Assessing Transformation Practices in China under Energy and Environmental Policy Goals: A Green Design Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Construct and Assess China’s Regional Comprehensive GDI
3.1. Construction of GDI
3.2. Assessing the Development of GDI in Regions of China
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pierrehumbert, R. There is no Plan B for dealing with the climate crisis. Bull. At. Sci. 2019, 75, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Liu, H. CO2 mitigation potential in China’s building construction industry: A comparison of energy performance. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Du, K. Energy and CO2 emissions performance in China’s regional economies: Do market-oriented reforms matter? Energy Policy 2015, 78, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Edziah, B.K.; Sun, C.; Kporsu, A.K. Institutional quality, green innovation and energy efficiency. Energy Policy 2019, 135, 111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantschnig, W.J. Green design: An introduction to issues and challenges. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part A 1994, 17, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskamp, S. A sustainable future for humanity? How can psychology help? Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, P.E.; Smith Cooper, J. Life cycle energy analysis as a method for material selection. J. Mech. Des. 2004, 126, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Zou, P.X.; Stewart, R.A.; Bertone, E.; Sahin, O.; Buntine, C.; Marshall, C. Government championed strategies to overcome the barriers to public building energy efficiency retrofit projects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Majid, M.Z.A. A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. Sustainable construction: Green building design and delivery. Intell. Build. Int. 2013, 5, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNaughton, P.; Cao, X.; Buonocore, J.; Cedeno-Laurent, J.; Spengler, J.; Bernstein, A.; Allen, J. Energy savings, emission reductions, and health co-benefits of the green building movement. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lau, S.S.Y. Introduction to the building research establishment environmental assessment method (BREEAM) in UK. New Archit. 2002, 80, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, A.; Meier, M.; York, J. Rating environmental performance in the building industry: Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED). Darden Bus. Publ. Cases 2017, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, D.L.; Wilson, C.; Bevione, M.; Carrara, S.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Emmerling, J.; Guivarch, C.; Karkatsoulis, P.; Keppo, I.; Krey, V.; et al. Interaction of consumer preferences and climate policies in the global transition to low-carbon vehicles. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivak, M.; Schoettle, B. Eco-driving: Strategic, tactical, and operational decisions of the driver that influence vehicle fuel economy. Transp. Policy 2012, 22, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Fuel Economy Guide. 2011. Available online: http://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/download.shtml (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Menzies, T.R., Jr. New TRB Special Report: Tires and Passenger Vehicle Fuel Economy: Informing Consumers, Improving Performance. TR News, 14 September 2006; pp. 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Garcha, A.; Norup, S.; Kormylo, A. 2007 Canadian Vehicle Survey: Summary Report; Office of Energy Efficiency: Ottawa, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, P. We Test the Tips: What Really Saves Gas? And How Much? 2009. Available online: http://www.edmunds.com/fuel-economy/we-test-the-tips.html (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Handfield, R.B.; Walton, S.V.; Seegers, L.K.; Melnyk, S.A. ‘Green’value chain practices in the furniture industry. J. Oper. Manag. 1997, 15, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, A.M. A system model for green manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahajwalla, V.; Pahlevani, F.; Maroufi, S.; Rajarao, R. Green manufacturing: A key to innovation economy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.J. The sharing economy: A pathway to sustainability or a nightmarish form of neoliberal capitalism? Ecol. Econ. 2016, 121, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cici, B.; Markopoulou, A.; Frias-Martinez, E.; Laoutaris, N. Assessing the potential of ride-sharing using mobile and social data: A tale of four cities. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–17 September 2014; pp. 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, P.; Resta, G.; Szell, M.; Sobolevsky, S.; Strogatz, S.H.; Ratti, C. Quantifying the benefits of vehicle pooling with shareability networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13290–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Argiriou, A.; Vallindras, M. Design and operation of a low energy consumption passive solar agricultural greenhouse. Sol. Energy 1994, 52, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutter, O.D. Report Submitted by the Special Rapporteur on the Right to Food, Olivier de Schutter: Women’s Rights and the Right to Food; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- López-Ridaura, S.; Masera, O.; Astier, M. Evaluating the sustainability of complex socio-environmental systems. The MESMIS framework. Ecol. Indic. 2002, 2, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Østergaard, P.A.; Connolly, D.; Mathiesen, B.V. Smart energy and smart energy systems. Energy 2017, 137, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarashynskaya, A.; Prus, P. Smart Energy for a Smart City: A Review of Polish Urban Development Plans. Energies 2022, 15, 8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, M.; Buonanno, A.; Caliano, M.; Graditi, G.; Piazza, G.; Bracco, S.; Delfino, F. Stochastic Operation Optimization of the Smart Savona Campus as an Integrated Local Energy Community Considering Energy Costs and Carbon Emissions. Energies 2022, 15, 8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, B. Decomposition analysis of patenting in renewable energy technologies: From an extended LMDI approach perspective based on three Five-Year Plan periods in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.H.; Helmers, C. Innovation and diffusion of clean/green technology: Can patent commons help? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2013, 66, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, G. Manufacturer vs. consumer subsidy with green technology investment and environmental concern. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaieh, M.; Lashin, M.; Elbably, A. Going green in architectural education: An urban living lab experiment for a graduation green design studio in Saint Catherine, Egypt. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonnard, D.R.; Allen, D.T.; Nguyen, N.; Austin, S.W.; Hesketh, R. Green engineering education through a US EPA/Academia collaboration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5453–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, K.; Xue, B.; Fujita, T. Creating a “green university” in China: A case of Shenyang University. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 61, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, D.; Wu, W. Policies for green design. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1998, 36, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, T.; Runkel, M. Efficient policies for green design in a vintage durable good model. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2005, 30, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C. Businesses, green groups and the media: The role of non-governmental organizations in the climate change debate. Int. Aff. 2001, 77, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, C.L.; Stafford, E.R. Green alliances: Building new business with environmental groups. Long Range Plan. 1997, 30, 184–196, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der-Petrossian, B.; Johansson, E. Construction and Environment-Improving energy efficiency. Build. Issues 2000, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Schonewald-Cox, C.M.; Bayless, J.W. The boundary model: A geographical analysis of design and conservation of nature reserves. Biol. Conserv. 1986, 38, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonheur, N.; Lane, B.D. Natural resources management for human security in Cambodia’s Tonle Sap Biosphere Reserve. Environ. Sci. Policy 2002, 5, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. Analysis of the artistic effect of garden plant landscaping in urban greening. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autixier, L.; Mailhot, A.; Bolduc, S.; Madoux-Humery, A.S.; Galarneau, M.; Prévost, M.; Dorner, S. Evaluating rain gardens as a method to reduce the impact of sewer overflows in sources of drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camagni, R.; Capello, R.; Nijkamp, P. Towards sustainable city policy: An economy-environment technology nexus. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 24, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, W. How does environmental regulation affect haze pollution governance?—An empirical test based on Chinese provincial panel data. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, S.H. A crisis in governance: Urban solid waste management in Bangladesh. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Tan, R.R.; Siriban-Manalang, A.B. Sustainable consumption and production for Asia: Sustainability through green design and practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Fraser, I. On the flexibility of optimal policies for green design. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2001, 18, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.; Sovacool, B.K. Rethinking the future low-carbon city: Carbon neutrality, green design, and sustainability tensions in the making of Masdar City. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 62, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, H.W.; Lee, S.E. Demonstration intelligent building—A methodology for the promotion of total sustainability in the built environment. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T. Efficient vehicles versus efficient transportation. Comparing transportation energy conservation strategies. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Mi, Z.; Zhu, D.; Liu, G. Characterizing the stocks, flows, and carbon impact of dockless sharing bikes in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y. Assessing determinants of industrial waste reuse: The case of coal ash in the United States. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stijepovic, M.Z.; Linke, P. Optimal waste heat recovery and reuse in industrial zones. Energy 2011, 36, 4019–4031. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, R. Developers, regeneration and sustainability issues in the reuse of vacant industrial buildings. Build. Res. Inf. 1999, 27, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, C.; Wong, F.K.; Hui, E.C.; Shen, L.Y. Strategic assessment of building adaptive reuse opportunities in Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovea, M.D.; Ibáñez-Forés, V.; Pérez-Belis, V.; Quemades-Beltrán, P. Potential reuse of small household waste electrical and electronic equipment: Methodology and case study. Waste Manag. 2016, 53, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truttmann, N.; Rechberger, H. Contribution to resource conservation by reuse of electrical and electronic household appliances. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2006, 48, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.; Butler, D.; Fewkes, A. Water saving potential of domestic water reuse systems using greywater and rainwater in combination. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Schmidt, T.S. Managing tradeoffs in green industrial policies: The role of renewable energy policy design. World Dev. 2019, 122, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelen, D.; Manshoven, S.; Peeters, J.R.; Vanegas, P.; D’Haese, N.; Vrancken, K. A multidimensional indicator set to assess the benefits of WEEE material recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelný, I.; Michálková, D.; Kruliš, Z. An efficient method of material recycling of municipal plastic waste. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 85, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemeš, J.J. Industrial water recycle/reuse. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, B.; Laine, A.; Parsons, S.; Stephenson, T.; Judd, S. Technologies for domestic wastewater recycling. Urban Water 2000, 1, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.W. Fuzzy logic based decision model for product design. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 1998, 21, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partovi, F.Y. An analytic model for locating facilities strategically. Omega 2006, 34, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Yi, P.T. Character analysis of linear dimensionless methods. Stat. Res. 2008, 25, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, D.I. Modeling international trends in energy efficiency. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.; Palma, A. Technology Invention and Diffusion in Residential Energy Consumption. A Stochastic Frontier Approach. Stoch. Front. Approach 2015. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2662362 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Otsuka, A.; Goto, M. Estimation and determinants of energy efficiency in J apanese regional economies. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2015, 7, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Folmer, H.; Ji, M.; Tang, J. Energy efficiency in the Chinese provinces: A fixed effects stochastic frontier spatial Durbin error panel analysis. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2017, 58, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebali, E.; Essid, H.; Khraief, N. The analysis of energy efficiency of the Mediterranean countries: A two-stage double bootstrap DEA approach. Energy 2017, 134, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Long, H. A stochastic frontier analysis of energy efficiency of China’s chemical industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Yu, Y. Modelling energy efficiency in China: A fixed-effects panel stochastic frontier approach. Econ. Political Stud. 2018, 6, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Adams, S. Renewable energy, nuclear energy, and environmental pollution: Accounting for political institutional quality in South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
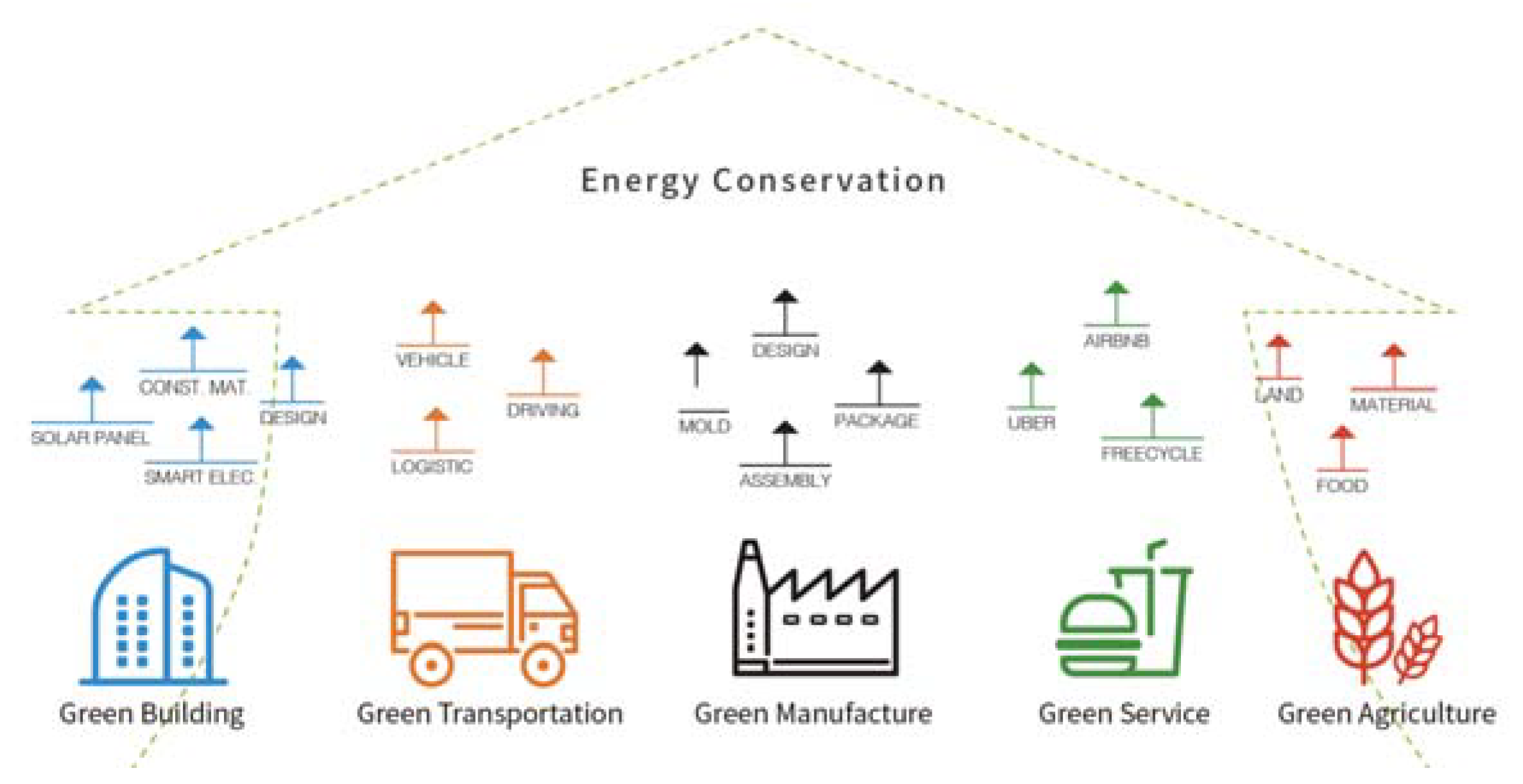
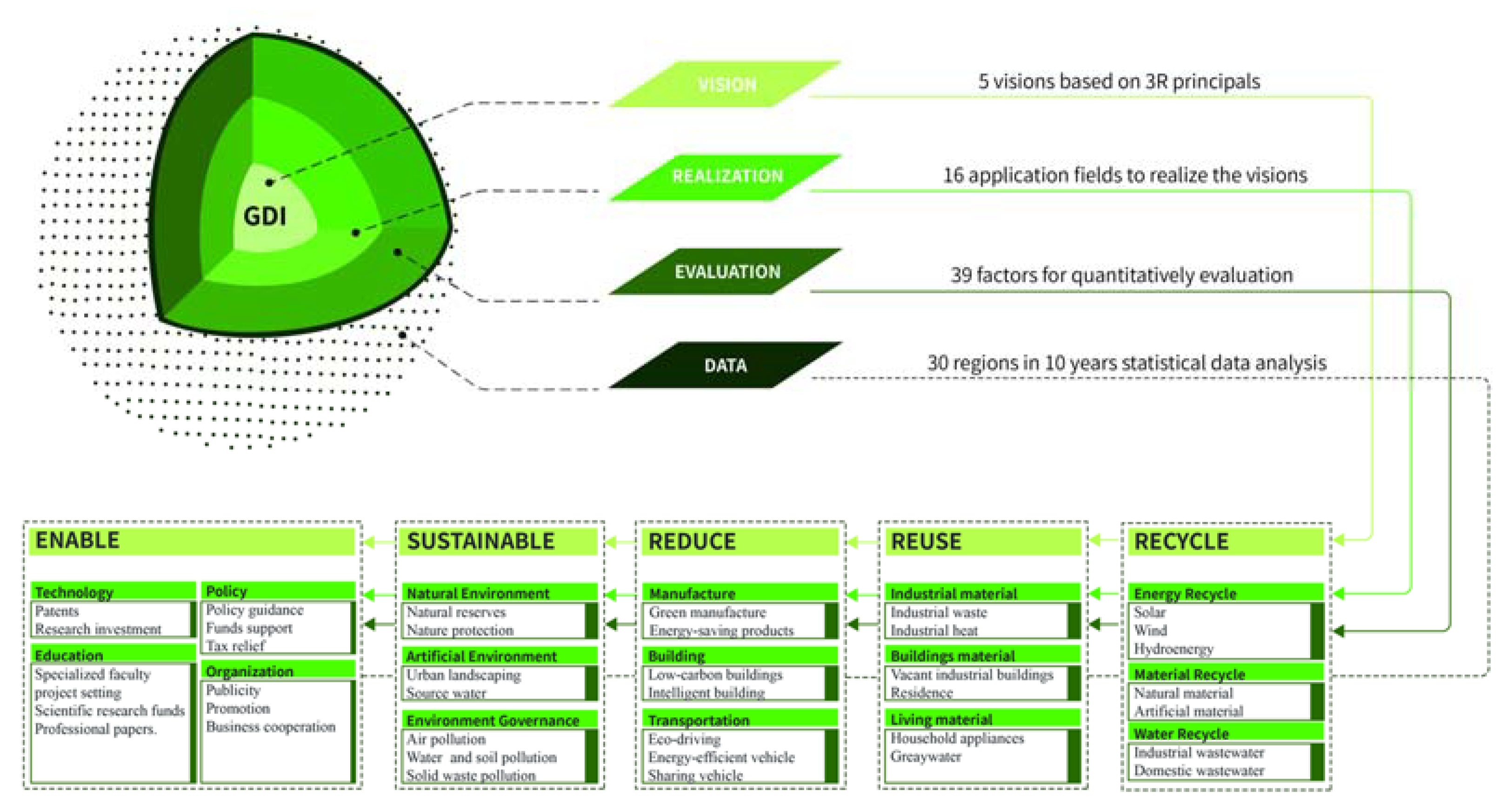
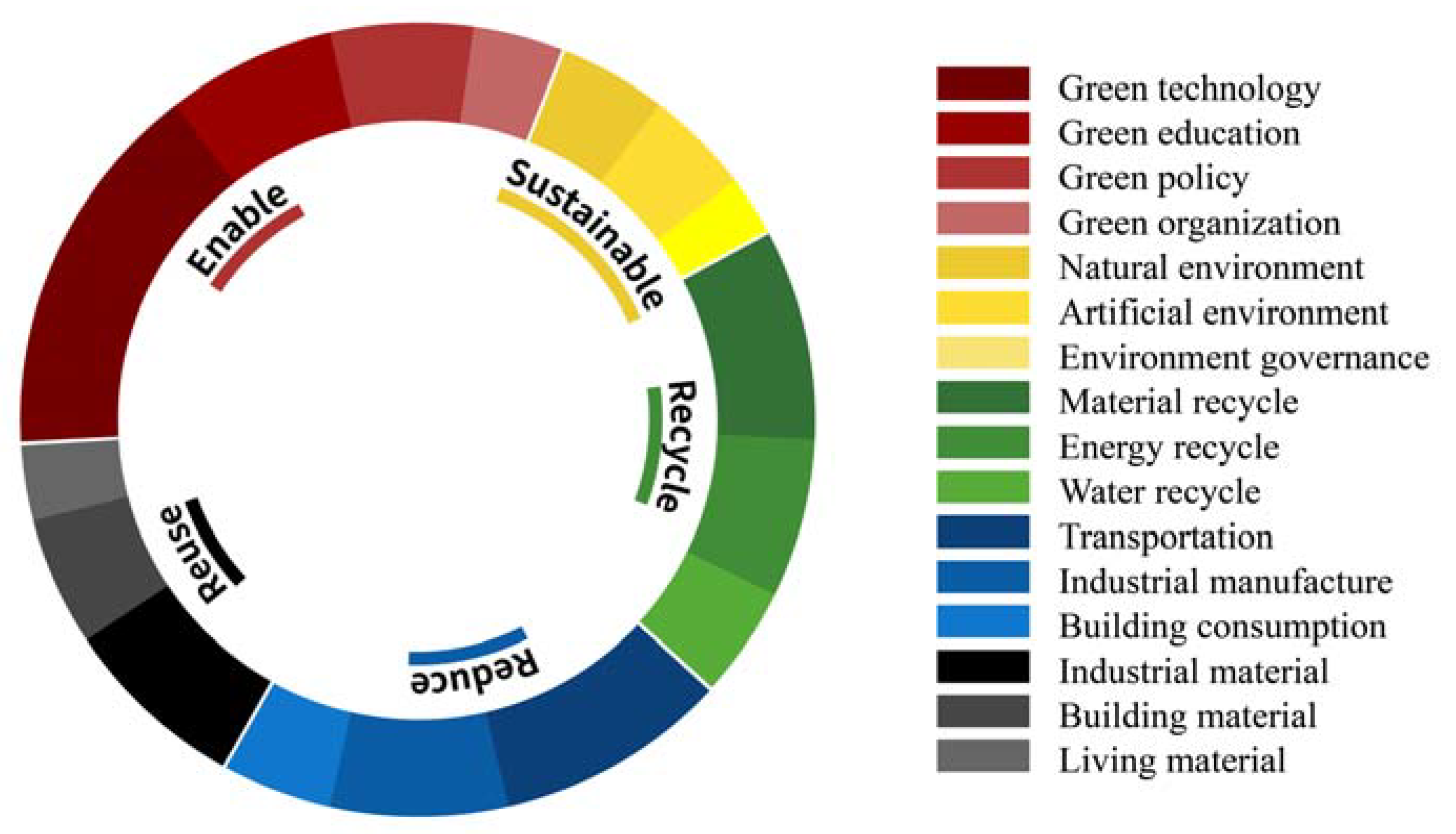


| Vision Level | Realization Level | Weights |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | Green technology | 0.139 |
| Green education | 0.068 | |
| Green policy | 0.063 | |
| Green organization | 0.049 | |
| Sustainable | Natural environment | 0.045 |
| Artificial environment | 0.045 | |
| Environment governance | 0.022 | |
| Recycle | Energy recycle | 0.067 |
| Material recycle | 0.082 | |
| Water recycle | 0.048 | |
| Reduce | Reduce the consumption of industrial manufacture | 0.075 |
| Reduce the consumption of building | 0.043 | |
| Reduce the consumption of transportation. | 0.094 | |
| Reuse | Reuse building material | 0.035 |
| Reuse industrial material | 0.078 | |
| Reuse living material | 0.048 |
| Year | N * | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | NGDIn < Mean |
| 2006 | 30 | 0.67 (Gansu) | 6.66 (Beijing) | 1.59 | 23 |
| 2007 | 30 | 0.79 (Gansu) | 7.53 (Beijing) | 1.83 | 23 |
| 2008 | 30 | 0.95 (Guizhou) | 9.20 (Beijing) | 2.27 | 22 |
| 2009 | 30 | 1.11 (Gansu) | 10.14 (Beijing) | 2.65 | 22 |
| 2010 | 30 | 1.36 (Gansu) | 10.34 (Beijing) | 2.96 | 21 |
| 2011 | 30 | 1.57 (Guizhou) | 11.43 (Beijing) | 3.63 | 21 |
| 2012 | 30 | 1.76 (Qinghai) | 14.51 (Beijing) | 4.26 | 21 |
| 2013 | 30 | 1.92 (Qinghai) | 15.48 (Beijing) | 4.80 | 19 |
| 2014 | 30 | 2.00 (Qinghai) | 16.10 (Beijing) | 4.85 | 22 |
| 2015 | 30 | 2.29 (Shanxi) | 17.54 (Beijing) | 5.66 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, S.; Zou, C. Assessing Transformation Practices in China under Energy and Environmental Policy Goals: A Green Design Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042948
Yi S, Zou C. Assessing Transformation Practices in China under Energy and Environmental Policy Goals: A Green Design Perspective. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042948
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Siliang, and Chuyuan Zou. 2023. "Assessing Transformation Practices in China under Energy and Environmental Policy Goals: A Green Design Perspective" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042948
APA StyleYi, S., & Zou, C. (2023). Assessing Transformation Practices in China under Energy and Environmental Policy Goals: A Green Design Perspective. Sustainability, 15(4), 2948. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042948






