Seasonal Dependence and Variability of Rainfall Extremes in a Tropical River Basin, South Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Data Processing
2.3.2. Extraction of Extreme Rainfall Indices
3. Results
3.1. Variability of Seasonal Rainfall in MRB
3.2. Seasonal Dependence of Rainfall Extremes in MRB
3.3. Variability of Rainfall Extreme in MRB
3.4. GEV Distributions for Rainfall Extremes
3.5. Moisture Transport and Its Divergence in Contrast to Monsoon Years
3.6. Seasonal Rainfall Extremes Associated with Large-Scale Circulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, V.; Wallace, J.M.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Relationship between hourly extreme precipitation and local air temperature in the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Precipitation Extremes Under Climate Change. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, J.; Sobel, A.H.; Shaevitz, D.A.; Wang, S. Dynamic amplification of extreme precipitation sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9467–9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hegerl, G.C.; Min, S.-K. Attributing intensification of precipitation extremes to human influence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5252–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andrés-Doménech, I.; García-Bartual, R.; Montanari, A.; Marco, J.B. Climate and hydrological variability: The catchment filtering role. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woldesenbet, T.A.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Hydrological responses to land use/cover changes in the source region of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troin, M.; Arsenault, R.; Martel, J.-L.; Brissette, F. Uncertainty of Hydrological Model Components in Climate Change Studies over Two Nordic Quebec Catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Poulin, A.; Leconte, R. Overall uncertainty study of the hydrological impacts of climate change for a Canadian watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, S.; Pushpawela, B.; Liyanage, G. The long-term trend in the diurnal temperature range over Sri Lanka from 1985 to 2017 and its association with total cloud cover and rainfall. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2022, 227, 105810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Mishra, V. Contrasting response of rainfall extremes to increase in surface air and dewpoint temperatures at urban locations in India. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roxy, M.K.; Ghosh, S.; Pathak, A.; Athulya, R.; Mujumdar, M.; Murtugudde, R.; Terray, P.; Rajeevan, M. A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shelton, S.; Dixon, R.D. Long-Term Seasonal Drought Trends in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Climate 2023, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzsch, F.; Andersson, A.; Ziese, M.; Schröder, M.; Raykova, K.; Schamm, K.; Becker, A. A Global ETCCDI-Based Precipitation Climatology from Satellite and Rain Gauge Measurements. Climate 2017, 5, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.J.U.; Islam, A.K.M.; Das, M.; Mohammed, K.; Bala, S.; Islam, G.M. Observed trends in climate extremes over Bangladesh from 1981 to 2010. Clim. Res. 2019, 77, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.M.; Manzoor, N.; Ashraf, J.; Adnan, M.; Collins, D.; Hameed, S.; Manton, M.J.; Ahmed, A.U.; Baidya, S.K.; Borgaonkar, H.P.; et al. Trends in extreme daily rainfall and temperature indices over South Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.N.; Venugopal, V.; Sengupta, D.; Madhusoodanan, M.S.; Xavier, P.K. Increasing Trend of Extreme Rain Events Over India in a Warming Environment. Science 2007, 314, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, D.; Kumar, A. The changing characteristics of monsoon rainfall in India during 1971–2005 and links with large scale circulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3881–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basher, M.A.; Stiller-Reeve, M.A.; Saiful Islam, A.K.M.; Bremer, S. Assessing climatic trends of extreme rainfall indices over northeast Bangladesh. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbhandari, R.; Shrestha, A.B.; Nepal, S.; Wahid, S.; Ren, G.-Y. Extreme climate projections over the transboundary Koshi River Basin using a high resolution regional climate model. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 8, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Bajracharya, S.R.; Sharma, A.R.; Duo, C.; Kulkarni, A. Observed trends and changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes over the Koshi river basin 1975–2010. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1066–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subba, S.; Ma, Y.; Ma, W. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Precipitation Extremities of Eastern Nepal in the Last Two Decades (1997–2016). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7523–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayawardena, S.; Darshika, D.; Herath, H. Recent Trends in Climate Extreme Indices over Sri Lanka. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2018, 07, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shelton, S. Evaluation of the Streamflow Simulation by SWAT Model for Selected Catchments in Mahaweli River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2021, 6, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramagamage, P. Spatial and temporal variation of rainfall trends of Sri Lanka. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, U.; Rathnayake, U. Spatiotemporal rainfall variability and trend analysis over Mahaweli Basin, Sri Lanka. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, S.; Prasanna, V.; Kwon, H.-H. Monitoring Water Resources over the Kotmale Reservoir in Sri Lanka Using ENSO Phases. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 4025964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Silva, M.T.; Hornberger, G. Identifying ENSO Influences on Rainfall with Classification Models: Implications for Water Resource Management of Sri Lanka. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2018, 2018, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, L. El Niño–southern oscillation influences on the Mahaweli streamflow in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbulana, N.; Gunawardana, S.; Shrestha, S.; Datta, A. Projections of extreme precipitation events under climate change scenarios in Mahaweli River Basin of Sri Lanka. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatilleke, U.; Sirisena, J.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Muttil, N.; Rathnayake, U. Monitoring the Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts in the Largest River Basin (Mahaweli River) in Sri Lanka. Climate 2023, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Ouyang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Min, L. Temporal variation of extreme rainfall events in China, 1961–2009. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, S.; Kouadio, K.Y.; Ali, K.E.; Toualy, E.; Aman, A.; Yoroba, F. West Africa Extreme Rainfall Events and Large-Scale Ocean Surface and Atmospheric Conditions in the Tropical Atlantic. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1940456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onyutha, C. Variability of seasonal and annual rainfall in the River Nile riparian countries and possible linkages to ocean–atmosphere interactions. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 47, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntegeka, V.; Willems, P. Trends and multidecadal oscillations in rainfall extremes, based on a more than 100-year time series of 10 min rainfall intensities at Uccle, Belgium. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeevan, M.; Bhate, J.; Jaswal, A.K. Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded daily rainfall data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Roxy, M.K. On the relationship between north India summer monsoon rainfall and east equatorial Indian Ocean warming. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 179, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, B.A.; Hulugalla, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Mikami, T. Precipitation trends in Sri Lanka since the 1870s and relationships to El Niño–southern oscillation. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1235–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranatunge, E.; Malmgren, B.A.; Hayashi, Y.; Mikami, T.; Morishima, W.; Yokozawa, M.; Nishimori, M. Changes in the Southwest Monsoon mean daily rainfall intensity in Sri Lanka: Relationship to the El Nino-Southern Oscillation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2003, 197, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, L.; Ropelewski, C.F. The Strengthening Relationship between ENSO and Northeast Monsoon Rainfall over Sri Lanka and Southern India. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.; Alexander, L.; Rowell, D.; Kent, E.; Kaplan, A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late Nineteenth Century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T.; Mackaro, J. Atmospheric Moisture Transports from Ocean to Land and Global Energy Flows in Reanalyses. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4907–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, S.; Pushpawela, B. Observed southwest monsoon rainfall changes in Sri Lanka and possible mechanisms. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 4165–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.I.P.; Santo, F.E.; Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M. Trends and correlations in annual extreme precipitation indices for mainland Portugal, 1941–2007. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espírito Santo, F.; Ramos, A.M.; de Lima, M.I.P.; Trigo, R.M. Seasonal changes in daily precipitation extremes in mainland Portugal from 1941 to 2007. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 1765–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; El Adlouni, S.; Servat, E. Trends and variability in extreme precipitation indices over Maghreb countries. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2013, 13, 3235–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, A.; Feng, Q.; Fu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, M.; Wang, G. Recent changes in precipitation extremes in the Heihe River basin, Northwest China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, E.; Peterson, T.C.; Obando, P.R.; Frutos, R.; Retana, J.A.; Solera, M.; Soley, J.; García, I.G.; Araujo, R.M.; Santos, A.R.; et al. Changes in precipitation and temperature extremes in Central America and northern South America, 1961–2003. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.A.; Aguilar, E.; Saindou, M.; Hassane, A.F.; Jumaux, G.; Roy, D.; Booneeady, P.; Virasami, R.; Randriamarolaza, L.Y.A.; Faniriantsoa, F.R.; et al. Observed trends in indices of daily and extreme temperature and precipitation for the countries of the western Indian Ocean, 1961–2008. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Pu, Q. New Techniques for the Detection and Adjustment of Shifts in Daily Precipitation Data Series. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 2416–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.C.; Santos, J.A.; Pinto, J.G. Climate change scenarios for precipitation extremes in Portugal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Notti, D.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Mora, O.; Cooksley, G.; Sánchez, M.; Arnaud, A.; Crosetto, M. Analysis with C- and X-band satellite SAR data of the Portalet landslide area. Landslides 2011, 8, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.-q.; Hu, R.-J.; Wang, S.-P.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Tong, L. Trends of precipitation extremes during 1960–2008 in Xinjiang, the Northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 111, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y. Characteristics of extreme temperature and precipitation in China in 2017 based on ETCCDI indices. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2018, 9, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.K.; Panigrahi, P.; Mohanty, S.; Mohanty, R.K.; Sethi, R.R. The 20th century transitions in basic and extreme monsoon rainfall indices in India: Comparison of the ETCCDI indices. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, N.; Das, D.K.; Mukherjee, J.; Sehgal, V.K.; Krishnan, P. Extreme temperature and rainfall events in National Capital Region of India (New Delhi) in the recent decades and its possible impacts. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 137, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Hewitson, B.; Stephenson, D.; Tsiga, A.; Kruger, A.; Manhique, A.; Gomez, B.; Coelho, S.; Ntiki Masisi, D.; Kululanga, E.; et al. Evidence of trends in daily climate extremes over southern and west Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D14102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.-H.; Nguyen, V.-T.-V.; Kpodonu, T.A. Characterizing extreme rainfalls and constructing confidence intervals for IDF curves using Scaling-GEV distribution model. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.P.; Soden, B.J. Large discrepancy between observed and simulated precipitation trends in the ascending and descending branches of the tropical circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratna, S.B.; Cherchi, A.; Joseph, P.V.; Behera, S.K.; Abish, B.; Masina, S. Moisture variability over the Indo-Pacific region and its influence on the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, S.; King, A.; Vincent, C.; Karoly, D.; Protat, A. Seasonal dependence of rainfall extremes in and around Jakarta, Indonesia. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2019, 24, 100202–100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanueva, A.; Rodríguez-Puebla, C.; Frías, M.D.; González-Reviriego, N. Variability of extreme precipitation over Europe and its relationships with teleconnection patterns. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q. Characteristics of consecutive dry days variations in China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 130, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Cheng, C.S. Hydrological impacts of precipitation extremes in the Huaihe River Basin, China. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J. Changes in climate extreme events in China associated with warming. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2735–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, S.; Arakawa, O. Change in the precipitation intensity of the East Asian summer monsoon projected by CMIP3 models. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 2055–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limsakul, A.; Limjirakan, S.; Sriburi, T. Observed changes in daily rainfall extremes along Thailand’s coastal zone. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 32, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, C.V.; Satyanarayana, G.C.; Durgalakshmi, K.; Malleswara Rao, L.; Nagaratna, K. Is winter monsoon rainfall over South Peninsular India increasing in global warming era? Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Nigam, S. The northeast winter monsoon over the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia: Evolution, interannual variability, and model simulations. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniadi, A.; Weller, E.; Min, S.-K.; Seong, M.-G. Independent ENSO and IOD impacts on rainfall extremes over Indonesia. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3640–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falga, R.; Wang, C. The rise of Indian summer monsoon precipitation extremes and its correlation with long-term changes of climate and anthropogenic factors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zwiers, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Wehner, M. Changes in annual extremes of daily temperature and precipitation in CMIP6 models. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3441–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
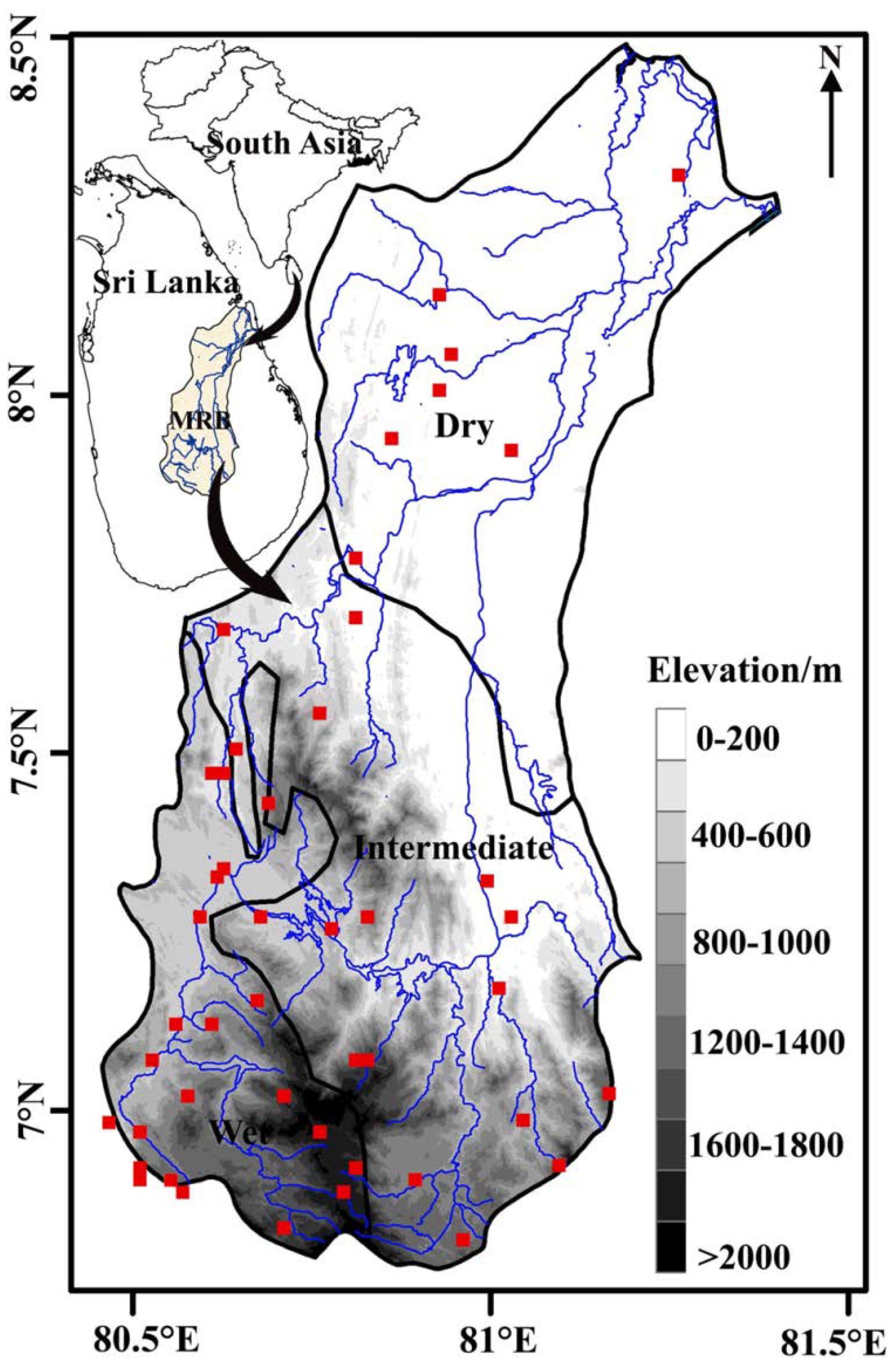

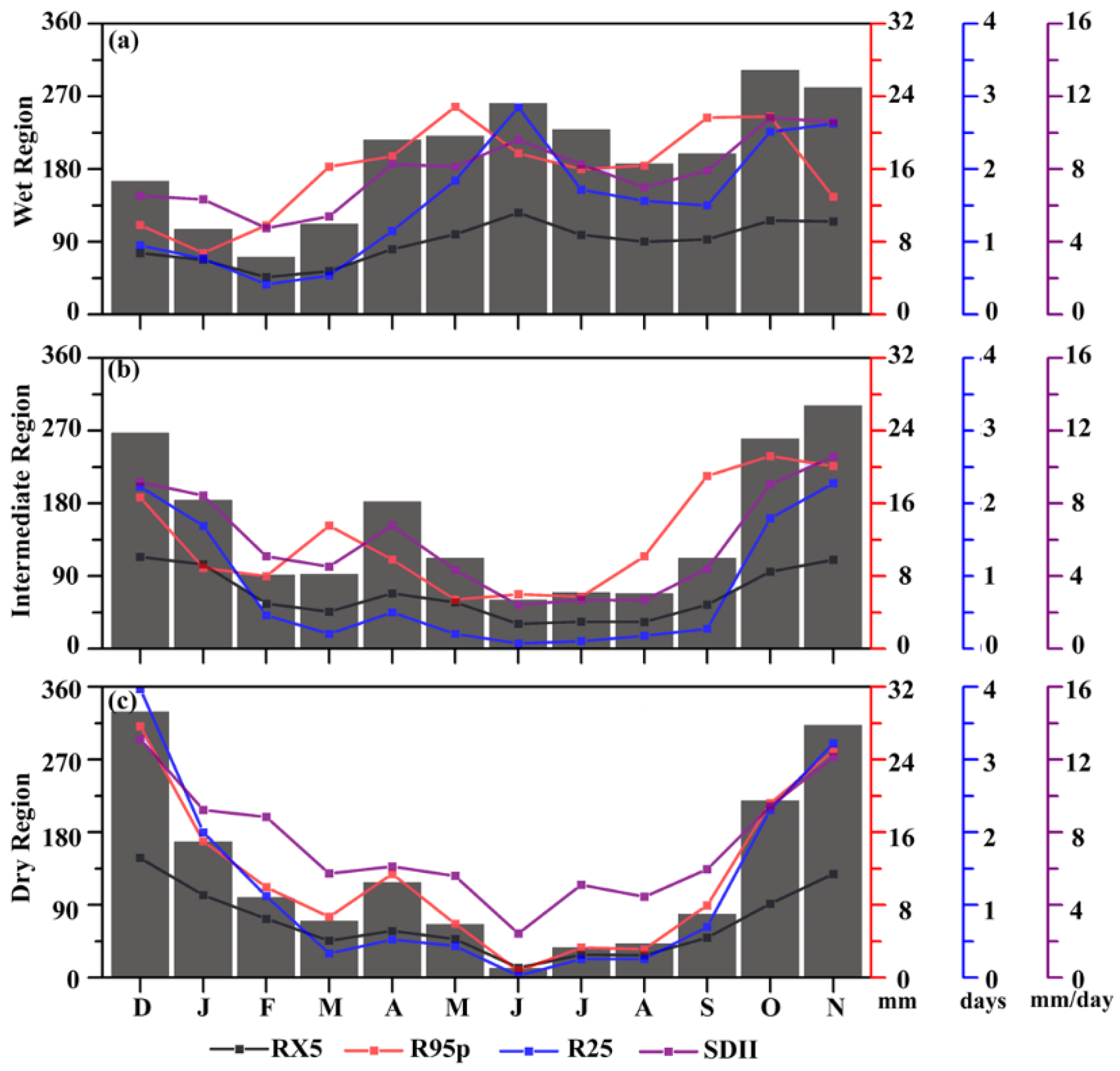
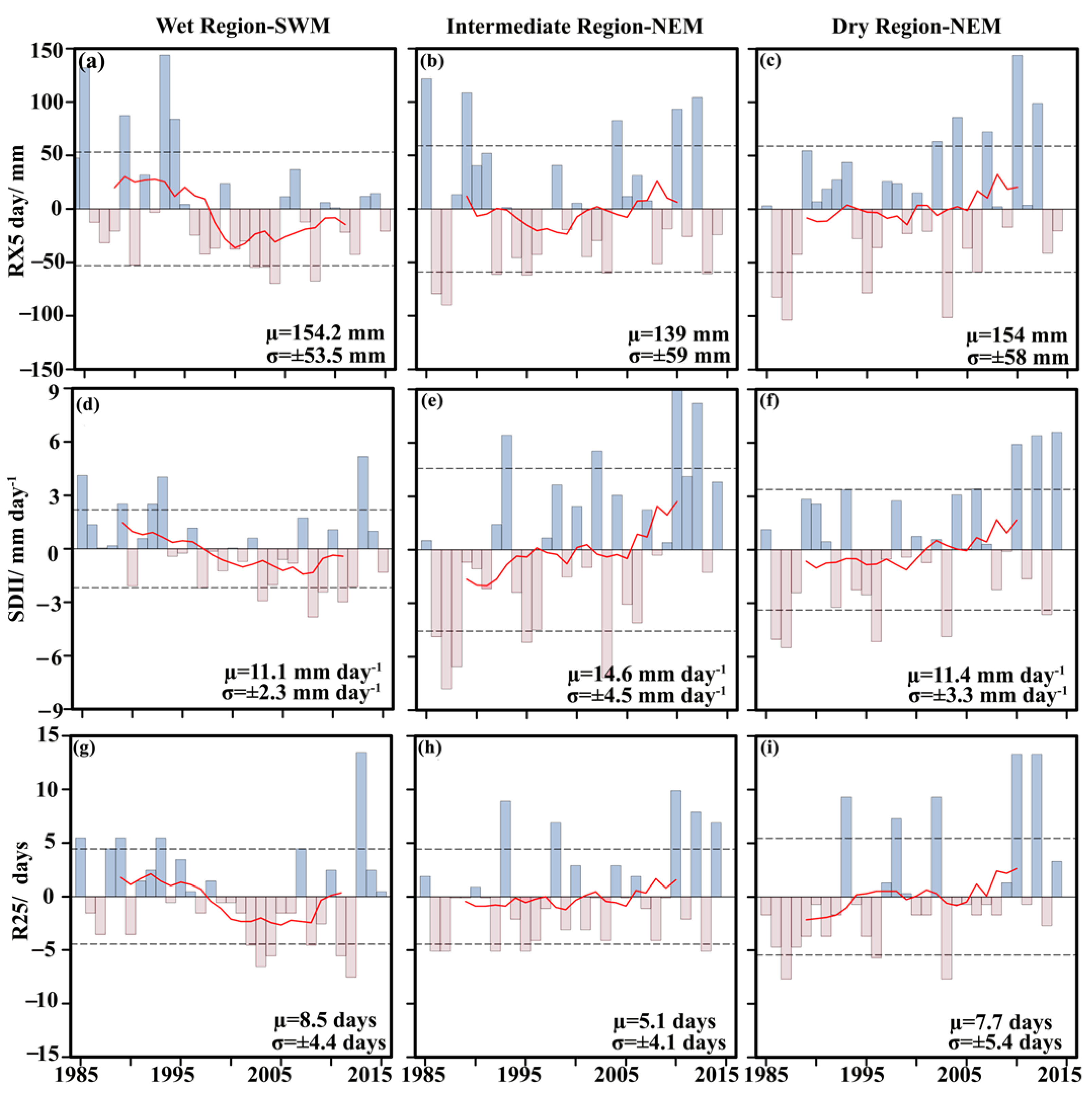
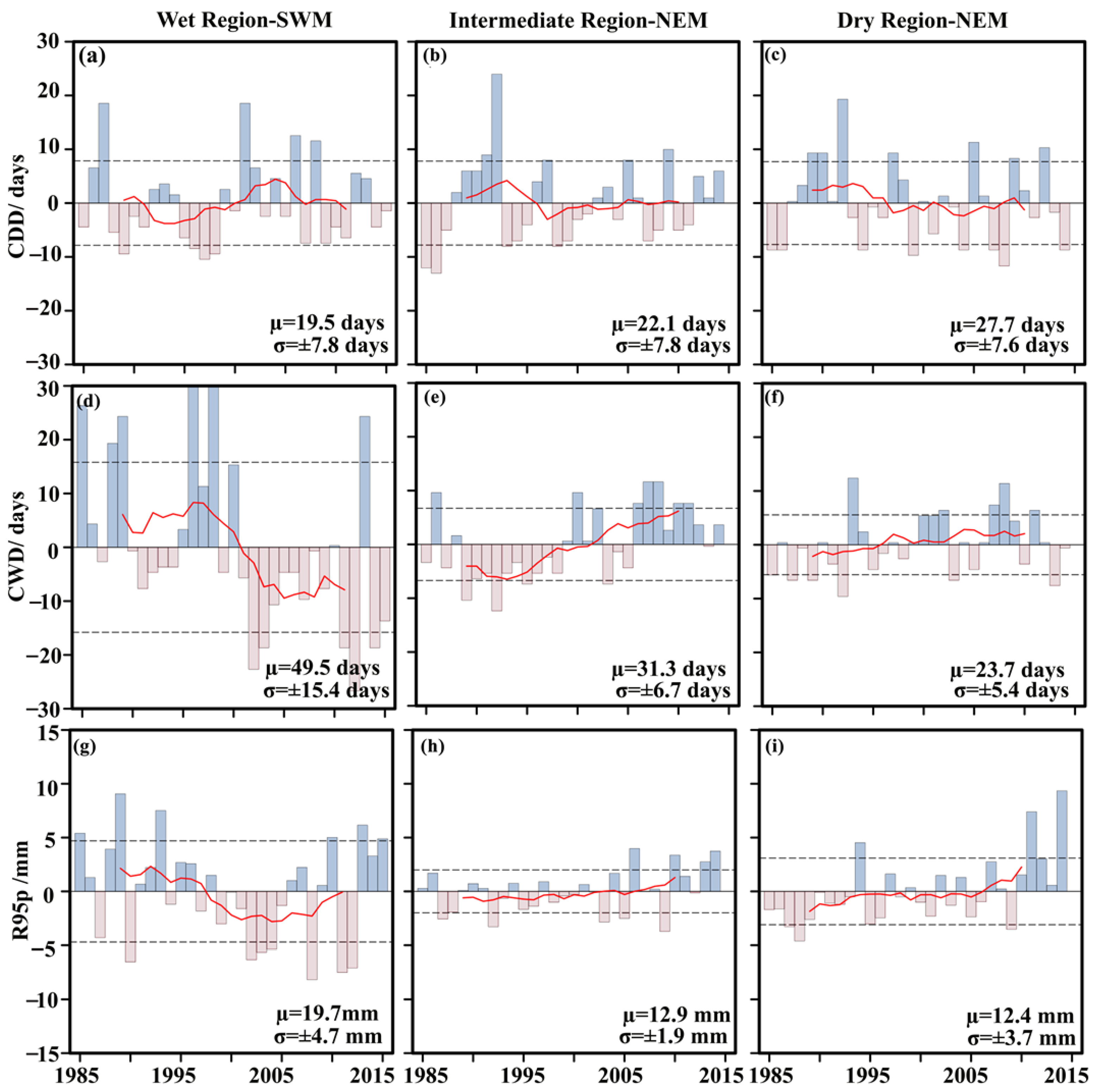


| Region | Station | lat | lon | Percentage of Missing | Annual Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet | Bopathalawa | 6.83 | 80.72 | 0.04 | 1937 |
| Katugasthota | 7.33 | 80.63 | 1.64 | 1873 | |
| Labukale | 7.02 | 80.72 | 2.57 | 3051 | |
| Maussakele | 6.85 | 80.55 | 0.15 | 3005 | |
| Galaha | 7.15 | 80.68 | 3.32 | 2553 | |
| Norton | 6.92 | 80.52 | 0.83 | 4533 | |
| Nuwaraeliya | 6.97 | 80.77 | 0.12 | 1881 | |
| Laksapana | 6.90 | 80.52 | 0.26 | 4601 | |
| Kurudu Oya | 7.07 | 80.83 | 3.01 | 2707 | |
| Intermediate | Haggala | 6.92 | 80.82 | 1.39 | 1771 |
| Baddulla | 6.98 | 81.05 | 0.04 | 1772 | |
| Aluthnuwara | 7.32 | 81.00 | 3.10 | 1898 | |
| Bandrawela | 6.82 | 80.97 | 1.27 | 1559 | |
| Kandekatiya | 7.17 | 81.02 | 1.37 | 1859 | |
| SpringVally | 6.92 | 81.10 | 1.91 | 2403 | |
| Cristal hil | 7.50 | 80.65 | 3.12 | 1831 | |
| Matale | 7.47 | 80.62 | 2.18 | 1844 | |
| Walimada | 7.47 | 80.63 | 1.64 | 1337 | |
| Dry | Pollonaruwa | 7.92 | 81.03 | 3.14 | 1517 |
| Bakamuna | 7.77 | 80.82 | 3.00 | 1670 | |
| Palwehera | 7.90 | 80.68 | 0.12 | 1549 | |
| Gerithale | 8.00 | 80.93 | 3.42 | 1489 | |
| Deyabeduma | 7.93 | 80.87 | 0.13 | 1577 | |
| Trincomalee | 8.58 | 81.25 | 2.80 | 1420 |
| Index | Unit | Description | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDD | days | Consecutive dry days | Maximum number of consecutive days without rainfall (daily rainfall) <1 mm in a year |
| CWD | days | Consecutive wet days | Maximum number of consecutive days with rainfall ≥1 mm in a year |
| R25 | days | Number of extremely heavy rainfall days | Annual count of days when RR ≥25 mm |
| R95p | mm | Extremely wet day rainfall | Annual total rainfall when r > 95th percentile of daily rainfall |
| RX5day | mm | Maximum consecutive 5-day rainfall amount | Annual maximum consecutive 5-day rainfall |
| SDII | mm/day | Simple daily intensity index | Annual total rainfall divided by the number of wet days |
| Region | Index | DMI (ENSO Removed) | ENSO (DMI Removed) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIM | NEM | SIM | SWM | FIM | NEM | SIM | SWM | ||
| Wet | Rain | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.14 | −0.54 a | −0.10 | −0.30 a | 0.23 | −0.30 a |
| RX5 | −0.25 | 0.14 | 0.12 | −0.47 a | −0.18 | −0.22 | 0.07 | −0.12 | |
| R25 | −0.22 | 0.04 | 0.11 | −0.30 a | −0.19 | −0.19 | 0.03 | −0.29 a | |
| SDII | −0.25 | 0.01 | 0.07 | −0.52 a | 0.00 | −0.29 a | 0.09 | −0.10 | |
| R95p | −0.13 | 0.07 | 0.07 | −0.39 a | 0.03 | −0.31 a | 0.01 | −0.29 a | |
| Int | Rain | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.45 a | −0.17 | −0.10 | −0.31 a | 0.24 | −0.28 |
| RX5 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.14 | −0.18 | −0.08 | −0.21 | 0.04 | −0.10 | |
| R25 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.05 | −0.22 | 0.03 | −0.08 | |
| SDII | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.41 a | −0.11 | 0.07 | −0.29 a | 0.17 | −0.23 | |
| R95p | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.36 a | −0.23 | 0.00 | −0.30 a | 0.01 | −0.22 | |
| Dry | Rain | −0.13 | 0.17 | 0.45 a | −0.07 | −0.01 | −0.31 a | 0.09 | −0.17 |
| RX5 | −0.16 | 0.18 | 0.17 | −0.05 | 0.00 | −0.24 | 0.05 | −0.31 a | |
| R25 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.46 a | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.29 a | 0.02 | −0.02 | |
| SDII | −0.05 | 0.15 | 0.42 a | −0.04 | 0.15 | −0.29 a | 0.08 | −0.14 | |
| R95p | −0.06 | 0.19 | 0.44 a | −0.06 | 0.11 | −0.33 a | 0.04 | −0.03 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelton, S.; Pushpawela, B. Seasonal Dependence and Variability of Rainfall Extremes in a Tropical River Basin, South Asia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065106
Shelton S, Pushpawela B. Seasonal Dependence and Variability of Rainfall Extremes in a Tropical River Basin, South Asia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(6):5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065106
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelton, Sherly, and Buddhi Pushpawela. 2023. "Seasonal Dependence and Variability of Rainfall Extremes in a Tropical River Basin, South Asia" Sustainability 15, no. 6: 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065106
APA StyleShelton, S., & Pushpawela, B. (2023). Seasonal Dependence and Variability of Rainfall Extremes in a Tropical River Basin, South Asia. Sustainability, 15(6), 5106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065106





