Emission Characteristics of Particle Number from Conventional Gasoline and Hybrid Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Comparison of PN emission characteristics from China IV, China V, and China VI vehicles (Section 3.1).
- Impact of mainstream engine techniques on PN emissions for China VI vehicles complying with the latest emission standards in China (Section 3.1).
- Effects of start-up stages on PN transient emissions (Section 3.2).
- Influences of driving conditions on PN emissions (Section 3.3).
2. Methodology
2.1. Test Vehicles and Fuels
2.2. Experimental Protocol and Driving Cycles
3. Results and Discussion
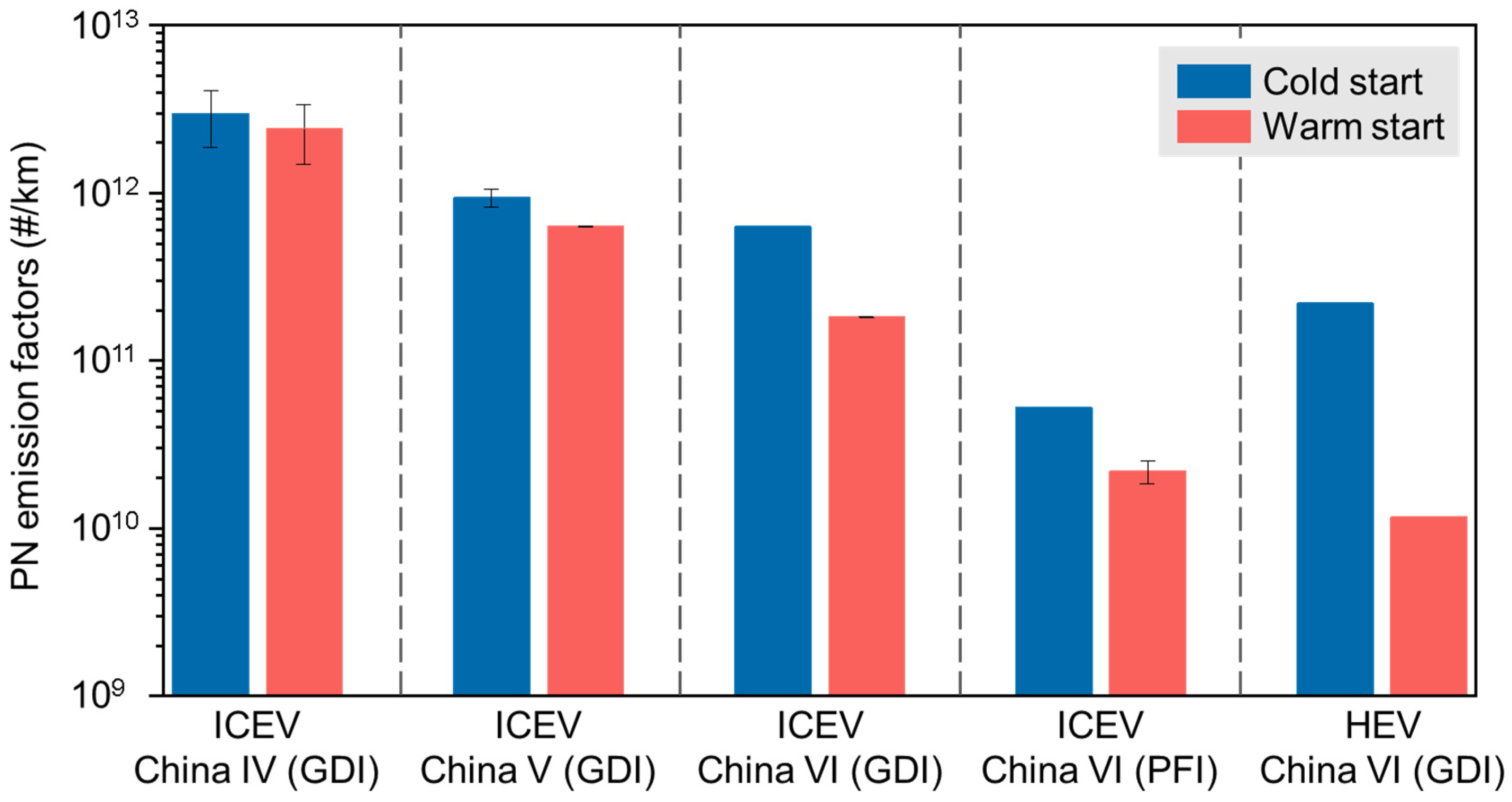
3.1. Effect of Technology Upgrades on PN Emissions
| Emission Standards | Engine Techniques | Testing Methods | PN Emission Factors (#/km) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China III | PFI | real driving emission | 8.56 × 1010 | [3] |
| China IV | PFI | real driving emission | 1.67 × 1010 | [3] |
| 1.2 × 1011–7.9 × 1011 | [8] | |||
| chassis dynamometer tests | 3.62 ×1011–1.13 × 1012 | [11] | ||
| GDI | real driving emission | 7.5 × 1010–1.4 × 1012 | [8] | |
| chassis dynamometer tests | 2.5 × 1012–3.91 × 1012 | [11] | ||
| 1.76 × 1012–3.74× 1012 | This study | |||
| China V | PFI | real driving emission | 1.01 × 1010 | [3] |
| 6.1 × 1010–7.7 × 1011 | [8] | |||
| chassis dynamometer tests | 3.35 × 1013 | [27] | ||
| GDI | real driving emission | 1.01 × 1011 | [3] | |
| 2.4 × 1011–3.9 × 1012 | [8] | |||
| chassis dynamometer tests | 4.62 × 1012 | [27] | ||
| 6.31 × 1011–1.02 × 1012 | This study | |||
| China VI | PFI | real driving emission | 6.0 × 1010–9.7 × 1010 | [11] |
| chassis dynamometer tests | 2.44 × 1013 | [27] | ||
| 1.85 × 1010–5.25 × 1010 | This study | |||
| GDI | real driving emission | 2.1 × 1011–3.5 × 1011 | [11] | |
| chassis dynamometer tests | 1.17 × 1012 | [27] | ||
| 1.84 × 1011–6.30 × 1011 | This study |
3.2. Effect of Start-Up on PN Emissions
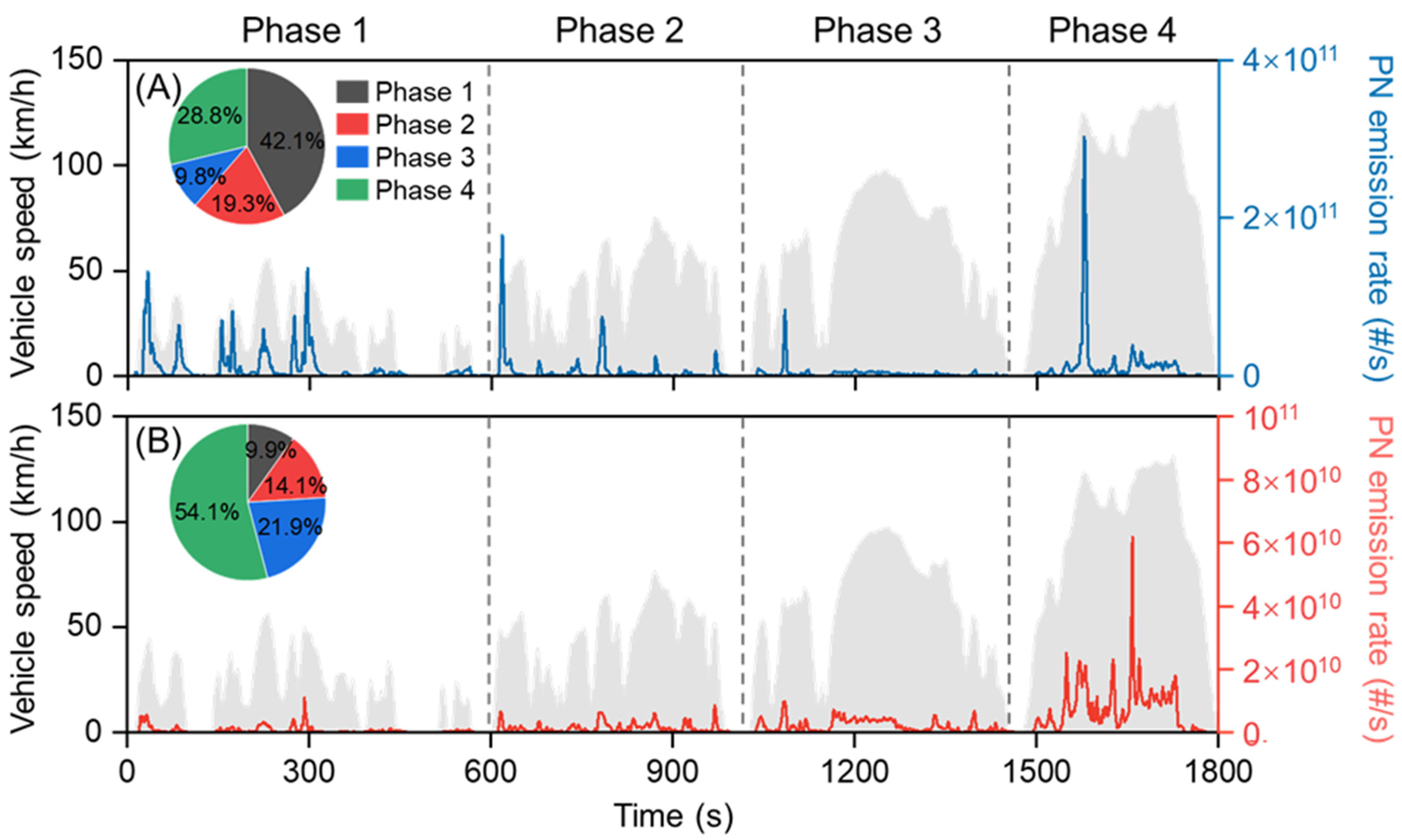
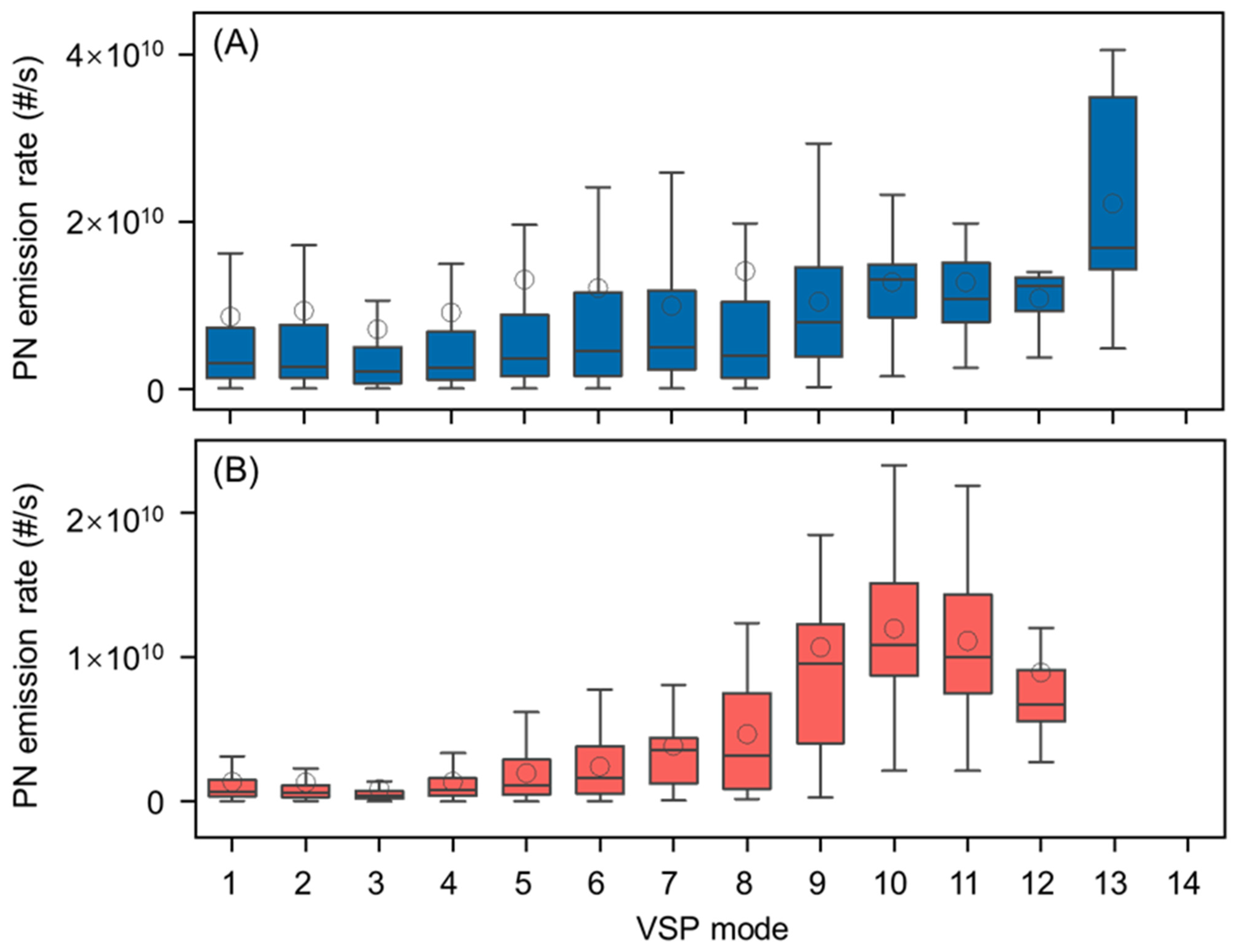
3.3. Effect of Driving Condition on PN Emissions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Xue, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; et al. Transcriptional pathways of elevated fasting blood glucose associated with short-term exposure to ultrafine particles: A panel study in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Matus, P.; et al. Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in 652 Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Shi, Y.; Kong, L.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Yao, X.; Yao, Z. Particle number emissions from light-duty gasoline vehicles in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Estimation of the contribution of road traffic emissions to particulate matter concentrations from field measurements: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.B.; Watts, W.F.; Johnson, J.P. Nanoparticle emissions on Minnesota highways. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-H.; Dhital, N.B.; Wang, L.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-T.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Huang, S.-C. Chemical Characterization of Fine Particulate Matter in Gasoline and Diesel Vehicle Exhaust. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hu, W.; Zhong, Q. Emissions of particle-phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Fu Gui-shan Tunnel of Nanjing, China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liao, S.; Zhu, M.; Sha, Q.e.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Characterizing the particle number emissions of light-duty gasoline vehicles under different engine technologies and driving conditions. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Hendren, J.; Brezny, R.; Gunter, G.C.; Lax, D.; Kubsh, J. Assessment of particle and gaseous emissions and reductions from gasoline direct injection passenger car and light-duty truck during passive regeneration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, S. Characterizing particulate matter emissions from GDI and PFI vehicles under transient and cold start conditions. Fuel 2017, 189, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zu, L.; Bao, X.; Lai, Y.; Su, S. The impact from the direct injection and multi-port fuel injection technologies for gasoline vehicles on solid particle number and black carbon emissions. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Lai, Y.; Zu, L.; Li, Y.; Su, S. Tailpipe emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicles at both low and high ambient temperatures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontses, A.; Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Particle number (PN) emissions from gasoline, diesel, LPG, CNG and hybrid-electric light-duty vehicles under real-world driving conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsmeister, J.; Storch, M.; Melder, J.; Richter, S.; Gaiser, N.; Schlichting, S.; Naumann, C.; Schuenemann, E.; Aigner, M.; Osswald, P.; et al. Soot formation of renewable gasoline: From fuel chemistry to particulate emissions from engines. Fuel 2023, 348, 128109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z. Investigation of combustion and particle number (PN) emissions in a spark induced compression ignition (SICI) engine for ethanol-gasoline blends. Fuel 2022, 316, 123155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaratos, A.; Toumasatos, Z.; Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Kontses, A.; Samaras, Z. Real-world gaseous and particle emissions of a Bi-fuel gasoline/CNG Euro 6 passenger car. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Laurikko, J.; Liu, Y.; Pellikka, A.-P.; Li, Y. Variations of significant contribution regions of NOx and PN emissions for passenger cars in the real-world driving. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, M.V.; Costagliola, M.A. Real driving emissions of Euro 6 electric/gasoline hybrid and natural gas vehicles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 113, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blickwede, J.; Tousen, M.; Droste, T.; VDI Berichte. C-NCAP vs. EuroNCAP—First experiences and estimations. In Proceedings of the 6th International VDI Congress on Car Safety, Berlin, Germany, 18–19 October 2007; pp. 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, H.; Yu, N.; An, X.P.; Li, J.Y.; Li, M.L. Development of China Light-Duty Vehicle Test Cycle. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2020, 21, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, R. A Research on the Establishment of Automated Driving Scenario Database using Natural Language Processing Method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image, Video Processing and Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 21–23 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Zheng, X.; Han, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y. Assessment of ethanol blended fuels for gasoline vehicles in China: Fuel economy, regulated gaseous pollutants and particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, C.; Ge, Y.; Hao, L.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, W.; Lin, Z.; et al. Fuel consumption and emission performance from light-duty conventional/hybrid-electric vehicles over different cycles and real driving tests. Fuel 2020, 278, 118340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H.C.; Rouphail, N.M.; Zhai, H. Speed- and Facility-Specific Emission Estimates for On-Road Light-Duty Vehicles on the Basis of Real-World Speed Profiles. Transp. Res. Rec. 2006, 1987, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, G.; Saleh, R.; Zhao, Y.L.; Presto, A.A.; Larnbe, A.T.; Frodin, B.; Sardar, S.; Maldonado, H.; Maddox, C.; May, A.A.; et al. Comparison of Gasoline Direct-Injection (GDI) and Port Fuel Injection (PFI) Vehicle Emissions: Emission Certification Standards, Cold-Start, Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Potential, and Potential Climate Impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6542–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.G.; Swanson, J.; Pham, L.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, S.S.; Mikailian, G.; Jung, H.S. Real-world particle and NOx emissions from hybrid electric vehicles under cold weather conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Guo, D.; Wei, N.; Wu, Y.; Fang, T.; Song, A.; Fan, C.; et al. Particulate emissions from gasoline vehicles using three different fuel injection technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.V.; Ramesh, A.; Mittal, M.; Bhat, S.S.; Parsi, A. Effect of Fuel Injection Timing on the Mixture Preparation in a Small Gasoline Direct-Injection Engine. In Proceedings of the Small Engine Technology Conference and Exhibition, Dusseldorf, Germany, 6–8 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Favre, C.; Bosteels, D.; May, J. Exhaust Emissions from European Market-Available Passenger Cars Evaluated on Various Drive Cycles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engines and Vehicles, Naples, Italy, 15–19 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Z.Q.; Xu, J.S.; Zhang, M.Q.; Wang, A.; Hatzopoulou, M. Quantifying start emissions and impact of reducing cold and warm starts for gasoline and hybrid vehicles. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Thomas, D.; Wang, X.; Su, S.; Li, H.; He, H. Real driving particle number (PN) emissions from China-6 compliant PFI and GDI hybrid electrical vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R. Particulate matter emissions from hybrid gasoline vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 199, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, R.; Longfei, C.; Felix, L.; Shiting, D. A Review of Particulate Number (PN) Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engines and Their Control Techniques. Energies 2018, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar]
- Attar, M.A.; Xu, H. Correlations between particulate matter emissions and gasoline direct injection spray characteristics. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 102, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, A.; Kondo, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Fujitani, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Takami, A.; Tanabe, K. Chemical composition and source of fine and nanoparticles from recent direct injection gasoline passenger cars: Effects of fuel and ambient temperature. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vehicle ID | Category | Model Year | Emission Standard | Engine Technology | Displacement (mL) | Mileage (104 km) | Max. Net Engine Power (kW) | Max. Authorized Mass (kg) | After Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | ICEV | 2011 | China IV | GDI | 1798 | 22.1 | 118 | 2000 | TWC |
| #2 | ICEV | 2011 | China IV | GDI | 1390 | 12.6 | 96 | 1930 | TWC |
| #3 | ICEV | -- | China V | GDI | 1798 | 8.0 | -- | -- | TWC |
| #4 | ICEV | 2018 | China V | GDI | 1798 | 14.7 | 132 | 2100 | TWC |
| #5 | ICEV | 2022 | China VI | GDI | 1490 | 2.9 | 89 | 1740 | TWC |
| #6 | ICEV | 2022 | China VI | GDI | 1490 | 5.2 | 89 | 1740 | TWC |
| #7 | ICEV | 2021 | China VI | PFI | 1498 | 6.6 | 83 | 1725 | TWC |
| #8 | ICEV | 2021 | China VI | PFI | 1498 | 5.5 | 83 | 1725 | TWC |
| #9 | HEV | 2022 | China VI | GDI | 1798 | 2.7 | 72 | 1845 | TWC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, M. Emission Characteristics of Particle Number from Conventional Gasoline and Hybrid Vehicles. Sustainability 2024, 16, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010012
Zhang Y, Yang X, Fu M. Emission Characteristics of Particle Number from Conventional Gasoline and Hybrid Vehicles. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Xinping Yang, and Mingliang Fu. 2024. "Emission Characteristics of Particle Number from Conventional Gasoline and Hybrid Vehicles" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010012
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yang, X., & Fu, M. (2024). Emission Characteristics of Particle Number from Conventional Gasoline and Hybrid Vehicles. Sustainability, 16(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010012









