Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Wuhan City Based on RSEI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
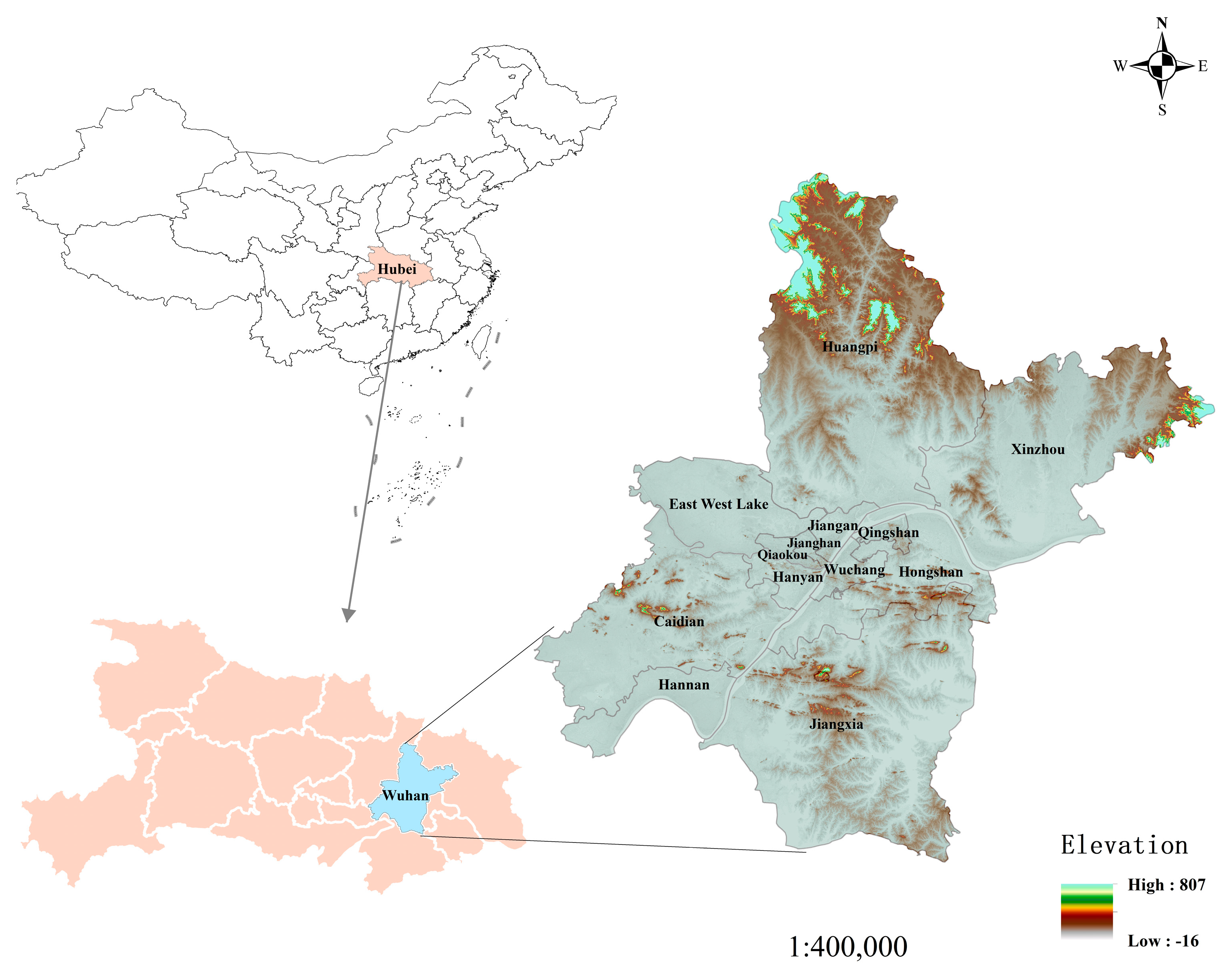
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Main Research Methods
2.3.1. RSEI
2.3.2. Geodetector
- (1)
- Factor detector
- (2)
- Interaction detector
2.3.3. PLS-SEM Model
3. Results
3.1. Wuhan RSEI Calculations
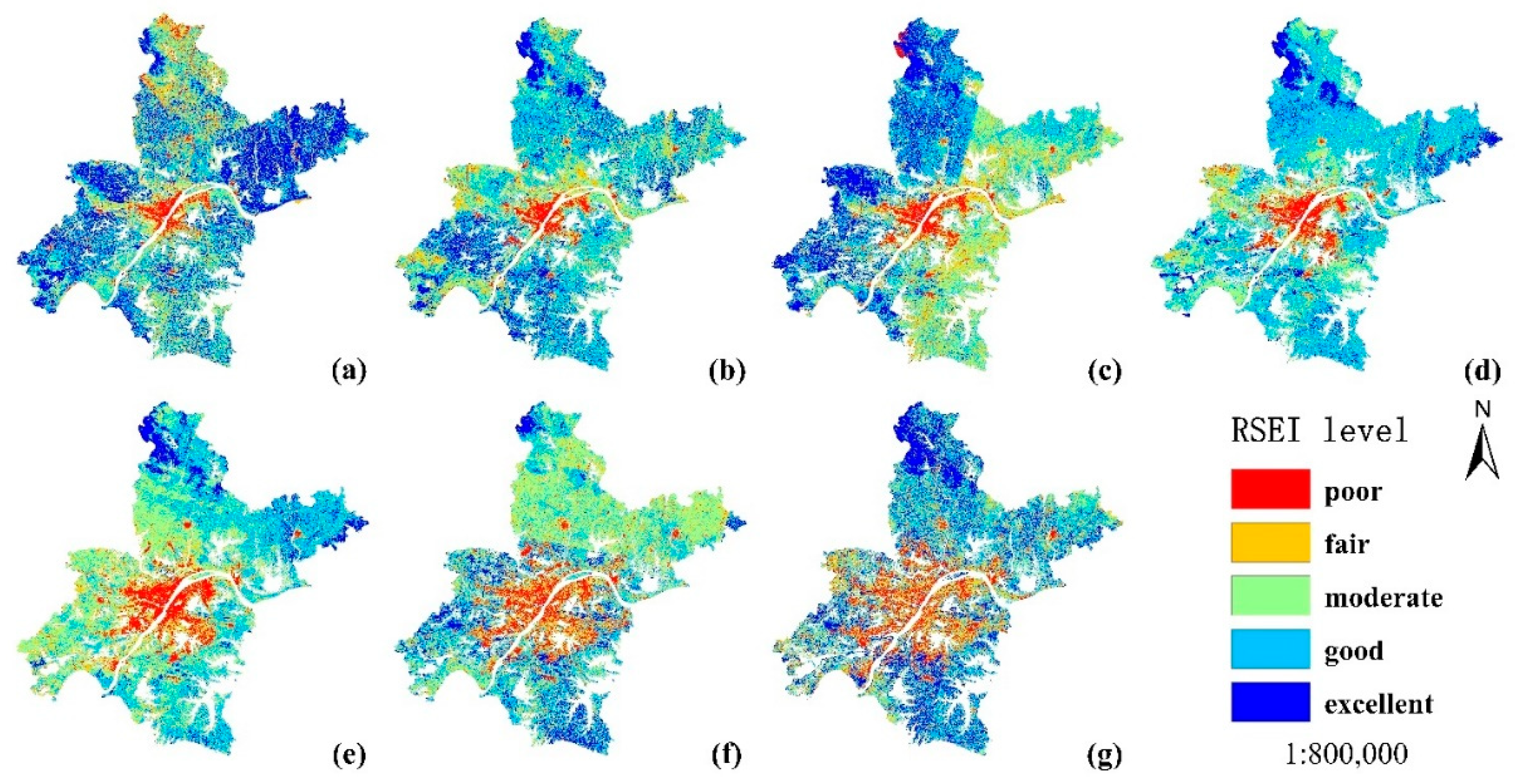
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of RSEI in Wuhan
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.2.2. Spatial Aggregation
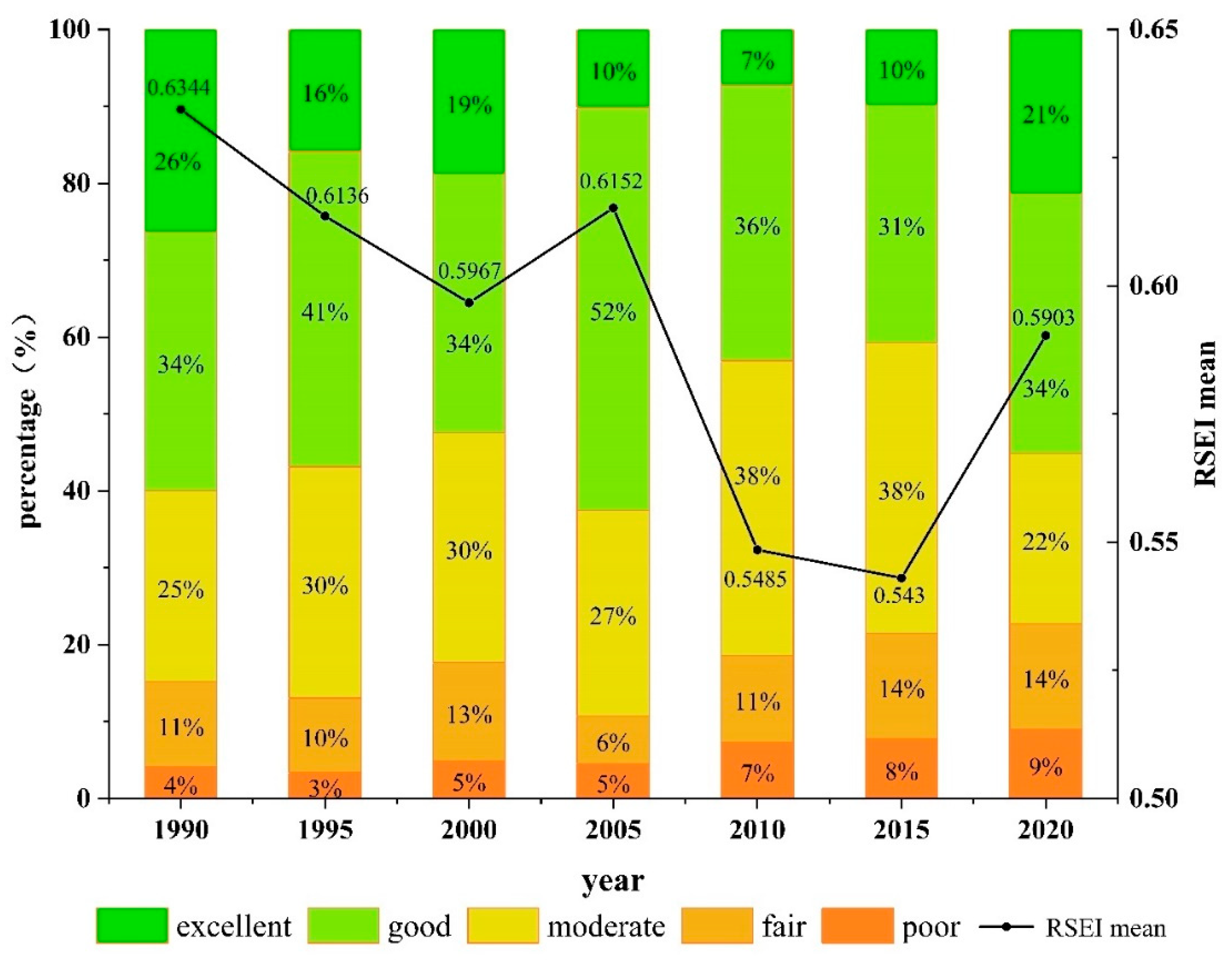
3.2.3. Characteristics of Quantitative Changes
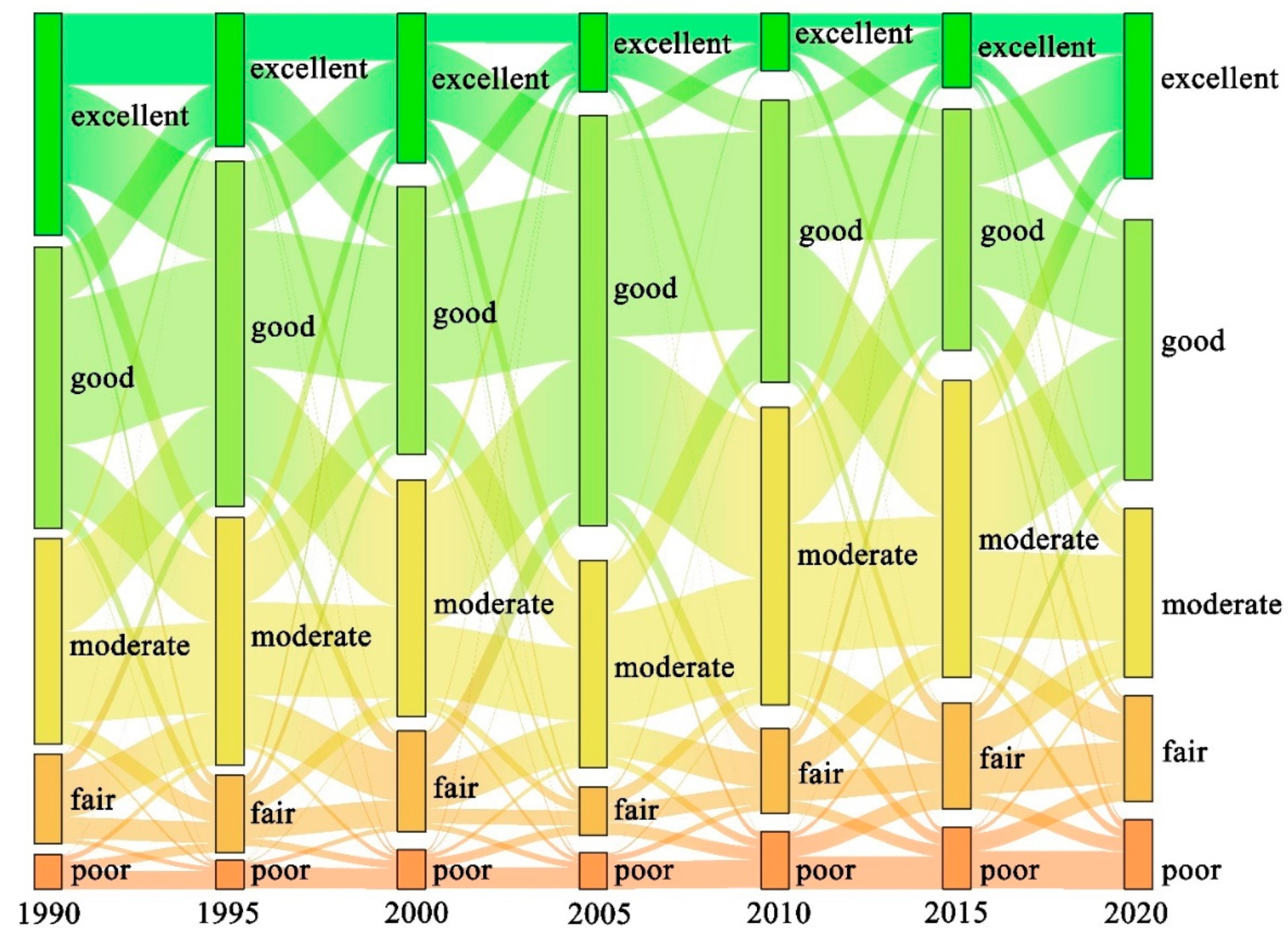
3.2.4. Characteristics of RSEI Area Transfer by Class
3.3. Influencing Factor Analysis by Geodetectors
3.4. Influencing Factor Analysis by PLS-SEM
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Ecological Environment Quality
4.2. Single-Factor Impact and the Interactive Effects of Dual Factors
4.3. Latent Variables Influence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.P.; Ren, J.; Wang, L. Review on monitoring method of ecological conservation and restoration project area based on multi-source remote sensing data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8789–8797. [Google Scholar]
- Avdan, Z.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Goncu, S.; Avdan, U. Monitoring the Water Quality of Small Water Bodies Using High- Resolution Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, C.J.; Durand, M.T. Remote Sensing of River Discharge: A Review and a Framing for the Discipline. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Kumar, P.; Pathan, S.K.; Sharma, K.P. Urban Neighborhood Green Index-A measure of green spaces in urban areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vits, E.; Cherlet, M.; Mehl, W.; Sommer, S. Estimating the ecological status and change of riparian zones in Andalusia assessed by multi-temporal AVHHR datasets. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Watts, J.M.; McElroy, S. Estimating soil moisture at the watershed scale with satellite-based radar and land surface models. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Xu, H.Q. Temporal and spatial changes of urban impervious surface and its influence on urban ecological quality: A comparison between Shanghai and New York. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, W. Study on the Relationship between the Impervious Surface Expansion and the Change of Ecological Environment Quality in Chengdu. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, M.M. The correlation analysis of land surface temperature and fractional vegetation coverage in Fujian Province. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Zhang, P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect across biomes in the continental, U.S.A. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Yu, K.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ai, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variation and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Fuzhou Based on RSEI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Feng, R.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K. Exploring the Driving Factors of Remote Sensing Ecological Index Changes from the Perspective of Geospatial Differentiation: A Case Study of the Weihe River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Halike, A.; Chen, L.; Wei, Q. Spatiotemporal changes of eco-environmental quality based on remote sensing-based ecological index in the Hotan Oasis, Xinjiang. J. Arid Land 2022, 14, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Tan, M. Using a geographical detector to identify the key factors that influence urban forest spatial differences within China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 49, 126623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.W.; Cao, W.D.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.F.; Wang, X.W. Temporal and Spatial Coupling Characteristics of Urbanization and Ecological Environment of Three Major Urban Agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 2586–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.L.; Sha, J.M.; Fan, Y.X.; Shuai, C.; Gao, S. Temporal and Spatial variations of impervious surface landscape pattern and the driving factors in Xiamen City, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Guo, J.X.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, H.; Han, Y. Spatial variations of ecological environment quality and its influencing factors in Poyang Lake area, Jiangxi, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C. The geography of parameter space: An investigation into spatial non-stationarity. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted Regression: A method for Exploring Spatial Non-stationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.M.; Feng, X.H.; Sun, R.F.; Gao, H. Spatial and temporal responses of habitat quality to urbanization: A case study of Chang-chun City, Jilin Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liu, C.W.; He, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.; Han, B.H.; Hao, H.Z. Spatial-temporal evolution of ecological land and influence factors in Wuhan urban agglomeration based on geographically weighted regression model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 987–998. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.F.; Rao, L.; Sun, K.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Cultivated land landscape ecological security: Influencing factors and spatial differences in the hilly region of South China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 6522–6533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, Z.M.; Guo, Q.; Wu, G.; Chen, R.; Li, S. Contributions of Climatic Factors to Interannual Variability of the Vegetation Index in Northern China Grasslands. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.R.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zuo, L.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Driving forces and their interactions of built-up land expansion based on the geographical detector—A case study of Beijing, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 2188–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Shrestha, S.; Xue, B.; Tan, Z. Vertical variations of soil water and its controlling factors based on the structural equation model in a semi-arid grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortizas, A.M.; Horák-Terra, I.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.; Bindler, R.; Cooke, C.A.; Kylander, M. Structural equation modeling of long-term controls on mercury and bromine accumulation in Pinheiro mire (Minas Gerais, Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, D.; Justin, P. CB-SEM vs PLS-SEM methods for research in social sciences and technology forecasting. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 173, 121092. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Fu, M.; Breuste, J. Dominant landscape indicators and their dominant areas influencing urban thermal environment based on structural equation model. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simandan, D. The wise stance in human geography. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2011, 36, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA JPL. NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 arc second V001 [Data set]. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. 2020. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/nasadem_hgtv001/ (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 233, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.Z.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of climate change trends over the loess plateau in china from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Z.; Ding, Y.X.; Wen, Z.M.; Chen, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.Y. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.X.; Peng, S.Z. Spatiotemporal trends and attribution of drought across China from 1901–2100. Sustainability 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Z.; Ding, Y.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2022); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2022); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Climate 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Xing, Q.; Du, W.; Cai, G. A dataset of built-up area of Chinese cities in 2020. China Sci. Data 2022, 7, 190–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, J. Remote sensing of urban heat islands by day and night. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Skoković, D.; Mattar, C.; Cristóbal, J. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Methods From Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor Data. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. IEEE 2014, 11, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikimaru, A.; Roy, P.S.; Miyatake, S. Tropical forest cover density mapping. Trop. Ecol. 2002, 43, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Howard, M.C.; Nitzl, C. Assessing measurement model quality in PLS-SEM using confirmatory composite analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 109, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Ran, D.; Yang, B. Spatial heterogeneity and formation mechanism of eco-environmental effect of land use change in China. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Hair, J.F.; Cheah, J.-H.; Becker, J.-M.; Ringle, M.C. How to specify, estimate, and validate higher-order constructs in PLS-SEM. Australas. Mark. J. AMJ 2019, 27, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, G. Organisation in the school dental service. Br. Dent. J. 1971, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, C. Urban Ecological Quality Assessment Based on Google Earth Engine and Driving Factors Analysis: A Case Study of Wuhan City, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhan, Q.; Zhan, D.; Zhao, H.; Yang, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Lakes under Rapid Urbanization: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Water 2021, 13, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Type | Data Format | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–2010 remote sensing images | .tif | 30 m | LANDSAT/LT05/C01/T1_SR http://www.usgs.gov (accessed on 2 March 2023) |
| 2015–2020 remote sensing images | .tif | 30 m | LANDSAT/LC08/C01/T1_SR http://www.usgs.gov (accessed on 2 March 2023) |
| 1990–2020 Wuhan water surface area | .tif | 30 m | JRC/GSW1_3/YearlyHistory [40] (accessed on 2 March 2023) |
| DEM | .tif | 30 m | NASA/NASADEM_HGT/001 [32] http://www.earthdata.nasa.gov (accessed on 2 March 2023) |
| 1990–2020 Wuhan landuse | .tif | 30 m | Annual China Land Cover Dataset, CLCD [33] |
| 1990–2020 Wuhan annual average precipitation | .tif | 1000 m | TPDC/CHINA_1KM_PRE_MONTH http://data.tpdc.ac.cn (accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| 1990–2020 Wuhan annual average temperature | .tif | 1000 m | TPDC/CHINA_1KM_AVG_TEM_MONTH http://data.tpdc.ac.cn (accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| Population density | .tif | 30 m | Wuhan Statistical Yearbook https://tjj.wuhan.gov.cn/ (accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| GDP | .tif | 30 m | Wuhan Statistical Yearbook https://tjj.wuhan.gov.cn/ (accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| Location | .shp | - | China’s 2020 built-up area dataset [41] (accessed on 20 March 2023) |
| Year | Indicator | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | NDVI | 0.7283 | 0.6547 | 0.0118 | 0.2015 |
| WET | 0.1615 | −0.4213 | −0.3800 | 0.8074 | |
| NDBSI | −0.5205 | 0.3992 | 0.5127 | 0.5538 | |
| LST | −0.4152 | 0.4841 | −0.7697 | −0.0265 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0244 | 0.0099 | 0.0031 | 0.0002 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 64.91% | 26.35% | 8.13% | 0.61% | |
| 1995 | NDVI | 0.8798 | 0.4409 | 0.0962 | 0.1491 |
| WET | 0.0309 | −0.3311 | −0.1949 | 0.9227 | |
| NDBSI | −0.4606 | 0.7141 | 0.3903 | 0.3542 | |
| LST | −0.1130 | 0.4311 | −0.8946 | −0.0304 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0242 | 0.0097 | 0.0049 | 0.0001 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 62.04% | 25.00% | 12.55% | 0.42% | |
| 2000 | NDVI | 0.7635 | 0.6122 | −0.0139 | 0.2051 |
| WET | 0.1797 | −0.5033 | −0.2074 | 0.8193 | |
| NDBSI | −0.5675 | 0.5358 | 0.3226 | 0.5353 | |
| LST | −0.2502 | 0.2911 | −0.9233 | −0.0001 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0242 | 0.0054 | 0.0018 | 0.0001 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 76.43% | 17.17% | 5.92% | 0.47% | |
| 2005 | NDVI | 0.8063 | −0.5736 | 0.1064 | −0.3762 |
| WET | 0.0532 | 0.1662 | −0.3473 | −0.0112 | |
| NDBSI | −0.3237 | −0.2363 | 0.8353 | −0.9213 | |
| LST | −0.4921 | −0.7664 | −0.4126 | −0.0971 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0154 | 0.0032 | 0.0013 | 0.00003 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 77.03% | 16.04% | 6.74% | 0.19% | |
| 2010 | NDVI | 0.8624 | −0.4077 | 0.2904 | −0.0748 |
| WET | 0.0132 | −0.0092 | −0.2983 | −0.9543 | |
| NDBSI | −0.2142 | 0.2417 | 0.9017 | −0.2871 | |
| LST | −0.4593 | −0.8804 | 0.1162 | −0.0341 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0122 | 0.0046 | 0.0021 | 0.00003 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 64.29% | 24.50% | 11.04% | 0.17% | |
| 2015 | NDVI | 0.8378 | −0.4504 | 0.2783 | −0.1331 |
| WET | 0.0886 | 0.2680 | −0.2727 | −0.9197 | |
| NDBSI | −0.5147 | −0.4672 | 0.6170 | −0.3687 | |
| LST | −0.1588 | −0.7119 | −0.6837 | −0.0201 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0228 | 0.0042 | 0.0023 | 0.00009 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 77.15% | 14.50% | 8.02% | 0.33% | |
| 2020 | NDVI | 0.8024 | −0.4324 | 0.3563 | −0.2053 |
| WET | 0.1519 | 0.2916 | −0.4626 | −0.8232 | |
| NDBSI | −0.5386 | −0.2482 | 0.6072 | −0.5286 | |
| LST | −0.206 | −0.8162 | −0.5387 | −0.0246 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0421 | 0.0039 | 0.0028 | 0.0002 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 85.78% | 8.06% | 5.70% | 0.46% |
| Scale (m) | Moran’s I | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |
| 1000 | 0.341 | 0.376 | 0.513 | 0.54 | 0.573 | 0.33 | 0.331 |
| 2000 | 0.267 | 0.276 | 0.452 | 0.441 | 0.495 | 0.281 | 0.267 |
| 3000 | 0.253 | 0.259 | 0.472 | 0.385 | 0.476 | 0.263 | 0.218 |
| 4000 | 0.225 | 0.292 | 0.393 | 0.444 | 0.46 | 0.157 | 0.148 |
| 5000 | 0.118 | 0.177 | 0.302 | 0.378 | 0.388 | 0.208 | 0.233 |
| Year | Annual Average Precipitation | Annual Average Temperature | Elevation | Slope | Landuse | GDP | Population Density | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
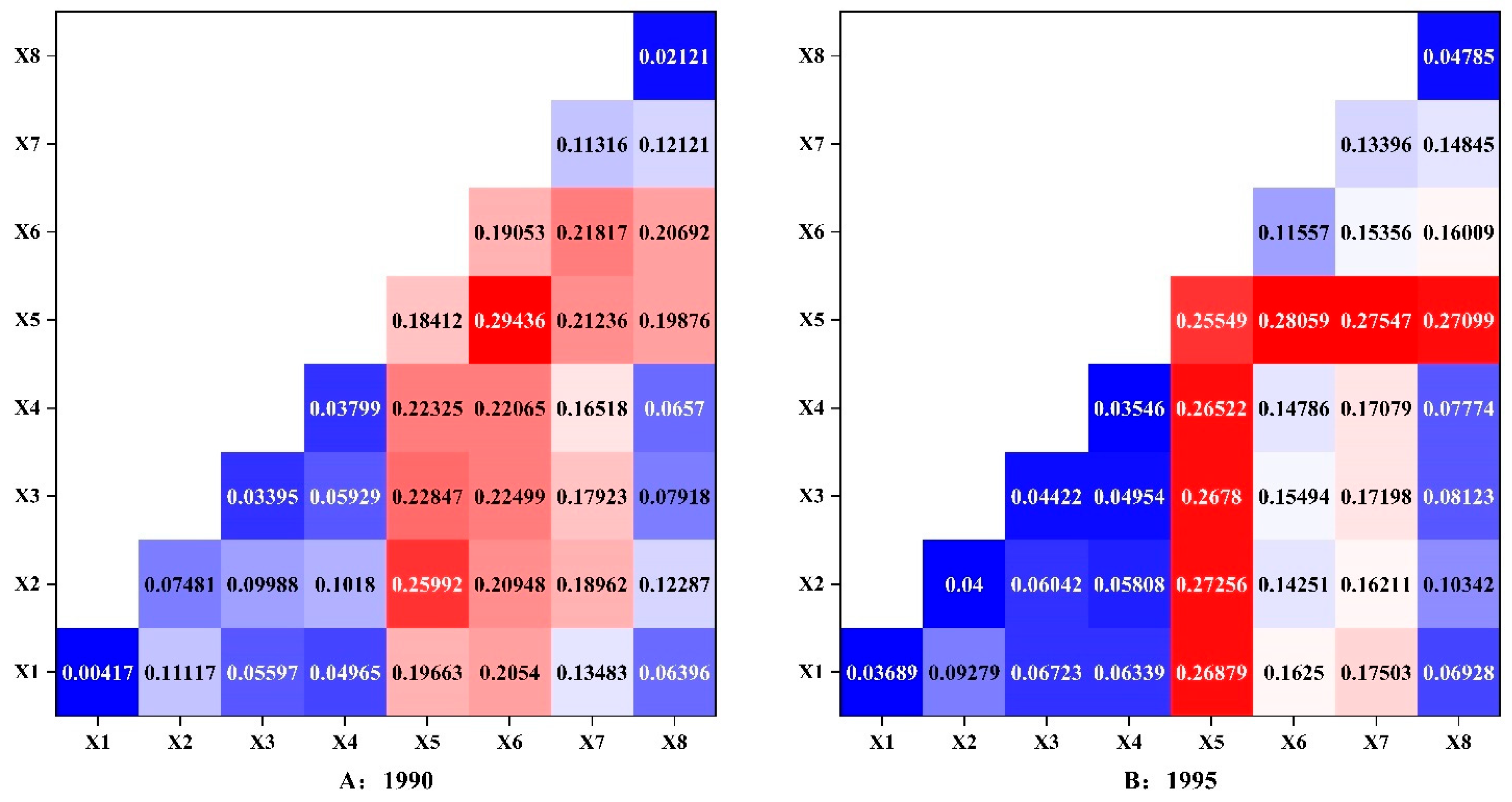
| 1990 | 0.0042 | 0.0748 | 0.034 | 0.038 | 0.1841 | 0.1905 | 0.1132 | 0.0212 |
| 1995 | 0.037 | 0.04 | 0.0442 | 0.0355 | 0.2555 | 0.1156 | 0.1339 | 0.0479 |
| 2000 | 0.0319 | 0.1382 | 0.0266 | 0.0235 | 0.2355 | 0.1078 | 0.1529 | 0.0781 |
| 2005 | 0.1166 | 0.0869 | 0.1092 | 0.0804 | 0.4131 | 0.176 | 0.2092 | 0.16 |
| 2010 | 0.1523 | 0.1987 | 0.1445 | 0.0929 | 0.457 | 0.1933 | 0.2241 | 0.2759 |
| 2015 | 0.0545 | 0.0126 | 0.0298 | 0.0318 | 0.3326 | 0.089 | 0.0893 | 0.0559 |
| 2020 | 0.0973 | 0.0592 | 0.077 | 0.0626 | 0.3174 | 0.0631 | 0.0848 | 0.1256 |
| Mean | 0.0705 | 0.0872 | 0.0665 | 0.0521 | 0.3136 | 0.1336 | 0.1439 | 0.1092 |
| VIF | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual average precipitation | 2.576 | 2.705 | 3.031 | - | 1.000 | 2.050 |
| Annual average temperature | 2.576 | 2.705 | 3.031 | - | - | 2.050 |
| Elevation | - | 2.075 | 2.048 | 2.052 | 2.034 | 2.049 |
| Slope | - | 2.075 | 2.048 | 2.052 | 2.034 | 2.049 |
| Landuse | 1.144 | 1.163 | 1.184 | 1.229 | 1.276 | 1.192 |
| GDP | 1.000 | - | 1.759 | 1.385 | 1.196 | 1.109 |
| Population density | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.759 | 1.385 | 1.196 | 1.109 |
| Location | 1.144 | 1.000 | 1.184 | 1.229 | 1.276 | 1.192 |
| Year | Path | Path Coefficient | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
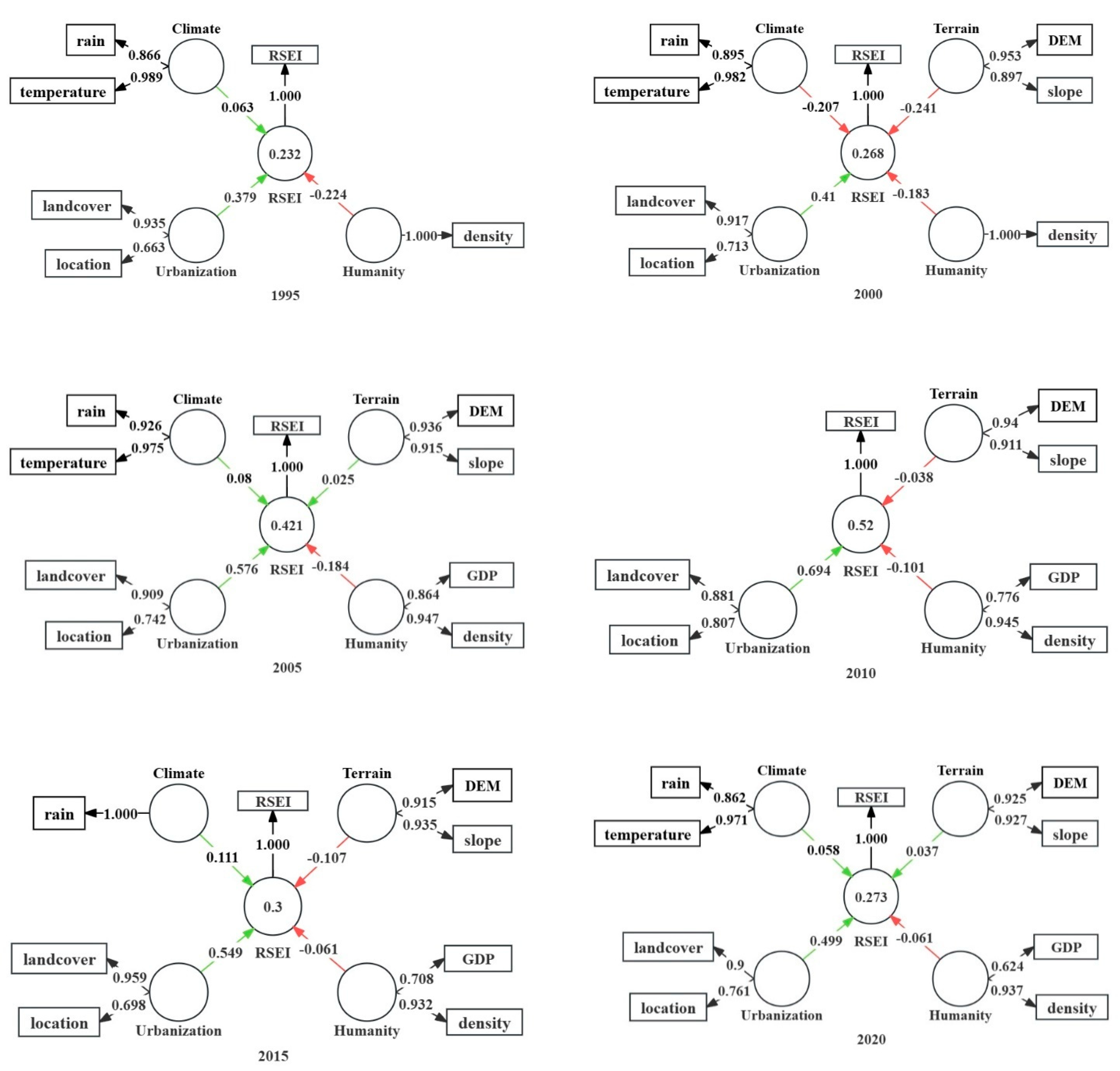
| 1995 | Climate → RSEI | 0.068 | 0.000 |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.227 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.37 | 0.000 | |
| 2000 | Climate → RSEI | −0.207 | 0.000 |
| Terrain → RSEI | −0.241 | 0.000 | |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.183 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.41 | 0.000 | |
| 2005 | Climate → RSEI | 0.08 | 0.000 |
| Terrain → RSEI | 0.025 | 0.028 | |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.184 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.576 | 0.000 | |
| 2010 | Terrain → RSEI | −0.038 | 0.000 |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.101 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.694 | 0.000 | |
| 2015 | Climate → RSEI | 0.111 | 0.000 |
| Terrain → RSEI | −0.107 | 0.000 | |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.061 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.549 | 0.000 | |
| 2020 | Climate → RSEI | 0.058 | 0.000 |
| Terrain → RSEI | 0.037 | 0.000 | |
| Humanity → RSEI | −0.061 | 0.000 | |
| Urbanization → RSEI | 0.499 | 0.000 |
| Year | Variables | CR Value | AVE Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | Climate | 0.926 | 0.864 |
| Urbanization | 0.788 | 0.657 | |
| 2000 | Climate | 0.938 | 0.883 |
| Terrain | 0.922 | 0.856 | |
| Urbanization | 0.803 | 0.675 | |
| 2005 | Climate | 0.949 | 0.904 |
| Terrain | 0.923 | 0.857 | |
| Urbanization | 0.814 | 0.688 | |
| Humanity | 0.902 | 0.822 | |
| 2010 | Terrain | 0.923 | 0.857 |
| Urbanization | 0.833 | 0.714 | |
| Humanity | 0.854 | 0.748 | |
| 2015 | Terrain | 0.922 | 0.856 |
| Urbanization | 0.822 | 0.703 | |
| Humanity | 0.81 | 0.685 | |
| 2020 | Climate | 0.915 | 0.843 |
| Terrain | 0.923 | 0.858 | |
| Urbanization | 0.818 | 0.694 | |
| Humanity | 0.769 | 0.634 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, X.; Du, X.; Duan, C.; Peng, L. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Wuhan City Based on RSEI. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135809
Gan X, Du X, Duan C, Peng L. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Wuhan City Based on RSEI. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135809
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Xintian, Xiaochu Du, Chengjun Duan, and Linhan Peng. 2024. "Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Wuhan City Based on RSEI" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135809
APA StyleGan, X., Du, X., Duan, C., & Peng, L. (2024). Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Wuhan City Based on RSEI. Sustainability, 16(13), 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135809





