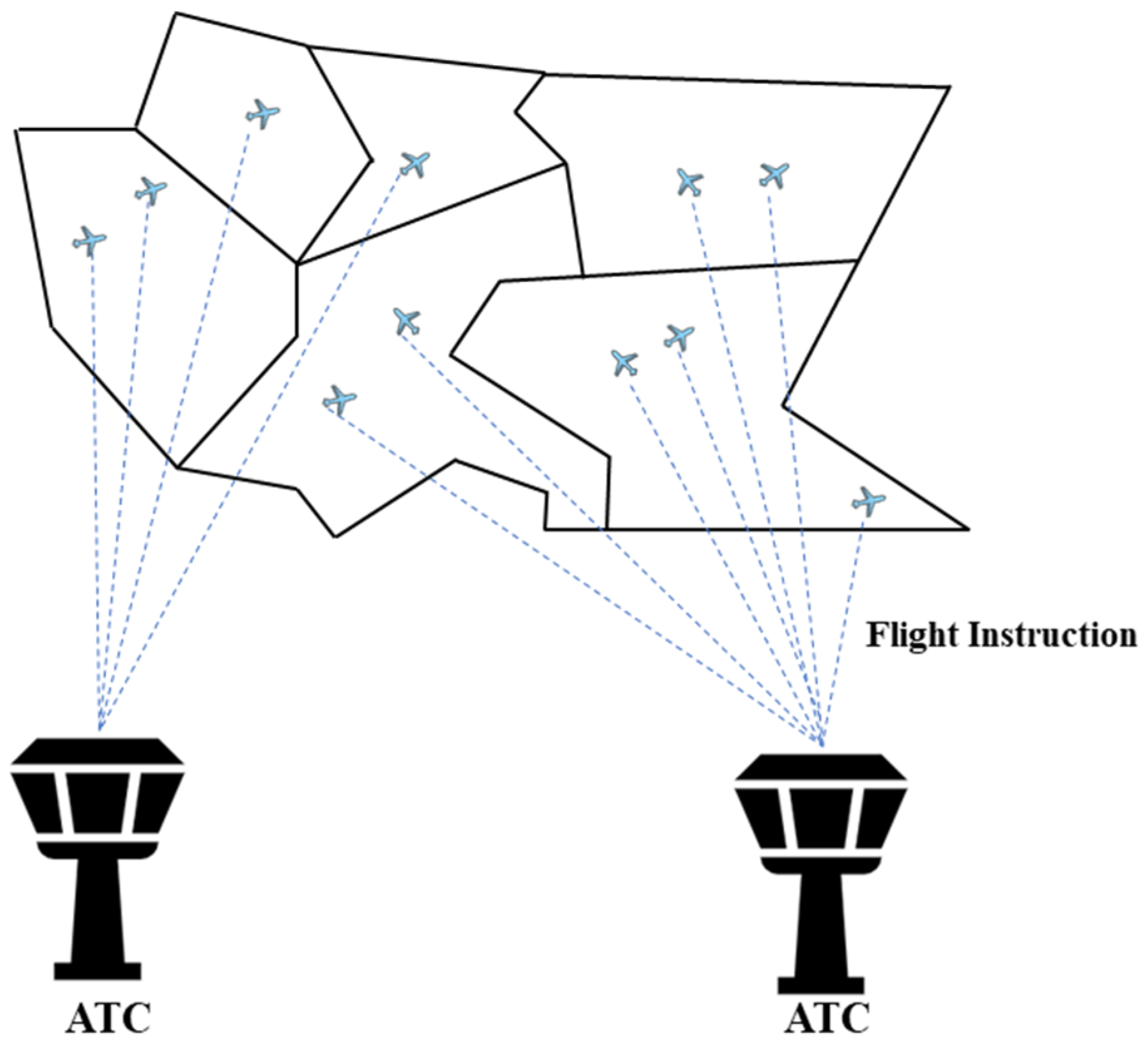
2.1. Air Traffic Sector Network Construction
- Abstract each sector as a node. Create an undirected edge between two nodes if there is a flight path connecting them.
- When there are multiple flight paths between two sectors, simplify these multiple flight paths as a single edge to represent the connection relationship.
- If sectors of varying altitudes share a common projection on the 2-dimensional plane, such sectors are paired to a node. In other words, keep the higher sectors and remove the lower ones.
2.2. Motif of ATSN
2.2.1. Network Subgraph Structure
2.2.2. Subgraph Structure Motif Analysis
- Frequency of motif
- 2.
- p Value of motif
- 3.
- Significance Value Z of motif
- Random network generation. Motif identification is performed by comparing the frequency of subgraphs in real networks with many random networks. To detect the motifs of an ATSN, it is necessary to first generate random networks with the same size and degree distribution as the real network [44].
- Subgraph detection. The aim of this step is to detect specific pattern subgraphs in the real network, and then, generate random networks, respectively. It can determine and categorize whether they are homogeneous subgraphs. Identifying whether the graph structure is isomorphic is an NP-hard problem. The commonly used subgraph methods include ESA, ESU, and Rand-ESU [45,46].
- Motif evaluation. The motif properties of each heterogeneous subgraph are determined by computing the above-mentioned statistical indicators (Frequency, p and Z).
2.3. Resilience of ATSN
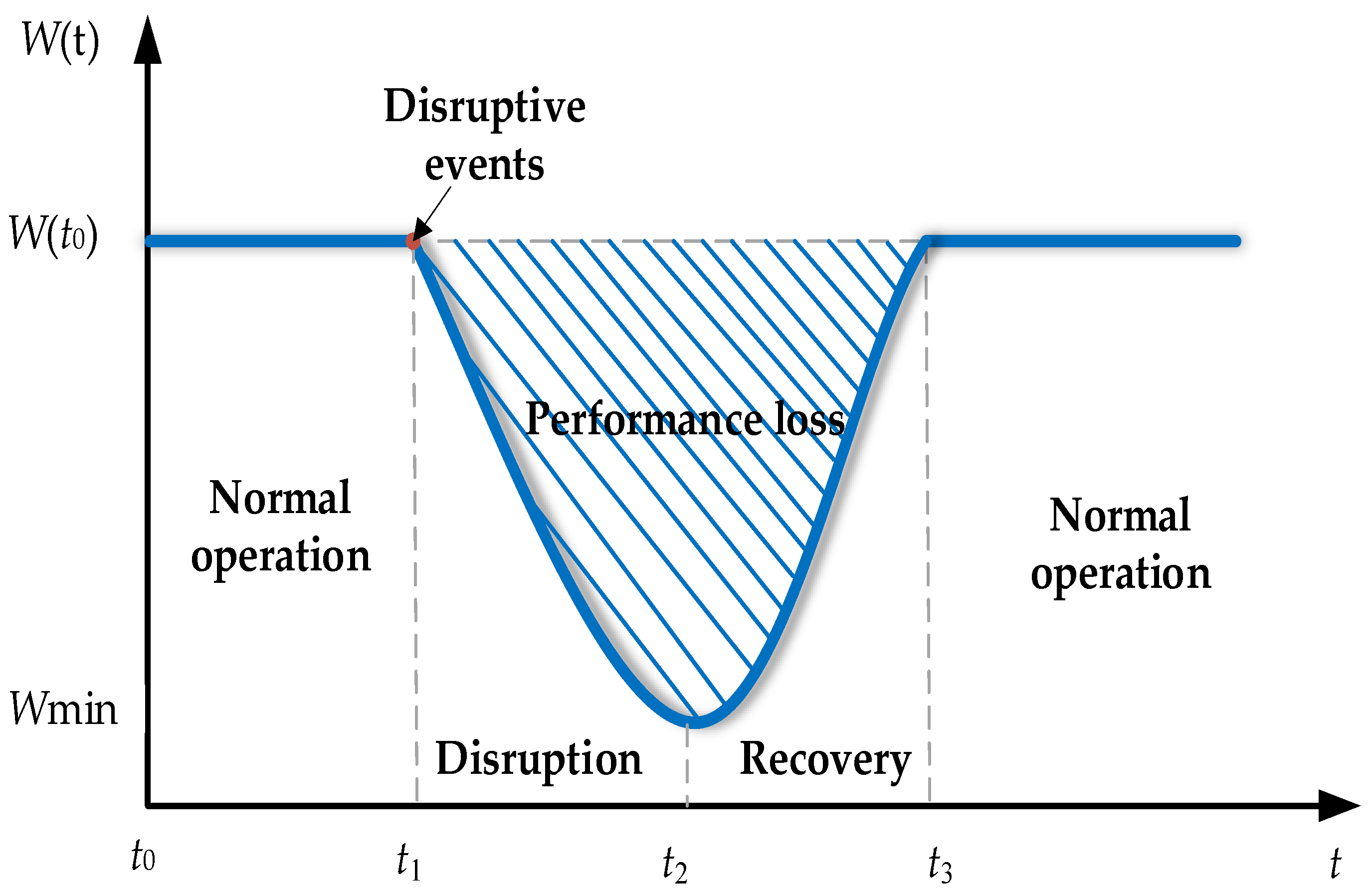
2.3.1. Resilience Conception
2.3.2. Subgraph Resilience Evaluation
- Subgraph motif concentration
- 2.
- Subgraph residual concentration
- 3.
- Subgraph resilience
2.3.3. Resilience Simulation Rules
3. Data Acquisition and Description
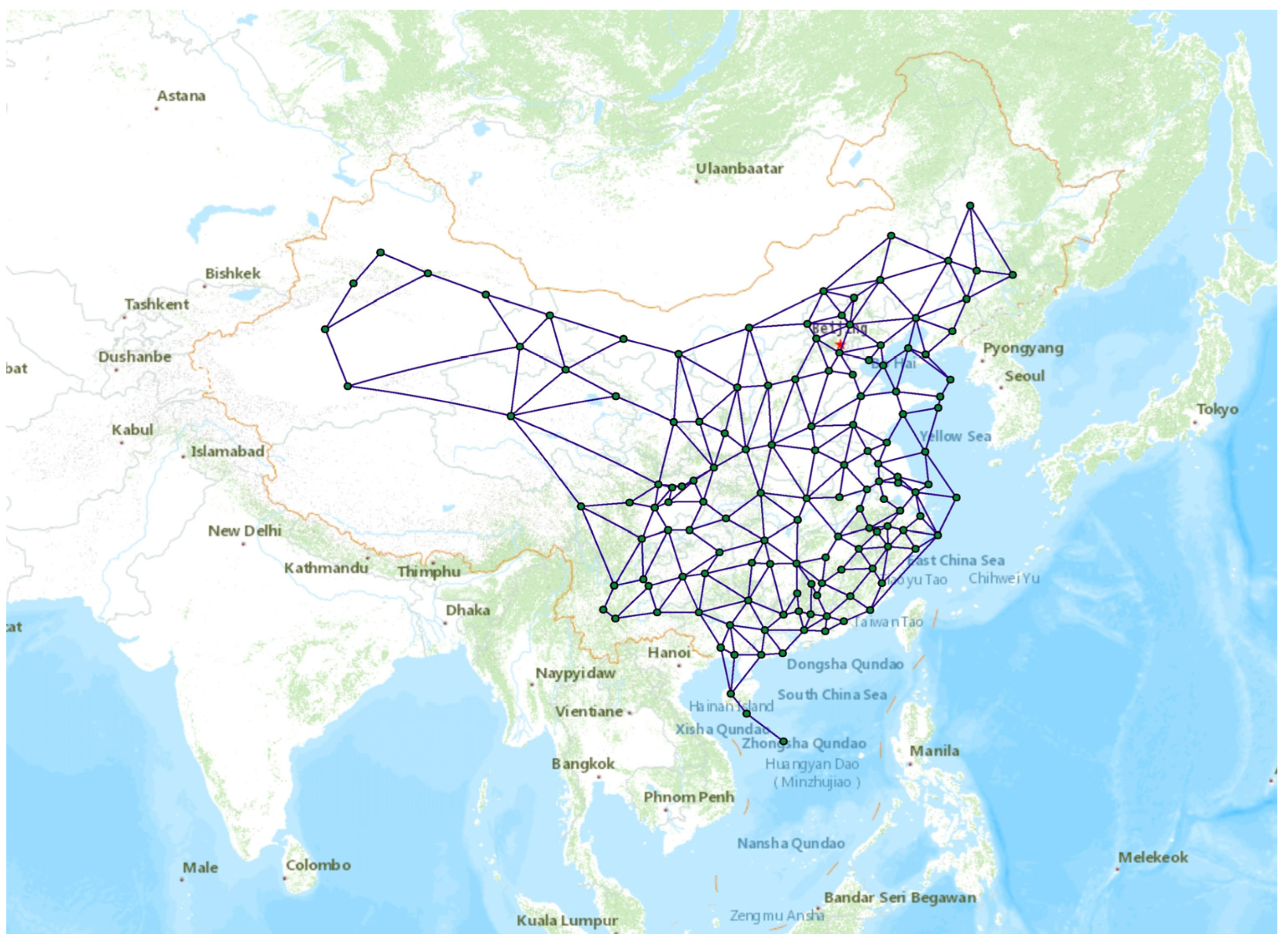
4. ATSN of China
4.1. Motif Identification
4.2. Subgraph Resilience Analysis
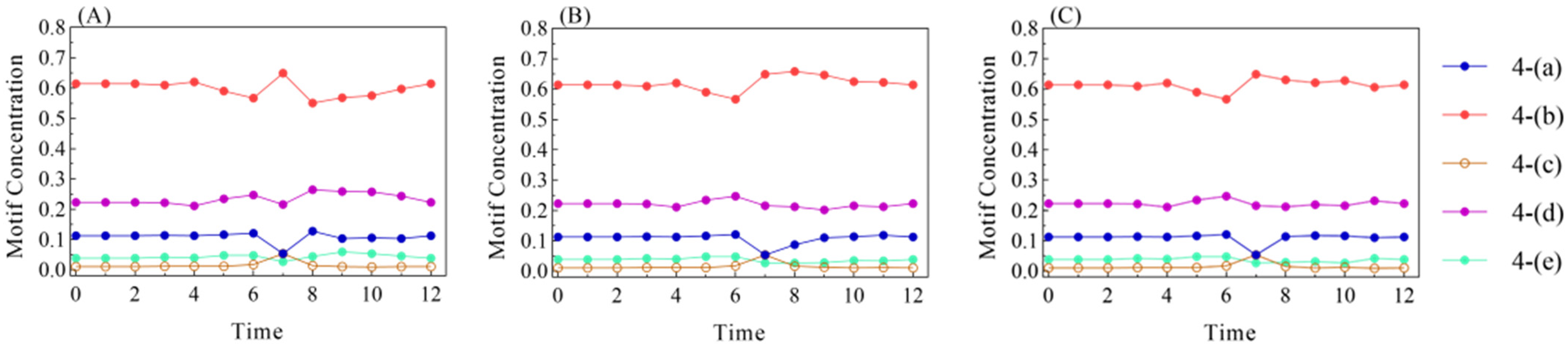
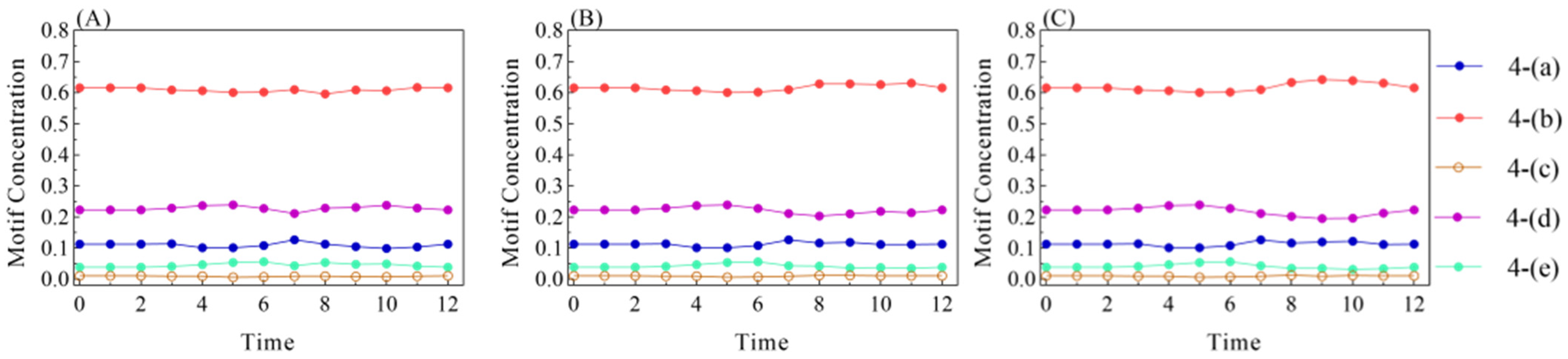
4.2.1. Subgraph Motif Concentration Analysis
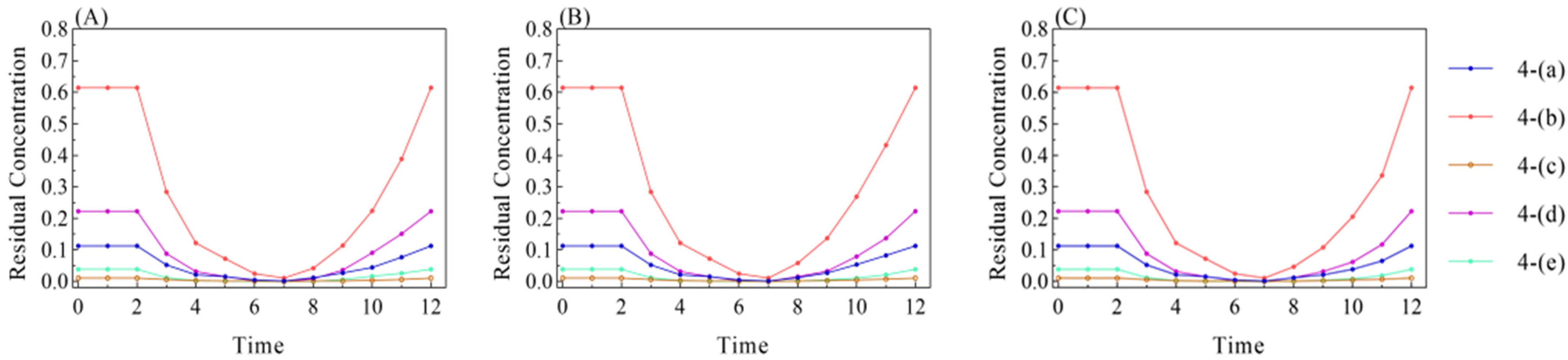
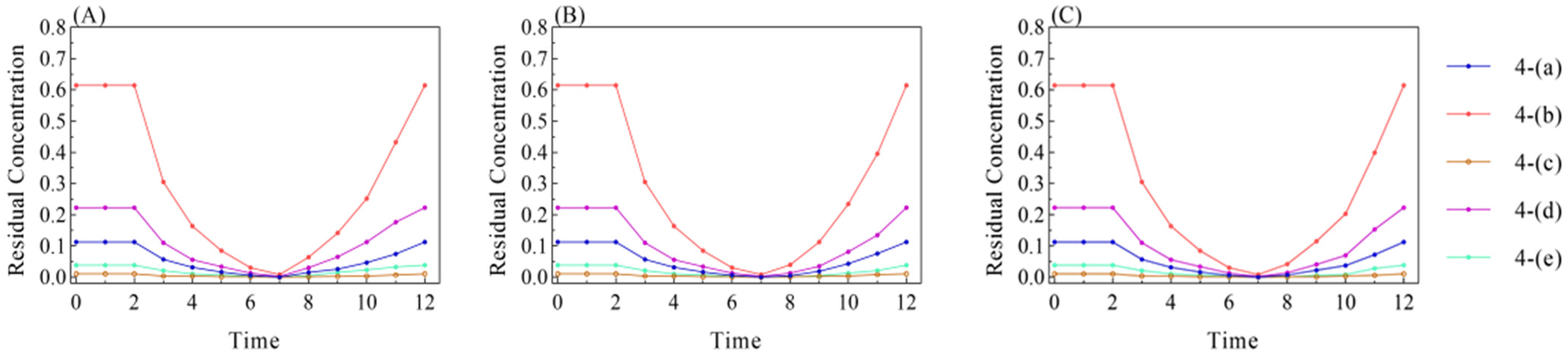
4.2.2. Subgraph Residual Concentration Analysis
4.2.3. System Resilience of ATSN
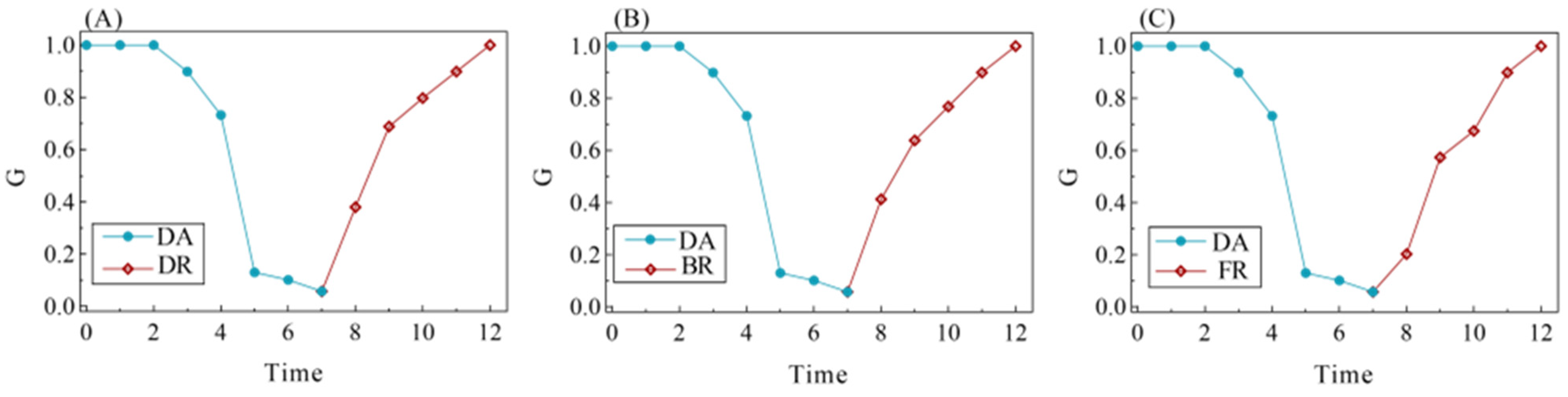
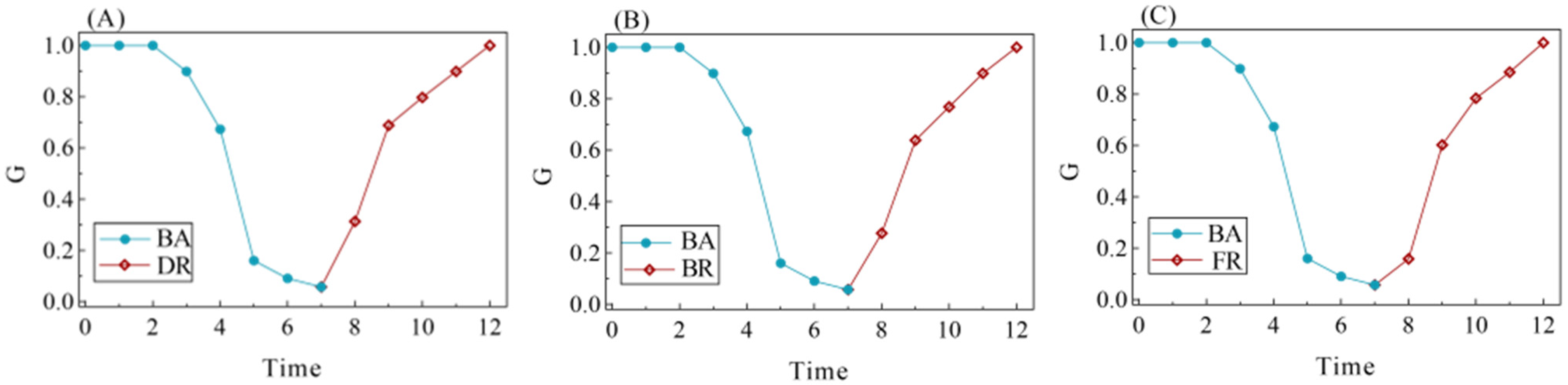
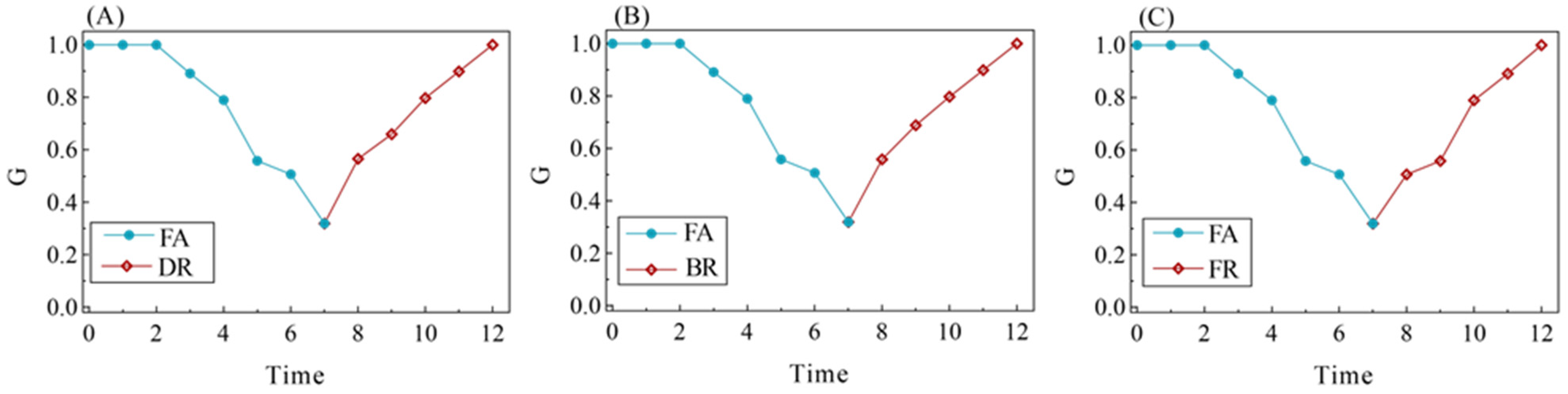
4.2.4. Comparison of Subgraph Resilience and System Resilience
5. Conclusions
- (1)
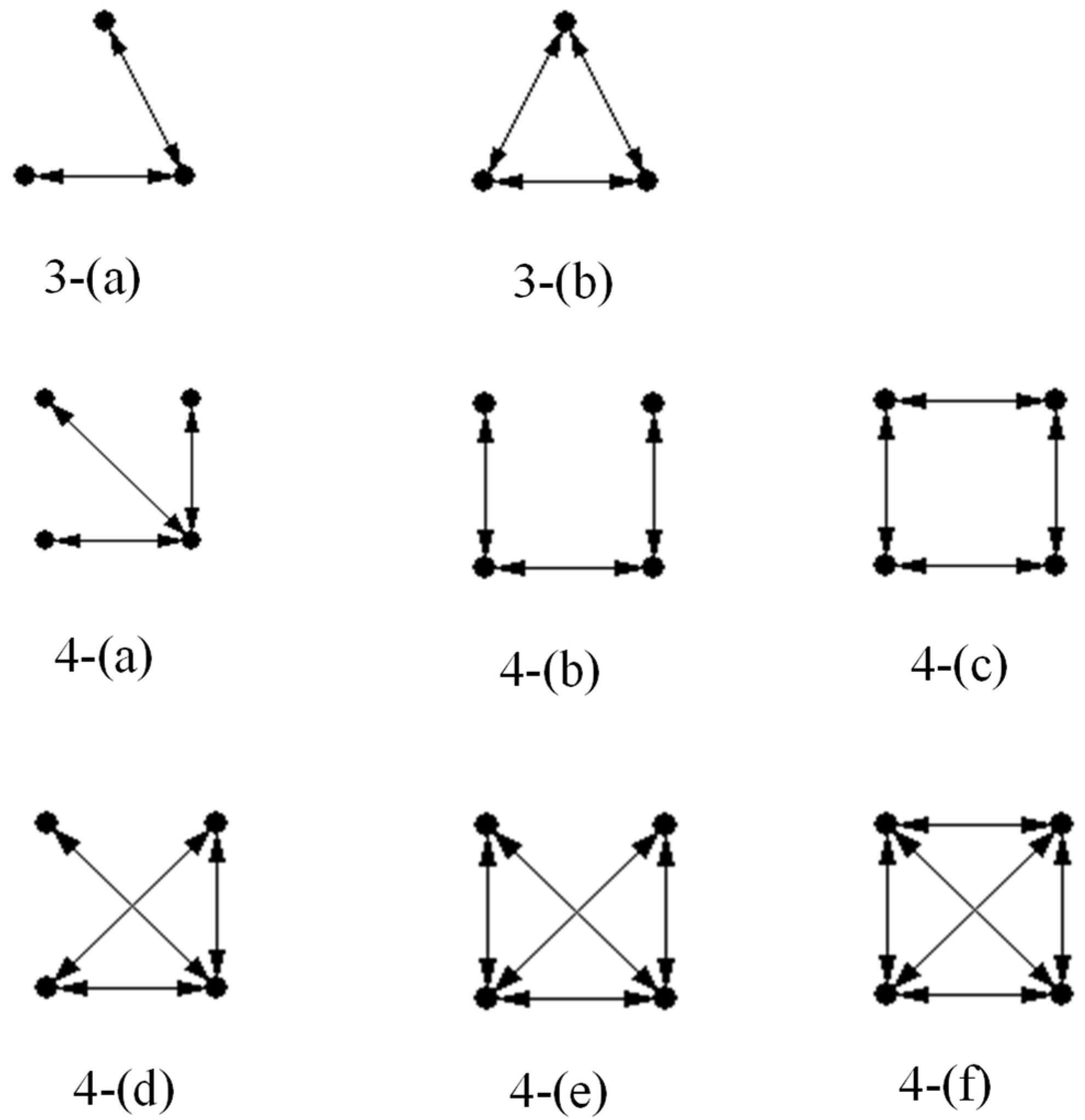
- Subgraphs with high connectivity are those with a motif structure in the ATSN (3-(b), 4-(d), and 4-(e)), while the subgraph structures 3-(a), 4-(a), and 4-(b), with lower connectivity, perform as anti-motifs.
- (2)
- The ATSN network comprises a considerable number of subgraph structures with low connectivity. The use of subgraph structures with moderate connectivity, as well as several with higher connectivity, has improved overall network accessibility.
- (3)
- There is a level of coherence between the macro- and micro-expressions of the resilience process in air traffic sector networks. The DA-FR process has the most substantial impact on resilience performance.
- (4)
- Structure-based perturbations are found to have a higher impact on network subgraph resilience as well as system resilience performance, whereas traffic flow has limited impact at both the macro and micro levels. In air traffic management, controllers should prioritize ensuring the normal functioning of sectors with a high degree and betweenness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guimera, R.; Mossa, S.; Turtschi, A.; Amaral, L.N. The worldwide air transportation network: Anomalous centrality. Communit structure, and cities’ global roles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7794–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Lu, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X. Analyzing the topological characteristic and key nodes of Chinese air sector network. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2019, 33, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.L.; Bhatia, U.; Kodra, E.A.; Ganguly, A.R. Resilience of the US national airspace system airport network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.P.; Cai, X. Structural changes caused by error and attack tolerance in US airport network. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2004, 18, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharali, A.; Baruah, D. On structure and robustness of airport network of India. Res. Rev. Discret. Math. Struct. 2018, 5, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Pien, K.-C.; Han, K.; Shang, W.; Majumdar, A.; Ochieng, W. Robustness analysis of the European air traffic network. Transp. A 2015, 11, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Coit, D.W.; Felder, F.A.; Wang, D. Resiliency-based restoration optimization for dependent network systems against cascading failures. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 207, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mo, H.; Wang, F.; Jin, F. Exploring the network structure and nodal centrality of China’s air transport network: A complex network approach. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuellner, D.R.; Roy, S.; D’Souza, R.M. Resilience and rewiring of the passenger airline networks in the United States. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 056101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requião da Cunha, B.; González-Avella, J.C.; Gonçalves, S. Fast Fragmentation of Networks Using Module-Based Attacks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, W.; Hu, M.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C. Empirical analysis of airport network and critical airports. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusella, P.; Grassberger, P.; Pérez-Reche, F.J.; Politi, A. Immunization and Targeted Destruction of Networks using Explosive Percolation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 208301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Anderson, R. An Experimental Evaluation of Robustness of Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2013, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, F. Robustness of China’s air transport network from 1975 to 2017. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 539, 122876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.M.; Dunn, S.; Ma, S. The vulnerability of the European air traffic network to spatial hazards. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.N.; Gao, J.D. Cascading failure invulnerability and optimization strategy of air space sector network. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2018, 39, 322579. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; He, M.; Liu, M.X. Air traffic CPS cascading failure and mitigation strategy. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2021, 47, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzasoleiman, B.; Babaei, M.; Jalili, M.; Safari, M. Cascaded failures in weighted networks. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 046114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wandelt, S.; Fricke, H.; Rosenow, J. The Impact of COVID-19 on Air Transportation Network in the United States, Europe, and China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen-Orr, S.S.; Milo, R.; Mangan, S.; Alon, U. Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia coli. Nature Genet. 2002, 31, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.; Heitzig, J.; Kurths, J. Detours around basin stability in power networks. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorochowski, T.E.; Grierson, C.S.; di Bernardo, M. Organization of feed-forward loop motifs reveals architectural 550 principles in natural and engineered networks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Barker, K.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E. A review of definitions and measures of system resilience. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 145, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, S.C. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamvakis, P.; Xenidis, Y. Comparative evaluation of resilience quantification methods for infrastructure systems. Procd. Soc. Behv. 2013, 74, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, P.; Frangopol, D.M.; Ummenhofer, T.; Zinke, T. Resilience and Sustainability of Civil Infrastructure: Toward a Unified Approach. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2014, 20, 04014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Y.; Sarker, M.N.I. Urban Resilience for Urban Sustainability: Concepts, Dimensions, and Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzaki, K. Risk Mitigation, Vulnerability Management, and Resilience under Disasters. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.-Y. Dynamic Flood Resilience Typology: A Systemic Transitional Adaptation from Peitou Plateau, Taiwan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama Dessavre, D.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E.; Barker, K. Multidimensional approach to complex system resilience analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 149, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Trakas, D.N.; Mancarella, P.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. Power Systems Resilience Assessment: Hardening and Smart Operational Enhancement Strategies. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyza, J.; Yusta, J.M. Integrated Risk Assessment for Robustness Evaluation and Resilience Optimisation of Power Systems after Cascading Failures. Energies 2021, 14, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liang, L.; Zhu, X. Improved Markov-chain-based ultra-short-term PV forecasting method for enhancing power system resilience. J. Eng. 2021, 2021, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Heinimann, H.; Han, K.; Luo, H.; Zhong, B. Evaluating resilience in urban transportation systems for sustainability: A systems-based Bayesian network model. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 121, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Heinimann, H.R. A resilience-oriented approach for quantitatively assessing recurrent spatial-temporal congestion on urban roads. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, R.; Bekera, B. A metric and frameworks for resilience analysis of engineered and infrastructure systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 121, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoni, A.; Cimellaro, G.P.; Domaneschi, M.; Sordo, S.; Mazza, A. Modeling the interdependency between buildings and the electrical distribution system for seismic resilience assessment. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubna, M.D.; Fowler, J. An application of the highly optimized tolerance model to electrical blackouts. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2003, 13, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, J.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Chen, P.; Hansen, M. Measuring the resilience of an airport network. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 2694–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Tan, S.; Chandramouleeswaran, K.R.; Tran, H.T. Data-driven analysis of resilience in airline networks. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 143, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Le, M.; Wang, D. Airline Network Structure: Motifs and Airports’ Role in Cliques. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xiu, C.; Song, W.; Yang, K. Study on Structural Characteristics of China’s Passenger Airline Network Based on Network Motifs Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.B.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.B.; Zhang, J. Delay causality network in air transport systems. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. 2018, 118, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurant, M.; Thiran, P. Extraction and analysis of traffic and topologies of transportation networks. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 036114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernicke, S.; Rasche, F. FANMOD: A tool for fast network motif detection. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, S. Efficient Detection of Network Motifs. IEEE-ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2006, 3, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernicke, S. A faster algorithm for detecting network motifs. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Algorithms in Bioinformatics (WABI ‘05). Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics, Mallorca, Spain, 3–6 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y.; Hero, A.O. Assessing and safeguarding network resilience to nodal attacks. IEEE Commun. Mag 2014, 52, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfraind, A. Optimizing topological cascade resilience based on the structure of terrorist networks. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Lillo, F. Modelling the air transport with complex networks: A short review. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 215, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Modeling Network | Author | Focus Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Airport network | Guimera et al. [1] Wang et al. [8] Cong et al. [11] | Normal operation |
| Clark et al. [3] Wang et al. [39] | Resilience of network | |
| Chi et al. [4] Bharali et al. [5] Pien et al. [6] Zhou et al. [7] Requião et al. [10] Clusella et al. [12] Kim et al. [13] Chen et al. [14] Winkinson et al. [15] | Destruction of network | |
| Mirzasoleiman et al. [18] | Cascading of network | |
| Sun et al. [19] | Operation under public emergencies | |
| Air traffic sector network | Ren et al. [2] | Normal operation |
| QI et al. [16] | Cascading of network | |
| Airline network | Wuellner et al. [9] Allen et al. [40] | Resilience of network |
| Multilayer network | Wang et al. [17] | Cascading of network |
| ID | Sample | Frequency (Original) | Mean-Freq (Random) | p | Value Z | Motif Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-(a) |  | 86.543 | 99.984 | 1.000 | −30.379 | Anti-motif |
| 3-(b) | 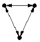 | 13.457 | 0.002 | ≤0.001 | 30.379 | Motif |
| 4-(a) |  | 11.296 | 22.943 | 1.000 | −77.855 | Anti-motif |
| 4-(b) |  | 61.458 | 76.057 | 1.000 | −63.236 | Anti-motif |
| 4-(c) | 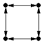 | 1.074 | 0.970 | 0.208 | 0.810 | Anti-motif |
| 4-(d) | 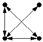 | 22.298 | 0.030 | ≤0.001 | 211.010 | Motif |
| 4-(e) |  | 3.8737 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.001 | 2127.300 | Motif |
| Disturbance Recovery Type | Subgraph Resilience Loss (Tk) | System Resilience (Rloss) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-(a) | 4-(b) | 4-(c) | 4-(d) | 4-(e) | ||
| DA-DR | 0.762 | 4.251 | 0.071 | 1.582 | 0.284 | 4.316 |
| DA-BR | 0.748 | 4.123 | 0.067 | 1.604 | 0.294 | 4.363 |
| DA-FR | 0.786 | 4.324 | 0.068 | 1.646 | 0.301 | 4.732 |
| BA-DR | 0.743 | 4.050 | 0.071 | 1.406 | 0.231 | 4.383 |
| BA-BR | 0.762 | 4.158 | 0.072 | 1.527 | 0.266 | 4.498 |
| BA-FR | 0.766 | 4.182 | 0.074 | 1.514 | 0.263 | 4.652 |
| FA-DR | 0.636 | 3.342 | 0.067 | 1.174 | 0.181 | 3.014 |
| FA-BR | 0.617 | 3.305 | 0.065 | 1.211 | 0.201 | 2.993 |
| FA-FR | 0.675 | 3.649 | 0.067 | 1.343 | 0.225 | 3.696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Air Traffic Sector Network: Motif Identification and Resilience Evaluation Based on Subgraphs. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813423
Shi Z, Zhang H, Li Y, Zhou J. Air Traffic Sector Network: Motif Identification and Resilience Evaluation Based on Subgraphs. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813423
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zongbei, Honghai Zhang, Yike Li, and Jinlun Zhou. 2023. "Air Traffic Sector Network: Motif Identification and Resilience Evaluation Based on Subgraphs" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813423
APA StyleShi, Z., Zhang, H., Li, Y., & Zhou, J. (2023). Air Traffic Sector Network: Motif Identification and Resilience Evaluation Based on Subgraphs. Sustainability, 15(18), 13423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813423







