Lifecycle Assessment of Two Urban Water Treatment Plants of Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goal and Scope Definition
2.2. Functional Unit
2.3. System Boundaries
- (i)
- Input and output flows for all material resources utilized in the treatment plants, encompassing production, transportation, and associated primary background processes like combustion and pipeline transport, among others;
- (ii)
- All sources of electricity generation within the grid mix that are used to power the water treatment plants;
- (iii)
- The construction and decommissioning of the treatment system and water abstraction systems (pipes, pumps, buildings, and reservoirs) were excluded from the scope of this study for two primary reasons: (a) they contribute only minimally to environmental impact [16,36,37], mainly due to their relatively longer functional lifespan [38], and (b) these processes do not directly impact the day-to-day operations of a water treatment system.
2.4. System Description of Case Study Example
2.5. Lifecycle Inventory Analysis
2.5.1. Data Quality
2.5.2. Inventory Analysis
2.6. Foreground Lifecycle Inventory Analysis
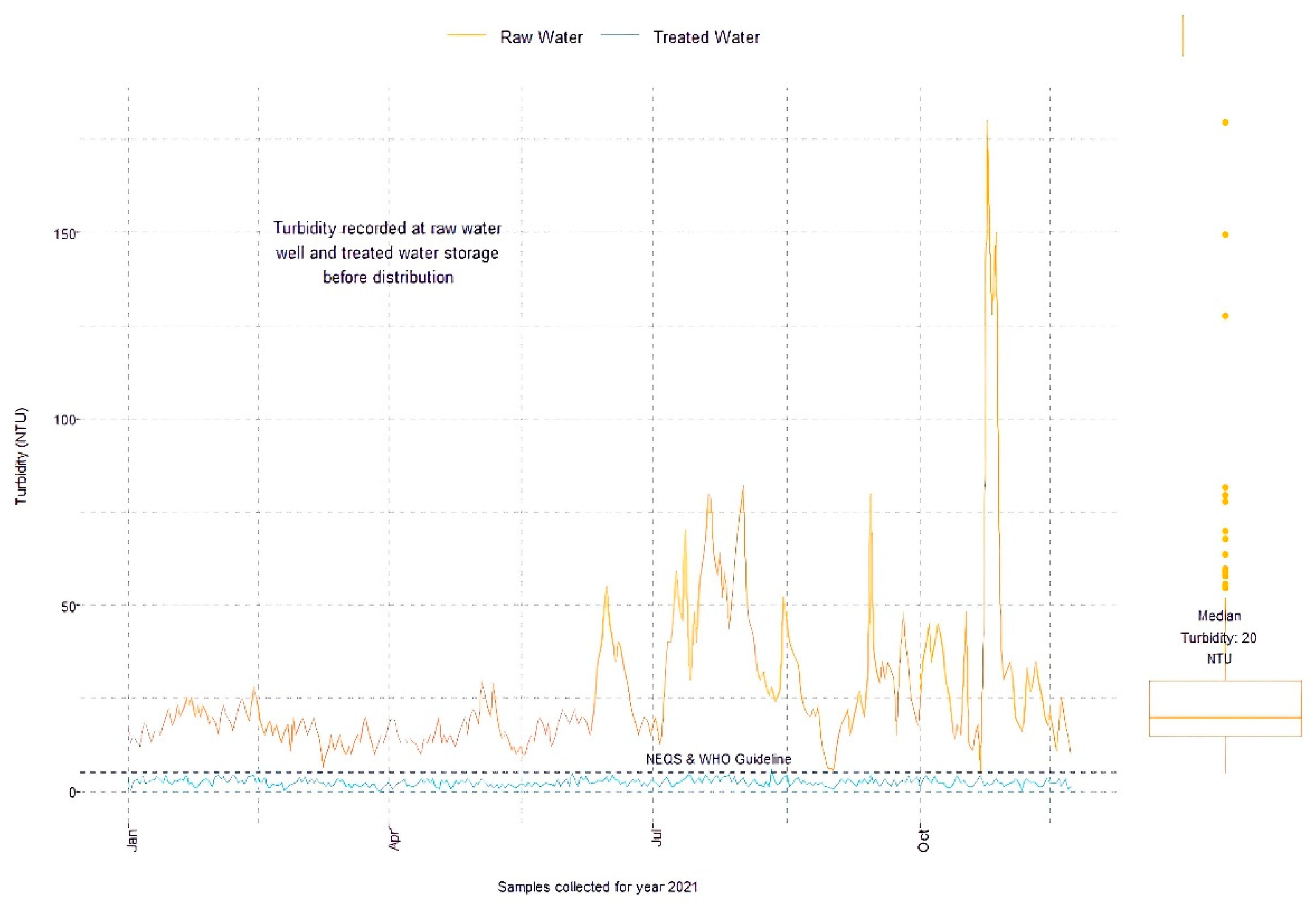
2.6.1. Water Quality
2.6.2. Waste Sludge
2.6.3. Energy Consumption
2.6.4. Chemical Consumption
2.7. Background Lifecycle Inventory Analysis
2.7.1. Electricity
2.7.2. Transport
2.7.3. Chemicals and Materials
2.8. Life Cycle Impact Assessment
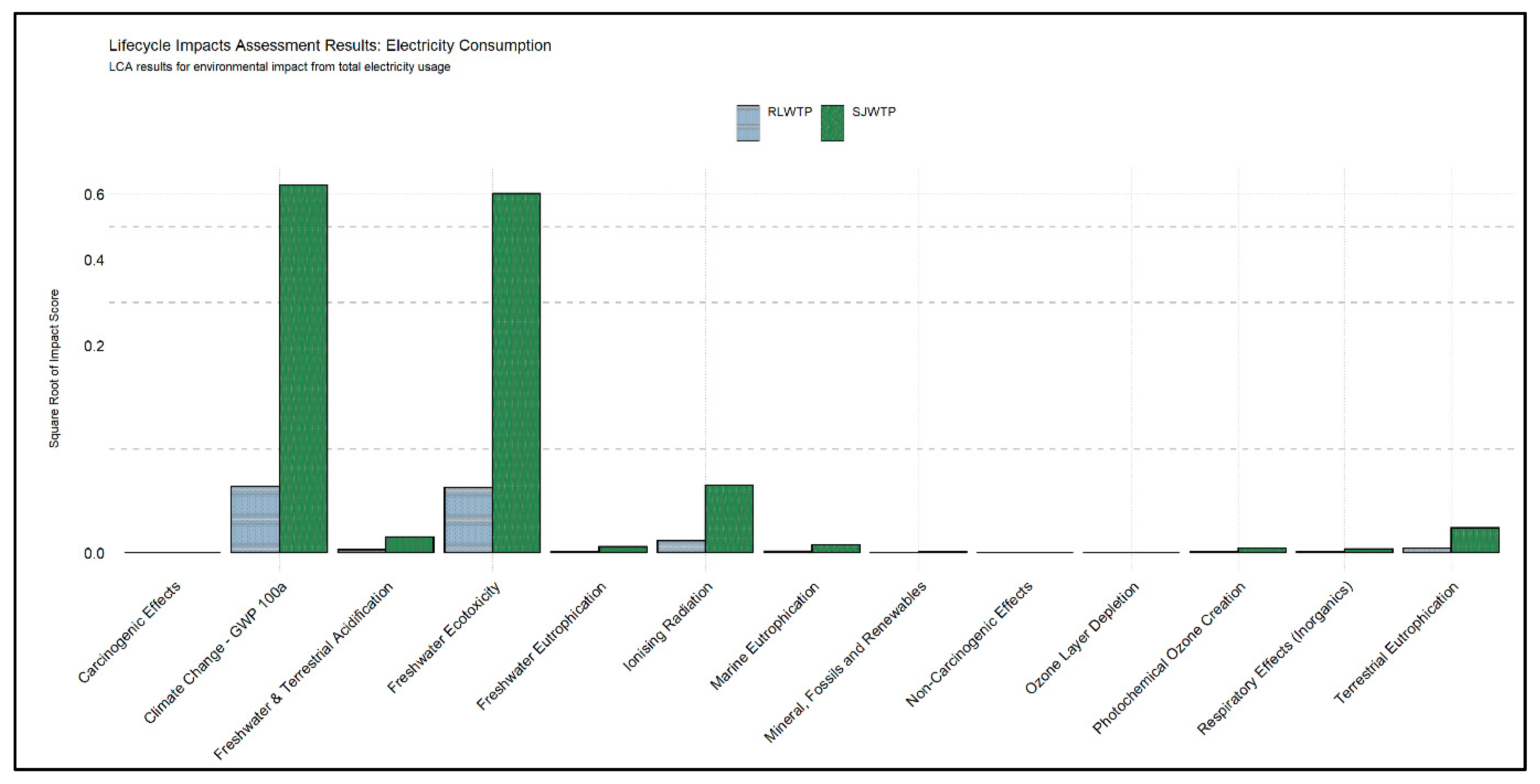
3. Results
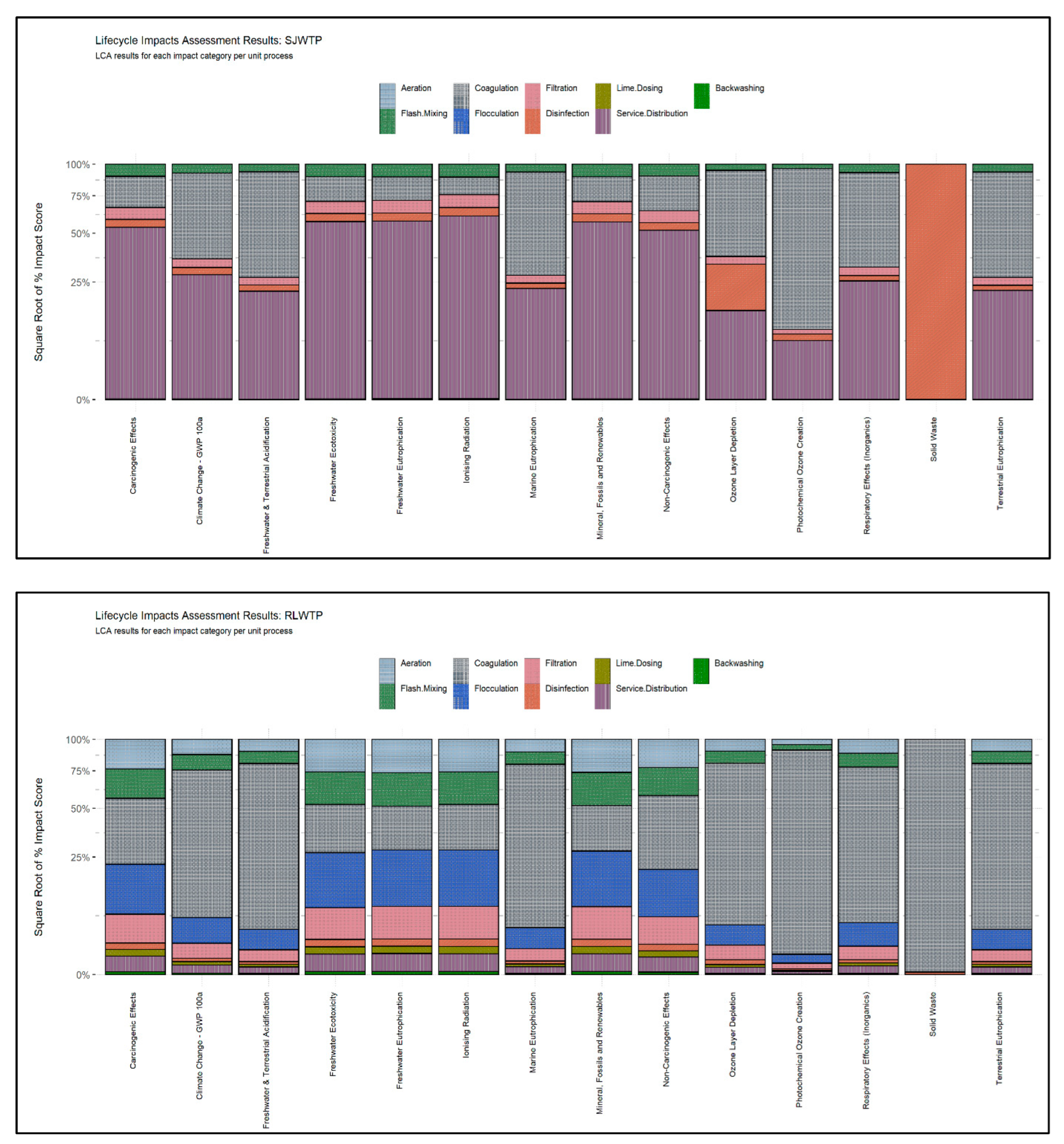
3.1. Contribution of Unit Processes
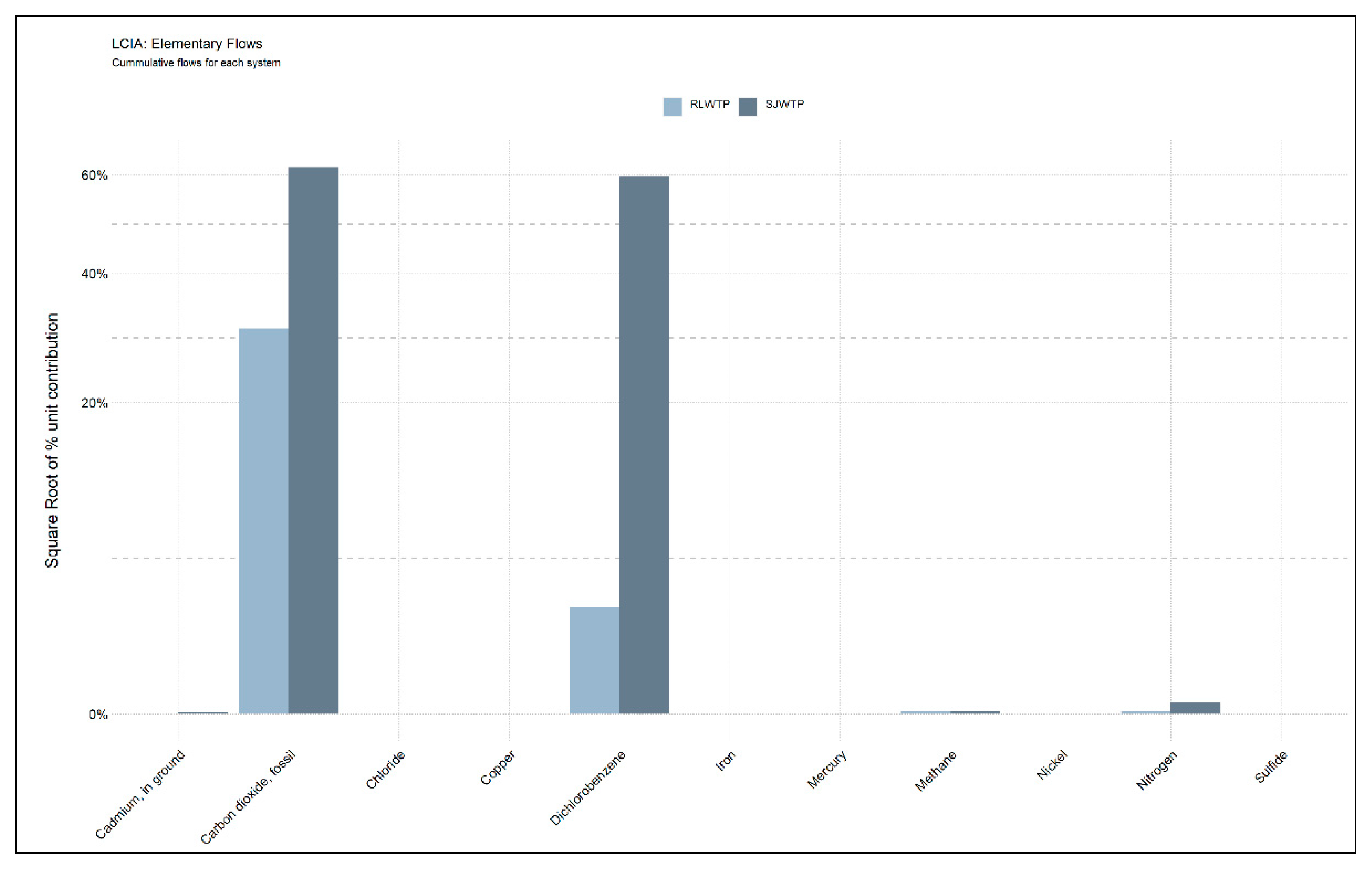
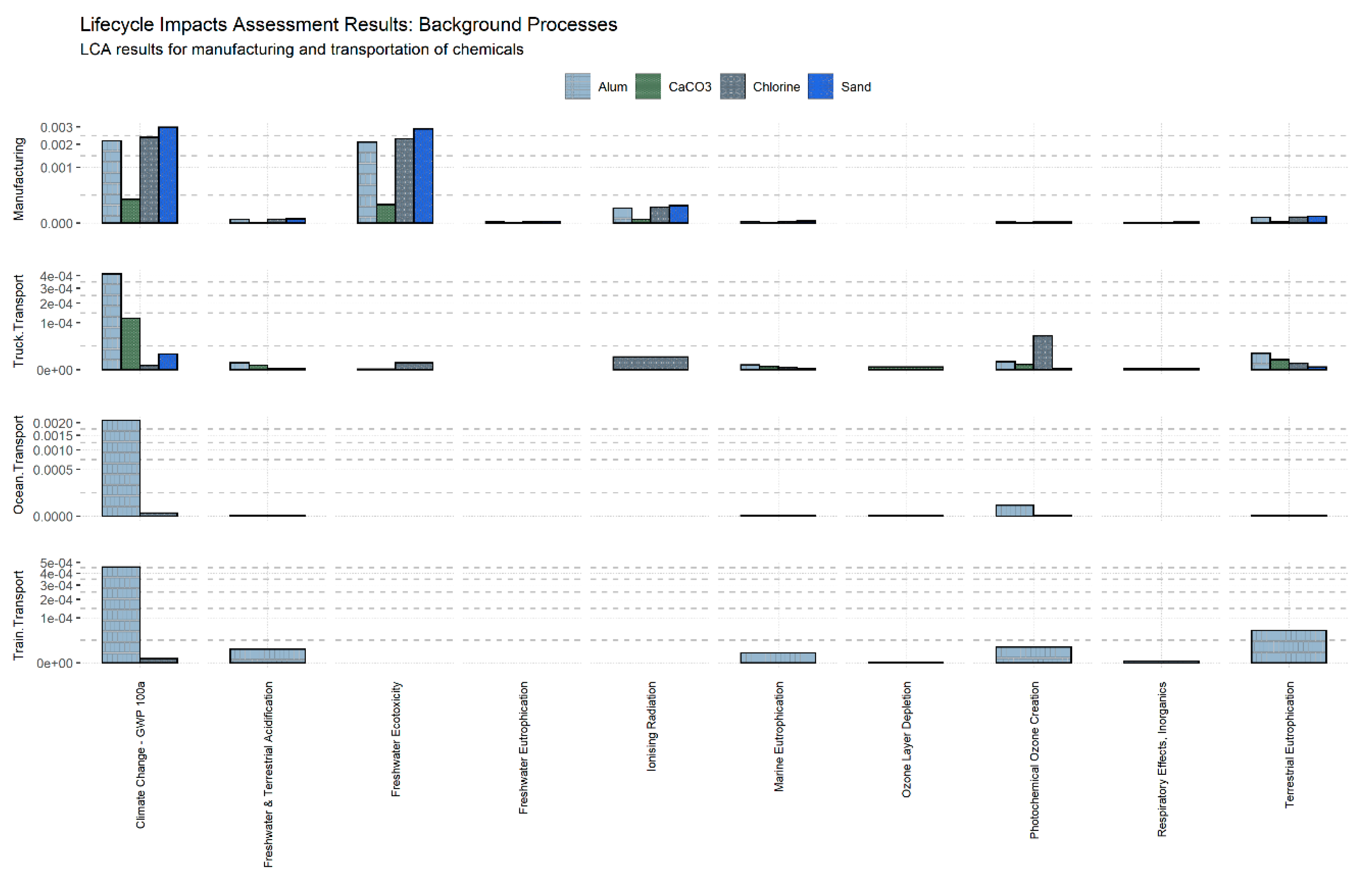
3.2. Contribution of Background Processes
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Both Systems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Term | Abbreviation |
| Green House Gases | GHGs |
| Environmental Impact Assessment | EIA |
| Net Environmental Benefit Analysis | NEBA |
| International Organization for Standardization | ISO |
| Rawal Lake Water Treatment Plant | RLWTP |
| Sang-Jani Water Treatment Plant | SJWTP |
| Water and Sanitation Agency | WASA |
| Rawalpindi Development Authority | RDA |
| Capital Development Authority | CDA |
| Islamabad Capital Territory | ICT |
| Total Dissolved Solids | TDS |
| Lime | CaCO3 |
| Life Cycle Inventory | LCI |
| European Platform on Lifecycle Assessment | ELCD |
| Heavy-Heavy Duty Trucks | HDTs |
| Medium-Heavy Duty Trucks | MDTs |
| Ocean-Going Vessel | OGV |
| Eastern Research Group | ERG |
| Environmental Footprint | EF |
| Antimicrobial Resistance Genes | ARGs |
| Virulence Factor Activity Relationships | VFARs |
References
- Kyung, D.; Kim, D.; Park, N.; Lee, W. Estimation of CO2 emission from water treatment plant—Model development and application. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucher, R.S. Risks and Benefits of Energy Management for Drinking Water Utilities Subject Area: Efficient and Customer-Responsive Organization; AWWA Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhary, S.; Batista, J.; Ahmad, S. Design aspects, energy consumption evaluation, and offset for drinkingwater treatment operation. Water 2020, 12, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, H.; Abid, R.; Ali, J.; Oswald, C.J.; Gilbride, K.A. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: Bibliometric Tracking of the Last Decade and Emerging Research Directions. Water 2023, 15, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Cashman, S.; Gaglione, A.; Mosley, J.; Weiss, L.; Ma, X.C.; Cashdollar, J.; Garland, J. Holistic analysis of urban water systems in the Greater Cincinnati region: (1) life cycle assessment and cost implications. Water Res. X 2019, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothausen, S.G.S.A.; Conway, D. Greenhouse-gas emissions from energy use in the water sector. Nat. Clim. Change 2011, 1, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. A Global Overview of National Regulations and Standards for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240023642 (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- Shahabadi, M.B.; Yerushalmi, L.; Haghighat, F. Impact of process design on greenhouse gas (GHG) generation by wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2679–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Brame, J.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Nanotechnology for a safe and sustainable water supply: Enabling integrated water treatment and reuse. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linley, S.; Leshuk, T.; Gu, F.X. Magnetically separable water treatment technologies and their role in future advanced water treatment: A patent review. Clean Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaoui, M.; Jellali, S.; Zorpas, A.A.; Dutournie, P. Membrane technology for sustainable water resources management: Challenges and future projections. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 25, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Peng, M.; Wu, D.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Sun, F.; Sharma, S.; Che, Y.; Yang, K. Greenhouse gas emissions from wastewater treatment plants in China: Historical emissions and future mitigation potentials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Xu, S.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, H.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Carbon footprint analysis and comprehensive evaluation of municipal wastewater treatment plants under different typical upgrading and reconstruction modes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Garrido, R.; Maziotis, A.; Mocholi-Arce, M.; Molinos-Senante, M. Assessing eco-efficiency of wastewater treatment plants: A cross-evaluation strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165839. [Google Scholar]
- Loubet, P.; Roux, P.; Loiseau, E.; Bellon-Maurel, V. Life cycle assessments of urban water systems: A comparative analysis of selected peer-reviewed literature. Water Res. 2014, 67, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonton, A.; Bouchard, C.; Barbeau, B.; Jedrzejak, S. Comparative life cycle assessment of water treatment plants. Desalination 2012, 284, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.S.; Harun, S.N.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Razman, K.K.; Liu, Y.Q.; Tholibon, D.A. Life Cycle Assessment and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment: A Brief Overview. Processes 2023, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040; Environmental Assessment—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Guinée, J. Handbook on Life Cycle Assessment—Operational Guide to the ISO Standards; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P.; Buonamici, R.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Life Cycle Assessment: Past; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nizam, N.U.M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Mahmoudi, E.; Halim, A.A.; Mohammad, A.W. The removal of anionic and cationic dyes from an aqueous solution using biomass-based activated carbon. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, D.; Dias, A.C.; Gabarrell, X.; Arroja, L. Environmental assessment of an urban water system. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Guzmán, C. Reducing CO2 emissions from drinking water treatment plants: A shadow price approach. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Qu, S. Investigation and evaluation of energy consumption performance for hospital buildings in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, R.; Siebel, M.; van der Helm, A.; Bosklopper, K.; Gijzen, H. Environmental and financial life cycle impact assessment of drinking water production at Waternet. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Elginoz, N.; Germirli Babuna, F.; Iskender, G. Life cycle assessment of a large water treatment plant in Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14823–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeen, A.H.; Noor, Z.Z.; Ngadi, N.; Almuraisy, S.; Raheem, A.B. Quantification of environmental impacts of domestic wastewater treatment using life cycle assessment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliet, O.; Soucy, G.; Houillon, G. Life Cycle Analysis: Understanding and Carrying Out an Eco-Balance; PPUR Presses Polytechniques: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 23, ISBN 2880748860. [Google Scholar]
- Kolotzek, C.; Helbig, C.; Thorenz, A.; Reller, A.; Tuma, A. A company-oriented model for the assessment of raw material supply risks, environmental impact and social implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.; Ugursal, V.I. A lifecycle assessment-based environmental analysis of building operationally energy efficient houses in Nova Scotia. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raluy, R.G.; Serra, L.; Uche, J. Life Cycle Assessment of water production technologies. Part 1: Life Cycle Assessment of different commercial desalination technologies (MSF, MED, RO). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2005, 10, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Li, W.; Zheng, L.; Li, M. Assessment of energy use and environmental impacts of wastewater treatment plants in the entire life cycle: A system meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Park, J.; Ha, Y. Trade-offs between water security and energy use: Lifecycle energy of water supply options in Paju, Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, D.K.; Seto, K.E.; Churchill, C.J. Erratum to: Impact of the selection of functional unit on the life cycle assessment of green concrete. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 1987–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleisa, E.; Al-Mutiri, A. Life Cycle Assessment for Tertiary Wastewater Treatment and Reuse versus Seawater Desalination. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 1026, p. 12001. [Google Scholar]
- Garfí, M.; Cadena, E.; Sanchez-Ramos, D.; Ferrer, I. Life cycle assessment of drinking water: Comparing conventional water treatment, reverse osmosis and mineral water in glass and plastic bottles. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, G.; Fitzsimons, L.; Horrigan, M.; Phelan, T.; Delaure, Y.; Corcoran, B.; Doherty, E.; Clifford, E. Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment plants in Ireland. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2016, 4, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijp, M.C.; Van der Laan, H. Life Cycle Assessment of Two Drinking Water Production Schemes. 2015, 38. Available online: https://rivm.openrepository.com/handle/10029/596126 (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Pak-EPA Water Quality Monitoring Report of Rawal Lake. Available online: https://environment.gov.pk/PublicationDetail/NDUwOGJiODYtMzEwOS00YmU1LWI5ZmMtMjdhMzMzNDQ2NTZl (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Pervez, S. Sang-Jani Water Treatment Plant Islamabad, Pakistan. New Tap. 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pervez, S. Rawal Lake Water Treatment Plant Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Netw. Water Technol. Asian Pac. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Economic Commission for Europe Carbon Neutrality in the UNECE Region: Integrated Life-Cycle Assessment of Electricity Sources UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE. 2021, 108. Available online: https://unece.org/sites/default/files/2021-10/LCA-2.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- USDA. Federal LCA Commons. Available online: https://www.lcacommons.gov/lca-collaboration/ (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- GreenDelta openLCA Nexus. Available online: https://nexus.openlca.org/ (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Rebello, T.A.; Roque, R.P.; Gonçalves, R.F.; Calmon, J.L.; Queiroz, L.M. Life cycle assessment of urban wastewater treatment plants: A critical analysis and guideline proposal. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnaningroem, N.; Anggraeni, D.R. Study of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) on Water Treatment. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 799, p. 12036. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, P.K.; Siebel, M.A.; Gijzen, H.J.; Van der Hoek, J.P.; Groot, C.A. Improving eco-efficiency of Amsterdam water supply: A LCA approach. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2002, 51, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, A.A.; Khan, I.A.; Ahmad, M.I. Analysis of Electric Power Generation Growth in Pakistan: Falling into the Vicious Cycle of Coal. Eng 2021, 2, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlik, M.J.; Kaehr, A.T.; Chester, M.V.; Horvath, A.; Taptich, M.N. Goods Movement Life Cycle Assessment for Greenhouse Gas Reduction Goals. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raccary, B.; Loubet, P.; Peres, C.; Sonnemann, G. Life cycle assessment of sample preparation in analytical chemistry: A case study on SBSE and SPE techniques. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERG. Available online: https://www.erg.com/ (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Amores, M.J.; Meneses, M.; Pasqualino, J.; Antón, A.; Castells, F. Environmental assessment of urban water cycle on Mediterranean conditions by LCA approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 43, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejane Rigon, M.; Zortea, R.; Alberto Mendes Moraes, C.; Célia Espinosa Modolo, R. Suggestion of Life Cycle Impact Assessment Methodology: Selection Criteria for Environmental Impact Categories. In New Frontiers on Life Cycle Assessment: Theory and Application; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J.B.; de Koning, A.; Heijungs, R. Life cycle assessment-based Absolute Environmental Sustainability Assessment is also relative. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Singh, S.K. A life cycle approach to environmental assessment of wastewater and sludge treatment processes. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Moussavi, S.; Li, S.; Barutha, P.; Dvorak, B. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of small water resource recovery facilities: Comparison of mechanical and lagoon systems. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, N.C. Characterization Methods and Models for Life Cycle Impact Assessment: Analysis and Subsidies for Application in Brazil; Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Commission, E. Environmental Footprint. Available online: https://eplca.jrc.ec.europa.eu/EnvironmentalFootprint.html (accessed on 24 June 2023).
- Saquib, S.; Gupta, A.; Joshi, A. Emerging water crisis: Impact of urbanization on water resources and constructed wetlands as a nature-based solution (NbS). In Current Directions in Water Scarcity Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 6, pp. 447–468. [Google Scholar]
- Martos, A.; Pacheco-Torres, R.; Ordóñez, J.; Jadraque-Gago, E. Towards successful environmental performance of sustainable cities: Intervening sectors. A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, D.M.; Lohman, H.A.C.; Cook, S.M.; Peters, G.M.; Guest, J.S. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of urban water infrastructure: Emerging approaches to balance objectives and inform comprehensive decision-making. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jensen, M.B. Green infrastructure for sustainable urban water management: Practices of five forerunner cities. Cities 2018, 74, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, J.; Angus, B. The role of civic environmentalism in the pursuit of sustainable communities. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2003, 46, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah-Akutteh, H.; Buamah, R.; Wiafe, S.; Nyarko, K.B. Raw water quality variations and its effect on the water treatment processes. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2122152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.H.; Silva, C.R.D.V.; Salvador, P.T.C. de O.; Silva, Í. de S.; Heller, L.; Uchôa, S.A. da C. Surveillance of Drinking Water Quality Worldwide: Scoping Review Protocol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, V.R. Safety of water used in food production. In Food Safety and Human Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 219–247. ISBN 9780128163337. [Google Scholar]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Sala-Garrido, R. Energy intensity of treating drinking water: Understanding the influence of factors. Appl. Energy 2017, 202, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenegger, A. California’s Water—Energy Relationship. California, USA 2005. Available online: http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2012/ph240/spearrin1/docs/CEC-700-2005-011-SF.PDF (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Wen, W.H.; Zhong, L.; Fu, X.; Spooner, S. World Resources Institute Water Energy Nexus in The Urban Water Source Selection: A Case Study from Qingdao; The World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhary, S.; Batista, J.; Ahmad, S. An analysis of energy consumption and the use of renewables for a small drinkingwater treatment plant. Water 2020, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Yusup, Y. Issues, impacts, and mitigations of carbon dioxide emissions in the building sector. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.E.-S.M.; van der Steen, N.P.; Abu-Zeid, K.; Vairavamoorthy, K. Towards sustainability in urban water: A life cycle analysis of the urban water system of Alexandria City, Egypt. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, R.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Ilavenil, S.; Rejiniemon, T.S. Towards sustainable wastewater treatment by biological methods—A challenges and advantages of recent technologies. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y. Enhancing nitrogen removal through directly integrating anammox into mainstream wastewater treatment: Advantageous, issues and future study. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, H.; Williams, M.R.; Jameel, S.; Hashsham, S.A. Antimicrobial resistance in the environment. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, H.; Williams, M.R.; Stedtfeld, T.; Chai, B.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Cole, J.R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Hashsham, S.A. Virulence factor activity relationships (VFARs): A bioinformatics perspective. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Recycling municipal, agricultural and industrial waste into energy, fertilizers, food and construction materials, and economic feasibility: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 765–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodato, C.; Tonini, D.; Damgaard, A.; Fruergaard Astrup, T. A process-oriented life-cycle assessment (LCA) model for environmental and resource-related technologies (EASETECH). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haun, P.; Müller, P.; Traverso, M. Improving automated Life Cycle Assessment with Life Cycle Inventory model constructs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, J.; Geyer, R.; Suh, S. A review of methods for characterizing the environmental consequences of actions in life cycle assessment. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, F.; Golabi, M.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Life cycle assessment, a decision-making tool in wastewater treatment systems: A case study wastewater treatment plant of Ahvaz, Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, D. Cradle-to-Gate LCA of Water Treatment Alternatives A case study performed for Norrvatten’ s future Cradle-to-Gate LCA of Water Treatment Alternatives A case study performed for Norrvatten’ s future waterwork expansion Siddharth Selvarajan Examiner 2020. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1519618/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Parravicini, V.; Nielsen, P.H.; Thornberg, D.; Pistocchi, A. Evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions from the European urban wastewater sector, and options for their reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Alsina, X.; Arnell, M.; Corominas, L.; Sweetapple, C.; Fu, G.; Butler, D.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Gernaey, K.V.; Jeppsson, U. Benchmarking strategies to control GHG production and emissions. In Quantification and Modelling of Fugitive Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Urban Water Systems; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 213–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, R.L.; Jin, L.; Sun, S.R.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Y. Quantification of greenhouse gas emission from wastewater treatment plants. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Operating Conditions | Aeration | Flash Mixer | Coagulant Dosing | Coagulant Mixing | Flocculation | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Flow Rate | Initial Turbidity | Final Turbidity | Number of blowers | Blower rating | Air flow rate | Number of mixers | Impeller Diameter | Velocity Gradient | Motor rating | Coagulant type | Coagulant Feed Rate | Number of pumps | Coagulant Feed pump rating | Solution Concentration | Hydraulic Retention Time | Number of motors | Motor rating | Shaft paddle flocculator | Clari-flocculator | Velocity Gradient | Flocculator motor | Clari-flocculator motor | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| UNITS | m3/d | NTU | NTU | No# | kW | m3/min | No# | m | s-1 | kW | Type | mg/L | No# | kW | % | min | No# | kW | No# | No# | s-1 | kW | kW | min |
| RLWTP | 79,500 | 10 | 0.5 | 2 | 9.2 | 6 | 2 | 1.6 | 450 | 9.2 | Alum | 20 | 3 | 0.9 | 15 | 1.2 | 2 | 11.186 | 3 | 3 | 26 | 4.5 | 13 | 15 |
| SJWTP | 98,000 | 8.33 | 1 | NA | NA | NA | 2 | 1.6 | 438 | 11 | Alum | 15 | 3 | 0.75 | 15 | 1.5 | 6 | 11 | Zig-Zag Flocculator | NA | NA | NA | NA | 29 |
| Sedimentation | Filtration | Service Pumps | Disinfection | Lime Dose | Storage & Distribution | Backwashing | Sludge | |||||||||||||||||
| Variables | Rotating full bridge clarifier | Rectangular Clarifier | Surface Loading Rate | Velocity Gradient | Rapid Sand Filter | Media Size | Filter Depth | Flow Rate | Pump rating | Operating hours | Feed Rate | Chlorine Dosing pump rating | Feed Rate | Dosing pump rating | Number of pumps | Power Factor A | Power Factor B | Pump kVA rating A | Pump kVA rating A | Pipeline | Air scour pump rating | Backwashing flow | Backwashing period | Sludge Volume |
| UNITS | No# | No# | m/h | m/min | No# | mm | m | m/h | kW | h/d | mg/L | kW | mg/L | kw | No# | NA | NA | kVA | kVA | m | kW | m3/m2.min | cycle/d | kg/m3 |
| RLWTP | 3 | 1 | 2.55 | 0.6 | 16 | 0.95 | 1.4 | 5.4 | 5.3 | 24 | 2 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.9 | NA | NA | NA | Gravity | Gravity | - | 93.25 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.01 |
| SJWTP | 0 | 8 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 20 | 0.6 | 0.76 | 5.3 | NA | 1 | 0.75 | NA | 6 | 0.4 (×3) | 0.8 (×3) | 970 | 1400 | 13,160 | 51.474 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.0083 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, S.; Pervez, S.; Sarwar, F.; Abid, R.; Jamil, S.U.U.; Waseem, H.; Gilbride, K.A. Lifecycle Assessment of Two Urban Water Treatment Plants of Pakistan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316172
Jamil S, Pervez S, Sarwar F, Abid R, Jamil SUU, Waseem H, Gilbride KA. Lifecycle Assessment of Two Urban Water Treatment Plants of Pakistan. Sustainability. 2023; 15(23):16172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316172
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Shayan, Saimar Pervez, Fiza Sarwar, Rameesha Abid, Syed Umair Ullah Jamil, Hassan Waseem, and Kimberley A. Gilbride. 2023. "Lifecycle Assessment of Two Urban Water Treatment Plants of Pakistan" Sustainability 15, no. 23: 16172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316172
APA StyleJamil, S., Pervez, S., Sarwar, F., Abid, R., Jamil, S. U. U., Waseem, H., & Gilbride, K. A. (2023). Lifecycle Assessment of Two Urban Water Treatment Plants of Pakistan. Sustainability, 15(23), 16172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316172








