Can Grassroots Governments’ Environmental Attention Effectively Improve Air Pollution? Empirical Evidence from Satellite Remote Sensing Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
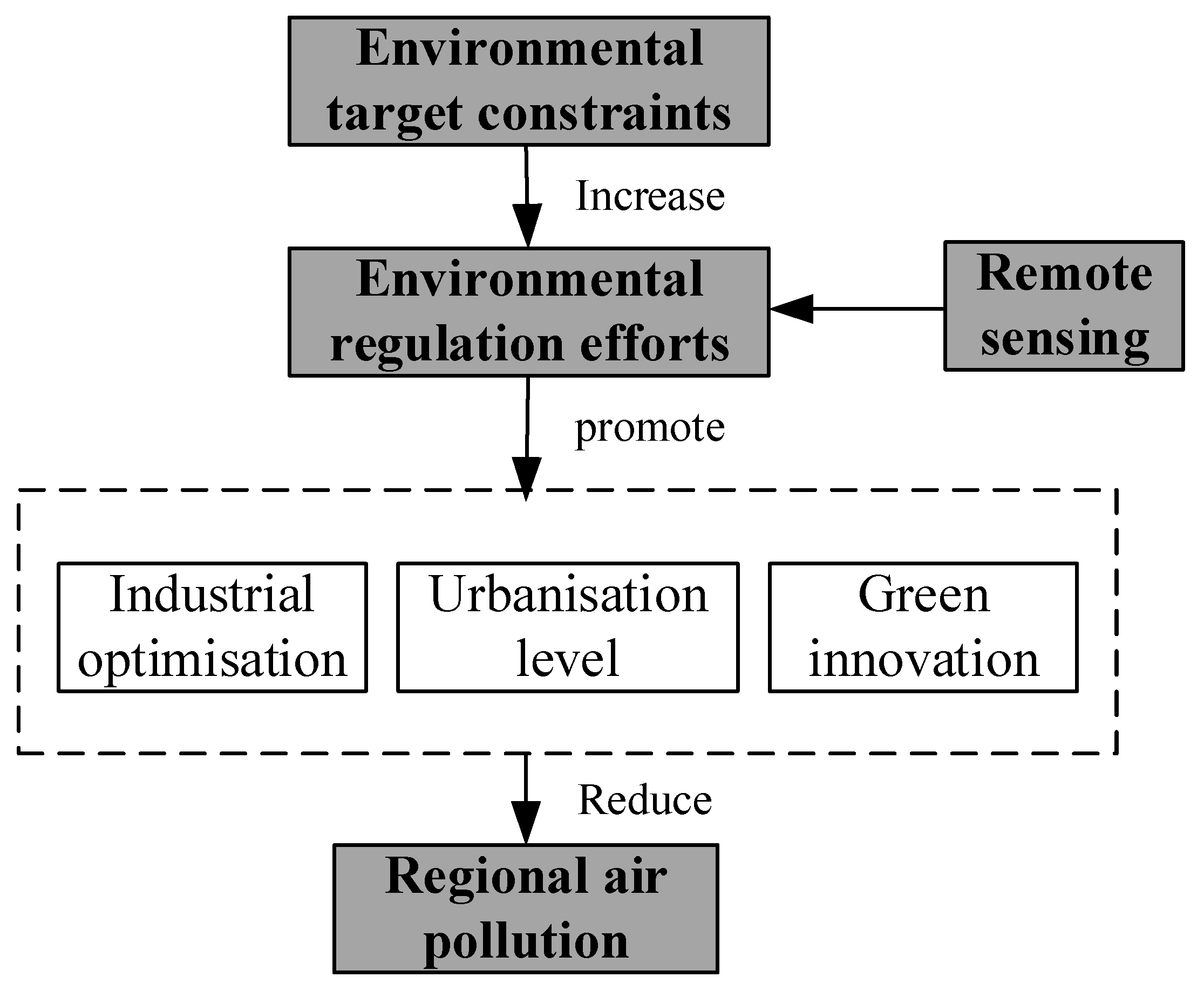
2.1. Environmental Target Constraints and the Impact of Remote Sensing Technologies
2.2. Transmission Mechanisms
3. Research Design and Data Sources
3.1. Policy Background
3.2. Sample and Data
3.3. Model Setting
3.4. Variable Measurement
3.4.1. Explained Variables ()
3.4.2. Core explanatory Variables ()
3.4.3. Mediating Variables
3.4.4. Other Control Variables
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Baseline Regression
4.2. Endogeneity Test
4.2.1. Instrumental Variable Approach
4.2.2. Propensity Score Matching
4.3. Robustness Tests
4.3.1. Replacement of Explanatory Variables
4.3.2. Excluding Samples
4.3.3. Exclusion of Other Policies
4.3.4. Placebo Test
5. Mediating Mechanism
6. Heterogeneity Analysis
6.1. Government Governance Orientation
6.2. Urban Location Characteristics
7. Further Discussion
8. Conclusions and Implications
8.1. Conclusions
8.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, W.; Lin, K.; Du, L.; Du, J. Can regional joint prevention and control of atmospheric reduce border pollution? Evidence from China’s 12th Five-Year Plan on air pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Viard, V.B.; Zhang, P. Air Pollution and Manufacturing Firm Productivity: Nationwide Estimates for China. Econ. J. 2021, 131, 3241–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B. Watering Down Environmental Regulation in China. Q. J. Econ. 2020, 135, 2135–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svechkina, A.; Portnov, B.A. Spatial Identification of Environmental Health Hazards Potentially Associated with Adverse Birth Outcomes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3578–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, J. Air Pollution Control and Enterprise Competitiveness—A Re-examination Based on China’s Clean Air Action. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Lin, W.; Du, J.; Jin, M.; Fan, M. Can Vertical Environmental Regulation Induce Enterprise Green Innovation? A New Perspective from Automatic Air Quality Monitoring Station in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuillé, M.L.; Gary-Bobo, R.J. Sharing Budgetary Austerity under Free Mobility and Asymmetric Information: An Optimal Regulation Approach to Fiscal Federalism. J. Public Econ. 2007, 91, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, L.A. Political Turnover and Economic Performance: The Incentive Role of Personnel Control in China. J. Public Econ. 2005, 89, 1743–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, X. Do Environmental Target Constraints of Local Government Affect High-quality Economic Development? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 56620–56640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenstone, M.; He, G.; Jia, R.; Liu, T. Can Technology Solve the Principal-Agent Problem? Evidence from China’s War on Air Pollution. Am. Econ. Rev. Insights 2022, 4, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhai, X. Green City Air Measurement and Health Exercise Big Data Monitoring Based on Remote Sensing Images and Sensors. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zivin, J.S.G.; Kou, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Going Green in China: Firms’ Responses to Stricter Environmental Regulations; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Lin, W.; Liu, B. Does the New Energy Demonstration Cities Construction Reduce CO2 Emission? Evidence from A Quasi-natural Experiment in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50408–50426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, P.G.; Millimet, D.L. Strategic Interaction and the Determination of Environmental Policy Across US States. J. Urban Econ. 2002, 51, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Lei, K.; Meng, W.; Khu, S.T. Industrial Structural Upgrading and Spatial Optimization Based on Water Environment Carrying Capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, T.; Meng, X. From Rrace-to-the-bottom to Strategic Imitation: How Does Political Competition Impact the Environmental Enforcement of Local Governments in China? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25675–25688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.S.; Walker, R. Why is Pollution from US Manufacturing Declining? The Roles of Environmental Regulation, Productivity, and Trade. Am. Econ. Rev. 2018, 108, 3814–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; Misato, S. The Impacts of Environmental Regulations on Competitiveness. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2017, 11, 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Tobias, S.; Woerter, M.; Arvanitis, S.; Peneder, M.; Rammer, C. How Different Policy Instruments Affect Green Product Innovation: A Differentiated Perspective. Energy Policy 2018, 114, 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kahn, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. The Consequences of Spatially Differentiated Water Pollution Regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Nie, H. Decentralization, Collusion, and Coal Mine Deaths. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2017, 99, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z. An Overview of Satellite Remote Sensing Technology Used in China’s Environmental Protection. Earth Sci. Inform. 2017, 10, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, S.; Wu, T. Does New-type Urbanization Curb Haze Pollution? A Case Study from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 20089–20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, W.W. Coal Smoke and the Costs of the Industrial Revolution; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Yuan, R. Regional Green Development Level and Its Spatial Relationship Under the Constraints of Haze in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Lin, L. Environmental Regulation and Responses of Local Governments. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 60, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Industrial Structure, Technical Progress and Carbon Intensity in China’s Provinces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Xiao, J.; Su, P.; Li, S. Industrial Structure Transformation and Provincial Heterogeneity Characteristics Evolution of Air Pollution: Evidence of a Threshold Effect from China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Collins, A.R.; Etienne, X.L.; Ding, D. The Environmental Effects of International Trade in China: Measuring the Mediating Effects of Technology Spillovers of Import Trade on Industrial Air Pollution. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, H. Economic Growth, Industrial Structure and Nitrogen Oxide Emissions Reduction and Prediction in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Genç, S.Y.; Kamran, H.W.; Dinca, G. Role of Green Technology Innovation and Renewable Energy in Carbon Neutrality: A Sustainable Investigation from Turkey. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X. Can Green-Technology Innovation Reduce Atmospheric Environmental Pollution? Toxics 2023, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Gou, X.; Feng, J.; Gao, X. CEO Educational Attainment, Green Innovation, and Enterprise Performance: Evidence from China’s Heavy-polluting Enterprises. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1042400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Failler, P.; Liu, Z. Impact of Environmental Regulations on Energy Efficiency: A Case Study of China’s Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Analysis of the Influencing Factors of Industrial Air Pollution in Shenzhen. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publ. 2020, 450, 012094. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Carbon Pricing Induces Innovation: Evidence from China’s Regional Carbon Market Pilots. AEA Pap. Proc. 2018, 108, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, F.; Di, D. Regional Competition, Environmental Decentralization, and Target Selection of Local Governments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X. Brain Drain: The Impact of Air Pollution on Firm Performance. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2021, 110, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, L. Does Environmental Regulation Drive Away Inbound Foreign Direct Investment? Evidence from A Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 123, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, A.; Kapur, S. Community Pressure for Green Behavior. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2012, 64, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Li, P.; Lu, Y. Career concerns and multitasking local bureaucrats: Evidence of a target-based performance evaluation system in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2018, 133, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, V.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Navigating and evaluating the labyrinth of environmental regulation in China. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2021, 15, 300–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Ren, H.; Song, D.; Xu, N. Environmentally-Inclined Politicians and Local Environmental Performance: Evidence from Publicly Listed Firms in China; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]



| Variable | N | Min | Max | Mean | sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | 33,807 | 0.045 | 4.245 | 2.812 | 0.984 |
| Constrain | 33,807 | 0 | 1 | 0.037 | 0.189 |
| lnlight | 33,807 | −12.320 | 4.346 | −1.687 | 2.455 |
| lnpop | 33,807 | −2.185 | 10.780 | 5.563 | 1.737 |
| lnpressure | 33,807 | 6.371 | 6.925 | 6.849 | 0.101 |
| lnrain | 33,807 | 3.132 | 8.044 | 6.751 | 0.516 |
| wind | 33,807 | 0.601 | 6.432 | 2.103 | 0.597 |
| lntemp | 33,807 | −1.567 | 3.243 | 2.548 | 0.419 |
| lnhumid | 33,807 | 3.317 | 4.506 | 4.196 | 0.170 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0065 *** | −0.0065 *** | −0.0066 *** |
| (0.0013) | (0.0013) | (0.0013) | |
| lnpressure | 0.1350 ** | 0.1461 ** | |
| (0.0583) | (0.0556) | ||
| lnrain | 0.0063 ** | 0.0065 ** | |
| (0.0021) | (0.0021) | ||
| wind | 0.0001 | 0.0011 | |
| (0.0013) | (0.0013) | ||
| lntemp | 0.0264 *** | 0.0228 *** | |
| (0.0040) | (0.0038) | ||
| lnhumid | 0.0023 | 0.0010 | |
| (0.0068) | (0.0067) | ||
| lnlight | −0.0025 *** | ||
| (0.0004) | |||
| lnpop | 0.0382 *** | ||
| (0.0077) | |||
| _cons | 2.8123 *** | 1.7681 *** | 1.4867 *** |
| (0.0000) | (0.3988) | (0.3820) | |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 33,807 | 33,807 | 33,807 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Constrain | lnso2 | |
| IV | 0.1641 *** | |
| (0.0143) | ||
| Constrain | −0.0332 ** | |
| (0.0105) | ||
| Control variables | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES |
| N | 33,807 | |
| R-sq | 0.119 | |
| The 1st stage F | 131.98 | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM | 124.144 *** | |
| (0.000) | ||
| Cragg–Donald Wald F | 512.417 | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F | 131.982 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0096 *** | −0.0066 *** | −0.0066 *** |
| (0.0027) | (0.0013) | (0.0013) | |
| _cons | 0.9055 | 1.4858 *** | 1.4867 *** |
| (1.7198) | (0.3819) | (0.3820) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2831 | 33,804 | 33,807 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| lnpm25 | lnpm25 | |
| Constrain | −0.0164 *** | −0.0150 *** |
| (0.0025) | (0.0024) | |
| _cons | 3.6805 *** | 6.2569 *** |
| (0.0001) | (1.6549) | |
| Control variables | NO | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES |
| N | 33,807 | 33,807 |
| R-sq | 0.982 | 0.984 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0063 *** | −0.0042 ** | −0.0063 *** | −0.0112 *** |
| (0.0015) | (0.0017) | (0.0015) | (0.0020) | |
| _cons | 1.7518 *** | 1.6137 *** | 1.5350 *** | 2.2009 *** |
| (0.3963) | (0.3942) | (0.3985) | (0.5010) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 28,108 | 30,951 | 28,396 | 21,196 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0077 *** | −0.0057 *** | −0.0075 *** | −0.0061 *** |
| (0.0015) | (0.0015) | (0.0015) | (0.0015) | |
| _cons | 1.5377 *** | 1.5112 *** | 1.3816 *** | 1.2654 ** |
| (0.3874) | (0.3783) | (0.3932) | (0.4016) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 29,722 | 31,616 | 30,979 | 28,332 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| City | Industry | Innovation | |
| Constrain | 0.0399 *** | −0.0520 ** | 0.0712 *** |
| (0.0119) | (0.0177) | (0.0112) | |
| _cons | −8.7281 * | −4.6390 | −7.5295 |
| (4.6472) | (5.6747) | (4.9343) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 26,713 | 20,355 | 32,012 |
| R-sq | 0.962 | 0.777 | 0.945 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental priority Cities | Non-environmental priority cities | Economic Constraints | Non-Economic Constraints | |
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0081 *** | −0.0024 | −0.0040 ** | −0.0121 *** |
| (0.0018) | (0.0018) | (0.0020) | (0.0023) | |
| _cons | 2.5474 ** | 1.2277 ** | 1.7271 ** | 1.5992 *** |
| (0.7814) | (0.4054) | (0.7004) | (0.4511) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 13,187 | 20,620 | 21,419 | 12,388 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large-scale | Small and medium-scale | Eastern Region | Central and Western Region | |
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain | −0.0087 *** | −0.0019 | −0.0035 * | −0.0085 *** |
| (0.0016) | (0.0023) | (0.0021) | (0.0016) | |
| _cons | 1.8348 ** | 1.4488 *** | 0.7562 | 1.6227 *** |
| (0.7911) | (0.4079) | (1.3197) | (0.4036) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 16,358 | 17,449 | 11,664 | 22,143 |
| R-sq | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | lnso2 | |
| Constrain×GreenO | −0.0218 *** | −0.0248 *** | ||
| (0.0035) | (0.0037) | |||
| Constrain×Envi | −0.0103 * | −0.0096 * | ||
| (0.0054) | (0.0055) | |||
| Constrain | −0.0059 *** | −0.0059 *** | 0.0020 | 0.0014 |
| (0.0014) | (0.0014) | (0.0044) | (0.0045) | |
| GreenO | 0.0113 *** | 0.0104 *** | ||
| (0.0032) | (0.0031) | |||
| Envi | 0.0003 | 0.0011 | ||
| (0.0019) | (0.0019) | |||
| _cons | 2.8590 *** | 1.4623 ** | 2.9014 *** | 0.7093 |
| (0.0001) | (0.5388) | (0.0015) | (0.5642) | |
| Control variables | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 29,587 | 29,587 | 28,398 | 28,398 |
| R-sq | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, K.; Shi, Y.; Xu, H. Can Grassroots Governments’ Environmental Attention Effectively Improve Air Pollution? Empirical Evidence from Satellite Remote Sensing Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15309. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115309
Lin K, Shi Y, Xu H. Can Grassroots Governments’ Environmental Attention Effectively Improve Air Pollution? Empirical Evidence from Satellite Remote Sensing Technology. Sustainability. 2023; 15(21):15309. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115309
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Kai, Yanli Shi, and Hong Xu. 2023. "Can Grassroots Governments’ Environmental Attention Effectively Improve Air Pollution? Empirical Evidence from Satellite Remote Sensing Technology" Sustainability 15, no. 21: 15309. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115309
APA StyleLin, K., Shi, Y., & Xu, H. (2023). Can Grassroots Governments’ Environmental Attention Effectively Improve Air Pollution? Empirical Evidence from Satellite Remote Sensing Technology. Sustainability, 15(21), 15309. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115309





