Three Gorges Dam Operation Altered Networks of Social–Economic–Ecological System in the Yangtze River Basin, China
Abstract
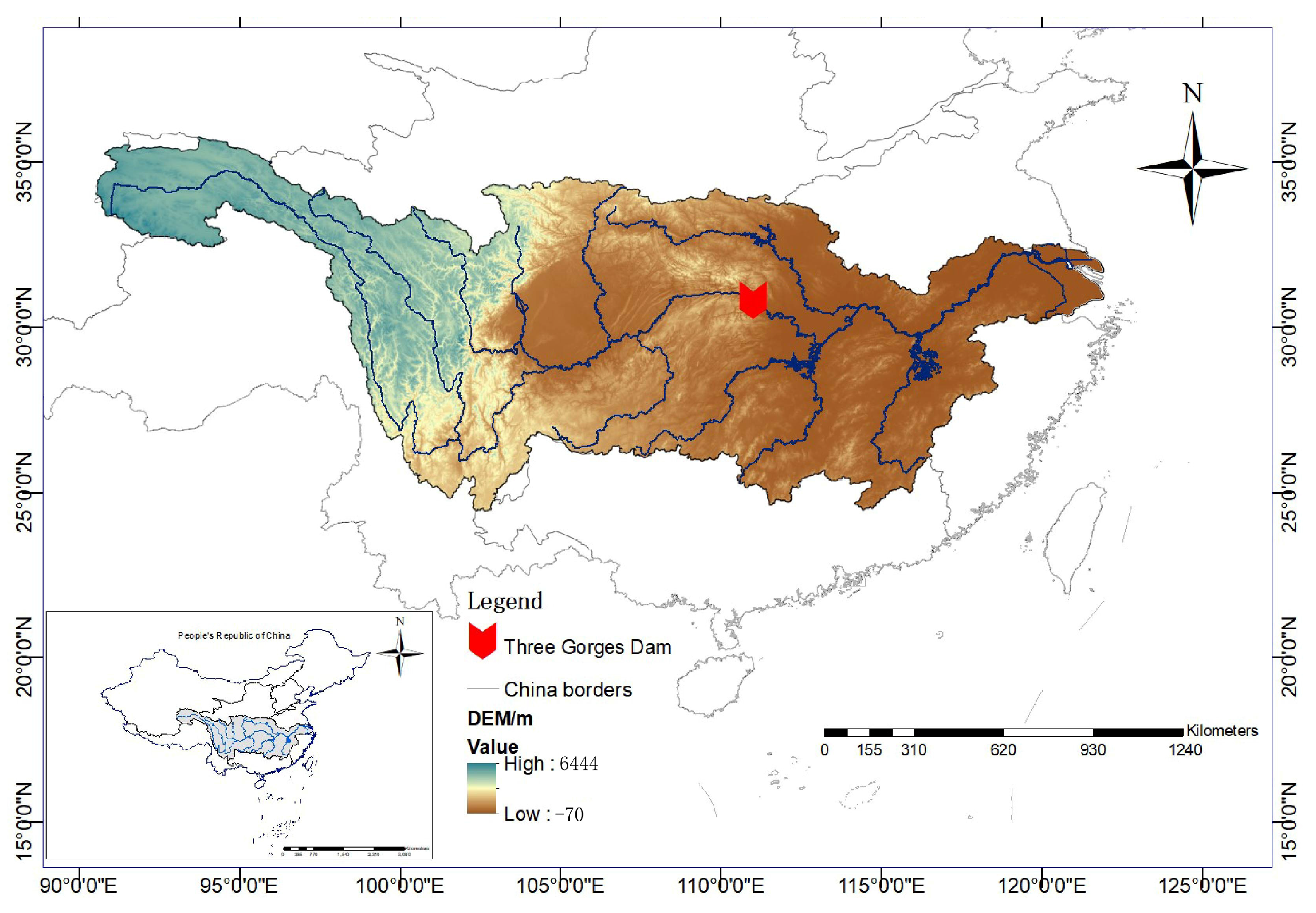
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Indicator Selection
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Interactions among Indicators
2.4. Network Analyses
| Network Metric | Definition | Meaning in the Indicators Network |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Proportion of positive or negative links to all possible links in the network, weighted by the strength of the links [25]. | More indicators can be achieved simultaneously if the synergy networks have a higher connectivity value. More indicators cannot be achieved simultaneously if the trade-off networks have a higher connectivity value. |
| Modularity | A module represents a group of nodes that are highly inter-connected, and loosely connected to others. Modularity represents the strength of the partition of a network into modules [25]. | In a highly modular network, indicators can be divided into groups based on their connections, while in a less modular network, the interactions of all indicators are closer. When edges are randomly formed, the modularity value is close to zero. If the modularity score is higher than 0.3, the network structure could be regarded as significant [44]. |
| NESH | Changes in networks of a single node [42] | In a higher NESH value, the nodes contribute more to the entire network changes. This node may be regarded as the driver node of the alteration. |
2.5. Regime Shift Detection
3. Results
3.1. Highly Connected Indicators
3.2. Disruption of Indicator Modules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C. A Dynamic Assessment of Water Scarcity Risk in the Lower Brahmaputra River Basin: An Integrated Approach. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Change and Driving Factors of the Eco-Environment Quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penghao, C.; Pingkuo, L.; Hua, P. Prospects of Hydropower Industry in the Yangtze River Basin: China’s Green Energy Choice. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 1168–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Diamond, J. China’s Environment in a Globalizing World. Nature 2005, 435, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, E.Y.; Meng, Z.; Song, Y. Environmental Regulation, Green Technological Innovation, and Eco-Efficiency: The Case of Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 155, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhu, C.; Wu, L.; Huang, L. Problems Caused by the Three Gorges Dam Construction in the Yangtze River Basin: A Review. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, M.; Shen, L.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. Rapid Change in Yangtze Fisheries and Its Implications for Global Freshwater Ecosystem Management. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wu, B.F.; Lü, Y.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Cao, J.H.; Niu, D.; Yang, G.S.; Zhou, Y.M. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and Challenges for the Environment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Biodiversity Decline of Fish Assemblages after the Impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Berg, M.; Yao, Z.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, D.; Pfluger, A. How Polluted Is the Yangtze River? Water Quality Downstream from the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Blanchet, S.; Loot, G.; Villéger, S.; Zhang, T.; Lek, S.; Lek-Ang, S.; Li, Z. Temporal Changes in the Taxonomic and Functional Diversity of Fish Communities in Shallow Chinese Lakes: The Effects of River-Lake Connections and Aquaculture. Aquat. Conserv. 2014, 24, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Peter, C.; Dai, G. Concerns about the Future of Chinese Fisheries Based on Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing on the Hanjiang River. Fish Res. 2018, 199, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Gupta, H.; Wu, G.; Li, D. Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the Hydrology and Ecology of the Yangtze River. Water 2016, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Chu, A.; Stive, M.; Du, J.; Li, J. Is the Three Gorges Dam the Cause behind the Extremely Low Suspended Sediment Discharge into the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary of 2006? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 585136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Gleason, C.J.; Wada, Y. Downstream Yangtze River Levels Impacted by Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. Impact of the Gezhouba and Three Gorges Dams on Habitat Suitability of Carps in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandziora, M.; Burkhard, B.; Müller, F. Interactions of Ecosystem Properties, Ecosystem Integrity and Ecosystem Service Indicators: A Theoretical Matrix Exercise. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Febria, C.M. The Heartbeat of Ecosystems. Science 2012, 336, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.M. How Do We Take the Pulse of an Aquatic Ecosystem? Current and Historical Approaches to Measuring Ecosystem Integrity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemer, F. Fish as Indicators for the Assessment of the Ecological Integrity of Large Rivers. Hydrobiology 2000, 422, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, L.E.; Allesina, S.; Bonn, A.; Eklöf, A.; Gaines, S.D.; Hines, J.; Jacob, U.; McDonald-Madden, E.; Possingham, H.; Schröter, M.; et al. Operationalizing Network Theory for Ecosystem Service Assessments. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Soliveres, S.; Penone, C.; Fischer, M.; Ammer, C.; Boch, S.; Boeddinghaus, R.S.; Bonkowski, M.; Buscot, F.; Fiore-Donno, A.M.; et al. Land-Use Intensity Alters Networks between Biodiversity, Ecosystem Functions, and Services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28140–28149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali Swain, R.; Ranganathan, S. Modeling Interlinkages between Sustainable Development Goals Using Network Analysis. World Dev. 2021, 138, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, K.; Yi, T. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation of the Coupling Coordinated Development of Regional Energy-Economy-Ecology System: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, J. Decoupling of SDGs Followed by Re-Coupling as Sustainable Development Progresses. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network Medicine: A Network-Based Approach to Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, Ö.; Alexander, S.M.; Baggio, J.; Barnes, M.L.; Berardo, R.; Cumming, G.S.; Dee, L.E.; Fischer, A.P.; Fischer, M.; Mancilla Garcia, M.; et al. Improving Network Approaches to the Study of Complex Social–Ecological Interdependencies. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Lei, K. Influence of Human-Water Interactions on the Water Resources and Environment in the Yangtze River Basin from the Perspective of Multiplex Networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, M.; Muhar, S.; Schmutz, S. Re-Establishing and Assessing Ecological Integrity in Riverine Landscapes. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J. Ecological Integrity of Aquatic Systems. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1995, 11, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V. International Conference: Sustaining the Ecological Integrity of Large Floodplain Rivers. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1995, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hughes, R.M. Challenges to Saving China’s Freshwater Biodiversity: Fishery Exploitation and Landscape Pressures. Ambio 2020, 49, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Opperman, J.J.; Tickner, D.; Speed, R.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D. Managing the Three Gorges Dam to Implement Environmental Flows in the Yangtze River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Xu, C.; Sun, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhou, L.; Jeppesen, E.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Can the “10-Year Fishing Ban” Rescue Biodiversity of the Yangtze River? Innovation 2022, 3, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogtay, N.J.; Thatte, U.M. Principles of Correlation Analysis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lade, S.J.; Steffen, W.; de Vries, W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Donges, J.F.; Gerten, D.; Hoff, H.; Newbold, T.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J. Human Impacts on Planetary Boundaries Amplified by Earth System Interactions. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research. InterJ. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gábor, C.; Tamás, N.; Edoardo, M.A. Statistical Network Analysis with Igraph (R); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pons, P.; Latapy, M. Computing Communities in Large Networks Using Random Walks. J. Graph Algorithms Appl. 2006, 10, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebestyén, V.; Bulla, M.; Rédey, Á.; Abonyi, J. Network Model-Based Analysis of the Goals, Targets and Indicators of Sustainable Development for Strategic Environmental Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.M.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Turner, J.A.; Ray, K.L.; Mckay, D.R.; Glahn, D.C.; Beckmann, C.F.; Smith, S.M.; Fox, P.T. Behavioral Interpretations of Intrinsic Connectivity Networks. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 4022–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntal, B.K.; Chandrakar, P.; Sadhu, S.; Mande, S.S. ‘NetShift’: A Methodology for Understanding ‘Driver Microbes’ from Healthy and Disease Microbiome Datasets. ISME J. 2019, 13, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Algesheimer, R.; Tessone, C.J. A Comparative Analysis of Community Detection Algorithms on Artificial Networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauset, A.; Newman, M.E.J.; Moore, C. Finding Community Structure in Very Large Networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodionov, S.; Overland, J.E. Application of a Sequential Regime Shift Detection Method to the Bering Sea Ecosystem. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, S.N. Use of Prewhitening in Climate Regime Shift Detection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S. Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis: A Survey. Ecol. Econ. 2004, 49, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Tang, L.H.; Yang, D.W.; Lei, H.M. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Net Anthropogenic Nitrogen Inputs in the Upper Yangtze River Basin from 1990 to 2012. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The Modularity of Pollination Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Simonovic, S.P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W. What Are the Main Challenges Facing the Sustainable Development of China’s Yangtze Economic Belt in the Future? An Integrated View. Environ. Res. Commun. 2021, 3, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.Y. Human Impacts on Sediment in the Yangtze River: A Review and New Perspectives. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, L. Yangtze Dams Increasingly Threaten the Survival of the Chinese Sturgeon. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3640–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Xiong, F.; Wang, K.; Chang, Y. Status of Research on Yangtze Fish Biology and Fisheries. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 85, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lin, P.; Li, M.; Duan, Z.; Liu, H. Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the Spawning Stock and Natural Reproduction of Chinese Sturgeon in Changjiang River, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z. Three Gorges Dam Affects Regional Precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusseau, D.; Mancini, F. Income-Based Variation in Sustainable Development Goal Interaction Networks. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Thompson, J.R.; Pettorelli, N. The Quest for a Mechanistic Understanding of Biodiversity–Ecosystem Services Relationships. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Gertrud Berens, D.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Selva, N.; Brandl, R.; Farwig, N. Correlated Loss of Ecosystem Services in Coupled Mutualistic Networks. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čermáková, K.; Bejček, M.; Vorlíček, J.; Mitwallyová, H. Neglected Theories of Business Cycle—Alternative Ways of Explaining Economic Fluctuations. Data 2021, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, M.Á.R.; López, J.B.L.; Veiga, J.G. Present and Future in the Mirror of the Past: Capitalist Dynamics, Digital Technology and Industry in the Fifth Kondratiev. World Rev. Political Econ. 2019, 10, 449–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednář, O.; Čečrdlová, A.; Kadeřábková, B.; Řežábek, P. Energy Prices Impact on Inflationary Spiral. Energies 2022, 15, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, A. Investigating the relation between technology and economic growth with AK model: An application swamy’s random coefficient model (RCM). Int. J. Econ. Sci. 2018, 7, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Blanc, D. Towards Integration at Last? The Sustainable Development Goals as a Network of Targets. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Forero, L.; Castañeda, G.; Guerrero, O.A. Estimating Networks of Sustainable Development Goals. Inf. Manag. 2020, 59, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörgo, G.; Sebestyén, V.; Abonyi, J. Evaluating the Interconnectedness of the Sustainable Development Goals Based on the Causality Analysis of Sustainability Indicators. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Chisholm, E.; Griggs, D.; Howden-Chapman, P.; McCollum, D.; Messerli, P.; Neumann, B.; Stevance, A.S.; Visbeck, M.; Stafford-Smith, M. Mapping Interactions between the Sustainable Development Goals: Lessons Learned and Ways Forward. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicator Type | Indicator Code | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable ecological integrity | Ecological integrity | Biological integrity (ecological processes and functions) | Fishery resources | Y1 |
| Y2 | ||||
| Y3 | ||||
| Y4 | ||||
| Y5 | ||||
| Y6 | ||||
| Y7 | ||||
| Y8 | ||||
| Y9 | ||||
| Y10 | ||||
| Y11 | ||||
| Diatom | Y12 | |||
| Y13 | ||||
| Y14 | ||||
| Physical integrity (habitat quality) | Water and sediment effect | X17 | ||
| X18 | ||||
| X19 | ||||
| Landscape mosaic structure | X11 | |||
| X12 | ||||
| X13 | ||||
| Watershed connectivity | X24 | |||
| Temperature | X20 | |||
| Chemical integrity (biogeochemical cycle) | Nutriment | X15 | ||
| X16 | ||||
| X21 | ||||
| X23 | ||||
| Water quality | X22 | |||
| Economic and social condition | Dam conditions | X3 | ||
| Pollution status | X4 | |||
| X5 | ||||
| X6 | ||||
| Agricultural fertilization status | X9 | |||
| X10 | ||||
| X14 | ||||
| Economic conditions | X2 | |||
| X7 | ||||
| X8 | ||||
| X1 | ||||
| Indicators | Indicator Code | Units | Start Year | End Year | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Data Number | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual catch of fish | Y1 | 10,000 tons | 1949 | 2018 | 5 | 43 | 70 | China Three Gorges Corporation and [7] |
| Number of Breeding population of Chinese sturgeon | Y2 | tail | 1972 | 2018 | 18 | 2309 | 40 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Hilsa fishing yield | Y3 | ton | 1961 | 1986 | 0 | 1582 | 13 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Sand mined in mainstream of middle and lower Yangtze River | X1 | 10,000 tons | 2004 | 2016 | 29,467 | 107,552 | 13 | [32] |
| Total cargo volume in the Yangtze River Basin | X2 | 10,000 tons | 1998 | 2017 | 48 | 444 | 20 | [32] |
| Total estimated number of adult Chinese paddlefish below the Gezhouba Dam in the mainstream of the Yangtze River | Y4 | tail | 1981 | 2010 | 0 | 32 | 24 | [32] |
| Total number of the four major carp species fry (hundred million) below Gezhouba Dam in the mainstream Yangtze River | Y5 | 100 million | 1997 | 2016 | 1 | 67 | 21 | [32] |
| Total catch of bronze gudgeon below Gezhouba Dam in the mainstream Yangtze River | Y6 | ton | 2000 | 2015 | 74 | 2716 | 15 | [32] |
| Total catch of Yellow catfish below Gezhouba Dam in the mainstream Yangtze River | Y7 | ton | 2001 | 2015 | 35 | 248 | 15 | [32] |
| Cumulative reservoir storage capacity upstream of TGD | X3 | km3 | 1956 | 2017 | 1 | 130 | 62 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Industrial wastewater in the Yangtze River Economic Belt | X4 | 10,000 tons | 1985 | 2010 | 938,071 | 1,424,127 | 26 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Domestic sewage in the Yangtze River Economic Belt | X5 | 10,000 tons | 1985 | 2010 | 0 | 1,584,570 | 26 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Sewage treatment rate | X6 | % | 1991 | 2017 | 15 | 95 | 27 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| GDP of Yangtze River Economic Belt | X7 | 100 million Yuan | 1949 | 2018 | 58 | 402,985 | 70 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Population of Yangtze River Economic Belt at year end | X8 | 10,000 | 1949 | 2018 | 18,778 | 59,873 | 70 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Nitrogen application amount | X9 | 10,000 tons | 1979 | 2018 | 361 | 994 | 40 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Application amount of compound fertilizer | X10 | 10,000 tons | 1980 | 2018 | 8 | 697 | 39 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Total planting area in the Yangtze River Economic Belt | X11 | 1000 Ha | 1978 | 2018 | 60,915 | 67,622 | 41 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Forest area of Yangtze River Economic Belt | X12 | 10,000 Ha | 1980 | 2018 | 3998 | 9048 | 39 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Grassland area in the Yangtze River Economic Belt | X13 | 1000 Ha | 1980 | 2017 | 53,814 | 64,621 | 38 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Application amount of phosphate fertilizer in the Yangtze River Economic Belt | X14 | 10,000 tons | 1979 | 2018 | 112 | 322 | 40 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| LTN | X15 | kg/(km2·yr) | 1980 | 2015 | 969 | 1942 | 36 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| LTP | X16 | kg/(km2·yr) | 1980 | 2015 | 71 | 166 | 36 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Average number of upstream fish species | Y8 | 1997 | 2015 | 42 | 76 | 17 | China Three Gorges Corporation | |
| Percentage of upstream endemic fish species | Y9 | % | 1997 | 2015 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 17 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Downstream (Jianli) Four Carp Eggs and larvae (billion) | Y10 | billion | 1997 | 2016 | 0 | 4 | 20 | [33] |
| Downstream (Jianli) fry runoff 100 million fish | Y11 | 100 million fish | 1964 | 2016 | 0 | 72 | 25 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Mean annual discharge | X17 | m3/s | 1959 | 2018 | 10,577 | 18,343 | 60 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Annual precipitation | X18 | mm | 1951 | 2018 | 805 | 1530 | 68 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Sediment concentration | X19 | kg/m3 | 1960 | 2018 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 59 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Absolute diatom abundance | Y12 | PCS/g dry weight | 1962 | 2012 | 1060 | 15,729 | 11 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Diatom aroma—Wiener count | Y13 | 1962 | 2012 | 2 | 5 | 11 | China Three Gorges Corporation | |
| Diatom abundance index | Y14 | 1962 | 2012 | 2 | 4 | 11 | China Three Gorges Corporation | |
| Water temperature | X20 | Degrees Celsius | 1958 | 1985 | 17 | 21 | 28 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Total ion | X21 | mg/L | 1958 | 1985 | 186 | 226 | 28 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Oxygen consumption (Dissolved oxygen) | X22 | mg/L | 1958 | 1985 | 1 | 4 | 41 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Ion flow rate | X23 | g/s | 1960 | 1984 | 3,023,841 | 4,998,834 | 25 | China Three Gorges Corporation |
| Cumulated area of isolated lake | X24 | km2 | 1949 | 2019 | 357 | 8195 | 70 | [34] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Bao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wen, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Sun, M. Three Gorges Dam Operation Altered Networks of Social–Economic–Ecological System in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054465
Liu X, Wang Y, Hu M, Bao Y, Wu X, Wen J, Li S, Zhang D, Sun M. Three Gorges Dam Operation Altered Networks of Social–Economic–Ecological System in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(5):4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xixi, Yuchun Wang, Mingming Hu, Yufei Bao, Xinghua Wu, Jie Wen, Shanze Li, Di Zhang, and Meng Sun. 2023. "Three Gorges Dam Operation Altered Networks of Social–Economic–Ecological System in the Yangtze River Basin, China" Sustainability 15, no. 5: 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054465
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, Y., Hu, M., Bao, Y., Wu, X., Wen, J., Li, S., Zhang, D., & Sun, M. (2023). Three Gorges Dam Operation Altered Networks of Social–Economic–Ecological System in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sustainability, 15(5), 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054465







