Enhancement in Dewatering Efficiency of Disrupted Sludge through Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation—Sustainable Sludge Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Excess Sludge and Flocculants
2.2. Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation
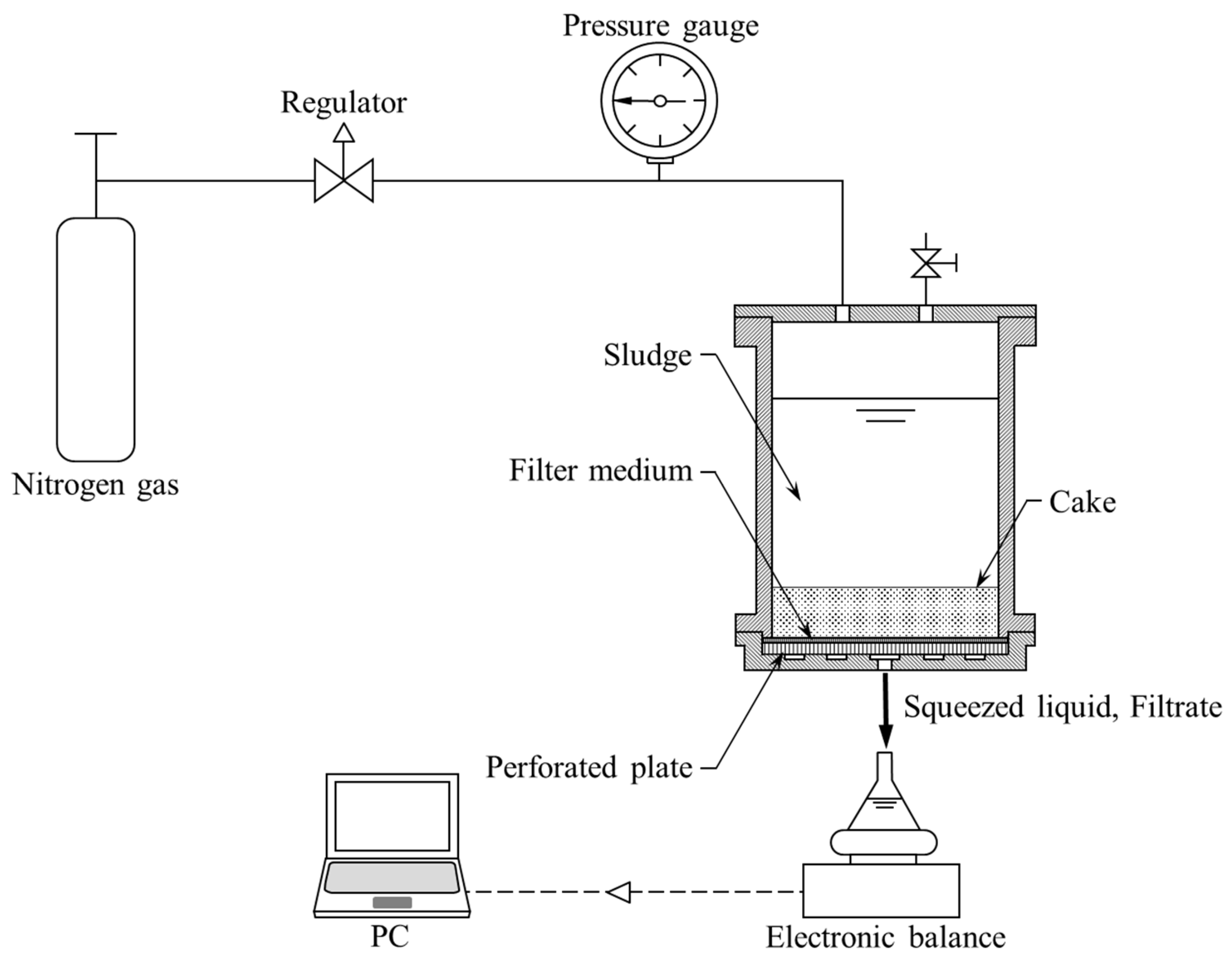
2.3. Filtration and Mechanical Expression
3. Results and Discussion
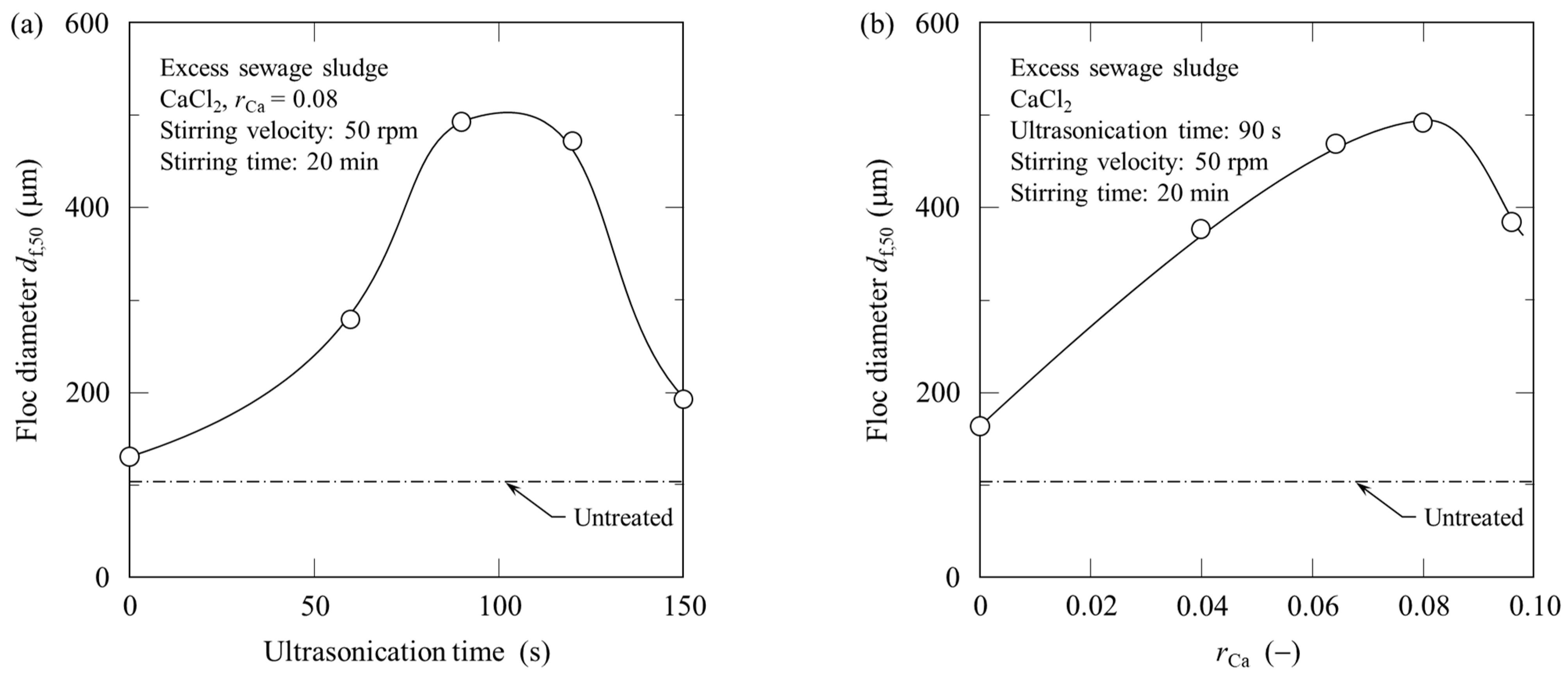
3.1. Self-Flocculation by Ultrasonication
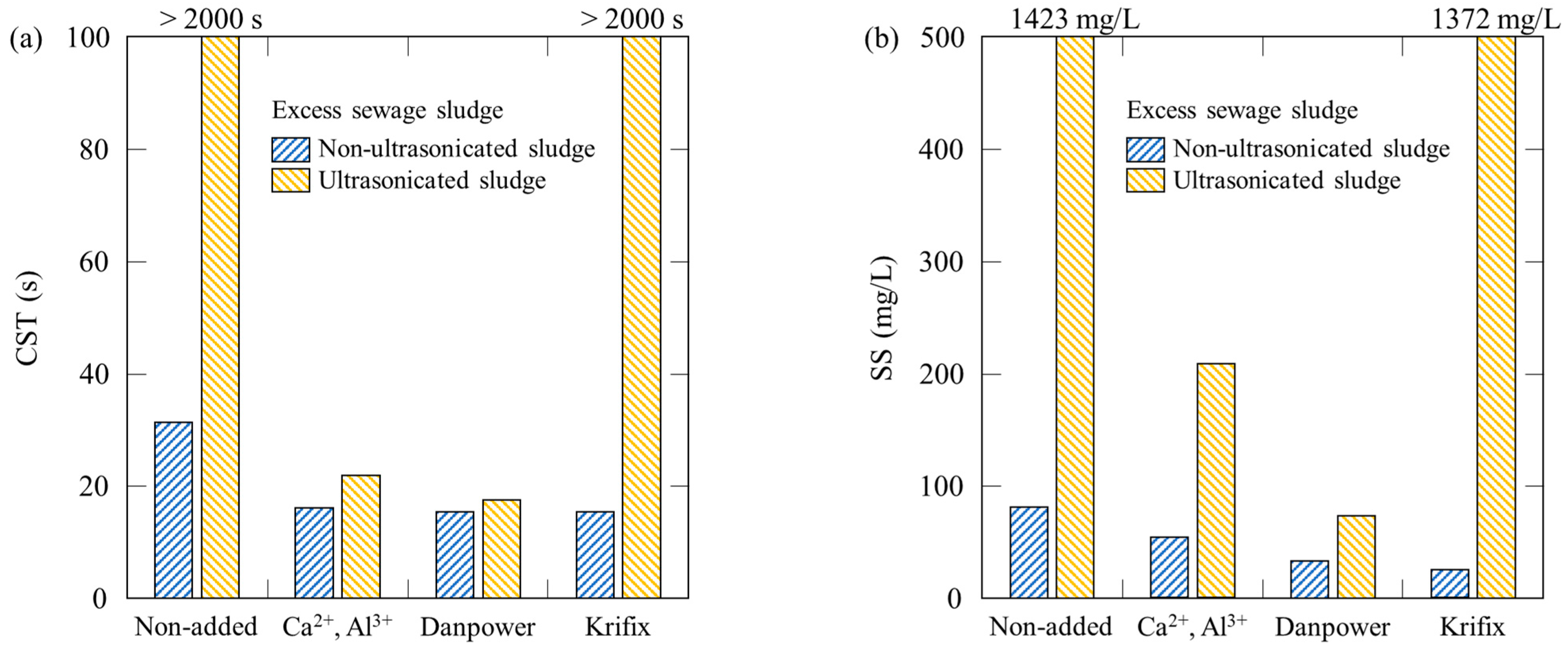
3.2. Salt Addition to Ultrasonicated Sludge
3.3. Effect of Polymeric Flocculants
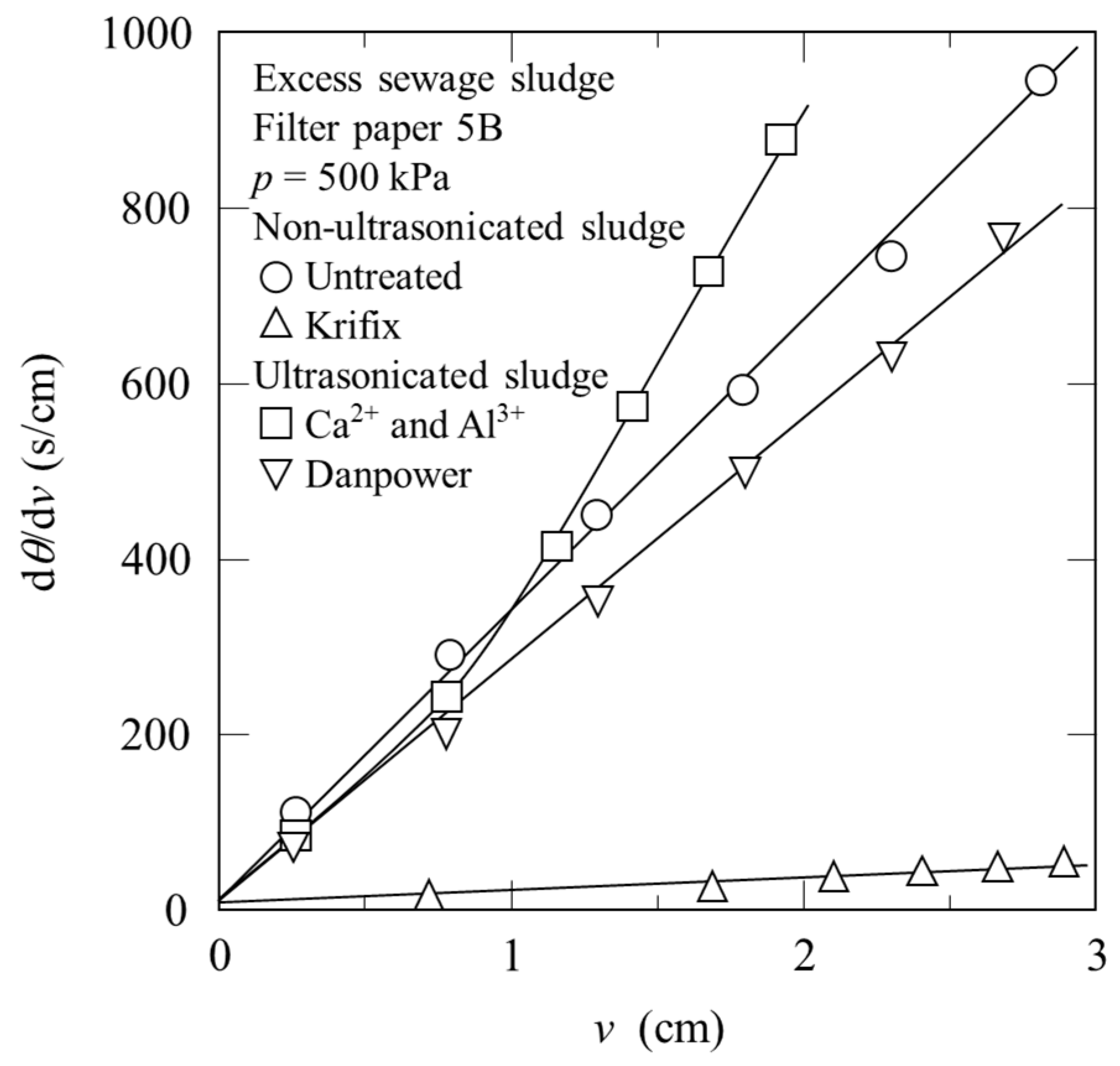
3.4. Filtration and Mechanical Expression Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugurbekova, G.; Nagyzbekkyzy, E.; Sarsenova, A.; Danlybayeva, G.; Anuarbekova, S.; Kudaibergenova, R.; Frochot, C.; Acherar, S.; Zhatkanbayev, Y.; Moldagulova, N. Sewage sludge management and application in the form of sustainable fertilizer. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubus, M. Current trends in sustainable sewage sludge management—A case study for Poznań Country, Poland. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, S. Sludge derived fuel and its potential markets. Japan J. Water Pollut. Res. 1986, 9, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Tan, W.; Zhong, N.; Liu, L. Effects of thermal treatment on physical and expression dewatering characteristics of municipal sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Matsuda, A.; Murase, T. The effect of freezing and thawing process on the expression characteristics and final moisture content of excess activated sludge. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 1990, 16, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J. Effect of initial water content on the dewatering performance of freeze-thaw preconditioned landfill sludge. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Yan, S.; Xing, X.H.; Sun, X.; Jurcik, B. Progress and perspectives of sludge ozonation as a powerful pretreatment method for minimization of excess sludge production. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, M.; Vaxelaire, J.; Olivier, J.; Dieudé-Fauvel, E.; Baudez, J.C. Compression dewatering of municipal sludge: Effects of salt and pH. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4448–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeneneh, A.M.; Chong, S.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, H.M.; Kayaalp, A. Effect of ultrasonic, microwave and combined microwave-ultrasonic pretreatment of municipal sludge on anaerobic digester performance. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.Y.; Sun, J.P.; Li, S.F.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, A.Q. Effect of microwaves combined with peracetic acid to improve the dewatering performance of residual sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 44885–44899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, N.; Nakashima, K.; Obata, H. High-level dewatering of activated sludge using osmotic pressure. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 2022, 48, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X. Effect of electrolytic zero-valent iron activated sodium hypochlorite on sludge dewatering performance. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Enhanced technology based for sewage sludge deep dewatering: A critical review. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.; Su, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, S.; Pang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Wu, B.; Lian, J.; Deng, L. Coupling mechanism and parameter optimization of sewage sludge dewatering jointly assisted by electric field and mechanical pressure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Wu, Y. Enhanced technology for sewage sludge advanced dewatering from an engineering practice perspective: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Q.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J.; Shen, L.; Teng, J.; Lin, H. Enhanced sludge dewatering using a novel synergistic iron/peroxymonosulfate-polyacrylamide method. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wei, H.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Lu, H. Preparation, properties, and application of biochar for improving sewage sludge dewatering performance: A review. Water 2023, 15, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cao, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Sanchuan, M.; Wang, Z. Study on ultrasonic treatment for municipal sludge. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 57, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N.; Minato, J.; Nishikawa, M.; Kawasaki, K. Improvement in settling performance of disrupted sludge by stepwise addition of inorganic salts. Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 2018, 44, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçal, T. Enhancing sludge conditioning and dewatering characteristics by active surfaces modified with fast recombining immobilized nanoparticles. Drying Technol. 2022, 40, 2128–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, X.; Luo, K.; Song, Y.H.; Liu, R.G. Settleability and dewaterability of sewage sludge with modified diatomite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 72159–72168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.O.; Forster, C.F. Effects of sonication on activated sludge. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1990, 12, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Goutvrind, R. The use of ultrasonics in the treatment of waste activated sludge. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 14, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Goutvrind, R. Ultrasonic treatment of waste activated sludge. Environ. Prog. 2006, 25, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.X.; Wong, W.C. Optimization of extracellular polymeric substance extraction method and its role in the dewaterability of sludge. Huanjing Kexue 2013, 34, 2752–2757. [Google Scholar]
- Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N.; Yamada, M.; Hwang, K.J.; Cheng, T.W. Ultrahigh-pressure expression of activated sludge assisted with self-flocculation caused by ultrasonication. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 112, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Guo, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Yue, Q.; Shi, W.; Feng, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, B. Effect of coagulation treatment on sludge dewatering performance: Application of polysilicate and their mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Mizukawa, Y. Measurement of bound water in excess activated sludges and effect of freezing and thawing process on it. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1992, 25, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, S.; Kimura, T.; Kondo, T.; Mitome, H. A standard method to calibrate sonochemical efficiency of an individual reaction system. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2003, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, H.P. Resistance and compressibility of filter cakes. Part I. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1953, 49, 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tiller, F.M.; Lu, W.M. The role of porosity in filtration VIII: Cake nonuniformity in compression-permeability cells. AIChE J. 1972, 18, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, N.; Kuwajima, Y.; Kawahara, H.; Yamashita, R.; Iritani, E. Special features of microbial cake under high pressure conditions in microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 303, 122234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Gong, W.X.; Liu, X.W.; Tian, L.; Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y. Production of a novel bioflocculant by culture of Klebsiella mobilis using dairy wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 36, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, T.T.; Yan, S.; Hoang, N.V.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Bacterial polymer production using pre-treated sludge as raw material and its flocculation and dewatering potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, B.; Zhao, S.; Li, F. Combined conditioning of inorganic coagulant and polyamine to improve the dewaterability of municipal sludge, minimize dosage and reduce the influence of filtrate. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 1600–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakii, K.; Kato, H.; Ohara, K.; Kawai, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Kuriyama, M.; Shirakashi, T. Reflocculation of sewage activated sludge disrupted by ultrasonication. Seibutu-Kogaku Kaishi 1994, 72, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambo, N.; Watanabe, Y. Physical characteristics of flocs-I. The floc density function and aluminum floc. Water Res. 1979, 13, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, B.F. Studies in filtration. III. Derivation of general filtration equations. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1935, 27, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, N.; Uchida, T.; Takahashi, H.; Iritani, E. An evaluation of the relationship between membrane properties and the fouling mechanism based on a blocking filtration model. Separations 2024, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohwada, T.; Sagisaka, S. Osmoregulation of bacteria. Kagaku Seibutsu 1990, 28, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Thapa, K.B.; Hoadley, A.F.A. Application of filtration aids for improving sludge dewatering properties—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Floc diameter df,50 (µm) | 103.5 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | 497.4 |
| Density of solid (kg/m3) | 1450 |
| Solid content (g/L) | 5 |
| CST (s) | 31.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azadi, J.; Yamauchi, K.; Matsubara, K.; Katagiri, N. Enhancement in Dewatering Efficiency of Disrupted Sludge through Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation—Sustainable Sludge Management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177427
Azadi J, Yamauchi K, Matsubara K, Katagiri N. Enhancement in Dewatering Efficiency of Disrupted Sludge through Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation—Sustainable Sludge Management. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177427
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzadi, Juya, Kenji Yamauchi, Kento Matsubara, and Nobuyuki Katagiri. 2024. "Enhancement in Dewatering Efficiency of Disrupted Sludge through Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation—Sustainable Sludge Management" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177427
APA StyleAzadi, J., Yamauchi, K., Matsubara, K., & Katagiri, N. (2024). Enhancement in Dewatering Efficiency of Disrupted Sludge through Ultrasonication and Re-Flocculation—Sustainable Sludge Management. Sustainability, 16(17), 7427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177427






