Abstract
Tourism eco-efficiency has played a significantly essential role in the sustainable development of tourism destinations and tourism industries, providing ideal inputs and outputs amidst the deepening environmental crisis. This study evaluates the development level of tourism eco-efficiency using the Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs, employing the Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index to analyse the internal optimisation forces of tourism eco-efficiency. Furthermore, human capital is assessed through both horizontal and vertical education levels, followed by a panel Tobit econometric analysis to explore the external impact mechanisms on tourism eco-efficiency. The results show that (1) Technological advancement is the core intrinsic driver for optimising tourism eco-efficiency. (2) In the analysis of influencing mechanisms, Human capital significantly contributes to enhancing tourism eco-efficiency, a conclusion upheld even after conducting robustness tests. (3) Analysis of mediating mechanisms indicates that tourism industry agglomeration is a critical pathway through which human capital enhances tourism eco-efficiency. This correlation has been proven reliable by regional regression analysis. (4) Results of the threshold model test suggest a law of “increasing marginal effect” concerning the positive impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency within the regulation of tourism industry agglomeration. Consequently, regions should actively promote the roles of human capital and tourism industry agglomeration in advancing tourism eco-efficiency, improving resource utilization efficiency, and tourism industry specialization to foster sustainable tourism development.
1. Introduction
Against the backdrop of industrialization, informatization, and globalization, the swift economic advancement across nations and the ongoing enhancement of living standards have spurred a growing energy demand. This surge, in turn, has precipitated a range of ecological challenges, including energy scarcity, environmental pollution, and global climate disturbances [1]. Faced with the polluted living environment, people are increasingly recognizing the seriousness of the ecological challenges. For this reason, the concept of ‘sustainable development’ has emerged, emphasizing the harmonious coexistence of humans with economic, social, and ecological systems [2]. Under this context, the importance of sustainable development in the tourism sector has garnered increased attention [3,4]. Tourism is a significant industry that generates income for the national economy and plays a crucial role in promoting employment among the population and narrowing the urban-rural gap. However, studies have shown that tourism-related carbon emissions contribute about 8.3% of the total global carbon emissions [5], projecting continued growth in global carbon emissions from tourism until 2035 [6]. The environmental challenges within China’s tourism industry are equally bleak, with scholars observing a staggering average annual growth rate of total carbon emissions from the tourism industry at 9.521% between 1990 and 2019 [7]. Therefore, there is a pressing need to adopt a low-carbon, environmentally friendly approach to sustainable tourism development to address these issues [4,7].
In 2023, the number of tourists in China reached 4.891 billion, with tourism revenue totaling 4.91 trillion yuan, reflecting a 140.3% year-on-year increase compared to the previous year. This highlights the tourism industry as a crucial engine for economic recovery post the COVID-19 pandemic. Faced with the economic benefits and environmental challenges stemming from the development of the tourism industry, China continues to prioritise the promotion of sustainable development in the sector. Since the 18th National Congress, China has introduced the concept of new development, emphasizing the imperative for the tourism industry to embrace green practices [8]. The 2021 14th Five-Year Plan reiterated the significance of ecological protection and outlined targets for achieving “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality”. With this context, discussions around the concept of “eco-efficiency” have gained prominence. Eco-efficiency aims to maximise economic value while minimizing energy consumption [9]. This concept aligns with the goal of sustainable development in the tourism industry, which seeks to reduce the negative impacts of tourism activities on the ecological environment while fostering economic growth within the sector [10]. This striving is also known as the pursuit of “tourism ecological efficiency” [4]. Therefore, enhancing “tourism ecological efficiency” has become a focal point in research on the sustainable development of the tourism industry.
Relevant studies have concluded that the impact of human capital on the environment exhibits a ‘two-sided’ character [11]. Human capital contributes vitality to the high-quality development of the tourism economy, while the tourism economy sector enhances human capital quality through the circulation of capital factors [12]. The synergistic evolution of the two elements enables human capital to facilitate the transformation from a rough economic development mode to a more sophisticated one, thereby enhancing the ecological environment through structure optimization within industries [13]. However, in the process of human capital development, the movement of people can lead to an increase in the carbon footprint of tourism [14], potentially harming the environment of tourism destinations. Nonetheless, the expansion of the population size does not necessarily positively correlate with carbon emissions, and its negative impacts are somewhat constrained [15]. For instance, the expansion of human capital brings about resource constraints along with technological advancements, which can positively impact the environment [16]. Therefore, there is a need for further exploration and clarification of the relationship between human capital and the eco-efficiency of the tourism industry.
Simultaneously, in areas with relatively abundant human capital, there tends to be a greater potential for industrial agglomeration [17]. Therefore, human capital can serve as a catalyst for tourism industry agglomeration. This, in turn, plays a crucial role in enhancing the effective allocation of resources, promoting technology diffusion [18], and bolstering the resilience of the regional tourism environment [19]. It is evident that human capital is a common indicator affecting tourism industry agglomeration and tourism eco-efficiency. Is there a progressive relationship between the three? How does human capital affect tourism eco-efficiency under the context of tourism industry agglomeration? To address these questions, it is necessary to delve into the mechanisms governing the interactions among these elements. This exploration is of great significance in realizing the economic empowerment of the tourism sector and advancing sustainable tourism development. While relevant studies have identified factors influencing tourism eco-efficiency [20], the specific mechanism through which human capital influences tourism eco-efficiency remains unclear. In addition, there is a dearth of research that delineates the various dimensions of human capital and their correlation with the tourism environment. Therefore, it is essential to examine human capital from a multidimensional perspective, both horizontally and vertically, extending its environmental impact to the realm of tourism.
This study aims to investigate the sustainable development of tourism, using data from 30 provinces and cities in China from 2011 to 2020 as the sample set. We employ the Super-SBM-ML model with undesirable output to assess the level of tourism eco-efficiency development and explore its internal drivers. In the analysis of external influences, human capital is evaluated based on horizontal and vertical education levels, while the influence of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency is examined by econometric regression analysis. The main objectives of this study are as follows: (1) exploring the internal factors in optimizing tourism eco-efficiency; (2) building the theoretical framework through which human capital influences tourism eco-efficiency; (3) empirically exploring the influence of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency; (4) analysing regional disparities in the influence of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency; and (5) explicating and validating the mechanisms and specific pathways through which human capital influences tourism eco-efficiency. This study concludes by summarizing the findings and implications to provide a theoretical foundation and practical guidance to inform inter-regional ecological environment optimization and promote sustainable development within the tourism sector.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Human Capital
In the 1960s, American economist Schultz formally introduced the human capital theory, positing that human capital embodies the quality of laborers and is an essential part of a country’s economic development and capital assets [21]. The advent of the New Economic Growth Theory prompted a growing recognition of the intrinsic impact of human capital, emphasizing its role in fostering economic growth through spillover effects [22]. After the integration of human capital theory into China’s discourse, scholars have delved into assessing the impact of human capital on the urban-rural income gap within the country [23,24,25]. This research has explored differences between eastern, central, and western regions [24], as well as disparities between developed and less developed areas [25]. Most of the studies have underscored the promotion of human capital and its spillover effects on regional economic growth. With the increasing prominence of environmental issues, scholarly attention has shifted towards examining the environmental implications of human capital. The main views of this exploration can be classified into three perspectives: the promotional relationship of the action mechanism [26,27,28], the inhibitory relationship [29,30], and the nonlinear relationship [31,32]. In addition, studies have revealed highly heterogeneous effects of human capital on the environment. For instance, Appiah-Twum et al. (2023) found that human capital negatively affects environmental efficiency only in South Asia while demonstrating a beneficial effect in other Asia-Pacific regions [33]. Common metrics for measuring human capital include indicators such as population size [29,31], population industrial structure [30], population ageing, [34], population urban-rural structure [35], and population educational attainment [36]. In summary, scholarly investigations have featured a diverse range of variables and have detailed the impact of human capital on the ecological environment. However, there is a scarcity of literature discussing the role of human capital in the ecological environment of tourism.
2.2. Tourism Eco-Efficiency
“Eco-efficiency” serves as a comprehensive indicator to gauge the impact of economic activities on the environment [4]. Gössling was the first to introduce eco-efficiency to the domain of tourism, defining it as the ratio of carbon emissions of tourism to the economic gains from tourism [37]. Domestic scholars have highly aligned their interpretation of tourism eco-efficiency, viewing it as a critical component for fostering sustainable tourism development [4,38,39]. The specific target is to maximise the economic benefits from tourism while minimizing environmental harms. With the continuous deepening of research, studies have focused on various facets of tourism eco-efficiency, encompassing measurement techniques [40,41], analysis of influential factors [20,42], destination management [43,44], and evaluation of spatial-temporal changes [45,46]. The abundant studies on tourism eco-efficiency have led to relatively matured measurement indexes and methodologies, with minimal room remaining for conceptual and methodological innovations. Therefore, recent research has gradually tended to explore the factors influencing tourism eco-efficiency and reveal its temporal and spatial dynamics. Numerous studies have highlighted the impact of economic development levels, the structure of the tourism industry, environmental regulations, public management, and other factors on tourism eco-efficiency [20,42,45]. However, most studies merely identify potential factors influencing tourism eco-efficiency without delving into the underlying mechanisms or pathways of influence. Moreover, there is a noticeable dearth of examinations of regional disparities within the same country concerning their roles in shaping tourism eco-efficiency.
2.3. Influence Mechanism of Human Capital and Tourism Industry Agglomeration on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
In terms of investigating the mechanism through which human capital influences tourism eco-efficiency, most studies treat it as a control variable. Researchers often use indicators such as education costs [45] and the quality of education [20] to argue for the promotional effect of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. Studies that position human capital as a core variable focus their explorations on such as eco-efficiency [31,32,35], agro-ecological efficiency [34], and sustainable development [27]. In the studies involving the influencing factors of industrial agglomeration, existing literature generally evaluates the effects of human capital and industrial agglomeration on economic efficiency separately [47,48]. Specifically, human capital is seen to drive economic growth by upgrading technological structures [47], while industrial agglomeration promotes high-quality development by leveraging economies of scale [48]. As for the impact of tourism industry agglomeration on the tourism ecological environment, most scholars posit two main relationships: an initial inhibitory phase followed by promotion in a “U” shape [18] and a promotion phase followed by inhibition in an inverted “U” shape [41]. However, studies on the mechanism linking human capital and industrial agglomeration are relatively scarce. The bulk of relevant research mainly focuses on regional innovation and other economic domains [49,50], overlooking in-depth analysis of the environmental repercussions.
From the above analysis, most scholars tend to view human capital as a control variable rather than a core variable in the research exploring its impact on the economy or the environment. In addition, there is a noticeable scarcity of research on the direct influence of human capital on the tourism sector, along with an inadequacy in the comprehensive investigation of its impact mechanism. Therefore, this study aims to enrich the existing research results by taking tourism industry agglomeration as the starting point, constructing a theoretical framework delineating the relationship between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency, and empirically investigating the mechanism through which human capital influences tourism eco-efficiency.
3. Theoretical Hypotheses
3.1. The Direct Impact of Human Capital on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
Human capital has the characteristic of endogeneity, facilitating the enhancement of tourism eco-efficiency through personal ability development and internal expertise accumulation. Enhancing personal abilities can promote individual capital and skills, resulting in increased personal benefits [51]. Individuals with advanced knowledge and skills tend to consider the long-term costs and benefits of environmental optimization, thereby reducing reliance on traditional resources such as non-renewable energy [52]. They are inclined to choose low-carbon and environmentally friendly renewable energy sources in daily consumption practices and engage in behaviors that promote environmental protection [53]. Therefore, human capital contributes to both economic prosperity and environmental preservation at an individual level, aligning with the principles of sustainable tourism development. Furthermore, the accumulation of internal technological prowess through human capital can mitigate the diminishing marginal returns of material capital and elevate labor productivity through established production technologies [54]. A high level of human capital fosters technological progress and industrial innovation, enhancing the efficiency of production factor allocation within the tourism sector. This, in turn, propels the advancement of tourism eco-efficiency [20].
On the flip side, human capital also possesses the attribute of externality, which facilitates the spread of environmental protection ideologies and the transfer of specialised knowledge and technology. With regard to the spread of environmental protection ideologies, individuals with high-quality human capital possess a profound understanding of sustainable development principles [27], leading them to curtail the negative impact of their actions on the environment. They impart their environmental ethos to social groups through market mechanisms or political avenues, catalyzing a shift from individual environmental awareness to collective engagement in environmental protection efforts [52]. Since the tourism sector involves frequent human interactions, the demeanor and mindset of the local populace significantly impact tourists’ perceptions of the destination [45]. Tourism practitioners can instill environmental consciousness among tourists during interactions, encouraging them to respect and treasure the ecological environment of the destination. In addition, government bodies in tourist destinations and relevant tourism environmental protection organizations can guide tourists’ environmental conduct by establishing mechanisms for environmental public interest litigation [43]. Regarding the spread of specialised knowledge and technology, human capital leverages talent interaction to reduce the costs associated with knowledge learning. Through a mix of competition, cooperation, formal training, and informal knowledge exchanges, employees can synergise their expertise to yield greater environmental benefits [55]. This collaborative environment facilitates knowledge sharing and skills enhancement, enabling tourism practitioners to glean insights from renowned tourist attractions globally. Furthermore, by assimilating advanced cleaning and pollution control technologies, they can effectively optimise tourism eco-efficiency at tourist destinations. Therefore, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Human capital fosters the enhancement of tourism eco-efficiency.
3.2. Mediating Mechanisms of the Impact of Human Capital on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
The main driver of industrial agglomeration growth lies in the accumulation of human capital [56]. In general, human capital primarily exerts its influence through both “internal effects” and “external effects” to promote tourism industry agglomeration. Leveraging its internal characteristics, human capital can cultivate advantages in industrial agglomeration through factors such as individual and collective technology accumulation, product design, and technology innovation [57]. Consequently, the tourism sector can enhance its competitiveness by improving the overall skills and knowledge levels of individuals and groups through the internal skill and knowledge transfer process. With its external characteristics, human capital facilitates the diffusion of science, technology, knowledge, and skills via seamless exchanges among personnel [55]. Under such a ripple effect, higher education institutions can forge robust collaborations through the “industry-university-research” platform [55], engaging in activities such as expert consultation, industry partnerships, and institutional enhancements. By tapping into the synergies of the “industry-university-research” mechanism, the tourism industry can facilitate cross-disciplinary innovation through horizontal exchanges with the “tourism +” sector. This approach, in tandem with vertical industry chain expansions, fosters in-depth collaborations, thus promoting tourism industry agglomeration.
Viewed from a different angle, tourism industry agglomeration can leverage scale effects, spillover effects, and other utility mechanisms to enhance the optimization of tourism eco-efficiency [41]. Firstly, industrial agglomeration facilitates knowledge and facility sharing, fostering intensive development of public infrastructure and effectively reducing operation costs [48], thus minimizing the waste of resources. Secondly, the continuous convergence of tourism flow, capital flow, and information flow resulting from tourism industry agglomeration intensifies competition among enterprises [18]. Against such scenarios, stimulated by external incentives, tourism enterprises are driven to engage in internal technological innovations for energy conservation, thus achieving the development of tourism eco-efficiency [58]. Based on this analysis, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Human capital can effectively harness the impact of tourism industry agglomeration to enhance tourism eco-efficiency through a mediating mechanism.
3.3. Threshold Effect of Human Capital on Tourism Eco-Efficiency Influence
The ultimate consumers of tourism products are the tourists themselves, and as such, during the process of their tourism activities, the carbon emissions generated should be attributed to the tourists [59]. As the implementation of the new development concept progresses, individuals’ inclination towards pursuing green and environmentally friendly tourism experiences deepens [8]. The rise in education attainment has heightened awareness among individuals regarding the importance of adopting low-carbon behaviors [7], leading to the internal accumulation and external dissemination of “pro-environmental behaviors” [52]. Therefore, from a standpoint of personal volition, the enhancement of human capital quality facilitates the adoption of environmentally conscious practices. From a technological standpoint, the diminishing marginal cost of human capital over material capital, alongside the expanding scale effect [54], leads to a geometrical increase in energy use efficiency. This phenomenon significantly impacts tourism eco-efficiency.
With the use of green innovation technology, the environmental and innovation benefits of industrial agglomeration are deepening [60]. Simultaneously, the favorable externalities stemming from tourism industrial agglomeration enhance tourism eco-efficiency by reducing energy waste [41]. Faced with the dual spillover effects of human capital and industrial agglomeration, a benign causal relationship between the two is gradually evolving in a circular and cumulative manner [50]. This relationship mechanism continuously amplifies the positive impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. Based on the aforementioned analysis, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
There exists a threshold effect of a marginal increase in the impact of tourism industry agglomeration on human capital and tourism eco-efficiency.
To more intuitively illustrate the impact mechanism of human capital and tourism industry agglomeration on eco-efficiency, a theoretical model has been constructed in this paper, as depicted in Figure 1.
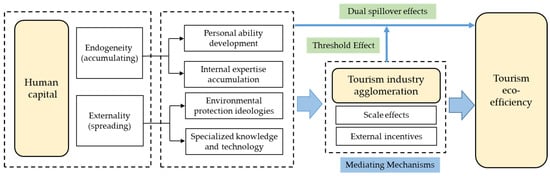
Figure 1.
The theoretical model.
4. Materials and Methods
To validate the correctness of the aforementioned theoretical analysis, this study con-ducts empirical research and analysis. Specifically, 30 provinces and cities in China are taken as the research subjects, gathering indicator data from 2011 to 2020 by examining statistical sources such as data yearbooks. The primary indicators are quantified using the Super-SBM model with undesirable output and the location entropy. The Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index is further employed to decompose the tourism eco-efficiency, aiming to explore the internal driving factors of tourism eco-efficiency in China. In addition, Tobit regression, mediation regression, and threshold regression are applied to identify the external driving factors of China’s tourism eco-efficiency. The detailed analysis is shown below.
4.1. Research Methods
4.1.1. Super-SBM Model
The Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) can measure relative efficiency among multiple input and output factors [61]. However, this method does not address slack variables in inputs and outputs. Subsequently, the BCC and CCR models were introduced to decompose efficiency values, yet they tend to overestimate efficiency for decision units or overlook changes in inputs or outputs [62]. Consequently, computational results may deviate from actual outcomes. In 2001, Tone proposed the SBM model to address slack variables in a non-radial, non-angular manner [63]. However, it cannot compare decision units all rated as 1 in efficiency. Therefore, Tone’s enhanced Super Efficiency SBM model overcomes these issues [64]. In contrast to the BCC and CCR models, it does not require proportional changes in input-output indicators and considers non-desirable outputs such as environmental pollution often generated by tourism activities. The specific model is as follows:
where ρ represents the tourism eco-efficiency value, ρ ≥ 1 indicates that the decision-making unit is relatively effective; 0 < ρ < 1 indicates that it is relatively ineffective, n denotes the number of decision-making units, j indicates the decision-making unit, and h refers to the number of production periods. The variables m, f1, and f2 correspond to the quantities of input indicators i, desirable output indicators g, and undesirable output indicators w, respectively. The elements x, yd, and yµ pertain to the matrices constructed for inputs, desirable outputs, and undesirable outputs. , , and are the corresponding vector values. Lastly, λj represents the weight vector.
4.1.2. Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) Index Model
The super-SBM model can be used to measure the static tourism eco-efficiency of each province, but it cannot dynamically assess the development level of efficiency values. To further explore the dynamic changes in tourism eco-efficiency among 30 provinces in China and the internal driving factors, the ML index constructed by Chung et al. [65] is employed to decompose the efficiency values. Under the constant returns to scale (CRS) condition, the ML index can be decomposed into the efficiency change index (EC) and the technological progress index (TC). If under the variable returns to scale (VRS) condition, EC can be further decomposed into the pure technical efficiency change index (PEC) and the scale efficiency change index (SEC). The relevant computational formulas are as follows:
In the formula, subscript c denotes CRS (Constant Returns to Scale), and subscript v denotes VRS (Variable Returns to Scale). represents the directional distance function under the CRS condition, and represents the directional distance function under the VRS condition. Dt(xt, yt, bt) is the distance function for period t with inputs xt, outputs yt, and bad outputs bt. Dt+1(xt+1, yt+1, bt+1) represents the distance function for period t + 1 under the conditions of inputs xt+1, outputs yt+1, and bad outputs bt+1. Dt(xt+1, yt+1, bt+1) denotes the mixed distance function in period t + 1 under the technology level of period t. Dt+1(xt, yt, bt) denotes the mixed distance function in period t under the technology level of period t + 1. When the ML index, TC index, EC index, PEC index, and SEC index are greater than 1, it indicates an improvement in tourism eco-efficiency, technological progress, technical efficiency, production level, and scale efficiency from period t to t + 1; conversely, values less than 1 indicate a decline in these metrics.
4.1.3. Tobit Regression Model
Since the SBM model measurements exceed 0, which is truncated data, the use of ordinary least squares regression may introduce a certain degree of bias to the results [41]. Therefore, we draw on the research findings of Ma et al. [41] and Qin et al. [51] to establish a panel Tobit regression model to investigate the impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. The model expression is as follows:
Among this, i represents the year, and t represents the province. Teeit represents the explanatory variable (i.e., tourism eco-efficiency); hcit is the core explanatory variable, human capital; controlit comprises a set of control variables; µi denotes the individual effect, and δit represents the random error term.
4.1.4. Mediation Effects Model
In this study, the sequential test regression coefficient method is employed to assess whether tourism industry agglomeration functions as a mediating variable between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency. The specific testing steps are as follows: by taking the significance of the coefficient of α1 in Equation (1) as the basis, a linear regression equation is constructed to analyze the relationship between human capital and tourism industry agglomeration, followed by the regression equations for human capital and tourism industry agglomeration concerning tourism eco-efficiency. The significance of the coefficients of φ1, γ1, and γ2 is scrutinised to determine the efficacy of the mediating effect. The models are as follows:
In the equation, Tagit serves as a mediating variable, indicating the tourism industry agglomeration. “Control” represents a series of control variables. µi denotes individual effects. ηit and τit are random error terms.
4.1.5. Threshold Effects Model
In evaluating the impact mechanism of the mediation effect model, it is also crucial to account for the spillover impacts of tourism industry agglomeration and the economies of scale effect. Tourism industry agglomeration could potentially impact the nonlinear spillover of human capital, thereby enhancing tourism eco-efficiency. Therefore, the following panel threshold model is derived:
where Thit represents the threshold variable; θ denotes the threshold value requiring estimation; I( ) serves as an indicator function, taking a value of 1 when satisfying specific conditions and 0 otherwise. Initially, the equation contains a single threshold scenario, but it can be extended to encompass more threshold cases based on the results of the econometric testing.
4.2. Indicator Construction and Variable Selection
4.2.1. Explained Variable
Tourism eco-efficiency: The construction of the indicator system for tourism eco-efficiency has reached a relatively mature stage. Leveraging insights from the research results of Wang et al. [58] and Xu et al. [66], and considering data availability, the Super-SBM model with undesirable output is used to formulate the indicator system. Specific indicators are shown in Table 1. It should be noted that, due to the intersectionality and extensiveness of tourism industry activities, official statistical data on the “three wastes” indicators within the tourism sector are not readily available [46]. Drawing inspiration from the research method of Xu et al. [66], the ratio of overall total tourism revenue to regional GDP is employed as a conversion tool for industry “three wastes” data. Fixed asset investment in the tourism sector is similarly transformed using this method. The results of national and regional calculations are shown in Figure 2. (The eastern region comprises Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan. The central region encompasses Shanxi, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Liaoning, Jilin, and Heilongjiang. The western region includes Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang.).

Table 1.
Index system for tourism industry eco-efficiency.
4.2.2. Explanatory Variable
Human capital: Human capital represents the reservoir of knowledge and skills possessed by laborers, primarily acquired and enhanced through education to a high level [22]. A well-educated population is an important driving force for advancing regional tourism development [45]. Therefore, this study incorporates the horizontal level of education coverage (Chc) along with the vertical level of schooling duration (Lhc), with the product of the two factors to gauge human capital. The horizontal level is quantified by the ratio of tertiary enrollment to the total population [52], while the vertical level is determined by the average schooling duration, computed following the methodology outlined by Qin et al. [51]. The measurement results are shown in Figure 2.
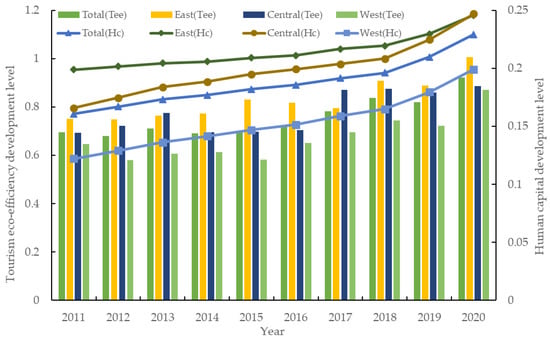
Figure 2.
Tourism eco-efficiency and human capital development levels by region from 2011 to 2020.
4.2.3. Mediating Variable
Tourism industry agglomeration: Location entropy is commonly used to assess the degree of specialization and agglomeration within regional industries [50]. Drawing on the study of Ma et al. [41], we adopt location entropy as a metric to evaluate the level of tourism industry agglomeration.
where Tit represents the total tourism revenue of province i in year t, Tt represents the gross domestic product (GDP) of province i in year t, Ht denotes the national total tourism revenue in year t, and H represents the national GDP in year t.
4.2.4. Control Variables
Referring to the existing literature [36,41,46], four control variables, namely foreign investment level, government intervention degree, tourism consumption capacity, and industry structure ratio are introduced into the regression model. The impact of foreign investment level on tourism eco-efficiency remains uncertain due to the “pollution halo” and “pollution paradise” hypothesis, necessitating its inclusion as a crucial influencing factor in the regression model. Government fiscal expenditure serves as a key mechanism for macroeconomic governance, facilitating the flow of resources and affecting environmental quality. Per capita tourism consumption offers insights into the impact of regional tourists’ consumption capacity on tourism eco-efficiency, accounting for data heteroskedasticity through logarithmic transformation. Additionally, the industrial structure weight reflects the extent of “pro-environmental” practices in urban development, further impacting the ecological environment. The specific definitions of these variables are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Definition and description of the variables.
4.3. Data Sources
Panel data of 30 provinces (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, and Tibet due to data unavailability) spanning from 2011 to 2020 are selected for analysis. The original datasets are sourced from China Statistical Yearbook, China Regional Economic Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook, China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, China Culture, Heritage and Tourism Statistical Yearbook, China’s economic and social big data research platform (https://data.cnki.net, accessed on 19 February 2024), as well as the Statistical Yearbook, Statistical Bulletin, and platforms of government statistical departments of relevant provinces. In case of missing data points, the linear regression method is adopted to supplement the completeness.
5. Results
5.1. Analysis of the Dynamic Evolution and Internal Driving Forces of Tourism Eco-Efficiency
To further analyze the intrinsic driving factors and characteristics of the decomposed indicators of tourism eco-efficiency, we utilised the Matlab 2021 software to calculate and decompose the ML index values. The results for each province are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Average annual tourism eco-efficiency ML Indices and their decomposition for chinese provinces from 2011 to 2020.
Overall, the average ML index from 2011 to 2020 was 1.165, indicating a positive trend in the development of tourism eco-efficiency, with an annual growth rate of 16.5%. When examining the decomposed indicators, the average values for TC, EC, PEC, and SEC were 1.113, 1.069, 1.062, and 1.039, respectively. This suggests that the main internal driver for optimizing tourism eco-efficiency is technological progress, while the impact of efficiency improvement is not as pronounced as technological progress. Further decomposition of EC into PEC and SEC reveals that the growth rate of pure technical efficiency is 2.3% higher than that of scale efficiency, indicating its greater contribution to tourism eco-efficiency. Table 3 further indicates that provinces with higher ML indices generally exhibit higher overall levels of development in terms of TC and PEC.
Figure 3 illustrates the average indices of tourism eco-efficiency for various stages in China. It can be observed that, except for the 2019–2020 period, the average ML index exceeds 1 in all other stages. The ML index decreased by 4.7% overall during 2019–2020, partially due to the negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The decomposition of the index reveals that prior to 2019, the improvement in tourism eco-efficiency was mainly driven by technological progress. However, during 2019–2020, the role of efficiency gains became increasingly prominent. In this period, the enhancement of scale efficiency was the main contributor to improved efficiency, with both showing synchronous growth. Notably, there were significant improvements in internal management and resource utilization among tourism enterprises during this stage [67]. Overall, technological progress remains the essential driving factor for the enhancement of tourism eco-efficiency.
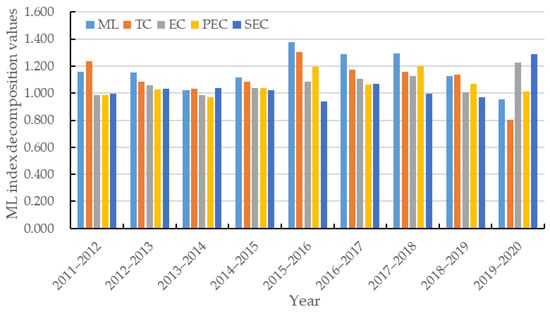
Figure 3.
Average ML indices of tourism eco-efficiency and their decomposition for each year in china from 2011 to 2020.
5.2. Analysis of the Impact of Human Capital and Tourism Industry Agglomeration on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
5.2.1. Benchmark Regression Analysis
Tobit regression is conducted using Stata 16.0 software to examine the impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. The LR test under the maximum likelihood method yields a p-value of 0.000, strongly rejecting the original hypothesis. Then, panel regression is conducted using the random Tobit model with individual effects. Models (1) to (5) presented in Table 4 demonstrate a significantly positive correlation between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency, even with the inclusion of control variables, thus supporting the validity of Hypothesis 1. Furthermore, the variance inflation factor (VIF) has a maximum value of 1.28 and a mean value of 1.128, significantly lower than 10, indicating the absence of any significant multicollinearity issue.

Table 4.
Benchmark regression results.
Among the control variables, the foreign investment level and the degree of government intervention are not significantly negatively correlated. The former implies the potential existence of the “pollution paradise” hypothesis, although the inhibitory effect may not be evident probably due to the obscured impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and time lag [41]. The latter suggests that the increase in the proportion of fiscal expenditure fails to promote tourism eco-efficiency, highlighting the implications of ecological investment being marginalised in favor of a singular “GDP-only” appraisal orientation, often lacking sustainable policy mechanisms [68]. Moreover, tourism consumption capacity significantly inhibits tourism eco-efficiency, suggesting that high consumption levels drive income growth alongside an expanding carbon footprint, with energy consumption rising at a rate surpassing economic growth. Conversely, the industrial structure ratio exhibits a significant positive correlation, probably due to the tertiary industry’s more obvious “pro-environmental” attributes compared to primary and secondary industries, where a higher tertiary industry ratio corresponds to reduced negative environmental impact [36].
5.2.2. Robustness Test
This study employs three primary methods to assess the robustness of the model. Firstly, the core explanatory variables are substituted with alternative metrics. Specifically, the horizontal level of education coverage (Chc), the vertical level of schooling duration (Lhc), and the overall evaluation value of human capital quantified by the entropy method are integrated into the original model. Results from Models (1)–(3) in Table 5 demonstrate robust regression outcomes. Secondly, the sample regression period is modified. Given the great impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tourism sector since late 2019, data spanning 2011–2018 is used for regression analysis, confirming the robust of the findings as indicated in Model (4). Lastly, the regression model itself is altered. Generalised Method of Moments estimation (IV-GMM) is employed for robustness testing, with human capital lagged by one period serving as the instrumental variable. Model (5) affirms the robustness of the results. Notably, the LM test convincingly rejects the initial hypothesis of unidentifiable instrumental variables. Furthermore, the Wald F-statistic is 13.666, exceeding the critical value for the weak identification test at the 15% level, refuting the original notion of weakly identifiable instrumental variables and validating their selection in the analysis.

Table 5.
Robustness testing results.
5.2.3. Regional Heterogeneity Tests
In this study, to further explore regional disparities, the sample is divided into eastern, central, and western regions. From Table 6, with and without the inclusion of control variables, the positive correlation in the three major regions’ mechanisms of action is pronounced. Regarding the contribution of human capital to enhancing tourism eco-efficiency, it is ranked as “center > east > west”. The central region benefits from its strategic position of “bridging the eastern and western areas and connecting the southern and northern parts”. It not only inherits spillover effects from the east but also benefits from policies promoting western development, leading to the most substantial impact within the region. Furthermore, the substantial impact of the central region can be attributed to the earlier exploitation of resources in the east, resulting in a reduced human capital dividend in the east due to the law of diminishing marginal returns. Then the impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency is comparatively lower in the east than in the central region. In contrast with the eastern and central regions, the western region faces a scarcity in human resources, highlighting the need to strengthen its influence on tourism eco-efficiency.

Table 6.
Results of the regional disparities test.
5.2.4. Mediation Effect Test
This study employs a stepwise regression analysis with tourism industry agglomeration as a mediating variable. The significance of Model (5) in Table 4 serves as a prerequisite for further analysis. Subsequently, the effect of human capital on enhancing tourism industry agglomeration is examined in Model (1) of Table 7, following a positive confirmation. The study then integrates tourism industry agglomeration into the regression model linking human capital and tourism eco-efficiency to assess the significance of the coefficient associated with tourism industry agglomeration and human capital, as demonstrated by the notably significant results in Model (2) of Table 7. Additionally, the investigation explores the impact of mediator variables on core explanatory variables by examining the changes in coefficient value; specifically, the regression coefficient of human capital decreases from 3.376 to 1.874, thereby confirming Hypothesis 2. Moreover, the comprehensive assessment of human capital, measured by the entropy method, is integrated into the stepwise regression equation to validate the robustness of the findings. The correlation coefficients and changes in significance levels are presented in Model (3) and Model (4) in Table 7.

Table 7.
Mediation effect test results.
Based on the outlined methodology, the mediating effects are further examined for each region to assess their validity. Analysis of the regression results in Table 6 and Table 8 indicate alternations in the coefficients representing the influence of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. Specifically, in the eastern region, the coefficient decreases from 2.858 to 2.385 while remaining significant; in the central region, it decreases from 5.125 to 2.615; and in the western region, it decreases from 2.174 to 0.971. These findings suggest that tourism industry agglomeration acts as a mediator between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency. This result also corroborates Hypothesis 2. It is worth noting that in Model (6) of Table 8, the effect of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency is found to be nonsignificant in the western region, suggesting a fully mediated effect that distinguishes it from the other regions. In cases of full mediation, the mediating variable fully explains the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. In essence, the total effect of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency in the western region operates entirely through the mediating variable of tourism industry agglomeration. The possible reasons for this are the factors such as undeveloped infrastructure, abundant high-quality tourism resources, and policy-oriented development frameworks, placing regional tourism in an early development stage. Therefore, the scale effects of industrial agglomeration have the potential to drive sustainable tourism growth most effectively in the western region at its current developmental phase.

Table 8.
Regional mediation effect test results.
5.2.5. Threshold Effect Test
Tourism industry agglomeration has been designated as a threshold variable, and empirical testing is conducted using a panel threshold regression model. Drawing upon Hansen’s method to confirm the presence of the threshold effect [69], the “self-help method” involves 300 iterations for a multi-threshold test. The Tag1 test results depicted in Table 9 reveal that tourism industry agglomeration successfully clears the double threshold test. Subsequently, employing a two-threshold model in Table 10 yields the results. Model (1) in Table 10 demonstrates that, with the moderating impact of tourism industry agglomeration, the positive influence of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency experiences continuous augmentation, thereby validating Hypothesis 3.

Table 9.
Threshold test results.

Table 10.
Results of the panel threshold model regression.
This study employs two methods to confirm the robustness of the threshold regression results. Firstly, the comprehensive evaluation value of human capital, as determined by the entropy method, is integrated into the threshold model. Model (2) in Table 10 affirms that hypothesis 3 still holds, with the corresponding threshold test results shown in Tag2 within Table 9. Secondly, tourism industry agglomeration facilitates industrial structure optimization by leveraging scale effects and technological spillovers [18]. Considering that an industrial structure can effectively leverage human capital to enhance environmental benefits [13,54], the tourism structure effect (Tis) is introduced as a new threshold variable for both the threshold test and regression analysis. The selection criteria for Tis are based on the methodology by Wang et al. [46]. The results delineated in Model (3) of Table 10 illustrate the sustained nonlinear characteristic of increasing “marginal effect”, with the respective results of the threshold test displayed under Tis in Table 9.
6. Discussion
This study underscores the important role of human capital in enhancing the ecological environment and extends this empowering effect to the domain of tourism. Under the requirements of sustainable tourism and high-quality development, it delves into the specific influence mechanisms through which human capital and tourism industry agglomeration impact tourism eco-efficiency. The findings of the study reveal that:
In the influencing mechanisms, technological progress serves as the intrinsic driving force behind optimizing tourism eco-efficiency, consistent with findings by Xue et al. [70]. In the regression analysis of external factors, human capital exerts a significantly positive promotional effect on tourism eco-efficiency, a finding corroborated through rigorous testing by multiple methodologies. This is consistent with the findings of Lu et al. [20] and Wei et al. [45], who, through regression analyses, demonstrated that human capital plays a pivotal role in enhancing tourism eco-efficiency. Specifically, they highlighted that a higher education level among tourism personnel contributes favorably to green sustainable development. This study differs from previous works by assessing human capital from two perspectives: the horizontal level of education coverage and the vertical level of schooling duration, as opposed to examining a singular factor. Beyond the tourism sector, the impact of human capital is further discussed in varied contexts, such as industrial development, urban construction, and environmental quality. Most scholars posit a positive correlation between human capital and environmental implications [26,27,28,51,52,55], as evidenced by studies demonstrating its role in bridging income gaps [26], reducing carbon emissions [28], and fostering a pro-environmental attitude [55]. In this study, the focus shifts to how the scale effect and agglomeration effect, catalyzed by internal and external human capital characteristics, optimise environmental conditions, echoing viewpoints from Qin et al. [51] and Hao et al. [55]. However, dissenting views exist, with some scholars believing that the increased population mobility, population size, and population density may exert environmental pressure on urban development [30,31,32]. Overall, human capital functions as a linchpin for enhancing tourism eco-efficiency. Therefore, advancing education levels and deepening education outreach to enhance environmental standards through heightened human capital is an imperative path for the sustainable development of the tourism industry.
There are two main conclusions in the realm of pathway influence. Firstly, tourism industry agglomeration plays an important intermediary role in harnessing human capital towards enhancing tourism eco-efficiency. Following regional regression analysis, this intermediary function persists, with a particularly pronounced impact observed in the western region. Secondly, a threshold effect of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency development is identified, with the optimization of tourism eco-efficiency experiencing incremental gains influenced by tourism industry agglomeration. This conclusion remains robust even after replacing core explanatory and threshold variables. Compared to the focus on human capital in facilitating sustainable development through green innovation and industrial upgrading as mediators, as identified by Ni et al. [27], this study emphasises tourism industry agglomeration as the mediating variable. Existing studies primarily examine the economic development facilitated by the interaction effects of industrial agglomeration without delving into the implications for the tourism sector and environmental outcomes [49,50,57]. Conversely, Zhao et al. highlighted the role of human capital in fostering environmental quality through technological innovation [13] and industrial restructuring [54] as moderating variables. These diverging paths of transmission delineate distinct research perspectives from this study, which prioritises the mediating role of tourism industry agglomeration, coupled with an in-depth analysis of its threshold function. Therefore, the contribution of this study lies in exploring the intricate mechanisms of the variables involved.
In the analysis of regional disparities, the positive correlation between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency is significant across the eastern, central, and western regions, with the central region reaping a more pronounced human capital dividend. Because of the divergence in selected regions and research objects, less literature aligns with the conclusions of this study. On a national scale, Wei et al. [45] asserted that the driving effect of population quality on tourism eco-efficiency is most potent in the eastern region, which a finding somewhat incongruent with this study. This disparity could be attributed to the temporal scope of Wei et al.’s study [45], spanning 2001–2016, predating the 2011–2020 period under examination in this study. Over the interval of 2016–2020, it is conceivable that the human capital dividend in the eastern region has gradually decreased. Nevertheless, it is acknowledged that the developmental impetus in the western region lags behind other regions. Therefore, regardless of temporal variations, sustainable tourism development in the western region remains a critical issue warranting attention.
7. Conclusions and Suggestions
7.1. Conclusions
This study, utilizing panel data from 30 provinces in China spanning from 2011 to 2020, employs methods like the super-SBM model, Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) index model, and econometric statistics to investigate the intrinsic factors of optimizing tourism eco-efficiency and the multidimensional impact of human capital on tourism eco-efficiency. The findings indicate the following:
Firstly, among internal factors, technological advancement contributes more to the improvement of tourism eco-efficiency than efficiency gains. Secondly, in the realm of external influencing mechanisms, human capital significantly and positively enhances tourism eco-efficiency, a conclusion upheld through robustness analysis and regional heterogeneity analysis. Particularly noteworthy is the pivotal role that human capital in the central regions plays in optimizing tourism eco-efficiency. Thirdly, Through the mediation of tourism industry agglomeration, human capital facilitates the enhancement of tourism eco-efficiency, with this mediating effect particularly pronounced in the western regions. Finally, within the threshold mechanism of tourism industry agglomeration, the incremental effectiveness of human capital in optimizing tourism eco-efficiency is observed, a conclusion robustly supported by the analysis.
Overall, these findings explore both internal and external factors influencing the optimization of tourism eco-efficiency. By integrating the intrinsic and extrinsic characteristics of human capital into tourism research, they underscore the critical role of human capital in addressing environmental challenges within the tourism industry. Moreover, they demonstrate that under the dual spillover effects of human capital and tourism industry clustering, efforts to optimise the tourism environment can be significantly more effective. These discoveries deepen our exploration and understanding of variable relationships, offering unique perspectives and conclusions for research fields such as ecotourism and sustainable tourism development.
7.2. Suggestions
To foster harmony relationship between the economy and the environment and advance the sustainable development of the tourism industry, this study puts forth the following recommendations.
Firstly, it is imperative to pay attention to talent cultivation mechanisms and enhance the structure of human capital. Human capital can directly or indirectly enhance tourism eco-efficiency. Therefore, governments should boost investment in education and formulate pertinent education policies to ensure equitable distribution of education resources. Additionally, tourism enterprises should proactively offer opportunities for knowledge enhancement and skills training, alongside incentives, to improve the quality and competence of their human capital.
Secondly, differentiated industrial positioning strategies should be formulated, and regional coordinated development should be fostered. Considering the varying effects of human capital promotion and mediation across regions, it is crucial to acknowledge and address regional disparities. Accordingly, in the eastern region where the human capital dividend has already manifested, efforts should be directed towards consolidating existing construction results and seeking innovative pathways to enhance tourism eco-efficiency. The central region, characterised by robust developmental momentum, can serve as a pivotal link for “East-West interoperability”, facilitating the swift exchange of talents and efficient resource allocation. In the resource-constrained western region, emphasis should be placed on strengthening infrastructure construction to guarantee talent cultivation for industrial agglomeration.
Thirdly, it is crucial to advance efficient industrial agglomeration and enhance the synergistic adaptation of factors. The intermediary and threshold effects underscore the key facilitative role of tourism industry agglomeration, necessitating a heightened focus on enhancing the level of tourism industry agglomeration. On the one hand, optimizing the industrial layout and fostering the cyclic accumulation and synergistic adaptation of human capital through the spillover effect and scale effect of industrial agglomeration are imperative. On the other hand, dismantling barriers to the flow of capital, talent, information, and other factors across regions and industries; improving resource utilization efficiency; and fostering sustainable tourism development through the enhancement of tourism eco-efficiency should be prioritised.
7.3. Limitations
In conclusion, while this study delves into the relationship between human capital and tourism eco-efficiency, there are still some limitations. Firstly, the exclusion of Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, and Tibet from the study due to data availability may impact the accuracy of the results. Secondly, The process of sustainable development entails mutual influence and interaction between regions. Future studies may benefit from integrating spatial mapping and spatial econometric modelling to examine potential spatial spillover effects in the correlation between human capital development and tourism eco-efficiency. This analysis could further underscore the significance of fostering regional interconnectivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.W. and N.W.; Data curation, Q.W. and M.W.; Formal analysis, Q.W. and M.W.; Funding acquisition, Q.C.; Writing—original draft, Q.W.; Writing—review and editing, M.W. and Q.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Innovation Teams in Higher Education Institutions of Fujian Province: Integrated development of agriculture, culture, and tourism and Rural Revitalisation (No. 72202301002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are not published due to privacy or ethical constraints and can be obtained from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liao, Q.; Zeng, J.; Qu, J. Overseas Environment and Health Development Strategic Plan and its Inspiration. J. Environ. Health 2014, 31, 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of Agricultural Extension Service for Sustainable Agricultural Development Using a Hybrid Entropy and TOPSIS Method. Sustainability 2021, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapera, I. Sustainable tourism development efforts by local governments in Poland. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y. The perspective of tourism sustainable development: A review of eco-efficiency of tourism. Tour. Trib. 2017, 32, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, M.; Sun, Y.Y.; Faturay, F.; Ting, Y.P.; Geschke, A.; Malik, A. The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, P.; Dubois, G. Tourism travel under climate change mitigation constraints. J. Transp. Geogr. 2010, 18, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zha, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Han, Y. Dual-carbon goal of China’s tourism industry under high-quality development: Evaluation & prediction, major challenges and realization path. J. Chin. Ecotour. 2021, 11, 471–497. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X. Comprehensive implementation of the new development concept is the road to high-quality development of the tourism industry. Tour. Trib. 2023, 38, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hickel, J. The sustainable development index: Measuring the ecological efficiency of human development in the anthropocene. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 167, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Ecological efficiency management of tourism scenic spots based on carbon footprint analysis. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2020, 15, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y. Research on the Influence Mechanism of Human Capital and Technological Innovation on Environmental Pollution: An Empirical Study Based on 285 Cities Across the Country. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q. Spatial difference of human capital promoting regional tourism economic efficiency: Empirical research based on “Hu Line”. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, J. Effect of Human Capital Accumulation on Environmental Pollution in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Based on the Moderating Effect of Technological Innovation. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2023, 43, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Mo, Y.; Ma, J. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Tourism Life Cycle: The Case of Guilin from 2011 to 2022. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Yu, B.F.; Zhe, G.Z. Population growth and the environmental Kuznets curve. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakar, N.D.; Gedikli, A.; Erdoğan, S.; Yıldırım, D.C. Exploring the nexus between human capital and environmental degradation: The case of EU countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zeng, X. Regional Human Capital, Resources Agglomeration Capacity and the Urban Sprawl. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 21, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Analysis on the Impact of Tourism Industry Agglomeration on Ecological Efficiency and it’s Regional Differences of Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 796–807. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J. Research on Associated Action between Tourism Industrial Agglomeration Development and Carrying Capacity Ascension in China’s Coastal Regions. Commer. Res. 2016, 10, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Gong, H. A study on the measurement, temporal and spatial characteristics and influencing factors of tourism eco-efficiency in China. Stat. Decis. 2020, 36, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, T.W. Investment in Human Capital. Ame. Eeon Rev. 1961, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, R.E. On the mechanics of economic development. J. Monet. Eeon. 1988, 22, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Ji, M. Development of Platform Economy and Urban–Rural Income Gap: Theoretical Deductions and Empirical Analyses. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Financial support for agriculture, human capital and income gap between urban and rural residents. Economic Survey. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 23, 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Sun, T.; Wang, S. Dividend from demographic structure, fiscal expenditure bias and urban-rural income gap in China. Econ. Perspect. 2021, 1, 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gulaliyev, M.G.; Muradov, R.S.; Hajiyeva, L.A.; Muradova, H.R.; Aliyev, E.S. Study of human capital development, economic indicators and environmental quality. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.K.; Ahmad, S.F.; Alshammari, T.O.; Liang, H.S.; Alsanie, G.; Irshad, M.; Alyafi-AlZahri, R.; Binsaeed, R.H.; Al-Abyadh, M.H.A.; Abu Bakir, S.M.M. The role of environmental regulation and green human capital towards sustainable development: The mediating role of green innovation and industry upgradation. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 421, 138497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.; Wang, Z.H.; Hassan, S.T. Renewable energy, economic growth, human capital, and CO2 emission: An empirical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 20619–20630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Murad, M.W.; Noman, A.H.M.; Ozturk, I. Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: Testing Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, J. The net work analysis on spatial correlation of environmental pollution in the Yangtze river Economic Belt: Based on the comprehensive indicator of water and air pollution. Econ. Prob. 2019, 9, 86–92+111. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Feng, K.; Hu, P. An empirical study of population growth, industrial structure optimization and regional ecological efficiency. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci.) 2019, 40, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Luo, N. Effect of urban scale on eco-efficiency and the regional difference analysis. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Appiah-Twum, F.; Long, X. Human capital, trade competitiveness and environmental efficiency convergence across Asia Pacific countries. Environ. Resour Econ. 2023, 85, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, W. Change of agricultural ecological efficiency under effect of rural population aging. J. South China Agr. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 20, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, X. Study on the effect of population structure on ecological efficiency in China. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2022, 44, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wen, Z. Environmental regulation, technological innovation and ecological efficiency: Empirical research on China’s provincial panel data based on 2006–2020. J. Tech. Econ. Manag. 2023, 4, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gössling, S.; Hansson, C.B.; Hörstmeier, O.; Saggel, S. Ecological footprint analysis as a tool to assess tourism sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 43, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yu, A.; Wang, M. Carbon footprint evaluation in tours: A case study of Zhoushan Islands. Tour Sci. 2011, 4, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Chen, T.; Yin, S.; Li, X. Regional tourism eco-efficiency model and an empirical research of Hainan Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Li, C.; Peng, H.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Tourism eco-efficiency at the provincial level in China in the context of energy conservation and emission reduction. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gan, C.; Wang, K. Relationship between tourism industry agglomeration and tourism eco-efficiency: An empirical analysis based on the provincial panel data of China. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 37, 99–107+116. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C. Influencing factors of regional tourism eco-efficiency under the background of green development in the western China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3512–3524. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, D. Dilemmas and ways out for tourist participation in tourism eco-efficiency optimization. Tour. Trib. 2016, 31, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Surugiu, C.; Surugiu, M.R.; Breda, Z.; Dinca, A.-I. An Input-Output Approach of CO2 Emissions in Tourism Sector in Post-Communist Romania. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2012, 3, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Guo, W. A study on the spatial-temporal characteristics and influential factors of tourism ecological efficiency. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. A study on spatial-temporal heterogeneity of environmental regulation on tourism eco-efficiency: Taking Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as an example. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 750–758. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, C. Human capital structure upgrading and economic growth: A reconsideration of disparities among China’s eastern, central and western regions. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 50–63. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Shi, P.; Hu, J. Industrial agglomeration and high- quality economic development: Examples of 107 prefecture- level cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Reform 2020, 1, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Research on the mechanism of industrial collaborative agglomeration promoting high-quality economic development: Nonlinear relationship, innovation efficiency path and the moderating role of human capital. West Forum 2022, 32, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Li, H. Industrial agglomeration, human capital and regional innovation: An empirical study based on the perspective of heterogeneous industrial agglomeration and cooperative agglomeration. Inq. Econ. Iss. 2017, 12, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Kang, L.; Liang, W. Research on innovation effect of regional human capital based on the view of green low-carbon development—An empirical study of regional industrial enterprises panel data in China. Hum. Resour. Dev. China 2018, 35, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Hu, J. Influences of human capital on environmental quality. Urban Prob. 2019, 10, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chankrajang, T.; Muttarak, R. Green returns to education: Doesschooling contribute to pro-environmental behaviours? Evidence from Thailand. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 131, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.D.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Hu, M. Mechanism of human capital, industrial structure adjustment and green development efficiency. China. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Li, Y. The impact of human capital on environmental quality: Empirical evidence and mechanism analysis. J. Environ. Econ. 2022, 7, 142–160. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yi, D. A study on the impact of human capital on China’s urbanization. Econ Theory. Bus Manag. 2017, 9, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K. Industrial agglomeration, human capital accumulation and high-quality growth of regional economy. J. Hubei Eng. Univ. 2023, 43, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, G. Research on the influence of tourism industry agglomeration in ethnic regions on tourism ecological efficiency—A case study of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture in Hubei. Commer. Sci. Res. 2021, 28, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liao, W.; Huang, M.; Deng, R. Calculation of tourism carbon footprint on final consumption: A case of Jiangxi Province. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 27, 121–124,168. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Huang, W. Agglomeration and green technology innovation efficiency of industrial enterprises—Based on spatial statistical analysis. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2022, 48, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Yan, P. Environmental efficiency and environmental total factor productivity growth in China’s regional economies. Econ. Res. J. 2010, 5, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, H. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Between China’s Tourism Eco-efficiency and Tourism Green Innovation Efficiency. J. Zhongzhou Univ. 2021, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Yin, R.; Yuan, X. The Tourism Eco-Efficiency Measurement and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Cai, C.; Liu, Y. Impact of tourism development on the construction of urban ecological civilization and its spatial spillover effect: An empirical study on 284 prefecture level and above cities in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2800–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold Effects in Non-dynamic Panels: Estimation, Testing, and Inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Li, X.; Ahmad, F.; Abid, N.; Mushtaq, Z. Exploring Tourism Efficiency and Its Drivers to Understand the Backwardness of the Tourism Industry in Gansu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).