Response of Soil Erosion to Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Changes in a High-Mountain Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Snowmelt Runoff Simulation
2.2.2. RUSLE Model
Rainfall Runoff Erosivity Factor
Soil Erodibility Factor
Slope Length and Steepness Factor
Cover Management Factor
Support Practice Factor
2.2.3. Detrended Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variation of Precipitation, Air Temperature, and NDVI
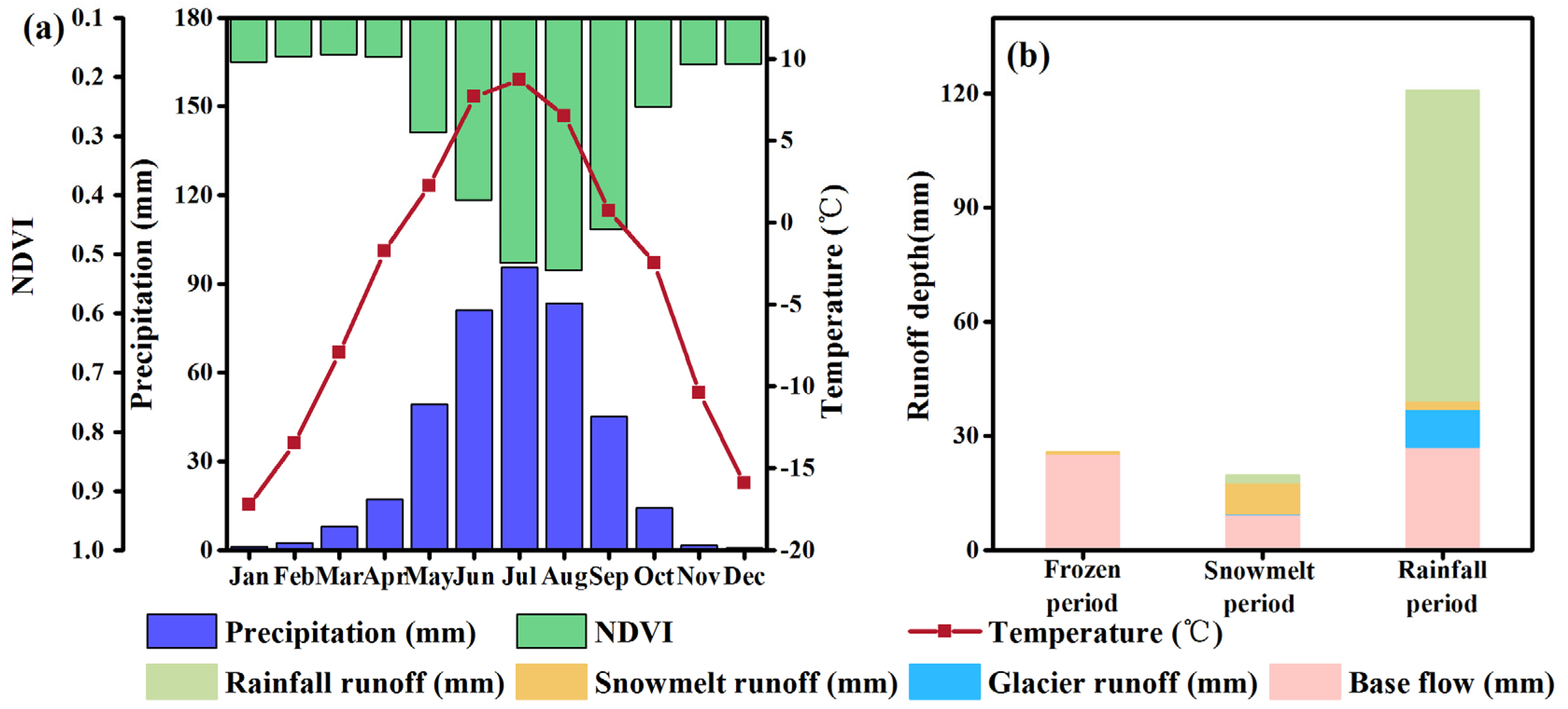
3.1.1. Seasonal Variation of Precipitation, Air Temperature, and NDVI
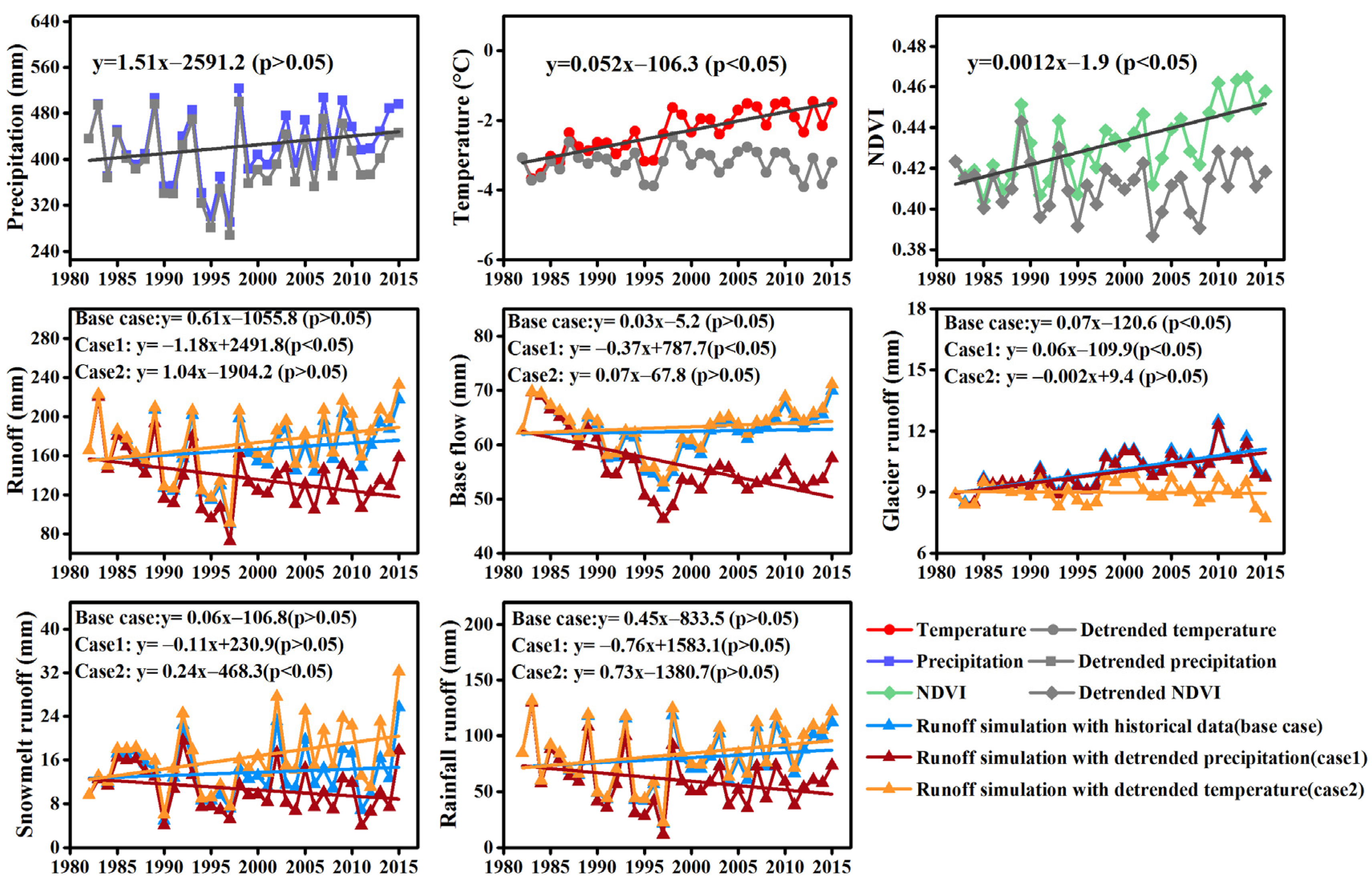
3.1.2. Changing Trends of Precipitation, Air Temperature, and NDVI during 1982–2015
3.2. Hydrological Modeling and Variation of Runoff
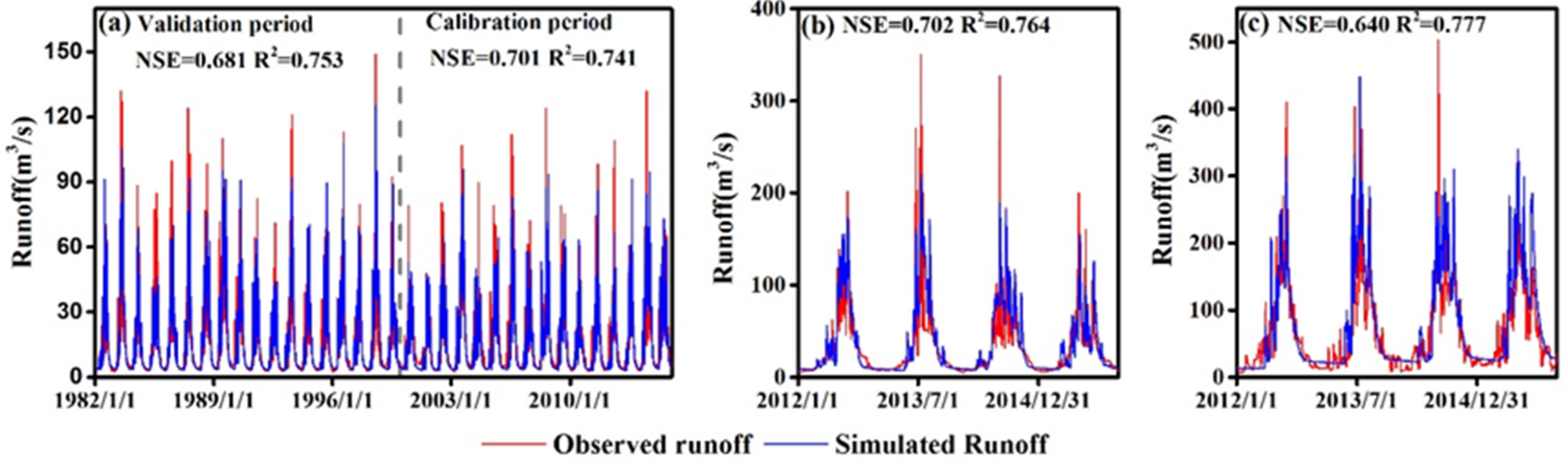
3.2.1. Model Calibration and Validation
3.2.2. Variation of Total Runoff and Runoff Components
3.3. Variation of RUSLE Factors and Soil Erosion Rate
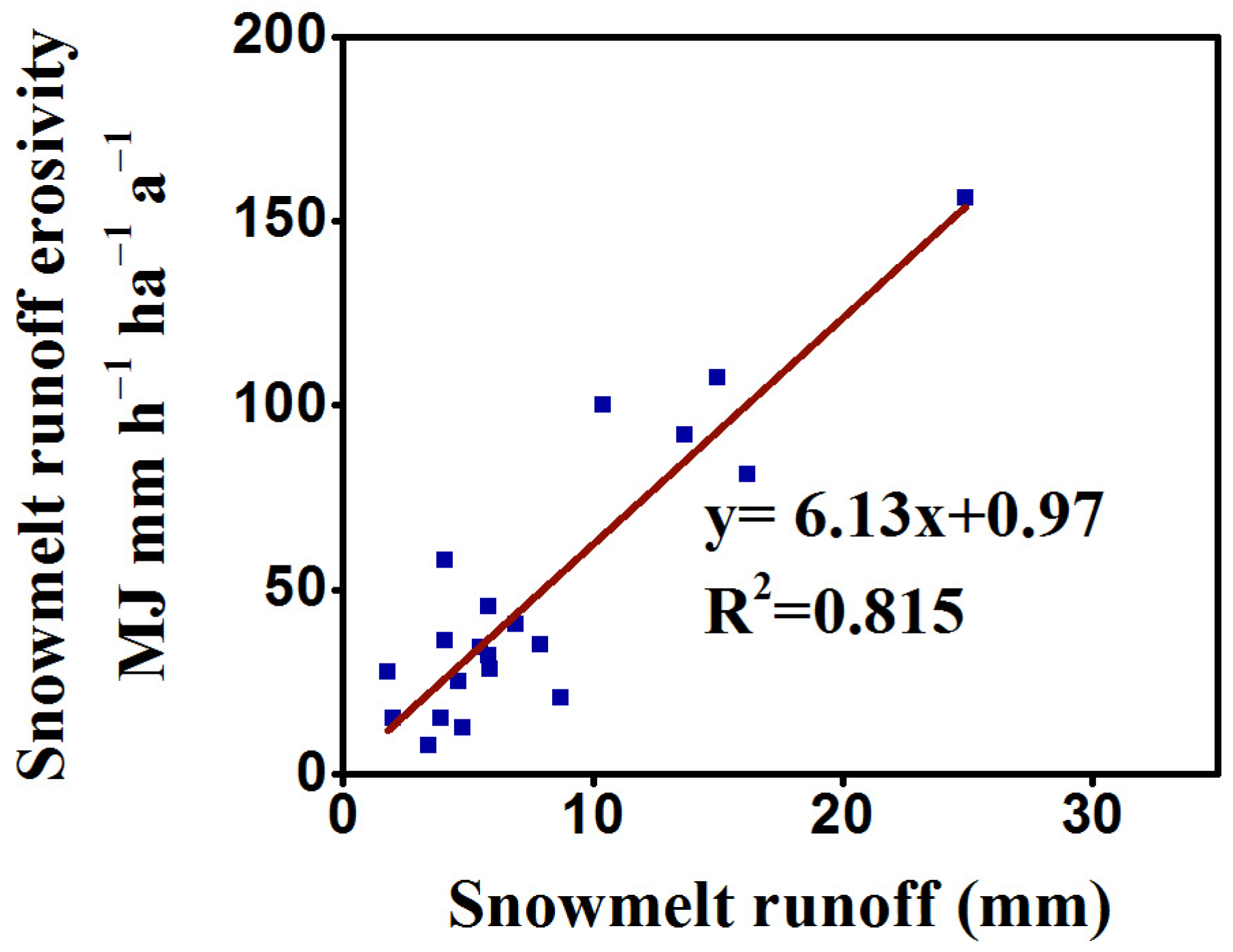
3.3.1. Snowmelt Runoff Erosivity during Snowmelt Period
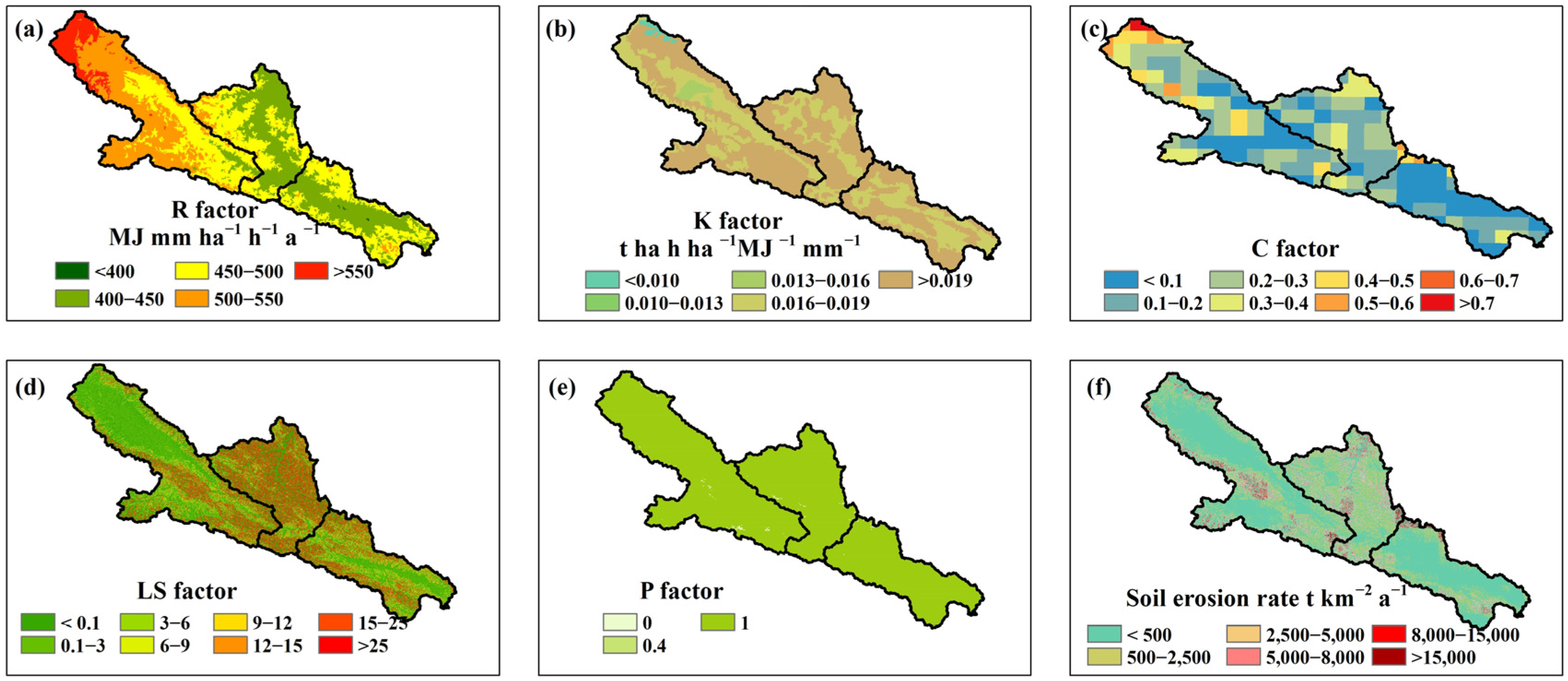
3.3.2. Spatial Distribution of RUSLE Factors and Soil Erosion Rate
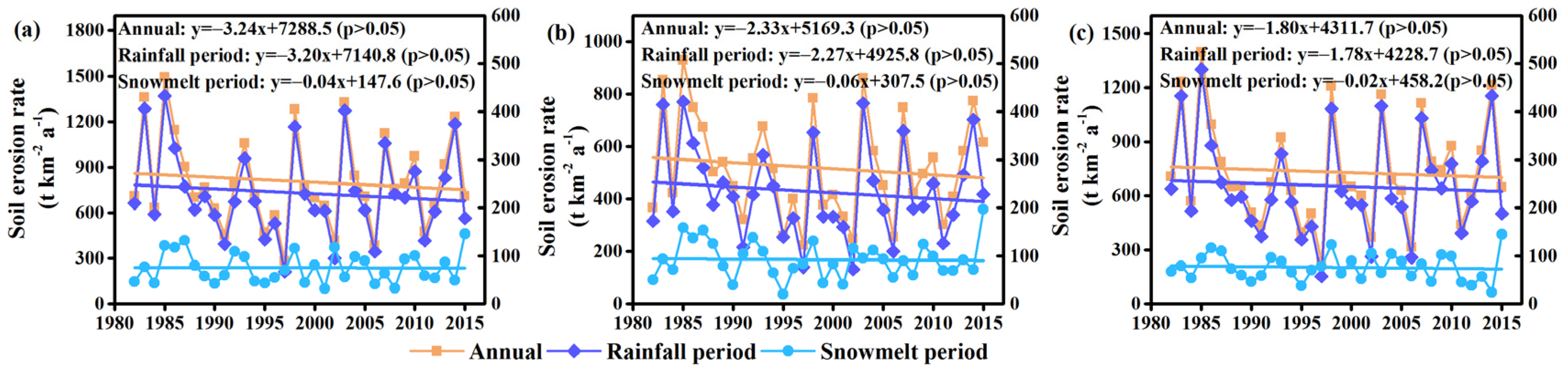
3.3.3. Changing Trends of RUSLE Factors and Soil Erosion Rate from 1982 to 2015
3.3.4. Influence of Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Change on Soil Erosion Rate
4. Discussions
4.1. Uncertainties in Soil Erosion Assessment in High-Mountain Areas
4.2. Implications of Soil Erosion Control
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Cao, W.; Guan, J.; Wang, Z. Dependence of the sediment delivery ratio on scale and its fractal characteristics. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 30, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, Z.; Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Assessment of soil erosion characteristics in response to temperature and precipitation in a freeze-thaw watershed. Geoderma 2018, 328, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Juying, J.; Bingzhe, T.; Binting, C.; Hang, L. Response of runoff and soil erosion to erosive rainstorm events and vegetation restoration on abandoned slope farmland in the Loess Plateau region, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.; Skidmore, A.K.; Toxopeus, A. Soil erosion and sediment yield and their relationships with vegetation cover in upper stream of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 409, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildhaber, Y.S.; Bänninger, D.; Burri, K.; Alewell, C. Evaluation and application of a portable rainfall simulator on subalpine grassland. Catena 2012, 91, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Yin, S.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Y. Increasing trends in rainfall-runoff erosivity in the Source Region of the Three Rivers, 1961–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D. Model-based assessment soil loss by wind and water erosion in China’s Loess Plateau: Dynamic change, conservation effectiveness, and strategies for sustainable restoration. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 172, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, P.; Fries, A.; Mejía, D.; Burneo, J.; Ruíz-Sinoga, J.; Cerdà, A. Effects of climate, land cover and topography on soil erosion risk in a semiarid basin of the Andes. Catena 2016, 140, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadić, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; He, C.; Burnham, M.; Zhang, L. Evaluating the coupling effects of climate aridity and vegetation restoration on soil erosion over the Loess Plateau in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, X.; Zeng, C.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Immerzeel, W. Recent stepwise sediment flux increase with climate change in the Tuotuo River in the central Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langbein, W.B.; Schumm, S.A. Yield of sediment in relation to mean annual precipitation. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1958, 39, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, P.M.; Heras, M.M.-D.L. Ecogeomorphic coevolution of semiarid hillslopes: Emergence of banded and striped vegetation patterns through interaction of biotic and abiotic processes. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Yetemen, O.; Saco, P.M.; Rodriguez, J.F.; Kumari, N.; Chun, K.P. Influence of orographic precipitation on coevolving landforms and vegetation in semi-arid ecosystems. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2022, 47, 2846–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.; Richter, G.; Bernsdorf, B.; Schmidt, R.-G.; Burney, J. Measurement of rill erosion by snowmelt on potato fields under rotation in Prince Edward Island (Canada). Can. J. Soil Sci. 1998, 78, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollesch, G.; Sukhanovski, Y.; Kistner, I.; Rode, M.; Meissner, R. Characterization and modelling of the spatial heterogeneity of snowmelt erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2005, 30, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K. Estimation of soil erosion in a rain shadow river basin in the southern Western Ghats, India using RUSLE and transport limited sediment delivery function. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agricultural Handbook no. 537; USDA, Science and Education Administration: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 1978; pp. 285–291.
- Gitas, I.Z.; Douros, K.; Minakou, C.; Silleos, G.N.; Karydas, C.G. Multi-temporal soil erosion risk assessment in N. Chalkidiki using a modified USLE raster model. EARSel Eproceedings 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Montanarella, Soil Erosion Risk: Assessment in Europe; European Soil Bureau, European Communities, EUR 19044 EN, 2000.
- Lin, W.-T.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chou, W.-C. Assessment of vegetation recovery and soil erosion at landslides caused by a catastrophic earthquake: A case study in Central Taiwan. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, X.; Overeem, I.; Walling, D.E.; Syvitski, J.; Kettner, A.J.; Bookhagen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Sturmlechner, I.; et al. Exceptional increases in fluvial sediment fluxes in a warmer and wetter High Mountain Asia. Science 2021, 374, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Shao, Q. Impacts of projected climate change on runoff in upper reach of Heihe River basin using climate elasticity method and GCMs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, H. Integrated study of the water–ecosystem–economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Niu, J.; Kang, S.; Adeloye, A.J.; Du, T. Crop production in the Hexi Corridor challenged by future climate change. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, F.; Tian, Y.; Han, F.; Gao, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Novel hybrid coupling of ecohydrology and socioeconomy at river basin scale: A watershed system model for the Heihe River basin. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 141, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, D. Study on rainfall-runoff erosivity index in Northeastern China. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, S. Impacts of climate change on the hydrological regime of the Koshi river basin in the Himalayan region. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeckman, J.; Nepal, S.; Chevallier, P.; Camensuli, G.; Delclaux, F.; Boone, A.; De Rouw, A. Comparing the ISBA and J2000 approaches for surface flows modelling at the local scale in the Everest region. J. Hydrol. 2018, 569, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatakho, R.; Talchabhadel, R.; Thapa, B.R. Evaluation of different precipitation inputs on streamflow simulation in Himalayan River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, D. Die Berechnung des Abflusses aus einer Schneedecke. Anal. Und Berechn. Oberird. Abflüsse 1980, 46, 97–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, S.; Khatiwada, K.R.; Pradhananga, S.; Kralisch, S.; Samyn, D.; Bromand, M.T.; Jamal, N.; Dildar, M.; Durrani, F.; Rassouly, F.; et al. Future snow projections in a small basin of the Western Himalaya. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, M.; Salzmann, N.; Stoffel, M.; Kulkarni, A.V. Missing (In-Situ) snow cover data hampers climate change and runoff studies in the Greater Himalayas. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468–469, S60–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Dou, S.; Deng, X.; Xue, X.; Wang, T. Assessment of wind and water erosion risk in the watershed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Yoder, D.C.; Lightle, D.T.; Dabney, S.M. Universal Soil Loss Equation and Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. In Handbook of Erosion Modelling; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 135–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N. EPIC-erosion/productivity impact calculator: 1, Model Documentation. USDA Technol. Bull. 1759, 1990, 235. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Oh, C.; Jeon, S.; Jung, H.; Choi, C. Soil erosion risk in Korean watersheds, assessed using the revised universal soil loss equation. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Zhou, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X. Calculation tool of topographic factors. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 13, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Sammons, G. Vegetation dynamics and erosion modeling using remotely sensed data (MODIS) and GIS. In Proceedings of the Tenth Biennial USDA Forest Service Remote Sensing Applications Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 5–9 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, W.; Wen, Z. Research on Soil Erosion Vegetation Factor Index Based on Community Structure. J. Soil Water Conservation 2008, 22, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agric. Handb. 1996, 703, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Naqvi, H.R.; Mallick, J.; Devi, L.M.; Siddiqui, M.A. Multi-temporal annual soil loss risk mapping employing Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model in Nun Nadi Watershed, Uttrakhand (India). Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4045–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Trends in pan evaporation and reference and actual evapotranspiration across the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Cairang, L. The impacts of climate change and land cover/use transition on the hydrology in the upper Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cong, Z. A distributed scheme developed for eco-hydrological modeling in the upper Heihe River. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Terrestrial Water Cycle Scheme in Heihe River Basin and Its Responses to Human Activities; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, C.Y. Annual base flow change and its causes in the upper reaches of Heihe River. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, X. Tracing Snowmelt Paths in an Integrated Hydrological Model for Understanding Seasonal Snowmelt Contribution at Basin Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 8874–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.G.; Adam, M.A. The impact of vegetative cover type on runoff and soil erosion under different land uses. Catena 2010, 81, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Fu, S.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Jagirani, M.D.; Zeng, C. Assessment of soil erosion risk and its response to climate change in the mid-Yarlung Tsangpo River region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Czymzik, M.; Yu, Z.; Aldahan, A.; Wang, J.; Yi, P.; Hou, X.; Guo, S.; Zheng, M. Tendency of soil erosion dynamics by coupling radioisotopes and RUSLE model on the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau in response to climate warming and human activity. Catena 2023, 223, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, P.M.; Willgoose, G.R.; Hancock, G.R. Eco-geomorphology of banded vegetation patterns in arid and semi-arid regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, M.; Puigdefábregas, J. Effects of spatially structured vegetation patterns on hillslope erosion in a semiarid Medi-terranean environment: A simulation study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Avissar, R.; Roy, S.B.; Barrett, D.J.; Cook, C.W.; Farley, K.A.; le Maitre, D.C.; McCarl, B.A.; Murray, B.C. Trading Water for Carbon with Biological Carbon Sequestration. Science 2005, 310, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. Changes in satellite-derived vegetation growth trend in temperate and boreal Eurasia from 1982 to 2006. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3228–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjursen, H.; Michelsen, A.; Holmstrup, M. Effects of freeze–thaw cycles on microarthropods and nutrient availability in a sub-Arctic soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 28, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. Soil erodibility and processes of water erosion on hillslope. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallet, B. A theoretical model of glacial abrasion. J. Glaciol. 1979, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.J.; Swift, D.A.; Kirkbride, M.P.; Knight, P.G.; Waller, R.I. The empirical basis for modelling glacial erosion rates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Wang, J.; Harbor, J.M.; Wang, F.; Zou, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, X. The relative efficiency and influence of glacial and fluvial erosion on Tibetan Plateau landscapes. Geomorphology 2020, 352, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbanshi, J.; Bhattacharya, S. Assessment of soil erosion, sediment yield and basin specific controlling factors using RUSLE-SDR and PLSR approach in Konar river basin, India. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Moran, C.; Prosser, I.P. Modelling sediment delivery ratio over the Murray Darling Basin. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Grauso, S. An improved correlation model for sediment delivery ratio assessment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mchugh, M.; Wood, G.; Walling, D.; Morgan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Anthony, S.; Hutchins, M. Prediction of Sediment Delivery to Watercourses from Land; National Soil Resources Institute, Cranfield University: Bedford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Borselli, L.; Cassi, P.; Torri, D. Prolegomena to sediment and flow connectivity in the landscape: A GIS and field numerical assessment. Catena 2008, 75, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil science. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollesch, G.; Kistner, I.; Meissner, R.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Modelling of snowmelt erosion and sediment yield in a small low-mountain catchment in Germany. Catena 2006, 68, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Xue, B.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.; Zuo, D.; Xu, Z. Spatial heterogeneity of changes in vegetation growth and their driving forces based on satellite observations of the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
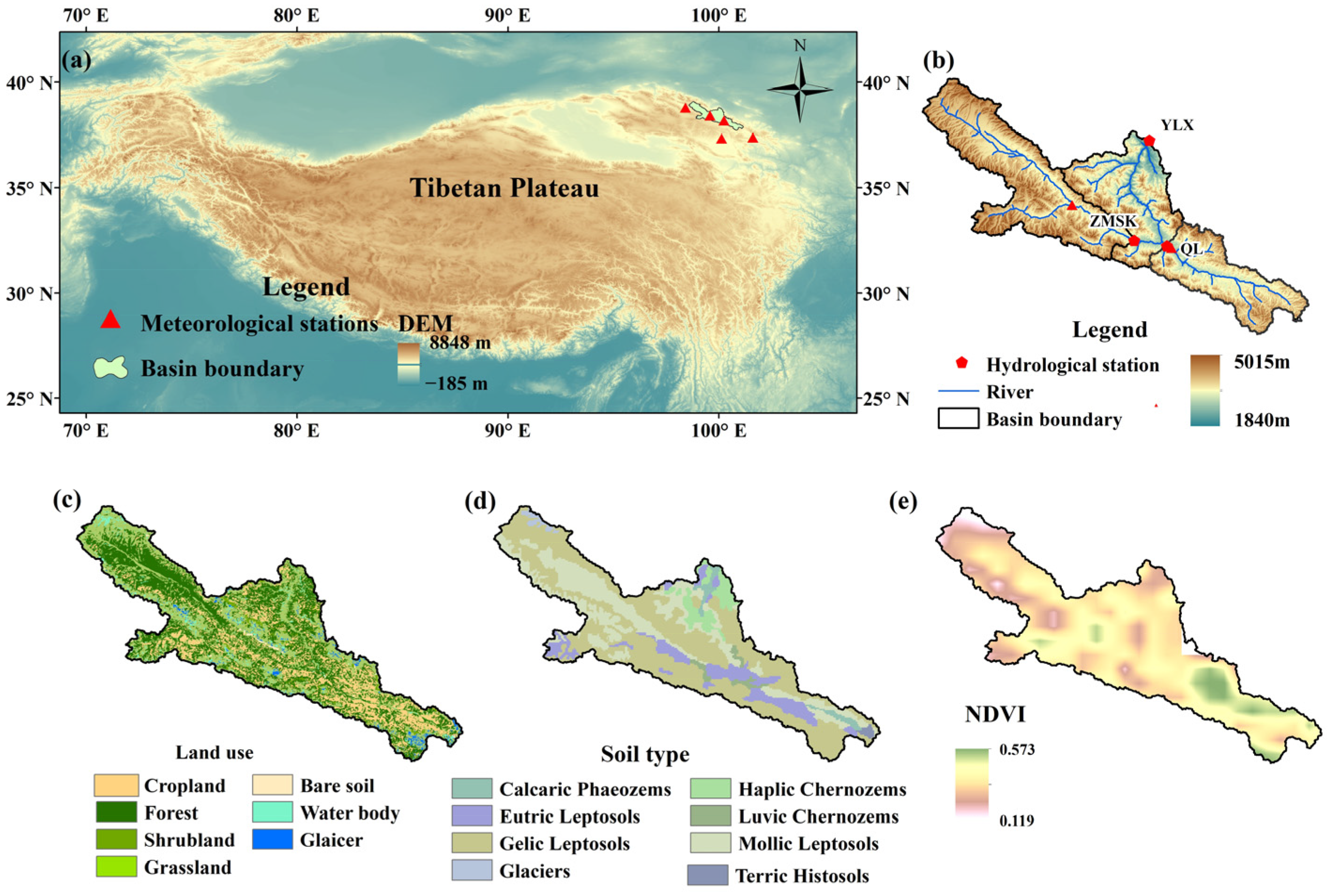



| Station | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | River | Available Runoff | Available Sediment Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qilian | 100.25 | 38.18 | BBR | 1982–2015 | 2000–2015 |
| Zhamashike | 90.99 | 38.23 | YNGR | 2012–2015 | 2012–2015 |
| Yingluoxia | 100.11 | 38.76 | UHR | 2012–2015 | - |
| Grade | Criterion of Erosion Rate *, # | Area (km2) | Soil Loss (105t a−1) | Soil Loss Percent (%) | Area Percent below 4000 m (%) | Area Percent above 4000 m (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slight | <500 | 6893.5 | 3.8 | 4.8 | 76.3 | 23.7 |
| Light | 500–2500 | 1930.6 | 23.9 | 30.1 | 72.2 | 27.8 |
| Moderate | 2500–5000 | 618.1 | 21.7 | 27.4 | 50.8 | 49.2 |
| Severe | 5000–8000 | 275.1 | 17.3 | 21.8 | 36.4 | 63.6 |
| Very severe | 8000–15,000 | 116.7 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 26.1 | 73.9 |
| Extreme | >15,000 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 12.9 | 87.1 |
| Case | Basin | Change in Soil Erosion Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Rainfall Period | Snowmelt Period | ||
| Detrended analysis of precipitation | UHRB | −11.2% | −11.9% | −4.00% |
| BBRB | −12.9% | −14.3% | −6.50% | |
| YNGRB | −10.7% | −11.2% | −5.20% | |
| Detrended analysis of temperature | UHRB | 7.20% | 4.80% | 30.7% |
| BBRB | 9.10% | 4.20% | 31.5% | |
| YNGRB | 7.40% | 4.90% | 30.3% | |
| Detrended analysis of NDVI | UHRB | 11.7% | 11.8% | 10.7% |
| BBRB | 13.1% | 13.4% | 12.0% | |
| YNGRB | 10.8% | 11.0% | 10.5% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, G.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Tang, H.; Zhao, G.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Response of Soil Erosion to Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Changes in a High-Mountain Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043220
Wang L, Zhang F, Wang G, Zeng C, Chen Y, Shi X, Tang H, Zhao G, Xu C, Li X. Response of Soil Erosion to Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Changes in a High-Mountain Basin. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043220
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Fan Zhang, Guanxing Wang, Chen Zeng, Yao Chen, Xiaonan Shi, Handuo Tang, Guangju Zhao, Chongyu Xu, and Xin Li. 2023. "Response of Soil Erosion to Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Changes in a High-Mountain Basin" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043220
APA StyleWang, L., Zhang, F., Wang, G., Zeng, C., Chen, Y., Shi, X., Tang, H., Zhao, G., Xu, C., & Li, X. (2023). Response of Soil Erosion to Climate and Subsequent Vegetation Changes in a High-Mountain Basin. Sustainability, 15(4), 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043220







