Achieving UN SDGs in Food Supply Chain Using Blockchain Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Blockchain
3. Food Supply Chain Sustainability Challenges
4. Research Method
4.1. Research Questions
4.2. Material Collection
4.3. Exclusion and Inclusion Criteria
4.4. Descriptive Analysis
4.5. Category Selection
5. Blockchain Adoption in the Food Supply Chain to Achieve SDGs
5.1. Food Safety and Quality
5.1.1. Food Traceability
5.1.2. Monitoring and Supervising
5.1.3. Food Provenance
5.2. Food Insecurity
5.3. Environmental Sustainability
5.3.1. Carbon Footprint Tracking
5.3.2. Transportation and Infrastructure Issues
5.3.3. Food Wastage and Loss
5.3.4. Lack of Warehouse and Cold Chain
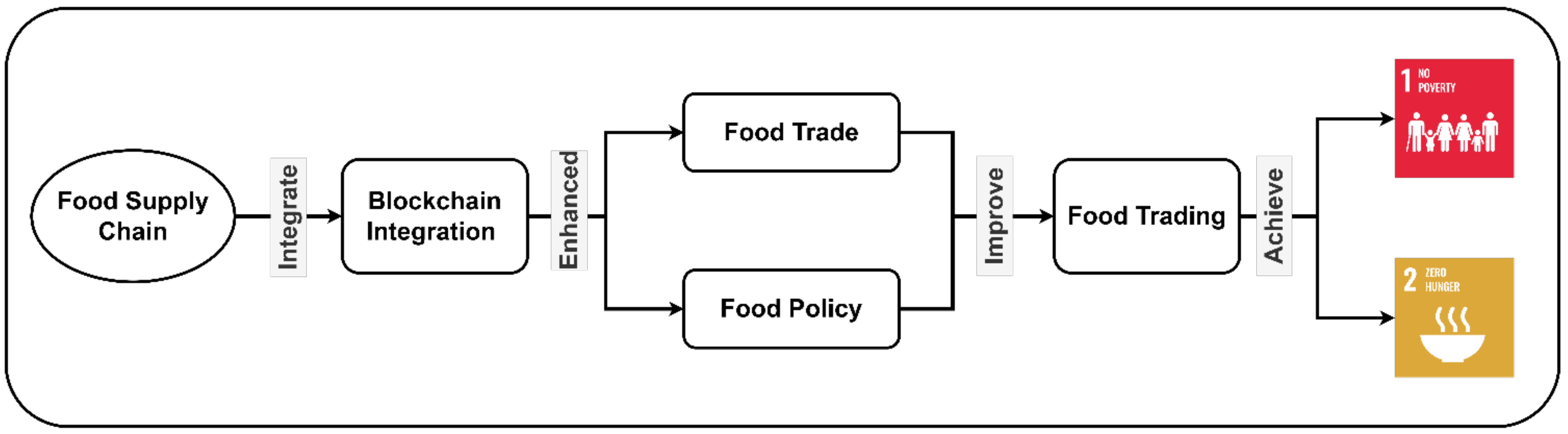
5.4. Food Trade and Policy
5.4.1. Food Trade
5.4.2. Food Policy
6. Discussion and Future Research Area
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The Future of Food and Agriculture—Trends and Challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization, United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i6583e/I6583E.pdfFAo (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Trienekens, J.; Zuurbier, P. Quality and safety standards in the food industry, developments and challenges. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 113, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Jõudu, I. Emerging issues and challenges in agri-food supply chain. In Sustainable Food Supply Chains; Accorsi, R., Manzini, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, C.; Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Are we successful in turning trade-offs into synergies? Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Trade and Markets Division, Trade reforms and food Security: Conceptualizing the Linkages; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2003; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/y4671e/y4671e.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- Henchion, M.; Hayes, M.; Mullen, A.M.; Fenelon, M.; Tiwari, B. Future Protein Supply and Demand: Strategies and Factors Influencing a Sustainable Equilibrium. Foods 2017, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bager, S.L.; Singh, C.; Persson, U.M. Blockchain is not a silver bullet for agro-food supply chain sustainability: Insights from a coffee case study. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 4, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. A systematic review of the research on disruptive technology—Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; pp. 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buterin, V. A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform; White Paper; Ethereum Foundation (Stiftung Ethereum): Zug, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Von Hagen, O.; Manning, S.; Reinecke, J. Sustainable Sourcing in the Food Industry: Global Challenges and Practices. Mod. Ernaehrung Heute Off. J. Food Chem. Inst. Assoc. Ger. Confect. Ind. 2010, 4, 1–9. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=1678472 (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- FAO. Food Outlook—Biannual Report on Global Food Markets: November 2019; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Emissions Due to Agriculture. Global, Regional and Country Trends 1990–2018; Food and Agriculture Organization, United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 18. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cb3808en/cb3808en.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Sharma, Y.K.; Mangla, S.K.; Patil, P.P.; Liu, S. When challenges impede the process: For circular economy-driven sustainabi-lity practices in food supply chain. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bánáti, D. Consumer response to food scandals and scares. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, H.; Kuznesof, S.; Dean, M.; Chan, M.-Y.; Clark, B.; Home, R.; Stolz, H.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, C.; Brereton, P.; et al. Chinese consumer’s attitudes, perceptions and behavioural responses towards food fraud. Food Control. 2018, 95, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, S.; Schwab, A.; Henn, R.; Huck, C.W. Food fraud: An exploratory study for measuring consumer perception towards mislabeled food products and influence on self-authentication intentions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukas, V.; Gkogkidis, A.; Kampa, A.; Spathoulas, G.; Kakarountas, A. Enhancing Food Supply Chain Security through the Use of Blockchain and TinyML. Information 2022, 13, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Mao, D.; Zhang, B.; Zuo, M.; Zhao, Z. A Novel Visual Analysis Method of Food Safety Risk Traceability Based on Blockchain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engels, S.V.; Hansmann, R.; Scholz, R.W.; Hansmann, R. Toward a Sustainability Label for Food Products: An Analysis of Experts’ and Consumers’ Acceptance. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2010, 49, 30–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.C.; Johnson, M. Integrating the supply chain… 25 years on. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddaway, A. What is a systematic literature review and how do I do one. Univ. Stirling 2014, I, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Crosby, M.; Pattanayak, P.; Verma, S.; Kalyanaraman, V. Blockchain technology: Beyond bitcoin. Appl. Innov. 2016, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F. An agri-food supply chain traceability system for China based on RFID & blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Kunming, China, 24–26 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, A.V.; Heeks, R. ICTs and climate change adaptation: Enabling innovative strategies, UK Strategy. Strateg. Brief-1 Clim. Chang. Innov. ICTs Proj. 2011, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stranieri, S.; Riccardi, F.; Meuwissen, M.P.; Soregaroli, C. Exploring the impact of blockchain on the performance of agri-food supply chains. Food Control. 2020, 119, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.W.; Byun, Y.-C.; Park, N. IoT-Blockchain Enabled Optimized Provenance System for Food Industry 4.0 Using Advanced Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, A.; Solanki, A.; Kondal, R.; Nayyar, A.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N. Blockchain-based efficient communication for food supply chain industry: Transparency and traceability analysis for sustainable business. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Soon, J.M. Development of sustainability indicator scoring (SIS) for the food supply chain. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 2097–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djama, M.; Fouilleux, E.; Vagneron, I. Standard-Setting, Certifying and Benchmarking: A Governmentality Approach to Sustainability Standards in the Agro-Food Sector. In Governing through Standards: Origins, Drivers and Limitations; Ponte, S., Gibbon, P., Vestergaard, J., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2011; pp. 184–209. Available online: http://agritrop.cirad.fr/561648/1/document_561648.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Trienekens, J.H.; Wognum, P.M.; Beulens, A.J.M.; van der Vorst, J.G.A.J. Transparency in complex dynamic food supply chains. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2012, 26, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, M.; Parry, G.C. Blockchain: Case studies in food supply chain visibility. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2020, 25, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A. Blockchain with IOT: Applications and use cases for a new paradigm of supply chain driving efficiency and cost. In Advances in Computers; Kim, S., Deka, G.C., Zhang, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 115, pp. 259–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivaldini, M. Blockchain in operations for food service distribution: Steps before implementation. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 995–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscotti, A.; Giannelli, C.; Keyi, C.F.N.; Lazzarini, R.; Sardone, A.; Stefanelli, C.; Virgilli, G. Internet of Things and Blockchain Technologies for Food Safety Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Bologna, Italy, 14 September 2020; pp. 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Bianchini, A.; Perazzo, P.; Vallati, C.; Dini, G. BRUSCHETTA: An IoT Blockchain-Based Framework for Certifying Extra Virgin Olive Oil Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Washington, DC, USA, 15 June 2019; pp. 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y. Blockchain-Based Safety Management System for the Grain Supply Chain. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36398–36410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, S.; Medeni, T.D.; Soylu, D. Assessment of Role of Innovative Technology through Blockchain Technology in Ghana’s Cocoa Beans Food Supply Chains. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 11–13 October 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hua, G.; Kang, Y.; Cheng, T.E.; Xu, Y. What value does blockchain bring to the imported fresh food supply chain? Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2022, 165, 102859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Evaluation on Frozen Shellfish Quality by Blockchain Based Multi-Sensors Monitoring and SVM Algorithm During Cold Storage. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 54361–54370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.; Risco, R.; Casaverde, L. Analysis of the implementation of Blockchain as a mechanism for digital and transparent food traceability in Peruvian social programs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE XXVII International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computing (INTERCON), Lima, Peru, 12–14 August 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragon, A.E.C.; Mondragon, C.E.C.; Coronado, E.S. Feasibility of Internet of Things and Agnostic Blockchain Technology Solutions: A Case in the Fisheries Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–18 April 2020; pp. 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Kim, J.S. Cloud-based Livestock Monitoring System Using RFID and Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/2020 6th IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), New York, NY, USA, 1–3 August 2020; pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Powell, W.; Foth, M.; Natanelov, V.; Miller, T.; Dulleck, U. Strengthening consumer trust in beef supply chain traceability with a blockchain-based human-machine reconcile mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikouli, P.; Wilde, A.S.; Dragoni, N.; Høgh-Jensen, H. On the benefits and challenges of blockchains for managing food supply chains. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. ProductChain: Scalable Blockchain Framework to Support Provenance in Supply Chains. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications (NCA), Cambridge, MA USA, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, D.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Mu, H. Blockchain application in food supply information security. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Singapore, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, F.; Hao, Z.; Li, H. Credit Evaluation System Based on Blockchain for Multiple Stakeholders in the Food Supply Chain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Cao, J.; Yang, Y.; Tung, C.L.; Jiang, S.; Tang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y. Data Management in Supply Chain Using Blockchain: Challenges and a Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2019 28th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), Valencia, Spain, 29 July–1 August 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, C.; Gritti, C.; Przytarski, D.; Mitschang, B. Trustworthy, Secure, and Privacy-aware Food Monitoring Enabled by Blockchains and the IoT. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 23 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftekhar, A.; Cui, X.; Hassan, M.; Afzal, W. Application of Blockchain and Internet of Things to Ensure Tamper-Proof Data Availability for Food Safety. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Cui, X.; Huang, X.; Leigh, A.M.; Gu, H. Food Safety Supervision System Based on Hierarchical Multi-Domain Blockchain Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51817–51826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runzel, M.A.S.; Hassler, E.E.; Rogers, R.E.L.; Formato, G.; Cazier, J.A. Designing a Smart Honey Supply Chain for Sustainable Development. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2021, 10, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.K.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Weber, I.; Rimba, P.; Lu, Q.; Staples, M. Digital-Physical Parity for Food Fraud Detection. In International conference on Blockchain; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.-Y. Blockchain Based Provenance for Agricultural Products: A Distributed Platform with Duplicated and Shared Bookkeeping. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, A.; Almogren, A.; Javaid, N.; Al-Zahrani, F.A.; Zuair, M.; Alam, M. Blockchain-Based Agri-Food Supply Chain: A Complete Solution. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69230–69243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakare, P.; Dighore, N.; Chopkar, A.; Chauhan, A.; Bhagat, D.; Tote, M. Implementation of Block Chain Technology in Public Distribution System. In Hybrid Intelligent Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.S.; Sonje, S.A.; Shukla, S. Food subsidy distribution system through Blockchain technology: A value focused thinking approach for prototype development. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2021, 27, 470–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetha, A.N.; Prabodh, C.P. Blockchain—Bringing Accountability in the Public Distribution System. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Recent Trends on Electronics Information, Communication & Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 17–18 May 2019; pp. 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Water for Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i7959e/i7959e.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Shakhbulatov, D.; Arora, A.; Dong, Z.; Rojas-Cessa, R. Blockchain Implementation for Analysis of Carbon Footprint across Food Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14 July 2019; pp. 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.L.; Matthews, H.S. Food-Miles and the Relative Climate Impacts of Food Choices in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, P.; Sunmola, F.; Wertheim-Heck, S. Blockchain Enabled Quality Management in Short Food Supply Chains. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohner, B.; Pauer, E.; Heinrich, V.; Tacker, M. Packaging-Related Food Losses and Waste: An Overview of Drivers and Issues. Sustainability 2019, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maity, M.; Tolooie, A.; Sinha, A.K.; Tiwari, M.K. Stochastic batch dispersion model to optimize traceability and enhance transparency using Blockchain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 154, 107134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Liu, R.; Shan, Z. Is Blockchain a Silver Bullet for Supply Chain Management? Technical Challenges and Research Opportunities. Decis. Sci. 2020, 51, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikish Kumar, S.V.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Sanjay Tharagesh, R.S.; Kumar, P.; Janavi, B. An Autonomous Food Wastage Control Warehouse: Distributed Ledger and Machine Learning based Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Hao, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Novel Automatic Food Trading System Using Consortium Blockchain. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 44, 3439–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chang, S.-C.; Chou, T.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Ruangkanjanases, A. Consumers’ Intention to Adopt Blockchain Food Traceability Technology towards Organic Food Products. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enescu, F.M.; Ionescu, V.M. Using Blockchain in the agri-food sector following SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarathunga, M. Improving Farmers’ Participation in Agri Supply Chains with Blockchain and Smart Contracts. In Proceedings of the 2020 Seventh International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS), Paris, France, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikci, Y.; Subramanian, N.; Dora, M.; Bhatia, M.S. Food supply chain in the era of Industry 4.0: Blockchain technology implementation opportunities and impediments from the perspective of people, process, performance, and technology. Prod. Plan. Control 2020, 33, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiscini, R.; Testarmata, S.; Ciaburri, M.; Ferrari, E. The blockchain as a sustainable business model innovation. Manag. Decis. 2020, 58, 1621–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.L.; Tricase, C.; De Cesare, L. Blockchain technology for a sustainable agri-food supply chain. Br. Food J. 2021, 123, 3471–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, I.; Batlle-Bayer, L.; Bala, A.; Fullana-I-Palmer, P.; Jambrak, A.R. Role of the Food Supply Chain Stakeholders in Achieving UN SDGs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob-John, J.; D’Souza, C.; Marjoribanks, T.; Singaraju, S. Synergistic Interactions of SDGs in Food Supply Chains: A Review of Responsible Consumption and Production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, G.V.; Avellan, A.; Gilbertson, L.M. Opportunities and challenges for nanotechnology in the agri-tech revolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, S.; Dey, K. Blockchain technology adoption, architecture, and sustainable agri-food supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 284, 124731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| # | Research Question | Research Objective |
|---|---|---|
| RQ 1 | To identify food supply chain sustainability challenges in line with UN SDGs? | This research question investigates FSC sustainability challenges and aligns them with the SDGs. |
| RQ 2 | What features of blockchain are being used in literature to solve the sustainability challenges identified in RQ 1? | The primary objective is to explore how blockchain was used in literature to solve sustainability challenges of the food supply chain to achieve SDGs. |
| RQ 3 | How can blockchain be used in achieving the SDG? | The primary objective was to uncover the interaction among identified FSC challenges, blockchain applications and SDG. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandan, A.; John, M.; Potdar, V. Achieving UN SDGs in Food Supply Chain Using Blockchain Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032109
Chandan A, John M, Potdar V. Achieving UN SDGs in Food Supply Chain Using Blockchain Technology. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032109
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandan, Anulipt, Michele John, and Vidyasagar Potdar. 2023. "Achieving UN SDGs in Food Supply Chain Using Blockchain Technology" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032109
APA StyleChandan, A., John, M., & Potdar, V. (2023). Achieving UN SDGs in Food Supply Chain Using Blockchain Technology. Sustainability, 15(3), 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032109







