Investigating the Impact of Recent and Future Urbanization on Flooding in an Indian River Catchment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1).
- What is the impact of recent urbanization and potential future urbanization on flooding in the Meenachil river catchment and the Kuttanad administrative area in central Kerala, India?
- (2).
- How much benefit will NBSs provide in reducing the flooding risk?
- (3).
- What regional-scale planning recommendations are needed to minimize the flood risk in the Kuttanad administrative area under future developments?
2. Materials and Methods
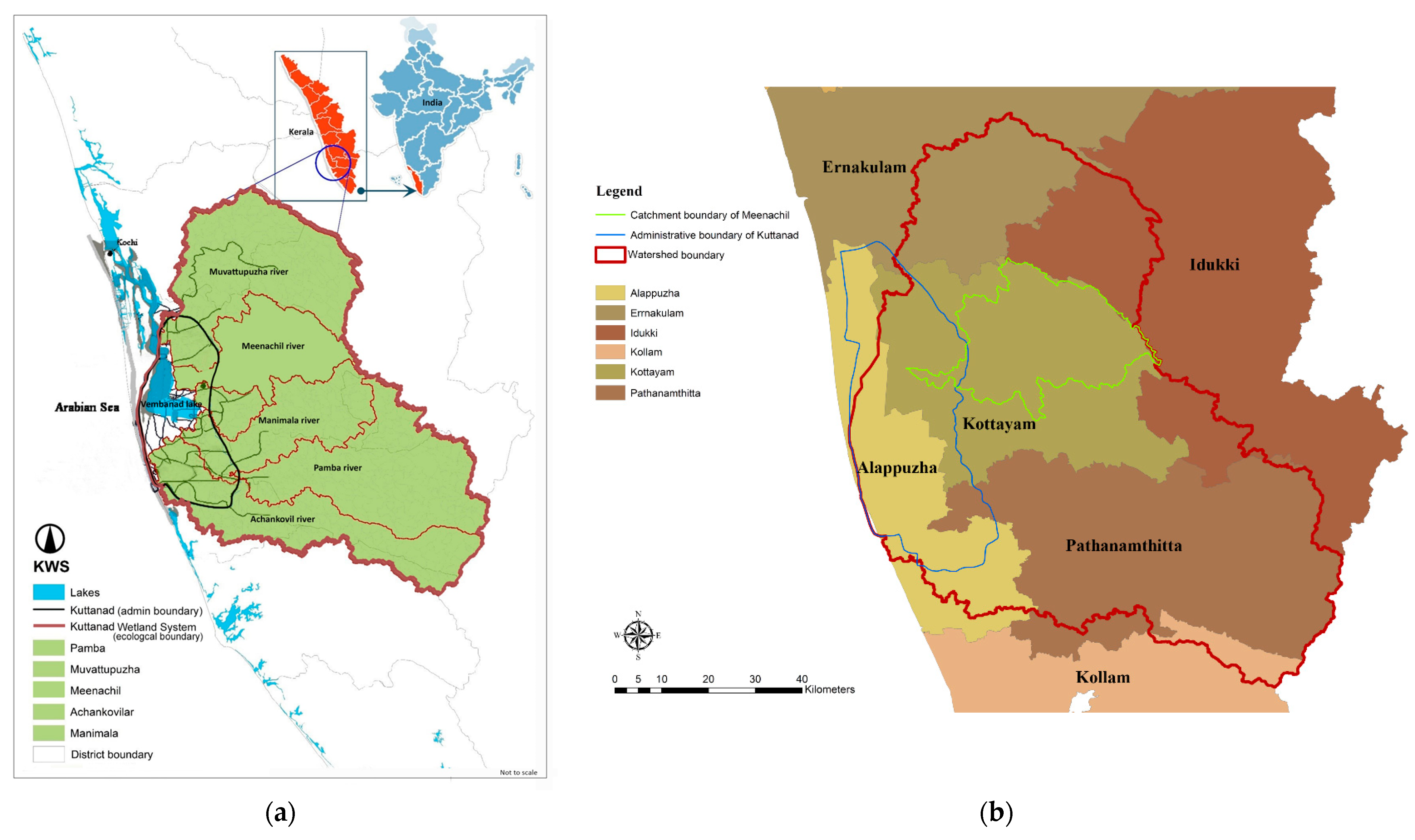
2.1. Kuttanad Wetland System
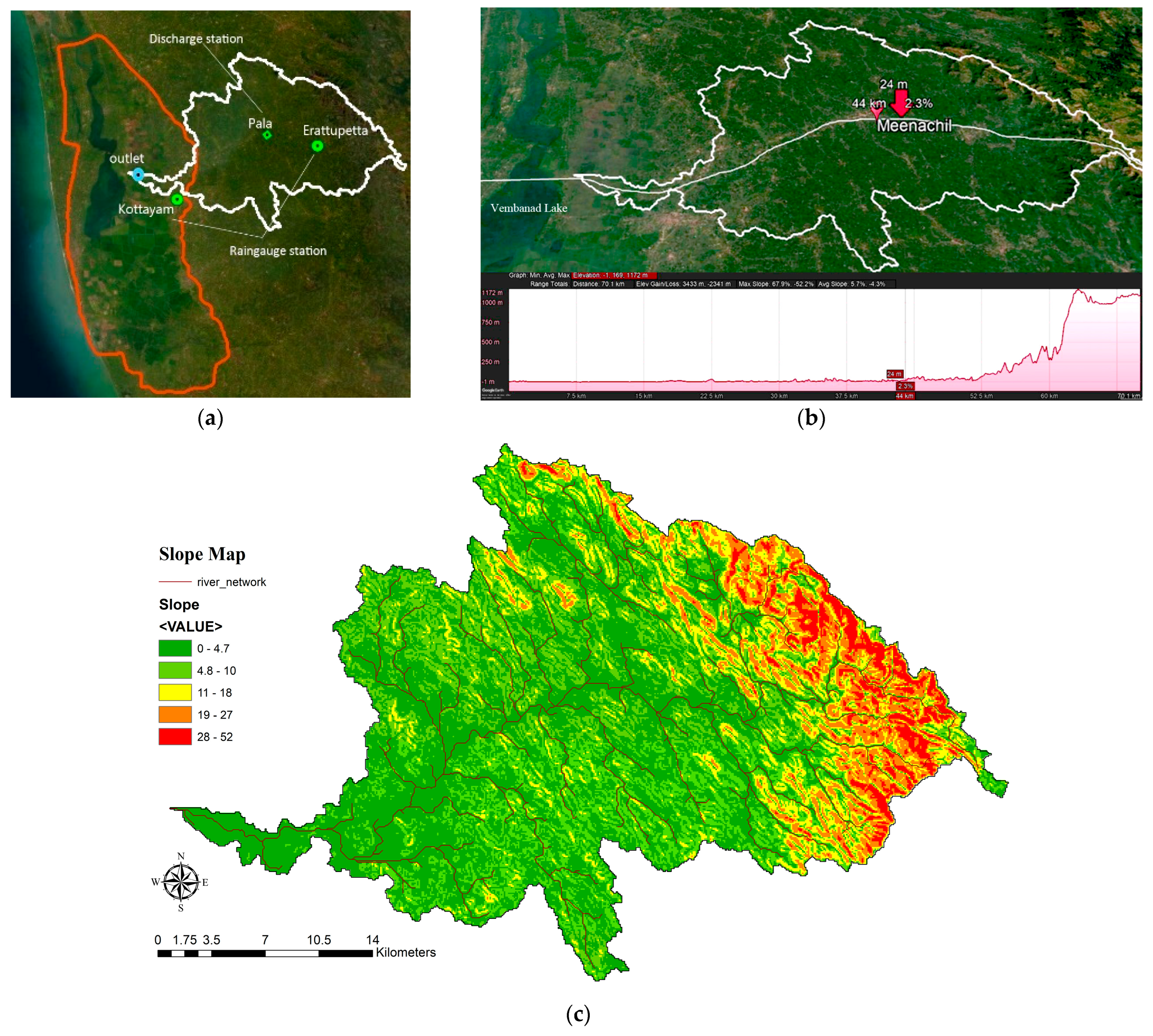
2.2. Meenachil River Basin and Data
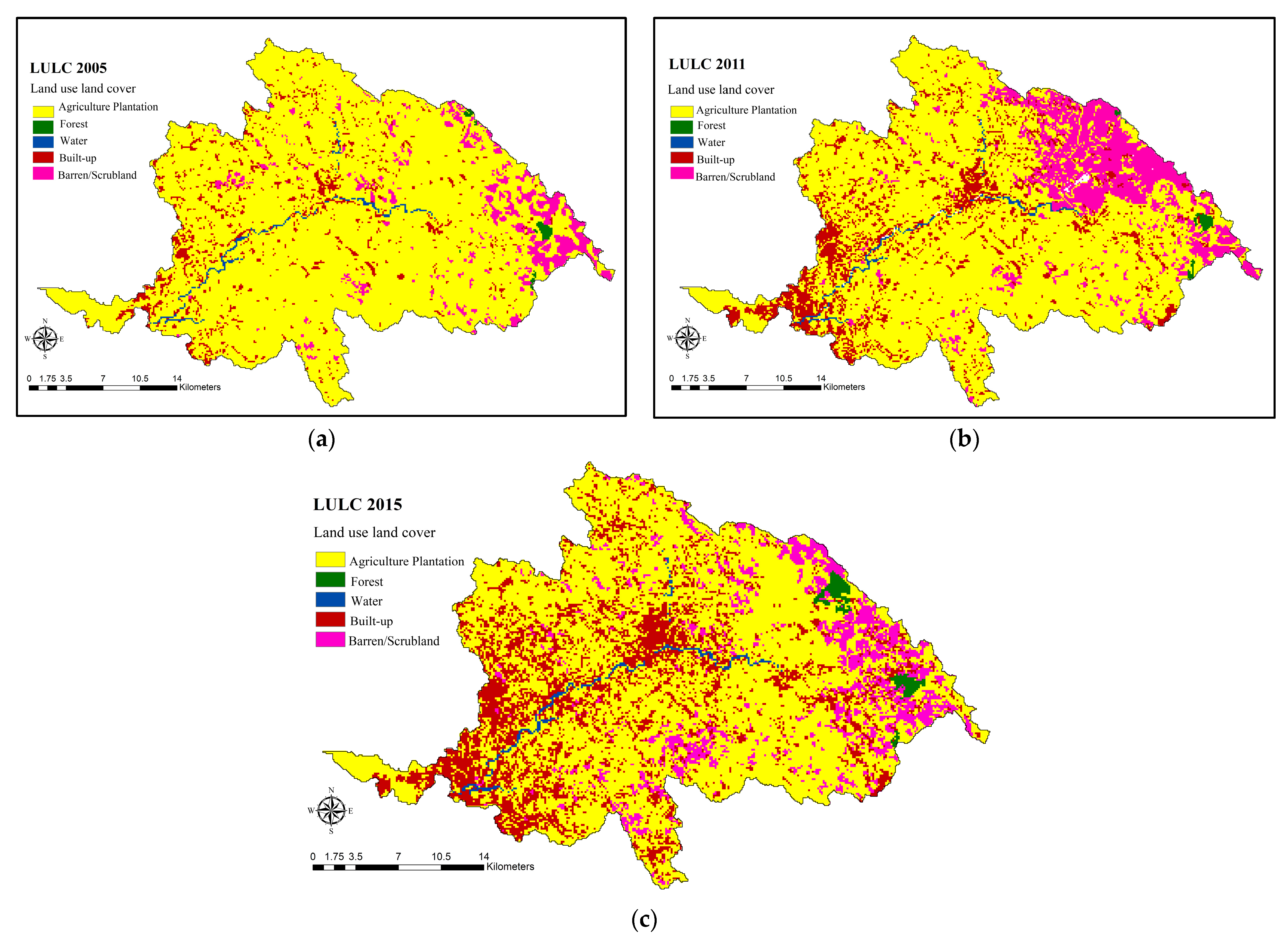
2.3. Future LULC Maps
2.4. Hydrologic Modeling
2.5. Hydraulic Modeling
2.6. Nature-Based Solution
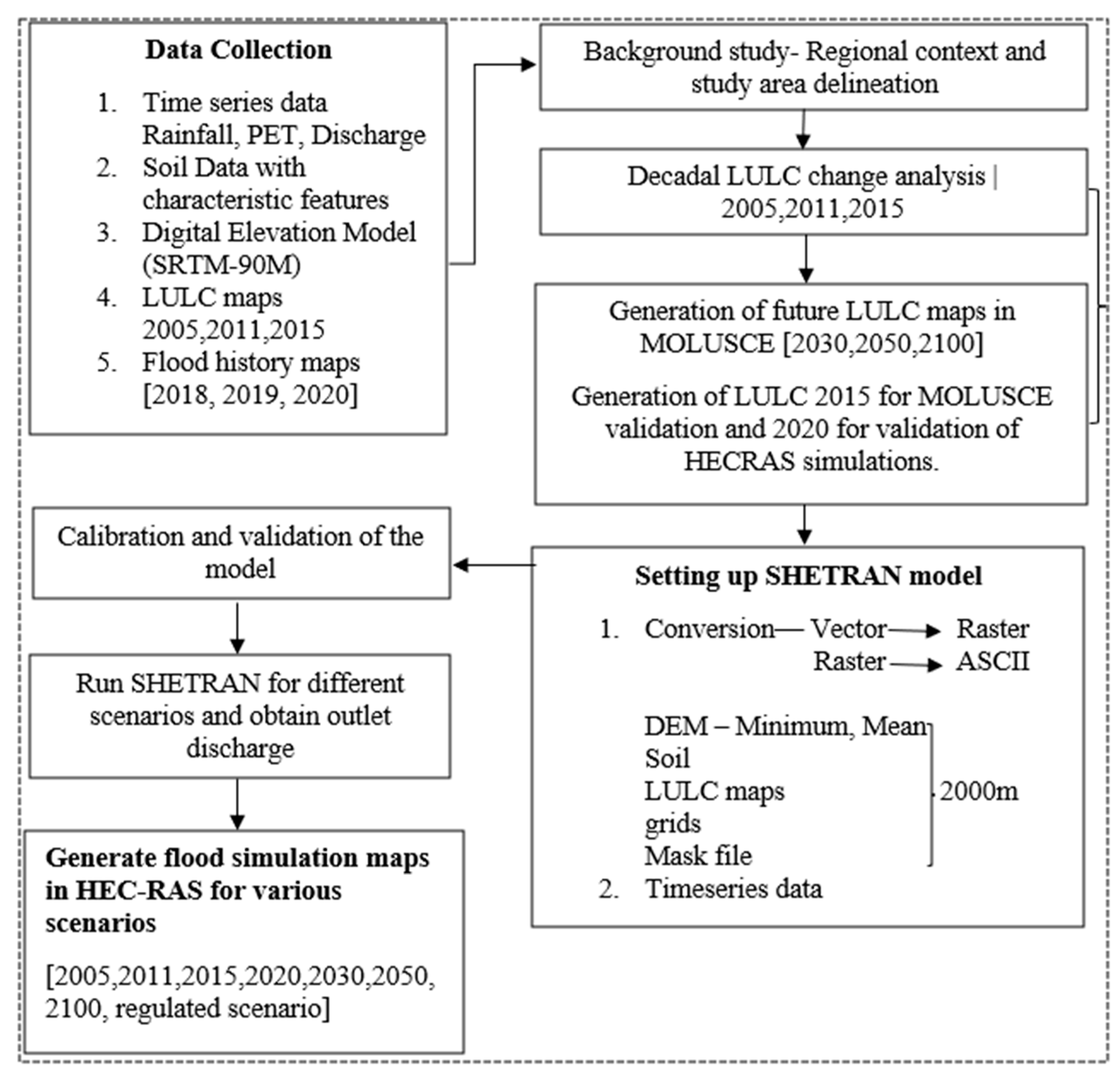
2.7. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Validation of 2015 LULC Map and Future LULC Scenarios
3.2. SHETRAN Calibration
3.3. SHETRAN LULC Simulations
3.4. HEC-RAS Simulations Validation
3.5. HEC-RAS LULC Scenario Simulations
4. Discussion
4.1. Land Cover and NBS
4.2. Planning Policy
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alshammari, E.; Rahman, A.A.; Rainis, R.; Seri, N.A.; Fuzi, N.F.A. The Impacts of Land Use Changes in Urban Hydrology, Runoff and Flooding: A Review. Curr. Urban Stud. 2023, 11, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in land-scape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, O.V.; Barr, A.D.; Donn, M.J. Effect of urbanisation on the water balance of a catchment with shallow groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 162–176. [Google Scholar]
- Sear, D.A.; Hornby, D.H.; Wheaton, J.; Hill, C.T. Understanding River Channel Sensitivity to Geomorphological Changes: Methods; Report FRS17183; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Verbeiren, B.; Van De Voorde, T.; Canters, F.; Binard, M.; Cornet, Y.; Batelaan, O. Assessing urbanisation effects on rainfall-runoff using a remote sensing supported modelling strategy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Bourke, R. Urbanization impacts on flood risks based on urban growth data and coupled flood models. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zope, P.E.; Eldho, T.I.; Jothiprakash, V. Impacts of urbanization on flooding of a coastal urban catchment: A case study of Mumbai City, India. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 887–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadashivam, T.; Tabassu, S. Trends of urbanization in India: Issues and challenges in the 21st century. Int. J. Inf. Res. Rev. 2016, 3, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, P.; Nair, S.B. Urbanization in Kerala—What does the census data reveal? Indian J. Hum. Dev. 2017, 11, 356–386. [Google Scholar]
- Gosling, S.N.; Lewis, E.; Birkinshaw, S.J.; Tratalos, J.; Haines-Young, R. The Effects of Future Land-Cover Change on UK River Flows. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=073527e0ef77dc6aa88667a113f6dce694ecf61b (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Mekonnen, D.; Duan, Z.; Rientjes, T.; Disse, M. Analysis of the combined and single effects of LULC and climate change on the streamflow of the Upper Blue Nile River Basin (UBNRB): Using statistical trend tests, remote sensing landcover maps and the SWAT model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yereseme, A.K.; Surendra, H.J.; Kuntoji, G. Sustainable integrated urban flood management strategies for planning of smart cities: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: Importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C.; Ewen, J.; Parkin, G.; O’Connell, P.E.; Cooper, J.D. Validation of catchment models for predicting land-use and climate change impacts. 3. Blind validation for internal and outlet responses. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonu, T.S.; Bhagyanathan, A. The impact of upstream land use land cover change on downstream flooding: A case of Kuttanad and Meenachil River Basin, Kerala, India. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101089. [Google Scholar]
- Munoth, P.; Goyal, R. Impacts of land use land cover change on runoff and sediment yield of Upper Tapi River Sub-Basin, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2020, 18, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, C.A.; Lobo, F.D.L.; Dibike, Y.B.; Costa, M.P.D.F.; Dos Santos, V.; Novo, E.M.L. Modelling the effects of historical and future land cover changes on the hydrology of an Amazonian basin. Water 2018, 10, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.L.; Knouft, J.H.; Ghulam, A.; Guzman, J.A.; Pan, Z. Impacts of urbanization on river flow frequency: A controlled experimental modeling-based evaluation approach. J. Hydrol. 2013, 495, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hipt, F.O.; Diekkrüger, B.; Steup, G.; Yira, Y.; Hoffmann, T.; Rode, M. Modeling the effect of land use and climate change on water resources and soil erosion in a tropical West African catchment (Dano, Burkina Faso) using SHETRAN. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, S.; Eldho, T.I.; Jayasankar, T. Physically based distributed modelling of the hydrology and soil erosion under changes in landuse and climate of a humid tropical river basin. Catena 2022, 217, 106427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Xuan, Y.; Ye, M.; Xu, C. Global sensitivity analysis in hydrological modeling: Review of concepts, methods, theoretical framework, and applications. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, S.; Bin Abdullah, R.; Abustan, I.; Eslamian, S. Comparison between capabilities of HEC-RAS and MIKE11 hydraulic models in river flood risk modeling (A case study of Sungai Kayu Ara River basin, Malaysia). Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 270–291. [Google Scholar]
- Hadimlioglu, I.A.; King, S.A.; Starek, M.J. FloodSim: Flood simulation and visualization framework using position-based fluids. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India, L. Lakes of India Kuttanad: The Rice Bowl of Kerala. InfoSWMM Help Documentation. 2022, pp. 8–12. Available online: https://help.innovyze.com/space/infoswmm/17598253/Introduction (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Hartmann, T.; Juepner, R. The Flood Risk Management Plan: An Essential Step Towards the Institutionalization of a Paradigm Shift. Int. J. Water Gov. 2014, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Liu, M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Zevenbergen, C. Social, economic and environmental assessment of urban sub-catchment flood risks using a multi-criteria approach: A case study in Mumbai City, India. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowińska-Świerkosz, B.; García, J. What is Nature-based solutions (NBS)? Setting core ideas for concept clarification. Nat. Based Solut. 2022, 2, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, N.; Fritz, M.; Freitas, T.; de Boissezon, B.; Vandewoestijne, S. Nature-Based Solutions in the EU: Innovating with nature to address social, economic and environmental challenges. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, K.G.; Madhusoodhanan, C.G.; Eldho, T.I. Climate and Landuse Change Impacts on Sub-Sea Level Rice Farming in a Tropical Deltaic Wetland. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gopakumar, M. Kuttanad: The Next Vanishing Wetland? 2022. Available online: https://frontline.thehindu.com/environment/will-kuttanad-be-the-next-vanishing-wetland/article65546163.ece (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Varughese, A. Climate Change Has Cost Kuttanad Farmers Rs 9, 608 Crore This Year. Here’ s What Can Help. 2022. Available online: https://thewire.in/agriculture/kerala-kuttanad-farmers-rainfall-paddy (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Biju, E.P. Kainakari in Kerala’ s Kuttanad in knee-deep water for past 78 days. September 2018. pp. 1–3. Available online: https://www.newindianexpress.com/states/kerala/2018/Sep/01/kainakari-in-keralas-kuttanad-in-knee-deep-water-for-past-78-days-1866181.html#:~:text=The%20sexagenarian%20farmer%20has%20been,%2C%20and%20son%20Biju%2C%2038 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Shaji, K. In Kerala’s Kuttanad, Climate Change Is Forcing Locals to Abandon Their Homes. 2021, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://scroll.in/article/1003721/in-keralas-kuttanad-climate-change-is-forcing-residents-to-abandon-their-homes (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Kumar, B.A.; Gopinath, G.; Chandran, M.S. River sinuosity in a humid tropical river basin, southwest coast of India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRSC. Bhuvan|ISRO’s Geoportal|Gateway to Indian Earth Observation. Available online: https://www.nrsc.gov.in/ (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Vinayak, A.J. Borewells depleting water of future generations: Experts. 2018. Available online: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/borewells-depleting-water-of-future-generations-experts/article64332492.ece (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Meti, S.; Rao, D.V.K.N.; Nair, N.U.; Jacob, J. Distribution of natural rubber cultivation in relation to soil and landscape attributes in India. In Proceedings of the 29th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing 2008, ACRS 2008, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 10–14 November 2008; pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sethunath, K. Rubber Economy in Crisis. 2016, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.deccanchronicle.com/nation/current-affairs/100216/rubber-economy-in-crisis.html (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Onmanorama. Post Floods Slender Meenachil River Raises Concern. 2018. Available online: https://www.onmanorama.com/lifestyle/news/2018/09/01/post-floods-slender-meenachil-river-raises-concern.html (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Chughtai, A.H.; Abbasi, H.; Karas, I.R. A review on change detection method and accuracy assessment for land use land cover. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 22, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sheng, G.; Boyd, S.A. Use of Organoclays in Pollution Abatement. Adv. Agron. 1997, 59, 25–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer, R.J.; Xu, J.; Trabucco, A. Version 3 of the global aridity index and potential evapotranspiration database. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodroffe, C.D.; Falkland, A.C. Chapter 31 Geology and hydrogeology of the Cocos (Keeling) islands. Dev. Sedimentol. 2004, 54, 885–908. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.T.U.; Tabassum, F.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Saba, H.; Sarkar, L.; Ferdous, J.; Uddin, S.Z.; Zahedul Islam, A.Z.M. Temporal dynamics of land use/land cover change and its prediction using CA-ANN model for southwestern coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 29039035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzha, A.C.; Rufino, M.C.; Okoth, S.; Jacobs, S.; Nóbrega, R.L.B. Impacts of land use and land cover change on surface runoff, discharge and low flows: Evidence from East Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubea, K.W.; Ngigi, T.G.; Mundia, C.N. Assessing Application of Markov Chain Analysis in Nakuru. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoy, K.I.; Qi, F.; Shebitz, D.J. Analyzing and Predicting Land Use and Land Cover Changes in New Jersey Using Multi-Layer Perceptron–Markov Chain Model. Earth 2021, 2, 845–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Shi, W.; Zhu, X.; Abbas, S.; Khan, H.U.A. Future simulation of land use changes in rapidly urbanizing South China based on land change modeler and remote sensing data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leta, M.K.; Demissie, T.A.; Tränckner, J. Modeling and prediction of land use land cover change dynamics based on land change modeler (Lcm) in nashe watershed, upper blue nile basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, M.; Rangarajan, S. Predicting the future land use and land cover changes for Bhavani basin, Tamil Nadu, India, using QGIS MOLUSCE plugin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 86337–86348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O. QGIS-based modeling and analysis of urban dynamics affecting land surface temperature towards climate hazards in coastal zones of Portugal. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 7749–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.A.; Al Rakib, A.; Roy, S.; Ferdousi, J.; Raikwar, V.; Kona, M.A.; Al Fatin, S.A. Predicting changes in land use/land cover and seasonal land surface temperature using multi-temporal landsat images in the northwest region of Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, S.I.; Mohamed, M.M. Remote sensing and geophysical survey applications for delineating near-surface palaeochannels and shallow aquifer in the United Arab Emirates. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, T. Assessment and Predicting of LULC by Kappa Analysis and CA Markov model using RS and GIS Techniques in Udham Singh Nagar District, India. Res. Square 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewen, J.; Parkin, G.; O’Connell, P.E. SHETRAN: Distributed River Basin Flow and Transport Modeling System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderton, S.P.; Latron, J.; White, S.M.; Llorens, P.; Gallart, F.; Salvany, C.; O’Connell, P.E. Internal evaluation of a physically based distributed model using data from a Mediterranean mountain catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE (Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng.) 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. A rational performance criterion for hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.; Birkinshaw, S.; Kilsby, C.; Fowler, H.J. Development of a system for automated setup of a physically based, spatially distributed hydrological model for catchments in Great Britain. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 108, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, S.; Eldho, T.I.; Madhusoodhanan, C.G.; Jayasankar, T. Multiobjective sensitivity analysis and model parameterization approach for coupled streamflow and groundwater table depth simulations using SHETRAN in a wet humid tropical catchment. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krest Engineers. Manning’ s n (Roughness Coefficient) for HEC-RAS 2D Modeling. 2021. Available online: https://rashms.com/blog/mannings-n-roughness-coefficient-for-hec-ras-2d-modeling/ (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Dieck, J.; Ruhser, J.; Hoy, E.; Robinson, L. General Classification Handbook for Floodplain Vegetation in Large River Systems; U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 2; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso de Salis, H.H.; Monteiro da Costa, A.; Moreira Vianna, J.H.; Azeneth Schuler, M.; Künne, A.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Leal Pacheco, F.A. Hydrologic modeling for sustainable water resources management in urbanized karst areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suroso, S.; Santoso, P.B.; Birkinshaw, S.; Kilsby, C.; Bardossy, A.; Aldrian, E. Assessment of TRMM rainfall data for flood modelling in three contrasting catchments in Java, Indonesia. J. Hydroinform. 2023, 25, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechel, M.; Slater, L.; Dadson, S. Hydrological impact of widespread afforestation in Great Britain using a large ensemble of modelled scenarios. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.; Chapman, D. Impacts of afforestation on groundwater resources and quality. Hydrogeol. J. 2001, 9, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Watershed-Based Planning. Available online: https://wetlandswatch.org/watershed-based-planning/ (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Falconer, R.A.; Harpin, R. Catchment flood management: A UK perspective and experience. Water Int. 2005, 30, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.W.; Amado, A.A.; Schilling, K.E.; Weber, L.J. Evaluating the efficacy of distributed detention structures to reduce downstream flooding under variable rainfall, antecedent soil, and structural storage conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 96, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Huang, W.; Peng, W. Evaluating the effect of building patterns on urban flooding based on a boosted regression tree: A case study of Beijing, China. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; He, X.; Lin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X. Assessing the scale effect of urban vertical patterns on urban waterlogging: An empirical study in Shenzhen. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Enserink, B.; Balchand, A.N. Coastal regulation zone rules in coastal panchayats (villages) of Kerala, India vis-à-vis socio-economic impacts from the recently introduced peoples’ participatory program for local self-governance and sustainable development. Ocean Coast Manag. 2005, 48, 632–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Kächele, H.; Müller, K. Vulnerabilities to flood hazards among rural households in India. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1133–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hazra, S.; Haque, A.; Rahman, M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, T.; Salehin, M.; De Campos, R.S. Social vulnerability to environmental hazards in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta, India and Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 53, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kang, J. Participatory Framework for Urban Pluvial Flood Modeling in the Digital Twin Era. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Nedovic-Budic, Z. Integrating spatial planning and flood risk management: A new conceptual framework for the spatially integrated policy infrastructure. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 5768–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, S.; Eldho, T.I. Effects of grid-size on effective parameters and model performance of SHETRAN for estimation of streamflow and sediment yield. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.R.; Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Neves, R. Modeling Streamflow at the Iberian Peninsula Scale Using MOHID-Land: Challenges from a Coarse Scale Approach. Water 2022, 14, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op de Hipt, F.; Diekkrüger, B.; Steup, G.; Yira, Y.; Hoffmann, T.; Rode, M. Applying SHETRAN in a tropical west African catchment (Dano, Burkina Faso)—Calibration, validation, uncertainty assessment. Water 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

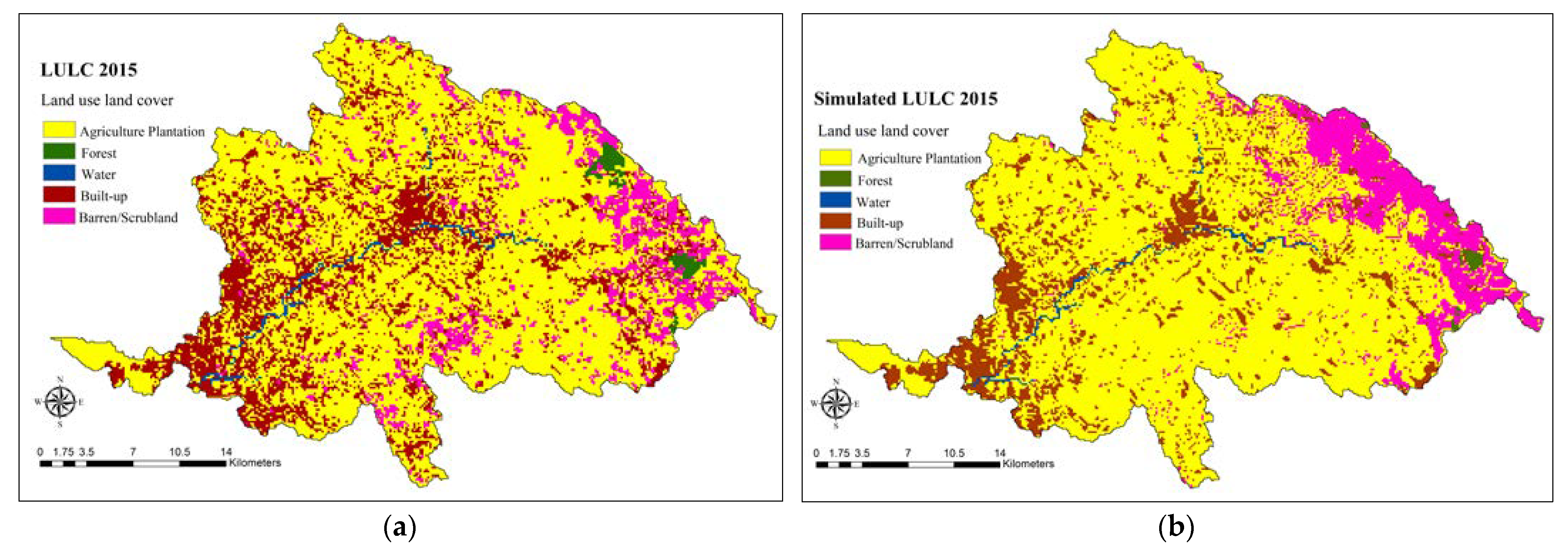

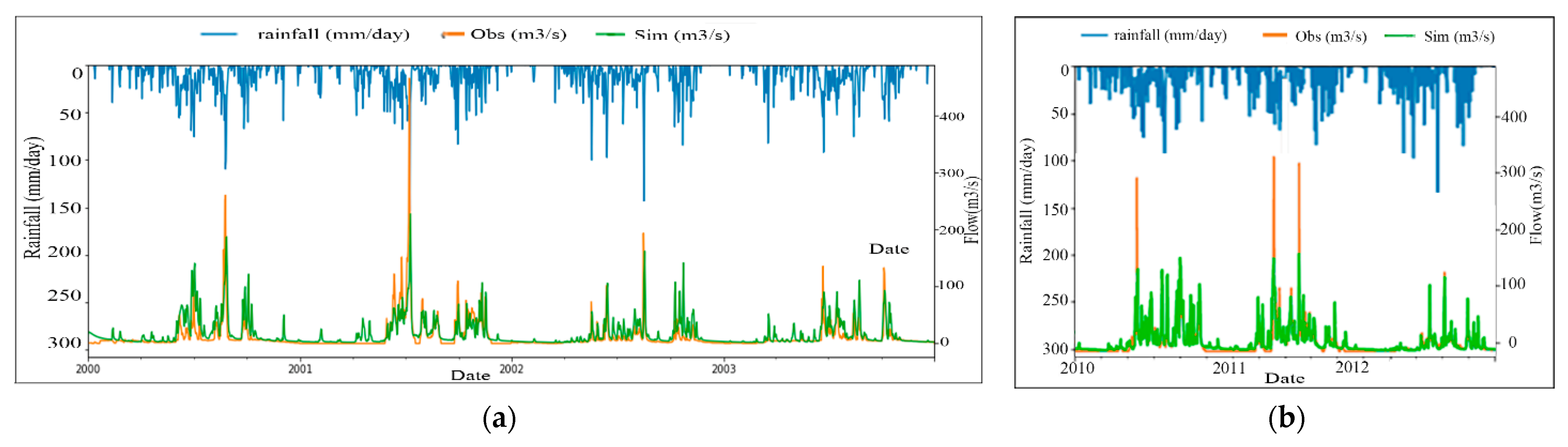

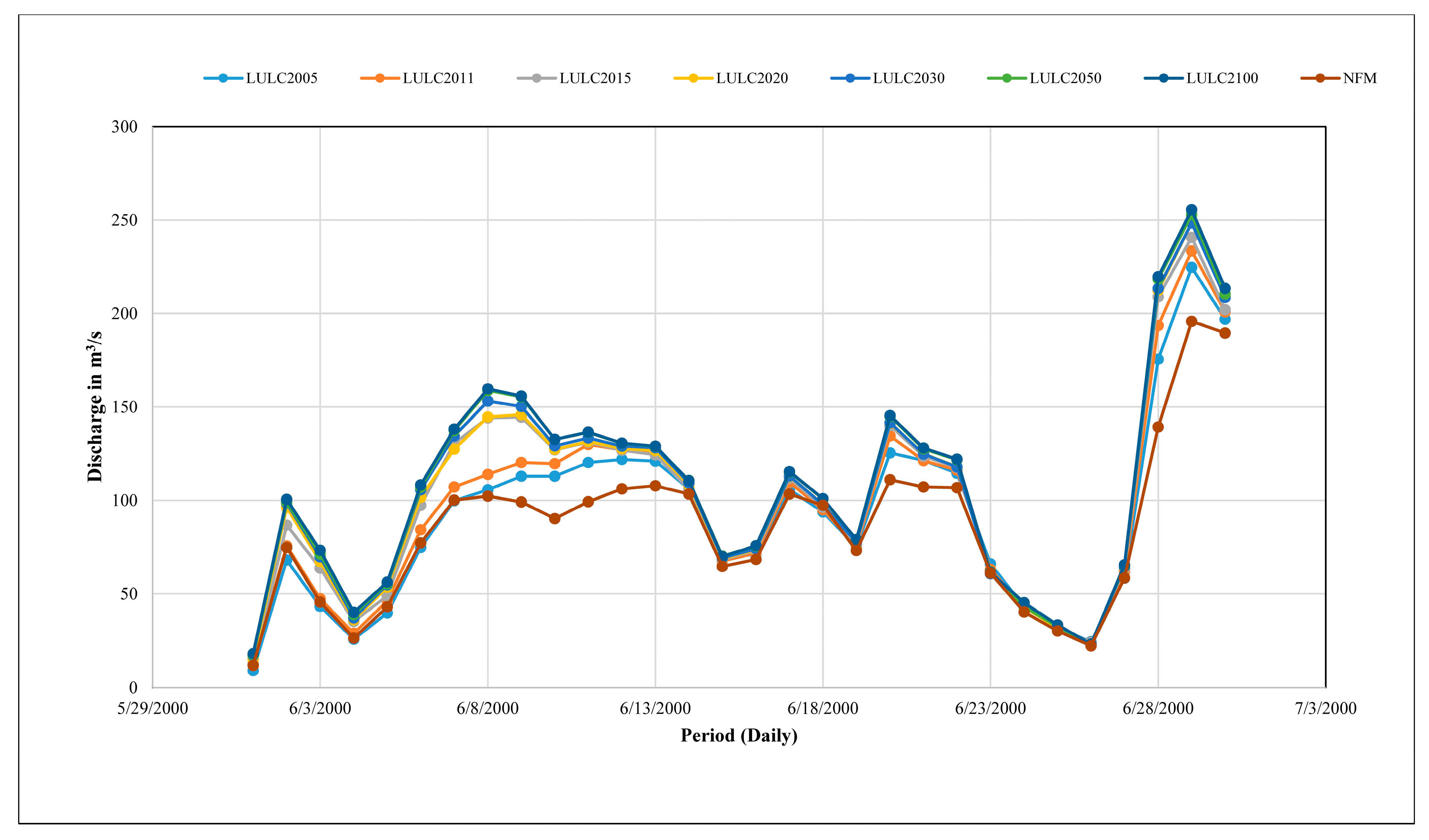
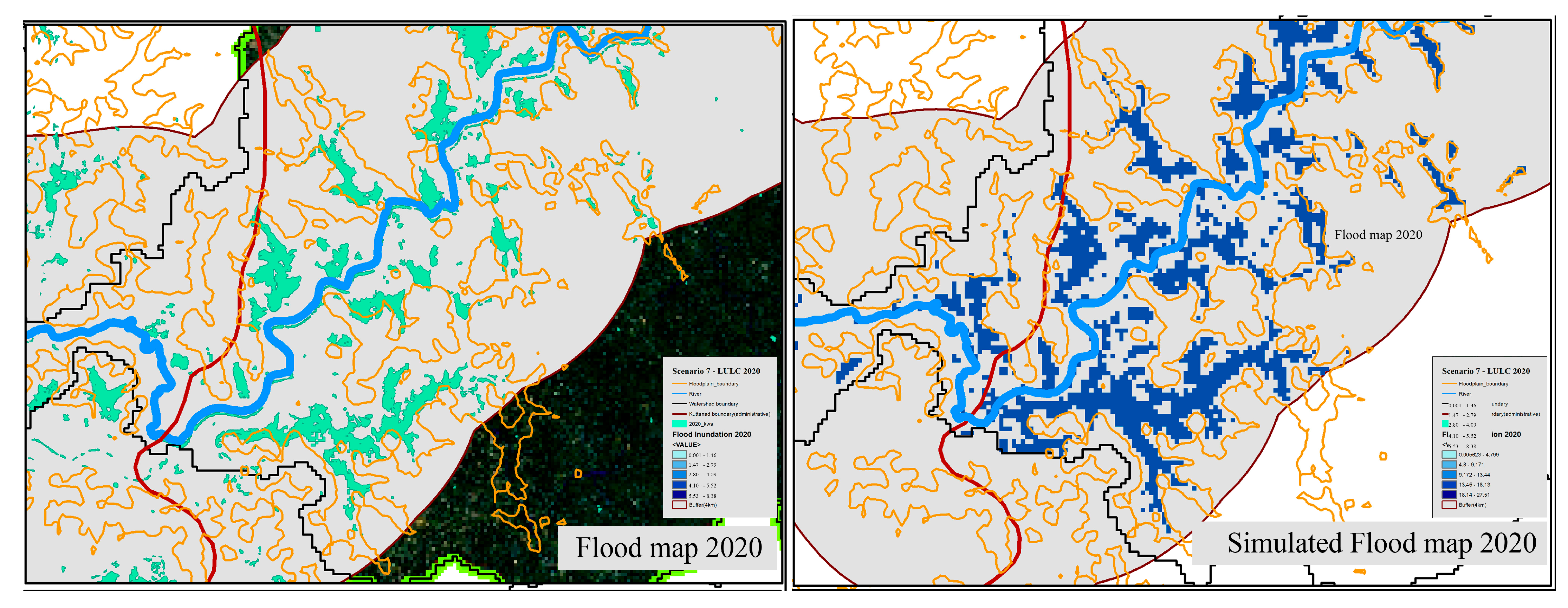

| Land Use | 2005 (km2) | 2011 (km2) | Difference (km2) | Difference (%) | 2015 (km2) | Difference (km2) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 739.9 | 613.4 | −126.5 | −17.09 | 567.1 | −172.8 | −23.35 |
| Forest | 2.7 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 3.7 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 203.7 |
| Water | 6.4 | 6.6 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 7.0 | 0.6 | 9.4 |
| Built-up/ urban | 53.1 | 108.4 | 55.3 | 104.1 | 192.5 | 139.4 | 262.5 |
| Barren | 51.9 | 122.8 | 70.9 | 136.6 | 79.2 | 27.3 | 52.6 |
| Land Use | 2015 (km2) | Regulated (km2) | Difference (km2) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 567.1 | 486.5 | −80.6 | −14.2 |
| Forest | 8.2 | 8.2 | 0.0 | |
| Water | 7.0 | 7.0 | 0.0 | |
| Built-up | 192.5 | 185.0 | −7.5 | −3.8 |
| Barren/Scrubland | 79.2 | 64.0 | −15.2 | −19.0 |
| NBS (Flood Plain) | - | 82.0 | 82.0 | - |
| NBS (Afforestation) | - | 21.3 | 21.3 | - |
| Land Use | 2015 (km2) | 2030 (km2) | 2050 (km2) | 2100 (km2) | Difference 2015–2100 (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 567.1 | 497.2 | 478.8 | 463.0 | −102.1 |
| Forest | 8.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −8.0 |
| Water | 7.0 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | −5.7 |
| Built-up/Urban | 192.5 | 278.4 | 297.8 | 314.0 | 121.5 |
| Barren | 79.2 | 76.9 | 75.9 | 75.5 | −3.7 |
| LULC | 2005 | 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | 2030 | 2050 | 2100 | NFM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southwest Monsoon: | ||||||||
| June | 91.8 | 96.2 | 102.1 | 103.9 | 105.5 | 107.5 | 108.4 | 85.3 |
| July | 79.9 | 81.9 | 83.9 | 84.9 | 85.4 | 86.0 | 86.9 | 75.6 |
| August | 138.5 | 143.0 | 146.5 | 148.5 | 149.2 | 150.6 | 151.3 | 122.7 |
| Northeast Monsoon: | ||||||||
| October | 45.4 | 46.8 | 47.7 | 48.0 | 48.5 | 49.0 | 49.6 | 42.8 |
| November | 10.6 | 10.8 | 11.2 | 11.2 | 11.3 | 11.4 | 11.5 | 10.3 |
| Scenario | Agriculture (%) | Built-Up/ Urban (%) | Barren (%) | NFM Forest/ Regulated (%) | Flood Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 86.6 | 6.2 | 6.0 | - | 1.88 |
| 2011 | 71.8 | 12.7 | 14.3 | - | 2.94 |
| 2015 | 66.4 | 22.6 | 9.3 | - | 3.04 |
| 2030 | 58.1 | 32.6 | 9.0 | - | 3.80 |
| 2050 | 56.0 | 34.9 | 8.9 | - | 3.84 |
| 2100 | 54.2 | 34.8 | 8.9 | - | 3.86 |
| Regulated | 56.96 | 21.6 | 7.49 | 12.1 | 1.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thaivalappil Sukumaran, S.; Birkinshaw, S.J. Investigating the Impact of Recent and Future Urbanization on Flooding in an Indian River Catchment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5652. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135652
Thaivalappil Sukumaran S, Birkinshaw SJ. Investigating the Impact of Recent and Future Urbanization on Flooding in an Indian River Catchment. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5652. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135652
Chicago/Turabian StyleThaivalappil Sukumaran, Sonu, and Stephen J. Birkinshaw. 2024. "Investigating the Impact of Recent and Future Urbanization on Flooding in an Indian River Catchment" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5652. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135652
APA StyleThaivalappil Sukumaran, S., & Birkinshaw, S. J. (2024). Investigating the Impact of Recent and Future Urbanization on Flooding in an Indian River Catchment. Sustainability, 16(13), 5652. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135652







