Assessments of Heavy Metals Accumulation, Bioavailability, Mobility, and Toxicity in Serpentine Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
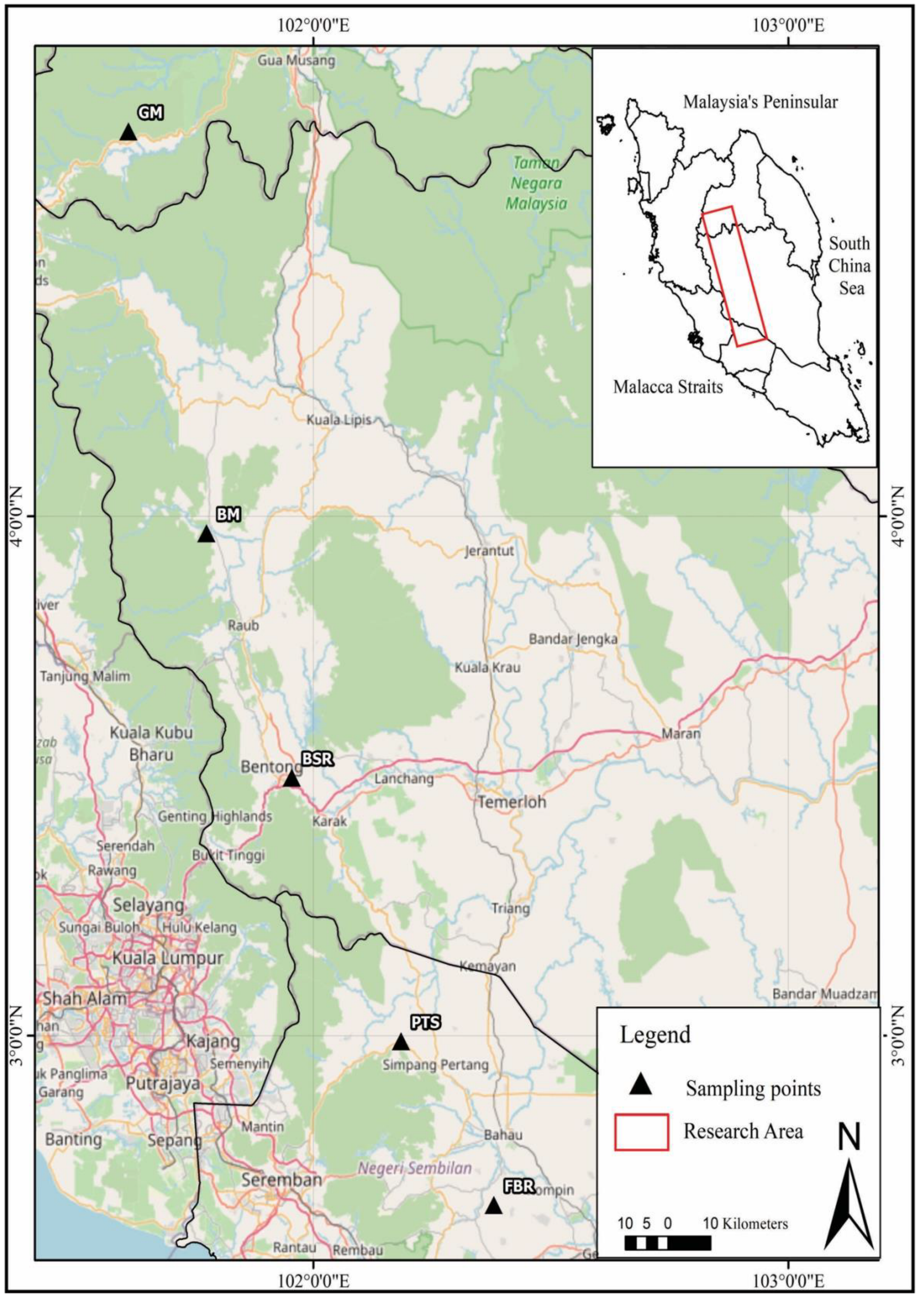
2.1. Site Description and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Physico-Chemical Characterization
- = Total beaker weight before the reaction.
- = Total beaker weight after the reaction.
- = Weight of soil (g).
2.3. Total Heavy Metals Content
2.4. Selective Sequential Extraction (SSE)
- F1: Soluble–exchangeable, the sample was shaken for 2 h at room temperature with 15 mL of 0.1 M of CaCl2 (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 10035-04-8).
- F2: Surface-adsorbed, the remaining residue was soaked with 30 mL of 1 M NaOAC (pH 5) (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 127-09-3) and shaken for 5 h at room temperature.
- F3: Organic matter, the remaining soil sample was put in a rotating water bath where the temperature was set to 90–95 °C for 30 min with 5 mL NaOCl (pH 8.5) (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 7681-52-9).
- F4: Mn oxides, the soil residue was mixed with 30 mL of 0.05 M NH2OH.HCl (pH 2) (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 5470-11-1) and shaken for 30 min at room temperature.
- F5: Poor crystalline Fe oxides, the remaining sample was mixed with 30 mL of 0.2 M oxalic acid (Systerm, CAS No. 6153-56-6) + 0.2 M NH4 oxalate (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 6009-70-7) (pH 3) and left shaking in a dark room for 2 h.
- F6: Crystalline Fe oxides, the soil sample was percolated with 40 mL of 6 M HCl (Systerm, Shah Alam, Malaysia, CAS No. 7647-01-0) and left shaking for 24 h at room temperature.
- F7: Residual, the remaining residue was digested using the total digestion method USEPA 3050B [40] using HNO3–H2O2.
2.5. Toxicity Characteristics Leaching Procedure (TCLP)
2.6. Quality Control and Assurance
2.7. Risk Assessments
2.7.1. Regulation Limits
2.7.2. Geoacumulation Index
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. General Soil Physico-Chemical Characteristics
Physico-Chemical Relations in Heavy Metal Leach and Sink
3.2. Total Heavy Metals Content
3.3. Risk Assessments
3.3.1. CLMCGs Regulatory Values
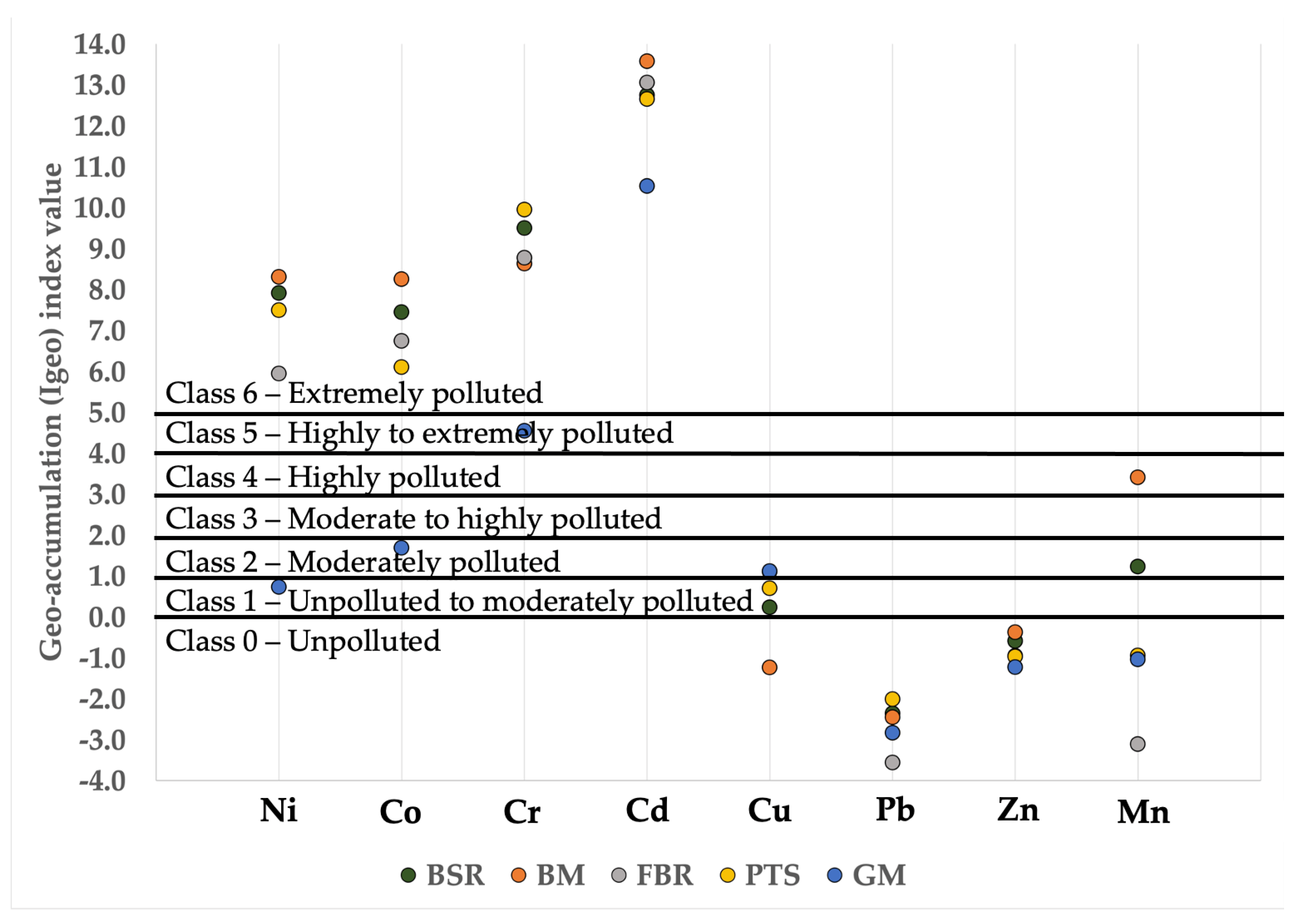
3.3.2. Igeo Bioaccumulation Indices
3.4. Selective Sequential Extraction (SSE)
Role of Parent Rock Weathering in the Distribution of Heavy Metals
3.5. Toxicity Characteristics Leaching Procedure (TCLP)
4. Conclusions
- This research has contributed to the knowledge about the accumulation of several heavy metal contaminants in contemporary serpentinite localities through geogenic processes.
- Based on the calculated Igeo values, 50% of the heavy metals (i.e., Cr, Cd, Ni, and Co) showed significant contamination in the topsoil. Meanwhile, another 12.5% of the heavy metals (Mn) showed moderate contamination. Another 12.5% of the heavy metals (Cu) showed unpolluted to moderate contamination. Only 25% of the heavy metals (Pb and Zn) showed uncontaminated status.
- The total concentration of heavy metals showed alarming accumulation values in the topsoil that exceeded the CLMCGs’ site screening values. Co and Cd showed, respectively, 3× and 2× higher concentrations than are designated for their concentrations in residential soil.
- A new, modified version of SSE utilized in tropical soils successfully extracted the bioavailability and mobility of heavy metals in these tropical soils.
- All heavy metals showed a dominant part bound to a residual fraction, indicating immobility in the environment. However, 60% of the heavy metals showed a minor yet concerning percentage of available fractions, indicating their tendency to be potentially bioavailable and easily transfer into the environment.
- The BM site showed the highest geogenic contamination of heavy metals. However, the GM site offered higher bioavailability and mobility of the resulting heavy metal accumulation, leading to higher toxicity levels than other sampling sites.
- The toxicity of the topsoils was still below the standard regulated USEPA toxicity value. Therefore, it does not pose harmful effects for the environment. However, when using the CLMCGs, 90% of the heavy metal toxicity values surpassed the stated screening values.
- For further study, the authors suggest bioavailability and toxicity tests on parts of plants (i.e., roots, stems, and leaves) growing in serpentinite soils.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macías, R.; Ramos, M.S.; Guerrero, A.L.; Farfán, M.G.; Mitchell, K.; Avelar, F.J. Contamination Assessment and Chemical Speciation of Lead in Soils and Sediments: A Case Study in Aguascalientes, México. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubus, M.; Bakinowska, E. The Effect of Immobilizing Agents on Zn and Cu Availability for Plants in Relation to Their Potential Health Risks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, N.; Pangerl, A.; Gómez-Alday, J.J.; Jirsa, F. Heavy Metals in Sediments and Greater Flamingo Tissues from a Protected Saline Wetland in Central Spain. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, V.; Macirella, R.; Sesti, S.; Pellegrino, D.; Ahmed, A.I.M.; Brunelli, E. Morphological and Molecular Alterations Induced by Lead in Embryos and Larvae of Danio Rerio. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, Mechanism and Health Effects of Some Heavy Metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merola, C.; Bisegna, A.; Angelozzi, G.; Conte, A.; Abete, M.C.; Stella, C.; Pederiva, S.; Faggio, C.; Riganelli, N.; Perugini, M. Study of Heavy Metals Pollution and Vitellogenin Levels in Brown Trout (Salmo Trutta Trutta) Wild Fish Populations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, R.A.; Jardine, T.D.; Chumchal, M.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Campbell, L.M. Biomagnification of Mercury in Aquatic Food Webs: A Worldwide Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13385–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Naidu, R. Assessment of Toxicity of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils by the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Boersch, J.; Frohne, T.; du Laing, G.; Rinklebe, J. Bioavailability and Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Garden Edible Vegetables and Soils around a Highly Contaminated Former Mining Area in Germany. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, J.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, H. A Case Study: Arsenic, Cadmium and Copper Distribution in the Soil–Rice System in Two Main Rice-Producing Provinces in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. Natl. Inst. Health 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, M.A.M. Chemical Speciation and Contamination Assessment of Pb and V by Sequential Extraction in Surface Sediment off Nile Delta, Egypt. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahibin, A.R.; Wan Mohd Razi, I.; Zulfahmi, A.R.; Tukimat, L.; Ramlan, O.; Liew, K.Y. Heavy Metal Content in Selected Flavouring Plants and in Ultrabasic Soil of Felda Bukit Rokan Barat, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Sains. Malays. 2012, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fubini, B.; Fenoglio, I. Toxic Potential of Mineral Dusts. Elements 2007, 3, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierczak, J.; Pietranik, A.; Pędziwiatr, A. Ultramafic Geoecosystems as a Natural Source of Ni, Cr, and Co to the Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwenzi, W. Occurrence, Behaviour, and Human Exposure Pathways and Health Risks of Toxic Geogenic Contaminants in Serpentinitic Ultramafic Geological Environments (SUGEs): A Medical Geology Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, S.; Abou El-Anwar, E.; Asmoay, A.; Mekky, H.; Abdel Wahab, W.; Elnazer, A. Chemical Fractionation and Risk Assessment of Some Heavy Metals in Soils, Assiut Governorate, Egypt. Egypt J. Chem. 2021, 64, 3311–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslaili, A.A.; Sahibin, A.R.; Ismail, S.; Wan Mohd Razi, I. Speciation and Availability of Heavy Metals On Serpentinized Paddy Soil and Paddy Tissue. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Ent, A.; Cardace, D.; Tibbett, M.; Echevarria, G. Ecological Implications of Pedogenesis and Geochemistry of Ultramafic Soils in Kinabalu Park (Malaysia). Catena 2018, 160, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-G.; Shi, J.-B.; He, B.; Liu, J.-F.; Liang, L.-N.; Jiang, G.-B. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Marine Sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with Sequential Extraction. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.A.; Cano, A.F.; Arocena, J.M.; Debela, F.; Martínez-Martínez, S. Distribution of Metals in Soil Particle Size Fractions and Its Implication to Risk Assessment of Playgrounds in Murcia City (Spain). Geoderma 2009, 149, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Modabberi, S.; van der Ent, A.; Echevarria, G. Impacts of Ultramafic Outcrops in Peninsular Malaysia and Sabah on Soil and Water Quality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tashakor, M.; Hochwimmer, B.; Imanifard, S. Control of Grain-Size Distribution of Serpentinite Soils on Mineralogy and Heavy Metal Concentration. Asian J. Earth Sci. 2015, 8, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delina, R.E.; Arcilla, C.; Otake, T.; Garcia, J.J.; Tan, M.; Ito, A. Chromium Occurrence in a Nickel Laterite Profile and Its Implications to Surrounding Surface Waters. Chem. Geol. 2020, 558, 119863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.; Pinho, C.; Albuquerque, T.; Araújo, J. Environmental Factors and Metal Mobilisation in Alluvial Sediments—Minas Gerais, Brazil. Geosciences 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.M. Biological Cycles for Toxic Elements in the Environment. Science 1974, 183, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, K.U.; Kruckeberg, A.R.; Bradshaw, H.D. Evolutionary Ecology of Plant Adaptation to Serpentine Soils. Annurev. Ecolsys. 2005, 36, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oze, C.; Skinner, C.; Schroth, A.W.; Coleman, R.G. Growing up Green on Serpentine Soils: Biogeochemistry of Serpentine Vegetation in the Central Coast Range of California. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3391–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Maity, J.P.; Mushtaq, S.; Vithanage, M.; Seneweera, S.; Schneider, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Khan, N.I.; Hamawand, I.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; et al. Medical Geology in the Framework of the Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EU Soil Strategy for 2030; Communication from the Commission to European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–699. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, P.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P.; Cruz, N.; Rodrigues, S.M. Assessment of Soil Physicochemical Characteristics and As, Cu, Pb and Zn Contamination in Non-Active Mines at the Portuguese Sector of the Iberian Pyrite Belt. Environments 2022, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedron, F.; Grifoni, M.; Barbafieri, M.; Franchi, E.; Vocciante, M.; Petruzzelli, G. Comparative Evaluation of Technologies at a Heavy Metal Contaminated Site: The Role of Feasibility Studies. Environments 2022, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environment Malaysia (DOEM). Contaminated Land Management and Control Guidelines No. 1: Malaysian Recommended Site Screening Levels for Contaminated Land; Kuala Lumpur; Department of Environment Malaysia (DOEM): Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2015.
- Guevara, P.; Pérez-Alberti, A.; Carballo, R.; Sánchez, M.; López, I.; Otero, X.L. Impact of Serpentinized Peridotite Mine Waste on the Composition and Quality of Sediments in the Ría de Ortigueira (Galicia, NW Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulos, C. Influence of Ultramafic Rocks and Hot Springs with Travertine Depositions on Geochemical Composition and Baseline of Soils. Application to Eastern Central Greece. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.L.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; O’Connor, G.A.; Chang, A.C. Heavy Metal Sequential Extraction Methods—A Modification for Tropical Soils. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metson, A.J. Methods of Chemical Analysis for Survey Samples. Soil Bereau Bull. 1956, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geotechnical Research Centre. Laboratory Handbook; Geotechnical Research Centre: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Acid Digestion of Sludges, Solids, and Soils. USEPA 3050B 1996, SW-846 Pt 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tashakor, M. Geochemistry of Serpentinite and Its Effect on the Environment: Case Study at Peninsular and Sabah Malaysia; Doctor of Philosophy, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM): Bangi, Malaysia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure. Method 1992, 1311, 1–35.
- Tashakor, M.; Zuhairi Wan Yaacob, W.; Mohamad, H.; Abdul Ghani, A.; Saadati, N. Assessment of Selected Sequential Extraction and the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Test as Indices of Metal Mobility in Serpentinite Soils. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2014, 26, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, A.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zou, D. Speciation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Pyrolytic Biochar of Swine and Goat Manures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 132, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Leng, L.; Chen, X.; Zeng, G.; Li, F.; Cao, L. Chemical Speciation, Mobility and Phyto-Accessibility of Heavy Metals in Fly Ash and Slag from Combustion of Pelletized Municipal Sewage Sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tashakor, M.; Wan Zuhairi, W.Y. Hamzah Mohamad Serpentine Soils, Adverse Habitat for Plants Case Study at Peninsular. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 9, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahibin, A.R.; Ivy, J.J.; Diana Demiyah, M.H.; Nur Zaida, Z.; Musta, B. Physico-Chemical Properties of Ultrabasic Soil from Mibang, Ranau, Sabah. Trans. Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Umor, M.R.; Mohamad, H.; Twaiq, O.A.; Tan, M.M.; Isahak, A.; Musta, B. Petrographic and Geochemical Study of Ultrabasic Rocks in the Vicinity of Ranau, Sabah. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2003, 46, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sariam, O. Pembajaan Asas Dan Tambahan; Serdang: Selangor, Malaysia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sahibin, A.R.; Diana Demiyah, M.H.; Musta, B. Heavy Metals Content in Ultrabasic Soil and Plant around Ranau Sport Complex, Sabah, Malaysia. In Proceedings of the Warta Geologi; Geological Society of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2019; pp. 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Oze, C.; Fendorf, S.; Bird, D.K.; Coleman, R.G. Chromium Geochemistry of Serpentine Soils. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 46, 97–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.-Y.; Zehetner, F.; Fujii, K.; Watanabe, T.; Nakao, A. Geochemical Fractionation of Chromium and Nickel in Serpentine Soil Profiles along a Temperate to Tropical Climate Gradient. Geoderma 2018, 327, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarathilaka, P.; Dissanayake, C.B.; Vithanage, M. Geochemistry of Serpentinite Soils: A Brief Overview. J. Geol. Soc. Sri Lanka 2014, 16, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Weerasinghe, H.A.S.; Iqbal, M.C.M. Plant Diversity and Soil Characteristics of the Ussangoda Serpentine Site. J. Natl. Sci. Found. 2011, 39, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, A.; Wood, J.J. The Orchid Review; Orchid Review Limited: London, UK, 2013; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mccauley, A. Soil PH and Organic Matter; Nutrient Management Module: Bozeman, Montana, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W. Soil Organic Matter in Major Pedogenic Soil Groups. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil Physical Quality: Part I. Theory, Effects of Soil Texture, Density, and Organic Matter, and Effects on Root Growth. Geoderma 2004, 120, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, H. The Soil Resource: Origin and Behavior; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 37. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, E.B.; DuShey, J. Topographic and Soil Differences from Peridotite to Serpentinite. Geomorphology 2011, 135, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.W.; Adezrian, J.; Khairiah, J.; Ismail, B.S.; Ahmad-Mahir, R. The Uptake of Heavy Metals by Paddy Plants (Oryza Sativa) in Kota Marudu, Sabah, Malaysia. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 6, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, D.A.; Selkirk, J.M.; Seppelt, R.D. Serpentinite, Harzburgite, and Vegetation on Subantarctic Macquarie Island. Arct. Alp. Res. 1993, 25, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, M.E.; Freppaz, M.; Zanini, E.; Bonifacio, E. Primary Vegetation Succession and the Serpentine Syndrome: The Proglacial Area of the Verra Grande Glacier, North-Western Italian Alps. Plant Soil 2017, 415, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.-Y.; Su, Y.-C.; Zehetner, F.; Hsi, H.-C. Leaching Potential of Geogenic Nickel in Serpentine Soils from Taiwan and Austria. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratié, G.; Garnier, J.; Vieira, L.C.; Araújo, D.F.; Komárek, M.; Poitrasson, F.; Quantin, C. Investigation of Fe Isotope Systematics for the Complete Sequence of Natural and Metallurgical Processes of Ni Lateritic Ores: Implications for Environmental Source Tracing. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 127, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahibin, A.R.; Wan Mohd Razi, I.; Zulfahmi, A.R.; Tukimat, L.; Muhd Barzani, G.; Jumaat, H.A.; Low, H.K. Heavy Metals Uptake by Terung Pipit (Solanum Torvum) in Ultrabasic Soil at Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan. Sains Malays 2008, 37, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sahibin, A.R.; Wan Mohd Razi, I.; Tukimat, L.; Jalaludin, A.K.; Azman, H.; Nur Diyana, M.I. Heavy Metals Uptakes by Curry Leaf Tree (Murraya Koenigi) in Ultrabasic Soils from Felda Bukit Rokan, Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Sains Malays 2013, 42, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Trescases, J.J.; Melfi, A.J.; Barros de Oliveira, S.M. Nickeliferous Laterites of Brazil Laterisation Processes; IBH Publishing: New Delhi, India, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, U.R.; Maulana, A.; Muhammad, F. Role of Bedrock Serpentinization on the Development of Nickel Laterite Deposit in Sorowako, Sulawesi, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 921, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M.; Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K. Structural Mapping of the Bentong-Raub Suture Zone Using PALSAR Remote Sensing Data, Peninsular Malaysia: Implications for Sediment-Hosted/Orogenic Gold Mineral Systems Exploration. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahenbuhl, R. Magmatism, Tin Mineralization and Tectonics of the Main Range, Malaysian Peninsula: Consequences for the Plate Tectonic Model of Southeast Asia Based on Rb-Sr, K-Ar and Fission Track Data. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 1991, 29, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoo, T.T.; Tan, B.K. Geological Evolution of Peninsular Malaysia. In Proceedings of the Workshop on the stratigraphic correlation of Thailand and Malaysia, Haad Yai, Thailand, 8 September 1983; pp. 253–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jaafar Ahmad Geology and Mineral Resources of the Karak and Termeloh Areas, Pahang. Geol. Surv. Malays. 1976, 15, 138–150.
- Alexander, J.B. The Geology and Mineral Resources of the Neighbourhood of Bentong Area, Pahang. Geol. Surv. Malays. 1968, 8, 250–260. [Google Scholar]
- Khoon, S.Y. Osmiridium-A Discovery in Cheroh, Pahang, Peninsular Malaysia, and Its Significance. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 1982, 15, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, J.A. The Geology and Mineral Resources of the Neighbourhood of Raub, Pahang, Federated Malay States. Geol. Surv. Dep. Malays. 1939, 3, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Tack, F.M.G.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.F.; Gao, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Speciation, Transportation, and Pathways of Cadmium in Soil-Rice Systems: A Review on the Environmental Implications and Remediation Approaches for Food Safety. Environ. Int 2021, 156, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, O.; Ince, M.; Yaman, M. Sequential Extraction of Cadmium in Different Soil Phases and Plant Parts from a Former Industrialized Area. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Wan Zuhairi, W.Y. Hamzah Mohamad Speciation and Availability of Cr, Ni, and Co in Serpentine Soils of Ranau, Sabah. Am. J. Geosci. 2011, 2, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, Y.; Shamshuddin, J. Sains Tanah; Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1982.
- Kumar, D.; Khan, E.A. Remediation and Detection Techniques for Heavy Metals in the Environment. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zinn, Y.L.; de Faria, J.A.; de Araujo, M.A.; Skorupa, A.L.A. Soil Parent Material Is the Main Control on Heavy Metal Concentrations in Tropical Highlands of Brazil. Catena 2020, 185, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjia, H.D. Syed Sheikh Almashoor The Bentong Suture in Southwest Kelantan, Peninsular Malaysia. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 1996, 39, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Khoo, T.T. Clinopyroxene Composition and Tectonic Setting of the Bentong-Raub Belt, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1993, 8, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, J.; Abdullah, I. The Structure and Deformation History of the Serpentinite Bodies along the Bentong Suture: A Case Study at Bukit Rokan Barat. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2003, 46, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Heavy Metals | Site Screening Levels (SSLs) | Background Value (mg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soils (mg/kg) | Toxicity (mg/L) | ||||
| Residential Soil | Industrial Soil | Groundwater | |||
| Cadmium | Cd | 7.10 | 9.80 | 9.20 | 9.00 |
| Chromium | Cr (III) | 1.20 | 1.80 | 2.20 | 1.44 |
| Cr (VI) | 3.00 | 6.30 | 3.50 | ||
| Cobalt | Co | 2.30 | 3.50 | 6.00 | 1.19 |
| Copper | Cu | 3.10 | 4.70 | 8.01 | 1.98 |
| Lead | Pb | 4.00 | 8.00 | 1.50 | 3.60 |
| Manganese | Mn | 1.80 | 2.60 | 4.30 | 3.99 |
| Nickel | Ni | 1.50 | 2.20 | 3.90 | 2.89 |
| Zinc | Zn | 2.30 | 3.50 | 6.02 | 5.43 |
| Class | Igeo Value | Pollution Degree |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | <0 | Unpolluted |
| 1 | 0–1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted |
| 2 | 1–2 | Moderately polluted |
| 3 | 2–3 | Moderately to highly polluted |
| 4 | 3–4 | Highly polluted |
| 5 | 4–5 | Highly to extremely polluted |
| 6 | >5 | Extremely polluted |
| Sampling Locations | Physico-Chemical Properties | pH | SOM (%) | CEC (meq/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSR (n = 5) | Max | 6.20 | 10.00 | 3.02 |
| Min | 5.28 | 3.90 | 1.65 | |
| Mean | 5.64 | 6.11 | 2.15 | |
| Std | 0.36 | 2.63 | 0.43 | |
| BM (n = 5) | Max | 6.23 | 10.08 | 2.63 |
| Min | 5.05 | 2.75 | 1.59 | |
| Mean | 5.73 | 4.88 | 1.92 | |
| Std | 0.62 | 3.00 | 0.41 | |
| FBR (n = 5) | Max | 5.52 | 11.14 | 2.88 |
| Min | 4.48 | 4.65 | 1.36 | |
| Mean | 4.83 | 7.71 | 1.79 | |
| Std | 0.41 | 2.45 | 0.56 | |
| PTS (n = 5) | Max | 5.96 | 22.72 | 4.95 |
| Min | 5.25 | 3.51 | 1.87 | |
| Mean | 5.66 | 8.17 | 3.17 | |
| Std | 0.28 | 8.19 | 0.62 | |
| GM (n = 5) | Max | 5.44 | 29.70 | 2.34 |
| Min | 5.15 | 3.30 | 1.22 | |
| Mean | 5.28 | 9.28 | 1.72 | |
| Std | 0.12 | 11.47 | 1.27 | |
| Total Mean (n = 25) | 5.43 | 7.23 | 2.15 | |
| Locations | Range | Heavy Metals Concentrations (mg/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Co | Cr | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | Mn | ||
| BSR (n = 3) | Max | 1.89 | 4.93 | 2.86 | 1.28 | 5.90 | 1.19 | 9.12 | 3.85 |
| Min | 2.36 | 1.86 | 1.80 | 6.63 | 1.06 | 8.76 | 2.32 | 7.66 | |
| Mean | 1.04 | 3.10 | 1.56 | 9.24 | 3.49 | 1.05 | 5.39 | 1.40 | |
| Std | 8.27 | 1.62 | 1.34 | 3.21 | 2.42 | 1.59 | 3.45 | 2.12 | |
| B.M. (n = 2) | Max | 1.67 | 6.41 | 8.75 | 1.80 | 1.89 | 1.38 | 7.67 | 1.26 |
| Min | 1.06 | 4.46 | 8.30 | 1.48 | 6.29 | 5.90 | 4.86 | 1.25 | |
| Mean | 1.37 | 5.44 | 8.53 | 1.64 | 1.26 | 9.84 | 6.27 | 6.34 | |
| Std | 4.26 | 1.38 | 3.18 | 2.32 | 8.88 | 5.56 | 1.99 | 8.79 | |
| FBR (n = 3) | Max | 5.29 | 4.44 | 1.85 | 1.86 | 7.68 | 4.89 | 5.91 | 8.93 |
| Min | 1.11 | 4.39 | 3.26 | 7.29 | 5.59 | 4.07 | 3.12 | 3.91 | |
| Mean | 2.67 | 1.90 | 9.43 | 1.14 | 6.36 | 4.56 | 4.20 | 6.93 | |
| Std | 2.28 | 2.20 | 8.05 | 6.25 | 1.15 | 4.34 | 1.50 | 2.67 | |
| PTS (n = 1) | Max | 7.80 | 1.23 | 2.13 | 8.66 | 4.81 | 1.34 | 4.14 | 3.11 |
| Min | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | |
| Mean | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | |
| Std | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | N. A | |
| GM (n = 2) | Max | 7.64 | 6.63 | 5.77 | 2.07 | 8.70 | 1.03 | 3.88 | 3.92 |
| Min | 6.75 | 4.85 | 4.32 | 1.90 | 4.16 | 4.86 | 3.07 | 1.88 | |
| Mean | 7.19 | 5.74 | 5.05 | 1.99 | 6.43 | 7.57 | 3.47 | 2.90 | |
| Std | 6.30 | 1.26 | 1.02 | 1.20 | 3.21 | 3.83 | 5.72 | 1.44 | |
| Total Mean (n = 11) | 6.77 | 2.47 | 1.04 | 9.77 | 4.52 | 8.48 | 4.76 | 1.63 | |
| Sampling Locations | Heavy Metals | Concentration of Toxicity (mg/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Co | Cr | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | Mn | ||
| BSR (n = 5) | Max | ||||||||
| Min | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||||||
| Mean | |||||||||
| Std | |||||||||
| BM (n = 5) | Max | BDL | |||||||
| Min | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||||||
| Mean | BDL | ||||||||
| Std | BDL | ||||||||
| FBR (n = 5) | Max | ||||||||
| Min | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||||||
| Mean | |||||||||
| Std | |||||||||
| PTS (n = 5) | Max | BDL | |||||||
| Min | BDL | BDL | BDL | ||||||
| Mean | |||||||||
| Std | |||||||||
| GM (n = 5) | Max | BDL | |||||||
| Min | BDL | BDL | |||||||
| Mean | BDL | ||||||||
| Std | BDL | ||||||||
| Total Mean (n = 25) | |||||||||
| Heavy Metals | Regulatory Value of Toxicity (mg/L) | Concentration Ratio (Comparison with This Research by Factor X) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USEPA | DOEM | Tashakor et al. [43,82] | USEPA | DOEM | Tashakor et al. [43,82] | |
| Ni | BRV | 12 | 1 | |||
| Co | N.A. | N.A. | 56 | 1 | ||
| Cr | BRV | BRV | 7 | |||
| Cd | N.A. | BRV | 1 | N.A. | ||
| Cu | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 6 | N.A. | |
| Pb | N.A. | BRV | 8 | N.A. | ||
| Zn | N.A. | BRV | BRV | N.A. | ||
| Mn | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 95 | N.A. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Rashid, S.R.; Wan Yaacob, W.Z.; Umor, M.R. Assessments of Heavy Metals Accumulation, Bioavailability, Mobility, and Toxicity in Serpentine Soils. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021218
Abdul Rashid SR, Wan Yaacob WZ, Umor MR. Assessments of Heavy Metals Accumulation, Bioavailability, Mobility, and Toxicity in Serpentine Soils. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021218
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Rashid, Sheila Rozalia, Wan Zuhairi Wan Yaacob, and Mohd Rozi Umor. 2023. "Assessments of Heavy Metals Accumulation, Bioavailability, Mobility, and Toxicity in Serpentine Soils" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021218
APA StyleAbdul Rashid, S. R., Wan Yaacob, W. Z., & Umor, M. R. (2023). Assessments of Heavy Metals Accumulation, Bioavailability, Mobility, and Toxicity in Serpentine Soils. Sustainability, 15(2), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021218







