The Impact of Technology Convergence on the Sustainable Innovation of China’s Modern Manufacturing Enterprises: The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Technology Convergence and Innovation Performance
2.1.1. Betweenness Technology Convergence and Innovation Performance
2.1.2. Closeness Technology Convergence and Innovation Performance
2.1.3. Clustered Technology Convergence and Innovation Performance
2.2. The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base
2.2.1. Knowledge Base, Betweenness Technology Convergence, and Innovation Performance
2.2.2. Knowledge Base, Closeness Technology Convergence, and Innovation Performance
2.2.3. Knowledge Base, Clustering Technology Convergence, and Innovation Performance
3. Research Design
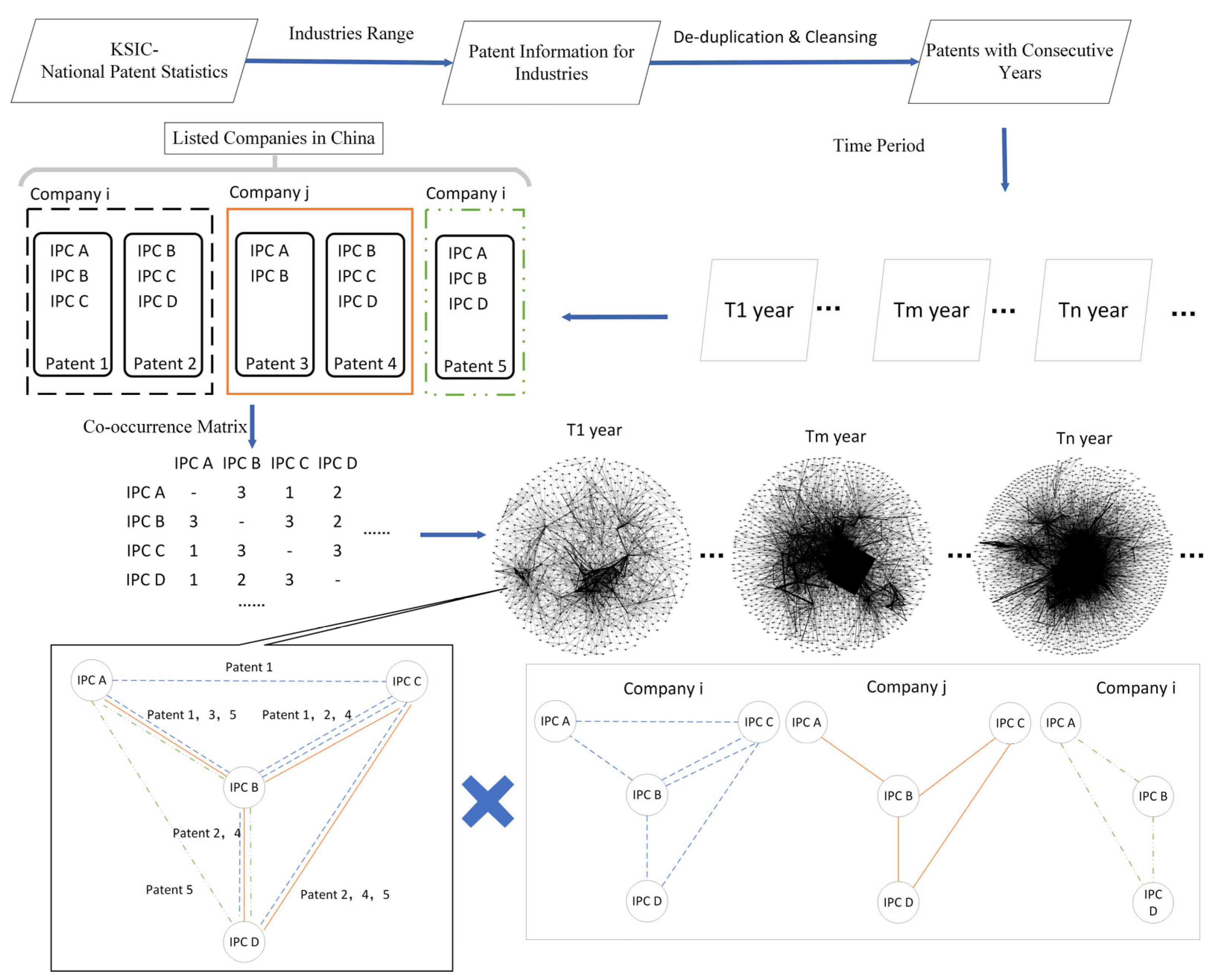
3.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
3.2. Variables and Measurement
- Innovation performance. Innovation performance is the outcome of a firm’s engagement in a diversified range of sustainable innovation activities [51]. It not only reflects the immediate effects of innovative actions but also indicates the company’s intent towards future sustainable innovation. Furthermore, the ongoing optimization of innovation performance transforms into an intrinsic driving force that propels the company to pursue sustainable innovation. The number of patent applications is a commonly used indicator of corporate innovation performance. The automotive industry is highly competitive, intellectual property rights are actively used among companies to expand their advantages, and patent information largely reflects the innovation activities of automotive companies. Therefore, this paper draws on previous research and adopts the number of enterprise patent applications to measure the innovation performance of enterprises [52].
- Technology convergence characteristics. This study draws on three technology convergence characteristics based on network structure characteristics selected as independent variables, namely, mediated technology convergence, proximity technology convergence, and clustering technology convergence. First, the intermediary centrality, proximity centrality, and local clustering coefficients of each IPC number in the technology fusion network are calculated by year. Then, the proportion of each IPC number in the patents under the control of each firm is calculated. Although individual firms holding patents in the same industry often share similar IPC numbers, the proportion of IPC numbers is different and can indicate differences in technology mastery among firms. Then, the three network structure characteristics of each IPC number are multiplied by the proportion of the IPC numbers of the enterprises, and the products are summed. Finally, when the structural characteristics of the points tend to follow a skewed distribution, the sum obtained is increased by 1 and then logarithmically processed to obtain the three technology integration characteristics.
- Knowledge base breadth. In this paper, we use technological diversity to represent knowledge base breadth (breadth) [32] and calculate it using the entropy index method [16], which is calculated as and classified according to the first three digits of the IPC classification number, where Pj is the share of technology unit j in the IPCi of patents held by enterprise i, i.e., the ratio of IPC number j to the total number of patents of the enterprise.
- Knowledge base depth. We use the average number of claims of patents under the control of enterprises to indicate the knowledge base depth. Patent claims are the scope of protection given to a patent application and often require the description of technical features such as the method or function of the patent in scientific terms. The greater the number of claims in a patent, the greater the number of corresponding technical features and the greater the number of patent owner requirements for patent protection and implementation, indicating that the patent is more important or is more cutting-edge.
- Control variables. In this study, financial leverage, return on total assets, internal R&D intensity, and enterprise age are selected as control variables. The financial leverage is measured by the gearing ratio, the internal R&D intensity is expressed by the logarithm of the ratio of R&D investment to main business revenue plus one, and the age of the enterprise is measured by the logarithm of the establishment time of the enterprise plus one.
3.3. Model Selection
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
4.2. Regression Analysis
4.3. Robustness Tests
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, B.; Yang, X.; Zhong, S.; Tian, S.; Liang, T. How do technology convergence and expansibility affect information technology diffusion? Evidence from the internet of things technology in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2024, 203, 123374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochinanwata, C.; Igwe, P.A.; Radicic, D. The institutional impact on the digital platform ecosystem and innovation. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2024, 30, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah-Amoah, J.; Abdalla, S.; Mogaji, E.; Elbanna, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K. The impending disruption of creative industries by generative AI: Opportunities, challenges, and research agenda. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 2024, 79, 102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X. Digital Transformation Drives Sustainable Innovation Capability Improvement in Manufacturing Enterprises: Based on FsQCA and NCA Approaches. Sustainability 2023, 15, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, H. How does digital transformation drive green total factor productivity? Evidence from Chinese listed enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delic, M.; Eyers, D.R. The effect of additive manufacturing adoption on supply chain flexibility and performance: An empirical analysis from the automotive industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, K.; Mirjat, N.H.; Shakih, S.A.; Harijan, K.; Kumar, L.; El Haj Assad, M. Optimizing Auto Manufacturing: A Holistic Approach Integrating Overall Equipment Effectiveness for Enhanced Efficiency and Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smania, G.S.; Arakaki, I.R.Y.; Oliveira, A.F.; Cauchick-Miguel, P.A.; Mendes, G.H.D.S. Car subscription services: Automakers’ shift towards servitized and sustainable business models. Sustain. Prod. Cons. 2023, 36, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillo, V.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Ardito, L.; Del Giudice, M. Understanding sustainable innovation: A systematic literature review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermundsdottir, F.; Aspelund, A. Sustainability innovations and firm competitiveness: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermesan, O.; John, R.; Pype, P.; Daalderop, G.; Kriegel, K.; Mitic, G.; Lorentz, V.; Bahr, R.; Sand, H.E.; Bockrath, S.; et al. Automotive Intelligence Embedded in Electric Connected Autonomous and Shared Vehicles Technology for Sustainable Green Mobility. Front. Future Transp. 2021, 2, 688482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Mitkova, L.; Wang, N. The paths of internationalization of Chinese innovative firms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yang, J.; Li, L. Early identification of technological convergence in numerical control machine tool: A deep learning approach. Scientometrics 2020, 125, 1983–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Zhou, P. Role of digitalization in energy storage technological innovation: Evidence from China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 171, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Cho, Y.; Kim, W. Dynamic patterns of technological convergence in printed electronics technologies: Patent citation network. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 975–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Yoon, B. Technological opportunity discovery for technological convergence based on the prediction of technology knowledge flow in a citation network. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1199–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meeteren, M.; Trincado-Munoz, F.; Rubin, T.H.; Vorley, T. Rethinking the digital transformation in knowledge-intensive services: A technology space analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2022, 179, 121631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, V.; Chiarello, F.; Melluso, N.; Fantoni, G.; Bonaccorsi, A. Text and dynamic network analysis for measuring technological convergence: A case study on defense patent data. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. Converging technology to improve firm innovation competencies and business performance: Evidence from smart manufacturing technologies. Technovation 2023, 123, 102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, T.; Sakata, I. Identifying technology convergence in the field of robotics research. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, E.; Staccioli, J.; Vivarelli, M. Automation and related technologies: A mapping of the new knowledge base. J. Technol. Transf. 2023, 48, 779–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Afifuddin, M.; Seo, W. A supervised learning-based approach to anticipating potential technology convergence. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 19284–19300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Xie, F. Knowledge activities of external knowledge network and technological capability: Evidence from China. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023, 14, 1343–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißmüller, K.S.; Ritz, A.; Yerramsetti, S. Collaborating and co-creating the digital transformation: Empirical evidence on the crucial role of stakeholder demand from Swiss municipalities. Public Policy Adm. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, J. Exploring a technology ecology for technology opportunity discovery: A link prediction approach using heterogeneous knowledge graphs. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 186, 122161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Coupling Open Innovation: Network Position, Knowledge Integration Ability, and Innovation Performance. J. Knowl. Econ. 2023, 14, 1538–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Sohn, S.Y. Technological convergence in standards for information and communication technologies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2016, 106, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmat, F.; Lim, W.M.; Moyeen, A.; Voola, R.; Gupta, G. Convergence of business, innovation, and sustainability at the tipping point of the sustainable development goals. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 167, 114170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, C.S.; Leker, J. Patent indicators for monitoring convergence—Examples from NFF and ICT. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2011, 78, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Elekes, Z.; Whittle, A.; Lee, C.; Kogler, D.F. Technology network structure conditions the economic resilience of regions. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 98, 355–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviggioli, F. Technology fusion: Identification and analysis of the drivers of technology convergence using patent data. Technovation 2016, 55–56, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jung, S.; Hwang, J. Technology convergence capability and firm innovation in the manufacturing sector: An approach based on patent network analysis. R&D Manag. 2019, 49, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayavaram, S.; Ahuja, G. Decomposability in knowledge structures and its impact on the usefulness of inventions and knowledge-base malleability. Adm. Sci. Q. 2008, 53, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Suh, Y. Multiple patent network analysis for identifying safety technology convergence. Data Technol. Appl. 2019, 53, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Han, E.J.; Sohn, S.Y. Predicting the pattern of technology convergence using big-data technology on large-scale triadic patents. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2015, 100, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.; McCarthy, A.; Ferri, P.; Shapira, P. Innovation intermediaries at the convergence of digital technologies, sustainability, and governance: A case study of AI-enabled engineering biology. Technovation 2024, 129, 102875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kogler, D.F.; Lee, D. Capturing information on technology convergence, international collaboration, and knowledge flow from patent documents: A case of information and communication technology. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Hwang, J.; Cho, E. Comparing technology convergence of artificial intelligence on the industrial sectors: Two-way approaches on network analysis and clustering analysis. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 407–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvis, P.; Herrera, M.E.B.; Googins, B.; Albareda, L. Corporate social innovation: How firms learn to innovate for the greater good. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 5014–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, D.; Jurowetzki, R.; Lee, S.; Zhou, Y. Machine learning and artificial intelligence for science, technology, innovation mapping and forecasting: Review, synthesis, and applications. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.K. The significance of network resources in the race to enter emerging product markets: The convergence of telephony communications and computer networking, 1989–2001. Strateg. Manag. J. 2007, 28, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, C. The nature of ICT in technology convergence: A knowledge-based network analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.; Caruana, A.; Ferreira, C. Innovation performance: The effect of knowledge-based dynamic capabilities in cross-country innovation ecosystems. Int. Bus. Rev. 2023, 32, 101866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, C.; Kang, H.G. How does knowledge affect IPO pricing? A new approach grounded in the knowledge-based view. J. Knowl. Manag. 2022, 26, 1849–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nie, Y. Managing the dynamic change of organizational knowledge base in collaboration networks. Balt. J. Manag. 2022, 17, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Tian, K. Understanding cognitive differences in the effect of digitalization on ambidextrous innovation: Moderating role of industrial knowledge base. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 983844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.F.; Yasin, I.M.; Latiff, A.R. Knowledge base for social capital’s role in scaling social impact: A bibliometric analysis. Bus. Ethics Environ. Responsib. 2023, 32, 742–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordão, R.V.D.; Novas, J.; Gupta, V. The role of knowledge-based networks in the intellectual capital and organizational performance of small and medium-sized enterprises. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaniba, I.M.; Su, H.N.; Lee, P.C. Knowledge recombination and technological innovation: The important role of cross-disciplinary knowledge. Innovation 2018, 20, 326–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wu, S. The influence of ambidextrous knowledge search on technological innovation: The mediating role of knowledge base. Sage Open 2023, 13, 21582440231221142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.J. Sustainability Orientation, Green Supplier Involvement, and Green Innovation Performance: Evidence from Diversifying Green Entrants. J. Bus. Ethics 2020, 161, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, G. Collaboration networks, structural holes, and innovation: A longitudinal study. Adm. Sci. Q. 2000, 45, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, R.C. R&D Alliances and Firm Performance: The Impact of Technological Diversity and Alliance Organization on Innovation. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 364–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Wigand, R.T.; Hossain, L. Measuring social capital through network analysis and its influence on indi-vidual performance. Libr. Inform. Sci. Res. 2014, 36, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Kaplanidou, K. Social Capital and Running: A Network Social Capital Perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, R.; Jackson, M.O.; Kuchler, T.; Stroebel, J.; Hendren, N.; Fluegge, R.B.; Gong, S.; Gonzalez, F.; Grondin, A.; Jacob, M.; et al. Social capital I: Measurement and associations with economic mobility. Nature 2022, 608, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable Name | Variable Abbreviation | Number | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation performance | pat | 1668 | 141.764 | 374.766 | 0 | 4021 |
| Betweenness convergence | bet | 1642 | 8.954 | 1.406 | 1.806 | 12.687 |
| Closeness convergence | clo | 1645 | −1.025 | 0.239 | −3.880 | −0.717 |
| Cluster convergence | clu | 1645 | −1.112 | 0.278 | −3.457 | 0.000 |
| Knowledge base breadth | kbb | 1610 | 3.381 | 1.221 | 0.234 | 6.373 |
| Knowledge base depth | kbd | 1650 | 4.945 | 1.770 | 1.000 | 15.750 |
| Financial leverage | lev | 1421 | 51.476 | 135.596 | 4.167 | 4193.939 |
| Return on total assets | roa | 1486 | 8.956 | 57.243 | 664.879 | 2078.546 |
| Internal R&D | rdi | 1290 | −17.209 | 0.696 | −24.681 | −12.585 |
| Business age | age | 1659 | 2.707 | 0.448 | 0.000 | 3.892 |
| Variable | VIF | pat | bet | clo | clu | kbb | kbd | lev | roa | rdi | age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pat | 1.63 | ||||||||||
| bet | 3.56 | 0.237 *** | |||||||||
| clo | 3.04 | 0.173 *** | 0.670 *** | ||||||||
| clu | 1.84 | −0.037 | −0.284 *** | 0.245 *** | |||||||
| kbb | 1.95 | 0.557 *** | 0.340 *** | 0.268 *** | 0.110 *** | ||||||
| kbd | 1.26 | 0.287 *** | 0.214 *** | 0.209 *** | 0.0240 | 0.299 *** | |||||
| lev | 1.29 | 0.020 | 0.050 * | 0.036 | −0.030 | −0.023 | −0.012 | ||||
| roa | 1.27 | −0.022 | −0.017 | −0.032 | −0.018 | −0.045 * | −0.046 * | −0.125 *** | |||
| rdi | 1.17 | −0.007 | 0.005 | 0.086 *** | 0.152 *** | 0.050 * | 0.236 *** | −0.187 *** | −0.146 *** | ||
| age | 1.18 | 0.185 *** | 0.226 *** | 0.248 *** | 0.040 | 0.354 *** | 0.190 *** | 0.039 | −0.028 | 0.004 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pat | pat | pat | |
| bet | 0.134 *** (4.84) | ||
| clo | 0.596 *** (3.87) | ||
| clu | 0.413 *** (3.82) | ||
| lev | −0.001 (−0.34) | −0.000 (−0.00) | 0.000 (0.25) |
| roa | −0.001 (−0.45) | −0.001 (−0.42) | −0.001 (−0.50) |
| rdi | 0.212 *** (5.72) | 0.207 *** (5.56) | 0.198 *** (5.29) |
| age | 1.281 *** (12.71) | 1.299 *** (12.51) | 1.481 *** (16.08) |
| Constant | 0.006 (0.01) | 1.667 ** (2.13) | 0.867 (1.16) |
| Observations | 1286 | 1286 | 1286 |
| Number of ID | 139 | 139 | 139 |
| Variable | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kbb | kbb | kbb | pat | pat | pat | |
| bet | 0.161 *** (8.49) | 0.088 *** (2.93) | ||||
| clo | 0.766 *** (8.38) | 0.395 ** (2.52) | ||||
| clu | 0.597 *** (9.57) | 0.068 (0.52) | ||||
| kbb | 0.538 *** (14.67) | 0.547 ***(14.87) | 0.546 *** (14.74) | |||
| lev | −0.004 *** (−4.04) | −0.003 *** (−3.20) | −0.002 ** (−2.11) | −0.001 (−1.00) | −0.001 (−0.78) | −0.001 (−0.69) |
| roa | −0.007 *** (−4.11) | −0.006 *** (−3.68) | −0.005 *** (−2.93) | 0.006 ** (2.33) | 0.006 ** (2.37) | 0.006 ** (2.12) |
| rdi | 0.091 *** (4.89) | 0.103 *** (5.59) | 0.113 *** (6.16) | 0.196 *** (5.67) | 0.189 *** (5.45) | 0.193 *** (5.50) |
| age | 1.697 *** (27.95) | 1.646 *** (25.57) | 1.895 *** (36.33) | 0.608 *** (6.23) | 0.590 *** (5.76) | 0.718 *** (7.75) |
| Constant | −0.855 ** (−2.13) | 1.694 *** (4.01) | 1.001 ** (2.58) | 0.178 (0.25) | 1.262 * (1.75) | 0.657 (0.95) |
| Observations | 1275 | 1275 | 1275 | 1275 | 1275 | 1275 |
| R-squared | 0.697 | 0.697 | 0.702 | |||
| Number of ID | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 |
| Variable | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kbd | kbd | kbd | pat | pat | pat | |
| bet | 0.188 *** (5.11) | 0.115 *** (4.09) | ||||
| clo | 0.434 ** (2.43) | 0.285 ** (2.00) | ||||
| clu | 0.309 ** (2.48) | 0.333 *** (3.08) | ||||
| kbd | 0.220 *** (11.88) | 0.218 *** (11.59) | 0.222 *** (11.93) | |||
| lev | −0.007 *** (−3.79) | −0.006 *** (−3.35) | −0.006 *** (−3.22) | 0.000 (0.28) | 0.001 (0.57) | 0.001 (0.75) |
| roa | −0.015 *** (−4.44) | −0.014 *** (−4.27) | −0.015 *** (−2.98) | 0.003 (1.05) | 0.002 (0.97) | 0.002 (0.95) |
| rdi | 0.011 (0.28) | 0.029 (0.78) | 0.042 (1.12) | 0.172 *** (5.07) | 0.170 *** (4.96) | 0.159 *** (4.59) |
| age | 2.067 *** (16.95) | 2.205 *** (17.07) | 2.346 *** (21.94) | 0.995 *** (10.14) | 1.087 *** (10.83) | 1.165 *** (12.97) |
| Constant | −1.849 ** (−2.30) | 0.194 (0.23) | −0.071 (−0.09) | −0.753 (−1.10) | 0.291 (0.40) | −0.052 (−0.08) |
| Observations | 1286 | 1286 | 1285 | 1286 | 1286 | 1286 |
| R-squared | 0.464 | 0.454 | 0.454 | |||
| Number of ID | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 | 139 |
| Variable | (1) pat | (2) pat | (3) pat | (4) pat | (5) pat | (6) pat | (7) pat | (8) pat | (9) pat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bet | 0.086 *** (4.67) | 0.098 *** (4.38) | 0.142 *** (7.51) | ||||||
| clo | 1.713 *** (4.82) | 2.709 *** (6.49) | 2.618 *** (7.15) | ||||||
| clu | 0.994 *** (3.86) | 0.326 (1.06) | 0.855 *** (3.34) | ||||||
| kbb | 0.669 *** (29.80) | 0.678 *** (30.07) | 0.664 *** (29.60) | ||||||
| kbd | 0.224 *** (20.95) | 0.219 *** (20.80) | 0.212 *** (19.99) | ||||||
| lev | −0.004 *** (−6.13) | −0.004 *** (−5.94) | −0.004 *** (−5.74) | 0.001 (1.11) | 0.001 (1.61) | 0.001 (1.25) | −0.006 *** (−8.27) | −0.006 *** (−7.89) | −0.005 *** (−7.72) |
| roa | 0.010 *** (7.30) | 0.010 *** (7.46) | 0.010 *** (7.33) | 0.009 *** (6.69) | 0.010 *** (7.16) | 0.009 *** (6.76) | 0.009 *** (6.86) | 0.010 *** (7.25) | 0.009 *** (6.80) |
| rdi | 0.164 *** (16.93) | 0.165 *** (17.01) | 0.164 *** (16.93) | 0.155 *** (15.85) | 0.157 *** (16.06) | 0.154 *** (15.80) | 0.118 *** (11.85) | 0.121 *** (12.19) | 0.120 *** (12.05) |
| age | 2.708 *** (44.82) | 2.662 *** (40.16) | 2.877 *** (64.84) | 1.294 *** (15.67) | 1.114 *** (12.44) | 1.521 *** (23.98) | 2.090 *** (31.20) | 2.053 *** (28.38) | 2.417 *** (48.83) |
| Observations | 597 | 597 | 597 | 582 | 582 | 582 | 595 | 595 | 595 |
| Number of ID | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Variable | (1) cited | (2) cited | (3) cited | (4) cited | (5) cited | (6) cited | (7) cited | (8) cited | (9) cited |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bet | 0.137 *** (3.75) | 0.056 (1.26) | 0.135 *** (3.35) | ||||||
| clo | 2.543 *** (2.81) | 2.673 *** (2.71) | 2.649 *** (2.81) | ||||||
| clu | 2.130 *** (3.43) | 1.177 (1.47) | 1.827 *** (2.84) | ||||||
| kbb | 0.719 *** (14.21) | 0.733 *** (14.71) | 0.723 *** (14.34) | ||||||
| kbd | 0.222 *** (6.22) | 0.226 *** (6.40) | 0.214 *** (6.02) | ||||||
| lev | −0.001 (−0.26) | −0.000 (−0.14) | 0.000 (0.14) | −0.001 (−0.53) | −0.001 (−0.52) | −0.001 (−0.35) | −0.001 (−0.42) | −0.001 (−0.32) | 0.000 (0.02) |
| roa | −0.001 (−0.18) | 0.001 (0.14) | 0.005 (0.84) | 0.019 *** (3.58) | 0.021 *** (3.94) | 0.020 *** (3.74) | 0.008 (1.30) | 0.010 (1.57) | 0.012 * (1.88) |
| rdi | 0.174 *** (3.05) | 0.167 *** (2.88) | 0.175 *** (2.98) | 0.188 *** (4.03) | 0.174 *** (3.80) | 0.185 *** (3.91) | 0.150 *** (2.86) | 0.141 *** (2.65) | 0.149 *** (2.75) |
| lage | 0.761 *** (4.34) | 0.799 *** (4.50) | 0.918 *** (5.32) | 0.087 (0.54) | −0.030 (−0.18) | 0.131 (0.83) | 0.682 *** (3.87) | 0.691 *** (3.88) | 0.822 *** (4.72) |
| Constant | 0.650 (0.56) | 0.836 (0.72) | 0.727 (0.62) | 1.153 (1.11) | 0.882 (0.88) | 1.095 (1.04) | −0.491 (−0.43) | −0.314 (−0.28) | −0.265 (−0.23) |
| Observations | 597 | 597 | 597 | 582 | 582 | 582 | 595 | 595 | 595 |
| Number of ID | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Gong, J.; Luo, J.; Qiu, Z. The Impact of Technology Convergence on the Sustainable Innovation of China’s Modern Manufacturing Enterprises: The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135307
Li C, Gong J, Luo J, Qiu Z. The Impact of Technology Convergence on the Sustainable Innovation of China’s Modern Manufacturing Enterprises: The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chenguang, Jingtong Gong, Jie Luo, and Zhenjun Qiu. 2024. "The Impact of Technology Convergence on the Sustainable Innovation of China’s Modern Manufacturing Enterprises: The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135307
APA StyleLi, C., Gong, J., Luo, J., & Qiu, Z. (2024). The Impact of Technology Convergence on the Sustainable Innovation of China’s Modern Manufacturing Enterprises: The Mediating Role of the Knowledge Base. Sustainability, 16(13), 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135307






