Impact of China’s Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
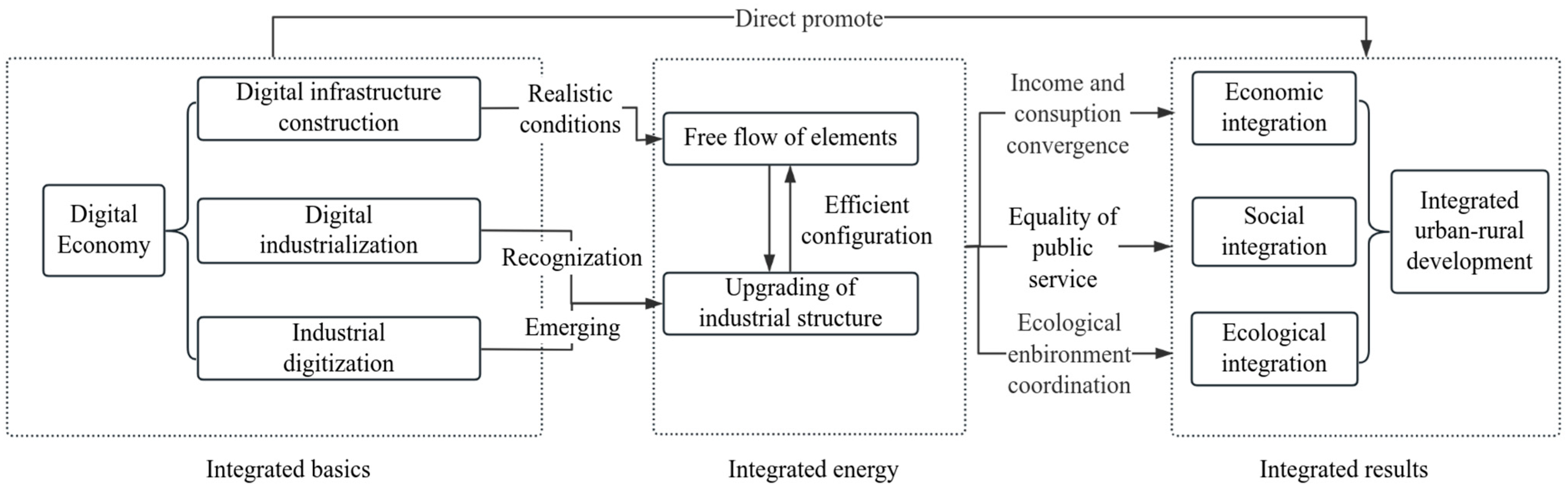
2.1. Mechanism of the Impact of Digital Economy on Urban–Rural Integration
2.2. Nonlinear Effect Analysis
3. Research Design
3.1. Methods
3.1.1. Two-Way Fixed Effects Model
3.1.2. Nonlinear Model
3.2. Variables
| Objective | Dimensions | Indicators | Calculation or Description | Indicator Type | Indicator Properties | Indicator Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Urban–Rural Development | Economic Integration | Income ratio | Per capita disposable income between urban and rural areas | Contrast | Negative | 0.076 |
| Consumption ratio | Rural–urban Engel coefficient difference | Contrast | Negative | 0.068 | ||
| Social Integration | Education | Teacher:student ratio in urban and rural compulsory education | Contrast | Negative | 0.047 | |
| Medical care | Ratio of medical and health institution beds per thousand people in urban and rural areas | Contrast | Negative | 0.042 | ||
| Employment | Ratio of unemployment insurance population to population aged 15 and above | Comprehensive | Positive | 0.448 | ||
| Transport | Highway mileage | Comprehensive | Positive | 0.218 | ||
| Ecological Integration | Energy conservation and emission reduction | Urban/rural domestic waste treatment rate | Contrast | Negative | 0.004 | |
| Environmental greening | Green coverage rate of urban built-up areas/green coverage rate of rural areas | Contrast | Negative | 0.056 | ||
| Industrial pollution | Sulfur dioxide emissions | Comprehensive | Negative | 0.042 |
| First-Level Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Unit | Indicator Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital infrastructure construction | Length of optical cable line | Kilometer | 0.075 |
| Mobile phone penetration rate | Department/100 people | 0.034 | |
| Internet access ports | Ten thousand | 0.071 | |
| Digital industrialization | Enterprises in the information transmission, software, and information technology industries | Piece | 0.142 |
| Employees in information transmission, software, and information technology industries | Ten thousand people | 0.164 | |
| Software business revenue | Ten thousand Yuan | 0.239 | |
| Industrial digitization | Computers used per 100 employees in the enterprise | Desk | 0.054 |
| Websites owned by every 100 enterprises | Piece | 0.014 | |
| Proportion of enterprises with e-commerce transaction activities | % | 0.034 | |
| Electronic sales | 100 million yuan | 0.174 |
3.3. Data Source
4. Empirical Test
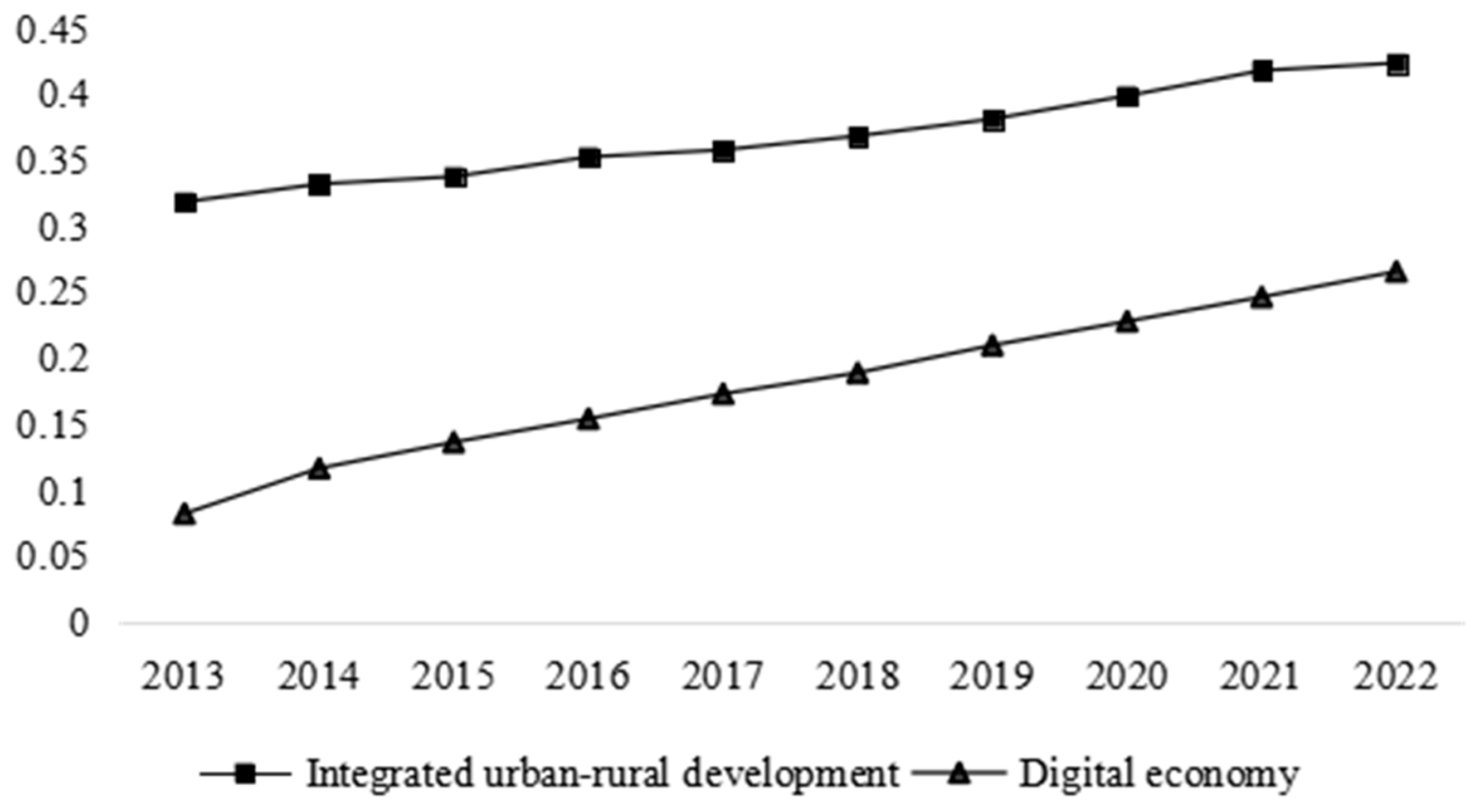
4.1. Impact of the Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development and Its Decomposition
4.2. Robustness Checks
4.2.1. Instrumental Variable Method
4.2.2. Independent Variable Replacement Method
4.2.3. Exclusion of Municipal Samples
4.3. Nonlinear Regression of the Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development
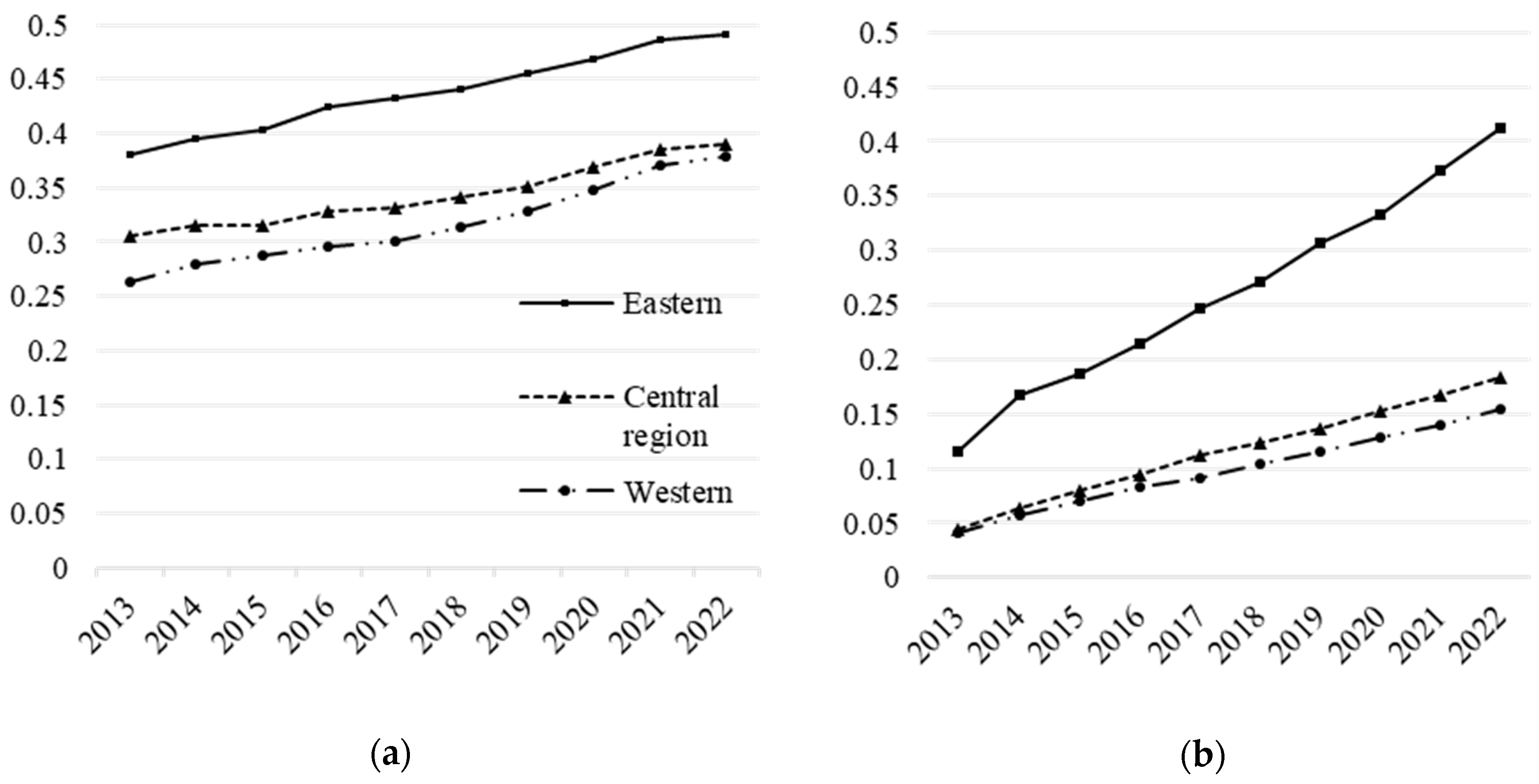
4.4. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
5. Conclusions, Implications, and Future Research
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Implications
5.3. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, A. An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations; The Commercial Press: Shanghai, China, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.F. Progress in Overseas Chinese Urban Geography Research. World Reg. Stud. 2007, 4, 28–35+114. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Sun, F. Research on the Impact of the Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration Development—Empirical Test Based on the Mediation Effect Model. J. Jianghan Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 40, 58–70+127. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Cheng, Y.X. Empowering Urban-Rural Integration through Labor Mobility: Theoretical Mechanism and Empirical Test—Based on a Questionnaire Survey of 1,002 Households in 6 Counties of Anhui Province. J. Chongqing Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci.) 2024, 1–18. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=VKFFl0Cm57adi6RyMdeJxIz0EQYM0Kumq0v1iIqYWU2WuX2H7gOStboeqUx47zA6GOShAksX2aS9qmFXl0D2rr5gfLazWXCC9A1uEscQs4bMbj_Fn3d8zxgFeh2NrOftVoTgk0V5U-k=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W. Spatial imbalance and evolutionary trends of urban-rural integration in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Soochow Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 44, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Yu, Y. Urban-rural industrial integration and the enhancement of farmers’ subjectivity. Issues Agric. Econ. 2024, 5, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.A. Analysis of the path to high-quality development of urban-rural integration in the process of Chinese-style modernization. J. Hainan Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 41, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Su, W. Study on the spatio-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of urban-rural integration in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Reg. Res. Dev. 2024, 43, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Lei, H.; Li, M. Research on the transmission mechanism and spatial effects of digital economy impacting urban-rural economic integration. J. Yunnan Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 1–13. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=VKFFl0Cm57bL9X8iKLJoHCHsL3hwwkqaollp_dL3fjN8DmvMS8iyj6WzSp5RQ98cjSjs8NBKMobO6SFbgOFQTmi8M97-9wgAlEHIek75NP125W2nHJZj3KhYnnV6TZW2PlSZvWF0j2I=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Zhao, M.; Ma, H. How do county markets promote urban-rural cultural integration?—A case study of Yangxinji in the Yellow River Delta region. Qinghai-Tibet. Plateau Forum 2024, 12, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.D.; Zhou, C. The Coordination Degree and Spatial Correlation of Rural Revitalization and Urban-Rural Integration Development. J. Agrotech. Econ. Manag. 2024, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, D.; Terrero-Dávila, J.; Stein, J.; Lee, N.C. Progressive cities: Urban-rural polarisation of social values and economic development around the world. Urban Stud. 2023, 60, 2329–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez Roldan, C.; Méndez Giraldo, G.A.; Lopez Santana, E.R. Sustainable Development in Rural Territories within the Last Decade: A Review of the State of the Art. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutu Sakketa, T. Urbanisation and rural development in sub-Saharan Africa: A review of pathways and impacts. Res. Glob. 2023, 6, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, J.H.; Hunter, L.M.; Leyk, S.; Connor, D.S.; Nieves, J.J.; Hester, C.M.; Talbot, C.B.; Gutmann, M.P. Place-level urban-rural indices for the United States from 1930 to 2018. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 236, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, Z.; Lucas, J.; Armstrong, D.A.; Bakker, R. The Development of the Urban-Rural Cleavage in Anglo-American Democracies. Comp. Political Stud. 2024, 57, 1339–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, Y.; Kohsaka, R. Strategies of Destination Management Organizations in Urban and Rural Areas: Using Text Analysis Method for SWOT Descriptions at Meta-level. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Adm. 2021, 24, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HM Treasury. Build Back Better: Our Plan for Growth; HM Treasury: London, UK, 2021.
- Arrow, K.Y. The Economic Implications of Learning by Doing. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1962, 29, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.C.; Zhang, M.H. Research on the Measurement of China’s Digital Economy Scale—From an International Comparative Perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2020, 5, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Song, L.J. Theoretical System and Research Prospect of the Digital Economy. Manag. World 2022, 38, 208–224+13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L. Measurement, Causes, and Economic Effects of Multidimensional Urban-Rural Disparities; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Long, H.L. Measurement and Evaluation of China’s Urban-Rural Integration Development and Its Spatiotemporal Pattern. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Gao, Y.L. The Industrial Linkage Effects of Provincial Digital Economy Development in China. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2022, 39, 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.Y.; Yu, Y.J.; Zhao, Q.Q. The Mechanism and Spatial Effects of the Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration Development—Empirical Analysis Based on the Spatial Durbin Model. World Reg. Stud. 2024, 1–17. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=VKFFl0Cm57Zr-60eWZca_mqtEvl8BVqiQyGy8Wrr42rGD1wbQzCdifEqPlkRZLnuaUXCpLg00YPf4RL938eCrLYMROXoFRM5jRqQnzq8HO_Ad4ADwTcXjMgGGg5LWL2HwFIpl249uH4=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Huang, Y.C.; Gong, S.J.; Zou, C. Digital Economy, Factor Allocation Efficiency, and Urban-Rural Integration Development. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.M.; Wang, X. Does the Digital Economy Promote China’s Urban-Rural Integration—Testing Based on the Mediation Effect Model and Spatial Durbin Model. Technol. Econ. 2022, 41, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y. Digital economy development and the urban-rural income gap: Evidence from Chinese cities. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florido-Benítez, L. Tourism promotion budgets and tourism demand: The Andalusian case. Consum. Behav. Tour. Hosp. 2024, 19, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.P.; Xu, K.N. The Impact of the Internet on Urban-Rural Income Gap: Evidence from China. Econ. Vis. 2019, 36, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. Labor Market Turn, New Technology Revolution, and Urban-Rural Integration Development. People’s Trib. Acad. Front. 2021, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y. Does digital economy promote urban-rural integration development: Immediate or long-term impact? Rural. Econ. 2024, 3, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, L. Characteristics and mechanisms of digital economy influencing income disparity between urban and rural residents. Chin. J. Soft Sci. 2022, 6, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Pan, T.; Shi, P. The impact of digital economy on income disparity between urban and rural residents and its mechanisms. Reform 2023, 4, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.X.; Lei, N.; Liu, X.Q. Can the Digital Economy Promote Urban-Rural Integration Development?—Empirical Evidence from 268 Cities in China. South China Financ. 2023, 12, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.H.; Xiao, Y.Y. Mechanism and Empirical Test of Digital Economy Promoting Urban-Rural Integration Development. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.Z.; Teng, Z.M. Research on the Influencing Factors of Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration Development. J. Party Sch. Fujian Prov. Comm. CPC (Fujian Adm. Inst.) 2022, 3, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.B.; Dai, Y.J. Digital Economy and Urban-Rural Integration Development: Theoretical Mechanism and Empirical Test. Resour. Environ. Arid. Areas 2024, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.T.; Luo, P.L. Does the Internet Promote China’s Total Factor Productivity? Manag. World 2016, 10, 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Q. Measurement of China’s Digital Economy Development Level and Evolution. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2021, 38, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.G. Risks and Countermeasures of Urban-Rural Integration Development in the Context of New Technology. People’s Trib. Acad. Front. 2021, 2, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.W.; Zhang, J.P. Internet Penetration and Urban-Rural Income Gap: Theory and Evidence. China Rural. Econ. 2019, 2, 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.G.; Ma, S.X. Research on the Spatial Spillover and Threshold Effects of the Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration Development—Taking Zhejiang Province as an Example. Investig. Res. 2022, 8, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Han, W.L. The Theoretical Logic and Realization Path of Digital Technology and Digital Economy Promoting Urban-Rural Integration Development. Issues Agric. Econ. 2022, 11, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.P. Digital Economy and Regional Economic Growth: Late-Mover Advantage or Late-Mover Disadvantage? J. Shanghai Univ. Financ. Econ. 2021, 23, 19–31+94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, J.J. The Impact of Digital Finance on Household Consumption: Evidence from China. Econ. Model. 2020, 86, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, B.Z. Impact of Digital Financial Inclusion on Consumption Inequality in China. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 163, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.J.; Zhou, J.P.; Chen, Y.T. Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Provincial Digital Economy and Its Urban-Rural Integration Effect in China. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chu, C.; Gu, Y.T. Research on the Impact of the Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration Development. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, G.H.; Zhang, J.J. Digital Economy, Inclusive Finance, and Inclusive Growth. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 54, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Y. Digital Economy and Urban-Rural Income Gap: “Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”. Bus. Res. 2022, 5, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, C. Industrial digital transformation under the strategic background of the “dual circulation” new development pattern: Theory and strategies. Financ. Trade Econ. 2021, 42, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold Effects in Non-Dynamic Panels: Estimation, Testing, and Inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Yin, Y.X.; Xu, X.G. Can the Digital Economy Promote Urban-Rural Integration: A Case Study of 11 Provinces in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Soft Sci. 2023, 5, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.P.; Yuan, F.Y.; Meng, H.W. Mechanism of Digital Infrastructure Empowering Urban-Rural Integration Development. Urban Probl. 2023, 12, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S. Mechanisms, practical challenges, and policy optimization of digital economy empowering urban-rural integration development. Econ. Obs. 2022, 12, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern and influencing factors of coupled and coordinated development between new urbanization and rural revitalization. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Economic Analysis. National Income and Product Accounts: Gross Domestic Product, 4th Quarter and Annual 2018 (Third Estimate). 2019. Available online: https://www.bea.gov/news/2019/initial-gross-domestic-product-4th-quarter-and-annual-2018 (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S. Research on measurement and driving factors of China’s digital economy. Shanghai Econ. Res. 2020, 6, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Sun, T. Transportation Infrastructure, Labor Allocation, and Urban-Rural Integration Development in China—From the Perspective of Labor and Industry, Regional Dual Coupling. J. Guangdong Univ. Financ. Econ. 2023, 38, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, J.T.; Mehlum, H. With or Without U? The Appropriate Test for a U-Shaped Relationship. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2010, 72, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shu, J. Study on the impact of digital economy on urban-rural integration from the perspective of factor mobility. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2023, 36, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhao, Q. Development of digital economy and common prosperity: Theoretical analysis and empirical evidence. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicators | Calculations | Numbers | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated urban–Rural development | Index calculated using the entropy weight method | 300 | 0.368 | 0.093 | 0.172 | 0.707 | 0.934 | 4.086 |
| Digital economy | Index calculated using the entropy weight method | 300 | 0.163 | 0.140 | 0.027 | 0.839 | 2.108 | 7.937 |
| Economic development | Gross regional product (10 trillion yuan) | 300 | 0.294 | 0.235 | 0.021 | 1.291 | 1.700 | 6.282 |
| Industrial structure | Value added by the tertiary industry/value added by the secondary industry | 300 | 1.338 | 0.736 | 0.314 | 5.297 | 3.011 | 13.708 |
| Inflation level | Consumer Price Index | 300 | 101.97 | 0.690 | 100.10 | 103.90 | 0.0125 | 3.044 |
| Government support | Expenditure on urban and rural community construction (100 million yuan) | 300 | 610.92 | 430.37 | 61.51 | 2413.84 | 1.293 | 4.776 |
| Infrastructure construction | Highway passenger volume (100 million people/100,000 km) | 300 | 0.419 | 0.358 | 0.007 | 1.572 | 1.035 | 3.348 |
| Degree of opening up | Total import and export volume (US $100 billion) | 300 | 1.546 | 2.410 | 0.003 | 12.796 | 2.456 | 9.067 |
| Variables | Integrated Urban–Rural Development | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Digital economy | 0.129 *** (0.042) | 0.115 *** (0.039) | - | - | - |
| Digital infrastructure construction | - | - | 0.482 * (0.258) | - | - |
| Digital industrialization | - | - | - | 0.155 *** (0.048) | - |
| Industrial digitization | - | - | - | - | 0.387 *** (0.111) |
| Economic development | 0.018 * | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.023 * | 0.021 |
| Industrial structure | 0.001 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.002 | −0.000 |
| Inflation level | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.002 | −0.002 | −0.002 |
| Government support | 0.004 | 0.012 ** | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.006 |
| Infrastructure construction | 0.019 ** | 0.028 *** | 0.025 ** | 0.017 * | 0.009 |
| Degree of opening up | −0.007 *** | 0.004 | −0.001 | −0.006 *** | 0.005 *** |
| Cons | 0.516 ** | 0.312 | 0.494 ** | 0.455 ** | 0.485 ** |
| Years fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Provinces fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Years | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Provinces | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| R2 | 0.8997 | 0.8872 | 0.8916 | 0.8962 | 0.8957 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Stage | Second-Stage | |||
| Instrumental variable | 0.006 *** (0.001) | - | - | |
| Digital economy | - | 0.223 *** (0.061) | 0.014 *** (0.003) | 0.101 *** (0.046) |
| Control variables | Control | Control | Control | Control |
| Cons | −1.343 *** | 0.856 *** | 0.552 ** | 0.533 ** |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | - | 15.91 (p-value = 0.0001) | - | - |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F statistic | - | 86.820 | - | - |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | - | 29.586 | - | - |
| Hansen J statistic | - | 0.000 | - | - |
| Years fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Provinces fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | - | 0.9834 | 0.8994 | 0.9154 |
| Components | Eigenvalue | Variance Contribution | Cumulative Variance Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.4088 | 0.5409 | 0.5409 |
| 2 | 2.0591 | 0.2059 | 0.7468 |
| 3 | 1.0398 | 0.1040 | 0.8508 |
| 4 | 0.5997 | 0.0600 | 0.9107 |
| 5 | 0.3303 | 0.0330 | 0.9438 |
| 6 | 0.1745 | 0.0175 | 0.9612 |
| 7 | 0.1379 | 0.0138 | 0.9750 |
| 8 | 0.1104 | 0.0110 | 0.9860 |
| 9 | 0.0832 | 0.0083 | 0.9944 |
| 10 | 0.0563 | 0.0056 | 1.0000 |
| KMO | 0.836 | ||
| Bartlett’s Test | 0.000 | ||
| Variables | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital economy | 0.332 *** (0.067) | - |
| The square term of the digital economy | −0.190 *** (0.064) | - |
| Digital economy < 0.3392 | - | 0.346 *** (0.089) |
| Digital economy ≥ 0.3392 | - | 0.250 *** (0.069) |
| Control variables | 0.661 *** | 0.714 *** |
| Cons | Control | Control |
| Years fixed | YES | YES |
| Provinces fixed | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.9053 | 0.7594 |
| Model | Fstat | p Value | BS Iterations | Threshold | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 5% | 1% | ||||
| Single threshold | 28.52 | 0.0167 | 300 | 22.058 | 24.000 | 30.795 |
| Double threshold | 21.78 | 0.1533 | 300 | 26.530 | 36.935 | 54.248 |
| Triple threshold | 16.93 | 0.5700 | 300 | 37.483 | 43.606 | 54.832 |
| Variables | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital economy | 0.109 ** (0.048) | 0.348 *** (0.094) | 0.211 (0.216) |
| Control variables | Control | Control | Control |
| Cons | 0.506 | 1.409 ** | 0.512 |
| R2 | 0.9111 | 0.9529 | 0.9347 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | |
| Dig1 | 0.235 (0.398) | 0.767 * (0.380) | 0.894 ** (0.356) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dig2 | - | - | - | 0.147 ** (0.063) | 0.154 (0.166) | −0.059 (0.192) | - | - | - |
| Dig3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.350 ** (0.146) | 0.829 *** (0.239) | −0.022 (0.488) |
| Control variables | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control |
| Cons | 0.401 | 1.564 ** | 0.619 ** | 0.437 | 1.397 * | 0.382 | 0.594 ** | 1.478 ** | 0.394 |
| Years fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Provinces fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.8961 | 0.9522 | 0.9418 | 0.9095 | 0.9480 | 0.9329 | 0.9096 | 0.9517 | 0.9329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, Z.; Liu, H. Impact of China’s Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145863
Huo Z, Liu H. Impact of China’s Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development. Sustainability. 2024; 16(14):5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145863
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Zhaoxin, and Huifang Liu. 2024. "Impact of China’s Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development" Sustainability 16, no. 14: 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145863
APA StyleHuo, Z., & Liu, H. (2024). Impact of China’s Digital Economy on Integrated Urban–Rural Development. Sustainability, 16(14), 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145863


_Li.png)



