The Significant Contribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Nitrogen Heterocycles to Light Absorption in the Winter North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Site and Inlet System
2.2. Real-Time Measurement Equipment
2.3. Quantification of the Absorption Contribution of BC, BrC and the Lensing Effect
2.4. Aerosol Sample Collection and BrC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
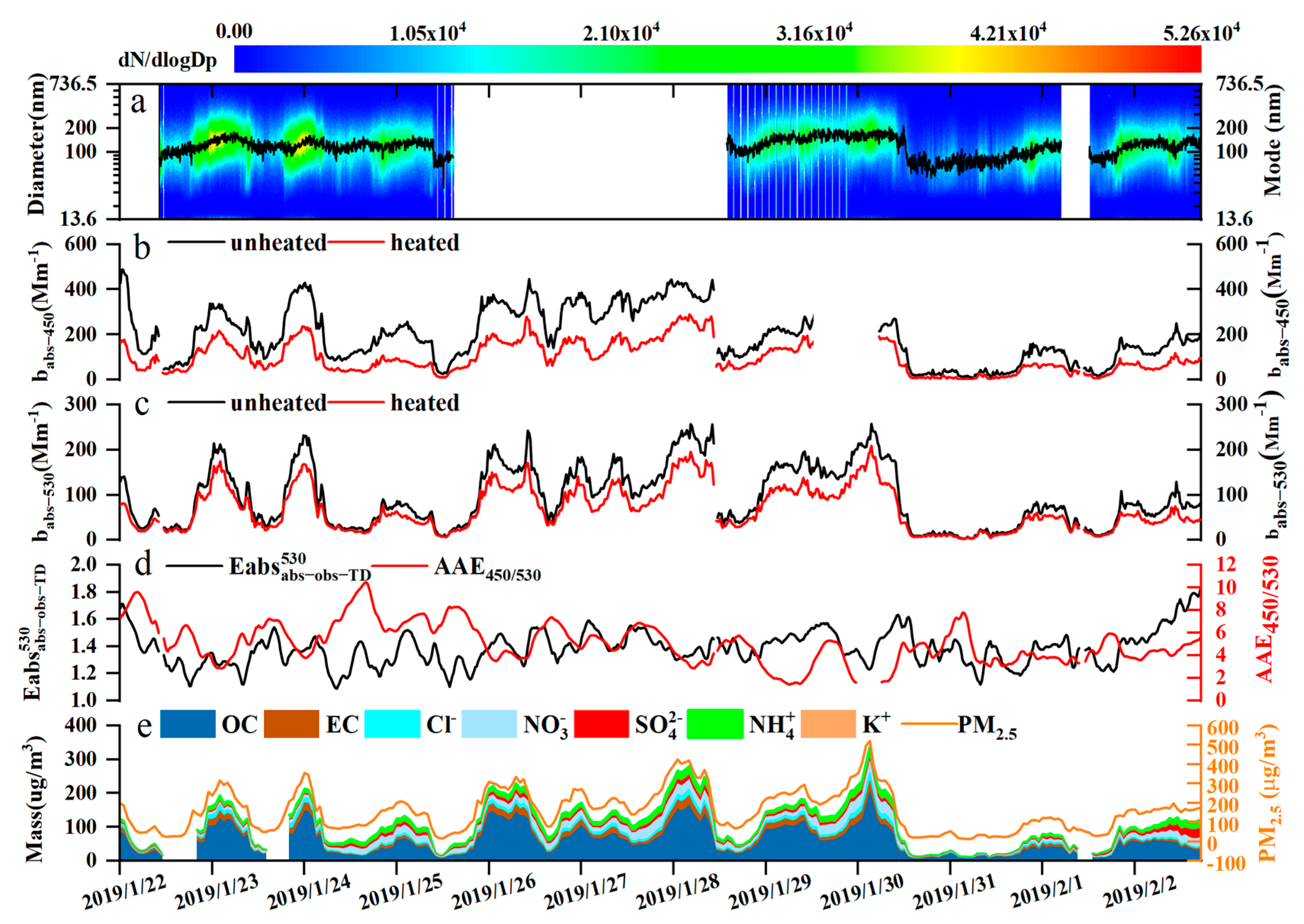
3.1. General Overview
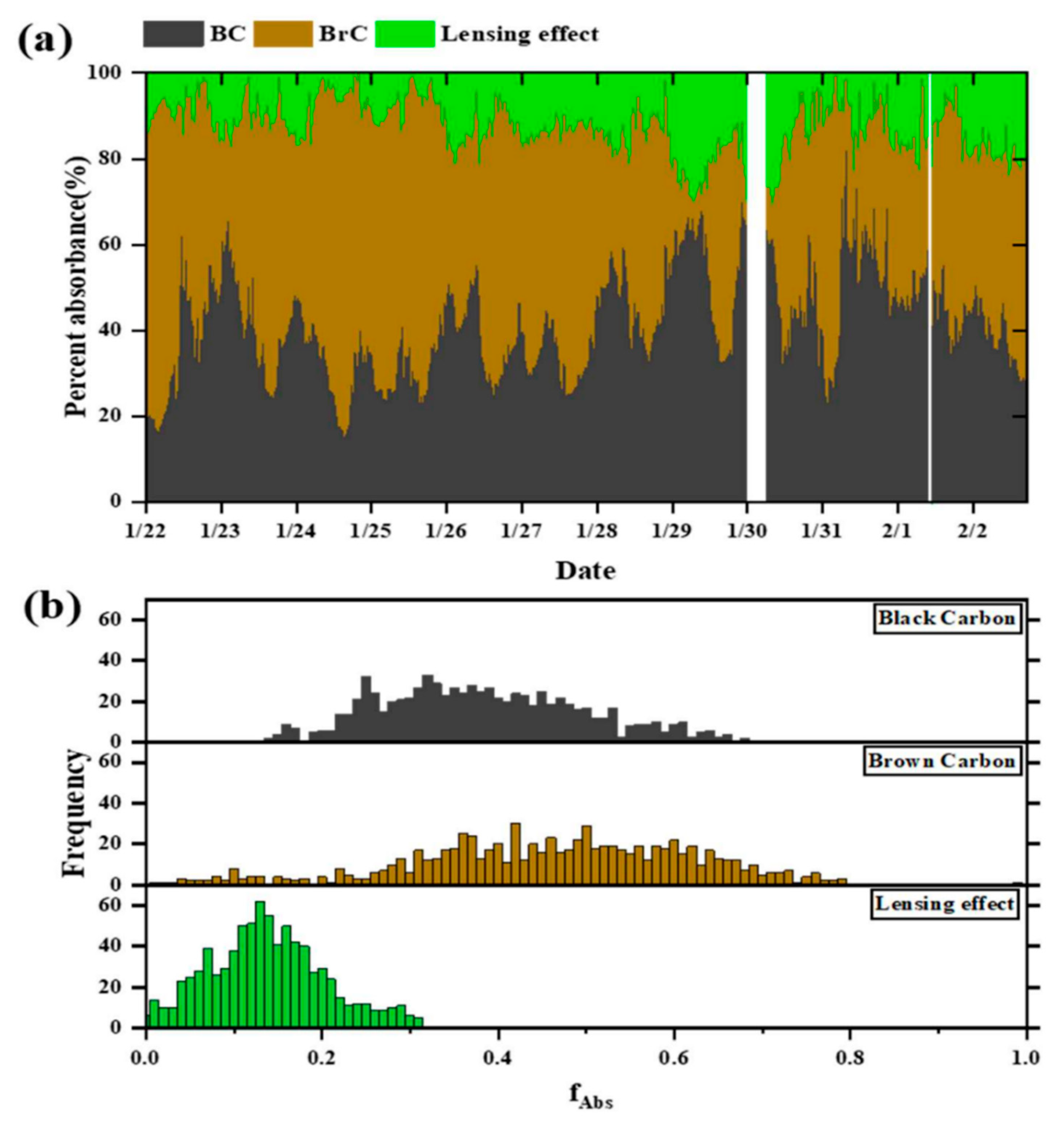
3.2. Absorption Attribution of BrC, BC and the Lensing Effect
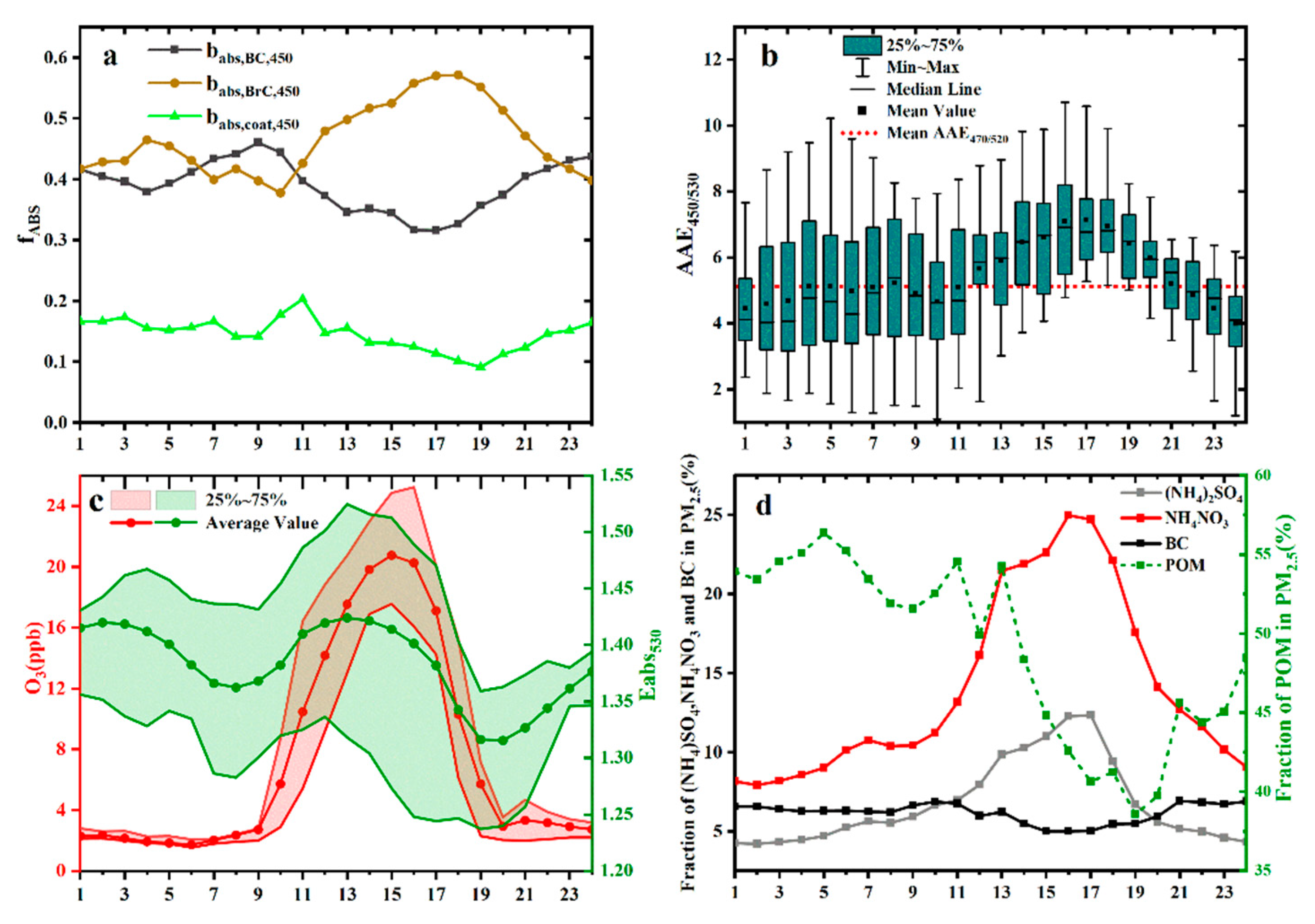
3.3. Diurnal Variation of the Optical Properties
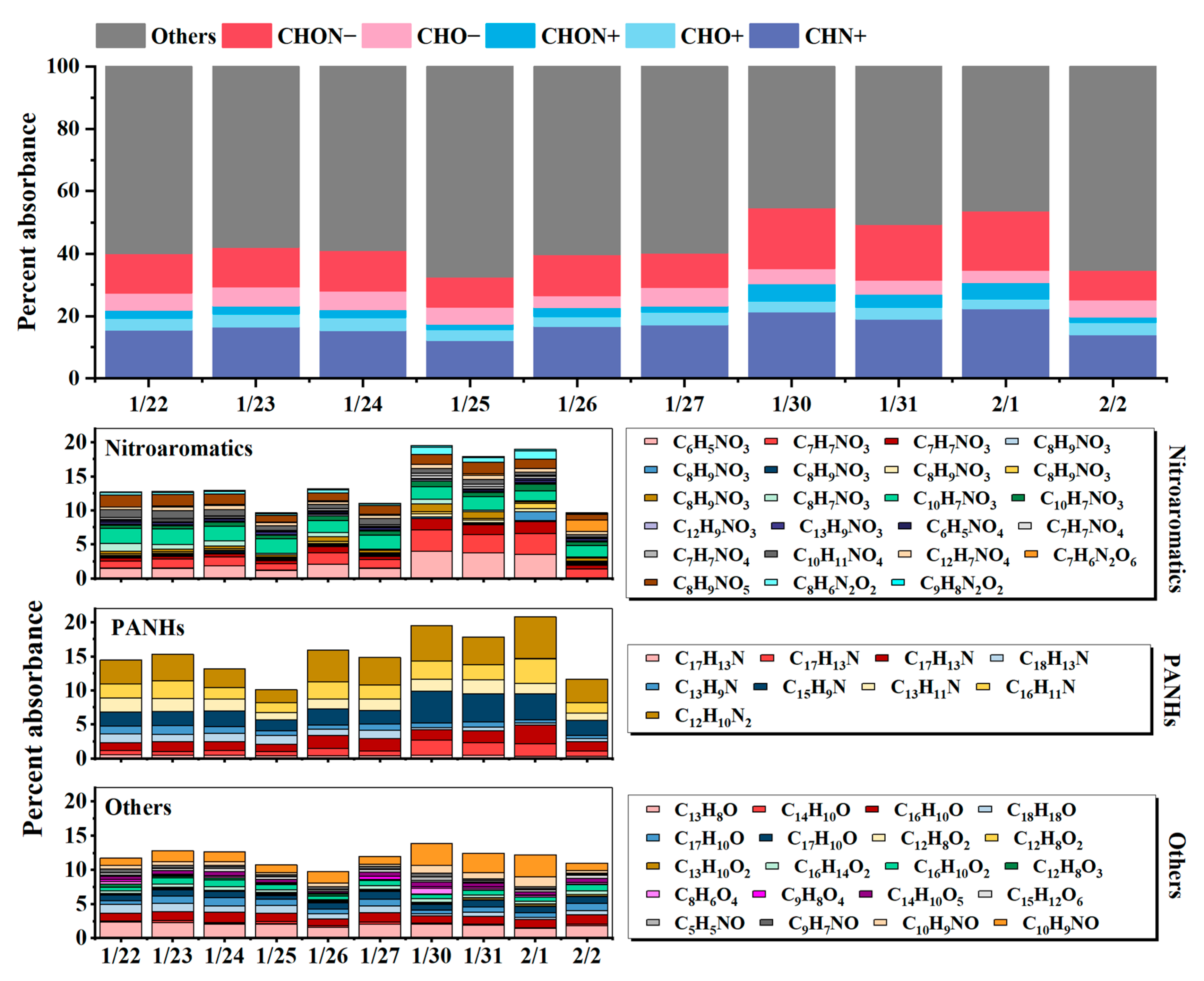
3.4. Quantifying the Contributions of the Identified BrC in the Ambient Samples to Light Absorption
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brodny, J.; Tutak, M. Analysis of the diversity in emissions of selected gaseous and particulate pollutants in the European Union countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 231, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yu, T.; Ciren, P.; Jiang, P. Assessment of human health impact from PM 10 exposure in China based on satellite observations. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Proietti, C.; Anav, A.; Ciancarella, L.; D’Elia, I.; Fares, S.; Fornasier, M.F.; Fusaro, L.; Gualtieri, M.; Manes, F. Impacts of air pollution on human and ecosystem health, and implications for the National Emission Ceilings Directive: Insights from Italy-NC-ND. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D.A. Aerosols, Climate, and the Hydrological Cycle. Science 2002, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric Aerosols: Composition, Transformation, Climate and Health Effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iii, P.; Arden, C. Lung Cancer, Cardiopulmonary Mortality, and Long-term Exposure to FineParticulate Air Pollution. Jama 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalizov, A.F.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, R. Enhanced light absorption and scattering by carbon soot aerosol internally mixed with sulfuric acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarnato, B.V.; Vahidinia, S.; Richard, D.T.; Kirchstetter, T.W. Effects of internal mixing and aggregate morphology on optical properties of black carbon using a discrete dipole approximation model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5089–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Chung, S.H.; Buseck, P.R. Shapes of soot aerosol particles and implications for their effects on climate. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, J.; Shilling, J.E.; Kathmann, S.M.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular characterization of brown carbon (BrC) chromophores in secondary organic aerosol generated from photo-oxidation of toluene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 23312–23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. The dark side of aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Climate response of direct radiative forcing of anthropogenic black carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.S.; Onasch, T.B.; Ahern, A.; Wrobel, W.; Slowik, J.G.; Olfert, J.; Lack, D.A.; Massoli, P.; Cappa, C.D.; Schwarz, J.P.; et al. Soot Particle Studies—Instrument Inter-Comparison—Project Overview. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 592–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Khalizov, A.F.; Pagels, J.; Zhang, D.; Xue, H.; McMurry, P.H. Variability in morphology, hygroscopicity, and optical properties of soot aerosols during atmospheric processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10291–10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.D.; Onasch, T.B.; Massoli, P.; Worsnop, D.R.; Bates, T.S.; Cross, E.S.; Davidovits, P.; Hakala, J.; Hayden, K.L.; Jobson, B.T.; et al. Radiative Absorption Enhancements Due to the Mixing State of Atmospheric Black Carbon. Science 2012, 337, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light absorption by carbonaceous particles: An investigative review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Sawada, Y.; Setoguchi, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Kawana, K.; Mochida, M.; Ikemori, F.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumi, Y. Properties of light-absorbing aerosols in the Nagoya urban area, Japan, in August 2011 and January 2012: Contributions of brown carbon and lensing effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12721–12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B. Numerical Investigation on Absorption Enhancement of Black Carbon Aerosols Partially Coated with Nonabsorbing Organics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B. Absorption enhancement of aged black carbon aerosols affected by their microphysics: A numerical investigation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 202, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Pei, S.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Pan, Q. Absorption enhancement of black carbon and the contribution of brown carbon to light absorption in the summer of Nanjing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, J.; Andersson, A.; Gustafsson, O. Radiative absorption enhancement from coatings on black carbon aerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, M.; Guo, S.; Du, Z.; Zheng, J.; Shang, D.; Levy Zamora, M.; Zeng, L.; Shao, M.; Wu, Y.S.; et al. Markedly enhanced absorption and direct radiative forcing of black carbon under polluted urban environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4266–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ding, A.; He, K. Amplification of light absorption of black carbon associated with air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9879–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierce, L.; Onasch, T.B.; Cappa, C.D.; Mazzoleni, C.; China, S.; Bhandari, J.; Davidovits, P.; Fischer, D.A.; Helgestad, T.; Lambe, A.T.; et al. Radiative absorption enhancements by black carbon controlled by particle-to-particle heterogeneity in composition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Chemistry of atmospheric brown carbon. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4335–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikkina, S.; Sarin, M. Brown carbon in the continental outflow to the North Indian Ocean. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.B.; Du, Z.Y.; Engling, G.; Liu, J.M.; Ma, Y.L.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. The characteristics of brown carbon aerosol during winter in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhu, C.; Dai, W.; Wang, K.; et al. Brown Carbon Aerosol in Urban Xi’an, Northwest China: The Composition and Light Absorption Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6825–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, R.-J.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Duan, J.; Guo, J.; Ni, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Measurement report: PM2:5-bound nitrated aromatic compounds in Xi’an, Northwest China—Seasonal variations and contributions to optical properties of brown carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 3685–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bond, T.C. Light absorption by organic carbon from wood combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hua, X.; Dyussenova, A. Evolution of the chromophore aerosols and its driving factors in summertime Xi’an, Northwest China. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Huang, X.F.; Cao, L.M.; Cui, J.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, C.N.; Lan, Z.J.; He, L.Y. Light absorption of brown carbon aerosol in the PRD region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, L.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mao, J.F.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Wang, L.N.; Chen, J.M. Water/Methanol-Insoluble Brown Carbon Can Dominate Aerosol-Enhanced Light Absorption in Port Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14889–14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budisulistiorini, S.H.; Riva, M.; Williams, M.; Chen, J.; Itoh, M.; Surratt, J.D.; Kuwata, M. Light-Absorbing Brown Carbon Aerosol Constituents from Combustion of Indonesian Peat and Biomass. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4415–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Langridge, J.M.; Bahreini, R.; Cappa, C.D.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schwarz, J.P. Brown carbon and internal mixing in biomass burning particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14802–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, B.; Wei, S.; Fan, X.; Peng, P. Molecular Characterization of Water-Soluble Humic like Substances in Smoke Particles Emitted from Combustion of Biomass Materials and Coal Using Ultrahigh-Resolution Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, M.; Fan, X.; Zou, C.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, B.; Yu, Z.; Jia, W.; Liao, Y.; Peng, P. Molecular Characterization of Water- and Methanol-Soluble Organic Compounds Emitted from Residential Coal Combustion Using Ultrahigh-Resolution Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13607–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, J.; Su, T.; Han, Y.; Mo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cui, M.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Molecular compositions and optical properties of dissolved brown carbon in biomass burning, coal combustion, and vehicle emission aerosols illuminated by excitation–emission matrix spectroscopy and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2513–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Cui, T.; Fiddler, M.N.; Pokhrel, R.P.; Surratt, J.D.; Bililign, S. Laboratory studies of fresh and aged biomass burning aerosol emitted from east African biomass fuels—Part 2: Chemical properties and characterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10169–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hayeck, N.; Bruggemann, M.; Abis, L.; Riva, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; George, C.; Wang, L. Chemical Characteristics and Brown Carbon Chromophores of Atmospheric Organic Aerosols Over the Yangtze River Channel: A Cruise Campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 2020JD032497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Ning, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Xu, H.; Ho, S.S.H.; et al. The Roles of N, S, and O in Molecular Absorption Features of Brown Carbon in PM2.5 in a Typical Semi-Arid Megacity in Northwestern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, 2021JD034791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.T.; Lin, P.; Roberts, J.M.; Selimovic, V.; Yokelson, R.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Molecular composition and photochemical lifetimes of brown carbon chromophores in biomass burning organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1105–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampf, C.J.; Filippi, A.; Zuth, C.; Hoffmann, T.; Opatz, T. Secondary brown carbon formation via the dicarbonyl imine pathway: Nitrogen heterocycle formation and synergistic effects. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 18353–18364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; He, Q.F.; Hettiyadura, A.P.S.; Kafer, U.; Shmul, G.; Meidan, D.; Zimmermann, R.; Brown, S.S.; George, C.; Laskin, A.; et al. Formation of Secondary Brown Carbon in Biomass Burning Aerosol Proxies through NO3 Radical Reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Bluvshtein, N.; Rudich, Y.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular Chemistry of Atmospheric Brown Carbon Inferred from a Nationwide Biomass Burning Event. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11561–11570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frka, S.; Sala, M.; Brodnik, H.; Stefane, B.; Kroflic, A.; Grgic, I. Seasonal variability of nitroaromatic compounds in ambient aerosols: Mass size distribution, possible sources and contribution to water-soluble brown carbon light absorption. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Zotter, P.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Xu, L.; Ng, N.L.; Herndon, S.C.; Williams, L.R.; Franklin, J.P.; Zahniser, M.S.; et al. Contribution of Nitrated Phenols to Wood Burning Brown Carbon Light Absorption in Detling, United Kingdom during Winter Time. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6316–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teich, M.; van Pinxteren, D.; Wang, M.; Kecorius, S.; Wang, Z.B.; Muller, T.; Mocnik, G.; Herrmann, H. Contributions of nitrated aromatic compounds to the light absorption of water-soluble and particulate brown carbon in different atmospheric environments in Germany and China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1653–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.L.; Herndon, S.C.; Trimborn, A.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Croteau, P.L.; Onasch, T.B.; Sueper, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. An Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) for Routine Monitoring of the Composition and Mass Concentrations of Ambient Aerosol. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysel, M.; Crosier, J.; Topping, D.O.; Whitehead, J.D.; Bower, K.N.; Cubison, M.J.; Williams, P.I.; Flynn, M.J.; McFiggans, G.B.; Coe, H. Closure study between chemical composition and hygroscopic growth of aerosol particles during TORCH2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 6131–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Jin, Z.D.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, G.C.; Kang, Y.M.; et al. Spatial and seasonal distributions of carbonaceous aerosols over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 2006jd008205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, R.P.; Beamesderfer, E.R.; Wagner, N.L.; Langridge, J.M.; Lack, D.A.; Jayarathne, T.; Stone, E.A.; Stockwell, C.E.; Yokelson, R.J.; Murphy, S.M. Relative importance of black carbon, brown carbon, and absorption enhancement from clear coatings in biomass burning emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5063–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D. Impact of brown and clear carbon on light absorption enhancement, single scatter albedo and absorption wavelength dependence of black carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4207–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Wan, J.; Liu, D.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, W.; et al. Light absorption enhancement of black carbon in urban Beijing in summer. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, R.; Hennigan, C.J.; Mcmeeking, G.R.; Chuang, W.K.; Robinson, E.S.; Coe, H.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Absorptivity of brown carbon in fresh and photo-chemically aged biomass-burning emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11509–11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, Q.; Schade, J.; Passig, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Meidan, D.; Laskin, A.; Rudich, Y. Dynamic changes in optical and chemical properties of tar ball aerosols by atmospheric photochemical aging. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Jang, M. Dynamic light absorption of biomass burning organic carbon photochemically aged under natural sunlight. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, E.C.; Zhang, X.; Franklin, J.P.; Ridley, K.J.; Kroll, J.H. Effect of heterogeneous oxidative aging on light absorption by biomass-burning organic aerosol. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.C.; Yuan, W.; Gong, Y.Q.; Guo, J.; Cao, W.J.; Duan, J.; Ni, H.Y.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Water-Insoluble Organics Dominate Brown Carbon in Wintertime Urban Aerosol of China: Chemical Characteristics and Optical Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7836–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Aiona, P.K.; Li, Y.; Shiraiwa, M.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, A. Molecular Characterization of Brown Carbon in Biomass Burning Aerosol Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11815–11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, M.; Stefenelli, G.; Pospisilova, V.; Tong, Y.; Bertrand, A.; Hueglin, C.; Ge, X.; Baltensperger, U.; Prevot, A.S.H.; et al. Organic aerosol source apportionment in Zurich using an extractive electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer (EESI-TOF-MS)—Part 2: Biomass burning influences in winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8037–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Xue, C.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Ye, C.; Zhang, H.; Guan, J. The contribution of residential coal combustion to atmospheric PM2.5 in northern China during winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11503–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shang, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, G.; Fu, Y.; Wu, D.; Sun, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Mu, Y.; et al. Significant impact of coal combustion on VOCs emissions in winter in a North China rural site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Du, W.; Sun, C.; Fu, P.; Wang, Z. Chemical composition of aerosol particles and light extinction apportionment before and during the heating season in Beijing, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12708–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization of nitrogen-containing organic compounds in the winter North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Vila, J.; Wang, H.; Bodnar, W.; Aitken, M.D. Diversity and Abundance of High-Molecular-Weight Azaarenes in PAH-Contaminated Environmental Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14047–14054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleeker, E.A.J.; Van der Geest, H.G.; Klamer, H.J.C.; De Voogt, P.; Wind, E.; Kraak, M.H.S. Toxic and genotoxic effects of azaarenes: Isomers and metabolites. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 1999, 13, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegman, S.; van Vlaardingen, P.L.A.; Bleeker, E.A.J.; de Voogt, P.; Kraak, M.H.S. Phototoxicity of azaarene isomers to the marine flagellate Dunaliella tertiolecta. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandowe, B.A.M.; Meusel, H.; Huang, R.; Hoffmann, T.; Cao, J.; Ho, K. Azaarenes in fine particulate matter from the atmosphere of a Chinese megacity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16025–16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huang, R.-J.; Brueggemand, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Ni, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Han, J.; Bilde, M.; et al. Urban organic aerosol composition in eastern China differs from north to south: Molecular insight from a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (Orbitrap) study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9089–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Cui, D.; Li, R.; Shi, Q.; Chung, K.H.; Long, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xu, C. Characterization of Middle-Temperature Gasification Coal Tar. Part 1: Bulk Properties and Molecular Compositions of Distillates and Basic Fractions. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 5719–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, M.; Zou, C.; Cao, T.; Fan, X.; Jiang, B.; Yu, Z.; Jia, W.; Peng, P.a. Molecular Characterization of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds in Humic-like Substances Emitted from Biomass Burning and Coal Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Brown carbon formation from ketoaldehydes of biogenic monoterpenes. Faraday Discuss. 2013, 165, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bones, D.L.; Henricksen, D.K.; Mang, S.A.; Gonsior, M.; Bateman, A.P.; Nguyen, T.B.; Cooper, W.J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Appearance of strong absorbers and fluorophores in limonene-O-3 secondary organic aerosol due to NH4+-mediated chemical aging over long time scales. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 2009JD012864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bai, Z.; Cui, X.; Chen, J.; Andersson, A.; Gustafsson, O. Light absorption enhancement of black carbon from urban haze in Northern China winter. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Ogren, J.A. Determining aerosol radiative properties using the TSI 3563 integrating nephelometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1998, 29, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Mao, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Chen, J. The Significant Contribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Nitrogen Heterocycles to Light Absorption in the Winter North China Plain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8568. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118568
Cheng Y, Mao J, Bai Z, Zhang W, Zhang L, Chen H, Wang L, Li L, Chen J. The Significant Contribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Nitrogen Heterocycles to Light Absorption in the Winter North China Plain. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8568. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118568
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yi, Junfang Mao, Zhe Bai, Wei Zhang, Linyuan Zhang, Hui Chen, Lina Wang, Ling Li, and Jianmin Chen. 2023. "The Significant Contribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Nitrogen Heterocycles to Light Absorption in the Winter North China Plain" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8568. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118568
APA StyleCheng, Y., Mao, J., Bai, Z., Zhang, W., Zhang, L., Chen, H., Wang, L., Li, L., & Chen, J. (2023). The Significant Contribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Nitrogen Heterocycles to Light Absorption in the Winter North China Plain. Sustainability, 15(11), 8568. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118568







