Reacquainting the Structural Characteristics of Pull-Apart Basins Based on Simulations with Wet Clay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design and Statistics
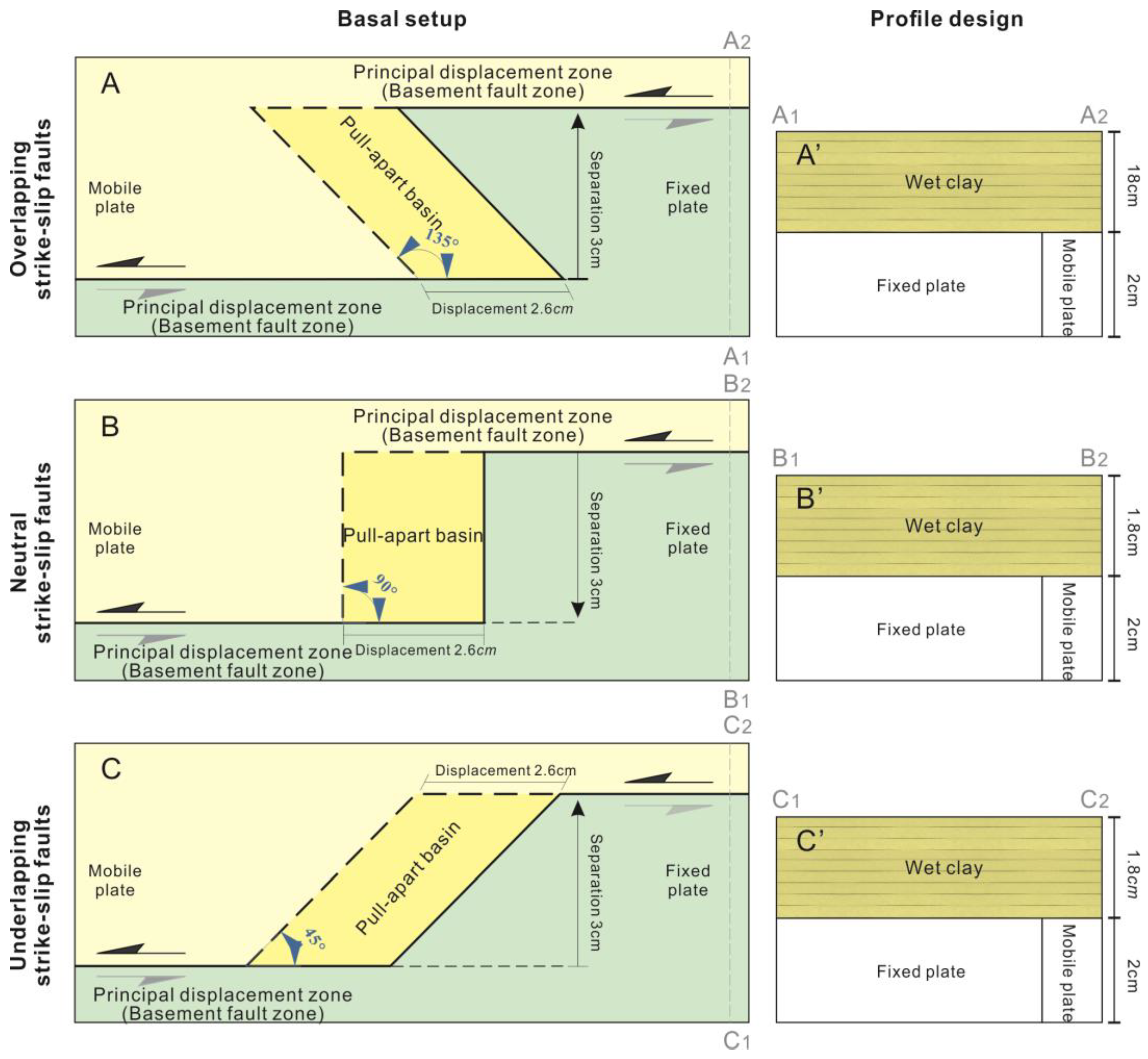
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Material
2.3. Fault Area Density Statistics
2.4. Division of Subsidiary Faults
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Evolution of a Strike–Slip Fault with Different Bends
3.2. Characteristics of Fault Area Density
3.3. Characteristics of Subsidiary Faults
3.3.1. Number of Subsidiary Faults
3.3.2. Strike of Subsidiary Faults
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological Characteristics of the PAB
4.2. Density and Number of Subsidiary Faults
4.3. Proportion of Different Subsidiary Faults
4.4. Strike–Slip Mode Analyzed by Subsidiary Faults
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palladino, G.; Rizzo, R.E.; Zvirtes, G.; Grippa, A.; Philipp, R.P.; Healy, D.; Alsop, G.I. Multiple episodes of sand injection leading to accumulation and leakage of hydrocarbons along the San Andreas/San Gregorio fault system, California. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 118, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarewitz, D.R.; Lewis, S.D. The Marinduque intra-arc basin, Philippines: Basin genesis and in situ ophiolite development in a strike-slip setting. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1991, 103, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumaya, A.; Kadri, A.; Ayed, N.B.; Kim, Y.-S.; Dooley, T.P.; Rajabi, M.; Braham, A. Deformation styles related to intraplate strike-slip fault systems of the Saharan-Tunisian Southern Atlas (North Africa): New kinematic models. J. Struct. Geol. 2020, 140, 104175. [Google Scholar]
- Neng, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, J.; Ma, X.; Zuo, L.; Chen, P. Deformation Styles and Multi-Stage Evolution History of a Large Intraplate Strike-Slip Fault System in a Paleozoic Superimposed Basin: A Case Study From the Tarim Basin, NW China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 837354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanghui, W.; Bingshan, M.; Jianfa, H.; Baozhu, G.; Xin, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, X. Origin and growth mechanisms of strike-slip faults in the central Tarim cratonic basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 595–607. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bian, Q.; Guo, Z. Tectonic analysis and petroleum significance of Cenozoic faults in Dongping-Niuzhong area in Altyn slope. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, Z.; Youde, X.; Guosheng, L.; Yongsheng, W.; Chenglong, X. Structural and deformational characteristics of strike-slippings along the middle-southern sector of the tan-lu fault zone. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2006, 41, 226–241+255. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Paul, D. Structural geometry and evolution of releasing and restraining bends: Insights from laser-scanned experimental models. AAPG Bull. 2011, 95, 1147–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.E.; McClay, K.; Whitehouse, P.; Dooley, T. 4D analogue modelling of transtensional pull-apart basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 1608–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.A.; Hariri, M.M.; Abdullatif, O.M.; Korvin, G.; Makkawi, M. Evolution history of transtensional pull-apart, oblique rift basin and its implication on hydrocarbon exploration: A case study from Sufyan Sub-basin, Muglad Basin, Sudan. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 79, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevitt, J.M.; Pollard, D.D.; Warren, J.M. Evaluation of transtension and transpression within contractional fault steps: Comparing kinematic and mechanical models to field data. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 60, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijker, G.; Beekman, F.; Bertotti, G.; Luthi, S.M. FEM analysis of deformation localization mechanisms in a 3-D fractured medium under rotating compressive stress orientations. Tectonophysics 2013, 593, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, G.; Nencini, R.; Skyttä, P. Modelling the influence of pre-existing brittle fabrics on the development and architecture pull-apart basins. J. Struct. Geol. 2020, 131, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, T.P.; Schreurs, G. Analogue modelling of intraplate strike-slip tectonics: A review and new experimental results. Tectonophysics 2012, 574–575, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.T. Geometry and kinematics of adhesive wear in brittle strike-slip fault zones. J. Struct. Geol. 2005, 27, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, K.; Kukowski, N.; Ratschbacher, L. The interaction of two indenters in analogue experiments and implications for curved fold-and-thrust belts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 302, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, G.; Dooley, T.P. Lithospheric-scale centrifuge models of pull-apart basins. Tectonophysics 2015, 664, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahe, B.; Ferrill, D.A.; Morris, A.P. Physical analog modeling of pull-apart basin evolution. Tectonophysics 1998, 285, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, T.; Mcclay, K. Analog modeling of pull-apart basins. AAPG Bull. 1997, 81, 1804–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Schrank, C.E.; Cruden, A.R. Compaction control of topography and fault network structure along strike-slip faults in sedimentary basins. J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Mitra, S. Deformation along oblique and lateral ramps in listric normal faults: Insights from experimental models. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 431–451. [Google Scholar]
- Fossen, H. Structural Geology; Cambridge University: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Atmaoui, N.; Kukowski, N.; Stöckhert, B.; König, D. Initiation and development of pull-apart basins with Riedel shear mechanism: Insights from scaled clay experiments. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2005, 95, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpfer, M.P.J.; Steyrer, H.P. Experimental modeling of strike-slip faults and the self-similar behavior. Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 2001, 193, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, D. The rheology of clay: A modeling material for geologic structures. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1993, 74, 569. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt, G.; Sims, D. Evaluating sand and clay models: Do rheological differences matter? J. Struct. Geol. 2005, 27, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withjack, M.O.; Henza, A.A.; Schlische, R.W. Three-dimensional fault geometries and interactions within experimental models of multiphase extension. AAPG Bull. 2017, 101, 1767–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Mitra, S. Analog modeling of divergent and convergent transfer zones in listric normal fault systems. AAPG Bull. 2010, 94, 1425–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withjack, M.O.; Schlische, R.W. Geometric and experimental models of extensional fault-bend folds. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2017, 253, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, A.E.; Schlische, R.W.; Withjack, M.O.; Ackermann, R.V. Influence of rift obliquity on fault-population systematics: Results of experimental clay models. J. Struct. Geol. 2000, 22, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henza, A.A.; Withjack, M.O.; Schlische, R.W. Normal-fault development during two phases of non-coaxial extension: An experimental study. J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henza, A.A.; Withjack, M.O.; Schlische, R.W. How do the properties of a pre-existing normal-fault population influence fault development during a subsequent phase of extension? J. Struct. Geol. 2011, 33, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withjack, M.O.; Jamison, W.R. Deformation produced by oblique rifting. Tectonophysics 1986, 126, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Mitra, S. Experimental models of transfer zones in rift systems. AAPG Bull. 2013, 97, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Peacock, D.C.P.; Sanderson, D.J. Fault damage zones. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.; Ferrill, D.A.; Stamatakos, J.A. Role of a ductile décollement in the development of pull-apart basins: Experimental results and natural examples. J. Struct. Geol. 1999, 21, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidinger, A.; Decker, K. 3D geometry and kinematics of the Lassee flower structure: Implications for segmentation and seismotectonics of the Vienna Basin strike–slip fault, Austria. Tectonophysics 2011, 499, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkodia, H.M.D.V.; Miyouna, T.; Delvaux, D.; Boudzoumou, F. Flower structures in sandstones of the Paleozoic Inkisi Group (Brazzaville, Republic of Congo): Evidence for two major strike-slip fault systems and geodynamic implications. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2020, 123, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Que, X.; He, Y.; Jia, L.; Xiao, Z.; Li, M. Paleogene geological framework and tectonic evolution of the central anticlinal zone in Lufeng 13 sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Pet. Res. 2019, 4, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, B.J.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Zach, C.; Bechtel, A.; Gratzer, R.; Kucher, F. Oil and gas in the Vienna Basin: Hydrocarbon generation and alteration in a classical hydrocarbon province. Pet. Geosci. 2018, 25, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsch, R.; Decker, K.; Wagreich, M. 3-D mapping of segmented active faults in the southern Vienna Basin. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Gong, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Lyu, W. Natural fractures and their contribution to tight gas conglomerate reservoirs: A case study in the northwestern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Su, X.; Gong, L.; Wang, Q.; Gao, S.; Xie, Z. Control of faults and fractures on shale oil enrichment. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 228, 212080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Liu, K.; Ju, W. Editorial: Advances in the study of natural fractures in deep and unconventional reservoirs. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1096643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.T.; Alavi, S.A.; Maerten, F. 2D finite-element elastic models of transtensional pull-apart basins. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2018, 350, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-x.; Wang, Z.-c.; Zheng, H.-j.; Xu, A.-n. Control of strike-slip faulting on reservoir formation of oil and gas in Nanpu sag. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2008, 35, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogonenkov, G.N.; Timurziev, A.I. Strike-slip deformations in the West Siberian Basin and their impact on exploration and development of oil and gas reservoirs. Cent. Eur. Geol. 2009, 52, 359–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Peng, G.; Zhu, D.; Li, S.; Suo, Y.; Zhan, H.; Zhao, L. Structure and formation mechanism of the Pearl River Mouth Basin: Insights from multi-phase strike-slip motions in the Yangjiang Sag, SE China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 226, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Shu, Y.; Yang, X.; Mei, L. Applying seismic geomorphology to delineate switched sequence stratigraphic architecture in lacustrine rift basins: An example from the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 78, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Hu, K.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X. Structural Features and its impacts on hydrcarbon accumlation of neogeoe in Enping sag, Pear River Mouth basin. Geoscience 2014, 28, 543–550. [Google Scholar]











| Material | Composition and Particle Size (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | Coefficient of Internal Friction | Cohesion (Pa) | Shear Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet clay [25] | Powdered kaolin, nepheline–syenite, and flint ≤0.1 | 1.63 (wet) | — | 40 (average) | — |
| Wet clay [26] | Powdered kaolin, nepheline–syenite, and flint ≤0.1 | 1.57–1.82 (wet) | — | 54–130 | — |
| Wet clay [27] | Kaolinite particles (<0.005 mm) and water (40% by weight) | 1.55–1.60 | 0.6 | 50 | — |
| Wet clay [28] | — | 1.6–1.65 | — | — | — |
| Stiff clay [8] | — | 1.85 | — | — | — |
| Soft water-based clay [8] | — | 1.6–1.65 | — | — | — |
| Wet clay [29] | Kaolinite and water (40% by weight) | 1.6 | 0.5 | 50 | — |
| Wet clay [30] | Powdered kaolin (≤0.1 mm) and water (40% by weight) | 1.65 | 0.5 | 50 | — |
| Wet clay [31] | Kaolinite particles (<0.005 mm) and water (40% by weight) | 1.55–1.60 | 0.6 | 50 | — |
| Wet clay [32] | Kaolinite particles (<0.005 mm) and water (40% by weight) | 1.55–1.60 | 0.6 | 50 | — |
| Clay [33] | Quartz, kaolinite, small amounts of smectite, illite, orthoclase, and talc | 1.6 | — | — | 10−3 |
| Wet clay [21] | — | 1.6–1.65 | — | — | — |
| Stiff clay [34] | — | 1.85 | — | — | — |
| — | 1.6–1.65 | — | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Lao, H.; Peng, C.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Sun, W.; Ju, Y.; Dong, G. Reacquainting the Structural Characteristics of Pull-Apart Basins Based on Simulations with Wet Clay. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914143
Xu H, Lao H, Peng C, Xu H, Liu C, Sun W, Ju Y, Dong G. Reacquainting the Structural Characteristics of Pull-Apart Basins Based on Simulations with Wet Clay. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914143
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hongyuan, Haigang Lao, Chao Peng, Hao Xu, Chuncheng Liu, Wei Sun, Yongtao Ju, and Guiyu Dong. 2023. "Reacquainting the Structural Characteristics of Pull-Apart Basins Based on Simulations with Wet Clay" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914143
APA StyleXu, H., Lao, H., Peng, C., Xu, H., Liu, C., Sun, W., Ju, Y., & Dong, G. (2023). Reacquainting the Structural Characteristics of Pull-Apart Basins Based on Simulations with Wet Clay. Sustainability, 15(19), 14143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914143






