Optimization of Accurate Spacing for Gas Extraction from Damaged Coal Seams Based on a Dual-Penetration Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Test Analysis
2.1. Coal Sample Preparation and Analysis
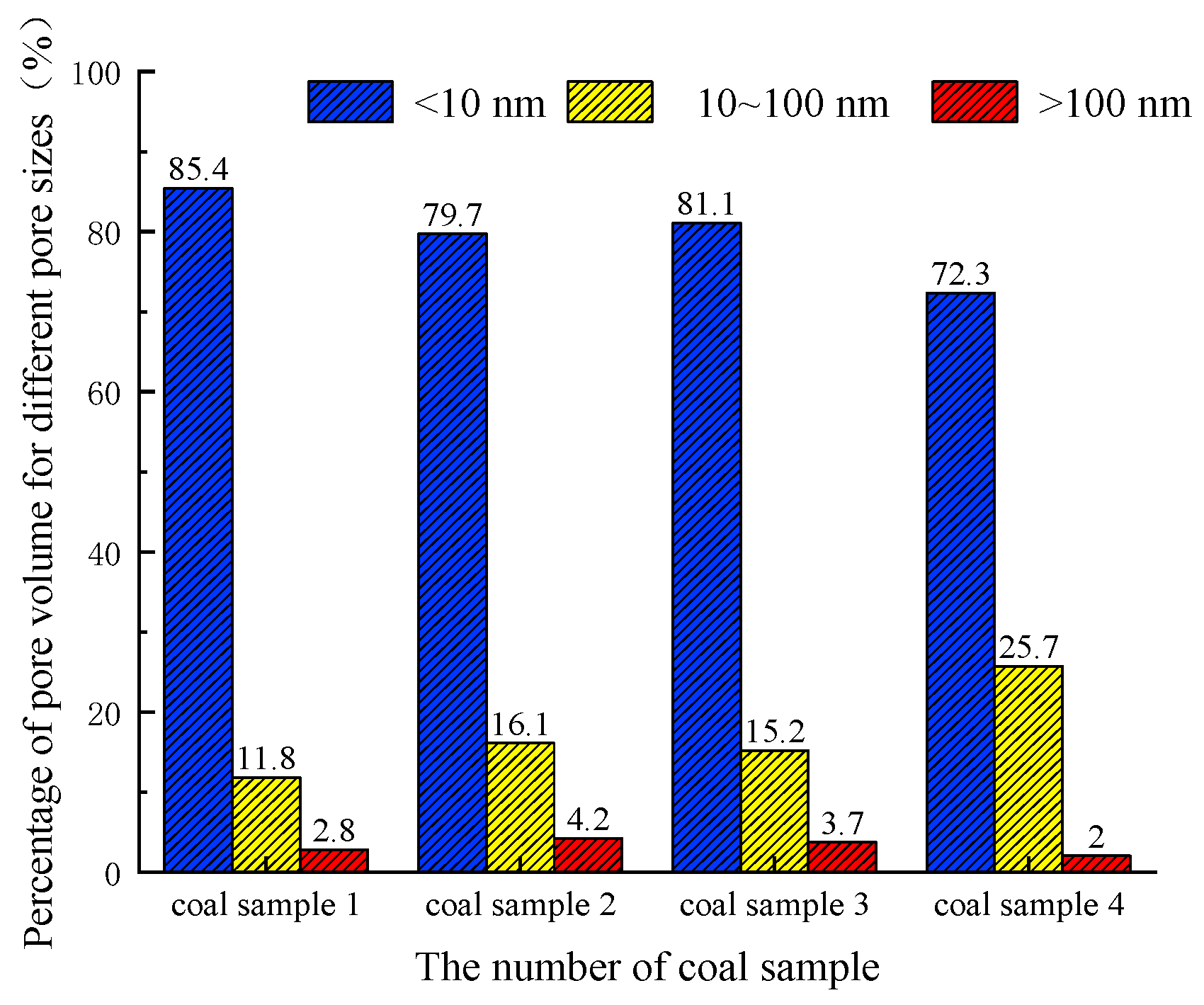
2.2. Specific Surface Area and Pore Volume Analysis
3. Mathematical Modeling of Coal Seam Gas Transportation and Flow–Solid Coupling
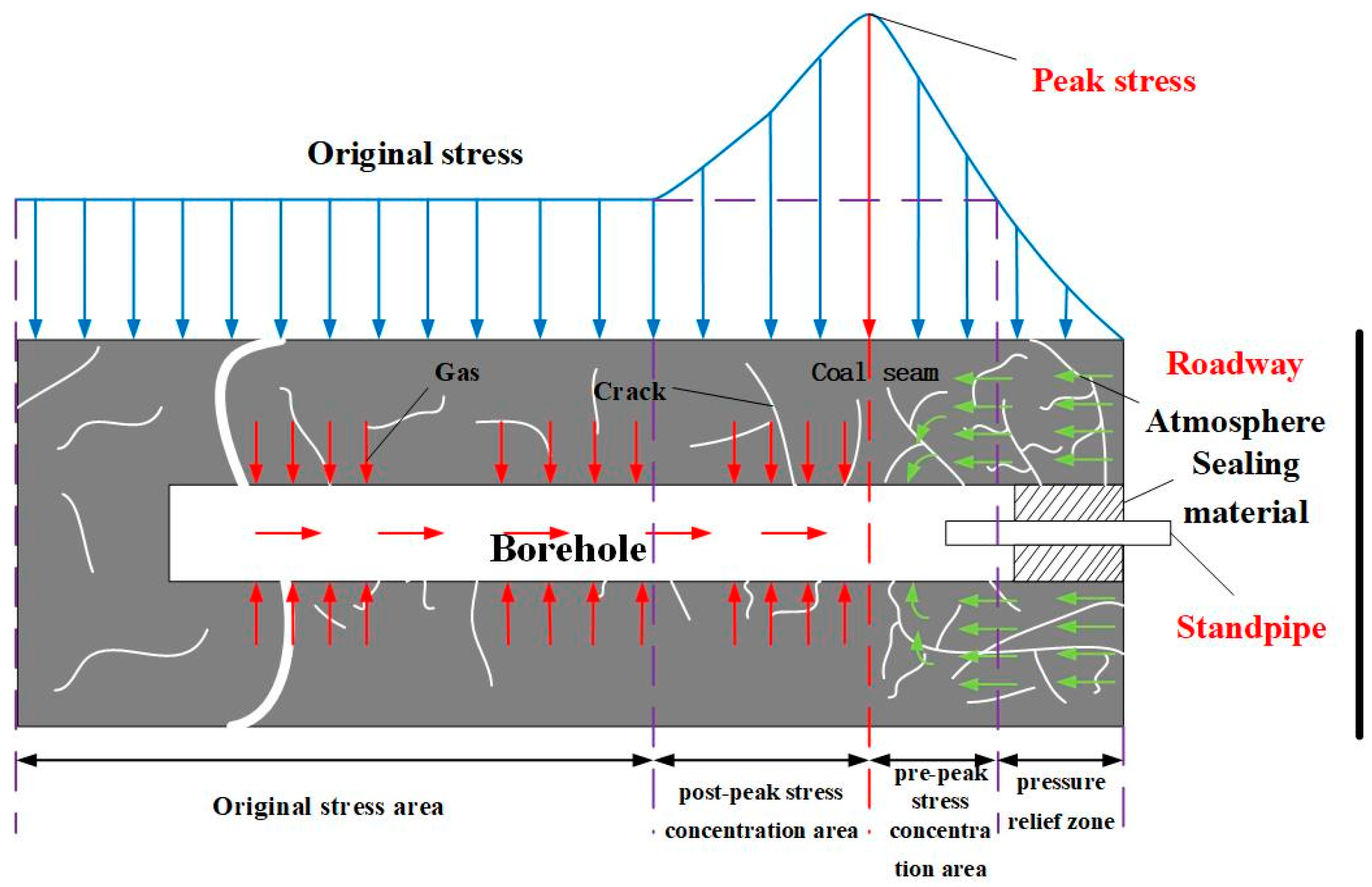
3.1. Ontological Relationships and Destruction Criteria for Coal
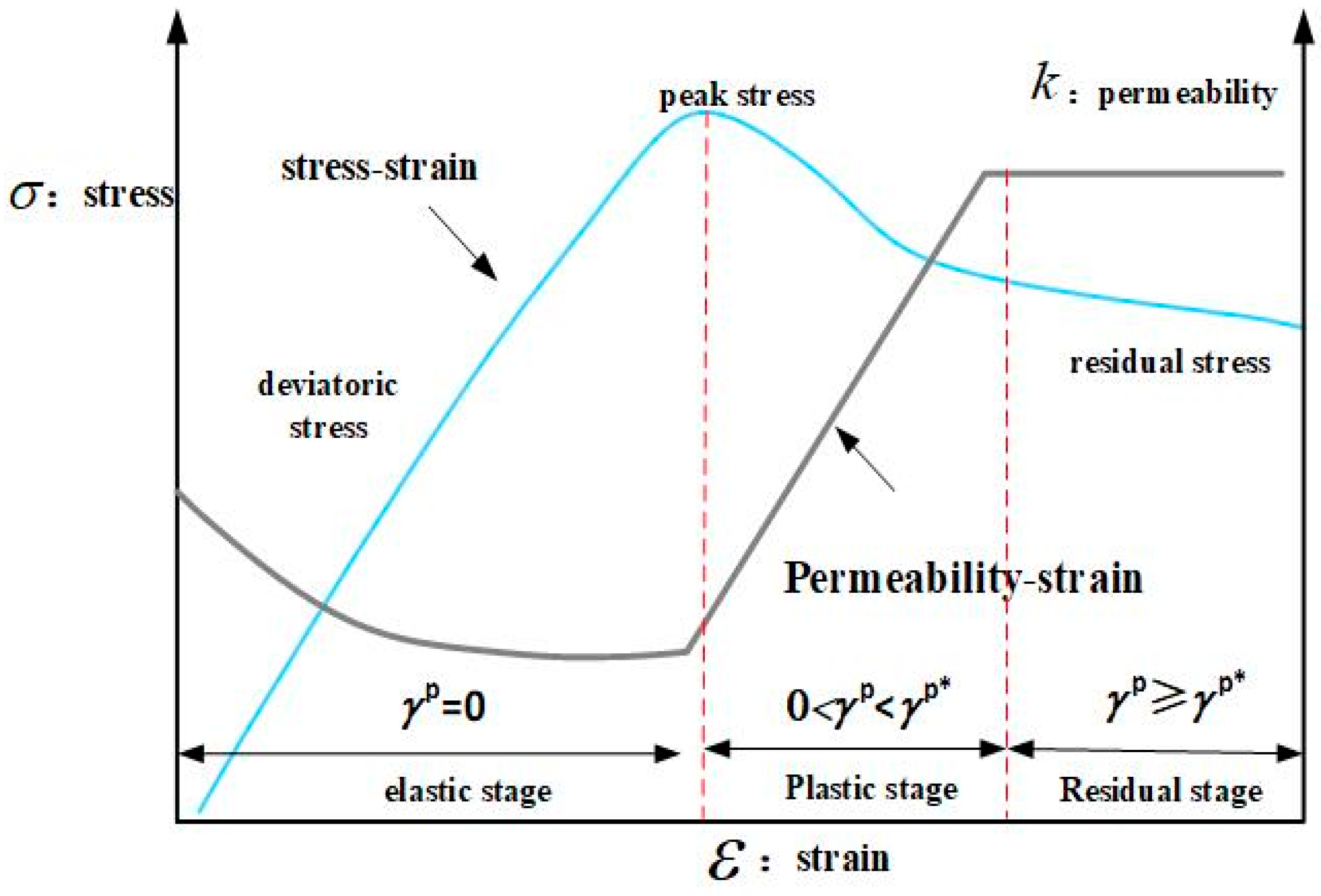
3.2. Evolution Equation of Porosity and Permeability of Damaged Coal Rock Body
3.3. Matrix Gas Diffusion and Seepage Equation
3.4. Fractured Gas Seepage Characteristics
4. Numerical Simulation of Gas Seepage
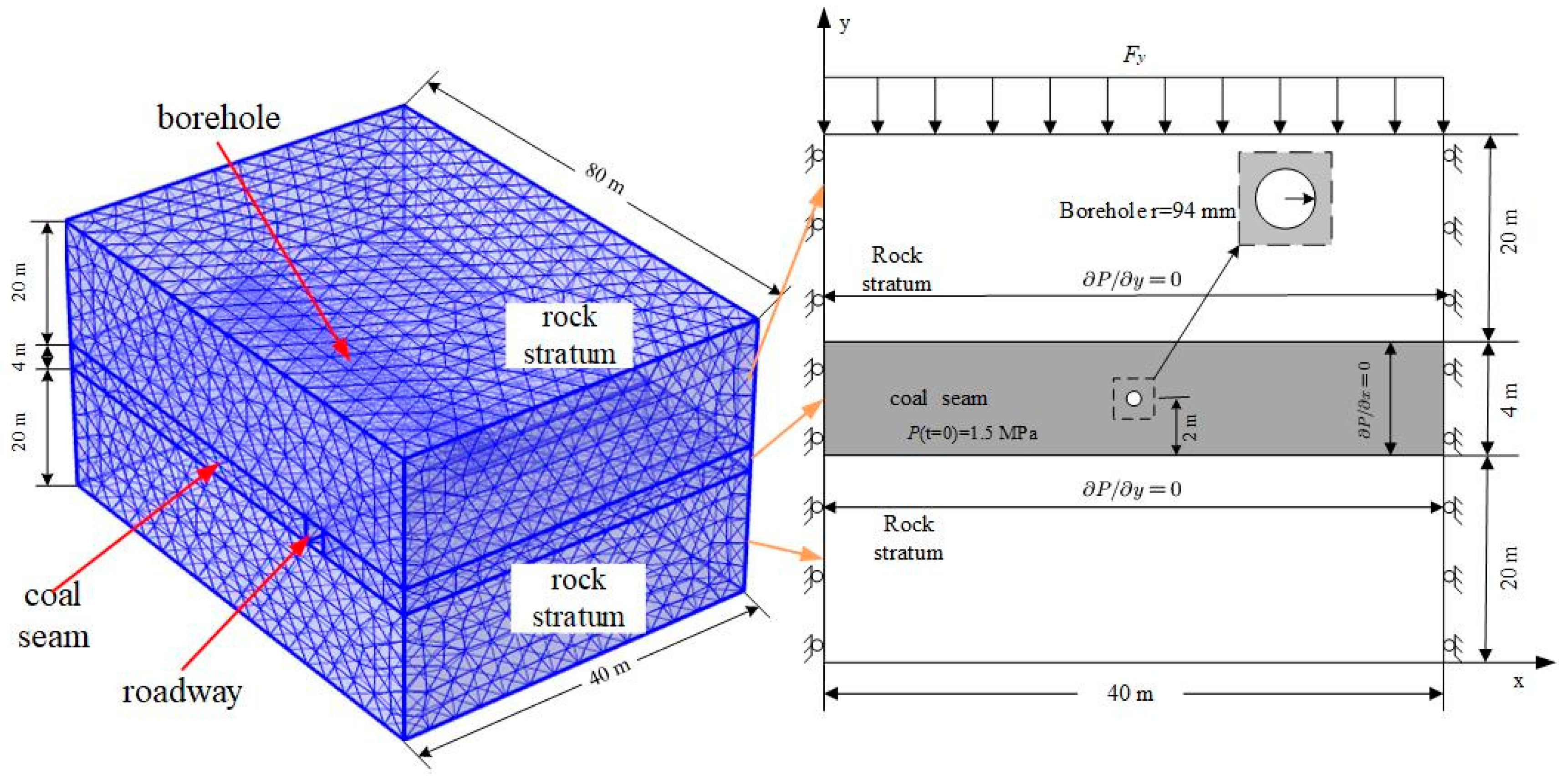
4.1. Numerical Model and Parameters
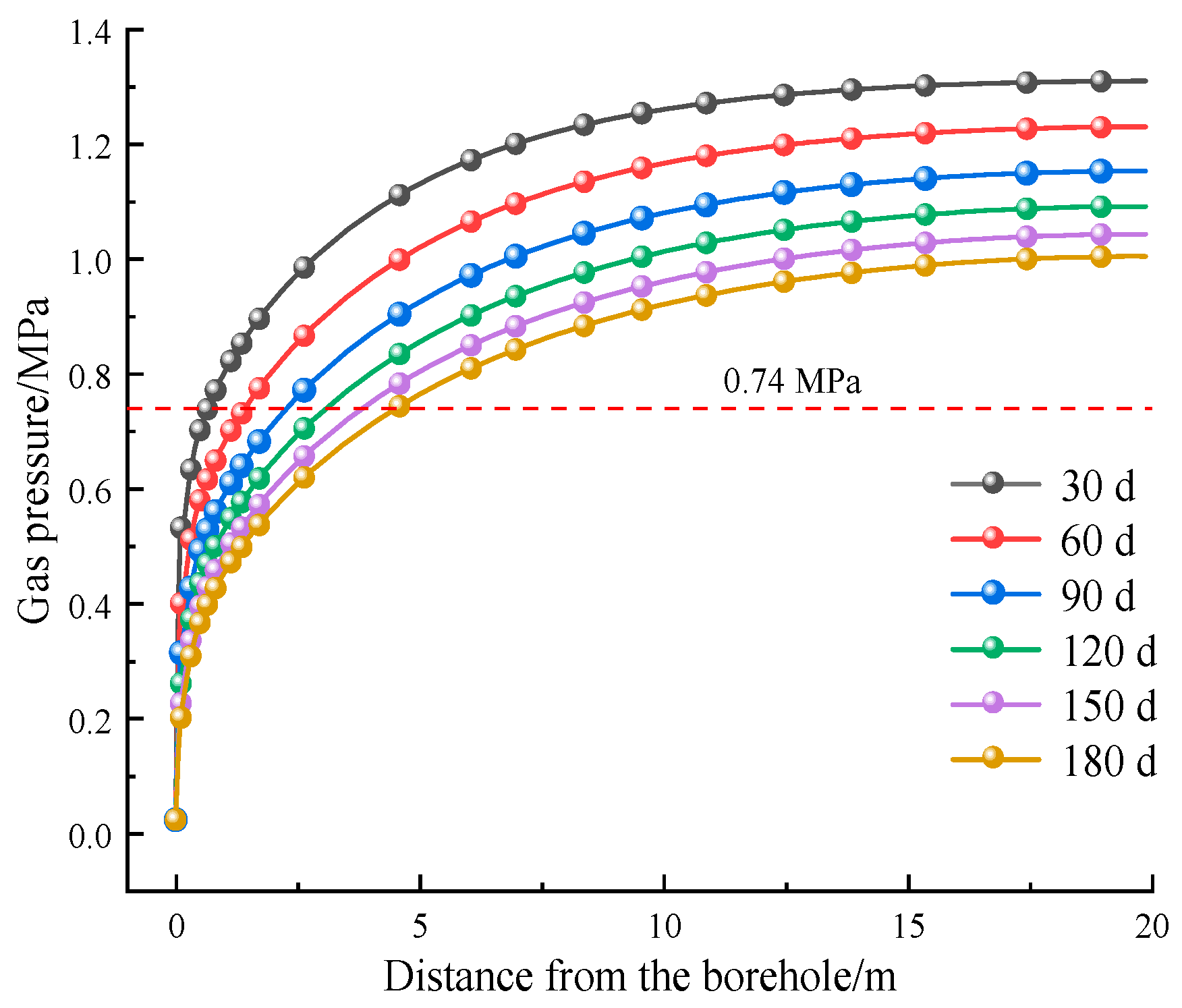
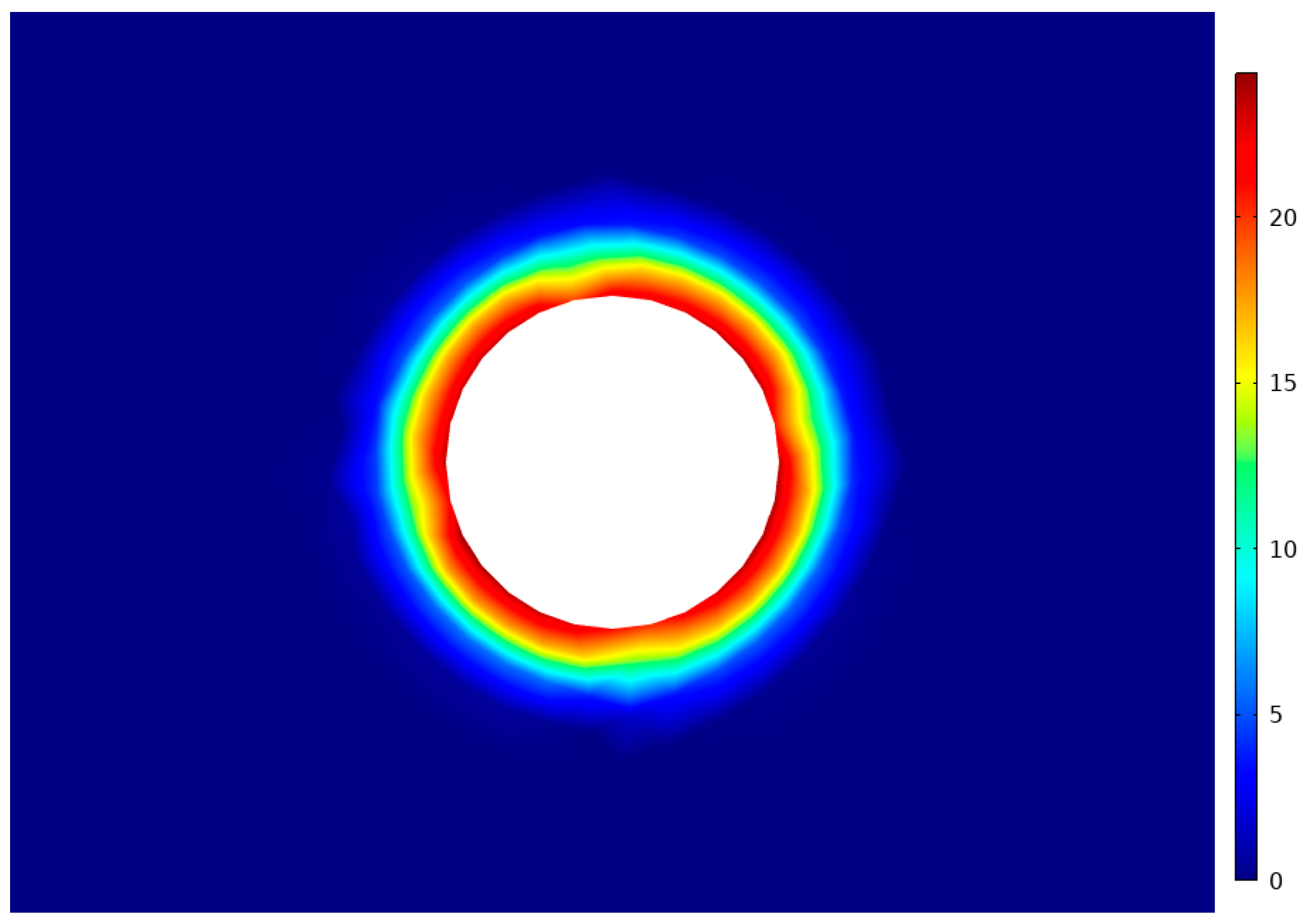
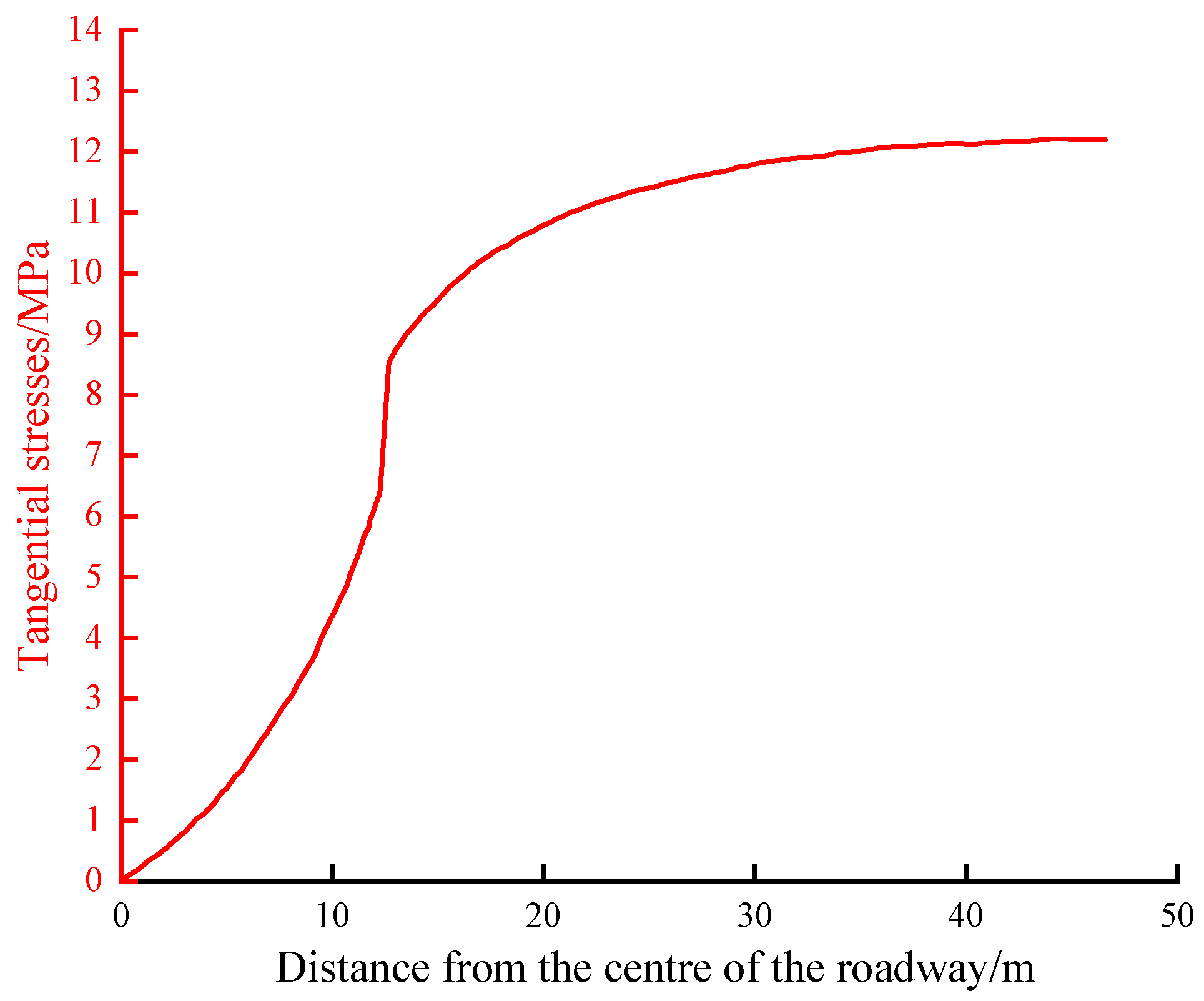
4.2. Effective Radius of Gas Extraction for Extraction Cycle
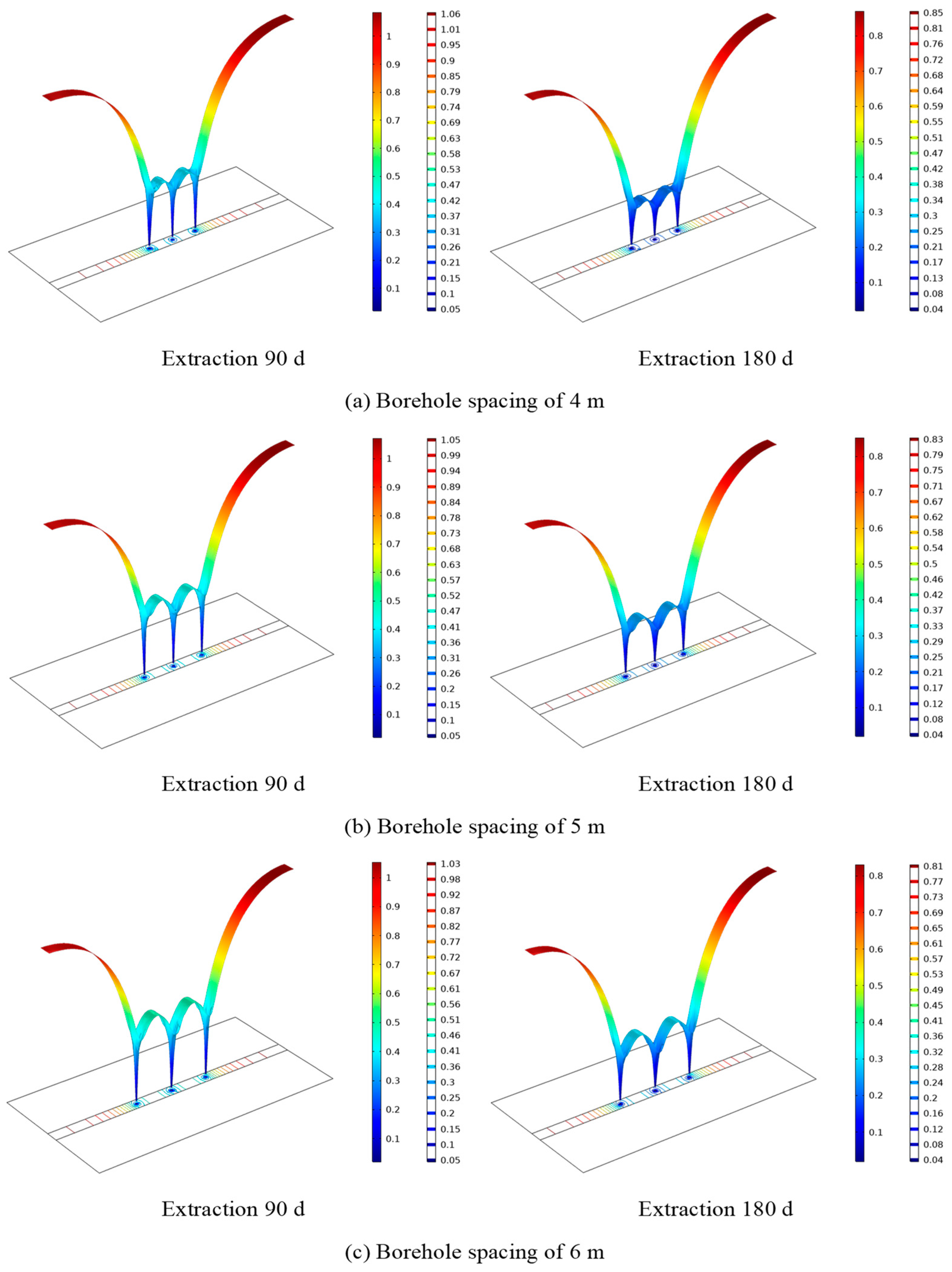
4.3. The Effect of Different Borehole Spacings on Gas Transportation
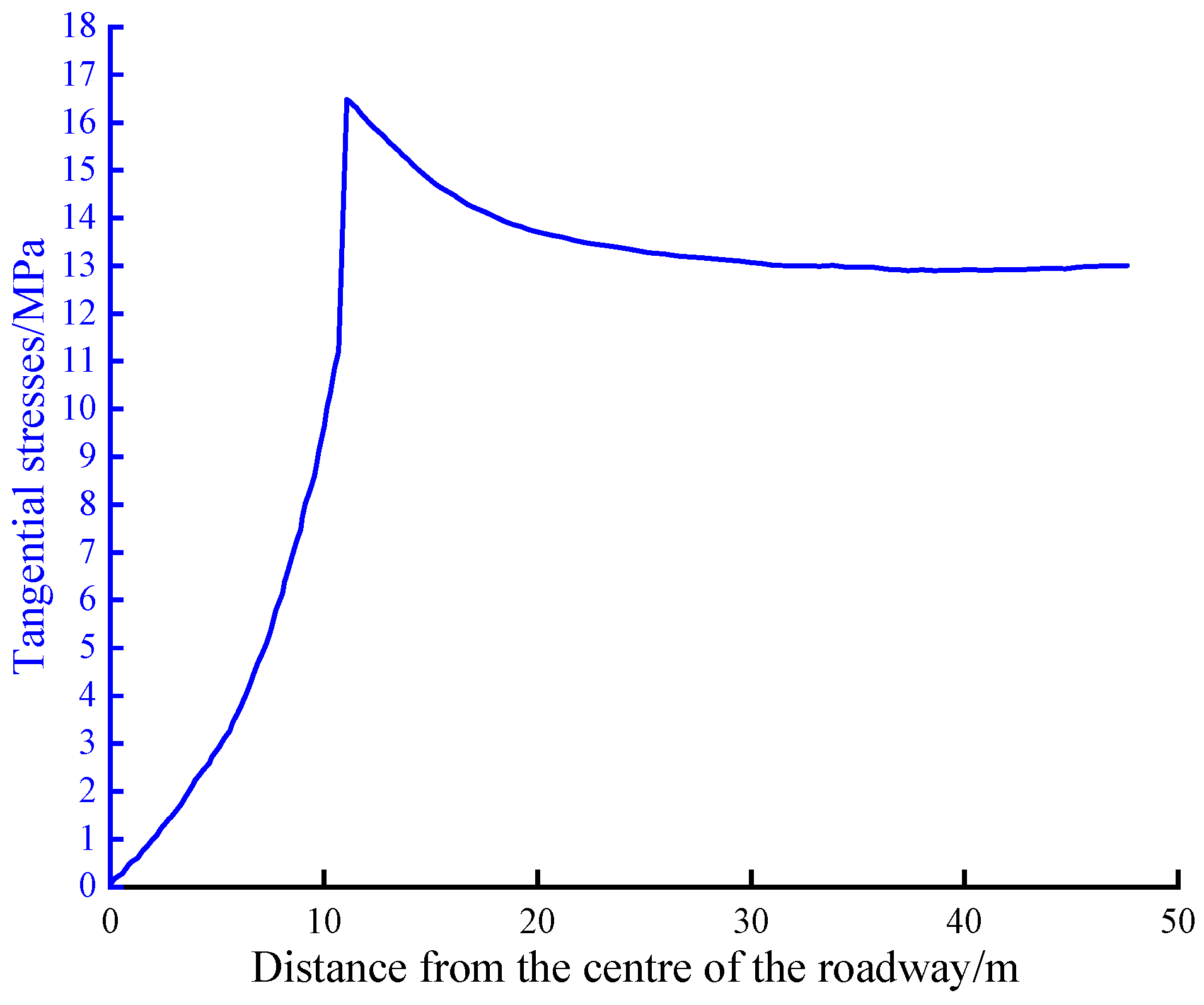
4.4. Coal Permeability Change Pattern
4.5. Effect of Drill Hole Spacing on Gas Extraction
5. Practical Verification of Coalbed Methane Mining
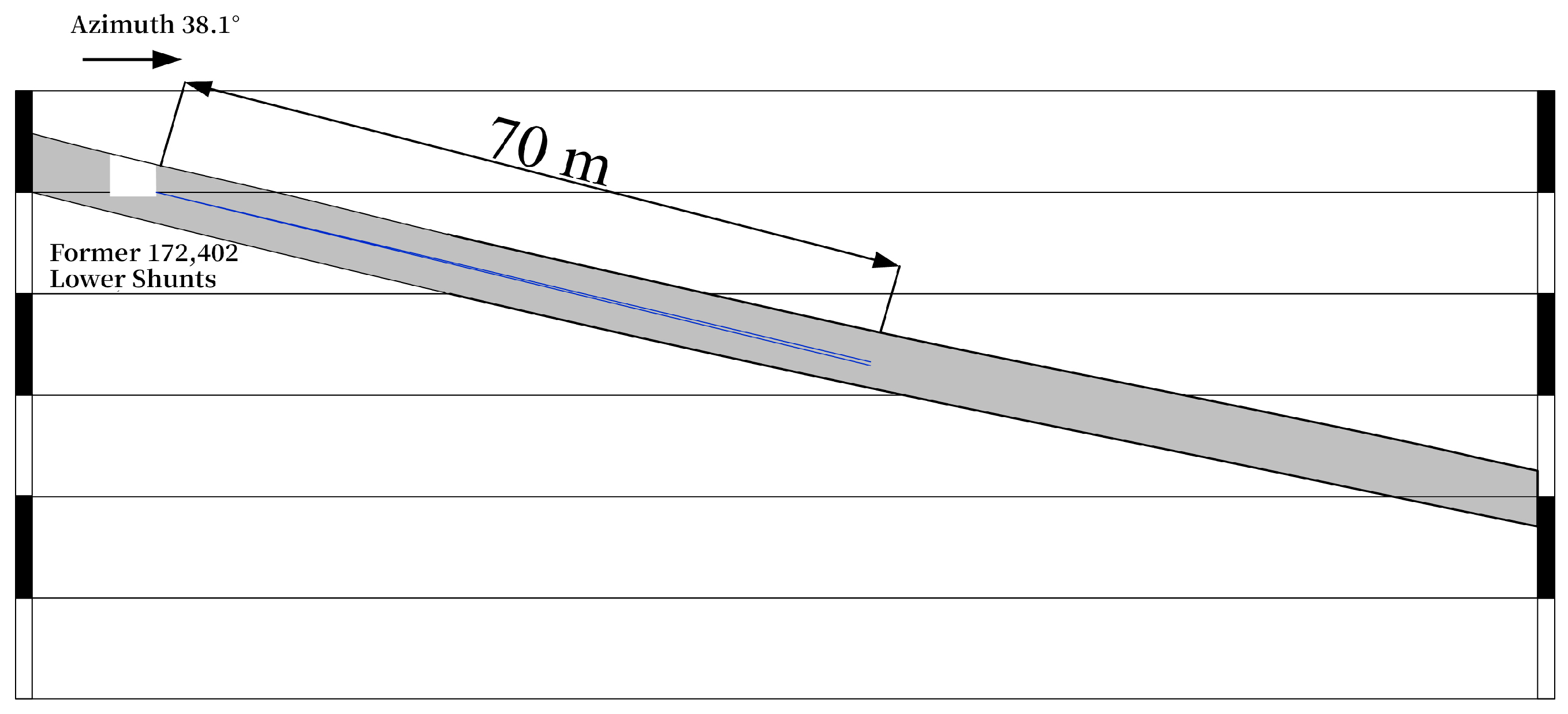
5.1. Overview of the Mining Area
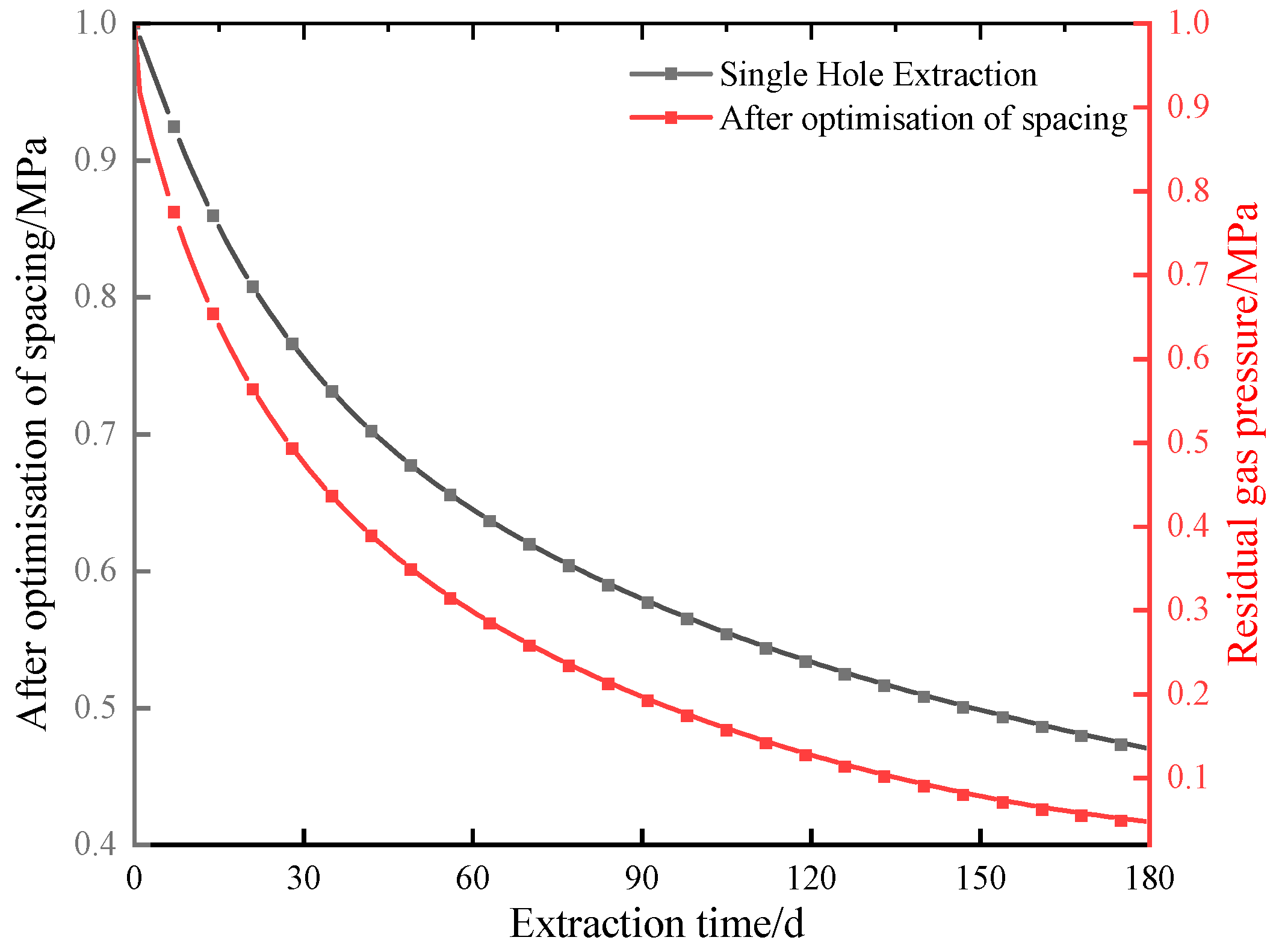
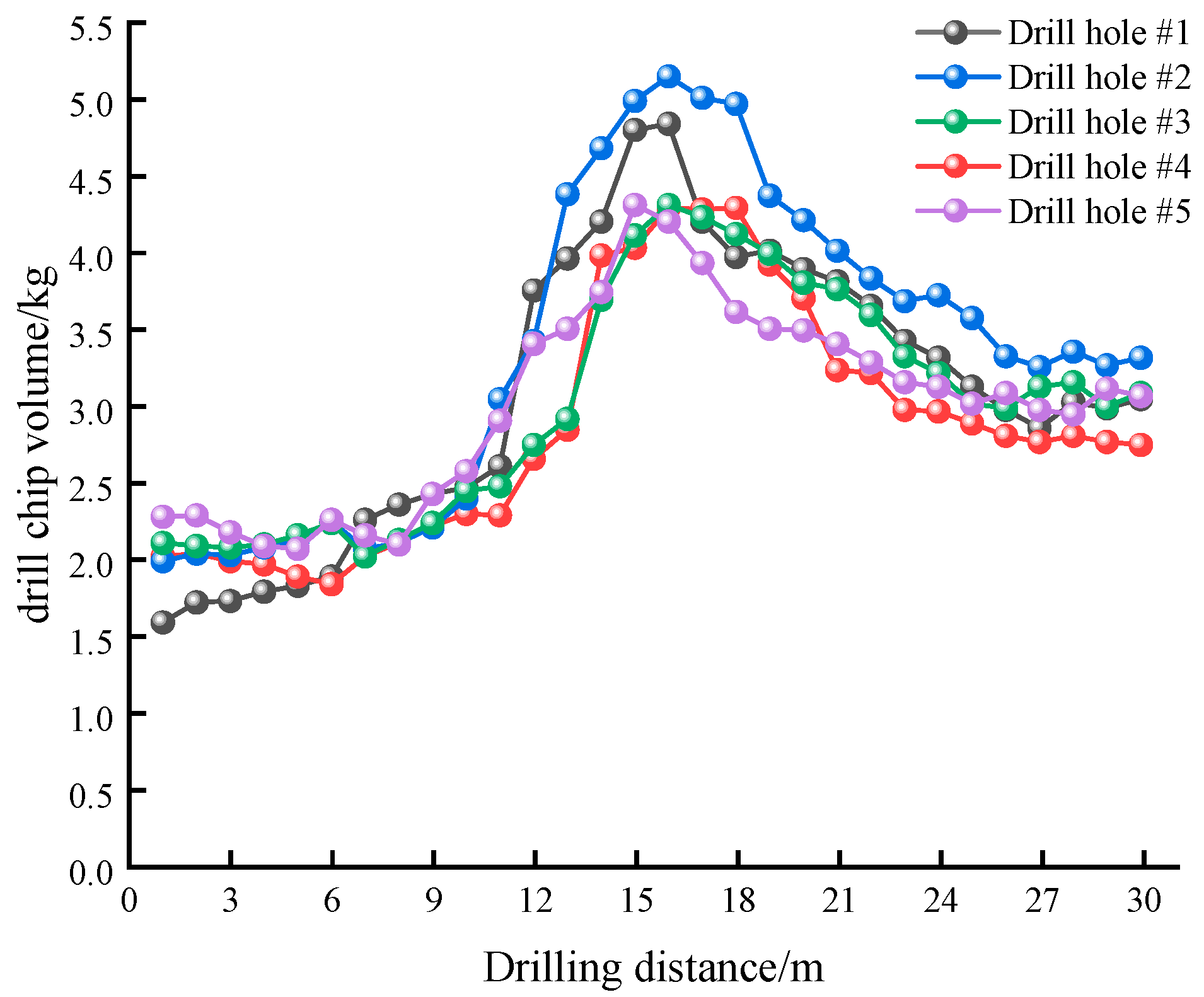
5.2. Validation of the Effectiveness of Gas Extraction
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The distribution of pore volume and pore-specific surface area in each pore size section of Dashucun Mine coal samples follows the law of microporous > small pore > mesopore; the pore distribution is extremely unbalanced, with more development of tiny pores and less development of mesopores and macropores, and the 2–20 nm micropores determine the capacity of gas adsorption.
- (2)
- Considering the coal-rock body as a “double-hole-double-permeability” system, the transport control equations of the gas diffusion and seepage fields were established; a three-stage coal-rock damage permeability evolution model was established based on the changes caused by the roadway excavation and drilling construction; and, finally, the double-hole double-permeability coal-bed damage flow–solid coupling model was solved using COMSOL.
- (3)
- The maximum effective extraction radius of single-hole pumping is 4.8 m. The permeability change in the pre-pumping process is the result of the competition between the matrix contraction effect and the skeleton deformation effect. In order to improve the efficiency of pumping, the permeability should be kept at a suitable and stable level in the process of gas pumping to ensure that the permeability change is within the range of stable borehole spacing for the 4 m < d < 8 m.
- (4)
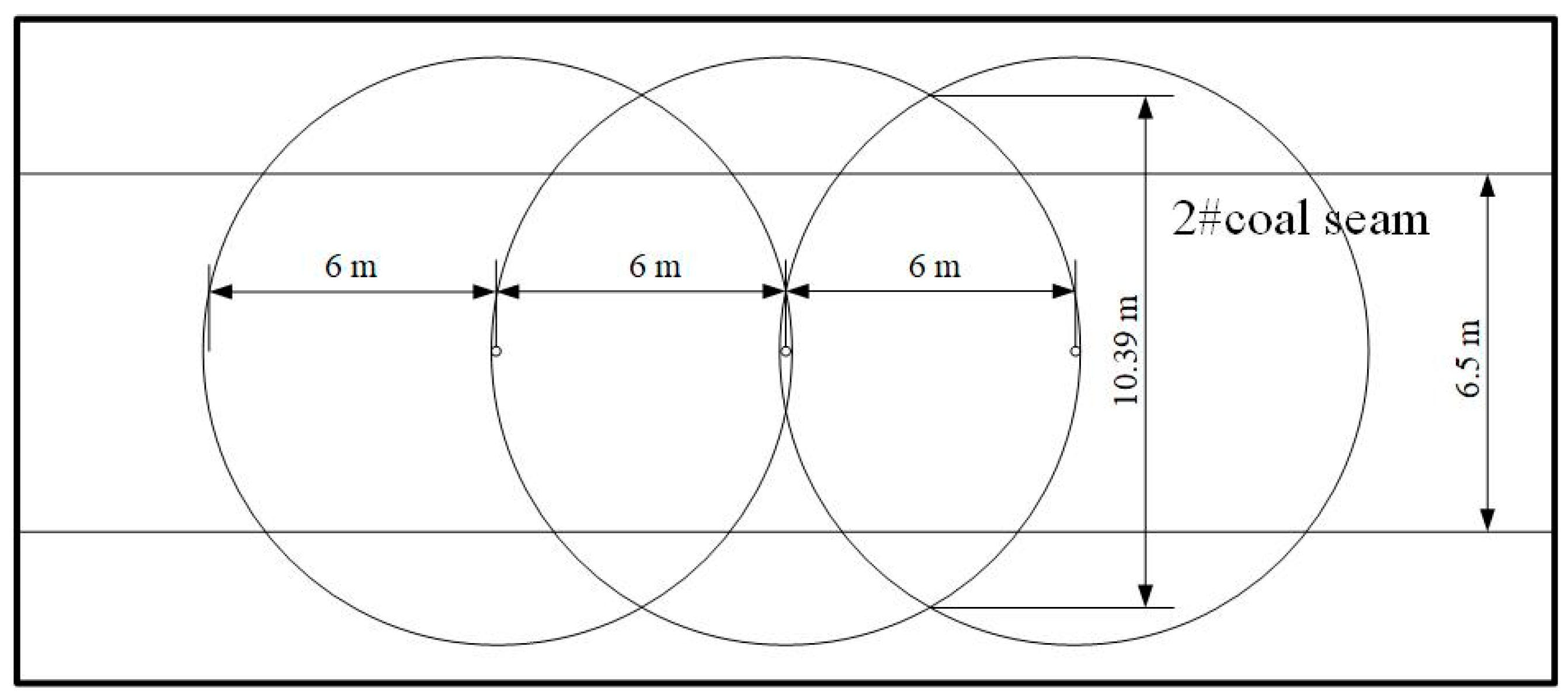
- In multi-hole extraction, the pressure value in the center of adjacent holes increases with the increase in spacing and the superposition effect of holes becomes stronger with the decrease in hole spacing. To avoid the superposition effect and the blind zone of extraction, the hole spacing range is 5 m < d < 7 m, the optimal hole spacing of Dashucun Mine is 6 m, the reasonable depth of the sealing hole is 16 m, and the effect of on-site engineering verification is good.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Zhou, R.; Song, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, K.; Xi, D. Deformation and damage dynamic characteristics of coal–rock materials in deep coal mines. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2019, 28, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinina, O.; Nechitailo, A.; Stroykov, G.; Tsvetkova, A.; Reshneva, E.; Turovskaya, L. Technical and Economic Assessment of Energy Efficiency of Electrification of Hydrocarbon Production Facilities in Underdeveloped Areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, D.; Wang, L. An experimental study of the damage characteristicsof gas-containing coal under the conditions of different loading and unloadingrates. J. Loss Prevent Proc. 2018, 55, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Song, W.; Jia, C. Analysis of the mechanism for coal and gas outburst and measures for optimizing the risk relief. J. Saf. Environ. 2020, 20, 530–538. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ren, T.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. Prediction of coalbed methane (CBM) production considering bidisperse diffusion: Model development, experimental test, and numerical simulation. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 5785–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Pan, J.-T. Study on gas seepage from coal seams in the distance between boreholes for gas extraction. J. Loss Prevent. Proc. Ind. 2018, 54, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Fully coupled model and engineering application for deformation and pressure-relief gas flow of remote coal and rock mass due to mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2010, 36, 1243–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Numerical Simulation Method and Theory for Coalbed Methane Desorption-Diffusion-Seepage Problem. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Pan, Z.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Zhou, F.; Connell, L.D.; Yang, Y. Experimental study of impact of anisotropy and heterogeneity on gas flow in coal. Part I: Diffusion and adsorption. Fuel 2018, 232, 444–453. [Google Scholar]
- Karbownik, M.; Krawczyk, J.; Godyń, K.; Schlieter, T.; Ščučka, J. Analysis of the Influence of Coal Petrography on the Proper Application of the Unipore and Bidisperse Models of Methane Diffusion. Energies 2021, 14, 8495. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.; Lu, Y.; Shi, S.; Wu, K.; Yin, H.; Huang, L.; Peng, S. Optimization on plastic zone scope of borehole based on gas extraction effect and its application. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 17, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ren, P.; Han, H.; Zuo, W. Optimization and experimental study on sealing parameters of crossing borehole based on creep effect. China Saf. Sci. J. 2021, 31, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Fluid–solid coupling model and simulation of gas-bearing coal for energy security and sustainability. Processes 2020, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Jiang, C.; Gan, Q.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Study on permeability anisotropy of bedded coal under true triaxial stress and its application. Transport Porous Med. 2020, 131, 1007–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Shen, K.; Ba, Q. The Influence of the Injected Water on the Underground Coalbed Methane Extraction. Energies 2020, 13, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, X.; Chu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. Study on mechanism of permeability improvement for gas drainage by cross-steam cavitation borehole. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B.; Qin, X.; Kon, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Structural characteristics of adsorption pores in low-rank coals and their effects on methane adsorption performance. Coal Geol. Explor. 2023, 51, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Ali, M. Study on sealing effect of pre-drainage gas borehole in coal seam based on air-gas mixed flow coupling model. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2020, 136, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Kang, Q. Simulation Study on the Characteristics of Gas Extraction from Coal Seams Based on the Superposition Effect and Hole Placement Method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Li, S.; Wang, E.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, P.; Shuang, H.; Li, S.; Wei, Z. Experimental and numerical investigations on dynamic mechanical responses and failure process of gas-bearing coal under impact load. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 142, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorenko, A.A.; Dmitriev, P.N.; Alekseev, V.Y.; Sidorenko, S.A. Improvement of technological schemes of mining of coal seams prone to spontaneous combustion and rock bumps. J. Min. Inst. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Qi, M.; Chen, X. Theoretical analysis of coal seam gas pressure distributionaround drainage hole and its application. China Saf. Sci. J. 2018, 28, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Research on the Outburst Elimination Effect Evaluation and Dynamic Inversion Model of Gas Parameters While Drilling for the Outburst Coal Seam Based on Directional Drilling. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. An improved model of gas flow in coal based on the effect penetration and diffusion. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 873–878. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Song, D.Y. Gas diffusion mechanism in multi-scale pores of coal particles and new diffusion model of dynamic diffusion coefficient. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, K.W.; Fan, Y.F. Numerical simulation of effective drainage radius and optimization of hole spacing under the influence of stack effect. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 48, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.N. Research on Numerical Simulation of Fluid-Solid and Field Application for Coalbed Methane Recovery. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, C.; Tao, M. Coal seam dual media model and its application to the proper interpolation among the boring-holes in gas extraction. J. Saf. Environ. 2018, 18, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, A.; Sereshki, F.; Ardejani, F.D.; Mirzaghorbanali, A. Simulation of macerals effects on methane emission during gas drainage in coal mines. Fuel 2017, 210, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichao, Z.O.U.; Song, X.I.N. Effective extraction radius of gas drilling in coal seam. China Saf. Sci. J. 2020, 30, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Wang, K.; Fan, L.; Kiryaeva, T.A. Gas-solid coupling laws for deep high-gas coal seams. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushin, Y.V.; Kapostey, E.I. Developing a Comprehensive Mathematical Model for Aluminium Production in a Soderberg Electrolyser. Energies 2023, 16, 6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, E.; Kong, X. Damage and deformation control equation for gas-bearing coal and its numerical calculation method. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2015, 25, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Sun, Z.-g.; Sun, W. A case study on the gas drainage optimization based on the effective borehole spacing in Sima coal mine. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 5510566. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Lin, B.; Yang, W.; Liu, T.; Kong, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y. Dynamic diffusion-based multifield coupling model for gas drainage. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2017, 44, 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Preusse, A.; Xie, S.; Hou, W. Research on damage-based coal permeability evolution for the whole stress–strain process considering temperature and pore pressure. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 149. [Google Scholar]







| Coal Sample | Mad (%) | Aad (%) | Vdaf (%) | Vad (%) | FCad (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| heavy coal | 0.93 | 18.15 | 6.43 | 4.38 | 61.15 |
| Parameter Name | Numerical Value | Parameter Name | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial substrate porosity, φ0 | 0.05 | Langmuir volume product, VL/(m3/t) | 38.59 |
| Initial cohesion, C0/MPa | 0.8 | Apparent density of coal, ρs/(kg/m3) | 1500 |
| Initial Fracture permeability, per_c0/m2 | 1 × 10−17 | Negative pressure of extraction, pb/MPa | 30 |
| Permeability impact factor, Cf/MPa−1 | 0.1 | Poisson’s ratio of coal, ν | 0.35 |
| Internal friction angle, φc/° | 35 | Modulus of elasticity of coal, E/GPa | 1 |
| Coefficient of kinetic viscosity, mu/Pa·s | 1.08 × 10−12 | Modulus of elasticity of coal matrix, Em/GPa | 0.75 |
| Langmuir pressure, PL/MPa | 1.25 | Initial gas diffusion coefficient, D0/(m2/s) | 5.48 × 10−12 |
| Attenuation coefficient, λ/s−1 | 5 × 10−17 | Limit adsorption deformation, εL | 0.012 |
| Coal seam temperature, T/K | 315.15 | The Klinkenberg factor, Kb/MPa | 0.76 |
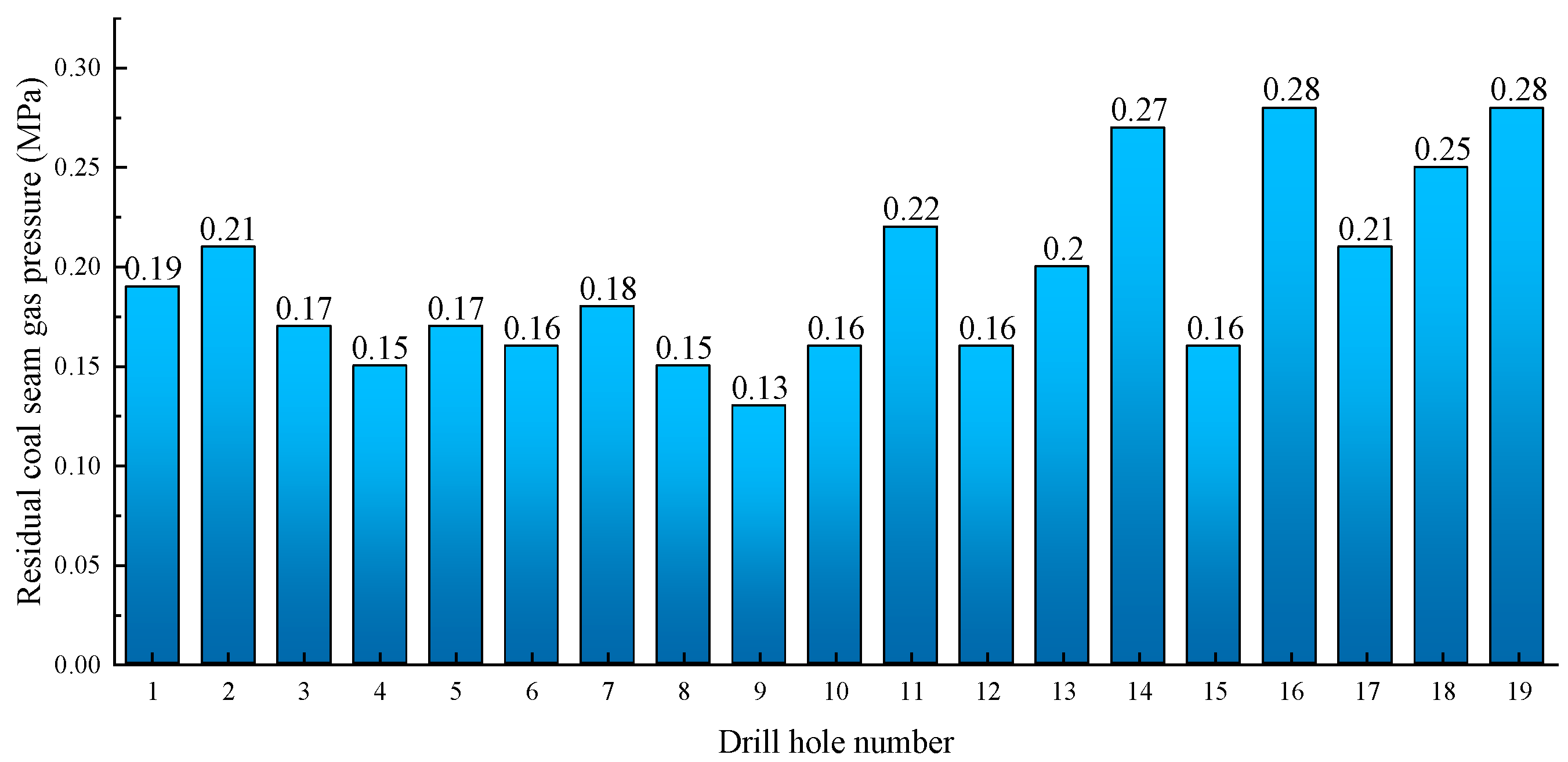
| Construction Location | Drill Number | NE | Inclination (°) | Sealing Length (m) | Residual Pressure (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172,403 upper shunts at point 25# | 1 | 38.2 | −12 | 16 | 0.19 |
| 6 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 2 | 38.1 | −12 | 16 | 0.21 |
| 15.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 3 | 38.1 | −12 | 16 | 0.17 |
| 37.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 4 | 38.1 | −12 | 16 | 0.15 |
| 54.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 5 | 38.1 | −12 | 16 | 0.17 |
| 23.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 6 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.16 |
| 39.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 7 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.18 |
| 61.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 8 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.15 |
| 1.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 9 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.13 |
| 22.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 10 | 38.1 | −14 | 16 | 0.16 |
| 39.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 11 | 38.1 | −14 | 16 | 0.22 |
| 60.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 12 | 38.1 | −14 | 16 | 0.16 |
| 77.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 13 | 38.1 | −14 | 16 | 0.20 |
| 12.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 14 | 38.1 | −14 | 16 | 0.27 |
| 28.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 15 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.16 |
| 50.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 16 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.28 |
| 71.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 17 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.21 |
| 1.3 m before point 35# on 172,403 | 18 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.25 |
| 20.3 m before point 35# on 172,403 | 19 | 38.1 | −15 | 16 | 0.28 |
| Construction Location | Drill Number | NE | Inclination (°) | Sampling Depth (m) | Gas Content (m3/t) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (OPQRS) region | 172,403 upper shunts at point 25# | 1(1) | 38.2 | −12 | 23 | 2.88 |
| 1(2) | 38.2 | −12 | 29 | 3.38 | ||
| 6 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 2(1) | 38.1 | −12 | 34 | 3.76 | |
| 2(2) | 38.1 | −12 | 40 | 3.04 | ||
| 15.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 3(1) | 38.1 | −12 | 44 | 3.11 | |
| 3(2) | 38.1 | −12 | 50 | 2.53 | ||
| 37.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 4(1) | 38.1 | −12 | 22 | 2.29 | |
| 4(2) | 38.1 | −12 | 27 | 2.68 | ||
| 54.8 m before point 25# on 172,403 | 5(1) | 38.1 | −12 | 34 | 3.11 | |
| 5(2) | 38.1 | −12 | 40 | 2.20 | ||
| 23.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 6(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 23 | 2.74 | |
| 6(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 29 | 2.98 | ||
| 39.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 7(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 45 | 2.70 | |
| 7(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 51 | 3.30 | ||
| 61.8 m before point 27# on 172,403 | 8(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 23 | 2.71 | |
| 8(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 29 | 2.09 | ||
| 1.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 9(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 35 | 2.36 | |
| 9(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 41 | 2.30 | ||
| 22.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 10(1) | 38.1 | −14 | 23 | 2.26 | |
| 10(2) | 38.1 | −14 | 29 | 2.85 | ||
| 39.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 11(1) | 38.1 | −14 | 35 | 3.10 | |
| 11(2) | 38.1 | −14 | 41 | 3.87 | ||
| 60.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 12(1) | 38.1 | −14 | 23 | 2.76 | |
| 12(2) | 38.1 | −14 | 28 | 2.94 | ||
| 77.6 m before point 31# on 172,403 | 13(1) | 38.1 | −14 | 34 | 2.69 | |
| 13(2) | 38.1 | −14 | 40 | 3.59 | ||
| 12.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 14(1) | 38.1 | −14 | 23 | 3.05 | |
| 14(2) | 38.1 | −14 | 28 | 3.52 | ||
| 28.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 15(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 45 | 2.21 | |
| 15(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 50 | 2.96 | ||
| 50.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 16(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 22 | 3.75 | |
| 16(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 27 | 3.03 | ||
| 71.8 m before point 33# on 172,403 | 17(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 36 | 3.01 | |
| 17(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 41 | 3.68 | ||
| 1.3 m before point 35# on 172,403 | 18(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 24 | 3.57 | |
| 18(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 29 | 3.36 | ||
| 20.3 m before point 35# on 172,403 | 19(1) | 38.1 | −15 | 42 | 3.28 | |
| 19(2) | 38.1 | −15 | 47 | 3.35 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Lei, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Yin, H. Optimization of Accurate Spacing for Gas Extraction from Damaged Coal Seams Based on a Dual-Penetration Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115339
Yan J, Lei K, Jiang Y, Zhang M, Zhang W, Yin H. Optimization of Accurate Spacing for Gas Extraction from Damaged Coal Seams Based on a Dual-Penetration Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(21):15339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115339
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Jin, Kejiang Lei, Yuangang Jiang, Minbo Zhang, Weizhong Zhang, and Hao Yin. 2023. "Optimization of Accurate Spacing for Gas Extraction from Damaged Coal Seams Based on a Dual-Penetration Model" Sustainability 15, no. 21: 15339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115339
APA StyleYan, J., Lei, K., Jiang, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, W., & Yin, H. (2023). Optimization of Accurate Spacing for Gas Extraction from Damaged Coal Seams Based on a Dual-Penetration Model. Sustainability, 15(21), 15339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115339







