“Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of PCSH
2.2.2. Adsorption Experiment
2.3. Characterization and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
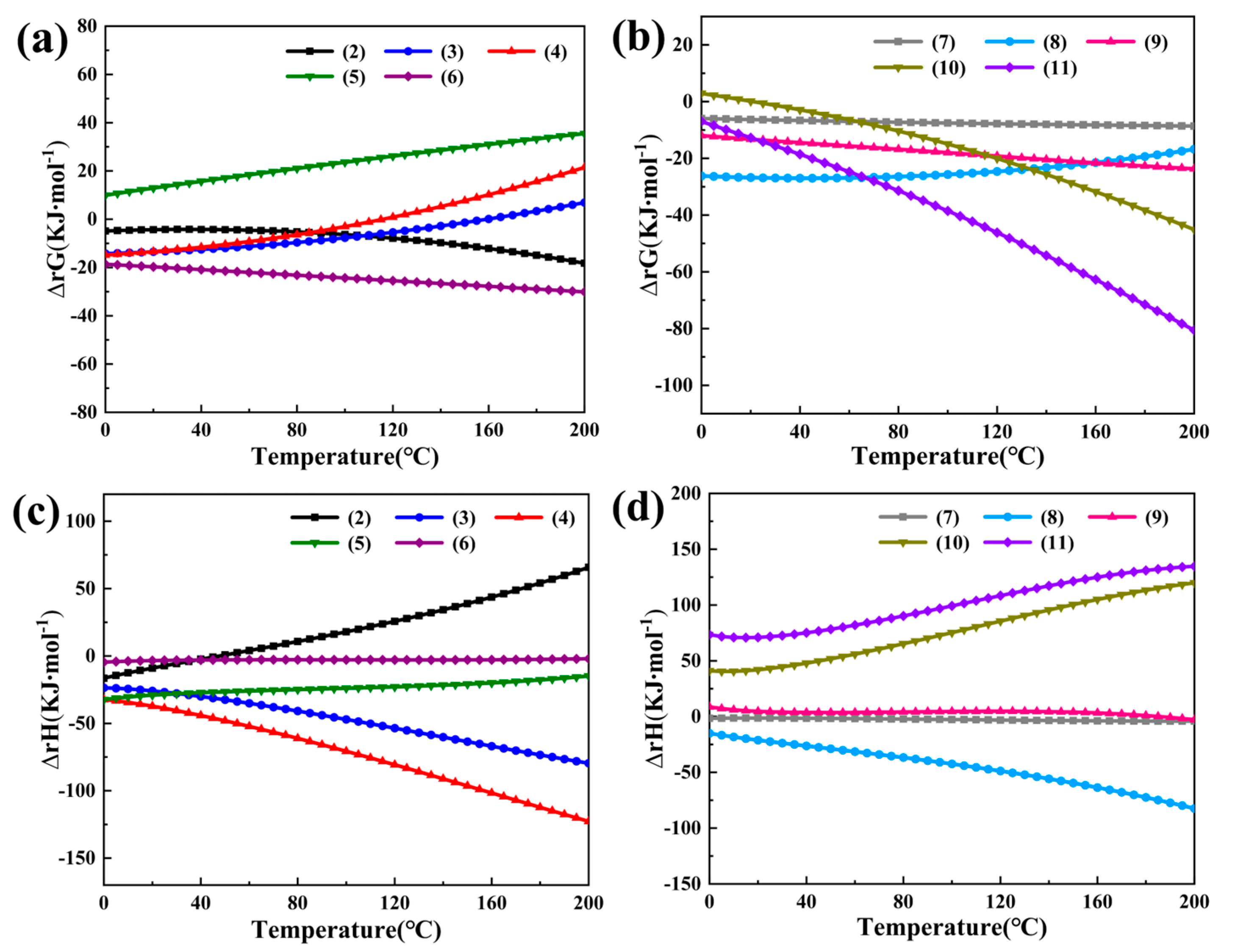
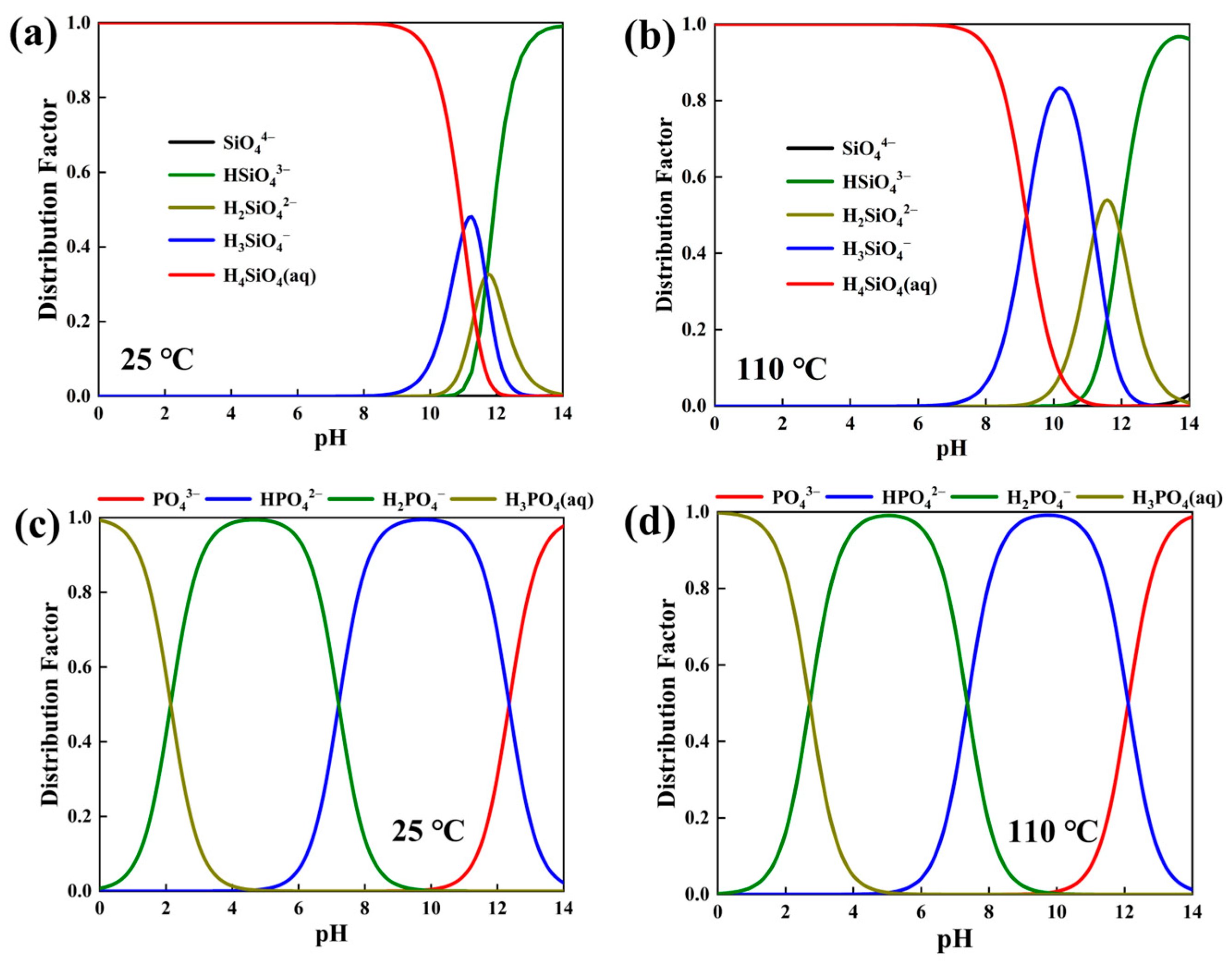
3.1. Synthetic Thermodynamic Analysis
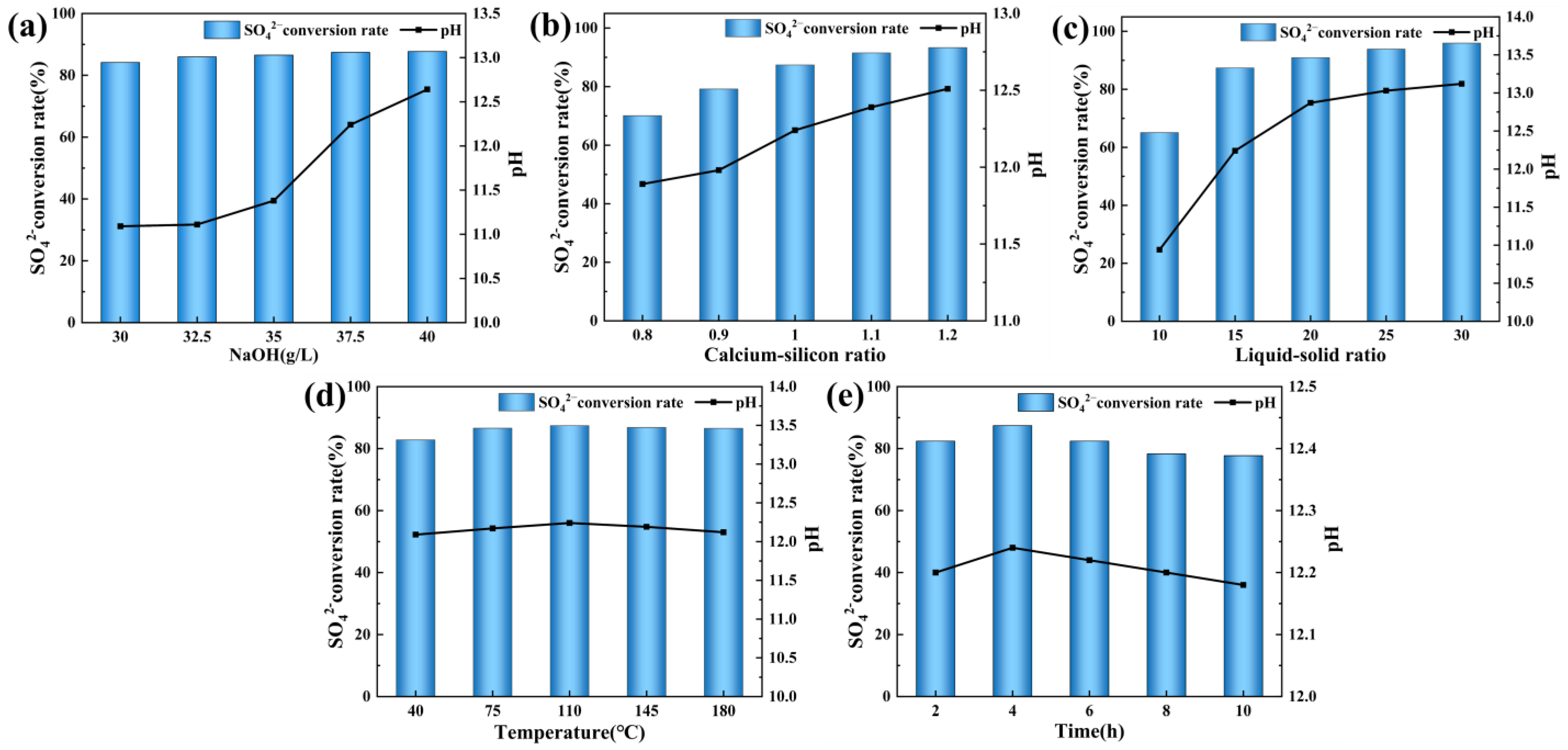
3.2. Effect of Different Condition Parameters on SO42− Conversion Rate in PG
3.3. SEM and BET Characterization of PCSH
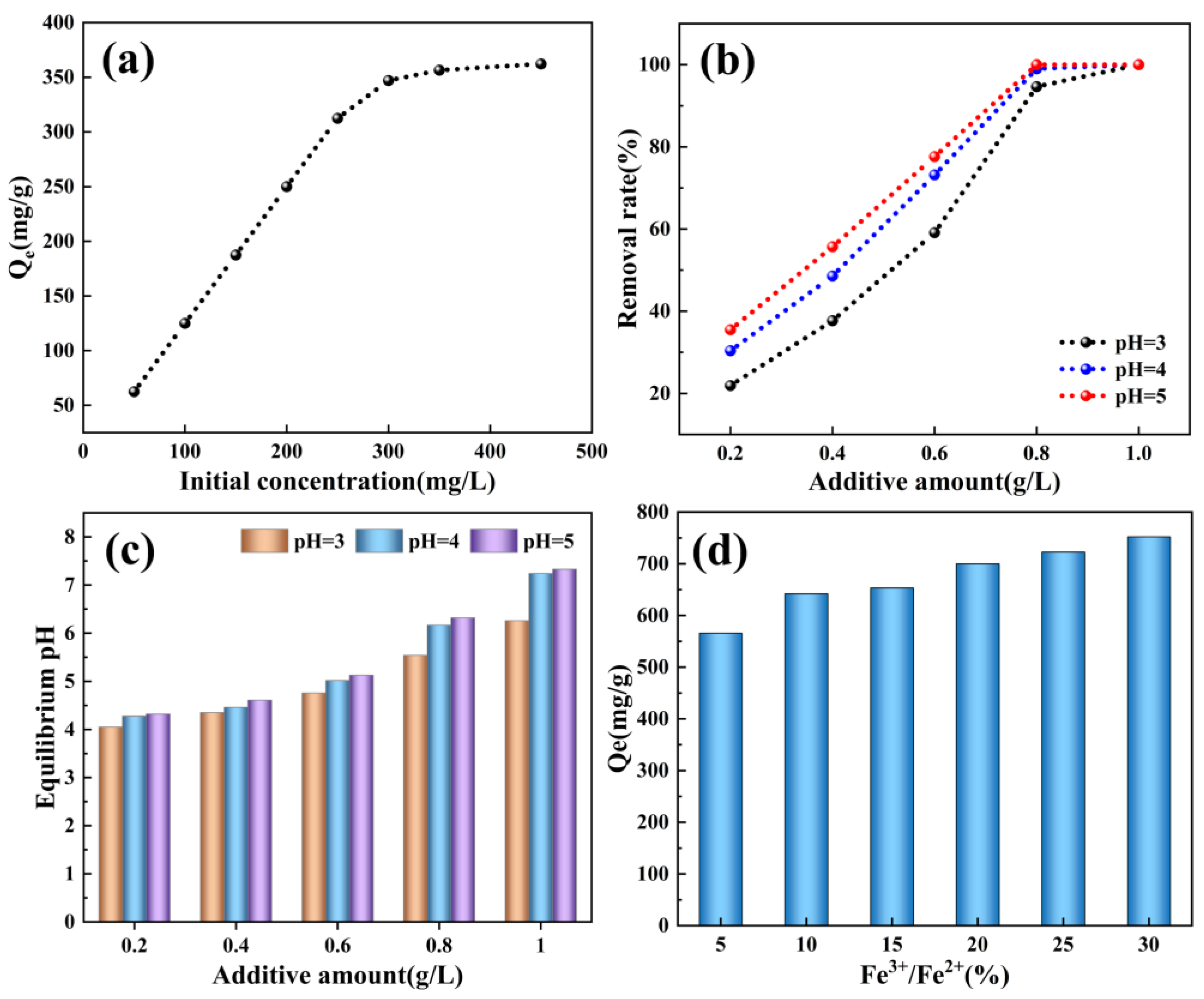
3.4. PCSH Adsorbs Fe2+ from Simulated Pickling Wastewater
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
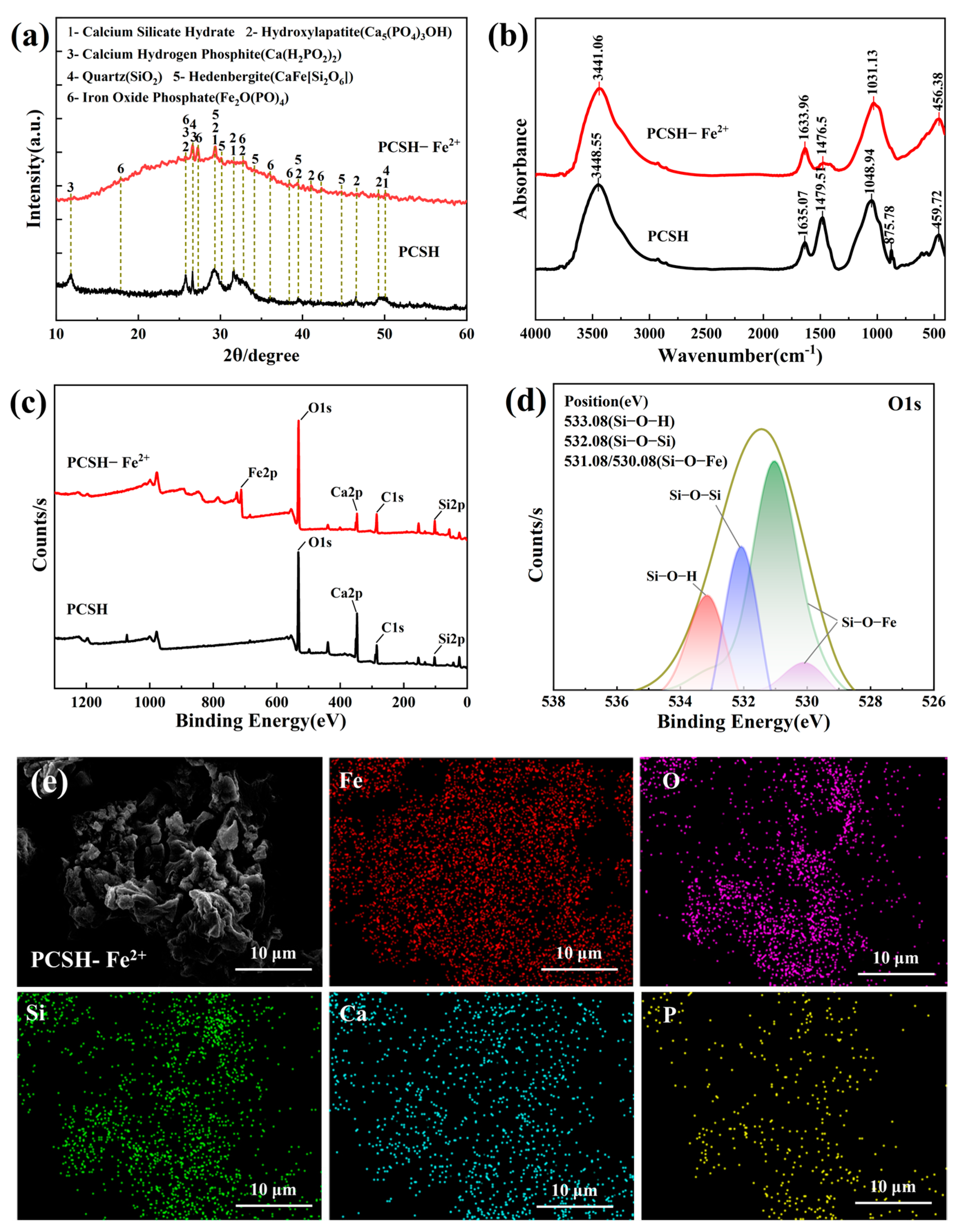
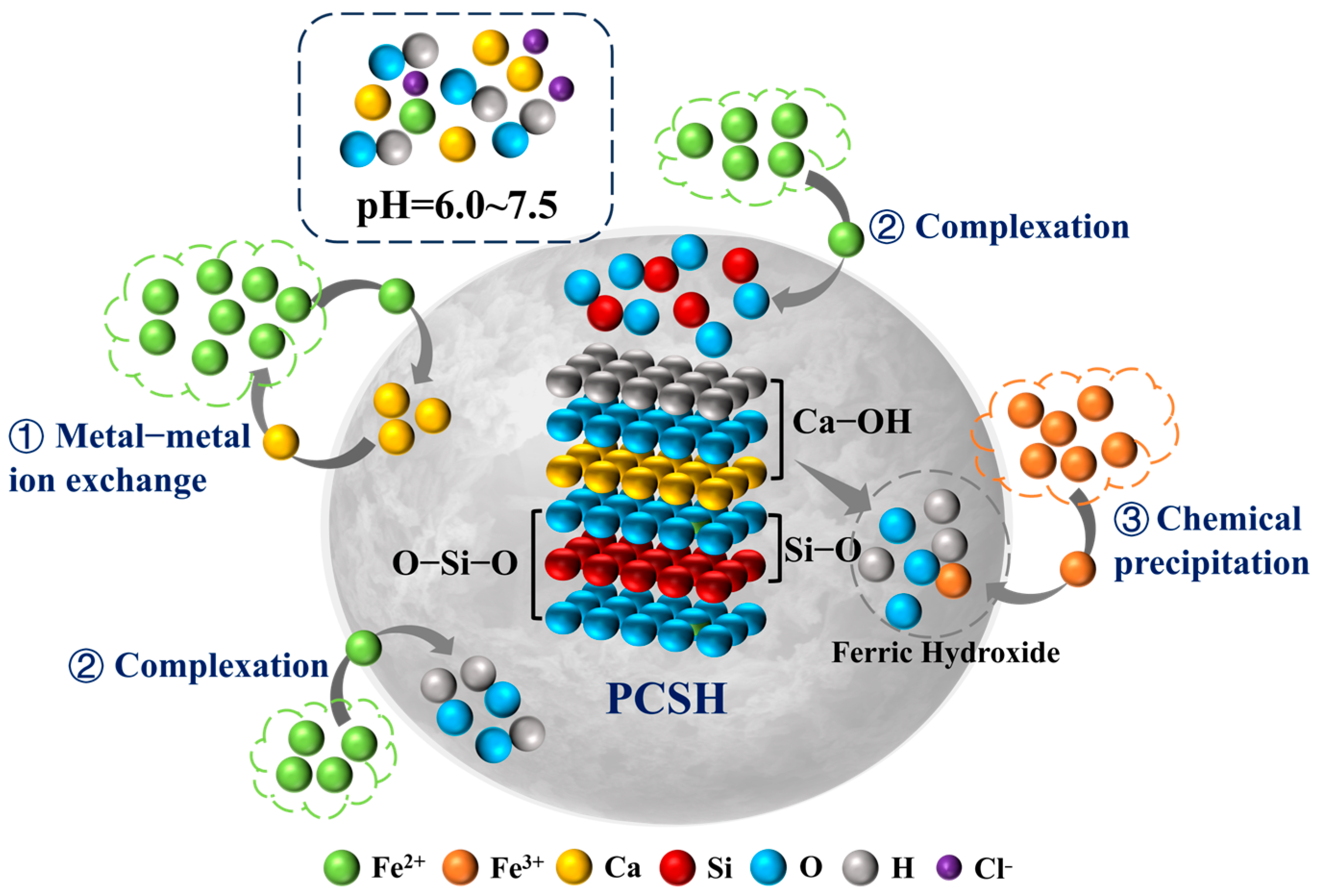
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Y.; Ni, Y. Treatment of paper mill wastewater using a composite inorganic coagulant prepared from steel mill waste pickling liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zong, L.; Liu, Z.; Du, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F. Sequential separation of Cu (II)/Ni (II)/Fe (II) from strong-acidic pickling wastewater with a two-stage process based on a bi-pyridine chelating resin. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2792–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, M.; Wirtz, S.; Scherer, V.; Bärhold, F. Spray roasting of iron chloride FeCl2: Numerical modelling of industrial scale reactors. Powder Technol. 2013, 245, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Fu, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Modified chemical mineralization-alkali neutralization technology: Mineralization behavior at high iron concentrations and its application in sulfur acid spent pickling solution. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Alcantará, B.; Castañeda-Záldivar, F.; Ortíz-Frade, L.; Antaño, R.; Rivera, F.F. Electrochemical study of iron deposit in acid media for its recovery from spent pickling baths regeneration. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 901, 115805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Luo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Ling, C.; Yu, L.; Yin, K. Distinctive adsorption and desorption behaviors of temporal and post-treatment heavy metals by iron nanoparticles in the presence of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.E.; Ahmed, H.M.; Alshammari, S.O.; El-Khateeb, M.A. Treatment of Heavy Metal Ions from Simulated Water using Adsorption Process via Modified Iron Magnetic Nanocomposite. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100071. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.I.; Lee, S.; An, H.R.; Kim, H.; Son, B.; Lee, H.U. Enhancing adsorption efficiency for environmentally-friendly removal of As (V) and Pb (II) using a biochar-iron oxide composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 667, 160348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, S. Synthesis and humidity control performances of natural opoka based porous calcium silicate hydrate. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, F.; Quintana, G.; Briso, A.; Ide, V.; Basualto, C.; Gaete, J.; Montes, G. Cu(II), Cd(II), Pb(II) and As(V) adsorption from aqueous solutions using magnetic iron-modified calcium silicate hydrate: Adsorption kinetic analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Li, S.; Yan, F.; Su, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. An all-in-one strategy for the adsorption of heavy metal ions and photodegradation of organic pollutants using steel slag-derived calcium silicate hydrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Ji, F.; Chen, Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and phosphorus recovery performance of porous calcium–silicate–hydrate. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Lei, X.; Li, L.; Yuan, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Hao, J. Preparation and evaluation of a mesoporous calcium-silicate material (MCSM) from coal fly ash for removal of Co (II) from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by calcium silicate powder from waste coal fly-ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, E.; Bellefqih, H.; Bourgier, V.; Mazouz, H.; Dumitraş, D.G.; Bard, F.; Haneklaus, N. Phosphogypsum circular economy considerations: A critical review from more than 65 storage sites worldwide. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. Using cemented paste backfill to tackle the phosphogypsum stockpile in China: A down-to-earth technology with new vitalities in pollutant retention and CO2 abatement. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1480–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qian, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Cheng, X. Phosphogypsum as a component of calcium sulfoaluminate cement: Hazardous elements immobilization, radioactivity and performances. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, K.; Chang, J.; Wang, L. Phosphogypsum-based building materials: Resource utilization, development, and limitation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shu, Z.; Yakubu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Calcium sulfate whisker reinforced non-fired ceramic tiles prepared from phosphogypsum. Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Vidr. 2018, 57, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachehab, A.; Mertah, O.; Kherbeche, A.; Hassoune, H. Utilization of phosphogypsum in CO2 mineral sequestration by producing potassium sulphate and calcium carbonate. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaciri, Y.; Bettach, M.; El Alaoui-Belghiti, H. Obtaining nano calcium fluoride and ammonium sulfate from phosphogypsum. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2024, 199, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Lan, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, J. Conversion of Phosphogypsum into Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for the Removal and Recycling of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from Wastewater. Molecules 2024, 29, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 342-2007; Water Quality-Determination of Sulfate-Barium Chromate Spectrophotometry. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HJ/T 345-2007; Water Quality-Determination of Iron-Phenanthroline Spectrophotometry. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Peng, S.Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lin, K.L. Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals from calcium-rich limestone sludge waste: Preparation, characterization, and application for Pb2+ adsorption in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 160, 111943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Xia, M. Innovative strategy of turning waste into treasure: High-efficiency adsorption of heavy metals pollutants by modified amorphous calcium phosphate prepared with phosphogypsum waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, H.; Tan, D.G.; Peng, T. Recovery of titanium compounds from Ti-enriched product of alkali melting Ti-bearing blast furnace slag by dilute sulfuric acid leaching. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigenzhenov, O.S.; Chepushtanova, T.A.; Altmyshbayeva, A.Z.; Temirgali, I.A.; Maldybayev, G.; Sharipov, R.H.; Dagubayeva, A.T. Investigation of thermodynamic and kinetic regularities of asbestos waste leaching processes. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Han, X.; Zhou, P.; Hao, M.; Wang, X.; Bian, L.; Liu, X. A novel highly dispersed calcium silicate hydrate nanosheets for efficient high-concentration Cu2+ adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 475, 134774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zuo, R.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y. Influence of colloidal Fe(OH)3 on the adsorption characteristics of strontium in porous media from a candidate high-level radioactive waste geological disposal site. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; White, C.E. Modeling of aqueous species interaction energies prior to nucleation in cement-based gel systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 139, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Feng, A.; Yu, A. Pb(II) uptake onto nylon microplastics: Interaction mechanism and adsorption performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, T.; Munandar, A.; Mawaddah, N.; Wisnubroto, M.S.; Siregar, P.M.S.B.N.; Palapa, N.R.; Lesbani, A.; Wibowo, Y.G. Synthesis and characterization of montmorillonite—Mixed metal oxide composite and its adsorption performance for anionic and cationic dyes removal. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 147, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.L.; Tran, H.N.; Juang, R.S. Revisiting temperature effect on the kinetics of liquid-phase adsorption by the Elovich equation: A simple tool for checking data reliability. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 136, 104403. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, F. Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of hydrochloric-acid-modified bentonite for Zn (II) in wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100279. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; Huang, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Ji, F. Evaluation of porous calcium silicate hydrate derived from carbide slag for removing phosphate from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, W.; Zhao, X. Fluoride recovery using porous calcium silicate hydrates via spontaneous Ca2+ and OH− release. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 165, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Feng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Hong, J. Toward the formation mechanism of synthetic calcium silicate hydrate (CSH)-pH and kinetic considerations. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 172, 107248. [Google Scholar]
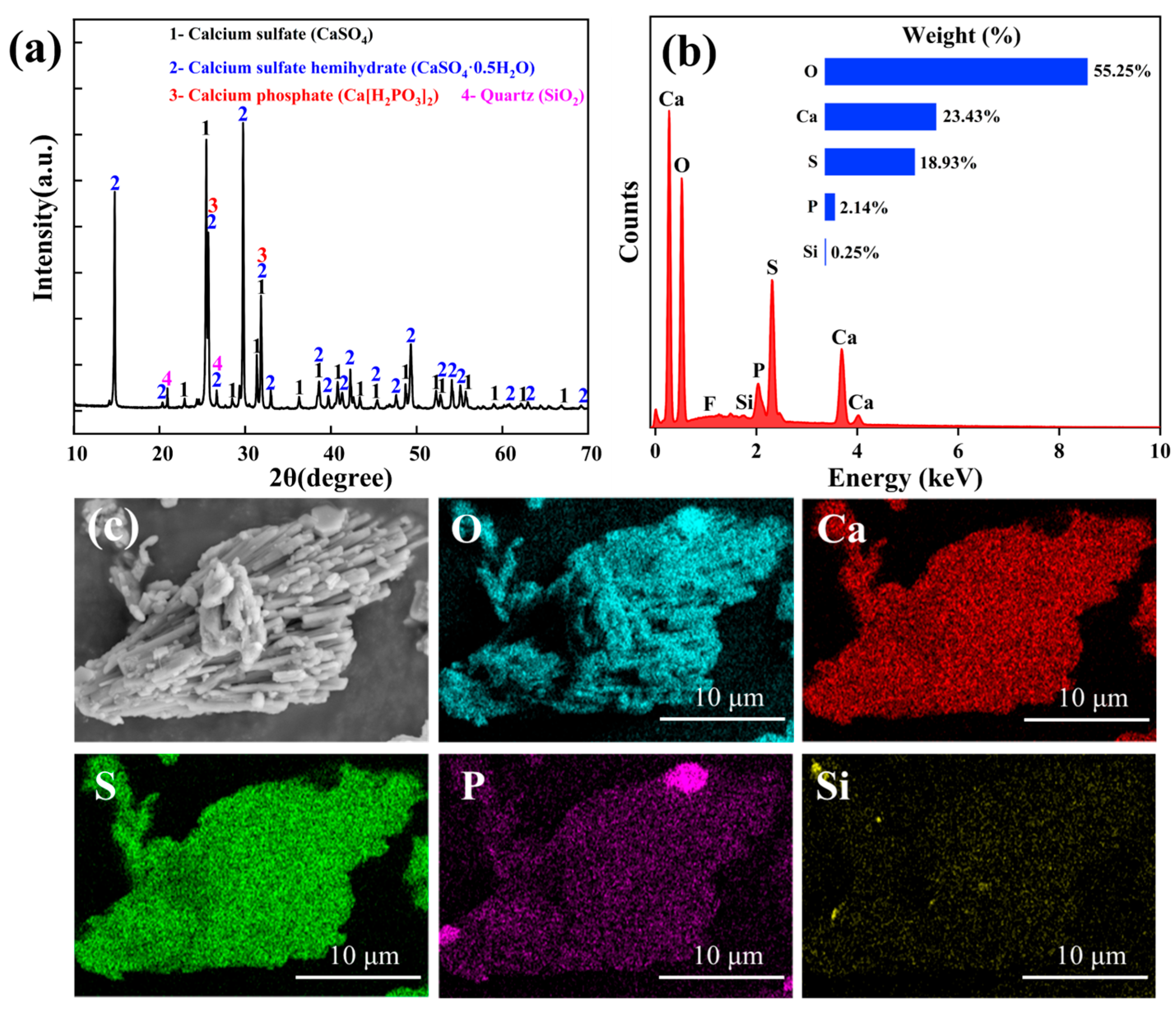





| Composition | SO3 | CaO | P2O5 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | Na2O | K2O | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 51.58 | 39.61 | 5.11 | 2.25 | 0.61 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| Material | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCSH | 93.5066 | 20.5658 | 0.4819 |
| Model | Concentration (mg/L) | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | K2 | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo- first-order | 200 | 0.9198 | 233.71 | 0.0643 | — | — | — |
| 250 | 0.8844 | 293.11 | 0.0953 | — | — | — | |
| 300 | 0.8386 | 328.45 | 0.1193 | — | — | — | |
| Pseudo- second-order | 200 | 0.9819 | 256.77 | — | 0.00035 | — | — |
| 250 | 0.9840 | 314.84 | — | 0.00048 | — | — | |
| 300 | 0.9769 | 349.69 | — | 0.00058 | — | — | |
| Elovich | 200 | 0.9767 | — | — | — | 83.34 | 0.0235 |
| 250 | 0.9569 | — | — | — | 411.02 | 0.0237 | |
| 300 | 0.9426 | — | — | — | 1391.66 | 0.0248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, P.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Chen, J. “Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7796. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177796
Liang P, Chen C, Li J, Chen J. “Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7796. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Pan, Chaoyi Chen, Junqi Li, and Jiahang Chen. 2024. "“Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7796. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177796
APA StyleLiang, P., Chen, C., Li, J., & Chen, J. (2024). “Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater. Sustainability, 16(17), 7796. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177796






