Hybrid Wind/PV E-Bike Charging Station: Comparison of Onshore and Offshore Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
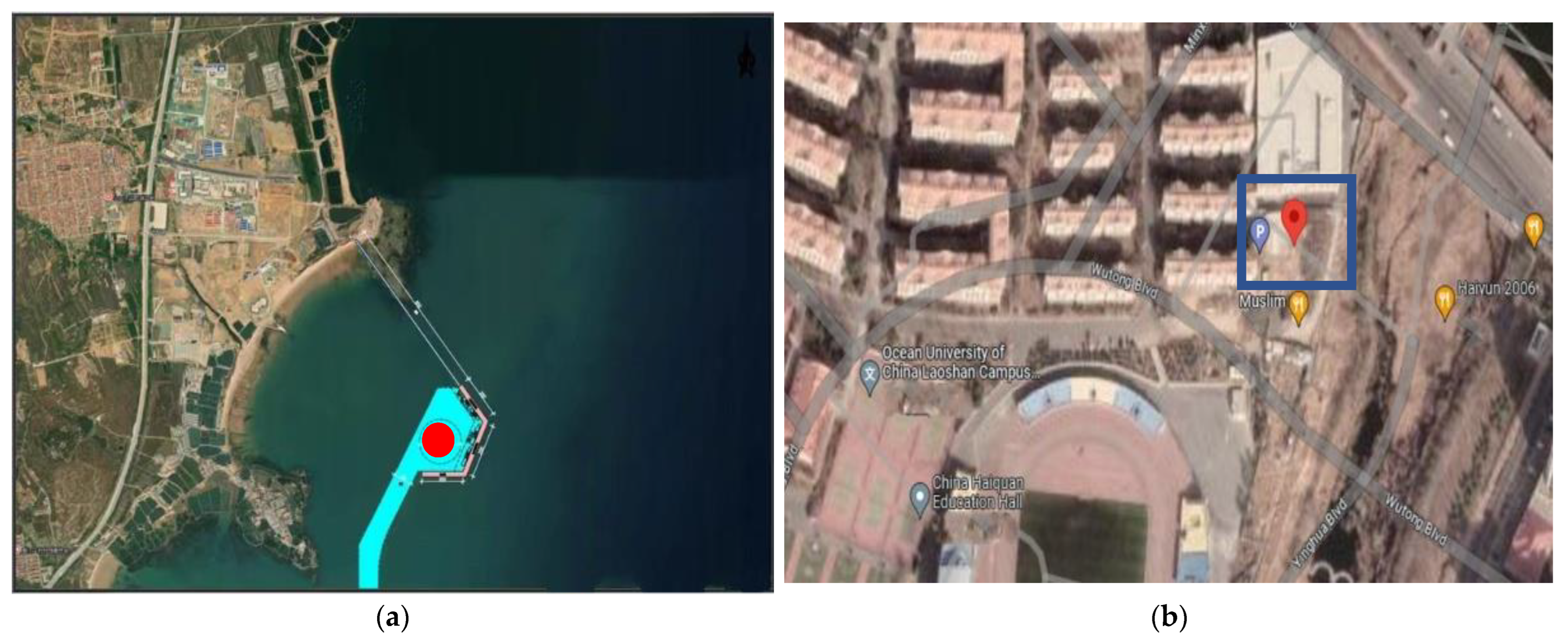
- To analyze the geographical location for the installation;
- Calculate the AEP (annual energy production) for wind turbine and solar PV (photovoltaic);
- Comparison of two different offshore and onshore sites;
- Modelling of wind–solar charging station on MATLAB/Simulink;
- Calculation of E-bike charging for both locations;
- To do the cost analysis of hybrid energy using COE.
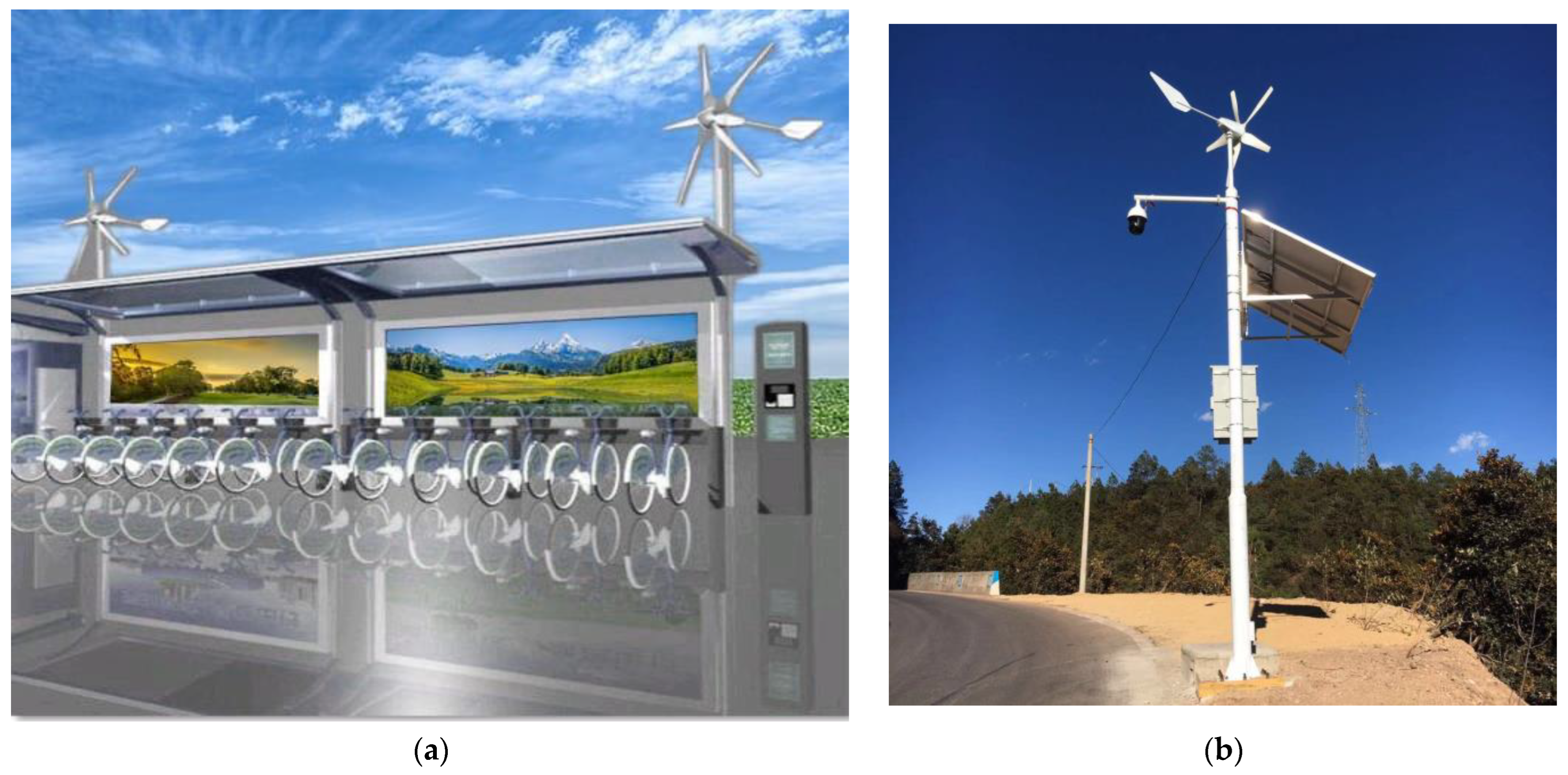
2. Essential Factors in Building E-Bike Charging Station
Designing Hybrid E-Bike Charging Station
- Number of E-bike that can be charged: The charging station should be constructed to support the maximum number of vehicles charged concurrently or within a specific amount of time.
- Charge time: The charging station needs the proper infrastructure to satisfy the necessary charge time, whether for fast or slow charging.
- Charging connectors: To assure compatibility with the charging of electric vehicles, the charging station should offer relevant sockets or connectors. Examples that are frequently used are Type 1 (J1772), Type 2 (Mennekes), and CHAdeMO.
- Battery type and capacity: There are various EV models with various battery kinds and capacities. The charging station should meet the capacity needs of different battery types, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and solid-state batteries.
- Potential of energy sources: When planning the charging station, it is essential to consider the potential and accessibility of energy sources such as grid electricity, solar power, and wind power. This will aid in determining the potential sources of energy and the necessary capacity.
- Dimensions of the station: Based on the available space and anticipated customer demand, the physical dimensions of the charging station, including the space needed for charging infrastructure, parking spaces, and any other facilities, should be decided.
3. Methodology
3.1. Wind Turbine
3.2. Mathematical Modelling of Wind Turbine
- Cp = aerodynamic coefficient;
- λ = tip speed ratio (TSR) = ωR/v;
- β = pitch angle;
- ρ = air density (1.22 kg/);
- A = rotor swept area ();
- v = instantaneous velocity of the wind (m/s).
3.3. Solar PV
3.4. Mathematical Modelling of Solar PV
- k = Boltzmann’s constant (J/K);
- t = temperature (K);
- q = electron charge in coulombs;
- Vt= voltage equivalent of the temperature = kT/q;
- Io = reverse saturation current (A).
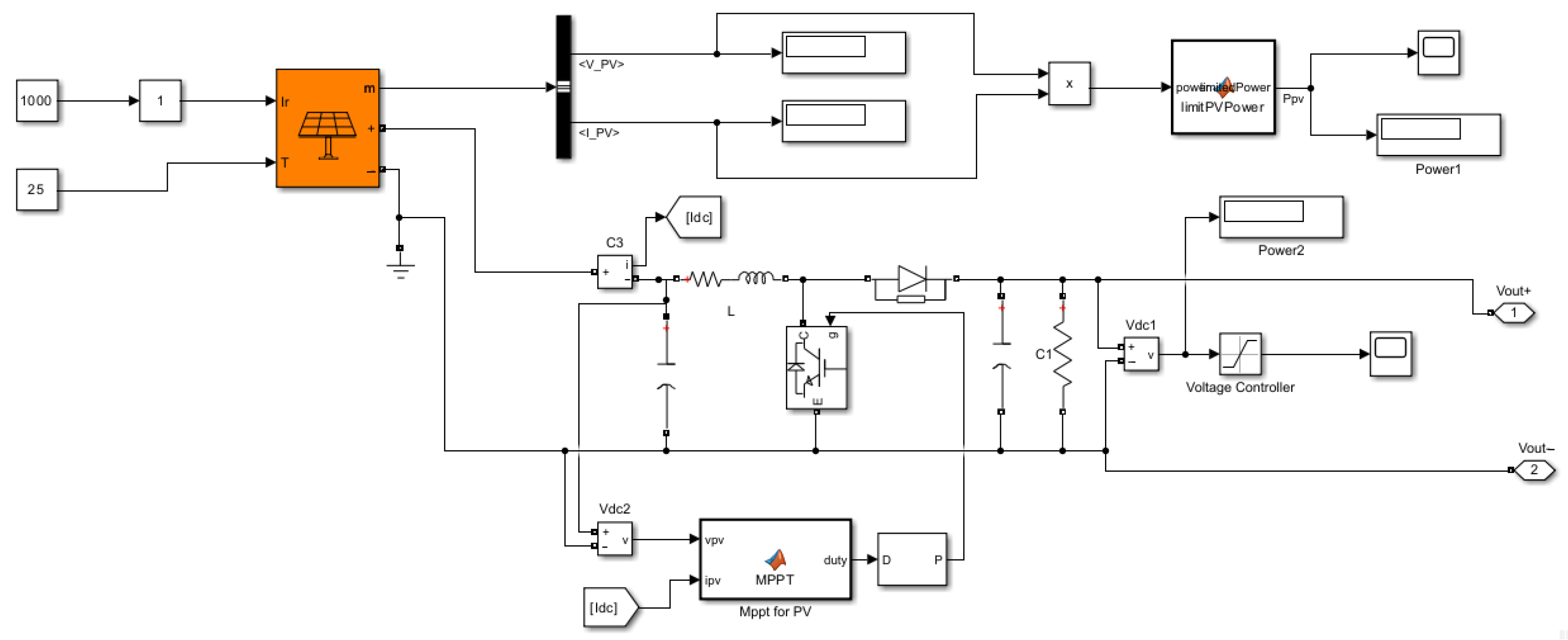
3.5. Simulink Modelling
3.6. Results & Discussions
3.7. AEP Analysis of Wind/Solar
4. E-Bike Calculations
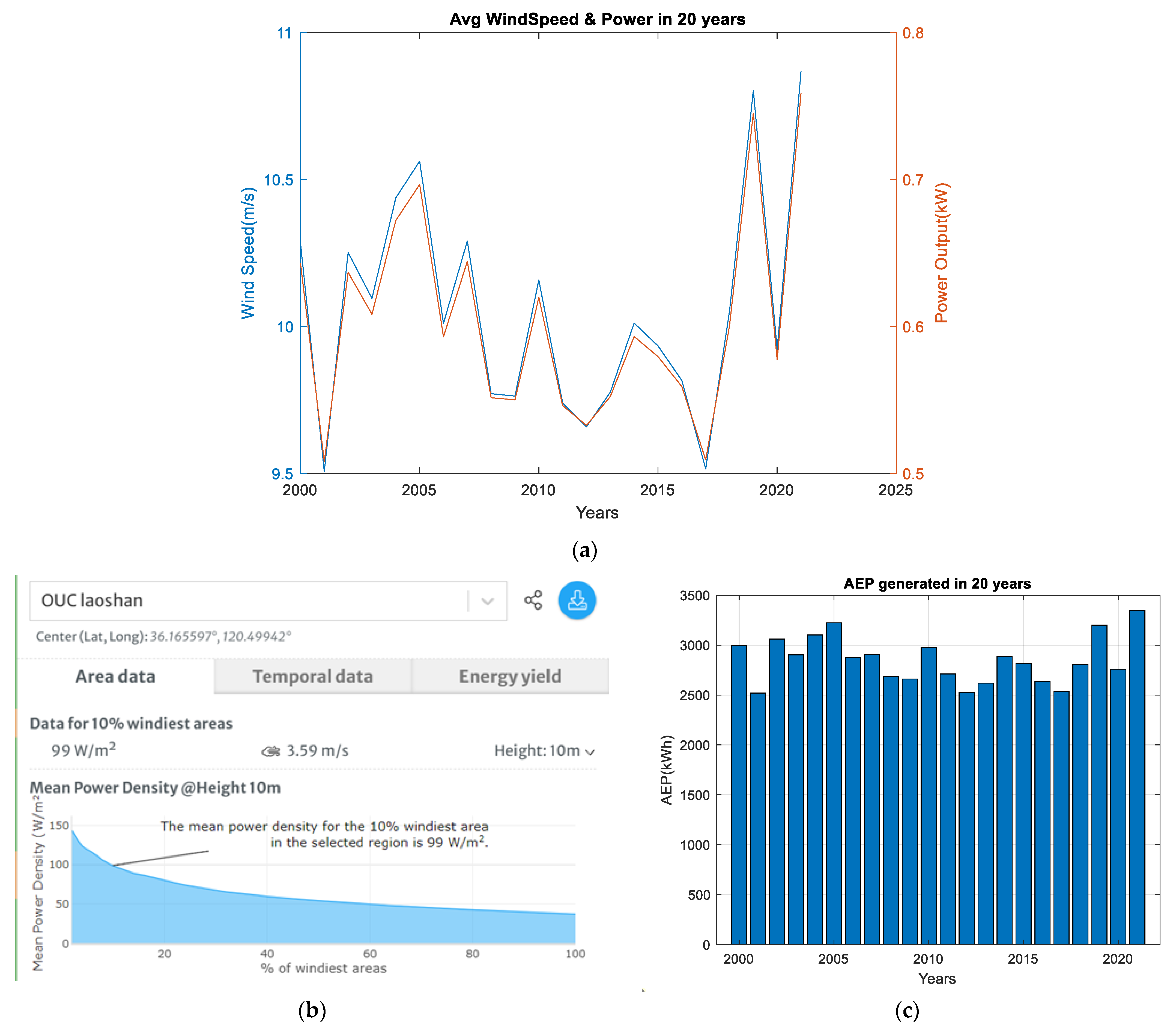
4.1. E-Bike Calculation for Case 1—Onshore (Laoshan)
- The electric bike charger has a power rating of 400 watts.
- The charging time required to charge one E-bike from the available power is 4 h.
- The battery voltage is 48 V, and the capacity of each battery block is 4.8 kWh (100 Ah × 48 V/1000).
- The charging efficiency is assumed to be 90% for wind and solar power.
- Wind turbine: 2988 kWh/year/365 days = 8.2 kWh/day;
- Solar PV: 96 kWh/year/365 days = 0.27 kWh/day;
- Lithium battery: 4.8 kWh.
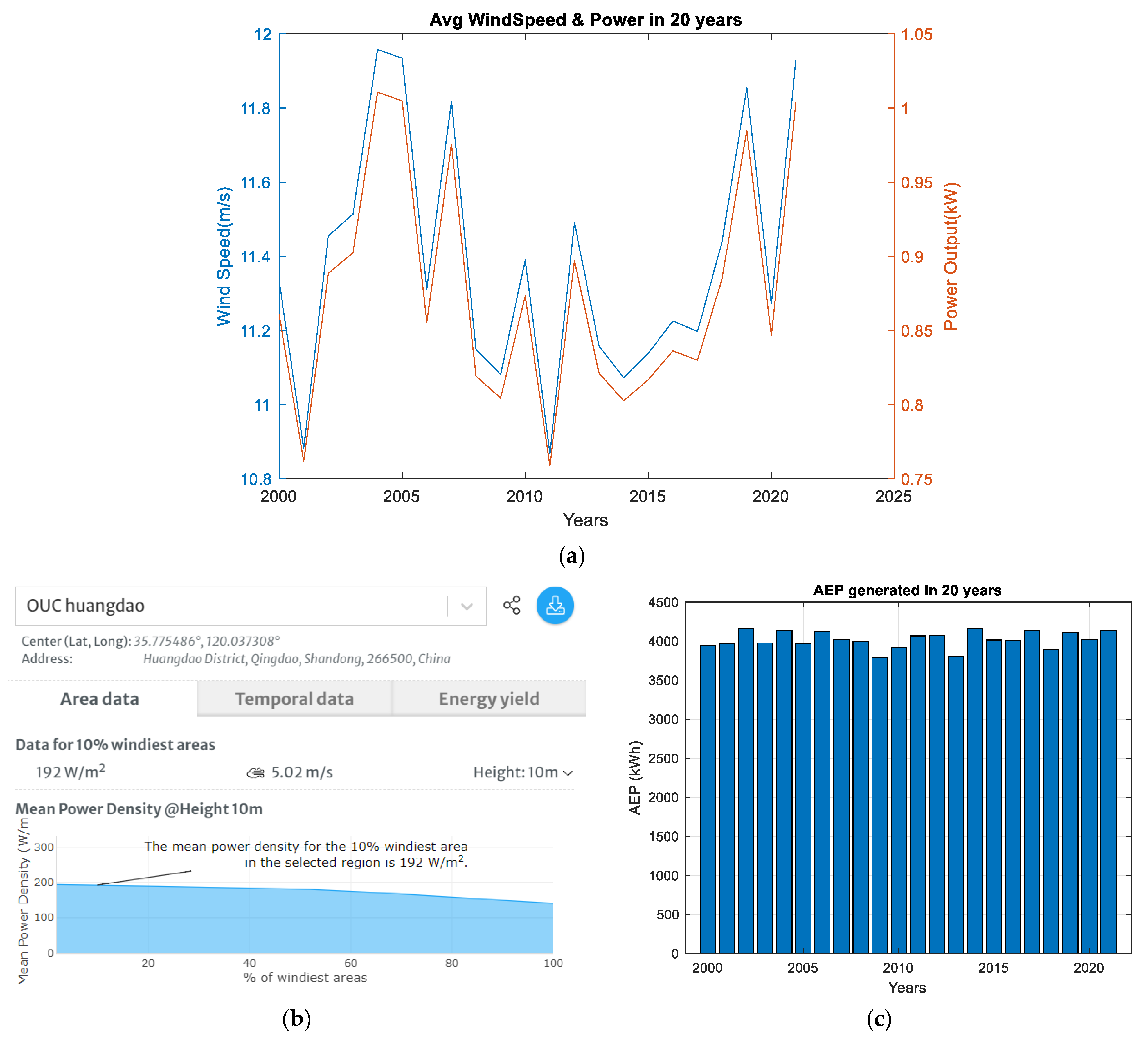
4.2. E-Bike Calculation for Case 2—Offshore (Huangdao)
- Wind turbine: 4045 kWh/year/365 days = 11 kWh/day;
- Solar PV: 100 kWh/year/365 days = 0.28 kWh/day;
- Lithium battery: 4.8 kWh.
5. Cost of Energy

6. Future Scope
7. Conclusions & Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/department-for-environment-food-rural-affairs (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Barman, P. Renewable energy integration with electric vehicle technology: A review of the existing smart charging approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, F.; Vargas, R.; Gastelo-Roque, J.A. Hybrid photovoltaic-wind microgrid with battery storage for rural electrification: A case study in Perú. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 8, 528571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruwatanachai, P.; Sukamongkol, Y.; Samanchuen, T. Predicting and Managing EV Charging Demand on Electrical Grids: A Simulation-Based Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiranvand, H.; Rahmani, R.; Sadough, S. A simulation-based analysis of a hybrid wind-solar electric bike charging station. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 172, 495–507. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, G.; Singh, R.R. Design of a microgrid architecture for rental E-bike charging stations. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 906, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihm, J.; Amghar, B.; Chun, S.; Park, H. Optimum design of an electric vehicle charging station using a renewable power generation system in South Korea. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkazaz, M.; Sumner, M.; Thomas, D. Energy management system for hybrid PV-wind-battery microgrid using convex programming, model predictive and rolling horizon predictive control with experimental validation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 115, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, G.R.C.; Van Duijsen, P.; Grazian, F.; Jamodkar, A.; Bauer, P.; Isabella, O. Sustainable E-bike charging station that enables AC, DC and wireless charging from solar energy. Energies 2020, 13, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Miao, Y.; Logan, K.G.; Michael, B.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Miao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; et al. The Potential of Photovoltaics to Power the Belt and Road Initiative. Joule 2019, 3, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Cui, N.; Hao, W.; Li, H.; Gong, D. High-resolution assessment of solar radiation and energy potential in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 240, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Hou, B.; Ye, G.; Wang, Z. China’s land-sea coordination practice in territorial spatial planning. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 237, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, E.; Koppelaar, R.; Jeanmart, H. Global available solar energy under physical and energy return on investment constraints. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 113968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouhi, A.; Rehman, S. Grid-connected hybrid renewable energy systems for supermarkets with electric vehicle charging platforms: Optimization and sensitivity analyses. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 3305–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Ou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, D.; Ma, J. Robust model of electric vehicle charging station location considering renewable energy and storage equipment. Energy 2022, 238, 121713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Que, L.; Feng, J. Spatiotemporal characteristics of wind energy resources from 1960 to 2016 over China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2020, 13, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Das, P.; Yamujala, S.; Bhakar, R.; Mathur, J. Resource potential and variability assessment of solar and wind energy in India. Energy 2020, 211, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Taubert, D.; Schindler, D. The temporal variability of global wind energy—Long-term trends and interannual variability. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 188, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Virguez, E.; Shan, R.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Patiño-Echeverri, D. High-resolution data shows China’s wind and solar energy resources are enough to support a 2050 decarbonized electricity system. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 117996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; He, J.; Zhao, T.; Singh, Y.V. Recent advances of wind-solar hybrid renewable energy systems for power generation: A review. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2022, 3, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvvala, J.; Kumar, K.S. Implementation of EFC Charging Station by Multiport Converter with Integration of RES. Energies 2023, 16(3), 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.Y.; Chin, H.H.; Klemeš, J.J. Solar Energy-Powered Battery Electric Vehicle charging stations: Current development and future prospect review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xue, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Xue, Y. Progress on offshore wind farm dynamic wake management for energy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Wind Atlas. Globalwindatlas.info. Available online: https://globalwindatlas.info/en (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Indragandhi, S. Resources, configurations, and soft computing techniques for power management and control of PV/wind hybrid system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Sunningsolar.com. 2023. Available online: http://www.sunningsolar.com/page55.html (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Molu, R.J.J. Optimization-based energy management system for grid-connected photovoltaic/battery microgrids under uncertainty. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Anandhakumar, G.; Jacob, A.A.; Singh, N.P.; Asha, S.; Jayadhas, S.A. Hybrid renewable power generation for modeling and controlling the battery storage photovoltaic system. Int. J. Photoenergy 2022, 2022, 9491808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.-L.; Colicchio, E.; Primiani, P.; Viglione, L.; Al-Haddad, K.; Woodward, L. A cost-effective standalone E-bike charging station powered by hybrid wind and solar power system including second-life BESS. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 11–15 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, F.; Min, H.; Tian, H.; Hu, W.; Liu, J.; Eghbalian, N. Energy management programming to reduce distribution network operating costs in the presence of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. Energy 2023, 263, 125695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reference | Objective | Methods | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | RES power production potential assessment | Yearly average solar radiation and wind speed data | Assess theoretical global solar and wind potential with constraints |
| [10] | Solar photovoltaic potential assessment | Geospatial estimation in 66 countries using the Belt and Road Initiative region | Evaluate the technical potential of solar photovoltaic power. |
| [11] | Solar power variability assessment | Multi-year hourly meteorological time-series data | Quantify spatiotemporal trends of global solar radiation and PV power in China. |
| [16] | Wind energy trends assessment | Analysis of annual and seasonal wind speed and energy resources | Significant decreasing trend in wind speed and energy resources in China |
| [14] | Optimal hybrid renewable energy system for Moroccan supermarkets with EV charging | Proposed PV/wind/battery system using HOMER grid software; analyzed three Moroccan cities | Dakhla site best with 71.66% renewable energy and low costs; sensitivity analysis performed |
| [15] | Robust EV charging station location optimization in micro-grids with renewables | Developed model considering EV demand and renewable uncertainty; used load fluctuation rate and kernel density estimation | Model demonstrated robustness and cost-effectiveness in simulations on IEEE 33-node network |
| [17] | Solar and wind potential assessment | Multi-year hourly satellite-derived MERRA-2 data | Analyze solar PV and wind resource potential and variability in India |
| [18] | Global wind energy trends assessment | Assessment of inter-annual variability and trends in wind energy | Identify significant trends in wind energy generation across countries |
| [19] | Long-term trend estimation | Accurate estimation of solar and wind energy potential | Importance of site-specific estimation for renewable energy expansion and resilience |
| [20] | Review wind-solar HRES for system modelling and optimization. | Analyzing models, HESS, converters, and algorithms while reviewing the literature. | Research in enhancing the performance of wind-solar HRES |
| [21] | Integrating PV-HESS with a multi-port DC-DC converter | PV-battery-EV charging integration used a bidirectional converter with a PI controller. | Enhanced integration, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, mitigating overload issues during EV charging. |
| [22,23] | Solar–wind energy characterization | Hourly time-series meteorological data for onshore and offshore sites | Explore spatiotemporal variability and complementarity of solar and wind energy potential in China |
| Charging Method | Charging Level | Charging Speed (Range per Hour) | Equipment | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 charging | Slow | 3–5 miles | Standard household outlet | Overnight charging and emergency top-ups (PHEVs) |
| Level 2 charging | Medium | 10–30 miles | 240-volt AC charging station | Daily charging for most BEVs and PHEVs |
| DC fast charging | Fast | Up to 60–80 miles (in 20 min) | High-power DC fast charger | Long-distance travel and quick top-ups on the road |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wind turbine rated power | Kw | 1 (each) |
| Rotor diameter | m | 1.6 |
| Cut-in speed | m/s | 3 |
| Maximum safe speed | m/s | 25 |
| Voltage | V | 24/48 |
| Outer diameter of tower | Mm | 60 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| PV power | kW | 1.2 |
| Conversion efficiency | % | 15 |
| Each panel O/P voltage | V | 30 |
| Maximum current O/P | A | 10 |
| Cases | SOC% Increase in 1 s | Time for 100% SOC |
|---|---|---|
| Max wind, no PV, no battery | 0.4% | 250 s |
| No wind, max PV, no battery | 0.35% | 285 s |
| Max wind, max PV, no battery | 0.5% | 200 s |
| Max wind, max PV, Li-battery (48 V) | 7% | 15 s |
| Parameters | Onshore (Laoshan) | Offshore (Huangdao) |
|---|---|---|
| AEP | ||
| Average wind speed | 8.0561 m/s | 11.3852 m/s |
| Average solar irradiance | 4.4727 kWh/m2 | 4.3261 kWh/m2 |
| AEP (solar) | ||
| E-bike charged on average | ||
| COE | $0.62/kWh | $0.46/kWh |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afzal, W.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Chen, G.-Z.; Xue, Y. Hybrid Wind/PV E-Bike Charging Station: Comparison of Onshore and Offshore Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014963
Afzal W, Zhao L-Y, Chen G-Z, Xue Y. Hybrid Wind/PV E-Bike Charging Station: Comparison of Onshore and Offshore Systems. Sustainability. 2023; 15(20):14963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014963
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfzal, Wardah, Li-Ye Zhao, Guang-Zhi Chen, and Yu Xue. 2023. "Hybrid Wind/PV E-Bike Charging Station: Comparison of Onshore and Offshore Systems" Sustainability 15, no. 20: 14963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014963
APA StyleAfzal, W., Zhao, L.-Y., Chen, G.-Z., & Xue, Y. (2023). Hybrid Wind/PV E-Bike Charging Station: Comparison of Onshore and Offshore Systems. Sustainability, 15(20), 14963. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014963








