Abstract
Reviews on sustainability assessment research have shown that Africa is lagging in this research area. As a result, few African countries have local sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure development. Considering the vital role of infrastructure to Africa’s development, the identification of only a few countries with local sustainability assessment processes raises questions on the overall state of sustainability assessment in the continent. To date, there is no study that gives a definite account of which African countries have local sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure. The aim of this study was to conduct a systematic literature review to identify and analyze local sustainability assessment process for infrastructure development in an African country. Using PRISMA to guide the review process, the study showed that six processes have been created for infrastructure development in Africa. The African countries with these processes are Egypt (three), Nigeria (one), Malawi and Kenya (one) and South Africa (one). The results showed that the sustainability assessment process correspond to most of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) targets with social and economic considerations taking the lead in the processes created for energy and transport infrastructure development projects, whereas the sustainability assessment processes created for water supply, waste and communications infrastructure development projects have a balance of social, economic and environmental sustainability considerations. The review has revealed a need to create energy, transport and water supply infrastructure sustainability assessment processes that address current sustainability concerns such as climate change, social justice, equity, fairness and equality.
1. Introduction
Infrastructure has been described by [1,2] as essential facilities, services and social structures that ensure the productivity and well-being (health and survival) of communities and cities. Ibragimova et al. and the United Nations Environment Program (U.N.E.P.) [3,4] make a distinction between economic infrastructure which foster economic growth such as transport, energy, information and communication technology and agricultural infrastructure, and social infrastructure which are systems that provide social services that are essential to the health and well-being of a society such as healthcare, education, rule of law, culture, water supply and sanitation infrastructure. In some cases, there is no clear distinction between economic and social infrastructures as some infrastructure systems such as water supply serve both economic and social needs of a society [4]. Another distinction between infrastructure typology is made by [5,6]. They distinguish between social infrastructure that provide spaces for social interactions such as education and healthcare facilities, and physical infrastructure which are structures, equipment and facilities used for economic production such as energy infrastructure and used by the public for specific activities such as walking and driving (transport infrastructure). Infrastructure has also been classified into hard and soft infrastructure by [4,7]. Hard infrastructure are the physical structures necessary for the functioning of a country such as energy, water supply and transport systems. Soft infrastructure are the knowledge, institutions and policy frameworks that support the functioning of hard infrastructure and that maintain the economic, health, cultural and social standards of a country such as financial, education, health, governance, security and judiciary systems. U.N.E.P. [4] brings together all these infrastructure typologies and notes that the grouping of infrastructure types depends on different usages of the term “infrastructure” among different groups of people.
But, unlike [3,6,7,8,9] do not draw lines on infrastructure types but identify five infrastructures that contribute to sustainable development: energy (non-residential buildings and civil engineering works that deliver energy services [10,11]), transport (non-residential buildings and civil engineering works that facilitate the movement of people and goods such as roads [10,11]), water supply (non-residential buildings and civil engineering works for water provision such as water pipelines [11]), sanitation and sewage (non-residential buildings and civil engineering works for waste removal and treatment such as sewers [11]), and communications (non-residential buildings and civil engineering works for information communication technologies such as telephone lines and internet systems [11]). This review will focus on these five infrastructures. They fall within economic infrastructures (energy, transport, communications) and social infrastructures (water supply and waste) as classified by [3]; within physical infrastructures they are classified by [5,6] and within hard infrastructures they are classified by [4,7]. The benefits of infrastructure to Africa’s development are well understood and documented in literature [8,12,13]. In the words of [13] (p. 65), “High-quality infrastructure is essential for Africa to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations (UN), Agenda 2063 of the African Union (AU), and the High Five Goals of the African Development Bank (AfDB). It is needed for raising economic productivity and sustaining economic growth”. Further infrastructure projects are key to promoting regional integration and uniting the continent not just economically but socially and culturally as well [14]. According to [15,16] infrastructure projects offer a greater opportunity to promote sustainability due to their large scope and long duration.
Fay et al. [11] estimates that in 2007, Africa’s investment on infrastructure development projects was about 1.5% of its regional gross domestic product (G.D.P.), and in 2014 the estimated investment on infrastructure development in sub-Saharan Africa (S.S.A.) is estimated to be 1.9% of its G.D.P. According to [14], the annual investment on infrastructure development in Africa was approximately USD 72 billion in 2014, USD 83 billion in 2015, USD 63 billion in 2016, USD 82 billion in 2017, USD 101 billion in 2018, USD 85 billion in 2019 and USD 81 billion in 2020. Figure 1 below gives details on the infrastructure investment share between energy, transport, water and sanitation, communication and other infrastructure projects in the continent. Although the figures show a decline in infrastructure development in 2019 and 2020, the 2021 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction points out that as the construction industry gains momentum after the COVID 19 pandemic brought it to a near halt in 2019, construction activities in developing countries (all African countries included) are expected to double as they correspond to growing needs for infrastructure systems [17,18].
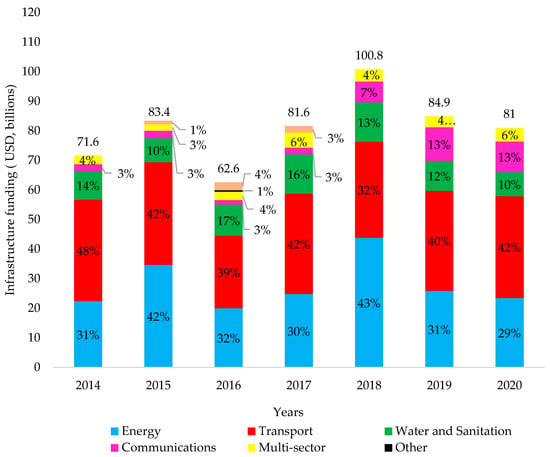
Figure 1.
Investment in infrastructure development in Africa, data from Ref. [14].
But equally documented is the detrimental environmental impact of infrastructure development including its contribution to carbon emissions and climate change [9,19,20]. To highlight the duality of the impact of infrastructure on sustainable development and environmental deterioration, the table below (Table 1) has been produced from a recent report by United Nations Office for Project Services (U.N.O.P.S) [10,21].

Table 1.
Contribution of infrastructure development on sustainable development goals (SDG) targets and greenhouse gas emission (GHG) [10,21].
Overall, infrastructure impacts about 72% of the 169 targets of 17 SDGs and contributes to about 79% of greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change [9,10]. Therefore, infrastructure is one of key elements in achieving sustainable development. In its report on Africa’s economic outlook 2022, the African Development Bank (AfDB) notes that infrastructure development decides the trajectory of countries’ sustainable development pathways, therefore the social and economic benefits of infrastructure development need to be decoupled from their negative environmental impact [22]. Sustainable development is described in the Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (Brundtland Report) as development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs [23].
Although sustainable development has sometimes been used to refer to sustainability by [24]. But others like Refs. [25,26] distinguish between the two. According to [25,26] the motive of sustainable development is to achieve sustainability, sustainability being a society’s vision on how it ought to utilize natural resources without depleting them [26]. Or according to [25] sustainability being a system’s ability to withstand or adapt to change indefinitely. In this review, sustainability and sustainable development are not used synonymously. Following [25,26] sustainability is considered as a goal and sustainable development as a process of stirring development towards this goal.
The need for sustainability in infrastructure development is not just to address its negative impact to the environment but also to harness the greater opportunity to foster sustainable socio-economic development through infrastructure projects. The need for sustainability in infrastructure is aptly explained by [4] which writes that infrastructure investment is key to improving productivity, stimulating economic growth, generating decent jobs, addressing inequalities and building resilience. However, infrastructure will only deliver on these objectives if sustainability is embedded at its core—increasing society’s resilience while reducing climate risk. Therefore, for Africa, where environmental deterioration and climate change pose the greatest challenges to its sustainable development and where infrastructure is crucial to its socio-economic development, the need for sustainability in its infrastructure projects is plain [27,28,29]. But sustainability is not a “one size fits all” concept, so defining it for the purpose of capturing it as an infrastructure development goal is a challenge [30,31,32]. As Ref. [33] point out, the definition of sustainability is often contested and subject to value judgements. Also as [28] notes, sustainability is not a definite state to be reached but a moving target. Similarly, according to [25,29], sustainability is a vague concept in peoples’ mindsets that represents an ideal, so its definition is influenced by what a particular society believes sustainability ought to be. As a result, there are various descriptions of infrastructure sustainability and sustainable infrastructure. Drawing from this review’s earlier distinction between sustainability and sustainable development and from [25,26], this review considers the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations (SDGs) [34] as the universal agreement of what society considers as sustainability. In this context, a SDG is considered represents a sustainability goal while its targets represent its sustainable development process.
Based on the above, this review describes infrastructure sustainability as sustainable development goals that an imbedded in an infrastructure development project, and sustainable infrastructure as infrastructure that contributes to achieving these goals. Similar descriptions of sustainable infrastructure have been presented by [7] who define sustainable infrastructure as infrastructure that supports/facilitates and contributes to the continuation of economic and environmental sustainability. Sustainable infrastructure is also described by [9] as infrastructure whose design, construction and maintenance are guided by socio-economic and environmental considerations and which in the long run will perpetuate and enhance the quality of life of the society it serves and the environment. It is also defined by [4] as systems that are planned, designed, constructed, operated, and decommissioned in a way that considers the economic and financial, social, environmental (including climate resilience) and institutional sustainability throughout its lifecycle. According to [35] sustainable infrastructure provides services in a way that ensures economic, financial, social, environmental, and institutional sustainability in line with the SDGs throughout its lifecycle. Acknowledging the difficulty in defining sustainability [30] prescribes the key to achieving infrastructure sustainability, which is developing infrastructure that not only addresses the current material demands but which will continue to meet the material demands of future generations. In defining sustainable infrastructure, [4] associates the concepts of inclusiveness, health and well-being, quality, service delivery, resilience and value for money with infrastructure sustainability. These definitions incorporate sustainability goals such as economy and finance [4,7,9,35], environment [4,7,9,35], quality of life [9], social [4,9,35], institutional [4,35] and the SDGs [35]. All these goals are integrated in UN’s SDGs [34].
Like other developing countries, African countries prioritise socio-economic considerations over environmental considerations because their infrastructure projects are aimed at providing public services and productive facilities that improve the quality of life and increase economic opportunities [12,36,37,38,39,40]. Some examples of socio-economic goals in sustainable infrastructure are creating employment opportunities, fostering democracy and equity, protecting of cultural and societal values and increase business opportunities [9,31]. On the other hand, because developed countries have already reached a point where most of their socio-economic needs are already met, they prioritise environmental goals [12,39,41]. Examples of environmental goals are minimizing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions (carbon emissions), protecting biodiversity and ecosystems and, preserving nature’s ability to regulate climate [10,42]. Despite these differences in priorities, the common aim of sustainable infrastructure is to develop methods and solutions for resilient and sustainable economic and social infrastructure facilities [9].
Persada et al. [28] write that because infrastructure development directly affects sustainable development, it is important to have a process that can be used to identify and deliver sustainable infrastructure. According to [43,44] if sustainability is to be defined and used to guide and support decision-making in infrastructure development, then sustainability goals have to be monitored, evaluated and reported with the aim of improving sustainable outcomes while lessening the negative impact to the environment. To this end, the construction industry uses impact assessment processes such as sustainability assessment processes. Ref. [45] defines impact assessment as a structured process for analysing the implications of a proposed action on people and their environment while there is still time to modify or abandon the proposed action. This implies that impact assessment is done prior to a proposed action (ex-ante). But [46] distinguishes between an ex-ante impact assessment process which is a prospective assessment of what the impact of an action might be to inform decision making. And ex-post impact assessment which is retrospective and focuses on the effect of an action [46].
The extensive use of impact assessments by countries, international organisations and corporations is highlighted by [44,47]. The functions of impact assessments are to either create choice opportunities for decision makers by generating information, enhance decision making by promoting pre-decision debate or deliberations, foster a shift in attitude or provide a structured approach for decision-makers to address complex issues and incorporate stakeholder inputs [45,48]. In Africa, where most of infrastructure development projects are public projects, impact assessment processes such as Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) are a mandatory decision support tool [47]. According to [44,48] impact assessments support evidence-based decision making and promote accountability in public projects. Examples of impact assessment processes are Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA), Health Impact Assessment (HIA), Risk Assessment and Sustainability Assessment (SA) [48]. This review focuses on sustainability assessment processes (SA).
A sustainability assessment process is a process that guides decision-making towards sustainability [33]. The processes operationalise a sustainability goal by breaking it down into smaller targets, then assesses the future consequences of current and planned actions on these targets [24,49,50,51]. According to [48] sustainability assessment integrates sustainability goals in decision-making. In so doing they give decision makers an effective way to assess the environmental impact of infrastructure development by putting sustainability goals at the center of the decision making process in an infrastructure development project where they receive the primary attention [52]. They foster sustainable infrastructure development by identifying the sustainability impact of an infrastructure project [48].
There is consensus among sustainability assessment scholars that sustainability assessment processes are impact assessment processes [51,53,54,55]. But there are different views on which impact assessment processes amount to sustainability assessment processes. Some scholars [54,56] consider traditional impact assessment processes used in infrastructure projects such as Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) as sustainability assessment processes. They argue that any impact assessment process that directs decision making toward sustainable development is a sustainability assessment process. Additionally, EIA is a mandatory decision-support tool used in infrastructure development projects in Africa, hence its acceptance as a sustainability assessment process in most African countries is unsurprising [47].
On the other hand, other scholars consider sustainability assessment processes as the third-generation impact assessment processes stemming out of the evolution of EIA and Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) [32,53,57], and make a clear distinction between traditional impact assessment processes and sustainability assessment processes [51]. According to [33] sustainability assessment emerged out of perceived inadequacies in EIA and SEA to balance sustainability goals and environmental goals are often traded off in favour of socio-economic goals). Also, [57] notes that sustainability assessment processes were introduced to advance traditional EIA into processes that support planning and decision making towards sustainable development. Furthermore, [51] writes that EIA is not a sustainability assessment process but an environmental management tool that focuses on the environmental impact of infrastructure projects.
In their work, [54] propose a framework to reconcile the various views on processes that amount to sustainability assessment. One of the uses of this framework is to establish one’s position on which impact processes amount to sustainability assessment processes [54]. Therefore, using [54]’s framework as a guide and various descriptions of sustainable infrastructure drawn from literature, this review considers sustainability assessment processes as processes that integrate and assess the impact of an infrastructure development project on sustainability targets that include economic and financial [4,7,9,35], environmental [4,7,9,35] and social and quality of life [4,9,35] targets. This definition reflects the position of [51,53] that a sustainability assessment process should involve a balanced assessment of all sustainability targets. Under this definition, EIA and SEA are not considered sustainability assessment processes; therefore, their related studies were not included in the systematic literature review. The SDGs represent an integrate, indivisible and balanced representation of these targets [34]. Therefore, they will be used as the basis for reviewing Africa’s local sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure development.
Another consideration in sustainability assessment processes is the assessment method [27,51]. Three groups of sustainability assessment methods—systems, standards, and tools have been identified by [27]. Sustainability assessment systems (systems) are methods that assess and classify/certify an infrastructure’s level of sustainability against predefined sustainability parameters [27]. Sustainability assessment standards (standards) refer to methods that assess an infrastructure to determine whether it complies with minimum sustainability requirements [27]. Lastly, sustainability assessment tools (tools) are created to guide construction industry practitioners such as engineers and designers to design and create sustainable infrastructure [27].
In Africa, where infrastructure is crucial to support socio-economic development and its sustainability, the need for sustainability assessment processes is plain [12,26,27,58]. But [15] point out that developing countries are lagging in creating sustainability assessment processes for their infrastructure development projects. According to [41] developing countries are either using international sustainability assessment processes, adapting international processes to fit their local context or creating their own local sustainability assessment processes. Of the three options, the first two have been criticised for failing to address the sustainability needs of a developing country because they were originally created for a different local context in most cases that of a developed country [15,38,39,41]. Hence, despite existing international sustainability assessment process and their customised versions, scholars in developing countries have opted to create local sustainability assessment processes to respond to particular/ specific sustainability goals of their countries [41]. The importance of having local sustainability assessment is emphasized in many studies [33,38,41,59,60]. They argue that having a sustainability assessment process purposely created to fit a country’s local context (a local sustainability assessment process) leads to a process that is practical and realistic in assessing an infrastructure’s sustainability according to that country’s sustainability and development targets. Therefore, for African countries to effectively assess the sustainability of their infrastructure, they need to use local sustainability assessment processes.
A recent study by [41] on sustainability assessment processes in developing and developed countries did not document any local sustainability assessment process for African countries. It can be deduced from several studies on sustainability assessment in the built environment that there is a scarcity of local sustainability assessment processes for Africa [27,61,62,63]. At the moment, there is no comprehensive study on the state of the infrastructure sustainability assessment processes for Africa. The need for documenting and analysing Africa’s sustainability assessment processes is underscored by both Africa’s need for sustainability in its infrastructure projects and the contribution infrastructure development in achieving the SDGs.
The aim of this review was to identify and analyse local sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure projects in Africa so as to document the progress made in creating local sustainability assessment processes. Additionally, as instruments for assessing and promoting sustainability in infrastructure projects, sustainability assessment processes reflect the sustainability priorities of a particular society [49,50]. Thus, the review also sheds light on which sustainable development goals are given the most attention in Africa’s sustainability assessment process. This also reveals the gaps in addressing some of the SDGs for future research to fill. Lastly, analysing these processes give insight to the types of sustainability assessment methods that are used in Africa’s infrastructure development projects.
A systematic literature review has been used by [64] to conduct a comprehensive review and analysis of research-based data, content-based data and method-based data of building sustainability assessment systems. Therefore, taking inspiration from [64], a systematic literature review of sustainability assessment research was conducted to find and analyse the local sustainability assessment processes created for infrastructure projects in African countries.
2. Materials and Methods
The methodology that was used to conduct the literature review is the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) presented by [65]. According to [65,66], PRISMA was designed to help reviewers systematically and transparently search, evaluate, synthesize and report on their review’s rationale, process and results. Also, [67] writes that using PRISMA enhances the quality and rigor of reviewing relevant literature. Some of the scholars that have also used PRISMA in reviews related to the sustainable built environments are [66,68,69].
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
To identify potential primary sources, an eligibility criterion comprising nine limitations was imposed on potential primary sources. These limitations or inclusion and exclusion criteria are shown in Table 2, below.

Table 2.
Eligibility criteria.
2.2. Grouping of Studies for Synthesis
To make sense and get a concise picture of the review results, the primary studies were grouped and analysed in three categories. The categories correspond to the aim of this review. These categories are as follows:
- Research-based data. This is the general data on yearly research publications (research trends from 2000 to 2022), productive countries in research publications (country of origin/ local context) and the scope of the published sustainability assessment process (type of infrastructure to be assessed) [64,72].
- Content-based data. This is the data on how the sustainability assessment processes contribute to the SDGs targets associated with their respective infrastructure type presented in Table 1, above.
- Method-based data. Method-based data refer to the type of sustainability assessment method (system, standard or tools) [27,64,73].
2.3. Sources of Studies
Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar are the primary academic databases used in scientific research [74]. However, in this review, only Scopus (https://www.scopus.com) and Google Scholar (https://www.google.com) were utilized to identify potential primary sources. Additionally, like [62,69], the reference lists of relevant reviews were searched to identify potential primary studies. The search on Scopus was conducted from 2nd to 9th May 2022 and Google Scholar was searched from 10th to 13th May 2022. The citation search was done on 9th June 2022.
Although both Web of Science and Scopus are credited for having reliable peer-reviewed publications, Scopus database was chosen over Web of Science. Scopus was chosen because it is the larger, more recent, faster growing, and currently the preferred citation and abstract database for research publications. Also, Refs. [62,63,75,76] note that there is a considerable number of duplicate studies between Scopus and Web of Science so there is high probability that searching both Web of Science and Scopus will yield the same results. Lastly, several reviews that relate to sustainability in the construction industry have also used Scopus to identify primary sources [41,61,62,63,76]. Google Scholar was also utilized because it has the most extensive collection of research articles than both Scopus and Web of Science [62,74]. Google Scholar has been criticized by some researchers [62,74] for including unreliable studies in its database. But due to the systematic and rigorous review process provided by PRISMA, any unreliable studies will be eliminated in the review process. Additionally, in their reviews, both [62,63] mention the scant amount of sustainability research in Africa. As the most extensive database, Google Scholar increases the chances of identifying more articles, no matter how few they are. Other review studies using Google Scholar to search for primary studies include [72].
The review studies whose reference lists were searched to identify potential primary sources are [41,61,62,63,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. These reviews also dealt with the sustainability of the built environment. Together they cover the period from 1990 to 2022 is within the study duration of this systematic literature review. This search identified more potential primary sources for the review. It also reduced the necessity of conducting a document search on Web of Science as it increases the chances of identifying duplicate records.
2.4. Search Strategy
Key words search strategy was used in both Scopus and Google Scholar to search for potential studies to include in the review. The search terms that were used on both databases were as follows: “SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT” OR “SUSTAINABILITY APPRAISAL” AND “BUILDINGS” OR “INFRASTRUCTURE” OR “BUILT ENVIRONMENT” AND “AFRICA” OR “DEVELOPING COUNTRY”. The initial search on Scopus and Google Scholar yielded a total of 207,500 document results. After applying the in-built refinement filters in both search engines, the results were filtered to 2492 documents.
2.5. Selection Process
The selection of potential primary studies to include in the review was done manually by a single reviewer. This selection was done against the inclusion and exclusion criteria described under Section 2.1. Like [84], two searches were done on Scopus. The first search on keywords, “SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT” OR “SUSTAINABILITY APPRAISAL” AND “BUILDINGS” OR “INFRASTRUCTURE” OR “BUILT ENVIRONMENT” AND “AFRICA” OR “DEVELOPING COUNTRY” focused on the narrower search fields of title, abstract and key words of publications. The second search with the same key words string focused the search field on the source title of publications. From these two searches, a total of 1492 documents results were obtained. The full search strategy and selection process including Scopus’s inbuilt filters that were used to narrow the document results are shown in Supplementary Materials.
The keyword search on Google Scholar also used the words “SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT” OR “SUSTAINABILITY APPRAISAL” AND “BUILDINGS” OR “INFRASTRUCTURE” OR “BUILT ENVIRONMENT” AND “AFRICA” OR “DEVELOPING COUNTRY” on the search bar of the website. The field of this search was article title, abstract, keywords and full text of publications in Google Scholar database. Google Scholar limits its search results to 1000 documents so this was the number of document results obtained from the website. The full search strategy and selection process including Google Scholar’s inbuilt filters that were used to narrow the document results are shown in the Supplementary Materials.
In addition to the searches on Scopus and Google Scholar, the reference lists of similar reviews were also screened to identify potential primary sources. A total of thirty-eight documents were identified from this screening. The PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for systematic reviews [65] directs that the title and the abstract screen should be done after duplicate documents are removed from search results. But in this review, the titles and abstracts were screened before the document results from Scopus and Google Scholar were combined and screened for duplicate records. The reason for doing this was to identify studies that were specific to the African continent. The search chain used on both Scopus and Google Scholar included the terms, “DEVELOPING COUNTRIES” or “DEVELOPING COUNTRY”. Therefore, the results on both databases included studies that focused on other developing countries outside of Africa.
After removing studies whose focus was on developing countries outside the African continent, the number of potential primary sources dropped to thirty-five studies from Scopus and a hundred and thirteen studies from Google Scholar, making a total of a hundred and forty-eight potential primary sources from academic databases and thirty-eight potential primary sources from reference list searches.
From here on, the selection process followed the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for systematic reviews presented by [65]. The steps that followed were removing duplicate studies and further screening of abstracts against the inclusion criteria. After these steps, the studies from academic databases were reduced to thirty-three, whilst the studies identified from citation searches remained at thirty-eight.
2.6. Data Collection Process and Data Items
The inbuilt refinement filters on the academic databases and the screening process had already eliminated most of studies that met the exclusion criteria on type of research, publication status, publication year, access type and language. Therefore, at this point, the specific data that was sought from thirty-three studies identified in the academic databases were on below-listed items. On the other hand, the thirty-eight studies that were identified from citation searches were evaluated against the eligibility criteria described under Section 2.1 and data on the following items were sought as well:
- Authors.
- Publication year.
- Research area.
- Country of origin.
- Local context.
The full texts of all the studies were retrieved to extract information on the above data items. This process was done manually by a single reviewer.
2.7. Synthesis Methods
The first step in analysing the data collected from the studies was tabulating the information obtained for each data item. This eased the process of data synthesis and analysis. Microsoft Excel (M.S. Excel) was used for data analysis and presentation.
3. Results
3.1. Selected Studies
The process of selecting studies to include in the review is summarized in Figure 2. Following this process, a total of eleven studies were selected as primary sources for the review. The details of these studies are tabulated in Table 3.
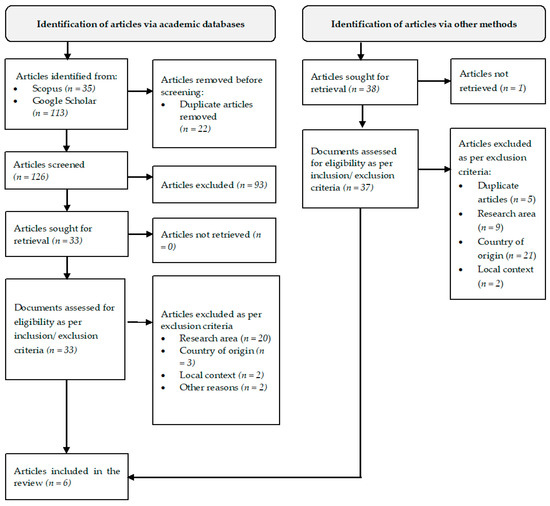
Figure 2.
Selection process flow chart adopted from [65,67].

Table 3.
Selected studies.
3.2. Results of Synthesis
As mentioned before the primary sources were grouped in three categories for synthesis. This section presents the results of the synthesis process.
3.2.1. Research-Based Data Results
- Yearly research publications.
Like [61], a bar chart (Figure 3) is also used to report the results on yearly research publications. The bar chart shows the number of published studies against the study duration of this review (2000 to 2022). According to the results, there has been a consistent publication of one sustainability assessment process in 2007, 2012, 2013 and 2017. In 2020 two studies that created sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure in Africa were published.
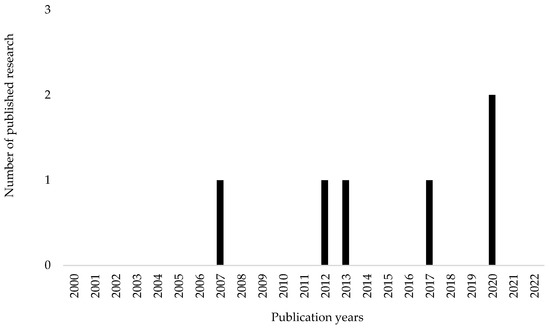
Figure 3.
Yearly research publications.
- Country of origin
The results on the country of origin of the created sustainability assessment process are also reported in a bar chart (Figure 4). The bar chart shows the number of published research against their country of origin. The countries that local sustainability processes for the built environments are Egypt, Malawi and Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa. Egypt has three processes whereas Malawi and Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa have one processes each. Malawi and Kenya are considered together because the sustainability assessment process by [88] considered the local contexts of both countries.
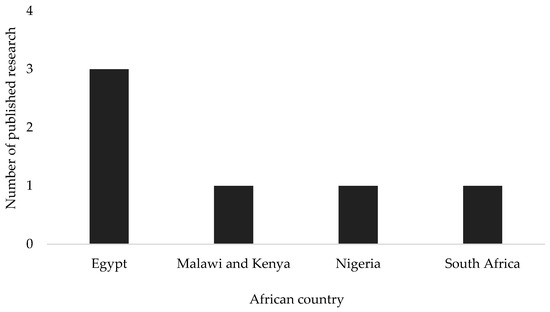
Figure 4.
Country of origin.
- Scope of the assessment process
The types of infrastructure in African countries for which a sustainability assessment process has been created for through research are as follows:
- Ref. [37] for infrastructure (unspecified) in South Africa;
- Ref. [85] for water pipeline infrastructure in Egypt;
- Ref. [87] for highway infrastructure in Egypt;
- Ref. [88] for solar energy infrastructure in Malawi and Kenya;
- Ref. [89] for railway infrastructure in Nigeria;
- Ref. [86] created a sustainability assessment process for damaged infrastructure assets (buildings and civil infrastructure) in Egypt.
Refs. [37,86] did not specify the type of infrastructure for their sustainability assessment processes. Therefore, working under the assumption that they meant for their assessment processes to be used in all infrastructure types, Table 4 below represents the results on the scope of the selected processes.

Table 4.
Scope of the selected sustainability assessment processes (types of infrastructure).
3.2.2. Content-Based Data Results
- Sustainability assessment processes for energy infrastructure development projects.
Table 5 below, summarizes how the sustainability assessment processes created by [37,86,88] for energy infrastructure development projects correspond to the SDG targets associated with energy infrastructure as presented by [21] (Table 1). According to [10] energy infrastructure has an impact on 72 targets across the 17 SDGs. But the content-based results show that there are 97 targets across the 17 SDGs that can be associated with energy infrastructure. In addition to the SDG targets identified from [21] (Table 1), another 25 targets were identified from the selected sustainability assessment process (4.7, 6.5, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9, 8.10, 10.2, 10.3, 11.4, 11.7, 11.c, 12.6, 12.7, 12.8, 12.b, 13.3, 14.5, 15.8, 15.9, 16.7, 16.8, 16.10 and 17.15). Out of the 97 targets, [37]’s sustainability assessment process corresponds to 68 targets (70%), [86]’s assessment process corresponded to 78 targets (80%) and [88]’s assessment process corresponded to 55 targets (57%). The degree to which the assessment processes correspond to the SDGs varies across the 97 targets, but all processes correspond to SDG targets 14.1, 14.3 and 14.b. While none of the processes correspond to targets 1.2, 5.4, 7.3, 8.1, 8.2, 9.a, 10.b, 12.1, 12.3, 12.c and 17.7. For full details on these results, refer to the Supplementary Materials.

Table 5.
Summary of content-based results on sustainability assessment processes for energy infrastructure development projects [21,34].
- Sustainability assessment processes for transport infrastructure development projects
Table 6 below, summarizes how the sustainability assessment processes created by [37,86,87,89] for transport infrastructure development projects correspond to the SDG targets associated with transport infrastructure as presented by [21] (Table 1). Ref. [10] writes that transport infrastructure has an impact on 76 targets across the 17 SDGs. But the content-based results show that there are 103 targets across the 17 SDGs that can be associated with transport infrastructure. In addition to the SDG targets identified from [21] (Table 1), another 28 targets were identified from the selected sustainability assessment process (4.7, 4.a, 5.1, 5.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9, 8.10, 9.c, 11.4, 11.7, 12.6, 12.7, 12.8, 12.b, 14.3, 14.5, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 15.5, 15.8, 15.9, 16.b and 17.15). Out of the 103 targets, [37]’s sustainability assessment process corresponds to 73 targets (71%), [86]’s assessment process corresponded to 81 targets (79%), [89]’s assessment process corresponded to 57 targets (55%) and [87]’s assessment process corresponded to 42 targets (41%). Although the degree to which the assessment processes correspond to the SDGs varies across the 103 targets. The results show that none of the processes correspond to targets 1.2, 1.3, 12.1 and 17.9. For full details on these results, refer to the Supplementary Materials.

Table 6.
Summary of content-based results on sustainability assessment processes for transport infrastructure development projects [21,34].
- Sustainability assessment processes for water supply infrastructure development projects
Table 7 below, summarizes how the sustainability assessment processes created by [37,85,86] for water supply infrastructure development projects correspond to the SDG targets associated with water supply infrastructure as presented by [21] (Table 1). Ref. [10] writes that water supply infrastructure can be associated with 61 targets across the 17 SDGs. But the content-based results show that there are 85 targets across the 17 SDGs that can be associated with water supply infrastructure. In addition to the SDG targets identified [21] (Table 1), another 21 targets were identified from the selected sustainability assessment process (4.7, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9, 8.10, 12.5, 12.6, 12.7, 12.8, 12.b, 13.3, 15.5, 15.8, 15.9, 16.7, 16.8, 16.10, 16.b, 17.15). Out of the 85 targets, [37]’s sustainability assessment process corresponds to 60 targets (71%), [86]’s assessment process corresponded to 68 targets (80%) and [85]’s assessment process corresponded to 67 targets (79%). The degree to which the assessment processes correspond to the SDGs varies across the 85 targets associate with water infrastructure. But all processes correspond to SDG targets 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, 14.1, 14.5, 15.1, 15.3, 15.5, 15.8 and 15.9. And none of the processes correspond to targets 4.1, 4.2, 5.4, 9.a, 10.b, 12.1 and 17.7. For full details on these results, refer to the Supplementary Materials.

Table 7.
Summary of content-based results on sustainability assessment processes for water supply infrastructure development projects [21,34].
- Sustainability assessment processes for sanitation and sewage (waste) infrastructure development projects
Table 8 below, summarizes how the sustainability assessment processes created by [37,86] for waste infrastructure development projects correspond to the SDG targets associated with waste infrastructure as presented by [21] (Table 1). According to [10] waste infrastructure can be associated with 36 targets across the 17 SDGs. But the content-based results show that there are 59 targets across the 17 SDGs that can be associated with waste infrastructure. In addition to the SDG targets identified from [21] (Table 1), another 23 targets were identified from the selected sustainability assessment process (5.1, 5.2, 5.5, 6.b, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9, 10.2, 11.4, 11.c, 12.6, 12.7, 12.8, 12.b, 15.5, 15.8, 15.9, 16.7, 16.10, 16.b and 17.15). Out of the 59 targets, [37]’s sustainability assessment process corresponds to 42 targets (71%) and [86]’s assessment process corresponded to 48 targets (81%). Although the degree to which the assessment processes correspond to the SDGs varies across the 59 targets, all processes correspond to SDG targets 3.9, 4.a, 6.3, 6.b, 14.1, 15.1, 15.5, 15.8 and 15.9. But none of the processes correspond to targets 1.2, 8.1, 8.2, 9.a, 10.b, 12.1, 12.3 and 17.7. For full details on these results, refer to the Supplementary Materials.

Table 8.
Summary of content-based results on sustainability assessment processes for sanitation and sewage (waste) infrastructure development projects [21,34].
- Sustainability assessment processes for communications infrastructure development projects
Table 9 below, summarizes how the sustainability assessment processes created by [37,86] for communications infrastructure development projects correspond to the SDG targets associated with waste infrastructure as presented by [21] (Table 1). According to [10] waste infrastructure can be associated with 81 targets across the 17 SDGs. But the content-based results show 98 targets across the 17 SDGs that can be associated with communications infrastructure. In addition to the SDG targets identified from [21] (Table 1), another 17 targets were identified from the selected sustainability assessment process (4.7, 5.1, 5.2, 5.5, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9, 12.6, 12.7, 12.b, 15.5, 15.8, 15.9, 16.b and 17.15). Out of the 98 targets, [37]’s sustainability assessment process corresponds to 61 targets (62%) and [86]’s assessment process corresponded to 64 targets (65%). The degree to which the assessment processes correspond to the SDGs varies across the 59 targets. However, none of the processes correspond to targets 1.2, 1.3, 3.c, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.6, 6.a, 7.a, 8.1, 8.2, 9.a, 10.5, 10.b, 10.c, 12.1, 12.3, 12.a, 17.7, 14.a, 17.1, 17.6, 17.7, 17.12, 17.18 and 17.19. For full details on these results, refer to the Supplementary Materials.

Table 9.
Summary of content-based results on sustainability assessment processes for communications infrastructure development projects [21,34].
3.2.3. Method-Based Data Results
The method-based data refers methods and procedures used in the assessment process which can either be an assessment system, standard or tool [27]. The table below (Table 10) shows the results of the method-based data.

Table 10.
Method-based data results.
4. Discussion
The following section presents a general discussion of the review results in line with the context of the objectives of this review, previous reviews on sustainability research in Africa and sustainability issues affecting the continent.
4.1. Discussion on Research-Based Data Results
- Yearly research publications from 2000 to 2022.
The results on yearly research publications (Figure 3) show that only six sustainability assessment processes have been created for Africa’s infrastructure in the 22-year study period. This number is very small but not unexpected as earlier studies on global sustainability assessment processes for the built environment have shown that Africa is the least productive continent [41].
These results also support the conclusions drawn from earlier studies on the applicability of prominent sustainability assessment processes in developing countries. In their work, [38,39] concluded that most of existing processes were created for use in developed countries. Therefore, most developing countries and, by extension, African countries do not have local sustainability assessment processes for their infrastructure. This conclusion highlights the gap in research on sustainability assessment processes and their creation. Other scholars such as [9] have also noted this research gap.
Figure 3 also shows the time lag between the sustainability assessment research publications. Although the number of studies published in these years is still low, the interval between the studies has decreased and there is an increase in published studies in 2020. This suggests that the interest in research in the sustainability research in Africa is increasing. This increasing interest is also observed in other reviews related to sustainability assessment in African. In their studies, both [62,63] reveal a progressive decrease in intervals between research publications accompanied by an increase in the number of published research related to sustainability research in Africa.
- Country of origin.
The review has found five African countries with local sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure projects (Figure 4). These countries are Egypt, Malawi, Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa. Egypt has three processes while Nigeria and South Africa have one process each and Malawi and Kenya share a process. These results are also consistent with other reviews on sustainability assessment research in Africa where both [62,63] found that Egypt, Nigeria, and South Africa as the most productive countries in creating sustainability assessment processes for their local built environments. Scholars such as [63] attributes Egypt’s, Nigeria’s, and South Africa’s leadership in built environment sustainability research to having higher education institutions among the top five hundred universities worldwide as ranked by Times Higher Education (T.H.E.).
Perhaps another reason for Egypt, Nigeria and South Africa having the most sustainability assessment processes for their built environment is their higher economy compared to other African countries. According to the [90], these countries have the highest Gross Domestic Product (G.D.P.) in Africa. Studies on the construction industry in developing countries argue that a country’s socio-economic development level is directly proportional to its level of construction activities [12,40]. The higher the level of construction activities, the higher their contribution to environmental deterioration and climate change and the greater the need for sustainability in construction activities. This may explain the more interest in and publication of sustainability assessment research in countries such as Egypt, Nigeria and South Africa as an effort to reduce the negative impact of their increasing construction activities without compromising their socio-economic development.
The absence of sustainability assessment processes for infrastructure in other countries processes for the remaining countries could be explained by low implementation of sustainable infrastructure projects. Ref. [27] write that the high cost of implementing sustainable projects is a major challenge to African countries as a result there is low implementation of sustainable infrastructure projects in Africa.
- Scope of the sustainability assessment processes (type of infrastructure).
Out of the six selected sustainability assessment processes, four can be used to assess the sustainability of transport infrastructure, three for energy infrastructure, three for water infrastructure, two for sewage and sanitation (waste) infrastructure and two for communication infrastructure (Table 2). Although this review did not set out to show the relationship between infrastructure development in Africa and sustainability assessment research in the continent, these results suggest that there is a positive relationship between the two. Transport infrastructure which receives the greatest share of infrastructure investment in the continent (Figure 1) also has the highest number of sustainability assessment processes whereas waste and communication infrastructures with the least share of infrastructure investment have the fewest processes to assess their sustainability. These results support the argument that the higher the level of construction activities, the higher their contribution to environmental deterioration and climate change and the greater the need for sustainability in construction activities [12,40]. Hence the higher the number if sustainability assessment processes created for infrastructure types such as transport, energy and water where most of the infrastructure development investment and activities are directed.
4.2. Discussion on Content-Based Data Results
- Sustainability assessment processes for energy infrastructure development projects [37,86,88].
The results show that the energy sustainability assessment processes corresponded to the most targets under SDG 2 (end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture), SDG 3 (ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages), SDG 14 (conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development) and SDG 16 (promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels). In their entirety, SDGs represent a balanced and integrated representation of social, economic and environmental considerations to achieve sustainability. However, these results show the assessment processes lean towards social and economic sustainability goals with social sustainability taking the lead. The results are consistent with the view that, like other developing countries, African countries prioritise socio-economic considerations over environmental considerations and their infrastructure projects are aimed at providing public services and productive facilities that improve the quality of life and increase economic opportunities [12,36,37,38,39,40]
On the other hand, the sustainability targets that were least represented are from SDG 1 (end poverty in all its forms everywhere), SDG 4 (ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all), SDG 5 (achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls) and SDG 7 (ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all). Climate change is the greatest threat to Africa’s sustainable development [29]. The increasing need for sustainability to address carbon dioxide emissions, justice and resilience, equity and fairness, etc., has led to a global commitment on just energy transition (from a carbon intensive energy system to cleaner and just energy system) [90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97]. The low representation of these targets reveals a shortfall in these processes in addressing the current challenges in energy infrastructure sustainability.
- Sustainability assessment processes for transport infrastructure development projects [37,86,87,89].
The sustainability assessment processes for transport infrastructure development projects also lean towards SDGs associated with social and economic considerations with economic considerations taking the lead. These SDGs whose targets correspond the most with the sustainability objectives in these assessment processes are as follows: SDG 6 (ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all), SDG 8 (promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all) and SGD 9 (build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation). These results further support the prioritization of socio-economic considerations in Africa’s infrastructure development projects.
The targets from SDG 4 (ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all), SDG 13 (take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts) and SDG 17 (strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development) are some of the least represented in the processes. Therefore, there is gap in processes’ ability to assess the achievement of these goals. Of particular concern is the goal on combating climate change and its impacts because transport infrastructure contributes to 16% of GHG emissions responsible for climate change [21].
- Sustainability assessment processes for water supply infrastructure development projects [37,85,86].
Unlike the processes for energy and transport infrastructure, the sustainability assessment processes for water supply infrastructure correspond the most to social, economic, and environmental sustainability considerations to a comparable extent. The processes corresponded to the following SDGs targets the most: SDG 2 (end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture), SDG 3 (ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages), SDG 6 (ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all), SDG 8 (promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all), SDG 9 (build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation), SDG 10 (reduce inequality within and among countries), SDG 11 (make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable), SDG 12 (ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns), SDG 14 (conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development), SDG 15 (protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss) and SDG 16 (promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels). The processes give equal opportunity to economic, social and environmental targets of the SDGs and present balanced and integrated sustainability assessment processes.
But the targets from SDG 4 (ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all) and SDG 5 (achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls) are the least represented in the sustainability assessment processes. Although the review shows a balance of social, economic and environment sustainability priorities, it also shows processes are lagging in incorporating equality goals in the sustainability assessment process.
- Sustainability assessment processes for sanitation and sewage (waste) infrastructure development projects [37,86].
Likewise, the results on the sustainability assessment processes for waste infrastructure show that the processes relate the most to sustainability targets that lean towards social, economic, and environmental goals to a similar extent. The targets they relate to the most fall under SDG 3 (ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages), SDG 4 (ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all), SDG 6 (ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all), SDG 8 (promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all), SDG 9 (build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation), SDG 10 (reduce inequality within and among countries), SDG 11 (make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable), SDG 12 (ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns), SDG 14 (conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development), SDG 15 (protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss) and SDG 16 (promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels). They priorities economic, social and environmental goals thus creating balanced and integrated sustainability assessment process.
- Sustainability assessment processes for communications infrastructure development projects [37,86].
The sustainability assessment processes for communications infrastructure development projects correspond to most of the targets of SDG 2 (end hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture), SDG 3 (ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages), SDG 4 (ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all), SDG 8 (promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all), SDG 9 (build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation), SDG 11 (make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable), SDG 12 (ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns), SDG 14 (conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development) and SDG 15 (protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss). These goals relate to economic, social and environmental considerations so the processes present a balance integration of these considerations in the sustainability assessment.
4.3. Discussion on Method-Based Data Results
The results on method-based data (Table 10) show that when it comes to creating local sustainability assessment processes for Africa’s infrastructure, assessment tools (tools) are preferred over assessment systems and standards. Considering that Africa is behind in sustainability research [27], it is logical that scholars would opt to create tools instead of systems. Systems are composed of sustainability ranking criteria and certification thus making them both research intensive and expensive to develop and use [62]. Unlike systems, the aim of tools is not to rank or certify the sustainability of an infrastructure but to support and guide decision-makers towards sustainable design and construction [27].
The results also show that none of the six selected studies created a local sustainability assessment standard (Table 10). The reason could be the low interest in research on sustainable infrastructure in Africa [27]. Regardless of the reasons, the absence of local sustainability standards further supports the dominance of tools as an assessment method, simply because, unlike sustainability standards, the aim of tools is not to ensure a particular infrastructure complies with a particular sustainability standard but to support sustainable design and construction (their use does not require a pre-defined sustainability standard that an infrastructure has to follow) [27]. In the absence of such standards, as in the case of African countries where EIA is the mandated tool for sustainability assessment [47], tools are a more logical choice to promote sustainability in infrastructure development projects.
5. Conclusions
The goal of this review was to find and analyse local sustainability assessment processes created for infrastructure development projects in Africa from 2000 to 2022. The research-based data (publication trends, productive countries, and infrastructure types), content-based data (how the sustainability assessment processes correspond to the SDGs) and method-based data (types of assessment processes) were analysed.
The review found six sustainability assessment tools created for various infrastructure types in Nigeria, South Africa, Egypt, Ghana, Malawi and Kenya. There are 97 SDG targets that can be associated with energy infrastructure development and the targets that Africa’s energy infrastructure sustainability assessment processes corresponded to the most relate to social and economic sustainability. For transport infrastructure, the review found 103 SDG targets that can be associated with transport infrastructure development projects, and the sustainability assessment processes for transport development projects in Africa correspond the most to social and economic sustainability considerations. The review also showed that 85 targets can be associated with water supply infrastructure and Africa’s local sustainability assessment processes give comparable priority to economic, social and environmental sustainability considerations. There are 59 SDG targets that relate to sewage and sanitation (waste) infrastructure development and the targets that Africa’s waste infrastructure sustainability assessment processes corresponded to economic, environment and social sustainability targets. Lastly, 98 SDG targets can be tied to communications infrastructure development and the review showed that Africa’s sustainability assessment processes correspond to economic, environmental and social sustainability considerations.
The review’s results support the assertion that developing countries priorities socio-economic sustainability goals in infrastructure development projects [12,36,37,38,39,40]. The review also revealed gaps in the sustainability assessment processes. The processes created for assessing energy infrastructure development projects fall short in incorporating sustainability objectives that relate to SDG 1, SDG 4, SDG 5, and SDG 7, all of which have targets that address the current global commitment on just energy transition. Therefore, future research on energy infrastructure sustainability assessment in Africa can focus on incorporating these targets into the assessment process. The review also found a gap in the local sustainability assessment processes created for transport infrastructure development. The targets from SDG 4, SDG 13 and SDG 17 were the least represented thus the gap in the processes’ ability to assess goals such as combating climate change and its impact. Considering that transport infrastructure’s contribution to climate change, we recommend future sustainability assessment research to looking into creating a process that addresses these goals. Another research gap was identified in the water supply sustainability assessment processes which corresponded the least on SDG 4 and SDG 5 targets that relate to equality considerations. Therefore, future sustainability assessment research for Africa can focus on incorporating these goals into water infrastructure sustainability assessment process.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su15021013/s1. Supplementary File S1: Search and selection strategy, Supplementary File S2: Detailed content-based data results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.T.K., I.M. and S.L.Z.; methodology, E.T.K., I.M. and S.L.Z.; validation, I.M. and S.L.Z.; formal analysis, E.T.K.; investigation, E.T.K.; resources, E.T.K., I.M. and S.L.Z.; data curation, E.T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, E.T.K.; writing—review and editing, E.T.K., I.M. and S.L.Z.; visualization, E.T.K.; supervision, I.M. and S.L.Z.; project administration, I.M. and S.L.Z.; funding acquisition, I.M. and S.L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Intra-Africa Mobility Scheme of the European Union in partnership with the African Union under the Africa Sustainable Infrastructure Mobility (ASIM) scheme. Opinions and conclusions are those of the authors and are not necessarily attributable to ASIM. The work is supported and part of collaborative research at the Centre of Applied Research and Innovation in the Built Environment (CARINBE), University of Johannesburg, South Africa.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su15021013/s1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Boyle, C.; Mudd, G.; Mihelcic, J.R.; Anastas, P.; Collins, T.; Culligan, P.; Edwards, M.; Gabe, J.; Gallagher, P.; Handy, S.; et al. Delivering Sustainable Infrastructure That Supports the Urban Built Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4836–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berawi, M.A. Managing Sustainable Infrastructure and Urban Development: Shaping a Better Future for Asean. Int. J. Technol. 2018, 9, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimova, A.; Wang, Y.; Ivanov, M. Infrastructure Development in Africa’s Regions: Investment Trends and Challenges. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 295, 01029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (U.N.E.P.). International Good Practice Principles for Sustainable Infrastructure, 2nd ed.; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022; Available online: http://www.un.org/Depts/Cartographic/english/htmain.htm (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Brown, A.R. Driving Down a Road and Not Knowing Where You’re At: Navigating the Loss of Physical and Social Infrastructure After the Camp Fire. Rural Sociol. 2022, 87, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choguill, C.L. Ten Steps to Sustainable Infrastructure. Habitat Intl. 1996, 20, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanipekun, A.O.; Aje, I.O.; Awodele, O.A. Contextualising Sustainable Infrastructure Development in Nigeria. FUTY J. Environ. 2014, 8, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Estache, A.; Garsous, G. The Impact of Infrastructure on Growth in Developing Countries; International Finance Corporation (IFC) Economic Notes (IFC): Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://www.infrastructureafrica.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Song, Y.; Wu, P. Earth Observation for Sustainable Infrastructure: A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1528. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, S.; Adshead, D.; Fantini, C.; Palmer, R.; Ghosal, R.; Adeoti, T.; Morgan, G.; Stratton-Short, S. Infrastructure for Climate Action; United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021; Available online: http://www.unops.org (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Fay, M.; Lee, H.I.; Mastruzzi, M.; Han, S.; Cho, M. Hitting the Trillion Mark A Look at How Much Countries Are Spending on Infrastructure; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Alagidede, P.; Odei Mensah, J. Construction Institutions and Economic Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa. Afr. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2018, 10, 136–163. [Google Scholar]
- African Development Bank (A.f.D.B.). Africa’s Infrastructure: Great Potential but Little Impact on Inclusive Growth. 2018. Available online: https://www.afdb.org/fileadmin/uploads/afdb/Documents/Publications/2018AEO/African_Economic_Outlook_2018_-_EN_Chapter3.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Infrastructure Consortium for Africa (I.C.A.). Key Achievements in the Financing of African Infrastructure in 2019–2020; 2020. Available online: https://www.icafrica.org/en/topics-programmes/key-achievements-in-the-financing-of-african-infrastructure-in-2019–2020/ (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Amaral, R.E.A.C.; Abraham, Y.S. Feasibility of a Sustainable Infrastructure Rating System Framework in a Developing Country. J. Infrastruct. Dev. 2020, 12, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevenger, C.M.; Ozbek, E.; Simpson, S. Review of Sustainability Rating Systems Used for Infrastructure Projects. In Proceedings of the 49th Associated Schools of Construction (ASC) Annual International Conference, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 10–13 April 2013; Sulbaran, T., Ed.; Associated Schools of Construction (ASC): Cheyenne, WY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). World Population Dashboard. 2022. Available online: https://www.unfpa.org/data/world-population-dashboard (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP). 2021 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction: Towards a Zero-Emission, Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector; United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2021; Available online: http://globalabc.org/resources/publications (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Hosny, H.E.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Eldars, E.A. Development of Infrastructure Projects Sustainability Assessment Model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 7493–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.; Zayed, T.; Fahmy, M. Development of Sustainability Assessment Tool for Existing Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, S.; Adshead, D.; Morgan, G.; Crosskey, S.; Bajpai, A.; Ceppi, P.; Hall, J.W.; O’Regan, N. Infrastructure: Underpinning sustainable development; United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; Available online: http://www.unops.org (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- African Development Bank (A.f.D.B.). African Economic Outlook 2022: Supporting Climate Resilience and a just Energy Transition in Africa; African Development Bank Group (A.f.D.B): Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2022; Available online: https://www.afdb.org/en/knowledge/publications/african-economic-outlook (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future. 1987. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5987our-common-future.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Hugé, J.; Waas, T.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F.; Koedam, N.; Block, T. A Discourse-Analytical Perspective on Sustainability Assessment: Interpreting Sustainable Development in Practice. Sustain. Sci. 2013, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovers, S.R.; Handmer, J.W. Uncertainty, sustainability and change. Glob. Environ. Change 1992, 2, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, R.; Angelstam, P.; Elbakidze, M.; Stryamets, N.; Johansson, K.E. Sustainable Development and Sustainability: Landscape Approach as a Practical Interpretation of Principles and Implementation Concepts. J. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 4, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz López, C.; Carpio, M.; Martín-Morales, M.; Zamorano, M. A Comparative Analysis of Sustainable Building Assessment Methods. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persada, C.; Sitorus, S.R.P.; Marimin; Djakapermana, R.D. Policy Model of Sustainable Infrastructure Development (Case Study: Bandarlampung City, Indonesia). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the International Conference on Science, Infrastructure Technology and Regional Development (ICoSITeR) 2016 "Energy Security for Enhancing National Competitiveness, South Lampung, Indonesia, 25–26 August 2017; Institute of Physics Publishing: South Lampung, Indonesia, 2018; Volume 124, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate and Development Knowledge Network, (CDKN). Accelerating Adaptation Action in Africa Insights from African Adaptation Experts. Climate and Development Knowledge Network, (CDKN); London, UK, 2021. Available online: https://cdkn.org/story/news-insights-from-african-experts-on-how-to-accelerate-adaptation-in-africa (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Andreas, G.; Allen, J.; Farley, L.; Kao, J.K.; Mladenova, I.; Georgoulias, A. Towards the Development of a Rating System for Sustainable Infrastructure: A Checklist or a Decision-Making Tool? Cities Future/Urban River Restor. 2010, 2010, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanda, J.O. Developing a Social Sustainability Assessment Framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, D.; Blackwood, D.; Banks, L.; Wilson, F. Sustainable Development Indicators for Major Infrastructure Projects. Munic. Eng. 2011, 164, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.; Morrison-Saunders, A.; Pope, J. Sustainability Assessment: The State of the Art. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2012, 30, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations (U.N.). Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable. 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%20Development%20web.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Sustainable Infrastructure Tools Navigator. Glossary. 2022. Available online: https://sustainable-infrastructure-tools.org/glossary/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Gibberd, J.A. Assessing Sustainable Buildings in Developing Countries-The Sustainable Building Assessment Tool (SBAT) and the Sustainable Building Lifecycle (SBL). In Proceedings of the 2005 World Sustainable Building Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 27–29 September 2005; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306177756 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Ugwu, O.O.; Haupt, T.C. Key Performance Indicators and Assessment Methods for Infrastructure Sustainability-a South African Construction Industry Perspective. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, R.F.M.; Mourshed, M. Urban Sustainability Assessment Framework Development: The Ranking and Weighting of Sustainability Indicators Using Analytic Hierarchy Process. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sarachaga, J.M. Development and Application of a New Sustainable Infrastracture Rating System for Developing Countries (SIRSDEC). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cantabria, Cantabria, Spain, 2017. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/41931438/PhD_Thesis_Development_and_Application_of_a_new_Sustainable_Infrastructure_Rating_System_for_Developing_Countries_SIRSDEC_ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Kirchberger, M. The Role of the Construction Sector; The United Nations University World Institute for Development Economics Research (UNU-WIDER): Helsinki, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghami, E.; Fatourehchi, D. Comparative Analysis of Rating Systems in Developing and Developed Countries: A Systematic Review and a Future Agenda towards a Region-Based Sustainability Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Tian, L. How to Advance China’s Carbon Emission Peak?— A Comparative Analysis of Energy Transition in China and the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, T.; Pires, S.M. Sustainability Assessment: The Role of Indicators. In Sustainability Assessment Tools in Higher Education Institutions: Mapping Trends and Good Practices Around the World; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashmore, M.; Richardson, T.; Hilding-Ryedvik, T.; Emmelin, L. Evaluating the effectiveness of impact assessment instruments: Theorising the nature and implications of their political constitution. Environ. Impact Assess Rev. 2010, 30, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association for Impact Assessment. Impact Assessment 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.iaia.org/wiki-details.php?ID=4 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). What is Impact Assessment. 2014. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/sti/inno/What-is-impact-assessment-OECDImpact.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Bond, A.; Pope, J.; Fundingsland, M.; Morrison-Saunders, A.; Retief, F.; Hauptfleisch, M. Explaining the Political Nature of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): A Neo-Gramscian Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugé, J.; Waas, T.; Eggermont, G.; Verbruggen, A. Impact Assessment for a Sustainable Energy Future-Reflections and Practical Experiences. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 6243–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasso, V.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; De Olde, E.; Sørensen, C.A.G. Generic Sustainability Assessment Themes and the Role of Context: The Case of Danish Maize for German Biogas. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waas, T.; Hugé, J.; Block, T.; Wright, T.; Benitez-Capistros, F.; Verbruggen, A. Sustainability Assessment and Indicators: Tools in a Decision-Making Strategy for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5512–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.; Bond, A.; Hugé, J.; Morrison-Saunders, A. Reconceptualising Sustainability Assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 62, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.B. Sustainability assessment: Basic components of a practical approach. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2006, 24, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.; Annandale, D.; Morrison-Saunders, A. Conceptualising Sustainability Assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2004, 24, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacking, T.; Guthrie, P. A Framework for Clarifying the Meaning of Triple Bottom-Line, Integrated, and Sustainability Assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, B.; Urbel-Piirsalu, E.; Anderberg, S.; Olsson, L. Categorising Tools for Sustainability Assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 60, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez-de-Salamanca, Á. Project Justification and EIA: Anything Goes? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 87, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, S.; Ciuffo, B.; Nijkamp, P. A Systemic Framework for Sustainability Assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. A systematic review of urban sustainability assessment literature. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhanova, G.; Nadeem, A.; Kim, J.R.; Azhar, S. A Framework of Building Sustainability Assessment System for the Commercial Buildings in Kazakhstan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, N.; Chithra, K. Evaluation of Sustainability Criteria for Residential Buildings of Tropical Climate: The Stakeholder Perspective. Energy Build. 2021, 232, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, N.; Chithra, K. Comprehensive Bibliometric Mapping of Publication Trends in the Development of Building Sustainability Assessment Systems. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 4899–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushi, F.V.; Nguluma, H.; Kihila, J. A Critical Review of African Green Building Research. Build. Res. Inf. 2022, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntona, O.A.; Aigbavboa, C.O.; Thwala, W.D. A scientometric analysis and visualization of green building research in Africa. J. Green Build. 2021, 16, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, N.; Chithra, K. A Comprehensive Literature Review on Development of Building Sustainability Assessment Systems. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.; Valladares, O.P.; Peña, D.M. Sustainability Performance by Ten Representative Intelligent Façade Technologies: A Systematic Review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, K.; Haron, R.C.; Kamaruddin, Z. Quantum Meruit Claim in Conservation Projects. J. Archit. Plan. Constr. Manag. 2020, 10, 92–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cortese, T.T.P.; De Almeida, J.F.S.; Batista, G.Q.; Storopoli, J.E.; Liu, A.; Yigitcanlar, T. Understanding Sustainable Energy in the Context of Smart Cities: A PRISMA Review. Energies 2022, 15, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnemolla, P.; Robinson, S.; Lay, K. Towards Inclusive Cities and Social Sustainability: A Scoping Review of Initiatives to Support the Inclusion of People with Intellectual Disability in Civic and Social Activities. City Cult. Soc. 2021, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Union. Protocol on Amendments to the Constitutive Act of the African Union. 2003. Available online: https://au.int/en/treaties/protocol-amendments-constitutive-act-african-union (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO). World Kiswahili Language Day. 2021. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000379076 (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Gurumurthy, A.; Soni, G.; Prakash, S.; Badhotiya, G.K. Review on Supply Chain Management Research—An Indian Perspective. IIM Kozhikode Soc. Manag. Rev. 2013, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Olde, E.M.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; de Boer, I.J.M. The choice of the sustainability assessment toll matters: Differences in thematic scope and assessment results. Ecological Economics. 2017, 139, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M.; Wong, J.K.W. Evolution in the Intellectual Structure of BIM Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2017, 28, 1060–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghimien, D.O.; Aigbavboa, C.O.; Oke, A.E.; Thwala, W.D. Mapping out Research Focus for Robotics and Automation Research in Construction-Related Studies: A Bibliometric Approach. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2020, 18, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Huo, X.; Owusu-Manu, D.G. A Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Global Green Building Research. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C. Critical Analysis of Green Building Research Trend in Construction Journals. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazem, N.; Abdelraouf, M.; Fahim, I.S.; El-Omari, S. A novel green rating system for existing buildings. Sustainability. 2020, 12, 7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rong, Y.; Ahmad, U.M.; Wang, X.; Zuo, J.; Mao, G. A comprehensive review on green buildings research: Bibliometric analysis during 1998–2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46196–46214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X. Research on the Literature of Green Building Based on the Web of Science: A Scientometric Analysis in Citespace (2002–2018). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zuo, J.; Wu, G.; Huang, C. A Bibliometric Review of Green Building Research 2000–2016. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2019, 62, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawumi, T.O.; Chan, D.W.M. A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Osei-Kyei, R. Scientometric Review of Global Research Trends on Green Buildings in Construction Journals from 1992 to 2018. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, A.; Giannotti, E.; Flores Molina, M.; Vásquez, A. From “Government to Governance”? A Systematic Literature Review of Research for Urban Green Infrastructure Management in Latin America. Front. Sustain. Cities 2020, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushady, A.M.; El-Sawy, S.A.R. Qualitative Assessment Framework to Evaluate Sustainability Indicators Affecting Infrastructure Construction Projects in Developing Countries Using the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP). WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 179, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarkouky, M.M.G. A Multi-Criteria Prioritization Framework (MCPF) to Assess Infrastructure Sustainability Objectives. J. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Kholy, A.M.; Akal, A.Y. Proposed Sustainability Composite Index of Highway Infrastructure Projects and Its Practical Implications. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 3635–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutatkar, N. Sustainability Assessment of Decentralised Solar Projects: Introducing a Multi-Criteria Approach. Master’s Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. Available online: http://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1117450 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Oraegbune, O.M.; Ugwu, O.O. Delivering Sustainable Transport Infrastructure Projects (Railway) in Nigeria: Frameworks, Indicators, Method and Tools. Niger. J. Technol. 2020, 39, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Monetary Fund (IMF). GDP of African Countries 2021, by Country. 2022. Available online: https://www-statista-com.eu1.proxy.openathens.net/statistics/1120999/gdp-of-african-countries-by-country/ (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Arora, A.; Schroeder, H. How to Avoid Unjust Energy Transitions: Insights from the Ruhr Region. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, G.; Rosendahl, K.E.; Böhringer, C. Balancing Cost and Justice Concerns in the Energy Transition: Comparing Coal Phase-out Policies in Germany and the UK. Clim. Policy 2022, 22, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S&P Global. What is energy transition? 2020. Available online: https://www.spglobal.com/en/research-insights/articles/what-is-energy-transition (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Jorgenson, S.; Stephens, J.C. Action Research for Energy System Transformation. Educ. Action Res. 2022, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Research on Supporting Developing Countries to Achieve Green Development Transition: Based on the Perspective of Renewable Energy and Foreign Direct Investment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaishi, T.; Chapman, A.; Kagawa, S. Shedding Light on the Energy-Related Social Equity of Nations toward a Just Transition. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2022, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślosarski, R. Clean Energy in the European Union: Transition or Evolution? Energy Environ. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).