Machine Learning-Based Classification of Asbestos-Containing Roofs Using Airborne RGB and Thermal Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Review
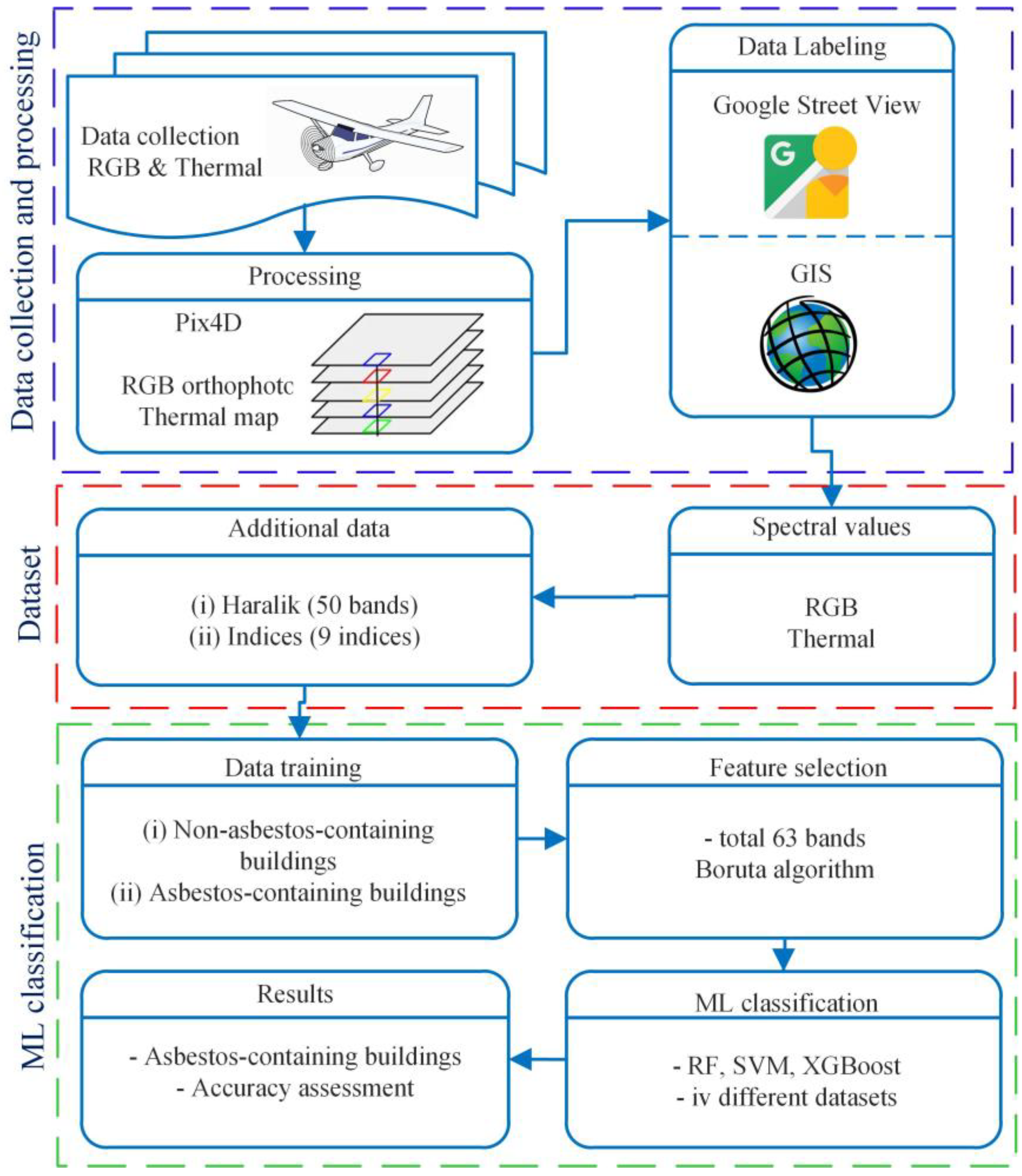
2. Materials and Methods
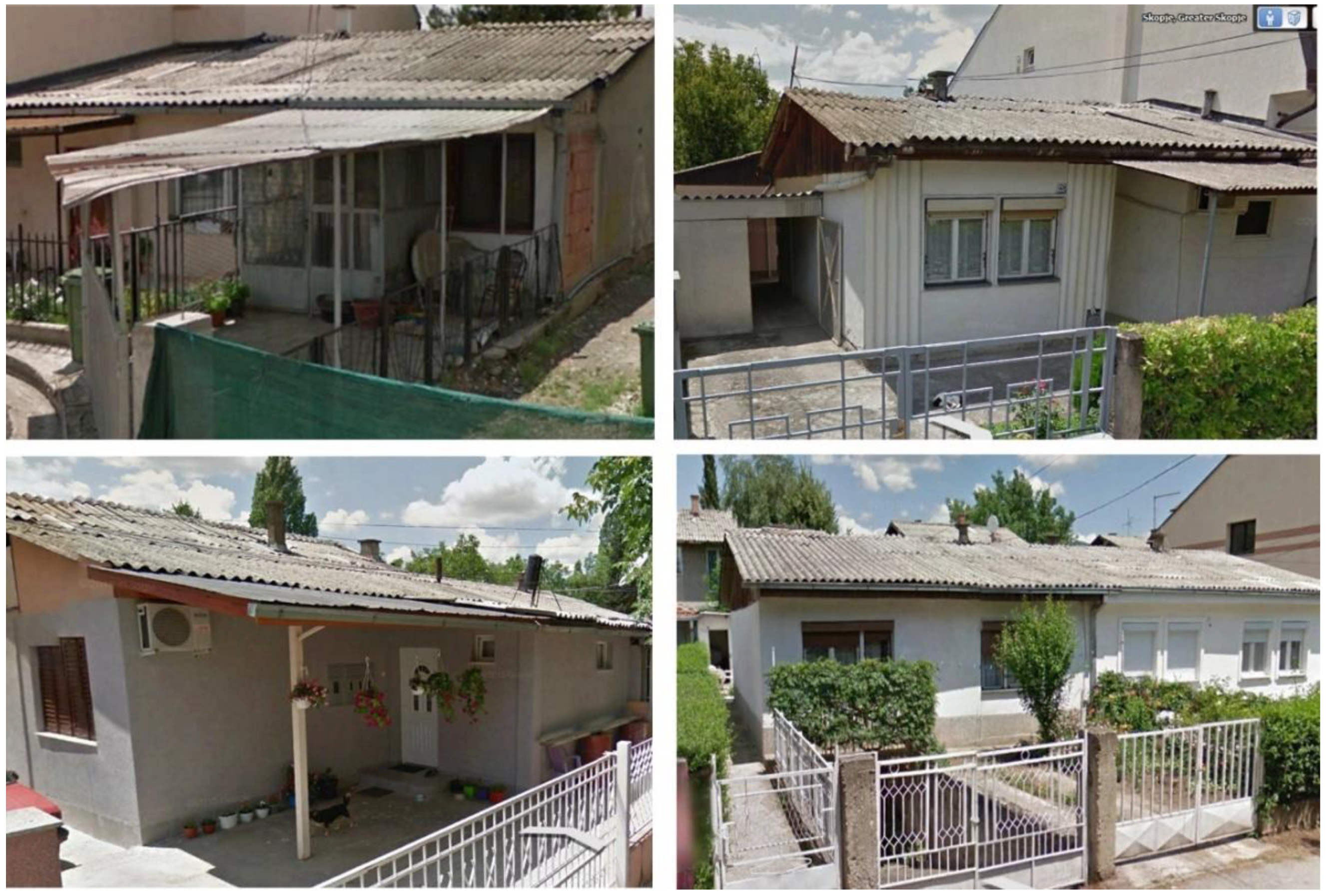
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Features
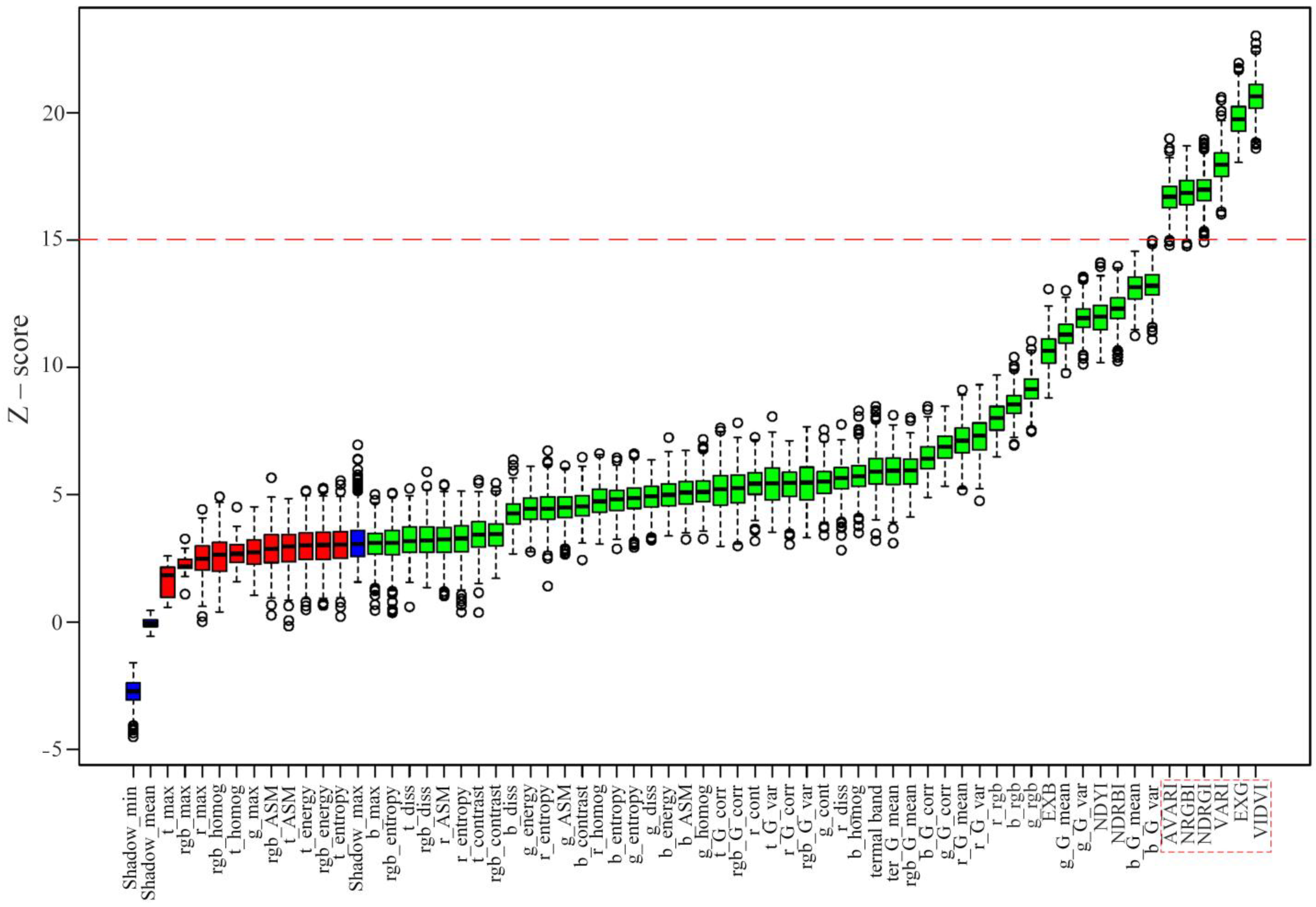
2.2.2. Feature Selection
2.2.3. Machine Learning Classification
2.2.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Feature Selection Results
3.2. Machine Learning Classification Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, M.; Langer, A.M.; Nord, G.L.; Nolan, R.P.; Lee, R.J.; Van Orden, D.; Addison, J. The mineral nature of asbestos. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, S26–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Arsenic and arsenic compounds. In Arsenic, Metals, Fibres and Dusts; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bassani, C.; Cavalli, R.M.; Cavalcante, F.; Cuomo, V.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S. Deterioration status of asbestos-cement roofing sheets assessed by analyzing hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campopiano, A.; Ramires, D.; Zakrzewska, A.M.; Ferri, R.; D’annibale, A.; Pizzutelli, G. Risk Assessment of the Decay of Asbestos Cement Roofs. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 53, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartrip, P.W. History of asbestos related disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 2004, 80, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, G.P.; Watt, S.J.; Maskell, N.A. An overview of how asbestos exposure affects the lung. BMJ 2009, 339, b3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, E.; de Klerk, N.; Musk, A.W. Asbestos-related disease. Int. Med. J. 2011, 41, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.; de Klerk, N.H.; Magnani, C.; Ferrante, D.; Berry, G.; Musk, A.W.; Merler, E. Mesothelioma risk after 40 years since first exposure to asbestos: A pooled analysis. Thorax 2014, 69, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.S.; Baelum, J.; Rasmussen, J.; Dahl, S.; Olsen, K.E.; Albin, M.; Hansen, N.C.; Sherson, D. Occupational asbestos exposure and lung cancer—A systematic review of the literature. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2014, 69, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, R.; Peto, J. Effects on Health of Exposure to Asbestos; Health & Safety Commission: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Roggli, V.L.; Vollmer, R.T. Twenty-five years of fiber analysis: What have we learned? Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilia, C.; Panigada, C.; Rossini, M.; Candiani, G.; Pepe, M.; Colombo, R. Mapping of Asbestos Cement Roofs and Their Weathering Status Using Hyperspectral Aerial Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Hollins, I.; Pickin, J.; Donovan, S. Asbestos Stocks and Flows Legacy in Australia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, E.; Krówczyńska, M.; Pabjanek, P.; Mędrzycki, P. Estimation of the amount of asbestos-cement roofing in Poland. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folić, R.; Laban, M.; Milanko, V. Reliability and sustainability analysis of large panel residential buildings in Sofia, Skopje and Novi Sad. Facta Univ.-Ser. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2011, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obmiński, A. Asbestos cement products and their impact on soil contamination in relation to various sources of anthropogenic and natural asbestos pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriha, D.; Kovács, Z.; Ninsawat, S.; Bertalan, L.; Bertalan-Balazs, B.; Szabo, S. Identification of roofing materials with Discriminant Function Analysis and Random Forest classifiers on pan-sharpened WorldView-2 imagery—A comparison. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2018, 67, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pinho, C.M.D.; Fonseca, L.M.G.; Korting, T.S.; de Almeida, C.M.; Kux, H.J.H. Land-cover classification of an intra-urban environment using high-resolution images and object-based image analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5973–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiumi, L.; Congedo, L.; Meoni, C. Developing expeditious methodology for mapping asbestos-cement roof coverings over the territory of Lazio Region. Appl. Geomat. 2014, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolakis, D.; Shaw, G. Detection algorithms for hyperspectral imaging applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisiol, F.; Lambertini, A.; Franci, F.; Mandanici, E. An Object-Oriented Approach to the Classification of Roofing Materials Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Stereo-Pairs. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Camps-Valls, G.; Scheunders, P.; Nasrabadi, N.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Analysis and Future Challenges. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassy, F.; Candiani, G.; Rusmini, M.; Maianti, P.; Marchesi, A.; Rota Nodari, F.; Dalla Via, G.; Albonico, C.; Gianinetto, M. Mapping Asbestos-Cement Roofing with Hyperspectral Remote Sensing over a Large Mountain Region of the Italian Western Alps. Sensors 2014, 14, 15900–15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, S.; Burai, P.; Kovács, Z.; Szabó, G.; Kerényi, A.; Fazekas, I.; Paládi, M.; Buday, T.; Szabo, G. Testing algorithms for the identification of asbestos roofing based on hyperspectral data. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krówczyńska, M.; Raczko, E.; Staniszewska, N.; Wilk, E. Asbestos–Cement Roofing Identification Using Remote Sensing and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasini, M.; Bacciottini, A.; Gherardelli, M. A QGIS Tool for Automatically Identifying Asbestos Roofing. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska-Skotak, K.; Ostrowski, W. Use of satellite and ALS data for classification of roofing materials on the example of asbestos roof tile identification. Tech. Sci. 2015, 18, 283–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Bi, H.; Dalla Mura, M.; Chanussot, J. Superresolution land cover mapping based on pixel-, subpixel-, and superpixel-scale spatial dependence with pansharpening technique. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4082–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Jogun, T. The effect of fusing Sentinel-2 bands on land-cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 822–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G. Assessing the effectiveness of PlanetScope synthesized panchromatic bands for spatial enhancement of Sentinel-2 data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 036504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, C.M.; Oliveira, S.; Oliveira, S.C.; Rocha, J. Land use/land cover change detection and urban sprawl analysis. In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 621–651. [Google Scholar]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Liou, Y.-A.; Rahman, A. Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Dobrinić, D. Green Infrastructure Mapping in Urban Areas Using Sentinel-1 Imagery. Croat. J. For. Eng. J. Theory Appl. For. Eng. 2021, 42, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.; Trinder, J.; Shaker, A. Evaluation of the self-organizing map classifier for building detection from lidar data and multispectral aerial images. J. Spat. Sci. 2009, 54, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmadiya, A.; Nabiyev, N.; Moldamurat, K.; Kismanova, A.; Prmantayeva, B.; Brimzhanova, S. Application of GLCM Textural Based Method With Sentinel-1 Radar Remote Sensing Data for Building Damage Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST), Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan, 28–30 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, G.B.; Kumarasamy, U.M.; Zarro, C.; Divakarachari, P.B.; Ullo, S.L. Land-use and land-cover classification using a human group-based particle swarm optimization algorithm with an LSTM Classifier on hybrid pre-processing remote-sensing images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Guldmann, J.-M. Measuring continuous landscape patterns with Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM) indices: An alternative to patch metrics? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.X.; Benediktsson, J.A. A multispectral and multiangle 3-D convolutional neural network for the classification of ZY-3 satellite images over urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 10266–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Mostafa, S.; Vieira, A.S.; Patorniti, N.; Stewart, R.A. Mapping Roofing with Asbestos-Containing Material by Using Remote Sensing Imagery and Machine Learning-Based Image Classification: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolska, R.; Shendova, V.; Necevska-Cvetanovska, G. The need of integrated renovation of the existing building stock in North Macedonia. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinadinovski, C.; McCue, K. 50 years since the Skopje 1963 Earthquake: Implications for Australian building standards. In Proceedings of the Australian Earthquake Engineering Society AEES Conference, Victoria, Australia, 24–25 November 2022; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, A.F.A.; Martins, R.N.; de Souza, G.S.A.; de Moura Araújo, G.; de Almeida, S.L.H.; Capelini, V.A. Segmentation of RGB images using different vegetation indices and thresholding methods. Nativa 2018, 6, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.D.; Jang, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Rodrogues, R.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Chung, Y.S. RGB images-based vegetative index for phenotyping kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256978. [Google Scholar]
- Sulik, J.J.; Long, D.S. Spectral considerations for modeling yield of canola. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y. Early-Season Mapping of Winter Crops Using Sentinel-2 Optical Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Willis, P.; Mueller, R. Impact of band-ratio enhanced AWIFS image to crop classification accuracy. In Proceedings of the Pecora 17—The Future of Land Imaging…Going Operational, Denver, CO, USA, 18–20 November 2008; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, B.; Ferraz, G.; Gonçalves, L.; Marin, D.; Maciel, D.; Ferraz, P.; Rossi, G. RGB vegetation indices applied to grass monitoring: A qualitative analysis. Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Lussem, U.; Bolten, A.; Gnyp, M.; Jasper, J.; Bareth, G. Evaluation of RGB-based vegetation indices from UAV imagery to estimate forage yield in grassland. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. The RapeseedMap10 database: Annual maps of rapeseed at a spatial resolution of 10 m based on multi-source data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2857–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deur, M.; Gašparović, M.; Balenović, I. Tree species classification in mixed deciduous forests using very high spatial resolution satellite imagery and machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Rathore, P.; Roy, D.; Chakraborty, D.; Jatav, R.S.; Sethi, D.; Kumar, P. Comparison of bagging, boosting and stacking algorithms for surface soil moisture mapping using optical-thermal-microwave remote sensing synergies. Catena 2022, 217, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Schmidt, K.; Amirian-Chakan, A.; Rentschler, T.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Sarmadian, F.; Valavi, R.; Davatgar, N.; Behrens, T.; Scholten, T. Improving the spatial prediction of soil organic carbon content in two contrasting climatic regions by stacking machine learning models and rescanning covariate space. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, A.; Virtanen, T. Data and resolution requirements in mapping vegetation in spatially heterogeneous landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 111207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. Support vector machines for classification in remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jin, S.; Savi, P.; Gao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. GNSS-R soil moisture retrieval based on a XGboost machine learning aided method: Performance and validation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, R.U.; Shankar, B.U. A novel multilabel classification of remote sensing images using XGBoost. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Bombay, India, 29–31 March 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy assessment in convolutional neural network-based deep learning remote sensing studies—Part 1: Literature review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantero, P.; Moser, G.; Serpico, S.B. Partially supervised classification of remote sensing images through SVM-based probability density estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, C.M.D.d.; Silva, F.; Fonseca, L.; Monteiro, A. Intra-urban land cover classification from high-resolution images using the C4. 5 algorithm. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress, Beijing, China, 3–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gibril, M.B.A.; Shafri, H.Z.; Hamedianfar, A. New semi-automated mapping of asbestos cement roofs using rule-based object-based image analysis and Taguchi optimization technique from WorldView-2 images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Audícana, M.; Otazu, X.; Fors, O.; Alvarez-Mozos, J. A low computational-cost method to fuse IKONOS images using the spectral response function of its sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minov, J.; Karadzinska-Bislimovska, J.; Ristovska, G. Health risks related to asbestos exposure in the environment-literature review and present status in Republic of Macedonia. Arch. Public Health 2015, 7, 5–12. [Google Scholar]




| Index | Abbreviation | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excess green | EXG | 2g − r − b | [43,44] |
| Excess blue | EXB | g − r − 2b | This study |
| Normalized difference yellowness index | NDYI | (g − b)/(g + b) | [45,46] |
| Normalized difference red-blue index | NDRBI | (r − b)/(r + b) | This study |
| Normalized difference red-green index | NDRGI | (r − g)/(r + g) | [47] |
| Visible-band difference vegetation index | VIDVI | (2g − b − r)/(2g + b + r) | [48] |
| Visible-band difference vegetation index | VARI | (g − r)/(g + r − b) | [49] |
| Additional VARI | AVARI | (g − r)/(g + r + b) | This study |
| Normalized red-green-blue index | NRGBI | NDRBI − NDYI | [45,50] |
| Dataset | Method | Kappa | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Balanced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.780 | 0.855 | 0.927 | 0.845 | 0.932 | 0.891 | |
| I | SVM | 0.813 | 0.940 | 0.900 | 0.821 | 0.970 | 0.922 |
| XGBoost | 0.793 | 0.861 | 0.933 | 0.856 | 0.935 | 0.897 | |
| RF | 0.824 | 0.928 | 0.918 | 0.841 | 0.965 | 0.923 | |
| II | SVM | 0.815 | 0.916 | 0.918 | 0.840 | 0.960 | 0.917 |
| XGBoost | 0.822 | 0.910 | 0.927 | 0.853 | 0.956 | 0.918 | |
| RF | 0.827 | 0.922 | 0.924 | 0.850 | 0.962 | 0.923 | |
| III | SVM | 0.819 | 0.922 | 0.918 | 0.841 | 0.962 | 0.920 |
| XGBoost | 0.819 | 0.916 | 0.921 | 0.844 | 0.959 | 0.918 | |
| RF | 0.813 | 0.898 | 0.927 | 0.851 | 0.951 | 0.912 | |
| IV | SVM | 0.825 | 0.950 | 0.910 | 0.831 | 0.973 | 0.930 |
| XGBoost | 0.823 | 0.921 | 0.921 | 0.845 | 0.962 | 0.922 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaplan, G.; Gašparović, M.; Kaplan, O.; Adjiski, V.; Comert, R.; Mobariz, M.A. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Asbestos-Containing Roofs Using Airborne RGB and Thermal Imagery. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6067. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076067
Kaplan G, Gašparović M, Kaplan O, Adjiski V, Comert R, Mobariz MA. Machine Learning-Based Classification of Asbestos-Containing Roofs Using Airborne RGB and Thermal Imagery. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):6067. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076067
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaplan, Gordana, Mateo Gašparović, Onur Kaplan, Vancho Adjiski, Resul Comert, and Mohammad Asef Mobariz. 2023. "Machine Learning-Based Classification of Asbestos-Containing Roofs Using Airborne RGB and Thermal Imagery" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 6067. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076067
APA StyleKaplan, G., Gašparović, M., Kaplan, O., Adjiski, V., Comert, R., & Mobariz, M. A. (2023). Machine Learning-Based Classification of Asbestos-Containing Roofs Using Airborne RGB and Thermal Imagery. Sustainability, 15(7), 6067. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076067















