Performance Evaluation of the Electro-Fenton Process for Distillery Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Analytical Procedure
2.2. Batch Reactor Setup
2.3. Batch Optimization Studies
2.4. COD Analysis
2.5. Specific Current Consumption
2.6. GC-MS Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
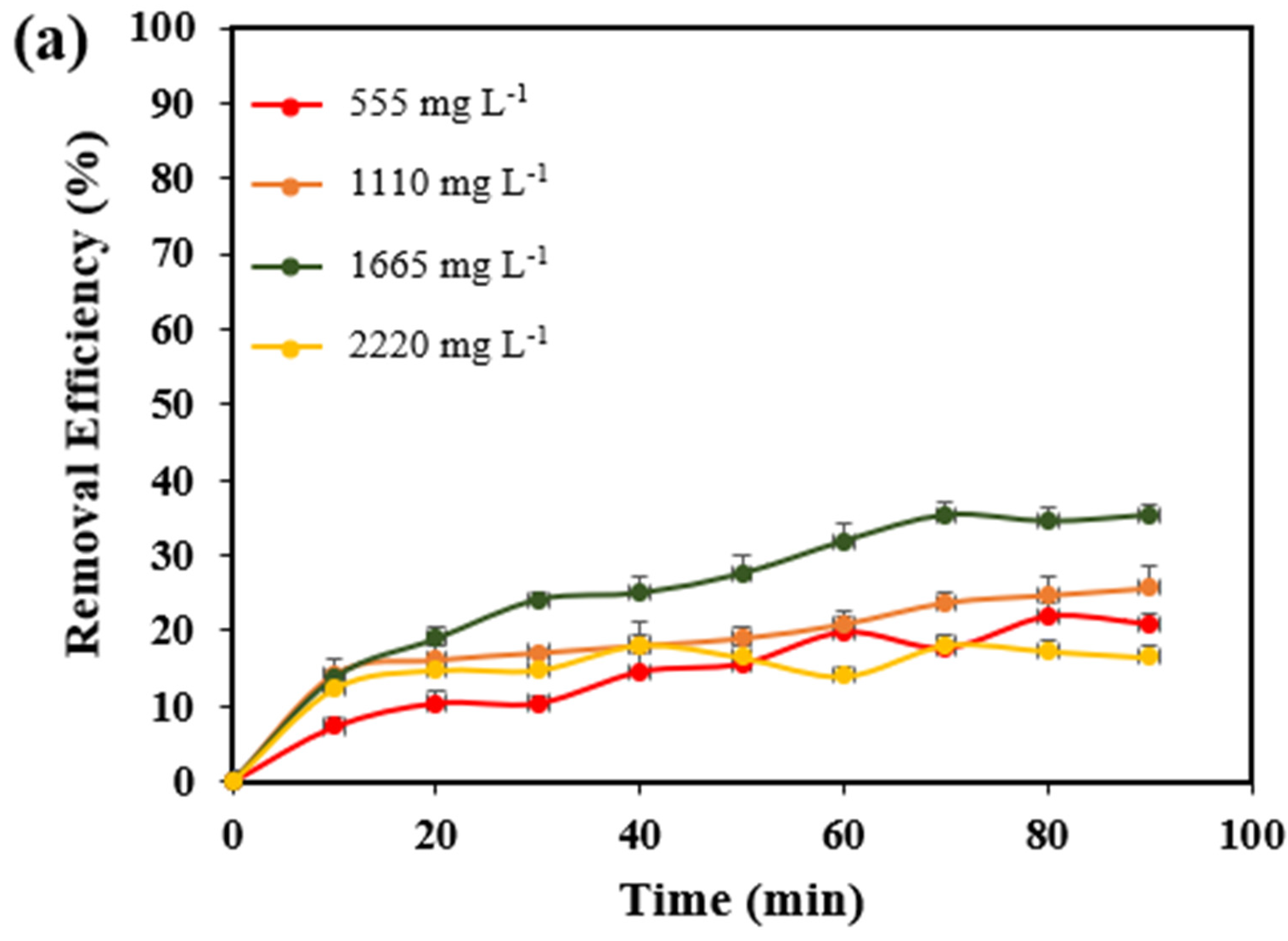
3.1. Optimization of H2O2 Dosage
3.2. Optimization of Spacing between the Electrodes
3.3. Optimization of Electrode Dipping Area
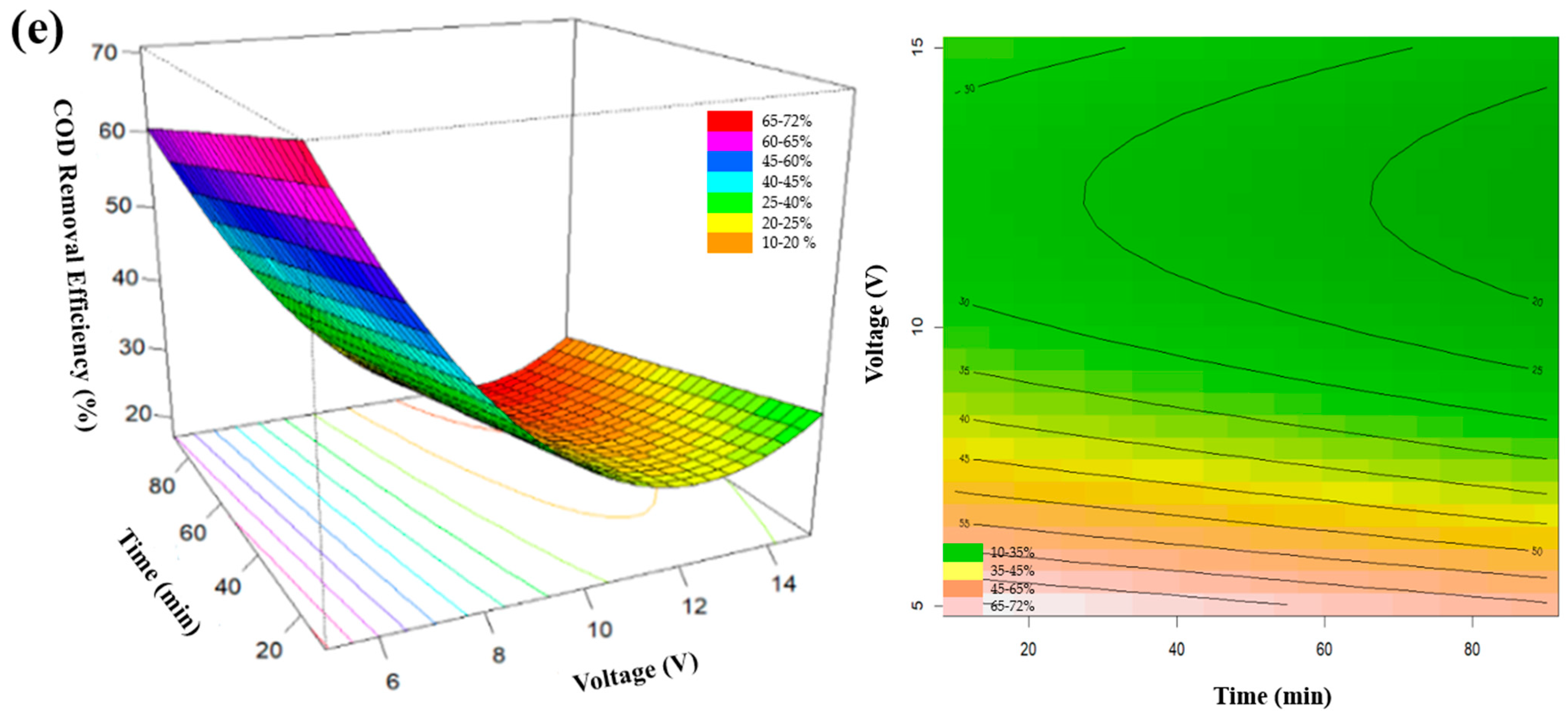
3.4. Optimization of Applied Voltage
3.5. Optimization of Initial pH
3.6. Determination of Kinetics
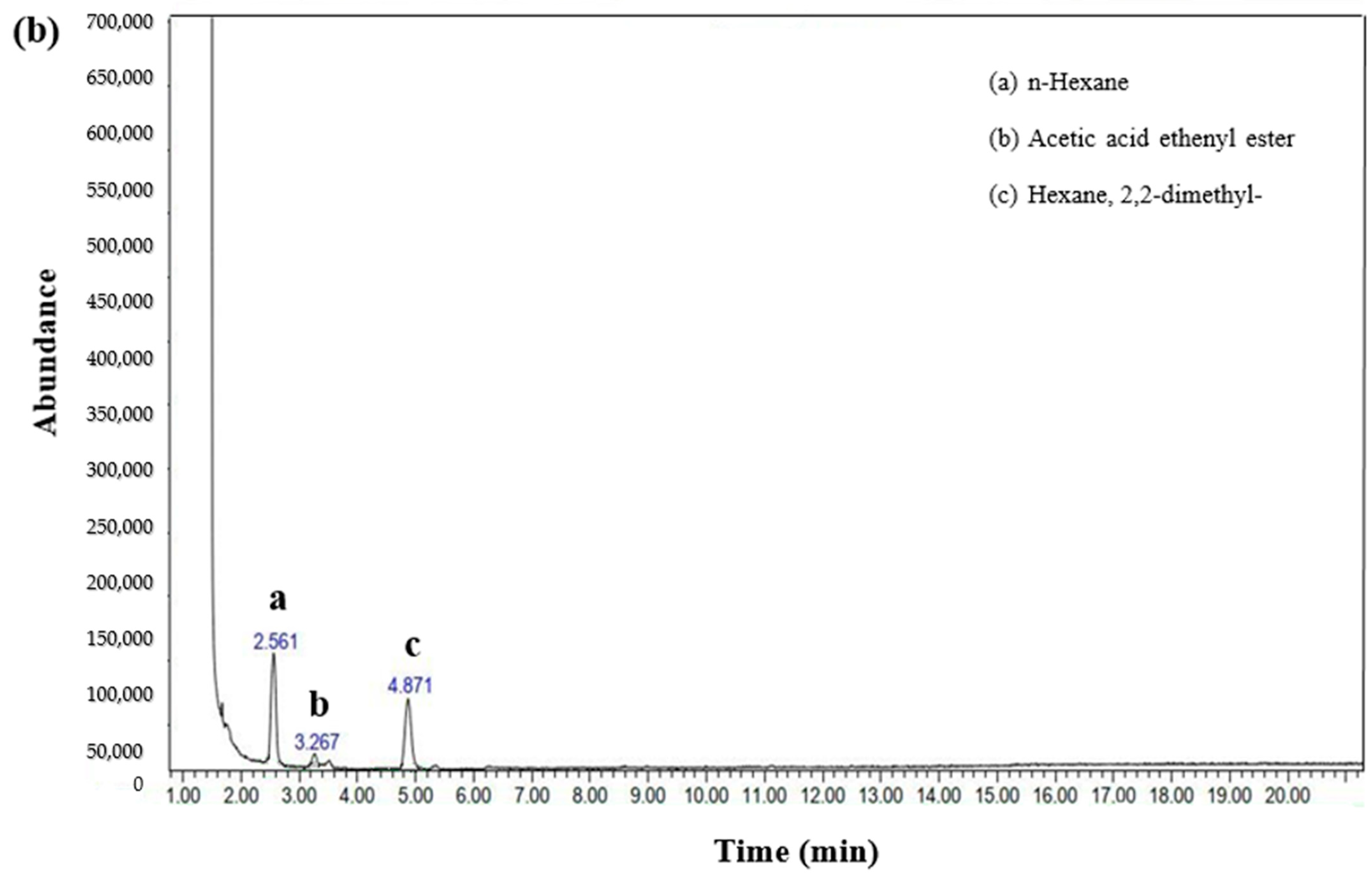
3.7. Organic Compound Transformation in Distillery Wastewater via the EF Process: GC-MS Insights
3.8. ANNOVA and RSM-CCD Optimization Statistical Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fito, J.; Tefera, N.; Van Hulle, S.W. Adsorption of distillery spent wash on activated bagasse fly ash: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5381–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Bakshi, S.; Bandyopadhyay, K.K.; Bose, S.; Nayak, R.; Paul, D. Enhanced biodegradation of melanoidin pigment from spentwash using PDMS-immobilized microbes via ‘repeated addition’ strategy. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Kundu, L.M.; Pandey, L.M. Enhanced melanoidin removal by amine-modified Phyllanthus emblica leaf powder. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, T.S.; Malik, S.N.; Suvidha, G.; Padmere, M.L.; Shanmugam, P.; Mudliar, S.N. Wet air oxidation pretreatment of biomethanated distillery effluent: Mapping pretreatment efficiency in terms color, toxicity reduction and biogas generation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita, F.; Vymazal, J. Opportunities and challenges of using constructed wetlands for the treatment of high-strength distillery effluents: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 196, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.D.; Mande, A.B.; Premalatha, M.; Sivasankar, T. Experimental studies on the impact of porous bed-induced solar evaporation (PBISE) and thermal degradation of the solid content of the distillery effluent using cocopeat—A sustainable approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPCB. Pollution Control Acts, Rules and Notifications Issued Thereunder; Central Pollution Control Board: Delhi, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.K. Color removal from distillery spent wash through coagulation using Moringa oleifera seeds: Use of optimum response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Shankar, R.; Chand, S. Treatment of distillery waste water using catalytic wet air oxidation. J. Future Eng. Technol. 2010, 6, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, S.N.; Khan, S.M.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Das, S.; Mudliar, S.N. Nano catalytic ozonation of biomethanated distillery wastewater for biodegradability enhancement, color and toxicity reduction with biofuel production. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei-Rad, Z.; Nickpour, M.; Adl, M.; Pazouki, M. Bioadsorption and enzymatic biodecolorization of effluents from ethanol production plants. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost-Boucle, S.; Pelus, L.; Becheau, E.; Cervoise, L.; Troesch, S.; Molle, P. Combination of sequencing batch reactor and vertical flow treatment wetlands: A full-scale experience for rum distillery wastewater treatment in a tropical climate. Nat.-Based Solut. 2023, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyawali, Y.; Balakrishnan, M. Treatment of distillery effluent in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) equipped with mesh filter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kaushik, A.; Batra, V.S.; Balakrishnan, M. Integrated treatment of molasses distillery wastewater using microfiltration (MF). J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, U.K.; Muthukrishnan, M.; Guha, B.K. Tertiary treatment of distillery wastewater by nanofiltration. Desalination 2008, 230, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parande, A.K.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Beulah, H.; Palaniswamy, N. Performance evaluation of lowcost adsorbents in reduction of COD in sugar industrial effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; García-García, I.; Martín, A.; Martín, M.A. Integrated ozonation and biomethanization treatments of vinasse derived from ethanol manufacturing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangave, P.C.; Pandit, A.B. Enhancement in biodegradability of distillery wastewater using enzymatic pretreatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, T.; Liu, Y.; Hou, D.; Yao, K.K.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; He, H.; Shi, W.; Wang, L.; et al. A novel Electro-Fenton process characterized by aeration from inside a graphite felt electrode with enhanced electrogeneration of H2O2 and cycle of Fe3+/Fe2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousset, E.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A. A complete phenol oxidation pathway obtained during electro-Fenton treatment and validated by a kinetic model study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, C.M.; Expósito, E.; Casado, J.; Montiel, V. Goethite as a more effective iron dosage source for mineralization of organic pollutants by electro-Fenton process. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezgui, S.; Ghazouani, M.; Bousselmi, L.; Akrout, H. Efficient treatment for tannery wastewater through sequential electro-Fenton and electrocoagulation processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.K.; Srivastava, S.N. Electrochemical degradation of distillery spent wash using catalytic anode: Factorial design of experiments. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 146, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- David, C.; Arivazhagan, M.; Tuvakara, F. Decolorization of distillery spent wash effluent by electro oxidation (EC and EF) and Fenton processes: A comparative study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 121, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.; Krishnan, C.; Kumar, M. A sequential electrochemical oxidation–algal photobioreactor system for the treatment of distillery wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarnejad, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Ismail, A.F. Petrochemical wastewater treatment by electro-Fenton process using aluminum and iron electrodes: Statistical comparison. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 3, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, I.; Kumar, M. Electrochemical oxidation of distillery wastewater by dimensionally stable Ti-RuO2 anodes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, K.; Peyghami, A.; Moharrami, A.; Vosoughi, M.; Dargahi, A. The efficacy of sono-electro-Fenton process for removal of Cefixime antibiotic from aqueous solutions by response surface methodology (RSM) and evaluation of toxicity of effluent by microorganisms. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6122–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiad, M.M.; Abbar, A.H. Efficient wastewater treatment in petroleum refineries: Hybrid electro-fenton and photocatalysis (UV/ZnO) process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 200, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.P.; Saravanakumar, M.P. Leachate xenobiotics electrocatalytic degradation and simultaneous carbon quantum dots synthesis for anti-counterfeiting applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Lee, T.W. Degradation of malachite green in aqueous solution by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Blaney, L. Advanced oxidation processes: Performance, advantages, and scale-up of emerging technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zhou, Z. Electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2100–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchou, F.E.; Zazou, H.; Afanga, H.; El Gaayda, J.; Akbour, R.A.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Hamdani, M. Removal of organic pollutants from wastewater by advanced oxidation processes and its combination with membrane processes. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 169, 108631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.; Sabeti, M.; Torabi, F.; Rahimbakhsh, A. COD Reduction of Aeration Effluent by Utilizing Optimum Quantities of UV/H2O2/O3 in a Small-Scale Reactor. Processes 2022, 10, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, O.A.; Adekalu, K.O.; Okunade, D.A. Electro-Fenton treatment process for brewery wastewater: Effects of oxidant concentration and reaction time on BOD and COD removal efficiency. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakika, D.C.; Sarto, S.; Mindaryani, A.; Hidayat, M. Decreasing COD in sugarcane vinasse using the fenton reaction: The effect of processing parameters. Catalysts 2019, 9, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarto, S.; Paesal, P.; Tanyong, I.B.; Laksmana, W.T.; Prasetya, A.; Ariyanto, T. Catalytic degradation of textile wastewater effluent by Peroxide oxidation assisted by UV light irradiation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapimmetha, A.; Srinophakun, P.; Amat, S.; Saisriyoot, M. Decolorization of molasses-based distillery wastewater by means of pulse electro-Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 1, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Liang, H.; Tsiakaras, P. Three-dimensional electro-Fenton system with steel-slag based particle electrode for the treatment of refinery spent caustic. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Advanced treatment of aged landfill leachate through the combination of aged-refuse bioreactor and three-dimensional electrode electro-Fenton process. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, H.H.P.; Dinh, N.T.; Thi, T.N.T.; Bao, L.T.N.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Nguyen, V.H. Fe2+, Fe3+, Co2+ as highly efficient cocatalysts in the homogeneous electro-Fenton process for enhanced treatment of real pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasri, N.; Hu, J.; Kibria, M.G.; Roberts, E.P. Electrocoagulation separation processes. In Multidisciplinary Advances in Efficient Separation Processes; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 167–203. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Cui, T.; Wang, Z.; Dang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Lin, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; et al. Energy-efficient removal of carbamazepine in solution by electrocoagulation-electrofenton using a novel P-rGO cathode. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 115, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouzeh, M.; Parivazh, M.M.; Danesh, E.; Dianat, M.J.; Abbasi, M.; Osfouri, S.; Rostami, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Dibaj, M.; Akrami, M. Application of Photo-Fenton, Electro-Fenton, and Photo-Electro-Fenton processes for the treatment of DMSO and DMAC wastewaters. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddah, S.; Samar, M.E.H.; Bououdina, M.; Khezami, L. Outstanding performance of electro-Fenton/ultra-violet/ultra-sound assisted-persulfate process for the complete degradation of hazardous pollutants in contaminated water. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sires, I.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A. Catalytic behavior of the Fe3+/Fe2+ system in the electro-Fenton degradation of the antimicrobial chlorophene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 72, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Zhou, M.; Qiu, S.; Sirés, I.; Brillas, E. Critical review on the mechanisms of Fe2+ regeneration in the electro-Fenton process: Fundamentals and boosting strategies. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 4635–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulai, T.; Kumar, J.E.; Kharmawphlang, W.; Sahoo, M.K. UV light and Fe2+ catalysed COD removal of AO 8 using NaOCl as oxidant. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, H.; Xu, B.; Lan, G. Three-dimensional electrochemical Fenton degradation of CIP by doping Ce and Cu in Jacaranda shell base as particle electrodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyapriya, G.; Nidheesh, P.V. Importance of graphene in the electro-Fenton process. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Hu, J.L.; Chou, W.L.; Kuo, Y.M. Removal of color from real dyeing wastewater by Electro-Fenton technology using a three-dimensional graphite cathode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.T.; Chou, W.L.; Kuo, Y.M. Removal of COD from laundry wastewater by electrocoagulation/electroflotation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleel, G.F.; Ismail, I.; Abbar, A.H. Kinetic modeling of a solar photo-electro-Fenton process for treating petroleum refinery wastewater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaithambi, P.; Yesuf, M.B.; Govindarajan, R.; Periyasamy, S.; Niju, S.; Pandiyarajan, T.; Kadier, A.; Nguyen, D.D.; Alemayehu, E. Sono-alternating current-electro-Fenton process for the removal of color, COD and determination of power consumption from distillery industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, V.V.; Balasubramanian, N. Removal of heavy metals by hybrid electrocoagulation and microfiltration processes. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, S.; Choudhury, M.R.; Bakr, A.R.; Anwar, N.; Rahaman, M.S. Effectiveness of electro-oxidation and electro-Fenton processes in removal of organic matter from high-strength brewery wastewater. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, M.; Ren, G.; Yang, W.; Liang, L. A highly energy-efficient flow-through electro-Fenton process for organic pollutants degradation. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 200, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Zhicheng, X.; Dan, Q.; Dan, W.; Hao, X.; Wei, Y.; Xiaoliang, J. Fabrication and characterization of porous titanium-based PbO2 electrode through the pulse electrodeposition method: Deposition condition optimization by orthogonal experiment. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkurdi, S.S.; Abbar, A.H. Removal of COD from petroleum refinery wastewater by electro-coagulation process using SS/Al electrodes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 870, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reategui-Romero, W.; Morales-Quevedo, S.E.; Huanca-Colos, K.W.; Figueroa-Gomez, N.M.; King-Santos, M.E.; Zaldivar-Alvarez, W.F.; Flores-Del Pino, L.V.; Yuli-Posadas, R.A.; Bulege-Gutierrez, W. Effect of current density on COD removal efficiency for wastewater using the electrocoagulation process. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 184, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Chen, T.E.; Lu, M.C.; Bellotindos, L.M. Removal of COD from TFT-LCD wastewater by electro-Fenton technology using a tubular reactor. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 43, 04017018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Choi, H.J.; Huang, C.P. Treatment of landfill leachate by Fenton’s reagent in a continuous stirred tank reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, J.L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.M.; Feng, N.X.; Han, W.; Yeung, K.L.; Zhou, S.; et al. Elimination of chloramphenicol through electro-fenton-like reaction: Reaction mechanism and electron transfer pathway. NPJ Clean Water 2023, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Mei, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xia, G.; Chen, J. Process optimization of electrochemical treatment of COD and total nitrogen containing wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, U.; Jang, M.; Jung, S.P.; Park, D.; Park, S.J.; Yu, H.; Oh, S.E. Electrochemical removal of ammonium nitrogen and COD of domestic wastewater using platinum coated titanium as an anode electrode. Energies 2019, 12, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, S.S.; Bahena, C.L. Chlorbromuron urea herbicide removal by electro-Fenton reaction in aqueous effluents. Water Res. 2009, 43, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. A comparative study of electrocoagulation, electrochemical Fenton, electro-Fenton and peroxi-coagulation for decolorization of real textile wastewater: Electrical energy consumption and biodegradability improvement. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Özcan, A.A.; Demirci, Y. Evaluation of mineralization kinetics and pathway of norfloxacin removal from water by electro-Fenton treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarnejad, R.; Azizi, J. Alcoholic wastewater treatment using electro-Fenton technique modified by Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2342–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R. Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: An overview. Desalination 2012, 299, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Chen, F.; Qu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, R. Optimization and control of Electro-Fenton process by pH inflection points: A case of treating acrylic fiber manufacturing wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvenc, S.Y.; Dincer, K.; Varank, G. Performance of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton processes for treatment of nanofiltration concentrate of biologically stabilized landfill leachate. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chou, W.; Chung, M.; Kuo, Y. COD removal from real dyeing wastewater by electro-Fenton technology using an activated carbon fiber cathode. Desalination 2010, 253, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, V.; Palanivelu, K. Destruction of cresols by Fenton oxidation process. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3062–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, M. Fenton process for the treatment of wastewater effluent from the edible oil industry. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimi, M.; Mohammadpour, M.; Fathinejadjirandehi, H. Treatment of petrochemical wastewater by modified electro-fenton method with nano porous aluminum electrode. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; He, D.; Ma, J.; Liu, T.; Waite, T.D. Kinetic modeling of the electro-Fenton process: Quantification of reactive oxygen species generation. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandi, M.; Rahmani, A.; Asgari, G.; Ahmadidoost, G.; Dargahi, A. Photocatalytic removal of cefazolin from aqueous solution by AC prepared from mango seed+ ZnO under uv irradiation. Glob. Nest J. 2018, 20, 399–407. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, N.O.; Ukpe, R.A.; Ameh, P.; Ogbodo, R.; Garg, R.; Garg, R. Theoretical and experimental studies on photocatalytic removal of methylene blue (MetB) from aqueous solution using oyster shell synthesized CaO nanoparticles (CaONP-O). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 81417–81432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, M.; Katoch, S.S. Techno-economical optimization using Box-Behnken (BB) design for COD and chloride reduction from Hospital wastewater by electro-coagulation. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 1387, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. Advanced oxidation of phenol: A comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 183, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, W.P.; Lu, M.C.; Huang, Y.H. Kinetics of 2, 6-dimethylaniline degradation by electro-Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopaj, F.; Oturan, N.; Pinson, J.; Podvorica, F.; Oturan, M.A. Effect of the anode materials on the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process for the mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 199, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra-Güere, C.D.; Dionisio, D.; Santos, G.O.S.; Lanza, M.R.V.; de Jesus Motheo, A. Application of Fenton, photo-Fenton and electro-Fenton processes for the methylparaben degradation: A comparative study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasni, A.B.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Arumugam, N.; Krishnan, S.; Din, M.F.M. Treatment of wastewater using response surface methodology: A brief review. CET J. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2020, 78, 534. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyakhsass, R.; Souabi, S.; Rifi, S.K.; Bouaouda, S.; Taleb, A.; Madinzi, A.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Anouzla, A. Applicability of central composite design and response surface methodology for optimizing treatment of landfill leachate using coagulation-flocculation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 197, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.A. Optimization for removal of COD and BOD through RSM-CCD by activated sludge treatment process for pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2023, 12, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, I.; Varank, G.; Murat Hocaoglu, S.; Yazici Guvenc, S. Medical laboratory wastewater treatment by electro-fenton process: Modeling and optimization using central composite design. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, D.; Dagdas, E.; Fil, B.A.; Bashir, M.J. Central composite modeling for electrochemical degradation of paint manufacturing plant wastewater: One-step/two-response optimization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
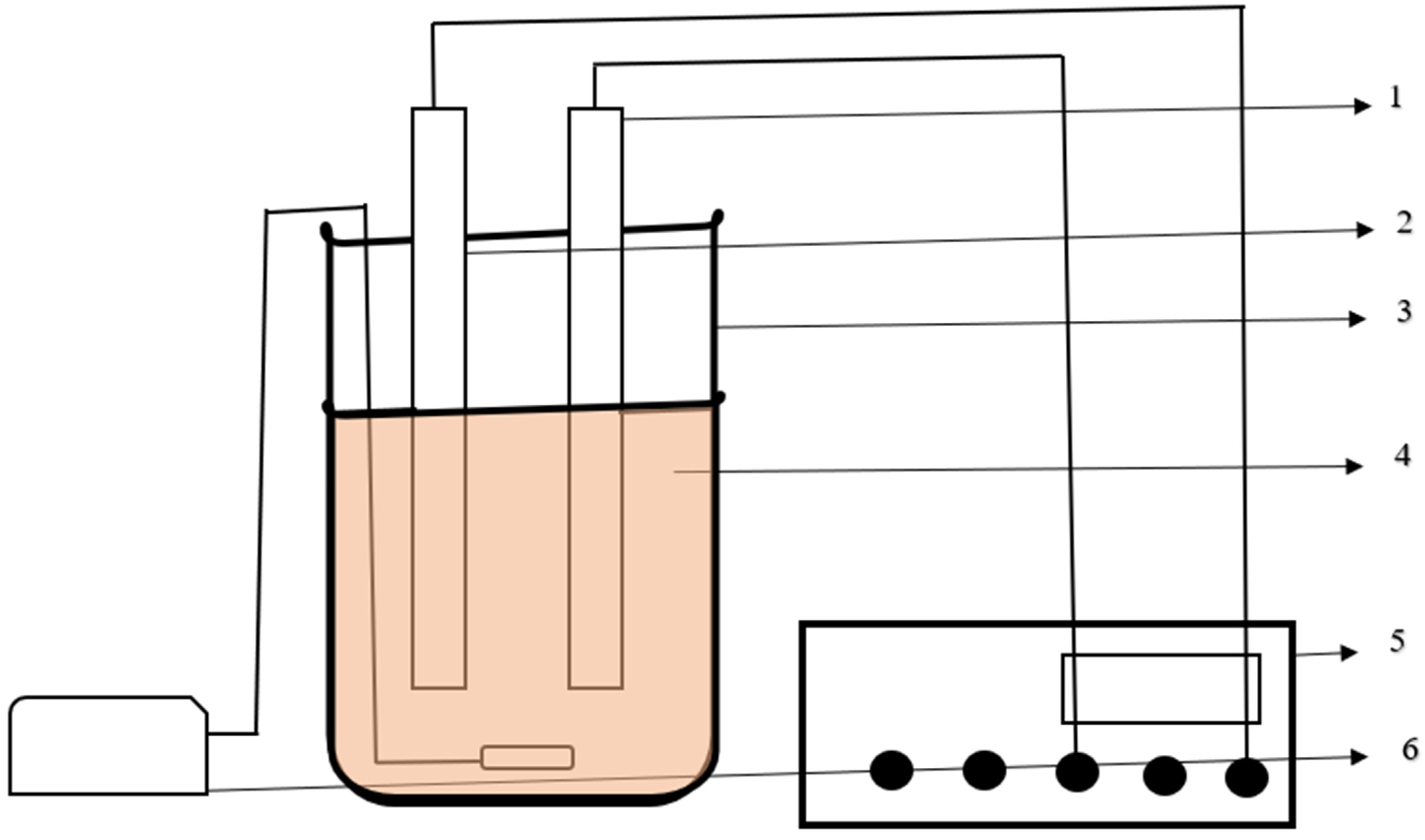






| S. No. | Parameter | Method Adopted—Code of Specification | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | pH | IS: 3025 Part 11:1983 (Reaff:2017) | 4.11 |
| 2. | Color | IS: 3025 Part 4: 2021 | Dark brown |
| 3. | COD (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 58:2006 (Reaff:2017) | 69,420 |
| 4. | BOD (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 44:1993 (Reaff:2019) | 20,680 |
| 5. | TS (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 15:1984 (Reaff:2019) | 64,090 |
| 6. | TSS (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 17:1984 (Reaff:2017) | 2490 |
| 7. | TP (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 31:1988 (Reaff:2019) | 231.4 |
| 8. | SO42− (mg L−1) | IS: 3025 Part 11:1983 (Reaff:2017) | 12,152 |
| Independent Variable | Sign | Unit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 dosage | A | mg L−1 | 555 | 1110 | 1665 | 2220 |
| Spacing between the electrode | B | cm | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 |
| Dipping area of electrode | C | cm2 | 35 | 45 | 55 | 65 |
| Initial pH | D | - | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 |
| Applied voltage | E | V | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 15 |
| H2O2 Dosage (mg L−1) | ES (cm) | DA (cm2) | pH | Voltage (v) | Ci (mg L−1) | Cf (mg L−1) | COD Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 555 | 45 | 4.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 4608 | 3600 | 21.9 |
| 1110 | 45 | 4.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 5040 | 3744 | 25.7 |
| 1665 | 45 | 4.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 5568 | 3600 | 35.3 |
| 2220 | 45 | 4.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 5808 | 4944 | 14.9 |
| 1665 | 45 | 2.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 5474 | 2784 | 49.1 |
| 1665 | 45 | 2.5 | 4 | 5.0 | 5376 | 1920 | 64.3 |
| 1665 | 45 | 3.0 | 4 | 5.0 | 4944 | 2400 | 51.5 |
| 1665 | 35 | 2.5 | 4 | 5.0 | 5232 | 3024 | 42.2 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 4 | 5.0 | 5376 | 1536 | 71.4 |
| 1665 | 65 | 2.5 | 4 | 5.0 | 5232 | 1776 | 66.1 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 2 | 5.0 | 5568 | 2304 | 58.6 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 3 | 5.0 | 5376 | 1104 | 79.5 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 7 | 5.0 | 4944 | 2832 | 42.7 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 | 5280 | 1248 | 76.4 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 3 | 10.0 | 5232 | 2304 | 56.0 |
| 1665 | 55 | 2.5 | 3 | 15.0 | 5808 | 2688 | 53.7 |
| (a) | ||||||
| Source | DF | Adj. SS | Adj. MS | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
| Model | 5 | 4330.20 | 866.04 | 7.09 | 0.004 | R2 = 91.30 % R2adj. = 80.43 % R2pred. = 36.56% Mean = 47.98 Std. Dev. = 18.91 Coef. Var. = 39.4 |
| Linear | 5 | 4330.20 | 866.04 | 7.09 | 0.004 | |
| H2O2 dosage | 1 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 0.01 | 0.028 | |
| ES | 1 | 1794.72 | 1794.72 | 14.68 | 0.003 | |
| DA | 1 | 538.29 | 538.29 | 4.40 | 0.062 | |
| pH | 1 | 420.56 | 420.56 | 13.44 | 0.003 | |
| Voltage | 1 | 168.33 | 168.33 | 1.38 | 0.068 | |
| Error | 10 | 340.84 | 85.210 | |||
| Total | 15 | 5552.50 | ||||
| (b) | ||||||
| Term | Effect | Coef. | SE Coef. | T-Value | p-Value | VIF |
| Constant | 39.49 | 6.41 | 6.16 | 0.000 | ||
| H2O2 dosage | −1.36 | −0.68 | 7.38 | −0.09 | 0.928 | 1.14 |
| ES | 36.41 | 18.20 | 4.75 | 3.83 | 0.003 | 1.34 |
| DA | 27.49 | 13.75 | 6.55 | 2.10 | 0.062 | 1.25 |
| pH | 26.83 | 13.41 | 7.23 | 1.85 | 0.008 | 1.13 |
| Voltage | −13.57 | −6.78 | 5.78 | −1.17 | 0.268 | 1.23 |
| Independent variable | Coded Variable | Equation for Polynomial Model | Optimum Condition for COD Removal | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | Experimental Value | Predicted Value by RSM Method | ||||||||
| Coded | Predicted | ||||||||||
| Time (min) | Independent Variable | Efficiency (%) | X1 | X2 | Time (min) | Independent Variable | Efficiency (%) | ||||
| H2O2 (mg L−1) | FO (X1, X2) + PQ (X2) | 70 | 1665 mg L−1 | 35.30 | 0.0 | −0.16 | 50 | 1402 mg L−1 | 32.94 | ||
| ES (cm) | FO (X1, X2) + PQ (X2) | 70 | 2.5 cm | 64.30 | 1.26 | 0.11 | 50 | 3 cm | 53.03 | ||
| EDA (cm2) | FO (X1, X2) + TWI (X1, X2) + PQ (X1, X2) | 60 | 55 cm2 | 70.64 | 0.73 | 0.2 | 87 | 60 cm2 | 68.26 | ||
| pH | FO (X1, X2) + PQ (X1, X2) | 60 | 3 | 79.46 | 0.52 | −0.27 | 75.93 | 2.18 | 68.3 | ||
| V (V) | FO (X1, X2) + PQ (X2) | 60 | 5 V | 79.46 | −0.8 | −0.33 | 10 | 5 V | 70.78 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minnalkodi Senguttuvan, K.R.; Sellappa, K.; Kuppusamy, S. Performance Evaluation of the Electro-Fenton Process for Distillery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156512
Minnalkodi Senguttuvan KR, Sellappa K, Kuppusamy S. Performance Evaluation of the Electro-Fenton Process for Distillery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability. 2024; 16(15):6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156512
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinnalkodi Senguttuvan, Keerthana Rani, Kanmani Sellappa, and Saranya Kuppusamy. 2024. "Performance Evaluation of the Electro-Fenton Process for Distillery Wastewater Treatment" Sustainability 16, no. 15: 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156512
APA StyleMinnalkodi Senguttuvan, K. R., Sellappa, K., & Kuppusamy, S. (2024). Performance Evaluation of the Electro-Fenton Process for Distillery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 16(15), 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156512







