1. Introduction
In Western societies, death and death practices are a highly sensitive area, rendering taboo most discussions surrounding the topic. Further, death is a social matter involving the passing of an individual, bidding farewell to loved ones and acknowledging their lives, and potential spiritual and religious beliefs concerning the afterlife [
1]. As the global population and, consequently, deaths increase, it is important to progress towards more sustainable ways of passing, especially considering the negative environmental impact of traditional death practices.
It is important to bear in mind that rituals and practices surrounding death vary around the world, with different societies and cultures having their own methods and practices. This paper aims to set in motion a larger debate around sustainable death practices but will take a case study approach as a first step, focusing on death practices within the United Kingdom (UK). Although many of the learnings are transferable across cultures, our research background, analysis, and understanding are firmly grounded within the dominant death practices of the UK. The UK was chosen for this case study, firstly, because a large share (around 50%) of the population does not identify with any religion [
2,
3] and, secondly, many of the Christianity-based death practices such as burials and cremation are also found across different religions and cultures [
4,
5]. Nonetheless, there are limitations to our findings, and the recommendations will need to be adjusted carefully and in a culturally sensitive manner to other cultural contexts.
The goals of this paper were twofold—firstly, to sketch a viable intervention designed to incite much-needed social change around death practices in the UK. With this paper, we want to spur conversation around the topic of death, hopefully increasing the overall demand for green death practices to help address the environmental problems arising from traditional death practices in the UK.
Secondly, we aimed to detail how multilayered installation design (MID), a lean and streamlined approach based on activity theory [
6] and installation theory [
7], can support the development of effective and detailed interventions. This paper builds on our in-depth analysis of sustainable death practices in the UK to develop a plan for a fully fledged intervention, including the sketch of a business model and a mock-up communication campaign involving stakeholders. Using the generative and creative power of the MID approach, this paper illustrates for pedagogical purposes how we can develop solutions for real-world problems and concretely demonstrates the usefulness and operational validity of the MID approach with an example.
This paper will proceed in the following way: First, we will present a discussion of the history of death practices in the UK, as well as an overview of the theoretical literature pertinent to the topic. Second, we will briefly outline our change model. We will then present our analysis of relevant stakeholders and installations for green burials in depth. Finally, we will present our proposed interventions and discuss our recommendations, as well as the broader implications of the project.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Death Practices in the UK
Death rituals are a way of expressing love and grief over losing a close person in a way that is meaningful to both the deceased and their loved ones [
8]. As such the varying rituals hold important value across societies, and funerals and funeral services are among the oldest rituals known to humans [
9]. Here members of the community, friends and family come together to commemorate and memorialise the person who has passed [
8,
9]. Though the context of funerals is changing, with more and more services being performed for the unaffiliated outside of church, they still remain a crucial part of saying goodbye in the Western world [
9].
A component of funerals is specific practices such as burials or cremations. These practices are embedded in religious, cultural, and social structures and carry symbolic meaning. Death practices in the UK have changed over time, with one of the oldest practices being burials [
10]. In the past decade, cremations have become equally if not more popular [
10].
Burials or cremations are accepted across many religions [
4,
5] and are typical of Christian funerals. Christian death practices remain steeped in rituals and traditions in the UK, with, for example, the funeral procession, wearing black clothing in mourning, and flowers [
10]. While Christianity has traditionally been the dominant religion in the UK, more recent surveys have shown an increase in individuals who are members of other religions, as well as trends indicating that those who do not hold any religion now represent nearly the majority of the UK population [
2,
3]. While many funeral traditions and rituals still hold strong today, a broad shift in death practices in the UK can be observed as well, from small changes such as a growing number of individuals replacing the use of flowers with charitable contributions, to larger changes with more individuals treating funerals as a ‘celebration of life’ and taking the focus away from death. In the UK, post-funeral pub gatherings are popularised, as well as the favourite colour of the deceased being worn and their favourite song being played [
10].
Alongside these changes to death practices, there is a growing demand for ‘green goodbyes’, with 72% of cemeteries reporting an increased demand for green burials [
11] as more people are becoming aware of the negative environmental implications of traditional death practices (burial and cremation) [
10].
2.2. Environmental Impact of Death Practices
The environmental costs of death practices are rarely discussed, and the reality is quite shocking. The environmental impact of modern, Western death practices is threefold. Firstly, they require a vast number of natural, potentially virgin resources such as water, wood, and land. Secondly, they may harm the ecological system with the chemicals employed. Thirdly, they produce a large amount of CO2.
Burials require a vast number of natural resources to produce coffins and headstones. Figures from the United States highlight the scale of the issue. The amount of wood needed to produce enough coffins per year equates to building 4.5 million homes. Further, 1.6 million tons of reinforced concrete and over 100,000 tons of steel are needed to create headstones and coffins annually [
12]. Another example can be found in the practice of embalming, a chemical process using a carcinogenic formaldehyde-based solution to preserve the body for open-casket ceremonies or for transport [
13]. Groundwater seepage occurs due to the depth at which burials take place. With bodies deteriorating deep underground, the heavy metals and toxins released cannot be filtered out by the soil and eventually find their way into the groundwater. In addition to this, land management is another key issue, as over half of the UK’s cemeteries will be full by 2030 [
14]. Notably, most available data come from the US, with figures from the UK being not readily accessible. Although a simple, direct comparison should not be drawn, these numbers highlight the scale of the issue at hand.
In England, cremations make up around 78% of death practices nowadays [
15]. They require a huge amount of energy to fully burn the body. One cremation requires 285 kWh of gas and 15 kWh of electricity, equivalent to the domestic energy use of one person for a whole month [
16]. In addition, one cremation produces over 240 kg of carbon dioxide, with 110 kg coming from the body alone, the same as a 500-mile car journey [
16]. Due to the heavy metals that are released from the body, scrubbing devices are required to filter the gases emitted. The maintenance demands of these devices are extensive, however, and cases have been found where the gases were not processed correctly [
17].
2.3. Green Death Practices
Green death practices are still a nascent field, but they could offer solutions to the problems with current passing practices discussed above. Green death practices can be defined as “a statement of personal values for those who seek to minimise their impact on the local and global environment” [
18].
While modern and complex approaches such as decomposers that turn the body into fertile soil [
19] and fungi bodysuits that decompose the body to create new life are still under development [
20], aquamation, which yields the same results as cremation but uses pressurised water, is newly available and growing in popularity [
21,
22]. The most common green death practice is a simple burial that replaces the casket with a linen sheet and swaps out the headstone for a tree sapling that goes on to create new life from the deceased [
16]. To mitigate the environmental impact of modern Western death practices, it is advisable to increase the popularity of these green death practices across the population.
3. Change Model
The analysis of death practices in the UK as well as the design of the intervention applied the multilayered installation design approach [
23] (MID). Following MID, we used activity theory [
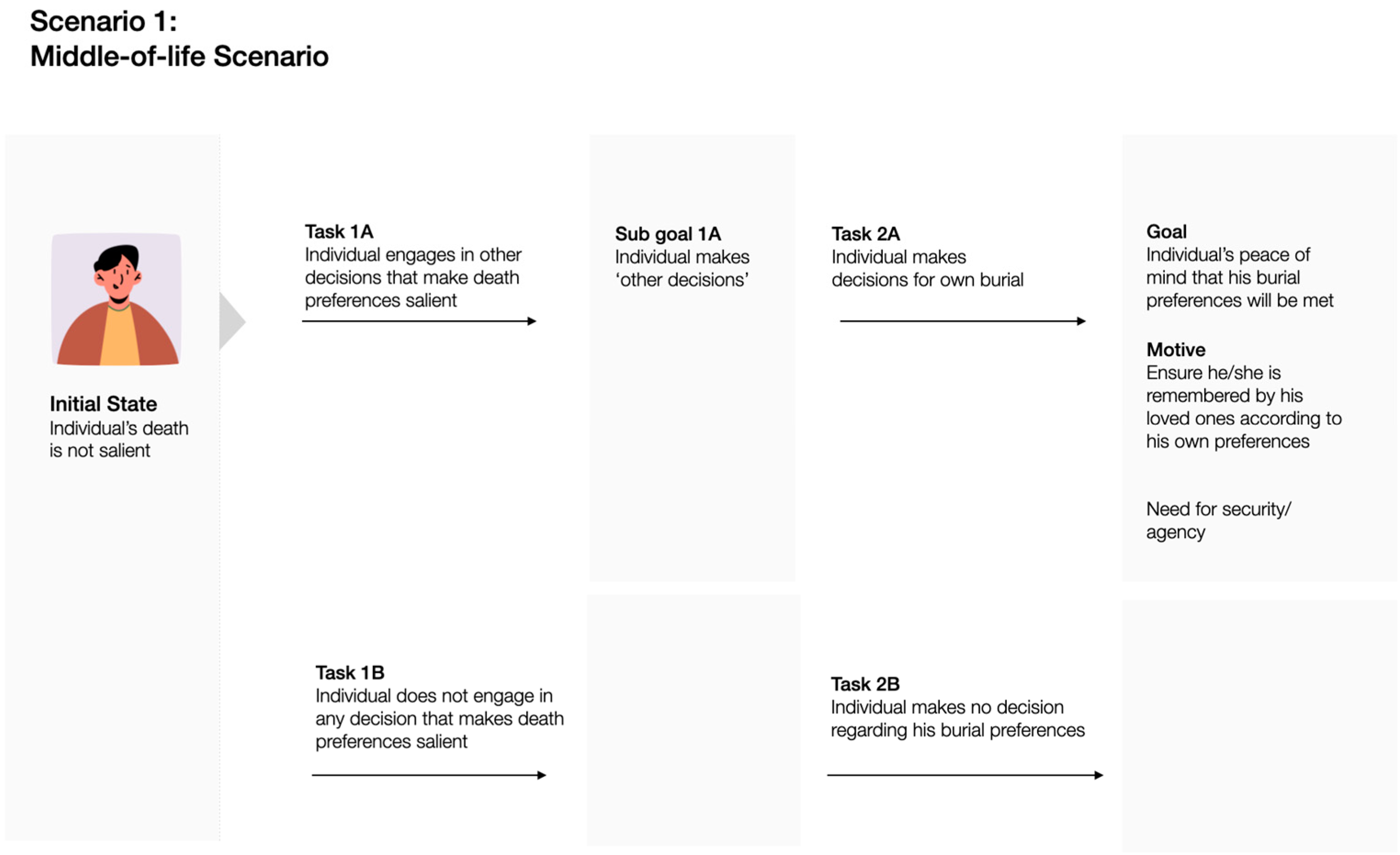
6] to trace the individual journeys of stakeholders in death practices, identifying potential issues and defining the scope of our intervention. Activity theory (AT) understands human activity as a goal-directed trajectory from a given status quo to a consciously represented, future state (
goal). The attainment of the goal is driven by the internal motives of the individual, which are satisfied once the desired state is reached, and typically passes through several subgoals that are achieved incrementally. This conceptualisation of activity is, therefore, highly subject-centric and focuses on the individual perception and experience of action.
We then used installation theory [
7] to design a multilayered intervention approach that bears in mind the interests and motives of several key stakeholders. Installation theory (IT) describes the way individuals and collectives are channelled into certain behaviours through ‘installations’ distributed at the physical, psychological, and societal levels. These installations not only channel individual behaviour but allow for the replication of cultures and society through practice, guidance, and the control of behaviour.
The physical layer analyses objects within the physical space and their physical affordances that allow or prohibit activity; they can be seen as “preconditions for activity” [
24]. Embodied competences refer to the “interpretive systems” or knowledge structures within an individual or collective, such as skills, experiences, habits, and common sense. Institutions refer to the social and cultural regulations that constrain or prescribe activity and are often enforced by other members of the group. These three layers assemble spontaneously in naturally emerging contexts and, in combination, act as a “cultural reactor” that produces ‘appropriate’ behaviours in a systematic and predictable manner [
23]. It is important to note here that installations have a dominant influence on individual behaviour and channel behaviour so thoroughly that individual decisions in installations tend to revolve mainly around the setting of goals, with trajectories for their attainment usually being predetermined. The MID approach, combining a thorough understanding of individual goals and activities, as well as the societal factors channelling this behaviour, is therefore particularly well-suited to designing effective and well-contextualised interventions.
The following section will outline three archetypical scenarios of potential green passers in the UK and their activity trajectories.
4. The Problem Scope: Applying Activity Theory
We identified two different scenarios that individuals or their families could encounter when dealing with death planning: ‘middle-of-life’ and ‘end-of-life’. In the ‘middle-of-life’ scenario (
Figure 1), an individual proactively plans ahead for the end of their life, for example, by taking up life insurance or writing a will so that their decisions and wishes can be made known. On the other hand, in the ‘end-of-life’ scenario (
Figure 2), when no prior decision has been made regarding the person’s death preferences, either the soon-to-be deceased makes the final arrangements concerning their passing, or their family does.
The following graphs illustrate the activities that each scenario would entail regarding death planning.
Considering the sensitivity of the topic, it is important to target the intervention at a point where the person feels comfortable and may even seek to inform themselves rather than being informed. ‘End-of-life’ care is particularly sensitive, requiring the utmost sensitivity from doctors and caretakers. Unfortunately, this is often not the case, and more than half the complaints lodged with the National Health Service (NHS) concern the communication about passing [
25]. On the other hand, findings implicate that millennials are willing to talk about death, with over half of participants in a recent study saying they had already discussed end-of-life care with a close family member [
26].
Since millennials were found to be more open-minded about death and the sensitivities of ‘end-of-life’ care, we determined ‘middle-of-life’ as a suitable starting point for intervention. Using activity theory, we identified and mapped out three different scenarios with varying behavioural sequences within the ‘middle-of-life’ context. In the following section, we illustrate these scenarios through three target groups that we believe are most likely to adopt sustainable death practices and become green passers: organ donors, future-minded individuals, and eco-conscious individuals.
4.1. Organ Donors
The first scenario concerns Benjamin. Benjamin is 26 and has recently heard about the UK’s new ‘opt-out’ system with regards to organ donations [
27]. Whilst gathering information and weighing his options to decide whether or not he wants to opt out, he sees an article on the NHS website about the green passer initiative. Intrigued, he takes a closer look at the article and sees that, similarly to the Organ Donation Scheme, there is an initiative where people can register to become a green passer. After learning more about both, Benjamin signs up to become both an organ donor and a green passer (an illustration of an organ donation and green passer card is shown in
Figure 3). The graphic below illustrates the process of Benjamin’s decision using activity theory (
Figure 4).
4.2. Future-Minded Individual
The second scenario is illustrated by Alice. Alice is a 35-year-old mother of three, who recently bought a house with her husband Marc. Being a mother and new homeowner has made Alice more conscious of the future, and she wants to make arrangements for her family in case anything should ever happen to her. While researching and browsing the different insurance websites, Alice comes across an offer for a funeral insurance plan within the green passer initiative. She is hesitant at first, not wanting to deviate far from the conventional Anglican funeral services that her and her family are accustomed to. However, after learning about the variety and customisability of services available, Alice decided it was appropriate to take charge of the planning of her own passing, in a way that minimises both the financial and environmental impact while still allowing her family to celebrate her life and honour her wishes. She is especially enamoured by the idea of being replanted into a tree, which to Alice serves the same symbolic purposes as a tombstone and beyond (see
Figure 5).
4.3. Eco-Conscious Individual
The final scenario is illustrated by Beth, a 27-year-old environmentally conscious individual. Beth tries to do her part by following a vegan diet and adopting a zero-waste lifestyle. On her way to university, Beth sees an advertisement on the tube for the green passer initiative. Although brought up Anglican, Beth does not identify with any particular religion and is intrigued by sustainable alternatives to traditional funeral proceedings. Beth bookmarks the website and gathers more information before deciding to sign up for the initiative. She believes the green passer initiative is symbolic and reflective of her personal values and is excited to wear the bracelet that comes with signing up to signal her involvement in this green movement (see
Figure 6).
5. The Intervention: Applying Installation Theory
The scenarios of Benjamin, Alice, and Beth provide a valuable illustration from which it is possible to locate possible intervention points that can be addressed using IT (see
Table 1 for an overview).
5.1. Stakeholders
An integral step in creating lasting behaviour change is understanding the current settings of an existing system through which behaviours are channelled [
7]. This requires a thorough assessment of the interests and motives of the stakeholders who are involved in the process.
Applying the MID approach to the context of death and funeral planning, numerous stakeholders were identified and mapped. Within the limited scope of this paper, we focused on six high-influence stakeholders: individuals (to be deceased), relatives of the (to-be) deceased, funeral insurance plan providers and financial advisors, the National Health Service (NHS), funeral directors, and religious organisations.
5.1.1. Individuals (To-Be Deceased)
As the largest and most influential generation, millennials are also the “death positive” generation [
28]. They are marked by a movement away from formal religious observations and memberships, especially in the UK [
29]. These individuals are more open to having a conversation about death and funeral planning, and this is reflected in the recent emergence of ‘death apps’, which are digital platforms designed to help millennials plan their own funerals by streamlining the arrangement process [
30]. In the same way that people personalise their wedding ceremonies, there is a growing trend of customising funerals and finding a unique and authentic way of being memorialised [
31]. More specific to the context of sustainable death, millennials are known to be more health-conscious and environmentally responsible than previous generations, leading to a rise in the interest in natural and green burials [
32].
5.1.2. Relatives of the (To-Be) Deceased
An important group to consider is the bereaved, who, in addition to the grieving process, are often confronted with a significant financial burden [
33] and the responsibility of making funeral decisions to best honour the wishes of the deceased. Though this process can be complicated and painful, these discomforts can be alleviated to a certain degree by planning ahead [
34]. Funeral insurance plans are a way to protect one’s family from the rising costs of traditional funerals and establish communication channels that help family members better understand one’s wishes. In this way, green burial practices can facilitate how relatives of the deceased manage the passing.
5.1.3. Funeral Insurance Plan Providers and Financial Advisors
Pre-paid funerals are a common way to assert one’s wishes, secure funeral prices against rising costs, and alleviate the burden and financial stress on the bereaved. These can be directly coordinated with a funeral guide or a plan provider, with coverage varying from plan to plan [
35]. Pre-paid funeral plans are usually provided by organisations that have established ties with a large network of funeral directors and sold by third parties such as funeral homes, strategic partners, and direct sales operations. Green passing could develop a new branch of business for insurance providers.
5.1.4. National Health Service (NHS)
The NHS’s Organ Donor Register (ODR) is a non-intrusive way to introduce the green passer initiative to the general population. The ODR is a confidential, national list of citizens who are willing to donate their organs after their death. As of March 2017, 36% of the UK population or 23.6 million people were registered [
36]. Individuals who have registered with the ODR experience increased mortality salience, which has been shown to impact one’s attitude and decision making [
37], as well as allowing for a delicate and seamless segue into the topic of funeral planning. Furthermore, as individuals clearly articulate their wishes and discuss them with their closest relatives as part of the green passing initiative, the management of what is to happen with the deceased will be significantly simplified for the NHS.
5.1.5. Funeral Directors
As millennials begin understanding their parents’ wishes regarding their deaths—in addition to their own—funeral directors should brace for the impact that these increasingly secular and eco-conscious millennials will have on the funeral industry [
38]. Innovative service offerings and strategic partnerships with green burial sites and arboretums would allow traditional funeral homes to be more adaptive and resilient against the changing funeral landscape and open up a new branch of business.
5.1.6. Religious Organizations
Finally, religious organisations play an important role for their members when it comes to passing. While there is a range of varying and overlapping practices and norms across religions that goes beyond the scope of this paper, most religions prescribe certain rituals and practices around burials pertaining to a ‘dignified’ ending to a physical life in accordance with the respective religion’s core tenets (see [
39] for an overview of the relationship that the largest religions across the world have with death, as well as shared philosophical and ethical approaches). These norms may sometimes be a barrier to green burial practices but can go hand in hand with them as well. Many religions promote simplicity in their funeral practices as a part of their rituals: for example, Judaism, whose followers traditionally use a plain pine casket, with the body wearing a plain white shroud [
40], and the Episcopal church, which actively encourages its members to write wills [
41].
Having identified the key stakeholders, we now present the proposed interventions to facilitate more sustainable passing practices across the three layers of the installation.
5.2. Physical Layer and Its Affordances
The physical layer and its affordances are vital components that shaped our proposed interventions and significantly increase their chances of success. We propose three interventions within this layer that act as scaffolds to channel desired behaviours while honouring the various rituals associated with traditional death practices.
5.2.1. Addressing Rituals Using Affordances
Rituals are a key aspect in the grieving process and resolution of grief, as they provide order and stability to a group who are undergoing significant change [
42]. As such, our intervention includes the ritual of planting a tree from the green passer bracelet, which is made from biodegradable materials, to facilitate this grieving process with minimal environmental impact (
Table 2).
5.2.2. Physical Installation 1: Green Passer Welcome Kit
The first intervention in the physical layer is a green passer welcome kit, which would be posted to a person’s home upon registering. This kit would include a welcome letter, a green passer card, and a green passer bracelet, made from biodegradable materials (
Figure 7).
The welcome letter would introduce the individual to the green passer community, providing them with further information regarding the environmental impact of their decision, as well as a list of partnering organisations including funeral plan providers and green burial service providers. The goal of these interventions is to consolidate the person’s previous knowledge, enforce their commitment to a green passing, and encourage them to take action in their purchase of a green funeral service from the list provided—all in the intimate context of their own homes, allowing them to evaluate their options privately and mindfully.
The green passer card and bracelet would act as social signalling devices by publicly advertising the owner’s eco-conscious mindset and their preference for green burials. The bracelet would also serve as a tool of distributed cognition, prompting conversations and shifting norms as the green passer initiative becomes more widely recognised [
43]. In the unfortunate event of an unexpected death, a bracelet worn on the wrist of the deceased, or a green passer card found in their wallet, could inform relatives of their wishes for a green burial.
5.2.3. Physical Installation 2: Tree Planting
Another intervention at the physical layer is the use of trees as physical representations of the bodies once they are buried. Green passers would have the option to have a tree planted in their name, marking the completion of their cycle of life. Depending on the plan purchased, they could opt for more customisation and select a specific type of tree from one of the partnering arboretums. This would provide an object and space for families and friends to gather and grieve over the loss of their loved one. This would also open up the possibility for green family plots where families can be buried together, creating tiny forests for their trees to grow together. Aside from the obvious environmental contribution, the symbolic contribution of this intervention is less overt but even more significant. The planting of the tree becomes a symbolic enactment that supports all three pillars of the bereavement process: transformation, transition, and connection [
42]. The tree acts as a ritualistic vehicle that holds the strong emotions of the bereaved groups in a physical object and location [
44]. It is also the more ecological option compared to tombstones and flowers and candles, which increasingly use plastic and batteries (see
Figure 8).
5.2.4. Physical Installation 3: Registration Website
A key finding regarding the culture around death practices is that if not presented with a trigger, the subject of death is largely not discussed. More generally, people are reluctant to think about death [
45], let alone plan for it. When the topic of death is brought up, it is likely to be perceived as a problem for the future. As such, important conversations with friends and families about one’s death preferences might be reduced to something that can be dealt with in the distant future. Any intentions discussed in these conversations will therefore fail to translate into future actions, making it difficult for close ones to know and carry out the person’s wishes when the time comes.
With this in mind, we propose the final physical intervention: the establishment of a database for green passers, where people can register themselves on a platform and thereby declare their interest in having a green burial upon passing (see
Figure 9).
The aim of this intervention is twofold: Firstly, to create an otherwise inexistent opportunity for an individual to register their interest in having a green burial in the distant future. Secondly, the website would serve as a public search database for families to look up their loved ones to understand their burial preferences when the time comes. Privacy concerns can be mitigated, as individuals who sign up could declare whether they would like to be found online or not. If they opt out of being searchable in the database, they would be asked to confirm that they have talked to a close relative about their decision, to ensure that their loved ones are aware of their choices. For those who opt in, social media integration could be offered for users to easily share their decision with their network, leveraging micro-influencing strategies through users’ personal networks, as well as potentially creating cascade effects.
5.3. Embodied Competencies
With traditional religious funerals on the decline, people in the UK are turning to direct cremation—a cheaper, no-frills alternative [
46]. While cremations have been touted as the more sustainable option compared to traditional burials, they also cause a significant negative effect on the environment through energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions [
47]. To facilitate the adoption of sustainable death practices, individuals must be informed and made aware of alternative options. With the green passer initiative, this knowledge will reach individuals via three avenues: the NHS partnership; funeral insurance and financial advisors; and social media campaigns, including public advertisements and obituaries.
5.3.1. Embodied Competencies Installation 1: Green Passer Website and Welcome Letter
Recall Benjamin, who is browsing the NHS website to learn about the organ donor program when he sees an embedded article linking to the green passer initiative (
Section 4.1). On the website, he is surprised to learn about the negative impacts of traditional funeral practices and decides to register as a green passer to plan ahead.
In the second and third scenarios (
Section 4.2 and
Section 4.3), Alice learns about green passing through a funeral plan provider, while Beth learns about it through an advertisement in the tube. Once an intention to acquire more knowledge about the initiative has been developed, all actors are enabled to do so through this website.
The green passer welcome letter would contain a list of green burial partners (including funeral homes that offer green burial services) and another list of funeral plan providers for those ready to begin making arrangements. The letter would also provide infographics and statistics to illustrate the quantifiable impact a green passer has made by deciding on a natural burial, accompanied by the green passer card and bracelet to further reinforce and signal their self-identity as an eco-conscious individual.
5.3.2. Embodied Competencies Installation 2: Strategic Partnerships with Key Stakeholders
Partnering with the green passer initiative would benefit funeral plan providers and funeral homes in several ways. As green burials are typically less costly than traditional burials [
48], providers may be able to increase profit margins by reducing material costs while introducing innovative service-based offerings to maintain current revenue figures. This could take the form of replacing tombstones with trees to reduce costs related to the acquisition and maintenance of tombstones. Providers could also partner with arboretums and charge a subscription fee for the upkeep of the tree that has been planted with the bracelet of the deceased. Taking inspiration from death apps and online funeral concierges, individuals may pay for additional features such as creating multimedia memorial portfolios, making digital estate arrangements, or even passing off the passwords of all the deceased’s digital accounts to loved ones after passing [
30]. The capacity to generate new revenue streams and adapt to changing consumer needs is a core competency for traditional businesses in today’s modernising market. Recognising this, the green passer initiative would also provide ongoing advisory services to support partnering funeral homes and plan providers in navigating the evolving funeral industry. In the future, green passing could become a default (opt-out) option for all those whose burial is dealt with by administrations (e.g., the army, the homeless, and those without family).
Another benefit for these green burial sites, funeral homes, and plan providers would be the additional exposure and publicity, as joining the green passer initiative would allow partners to piggyback off its social media campaigns. Essentially, the green passer initiative’s audience reach would provide partners with the added service of lead generation, identifying and funnelling through a specific group of individuals who are the perfect target market for their businesses.
5.4. Social Regulation
5.4.1. Social Regulation Intervention 1: Passer Card/Bracelet
The awareness campaigns aim to create social regulation through imitation and portraying the role and status that comes along with green passer behaviour, and to induce influence and persuasion towards becoming a green passer. By carrying the card or wearing the bracelet, people can signal their membership of the green passer initiative. Signalling theory states that information is shared between two people via one’s social status or membership in a group, or other social cues [
49]. In the suggested intervention, different identities and social memberships may be addressed or signalled, as our previous examples of Benjamin, Alice, and Beth showed (
Section 4).
5.4.2. Social Regulation Intervention 2: Social Media Integration
In addition to the social regulation generation that a physical card/bracelet can provide, the integration of social media from the registration website could be a significant tool to create further social regulation.
Social media provides a platform that allows individuals to present themselves through the creation of a virtual identity [
50]. The integration of social media into the green passer campaign would allow individuals to highlight their green passer credentials as a part of their virtual identity. Social networks are representations of the connections that form groups and organisations of individuals, and these connections have a significant power to influence behaviours and decision making [
51]. Social media provides a tool for individuals to create large social networks of previously unachievable sizes. Through the developments of social networks, the integration with social media could create further social influence through an availability cascade effect [
52], whereby leveraging the common embedding and “share to social media” functions to enable the sharing of one’s green passer status could influence individuals within the same networks to explore green passing (see examples in
Figure 10). The presence of homophily on social media furthers the effect that social media integration can have on social regulation [
53].
In our scenarios, Beth was environmentally conscious, and wearing the bracelet for her might have functioned as a pro-environmental signal. The bracelet became an object that enforced her identity of being an eco-friendly citizen and signalled to others that she cared for the environment, which may have led her friends who identified with similar values to imitate her. What is more, because the images and messages used in the green passer campaign, as well as through the social media integration, align with core “green” values, there would be a strong signalling need for those who hold these values to align themselves with the campaign in order to enforce their green identity.
Benjamin and Alice on the other hand, were more driven by a need for security and agency, whilst also being eco-conscious; they wanted to make informed decisions with which they felt comfortable. The green passer initiative would offer this by allowing them to plan ahead; additionally, by wearing the card or the bracelet, they could signal to others that they had thought about their death and had made arrangements.
In addition to using the bracelets, cards, and social media as signalling tools, another strategy for social regulation and bonding could be to include one’s decision to have a green burial in one’s obituary postings, again generating awareness and informing the general public about these sustainable alternatives. Finally, there are opportunities for arboretums to plant more trees in the name of the deceased (independent of their green burial choice) to signal that these people have added to the “circle of life”.
5.4.3. Social Regulation Intervention 3: Interfaith Initiative
Many religious organisations promote an open dialogue surrounding death and, as a result, should be included when trying to promote the option of green passing. In the UK, the National Health Service has the ‘hospital chaplaincy’ as an allied profession. Stemming from the Anglican clerical organisation, hospital chaplains assist families when talking about end-of-life care and support [
54]. The role that hospital chaplains provide highlights the value that religious groups and leaders can have in the promotion of green passing. The trust and authority of the clergy could thus be leveraged to raise awareness amongst believers of the notion that their faith does not stand in conflict with, and in fact in many cases includes and encourages, environmentally friendly burials.
Making sure religious organisations are involved in the green passing initiative is synergetic and would facilitate better respecting people’s environmental and spiritual wishes simultaneously. An interfaith initiative would be an excellent starting point to integrate green passing practices with various groups’ respective beliefs and would uncover pain points and important insights to adjust information on the green passing initiative to each group’s requirements. Working with religious groups who are pre-disposed to a level of openness regarding passing and whose members often value simplicity in their funeral rituals could leverage pre-existing social regulations and trust in these organisations to further integrate and promote green passing. As part of the initiative, broadly recognised leaders within these religions (such as the Archbishop of Canterbury or the Dalai Lama) could be sought out as champions of the cause. At the local level, clergy could then include this information in their guidance when they are in touch with individuals making preparations for the future.
6. Implications
In this paper, we provided an overview of how the uptake of sustainable passing practices could be increased in the UK. We believe this work offers relevant insights for a variety of stakeholders. Firstly, we hope the increase in green passers will raise the interest of policy makers in pushing for more sustainable ways of passing. Currently, when registering a death at the registrar, local authorities typically issue a ‘green form’ to the funeral director, which permits either a burial or cremation service [
55]. This draws away from green passers’ awareness-raising efforts, as people are naturally guided towards the default options. By altering the choice architecture and presenting green passing as an alternative option, governments have the opportunity to intervene at the final stage of the decision-making process. Since local councils oversee pauper funerals to bury or cremate those who do not have families or cannot afford it financially, there is also an opportunity to shift towards public green burials and incorporate them into conservation projects and woodland creation. Ultimately, the green passer initiative will alleviate the environmental costs associated with traditional funeral practices and support the UK in meeting its net-zero targets.
Secondly, we believe that market researchers and academics alike will be able to make use of the green passer database to further their work in the field. Access to this data will facilitate research and accelerate technological and social innovation in the sector. Moreover, the green passer database will be a key information repository to better understand grieving processes in an ever-changing, diverse, and globalised world.
Thirdly, we think that the general population will be able to benefit significantly from the insights gained in this study. On a pragmatic level, the green passer database and the associated green passing practices will alleviate the often substantial financial burden of funerals for consumers and enable the families of green passers to honour their wishes. Individuals who become green passers will also find comfort and spiritual fulfilment knowing that their body will return to nature and that they are leaving this world in a better place. The initiative would also allow for a more personalised way of honouring those who have passed, particularly for those interested in making their eco-conscious preferences visible. Finally, with increasing adoption, green passing could also develop a secular grieving community based on a shared eco-conscious mindset.
7. Limitations
As with any intervention, the proposal has a variety of limitations that shall be addressed below. Fundamentally, this paper was based around a case study, and as a result only a limited scope could be reached. Additionally, only the main interventions were highlighted and explored, with only one culture taken into account. Despite these limitations, we believe that the interventions proposed are relevant, feasible, and provide concrete and actionable solutions to the issues highlighted.
Further, we must also address forms of resistance towards an intervention such as ours. Of course, there is the subject of religion, in which there are traditional death practices in line with certain beliefs. We did not address these in detail in our intervention due to the extremely intricate and personal nature of the issue, with every religion having different practices and beliefs. Whilst this may be a weakness of our intervention, our aim was to first address millennials, who show higher willingness to talk about death, higher eco-consciousness, and overall less religious attitudes [
26,
29,
32]. Considering this first target group as an ideal starting point, we hope that in time other people will be convinced to sign up for the project and a conversation at the societal level will be sparked. Of course, it is also advisable to continue working with religious leaders to educate ourselves and exercise religious sensitivity.
Finally, we must address the fact that we targeted millennials, when it is the ‘boomer’ generation who will pass in the next few decades, with there being less space for burials nowadays [
14]. We are aware that we addressed a ‘less pressing’ population. Nonetheless, millennials are often more open to talk about and address issues of death and sustainability. As displayed in the example of Alice, the mother of three who just bought a house with her husband, we hope that people signing up for the green passer initiative will further persuade their peers (in Alice’s case, her parents). Thus, we hope there is a knock-on effect that is sensitive, organic, and self-induced rather than forced.
8. Conclusions
This paper developed a possible intervention aimed to increase green burials in the United Kingdom. Current funeral practices are usually very costly in both environmental and monetary terms. We discussed a variety of alternative, more sustainable practices. Using the multilayered installation design (MID) change model based on activity theory and installation theory, we presented three ideal-type scenarios for the decision processes of green-passers-to-be, in which it is feasible to intervene and foster behavioural change around making arrangements for one’s burial. We also identified a variety of stakeholders, ranging from individuals and families to funeral insurance providers, funeral directors, and the NHS. Based on this analysis, we proposed an intervention addressing the physical affordances, embodied competences, and social factors that would facilitate making death practices in the UK more sustainable in the long run. Whilst this is a pressing environmental issue, we are aware of course that it is also a highly sensitive and emotional social issue. We therefore stress the importance of our intervention targeting individuals who actively educate themselves or have an interest in informing themselves. We hope that by targeting individuals who are open to addressing the issue of death, there will be a shift in the cultural view of death in the UK in the long term, allowing the mitigation of the environmental impact of death practices and influencing the conversation surrounding the topic of death. This paper also presented a fully fledged example of the application of MID to a concrete problem, including an outline of the business model and the communication of the intervention, demonstrating the viability of the approach to develop impactful, concrete, and sustainable interventions for pressing real-world issues. We therefore believe that the MID approach is well-suited to be applied to other topics in the sustainability space and beyond.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O. and J.Y.X.; methodology, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O., J.Y.X. and M.H.; investigation, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O. and J.Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O. and J.Y.X.; writing—review and editing, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O., J.Y.X. and M.H.; visualization, A.C.F., G.E.M., M.V.O., J.Y.X. and M.H.; supervision, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Saadi Lahlou and Frédéric Basso for their support and guidance throughout the research process. We would further like to thank our Psychology of Economic Life cohort for their continued enthusiasm and willingness to discuss our project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shelvock, M.; Kinsella, E.A.; Harris, D. Beyond the corporatization of death systems: Towards green death practices. Illn. Crisis Loss 2021, 30, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humanist UK. Religion and Belief: Some Surveys and Statistics. Available online: https://humanists.uk/campaigns/religion-and-belief-some-surveys-and-statistics/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Sherwood, H. Less than Half of Britons Expected to Tick ‘Christian’ in UK Census. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2021/mar/20/less-that-half-of-britons-expected-to-tick-christian-in-uk-census (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Udell, J. Factsheet: Death and Funerals in World Religions. Available online: https://religionmediacentre.org.uk/factsheets/death-funeral-rituals-in-world-religions/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Marie Curie. Death Customs of Different Faiths. Available online: https://www.mariecurie.org.uk/talkabout/articles/death-customs-of-different-faiths/260276 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Nosulenko, V.N.; Barabanshikov, V.A.; Brushlinsky, A.V.; Rabardel, P. Man–technology interaction: Some of the Russian approaches. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2005, 6, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, S. Installation Theory: The Societal Construction and Regulation of Behaviour; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 9781316480922. [Google Scholar]
- Neimeyer, R.A.; Klass, D.; Dennis, M.R. A social constructionist account of grief: Loss and the narration of meaning. Death Stud. 2014, 38, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastenbaum, R. Why funerals? Generations 2004, 28, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fulton, L. The History and Traditions of Funerals in the UK. Available online: http://www.historyisnowmagazine.com/blog/2017/5/14/the-history-and-traditions-of-funerals-in-the-uk#.YaYQnb2mOEs= (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Konrad, W. More Americans Are Skipping Traditional Funerals in Favor of Green Burials. Available online: https://www.considerable.com/life/communication/green-burials-are-a-growing-trend/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Calderone, J. Burying Dead Bodies Takes a Surprising Toll on the Environment. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/burying-dead-bodies-environment-funeral-conservation-2015-10?r=US&IR=T (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- National Cancer Institute. Formaldehyde and Cancer Risk. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/substances/formaldehyde/formaldehyde-fact-sheet (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Strangwayes-Booth, B.A. Burial Space in England “Could Run out in 20 Years”. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-24283426 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Little, B. The Environmental Toll of Cremating the Dead. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.co.uk/environment-and-conservation/2019/11/the-environmental-toll-of-cremating-the-dead (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Krosofsky, A. What Are the Most Eco-Friendly Burial Methods? Available online: https://www.greenmatters.com/p/eco-friendly-burial-methods (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Hauke, C. The Environmental Impact and Potential Human Health Effects of Cremation. Available online: https://www.greenburialcouncil.org/environmental_impact_cremation.html (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Green Burial Society of Canada. What Is Green Burial. Available online: http://www.greenburialcanada.ca/greenburial (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Kiley, B. Seattle Could Get an Urban Death Project Human Composter in Just 7 Years. Available online: https://www.seattletimes.com/life/from-corpse-to-compost-the-urban-death-projects-modest-proposal/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Lee, J.R. Jae Rhim Lee: My Mushroom Burial Suit. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7rS_d1fiUc (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Mental Floss. 7 Eco-Friendly Options for Your Body after Death. Available online: https://www.mentalfloss.com/article/513564/7-eco-friendly-options-your-body-after-death (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Yakowicz, W. Entrepreneurs Find a Growing Business in Eco-Friendly Burials. Available online: https://www.inc.com/will-yakowicz/death-care-gets-eco-friendly-green-burial-services.html (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Lahlou, S.; Heitmayer, M.; Pea, R.; Russell, M.G.; Schimmelpfennig, R.; Yamin, P.; Dawes, A.P.; Babcock, B.; Kamiya, K.; Krejci, K.; et al. Multilayered Installation Design: A framework for analysis and design of complex social events, illustrated by an analysis of virtual conferencing. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2022, 6, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeno, J.G. Gibson’s affordances. Psychol. Rev. 1994, 101, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleeman, K. End-of-life communication: Let’s talk about death. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2013, 43, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, N. Can millennials talk about death. J. Health Adm. Educ. 2017, 34, 23–48. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Service. What Is the Opt-out System in England? Available online: https://www.organdonation.nhs.uk/helping-you-to-decide/about-organ-donation/faq/what-is-the-opt-out-system/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Cummins, E. Why Millennials Are the “Death Positive” Generation. Available online: https://www.vox.com/the-highlight/2020/1/15/21059189/death-millennials-funeral-planning-cremation-green-positive (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Percy, M. Sketching a shifting landscape: Reflections on emerging patterns of religion and spirituality among millennials. J. Study Spiritual. 2019, 9, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirtha, T. Death Apps Promise to Help People Curate Their Afterlives. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2016/mar/08/death-apps-everest-cake-safebeyond-everplans-afternote-funerals (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Morrison, H. Millennials Aren’t Killing the Funeral Industry—But It Is Changing. Available online: https://www.rewire.org/funeral-industry-changing/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Ford, J. Millennials Are Paving the Way for Sustainability. Available online: https://www.enviral.co.uk/millennials-are-paving-the-way-for-sustainability/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Corden, A.; Sainsbury, R.; Sloper, P. Money matters and bereavement support. Bereave. Care 2004, 23, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K. Death and grieving in a changing landscape: Facing the death of a loved one and experiencing grief during COVID-19. Health Soc. Care Chaplain. 2020, 8, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J. A Complete Guide to Funeral Plans. Available online: https://www.sunlife.co.uk/funeral-plans/funeral-plans-guide/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Sallis, A.; Harper, H.; Sanders, M. Effect of persuasive messages on National Health Service Organ Donor Registrations: A pragmatic quasi-randomised controlled trial with one million UK road taxpayers. Trials 2018, 19, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, M.B.; Saunders, B.A.; Cain, N.M. Priming mortality salience: Supraliminal, subliminal and “double-death” priming techniques. Death Stud. 2014, 38, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J. In 17 Years de-Churching Millennials Will Rock the Funeral Industry. Available online: https://connectingdirectors.com/52320-de-churching-millennials (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Moreman, C. The Routledge Companion to Death and Dying, 1st ed.; Moreman, C., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, V. Jewish funeral and mourning practices. In The Routledge Companion to Death and Dying, 1st ed.; Moreman, C., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Episcopal Church Foundation. Planning for the End of Life. Faithful Stewards of Your Good Gifts. Available online: http://www.episcopalfoundation.org/uploads/pages/files/Planning_End_of_Life_Booklet.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Romanoff, B.D. Rituals and the grieving process. Death Stud. 1998, 22, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, E. Cognition in the Wild; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; ISBN 9780262581462. [Google Scholar]
- Myerhoff, B. Rites of passage: Process and paradox. In Celebration: Studies in Festivity and Ritual; Turner, V., Ed.; Smithsonian Institute Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 108–135. ISBN 9780874749199. [Google Scholar]
- Jong, J. Why Contemplating Death Changes How you Think. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20160208-why-contemplating-death-changes-how-you-think (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- The Cremation Society. Progress of Cremation in the British Islands 1885–2021. Available online: https://www.cremation.org.uk/progress-of-cremation-united-kingdom (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Little, B. The Environmental Toll of Cremating the Dead. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/is-cremation-environmentally-friendly-heres-the-science (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Qureshi, H. Woodland Burials Are not Only Eco-Friendly: They’re Cheaper Too. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/money/2007/oct/07/ethicalmoney.ethicalliving (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Connelly, B.L.; Certo, S.T.; Ireland, R.D.; Reutzel, C.R. Signaling theory: A review and assessment. J. Manag. 2010, 37, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, U. The effect of social media on identity construction. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2017, 8, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiera, E. Social networks, social media, and social diseases. BMJ 2013, 346, f3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunstein, C.R. What’s available social influences and behavioral economics. Northwestern Univ. Law Rev. 2002, 97, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, L.M.; Barrat, A.; Schifanella, R.; Cattuto, C.; Markines, B.; Menczer, F. Friendship prediction and homophily in social media. ACM Trans. Web 2012, 6, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradby, H.; Kenten, C.; Deedat, S.; Morgan, M. ‘Having a different conversation around death’: Diverse hospital chaplains’ views on end-of-life care. Ethn. Health 2013, 18, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funeral Partners. Documents and Certificates. Available online: https://www.funeralpartners.co.uk/help-advice/what-to-do-when-someone-dies/documents-and-certificates/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).