Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Common Treatment Methods for Textile Dyes
3. Effluent from the Textile Industry: Human and Environmental Issues
3.1. Environmental Consequences
3.2. Impact of Textile Dyes on Human Health
4. Sustainable Wastewater Treatment for the Remediation
4.1. Bioadsorbents in Wastewater Treatment

| Name of Adsorbents | Performed Dyes | Adsorption Conditions | Removal (mg/g) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potato peel-based sorbent | Direct Blue 71 | pH 3 | 1704 | [161] |
| Rice husk ash | Brilliant Green dye | pH 4–10 | 66 | [162] |
| Sunflower stalk | Basic Red 9 dye | - | 317 | [163] |
| Cane pith | Basic Red 22 dye | pH 4.1 | 941.7 | [164] |
| Bagasse | Basic Red 22 dye | pH 4 | 942 | [165] |
| Enosis siliqua shell powder | - | - | 797 | [166] |
| Glutaraldehyde cross-linked magnetic chitosan beads | Direct Red 23 | pH 4 | 1250 | [167] |
| Popcorn derived activated carbon | Methyl Orange | pH 2–11 | 2090 | [168] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) hydrogel | Methyl Orange | pH 2 | 1825 | [169] |
| Non-cross-linked and cross-linked chitosan fibers | Acid Orange 7 | pH 7 | 4523 | [170] |
| Chitosan grafted with diethylenetriamine | Acid Orange 7 | - | 2108 | [171] |
| Chitosan grafted with poly(methyl methacrylate) | Reactive Blue 19 | pH 3 | 1498 | [172,173] |
| Chitin nanofiber-/nanowhisker-based hydrogels | Reactive Blue 19 | pH 1 | 1331 | [172] |
| Cationic cellulose nanocrystals-chitosan film (nanocomposite) | Reactive Blue 19 | pH 3 | 1320 | [174] |
| Hollow zein nanoparticles | Reactive Blue 19 | pH 9 | 1016 | [175] |
| Chitosan films | Reactive Blue 19 | pH 6.8 | 822.4 | [176] |
| Template ECH cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles | Reactive Black 5 | pH 3 | 2941 | [177,178,179] |
| Chitosan beads cross-linked with epichlorohydrin | Reactive Black 5 | pH 3 | 2043 | [180,181] |
| Glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan beads/microparticles | Reactive Black 5 | pH 10 | 1927 | [182] |
| Chitosan cross-linked with sodium edetate | Reactive Black 5 | pH 3 | 1648 | [183] |
| Chitosan hydrogel | Reactive Black 5 | - | 1560 | [184,185] |
| Mango bark powder | Malachite Green dye | pH > 6 | 4.22 × 103 mol/g | [186] |
| Calcium-rich biochar | Malachite Green dye | Neutral and alkaline pH | 12,502 | [187] |
| Pigments-extracted macro algae derived biochar | Methylene Blue | - | 5306.2 | [188] |
| Azolla-derived hierarchical nanoporous carbons | Methylene Blue | - | 4448 | [189] |
| Banana | Reactive Blue 235 Methyl Red, Malachite Green | - | - | [190] |
| Activated surface of banana and orange peels | Reactive Red 24 | - | - | [191] |
| Waste tea residue | Acid Blue 25 | - | - | [142] |
| Palladium nanoparticles synthesized from peel waste of cotton boll | Toxic azo dye | - | - | [192] |
| Wheat husk waste | Textile effluent water | - | - | [193] |
4.2. Dye Removal by Biological Methods
4.2.1. Biological Route of Dye Decolorization
4.2.2. Fungi
4.2.3. Algae
4.2.4. Enzymes
4.2.5. Bacteria
4.3. Membrane Separation
4.3.1. Ion Exchange
4.3.2. Evaporation
4.4. Other Techniques
4.4.1. Granular Activated Carbon (GAC)
4.4.2. The Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP)
4.4.3. Color Removal by Fenton Oxidation

4.4.4. Color Removal by Peroxide (H2O2)
4.4.5. Ozonation
4.4.6. Photocatalytic Oxidation
4.4.7. The Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
4.5. Treatment of Dyes Using Hybrid Technologies
4.5.1. Physiochemical Methods
4.5.2. Biochemical Methods
4.5.3. Combination-Based Hybrid Chemical–Chemical Scheme
4.5.4. The Z-Scheme Strategy
4.6. Sustainable Sludge Management
Methods of Sludge Treatment
4.7. Roadmap towards ZLD: Focus on Recovery and Reuse
4.7.1. Electrolyte Recovery from Reactive Dye Effluent
4.7.2. Alkali Recovery
4.7.3. Dye Recovery
4.8. The Need for Technoeconomic Analysis
4.9. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in WWTPs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rayhan Sarker, M.; Mithun Ali, S.; Kumar Paul, S.; Haque Munim, Z. Measuring Sustainability Performance Using an Integrated Model. Measurement 2021, 184, 109931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilagyi, A.; Mocan, M.; Verniquet, A.; Churican, A.; Rochat, D. Eco-Innovation, a Business Approach towards Sustainable Processes, Products and Services. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2018, 238, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crystal Gordon, Water: The Prime Essence Of Life. 2019. Available online: Https://Hubpages.Com/Education/Water-Is-the-Essence-of-Life-Itself (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Ajmal, M.; Siddiq, M.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, N. Magnetic Co–Fe Bimetallic Nanoparticle Containing Modifiable Microgels for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions, Organic Dyes and Herbicides from Aqueous Media. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43873–43884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global Water Pollution and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, R.; Taki, K.; Kumar, M. Efficacy of Nanoclays as the Potential Adsorbent for Dyes and Metal Removal from the Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent Advances in New Generation Dye Removal Technologies: Novel Search for Approaches to Reprocess Wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801–30818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owa, F.D. Water Pollution: Sources, Effects, Control and Management. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2013, 4, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Dhedan, S.K. Equilibrium Isotherms and Kinetics Modeling of Methylene Blue Adsorption on Agricultural Wastes-Based Activated Carbons. Fluid. Phase Equilib. 2012, 317, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A. Hassaan; Ahmed El Nemr Health and Environmental Impacts of Dyes: Mini Review. Am. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Aziz, N. Adsorption of Direct Dye on Palm Ash: Kinetic and Equilibrium Modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Sharma, N.R.; Singh, J.; Kanwar, R.S. Biological Methods for Textile Dye Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1836–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroze, S.; Sen, T.K. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Dye Adsorption from Water by Agricultural Solid Waste Adsorbents. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2018, 229, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.R. Pollution Abatement and Waste Minimisation in Textile Dyeing. In Environmental Aspects of Textile Dyeing; Christie, R.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2007; pp. 116–148. ISBN 9781845691158. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Reducing Environmental Pollution of the Textile Industry Using Keratin as Alternative Sizing Agent to Poly(Vinyl Alcohol). J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanbeigi, A.; Price, L. A Technical Review of Emerging Technologies for Energy and Water Efficiency and Pollution Reduction in the Textile Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Tehrani-Bagha, A. A Review on Microplastic Emission from Textile Materials and Its Reduction Techniques. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 199, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepacz-Smółka, A.; Sójka-Ledakowicz, J.; Paździor, K.; Ledakowicz, S. Application of Anoxic Fixed Film and Aerobic CSTR Bioreactor in Treatment of Nanofiltration Concentrate of Real Textile Wastewater. Chem. Pap. 2010, 64, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, G.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Militký, J. Color and Design for Textiles. In Fibrous Structures and Their Impact on Textile Design; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 119–148. [Google Scholar]
- Militký, J.; Venkataraman, M.; Periyasamy, A.P. (Eds.) Fibrous Structures and Their Impact on Textile Design; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; ISBN 978-981-19-4826-8. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Adeoye, I.O.; Bello, O.S. Adsorption of Dyes Using Different Types of Clay: A Review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Miralles, P.; Salvador, A. Hair Dyes in Cosmetics. In Analysis of Cosmetic Products; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K. Rajani Srivastava an Overview of Textile Dyes and Their Removaltechniques: Indian Perspective. Polution Res. Pap. 2017, 36, 790–797. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of Dyes in Textile Effluent: A Critical Review on Current Treatment Technologies with a Proposed Alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Adnan, M.A.; Muhd Julkapli, N.; Amir, M.N.I.; Maamor, A. Effect on Different TiO2 Photocatalyst Supports on Photodecolorization of Synthetic Dyes: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Periyasami, S. Critical Review on Sustainability in Denim: A Step toward Sustainable Production and Consumption of Denim. ACS Omega 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares Jack Ferre, J.A. A Simple Model to Predict Mass Transfer Rates and Kinetics of Biochemical and Biomedical Michaelis-Menten Surface Reactions. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2015, 80, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Evaluation of Microfiber Release from Jeans: The Impact of Different Washing Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 58570–58582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachidhanandham, A.; Periyasamy, A.P. Environmentally Friendly Wastewater Treatment Methods for the Textile Industry. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 2269–2307. [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandi, M.R.; Hadi, M.; Moayedi, S.; Barjesteh, A.F. Hadi Wo-Parameter Isotherms of Methyl Orange Sorption by Pinecone Derived Activated Carbon. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2009, 6, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Raval, N.P.; Shah, P.U.; Shah, N.K. Malachite Green “a Cationic Dye” and Its Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3407–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Darabdhara, J.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. Recent Advances of Copper- BTC Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Degradation of Organic Dye-Polluted Wastewater: Synthesis, Mechanistic Insights and Future Outlook. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2024, 5, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Jamil, F.; Rashad, M.A.; Hussain, M.; Inayat, A.; Akhter, P.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Park, Y.K. Wastewater from the Textile Industry: Review of the Technologies for Wastewater Treatment and Reuse. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 2060–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C.; Suteu, D.; Muresan, A.; Muresan, R.; Popescu, A. Textile Wastewater Treatment by Homogeneous Oxidation with Hydrogen Peroxide. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2009, 8, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutagalung, S.S.; Rafryanto, A.F.; Sun, W.; Juliasih, N.; Aditia, S.; Jiang, J.; Dipojono, H.K.; Suhardi, S.H.; Rochman, N.T.; Kurniadi, D. Combination of Ozone-Based Advanced Oxidation Process and Nanobubbles Generation toward Textile Wastewater Recovery. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1154739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Zamora, P.; Kunz, A.; De Moraes, S.G.; Pelegrini, R.; De Campos Moleiro, P.; Reyes, J.; Duran, N. Degradation of Reactive Dyes, I. A Comparative Study of Ozonation, Enzymic and Photochemical Processes. Chemosphere 1998, 38, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H. Catalytic Ozonation for Water and Wastewater Treatment: Recent Advances and Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paździor, K.; Wrębiak, J.; Klepacz-Smółka, A.; Gmurek, M.; Bilińska, L.; Kos, L.; Sójka-Ledakowicz, J.; Ledakowicz, S. Influence of Ozonation and Biodegradation on Toxicity of Industrial Textile Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcuk, H. Decolorization and Detoxification of Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Coagulation Processes. Dye. Pigment. 2005, 64, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Hybrid Ozonation Process for Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Principles and Applications: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Xu, B.; Meng, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Ozonation of Indigo Enhanced by Carboxylated Carbon Nanotubes: Performance Optimization, Degradation Products, Reaction Mechanism and Toxicity Evaluation. Water Res. 2015, 68, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, D.H.; Shin, H.J. Adsorption and Precipitation of Anionic Dye Reactive Red 120 from Aqueous Solution by Aminopropyl Functionalized Magnesium Phyllosilicate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuzer-Matos, A.J.; Testolin, R.C.; Pimentel-Almeida, W.; Radetski-Silva, R.; Deomar-Simões, M.J.; Poyer-Radetski, L.; Ariente-Neto, R.; Batista-Barwinski, M.J.; Somensi, C.A.; Radetski, C.M. Treatment of Wastewater Containing New and Non-Biodegradable Textile Dyes: Efficacy of Combined Advanced Oxidation and Adsorption Processes. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2022, 233, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor-Basulto, D.L.; Kadier, A.; Singh, R.; Navarro-Mendoza, R.; Bandala, E.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M. Post-Tanning Wastewater Treatment Using Electrocoagulation: Optimization, Kinetics, and Settlement Analysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, O.; Khataee, A.; Kobya, M.; Yoon, Y. Electrochemical Oxidation of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) from Simulated Soil Leachate and Landfill Leachate Concentrate. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Reduction of Acute Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Dye Effluent Using Fenton-Coagulation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervez, M.N.; Fu, D.; Wang, X.; Bao, Q.; Yu, T.; Naddeo, V.; Tian, H.; Cao, C.; Zhao, Y. A Bifunctional-FeOOH@GCA Nanocomposite for Enhanced Adsorption of Arsenic and Photo Fenton-like Catalytic Conversion of As(III). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.D.; Raut, P.D. Treatment of Textile Wastewater by Fenton’s Process as a Advanced Oxidation Process. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2014, 8, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Dias, A.A.; Sampaio, A.; Amaral, C.; Peres, J.A. Degradation of a Textile Reactive Azo Dye by a Combined Chemical–Biological Process: Fenton’s Reagent-Yeast. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.D.N.; Santana, C.S.; Velloso, C.C.V.; da Silva, A.H.M.; Magalhães, F.; Aguiar, A. A Review on the Treatment of Textile Industry Effluents through Fenton Processes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 366–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chen, M.L. Purification of Textile Wastewater Effluents by a Combined Fenton Process and Ion Exchange. Desalination 1997, 109, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkkä, H.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Recent Developments of Electro-Oxidation in Water Treatment—A Review. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 754, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A Review on Chemical Coagulation/Flocculation Technologies for Removal of Colour from Textile Wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, S. Removal of Some Reactive Dyes from Synthetic Wastewater by Combined Al(III) Coagulation/Carbon Adsorption Process. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 62, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Otaki, M. Effects of Photocatalysis on Biological Decolorization Reactor and Biological Activity of Isolated Photosynthetic Bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Textiles Wastewater Treatment Using Anoxic Filter Bed and Biological Wriggle Bed-Ozone Biological Aerated Filter. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3748–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Carballo, J.; Pérez, M.J.; Domínguez, J.M. Biological Treatment of Model Dyes and Textile Wastewaters. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; Pidou, M.; Soares, A.; Judd, S.; Jefferson, B. Modelling the Energy Demands of Aerobic and Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, N.D.; Franca, R.D.G.; Moreira, M.A.; Gil, F.N.; Viegas, C.A.; Pinheiro, H.M. Comparing Aerobic Granular Sludge and Flocculent Sequencing Batch Reactor Technologies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 104, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, M.C.; Mosca Angelucci, D.; Daugulis, A.J. Sequential Anaerobic-Aerobic Decolourization of a Real Textile Wastewater in a Two-Phase Partitioning Bioreactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinperi, N.C.; Ozturk, E.; Yigit, N.O.; Kitis, M. Treatment of Woolen Textile Wastewater Using Membrane Bioreactor, Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis for Reuse in Production Processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, C.T.; Qiu, H.; Chen, L.; Achmon, Y.; Zhong, Z. Ceramic Membrane Reactor Integrated with UV/O3/Catalyst Beads for Treating Real Textile Wastewater: Enhanced Effluent Quality, Fouling Control and Molecular Transformations of DOM. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, S.; Kizildag, N.; Dizman, B.; Unal, S. Solvent-Based Recovery of High Purity Polysulfone and Polyester from End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.Y.L.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Kan, C.W. Dyeing Cotton with Reactive Dyes: A Comparison between Conventional Water-Based and Solvent-Assisted PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Dyeing Systems. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Murthy, H.C.A.; Amare, E. Summary on Adsorption and Photocatalysis for Pollutant Remediation: Mini Review. J. Encapsulation Adsorpt. Sci. 2018, 08, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A Critical Review on Recent Advancements of the Removal of Reactive Dyes from Dyehouse Effluent by Ion-Exchange Adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, S.; Ahmed Basha, C. Chemical or Electrochemical Techniques, Followed by Ion Exchange, for Recycle of Textile Dye Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, A.; Caronna, T.; Fontana, F.; Marcandalli, B.; Selli, E. Photodecomposition of Substituted 4-Diethylaminoazobenzenes under Visible Light Irradiation in Different Solvents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2002, 152, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Microfiber Emissions from Functionalized Textiles: Potential Threat for Human Health and Environmental Risks. Toxics 2023, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Militky, J. Sustainability in Textile Dyeing: Recent Developments. In Sustainability in the Textile and Apparel Industries; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 37–79. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Rwahwire, S.; Zhao, Y. Environmental Friendly Textile Processing. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Lavate, S.S. Eco-Friendly Denim Processing. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 1559–1579. ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, C.D.; Mkandawire, M. GIS Based Spatial and Temporal Investigation of Groundwater and Soil Quality along Noyyal River, Tiruppur, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.; Dineshkumar, R.; Pancha, I.; Mishra, S. Prospects and Potential Role of Biological Treatment of Textile Effluent to Restore Water Reservoir. In Cost-efficient Wastewater Treatment Technologies; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 118, pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Indian Textile and Apparel Industry Expected to Reach US $344.1 Billion by 2027. Available online: https://in.apparelresources.com/business-news/trade/indian-textile-apparel-industry-expected-reach-us-344-1-billion-2027/ (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Rwawiire, S.; Zhao, Y. Sustainable Wastewater Treatment Methods for Textile Industry. In Sustainable Innovations in Apparel Production; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 21–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, S.; Singh, M.; Chadha, P. Adverse Impact of Textile Dyes on the Aquatic Environment as Well as on Human Beings. Toxicol. Int. 2021, 28, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.E.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Devnath, R.; Ahmed, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Khalid, K.; Wahab, Y.A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kamangar, S.; Hussien, M.; et al. Removal of Azo Dyes from Aqueous Effluent Using Bio-Based Activated Carbons: Toxicity Aspects and Environmental Impact. Separations 2023, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Militky, J. Denim Processing and Health Hazards. In Sustainability in Denim; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 161–196. [Google Scholar]
- Drumond Chequer, F.M.; de Oliveira, G.A.R.; Anastacio Ferraz, E.R.; Carvalho, J.; Boldrin Zanoni, M.V.; de Oliveir, D.P. Textile Dyes: Dyeing Process and Environmental Impact. In Eco-Friendly Textile Dyeing and Finishing; InTech: Isai, Romania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, R. Sustainability Challenges of the Textiles, Dyeing and Finsihing Industries: Opportunities for Innovation. ACS Webinar 2017, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.; Patel, V.; Khan, Z. Bioremediation of Dyes from Textile and Dye Manufacturing Industry Effluent; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128180952. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.A.; Liang, J.Y.; Li, R.J.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Chang, K.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Yang, Z.Y. Aromatic Amine Contents, Component Distributions and Risk Assessment in Sludge from 10 Textile-Dyeing Plants. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ning, X.A.; Kong, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, G.; Cai, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Yuan, Y. Elimination and Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Phthalic Acid Esters from Textile-Dyeing Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Keswani, K.; Bhatt, U.; Kumar, D.; Singh, H. In Vitro Propagation and Analysis of Mixotrophic Potential to Improve Survival Rate of Dolichandra Unguis-Cati under Ex Vitro Conditions. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, K.; Ng, T.S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, C.H. Sustainable Production of Bio-Oil and Carbonaceous Materials from Biowaste Co-Pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Gul, J.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ali, I.; Farooq, W.; Liaqat, R.; AlMohamadi, H.; Štěpanec, L.; Juchelková, D. Recent Progress in Microalgae-Derived Biochar for the Treatment of Textile Industry Wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Mudgal, N.; Rawat, D.; Poria, P.; Mukherjee, P.; Sharma, U.; Kumria, P.; Pani, B.; Singh, M.; Yadav, A.; et al. Integrating Microalgae into Textile Wastewater Treatment Processes: Advancements and Opportunities. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettaï, N.; Ait Amar, H. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Methyl Orange in Presence of Titanium Dioxide in Aqueous Suspension. Part I: Parametric Study. Desalination 2005, 185, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettaï, N.; Ait Amar, H. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Methyl Orange in Presence of Titanium Dioxide in Aqueous Suspension. Part II: Kinetics Study. Desalination 2005, 185, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Jessica; Yoshikawa, K.; Cross, J.S. Influence of Synthetic and Natural Microfibers on the Growth, Substance Exchange, Energy Accumulation, and Oxidative Stress of Field-Collected Microalgae Compared with Microplastic Fragment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 908, 167936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, G. Chemicals in Textiles: A Potential Source for Human Exposure and Environmental Pollution. Ph.D. Thesis, Stockholm University, Faculty of Science, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kopperi, H.; Hemalatha, M.; Ravi Kiran, B.; Santhosh, J.; Venkata Mohan, S. Sustainable Consideration for Traditional Textile Handloom Cluster/Village in Pollution Abatement—A Case Study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, S.K.; Hossain, A.K.M.N.-U.-; Hussain, S.Z.; Hasan, N. Utilization of Prawn to Reduce the Value of BOD and COD of Textile Wastewater. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G.; He, X.-L.-S.; Huang, J.-H.; Luo, R.; Ge, H.-Z.; Wołowicz, A.; Wawrzkiewicz, M.; Gładysz-Płaska, A.; Li, B.; Yu, Q.-X.; et al. Impacts of Heavy Metals and Medicinal Crops on Ecological Systems, Environmental Pollution, Cultivation, and Production Processes in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendón-Castrillón, L.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Ocampo-López, C.; González-López, F.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Treatment of Water from the Textile Industry Contaminated with Indigo Dye: A Hybrid Approach Combining Bioremediation and Nanofiltration for Sustainable Reuse. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.M.S.; Athira, K.K.; Alves, M.B.; Gardas, R.L.; Pereira, J.F.B. Textile Dyes Effluents: A Current Scenario and the Use of Aqueous Biphasic Systems for the Recovery of Dyes. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Yu, X.; Shao, Y.; McBride, L.; Hidalgo, H.; Yang, Y. Complete Recycling of Polymers and Dyes from Polyester/Cotton Blended Textiles via Cost-Effective and Destruction-Minimized Dissolution, Swelling, Precipitation, and Separation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamil Selvan, S. Eco-Technological Approaches for Textile Dye Effluent Treatment and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Capturing Using Green Microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Zahoor, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Ikram, M.; Zhu, D.; Umar, M.N.; Ullah, R.; Ali, E.A. Bioremediation of Azo Dye Brown 703 by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: An Effective Treatment Technique for Dye-Polluted Wastewater. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Maheshwari, K.; Solanki, Y.S. Investigation of Dye Effluent Treatment Using Unmodified and Modified Biobased Sorbent and Its Process Economics. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Environmentally Friendly Approach to the Reduction of Microplastics during Domestic Washing: Prospects for Machine Vision in Microplastics Reduction. Toxics 2023, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Ayed, L.; Aljarad, M.R.; Altayeb, H.N.; Abbes, S.; Chaieb, K. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis and Box-Behnken Design for the Optimization of the Decolourization of Mixture Textile Dyes by Halotolerant Microbial Consortium. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 276, 127481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Shao, Y.; McBride, L.; Hidalgo, H.; Yang, Y. Rapid Fiber-to-Fiber Recycling of Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) and Its Dye from Waste Textiles without Damaging Their Chemical Structures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chequer, F.M.D.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Ferraz, E.R.A.; Tsuboy, M.S.; Marcarini, J.C.; Mantovani, M.S.; de Oliveira, D.P. The Azo Dyes Disperse Red 1 and Disperse Orange 1 Increase the Micronuclei Frequencies in Human Lymphocytes and in HepG2 Cells. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 676, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, P.; Dangayach, G.S.; Bhardwaj, A.K. A Review on the Sustainability of Textile Industries Wastewater with and without Treatment Methodologies. Rev. Environ. Health 2018, 33, 163–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Chowdhary, P. Emerging and Eco-Friendly Approaches for Waste Management. In Emerging and Eco-Friendly Approaches for Waste Management; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motejadded Emrooz, H.B.; Maleki, M.; Rashidi, A.; Shokouhimehr, M. Adsorption Mechanism of a Cationic Dye on a Biomass-Derived Micro- and Mesoporous Carbon: Structural, Kinetic, and Equilibrium Insight. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2021, 11, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, F.; Gabbiye, N.; Sahu, O. Biosorption of Reactive Red Dye (RRD) on Activated Surface of Banana and Orange Peels: Economical Alternative for Textile Effluent. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 12, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyekanmi, A.A.; Ahmad, A.; Hossain, K.; Rafatullah, M. Adsorption of Rhodamine B Dye from Aqueous Solution onto Acid Treated Banana Peel: Response Surface Methodology, Kinetics and Isotherm Studies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harini, K.; Ramya, K.; Sukumar, M. Extraction of Nano Cellulose Fibers from the Banana Peel and Bract for Production of Acetyl and Lauroyl Cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Yarramuthi, V.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, D.-S. Removal of Anionic Dyes (Reactive Black 5 and Congo Red) from Aqueous Solutions Using Banana Peel Powder as an Adsorbent. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekoye, J.N.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Wangila, P.T.; Tonui, M.K. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Congo Red Dye Adsorption on Cabbage Waste Powder. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Facile Synthesis of Polypyrrole Decorated Chitosan-Based Magsorbent: Characterizations, Performance, and Applications in Removing Cationic and Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Medium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Tang, J.; Tam, M.; Xiao, R. Polyethylenimine-Modified Chitosan Materials for the Recovery of La(III) from Leachates of Bauxite Residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, N.; Lähde, A.; Abu-Danso, E.; Iqbal, J.; Bhatnagar, A. A Comparative Study of Magnetic Chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4) and Graphene Oxide Modified Magnetic Chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4GO) Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Torri, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Dye Removal by Biosorption Using Cross-Linked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, S.; Nasar, A. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Artificially Contaminated Water Using Citrus Limetta Peel Waste as a Very Low Cost Adsorbent. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 66, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, N.; Sharma, K.; Sinha, M.; Baral, E.R.; Koteswararao, R.; Dhyani, A.; Hwan Cho, M.; Cho, S. Bio-Sorbents, Industrially Important Chemicals and Novel Materials from Citrus Processing Waste as a Sustainable and Renewable Bioresource: A Review; Cairo University: Giza, Egypt, 2020; Volume 23, ISBN 8201027988476. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, V.; Prasad, S.; Kumar, D. Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Aqueous Media Using Citrus limonum (Lemon) Leaf. Microchem. J. 2014, 112, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, J.; Durgalakshmi, D.; Balakumar, S.; Aruna, P.; Ganesan, S.; Rajendran, S.; Naushad, M. Low Cost and Quick Time Absorption of Organic Dye Pollutants under Ambient Condition Using Partially Exfoliated Graphite. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Kim, D.-S. Adsorption of Anionic Azo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution by Cationic Modified Orange Peel Powder. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Development, Characterization, and Utilization of Magnetized Orange Peel Waste as a Novel Adsorbent for the Confiscation of Crystal Violet Dye from Aqueous Solution. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Biopolymers Composites with Peanut Hull Waste Biomass and Application for Crystal Violet Adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.C.N.; Vaz, M.G.; Gomes, R.F.; Pereira, A.G.B.; Fajardo, A.R.; Rodrigues, F.H.A. Starch/Rice Husk Ash Based Superabsorbent Composite: High Methylene Blue Removal Efficiency. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.D.; Kamani, H.; Mahvi, A.H. The Optimization Study of Direct Red 81 and Methylene Blue Adsorption on NaOH-Modified Rice Husk. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, S.; Nasar, A. Adsorptive Decontamination of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Crystal Violet Dye by Employing Terminalia Arjuna Sawdust Waste. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.; Sultan, M.; Akhtar, N.; Hameed, U.; Abid, T. Application of Natural and Modified Sugar Cane Bagasse for the Removal of Dye from Aqueous Solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, S115–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alshirifi, A.N.; Alkaim, A.F. Kinetics and Equilibrium Study for the Adsorption of Textile Dyes on Coconut Shell Activated Carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3381–S3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.A.; Vishesh, Y.; Sarvshrestha, N.; Bhardwaj, A.S.; Kumar, P.A.; Topare, N.S.; Raut-Jadhav, S.; Bokil, S.A.; Khan, A. Adsorption Isotherm Studies of Methylene Blue Using Activated Carbon of Waste Fruit Peel as an Adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; de Guzman, M.J.K.; Aberilla, J.M. Environmental Sustainability Assessment of Banana Waste Utilization into Food Packaging and Liquid Fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 37, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, K.C.S.; Guimarães, R.C.A.; Oliveira, K.R.W.; Nazário, C.E.D.; Ferencz, J.A.P.; Wender, H. Banana Peel Powder Biosorbent for Removal of Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Wastewater. Toxics 2023, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, A.; Roy, D.K. Removing Reactive Dyes from Textile Effluent Using Banana Fibre. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 16, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Das, E.; Rabha, S.; Talukdar, K.; Goswami, M.; Devi, A. Propensity of a Low-Cost Adsorbent Derived from Agricultural Wastes to Interact with Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.A.; Sabri, S.; Abu Bakar, A.A.; Azizan, N.S. Removal of Colour Using Banana Stem Adsorbent in Textile Wastewater. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1349, 12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, G.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Tehrani, A. Extraction of Micro, Nanocrystalline Cellulose and Textile Fibers from Coffee Waste. J. Test. Eval. 2023, 51, 20220487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Lokhande, R.S.; Sahu, R.; Jain, S.K.; Sharma, K.B.; Tripathi, B. Study on Adsorbent Characteristics of Coconut Coir as a Bio Sorbent for Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Macromol. Symp. 2021, 399, 2100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.T.; Bui, H.T.; Le, D.N.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, L.A.; Nguyen, H.N.; Nguyen, Q.S.; Nguyen, T.P.; Bich, N.T.; Duong, T.T.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Biochar Derived from Agricultural By-Products for Dye Removal. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 9161904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, A. Utilization of Tea Wastes for the Removal of Toxic Dyes from Polluted Water—A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2023, 13, 1399–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wu, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Han, H.; Ko, T.-H. Adsorption of Dye by Waste Black Tea Powder: Parameters, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 5431046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.N.; Tamboli, S.R.; Sutar, D.S.; Jadhav, S.R.; Marathe, J.V.; Shaikh, A.A.; Prajapati, A.A. Batch and Continuous Studies for Adsorption of Anionic Dye onto Waste Tea Residue: Kinetic, Equilibrium, Breakthrough and Reusability Studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisri, M.B. Application of Chitosan Derivatives as Promising Adsorbents for Treatment of Textile Wastewater; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780081024911. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, A.; Alalwan, B.; Eldirderi, M.M.; Mnif, W.; Ben Rebah, F. Cactus Material-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes: A Review. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, N.W. Colour Removal from Textile Effluent by Using Biomaterials—An Experimental Evaluation. J. Indian. Water Work. Assoc. 2020, LII. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.A.; Nazir, M.; Khan, E.A. Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B from Textile Wastewater Using Water Chestnut (Trapa natans L.) Peel: Adsorption Dynamics and Kinetic Studies. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2013, 95, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Ghoul, Y.; Ammar, C.; Alminderej, F.M.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Design and Evaluation of a New Natural Multi-Layered Biopolymeric Adsorbent System-Based Chitosan/Cellulosic Nonwoven Material for the Biosorption of Industrial Textile Effluents. Polymers 2021, 13, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Karunakaran, G.; Rwahwire, S.; Kesari, K. Nonwoven Fabrics Developed from Agriculture and Industrial Waste for Acoustic and Thermal Applications. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7329–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Nonwoven Fabrics from Agricultural and Industrial Waste for Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Applications. Textiles 2023, 3, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Escudero, L.B.; Bello, O.S.; Iqbal, M.; Nisar, J.; Adegoke, K.A.; Alakhras, F.; Kornaros, M.; Anastopoulos, I. The Utilization of Leaf-Based Adsorbents for Dyes Removal: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 728–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, F.; Saygideger, S.D. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Acid Orange 52 Dye Biosorption by Paulownia Tomentosa Steud. Leaf Powder as a Low-Cost Natural Biosorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Coronilla, I.; Morales-Barrera, L.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies of Amaranth Dye Biosorption from Aqueous Solution onto Water Hyacinth Leaves. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, F.; Karaman, S. Removal of Basic Red 46 Dye from Aqueous Solution by Pine Tree Leaves. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Kushwaha, A.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Adsorption Studies of Cationic Dyes onto Ashoka (Saraca asoca) Leaf Powder. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosoarca, G.; Vancea, C.; Popa, S.; Dan, M.; Boran, S. A Novel High-Efficiency Natural Biosorbent Material Obtained from Sour Cherry (Prunus cerasus) Leaf Biomass for Cationic Dyes Adsorption. Materials 2023, 16, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.; Ghafar, N.A.; Ngadi, N.; Razmi, F.A.; Inuwa, I.M.; Mat, R.; Amin, N.A.S. Effective Removal of Anionic Textile Dyes Using Adsorbent Synthesized from Coffee Waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.B.; Priyanka, S.V. Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Lemon Leaf Powder as an Adsorbent. J. Solid. Waste Technol. Manag. 2023, 49, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.K.; Poonia, V.; Kumar, R.; Kataria, N.; Sharma, P.; Lamba, J.; Bhattacharya, P. Congo Red Dye Removal Using Modified Banana Leaves: Adsorption Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Reusability Analysis. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Gazi, M.; Oladipo, A.A. Adsorptive Removal of Multi-Azo Dye from Aqueous Phase Using a Semi-IPN Superabsorbent Chitosan-Starch Hydrogel. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 112, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fan, S.; Li, Y. Removal Behavior of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Tea Waste: Kinetics, Isotherms and Mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Daraei, H.; Khodaei, F.; Aghdam, K.B.; Faez, E. Direct Blue 71 Dye Removal Probing by Potato Peel-Based Sorbent: Applications of Artificial Intelligent Systems. New Pub Balaban 2015, 57, 12281–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavlieva, M.P.; Genieva, S.D.; Georgieva, V.G.; Vlaev, L.T. Kinetic Study of Brilliant Green Adsorption from Aqueous Solution onto White Rice Husk Ash. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 409, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de O. Salomón, Y.L.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Netto, M.S.; Grassi, P.; Piccilli, D.G.A.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Dotto, G.L. Powdered Biosorbent from Pecan Pericarp (Carya illinoensis) as an Efficient Material to Uptake Methyl Violet 2B from Effluents in Batch and Column Operations. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.-S.; Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, F.-C. Role of Microporosity of Activated Carbons on Their Adsorption Abilities for Phenols and Dyes. Adsorption 2001, 7, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.-S.; Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L. Characterization and Use of Activated Carbons Prepared from Bagasses for Liquid-Phase Adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 201, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachoumi, I.; el Ouahabi, I.; Slimani, R.; Cagnon, B.; el Haddad, M.; el Antri, S.; Lazar, S. Adsorption Studies with a New Biosorbent Ensis Siliqua Shell Powder for Removal Two Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Sanlier, S.H.; Ak, G.; Yilmaz, H.; Ozbakir, G.; Cagliyan, O. Removal of Textile Dye, Direct Red 23, with Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked Magnetic Chitosan Beads. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 43, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qiao, N.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Fu, F.; Cao, R.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Xu, B. Fluffy Honeycomb-like Activated Carbon from Popcorn with High Surface Area and Well-Developed Porosity for Ultra-High Efficiency Adsorption of Organic Dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Shukry, N.; El-Sakhawy, M. Carboxymethyl Cellulose-g-Poly(2-(Dimethylamino) Ethyl Methacrylate) Hydrogel as Adsorbent for Dye Removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 73, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Okamoto, A.; Kataoka, T. Adsorption of Acid Dye on Cross-Linked Chitosan Fibers: Equilibria. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1993, 48, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xiang, B.; Li, Y.; Jia, Q. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Diethylenetriamine-Modified Chitosan Beads for Acid Dyes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y. Adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 from Aqueous Solution by Chitin Nanofiber-/Nanowhisker-Based Hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15804–15812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Tian, X. Adsorption of C.I. Reactive Blue 19 from Aqueous Solutions by Porous Particles of the Grafted Chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hua, F.; Lou, C.; Jiang, X. Cationic Cellulose Nanocrystals (CCNCs) and Chitosan Nanocomposite Films Filled with CCNCs for Removal of Reactive Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3927–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Biodegradable Hollow Zein Nanoparticles for Removal of Reactive Dyes from Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 125, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nga, N.K.; Chinh, H.D.; Hong, P.T.T.; Huy, T.Q. Facile Preparation of Chitosan Films for High Performance Removal of Reactive Blue 19 Dye from Aqueous Solution. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 25, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.C.; Chen, A.H. Competitive Biosorption of Azo Dyes from Aqueous Solution on the Templated Crosslinked-Chitosan Nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.H.; Huang, Y.Y. Adsorption of Remazol Black 5 from Aqueous Solution by the Templated Crosslinked-Chitosans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohagheghian, A.; Vahidi-Kolur, R.; Pourmohseni, M.; Yang, J.K.; Shirzad-Siboni, M. Application of Scallop Shell-Fe3O4 Nano-Composite for the Removal Azo Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2015, 226, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Park, S.S.; Cho, S.Y. Adsorption Characteristics of Reactive Black 5 onto Chitosan Beads Cross-Linked with Epichlorohydrin. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, M. Batch Adsorption of Reactive Red 120 from Waste Waters Using Activated Carbon from Waste Tea. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2012, III, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.H.; Chen, S.M. Biosorption of Azo Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Chitosans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jóźwiak, T.; Filipkowska, U.; Szymczyk, P.; Kuczajowska-Zadrożna, M.; Mielcarek, A. Application of Chitosan Ionically Crosslinked with Sodium Edetate for Reactive Dyes Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 2015, 20, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, T.; Filipkowska, U.; Szymczyk, P.; Zyśk, M. Effect of the Form and Deacetylation Degree of Chitosan Sorbents on Sorption Effectiveness of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, M.; Lichtfouse, E. (Eds.) Green Materials for Wastewater Treatment; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 38, ISBN 978-3-030-17723-2. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.; Rupainwar, D.C. Removal of Hazardous Triphenylmethane Dye through Adsorption over Waste Material-Mango Bark Powder. IJCT 2011, 18, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Zhu, W.; He, L.; Tan, F.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, Q.; He, M.; Hu, G. Calcium-Rich Biochar from Crab Shell: An Unexpected Super Adsorbent for Dye Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Lin, Y.C.; Ho, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, N.Q. Highly Efficient Adsorption of Dyes by Biochar Derived from Pigments-Extracted Macroalgae Pyrolyzed at Different Temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banna Motejadded Emrooz, H.; Maleki, M.; Rahmani, A. Azolla-Derived Hierarchical Nanoporous Carbons: From Environmental Concerns to Industrial Opportunities. J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, M.; Boudoukha, C.; Avalos Ramirez, A.; Haroun, M.F.; Maane, S. High Biosorption of Cationic Dye onto a Novel Material Based on Paper Mill Sludge. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perendija, J.; Ljubić, V.; Popović, M.; Milošević, D.; Arsenijević, Z.; Đuriš, M.; Kovač, S.; Cvetković, S. Assessment of Waste Hop (Humulus lupulus) Stems as a Biosorbent for the Removal of Malachite Green, Methylene Blue, and Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solution in Batch and Fixed-Bed Column Systems: Biosorption Process and Mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 394, 123770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasaiah, B.P.; Mandal, B.K. Remediation of Azo-Dyes Based Toxicity by Agro-Waste Cotton Boll Peels Mediated Palladium Nanoparticles. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, D.; Kumar, S.; Walia, Y.K. Removal of Dyes Using Wheat Husk Waste as a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Environ. Claims J. 2020, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A Critical Review on Textile Wastewater Treatments: Possible Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarayu, K.; Sandhya, S. Current Technologies for Biological Treatment of Textile Wastewater-A Review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, R.; Kandelbauer, A.; Robra, K.H.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Gübitz, G.M. Indigo Degradation with Purified Laccases from Trametes hirsuta and Sclerotium rolfsii. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 89, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misal, S.A.; Gawai, K.R. Azoreductase: A Key Player of Xenobiotic Metabolism. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila-Leal, L.D.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E. A Brief History of Colour, the Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dyes and Removal by Using Laccases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, R.M.F.; Almeida, M.R.; Bharmoria, P.; Freire, M.G.; Tavares, A.P.M. Improvements in the Enzymatic Degradation of Textile Dyes Using Ionic- Liquid-Based Surfactants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, J.P.; Kalyani, D.C.; Telke, A.A.; Phugare, S.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Evaluation of the Efficacy of a Bacterial Consortium for the Removal of Color, Reduction of Heavy Metals, and Toxicity from Textile Dye Effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.F.; Gan, H.M.; Rashid, N.A.A. Genome Sequence of Citrobacter Sp. Strain A1, a Dye-Degrading Bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5485–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondhi, S. Sustainable Approaches in Effluent Treatment; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780081028674. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.-S. Chemical Modification and Immobilization of Corynebacterium Glutamicum for Biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentirmai, É.; Massie, A.R.; Kapás, L. Lipoteichoic Acid, a Cell Wall Component of Gram-Positive Bacteria, Induces Sleep and Fever and Suppresses Feeding. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 92, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, I.M.; Nigam, P.; Singh, D.; Marchant, R. Microbial Decolorization of Textile-Dyecontaining Effluents: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye Biosorption Sites in Aspergillus Niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, N.A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Biosorption of Azo Dyes by Spent Rhizopus Arrhizus Biomass. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Bhowal, J.; Das, A.R.; Guha, A.K. Adsorption Behavior of Rhodamine B on Rhizopus Oryzae Biomass. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7265–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zamora, M.; Cristiani-Urbina, E.; Martínez-Jerónimo, F.; Perales-Vela, H.V.; Ponce-Noyola, T.; del Carmen Montes-Horcasitas, M.; Cañizares-Villanueva, R.O. Bioremoval of the Azo Dye Congo Red by the Microalga Chlorella Vulgaris. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10811–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamil Selvan, S.; Dakshinamoorthi, B.M.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Muthusamy, S.; Ramamurthy, D.; Balasundaram, S. Integrating Eco-Technological Approach for Textile Dye Effluent Treatment and Carbon Dioxide Capturing from Unicellular Microalga Chlorella Vulgaris RDS03: A Synergistic Method. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 25, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Dehghan, G.; Ebadi, A.; Zarei, M.; Pourhassan, M. Biological Treatment of a Dye Solution by Macroalgae Chara Sp.: Effect of Operational Parameters, Intermediates Identification and Artificial Neural Network Modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, N.; Ayazloo, M.; Khataee, A.R.; Pourhassan, M. Biological Decolorization of Dye Solution Containing Malachite Green by Microalgae Cosmarium Sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmesh, T.V.N.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Sekaran, G.; Velan, M. Application of Azolla Rongpong on Biosorption of Acid Red 88, Acid Green 3, Acid Orange 7 and Acid Blue 15 from Synthetic Solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 122, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmesh, T.V.N.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Sekaran, G.; Velan, M. Biosorption of Acid Blue 15 Using Fresh Water Macroalga Azolla Filiculoides: Batch and Column Studies. Dye Pigment 2006, 71, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, A.; Akkaya, G.; Turabik, M. Biosorption of Acid Red 274 (AR 274) on Enteromorpha Prolifera in a Batch System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 126, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamee, R.; Siddique, R. Biodegradation of Synthetic Dyes of Textile Effluent by Microorganisms: An Environmentally and Economically Sustainable Approach. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 9, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Mohamed, L.A. Bioremediation of the Textile Waste Effluent by Chlorella Vulgaris. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.Y.; Chng, L.M.; Leong, S.S.; Yeap, S.P.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Toh, P.Y. Removal of Synthetic Dye by Chlorella Vulgaris Microalgae as Natural Adsorbent. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 7385–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangola, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chaudhary, P.; Khati, P.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, A. Bioremediation of Industrial Waste Using Microbial Metabolic Diversity. In Microbial Biotechnology in Environmental Monitoring and Cleanup; IGI Global: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, L.; Feng, F. Improving the Indigo Carmine Decolorization Ability of a Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens Laccase by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Catalysts 2017, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, B.S.; Thayumanavan, T.; Nambukrishnan, V.; Sakthishobana, K. Heterogeneous Biocatalytic System for Effective Decolorization of Textile Dye Effluent. 3 Biotech. 2023, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, A.; Chakraborty, N.; Soren, K.; Chakraborty, P.; Bandopadhyay, R. Structural-Functional Analyses of Textile Dye Degrading Azoreductase, Laccase and Peroxidase: A Comparative in Silico Study. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 43, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, W.; Ying, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Azoreductase from Streptomyces Sp.: Application in Eco-Friendly Decolorization of Azo Dye Wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 140, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherifah, M.W.; Seun, A.E.; Kehinde, O.S.; Abiodun, A.O. Decolourization of Synthetic Dyes by Laccase Enzyme Produced by Kluyveromyces Dobzhanskii DW1 and Pichia Manshurica DW2. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, F.; Moradi, M.; Jolivalt, C.; Madzak, C. Laccase Production from Sucrose by Recombinant Yarrowia Lipolytica and Its Application to Decolorization of Environmental Pollutant Dyes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Zahid, M.T.; Ullah, F.; Zia, I.; Younas, A.; Batool, T.; Zahid, I. Bacterial Tools for the Removal and Degradation of Synthetic Dyes from the Wastewater. In Current Developments in Bioengineering and Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 339–370. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, S.; Makhanya, B.P.; Zwane, P.E. Use of Bacterial Isolates in the Treatment of Textile Dye Wastewater: A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís, M.; Solís, A.; Pérez, H.I.; Manjarrez, N.; Flores, M. Microbial Decolouration of Azo Dyes: A Review. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1723–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafqat, M.; Khalid, A.; Mahmood, T.; Siddique, M.T.; Han, J.; Habteselassie, M.Y. Evaluation of Bacteria Isolated from Textile Wastewater and Rhizosphere to Simultaneously Degrade Azo Dyes and Promote Plant Growth. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Sanganyado, E.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Song, H. Azo Dye Degrading Bacteria Tolerant to Extreme Conditions Inhabit Nearshore Ecosystems: Optimization and Degradation Pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, S.; Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Chitra, B.; Rangasamy, G. Biodegradation of Textile Dye Rhodamine-B by Brevundimonas Diminuta and Screening of Their Breakdown Metabolites. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulejmanović, J.; Kojčin, M.; Grebo, M.; Zahirović, A.; Topčagić, A.; Smječanin, N.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Sher, F. Functionalised Mesoporous Biosorbents for Efficient Removal of Hazardous Pollutants from Water Environment. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Xie, R.; Schagerl, M.; Khalil, M.A.; Sun, J. Decolorization of Reactive Azo Dye Using Novel Halotolerant Yeast Consortium HYC and Proposed Degradation Pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayutham, K.; Madhava, A.K.; Pushparaj, M.; Thanarasu, A.; Devaraj, T.; Periyasamy, K.; Subramanian, S. Biodegradation of Remazol Brilliant Blue R Using Isolated Bacterial Culture (Staphylococcus Sp. K2204). Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Wen, Z.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Huang, D. Decolorization Pathways of Anthraquinone Dye Disperse Blue 2BLN by Aspergillus Sp. XJ-2 CGMCC12963. Bioengineered 2017, 8, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, K.; Karunagaran, K.; Sharma, D.C. Recycling of Wastewaters of Textile Dyeing Industries Using Advanced Treatment Technology and Cost Analysis—Case Studies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcik-Canbolat, C.; Sengezer, C.; Sakar, H.; Karagunduz, A.; Keskinler, B. Recovery of Real Dye Bath Wastewater Using Integrated Membrane Process: Considering Water Recovery, Membrane Fouling and Reuse Potential of Membranes. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Canbolat, Ç.B.; Lin, J.; Luis, P. The Potential of Membrane Technology for Treatment of Textile Wastewater. In Sustainable Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Figoli, A., Criscuoli, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 349–380. ISBN 978-981-10-5623-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Chen, V. Nanofiltration of Textile Wastewater for Water Reuse. Desalination 2002, 143, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Fang, F.; Wu, X.; Xin, J.; Sun, S.; Wei, Y.; Ruan, R.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Influence of Nanofiltration Concentrate Recirculation on Performance and Economic Feasibility of a Pilot-Scale Membrane Bioreactor-Nanofiltration Hybrid Process for Textile Wastewater Treatment with High Water Recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, P.; Mohedano, A.F.; Casas, J.A.; Zazo, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. An Overview of the Application of Fenton Oxidation to Industrial Wastewaters Treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Truong, V.N.T.; Bu, X.; Xie, G. A Review of Effects and Applications of Ultrasound in Mineral Flotation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.; Ali, M. Fenton’s Peroxidation and Coagulation Processes for the Treatment of Combined Industrial and Domestic Wastewater. J Hazard Mater 2006, 136, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Tan, X.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Y.; Novotná, J.; Shah, K.V.; Stempień, Z.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Kejzlar, P.; Venkataraman, M.; et al. Insights into the Large-size Graphene Improvement Effect of the Mechanical Properties on the Epoxy/Glass Fabric Composites. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 7430–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.-T.; Lo, H.H.; Wang, L.K.; Taricska, J.R.; Li, K.H. Granular Activated Carbon Adsorption. In Physicochemical Treatment Processes; Wang, L.K., Hung, Y.-T., Shammas, N.K., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 573–633. ISBN 978-1-59259-820-5. [Google Scholar]
- Belaid, K.D.; Kacha, S.; Kameche, M.; Derriche, Z. Adsorption Kinetics of Some Textile Dyes onto Granular Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elela, S.I.; Ali, M.E.M.; Ibrahim, H.S. Combined Treatment of Retting Flax Wastewater Using Fenton Oxidation and Granular Activated Carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfin, T.; Varshney, N.; Singh, B. Ionic Liquid Modified Activated Carbon for the Treatment of Textile Wastewater. Green Mater. Wastewater Treat. Environ. Chem. A Sustain. World 2020, 38, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakht Shokouhi, S.; Dehghanzadeh, R.; Aslani, H.; Shahmahdi, N. Activated Carbon Catalyzed Ozonation (ACCO) of Reactive Blue 194 Azo Dye in Aqueous Saline Solution: Experimental Parameters, Kinetic and Analysis of Activated Carbon Properties. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilińska, L.; Gmurek, M.; Ledakowicz, S. Comparison between Industrial and Simulated Textile Wastewater Treatment by AOPs—Biodegradability, Toxicity and Cost Assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Yaashikaa, P.R. Sustainable Innovations in Apparel Production; Springer: Singapore, 2018; ISBN 978-981-10-8590-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, D. A Review on Recent Advances of Biochar from Agricultural and Forestry Wastes: Preparation, Modification and Applications in Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, F.; Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Dogan, C.; Kurt, U. Treatability of Raw Textile Wastewater Using Fenton Process and Its Comparison with Chemical Coagulation. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 162, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözen, S.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Hooshmand, M.; Orhon, D. Fenton Oxidation for Effective Removal of Color and Organic Matter from Denim Cotton Wastewater without Biological Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for In-Situ Production of Hydrogen Peroxide/Hydroxyl Radical for Textile Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, K.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y.; Boczkaj, G.; Wang, C. Thermally Activated Natural Chalcopyrite for Fenton-like Degradation of Rhodamine B: Catalyst Characterization, Performance Evaluation, and Catalytic Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethi, B.; Radhika, G.B.; Sonawane, S.H. Fundamentals of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater Treatment: Challenges and Opportunities. In Novel Approaches Towards Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Somensi, C.A.; Simionatto, E.L.; Bertoli, S.L.; Wisniewski, A.; Radetski, C.M. Use of Ozone in a Pilot-Scale Plant for Textile Wastewater Pre-Treatment: Physico-Chemical Efficiency, Degradation by-Products Identification and Environmental Toxicity of Treated Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.E.T.; Agustiono Kurniawan, T.; Lo, W. Degradation of Chelating Agents in Aqueous Solution Using Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP). Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevimli, M.F.; Sarikaya, H.Z. Ozone Treatment of Textile Effluents and Dyes: Effect of Applied Ozone Dose, PH and Dye Concentration. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gähr, F.; Hermanutz, F.; Oppermann, W. Ozonation- An Important Technique to Comly with New German Laws for Textile Waste-Water Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Koba-Ucun, O. Treatment of Reactive Dye Hydrolysates with UV-C- and Ozone-Activated Percarbonate and Persulfate. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2023, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirev, A.; Nenov, V. Ozonation of Two Acidic Azo Dyes with Different Substituents. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanchiang, J.M.; Tseng, D.H. Degradation of Anthraquinone Dye, C.I. Reactive Blue 19 in Aqueous Solution by Ozonation. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.R.S. Chapter 4—Physical Chemistry of Dyeing: Kinetics, Equilibrium, Dye-Fiber Affinity, and Mechanisms. In The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes; Venkataraman, K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974; pp. 115–275. ISBN 978-0-12-717007-7. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, L.; Weaver, M.A. The Chemistry and Application of Dyes; Waring, D.R., Hallas, G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 107–163. ISBN 978-1-4684-7715-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Liang, L.; Cao, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Quan, X. MgAl2O4 Incorporated Catalytic Ceramic Membrane for Catalytic Ozonation of Organic Pollutants. Appl. Catal. B. 2024, 343, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, I.; Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Sarafpour, M. Photocatalytic Discoloration of Denim Using Advanced Oxidation Process with H2O2/UV. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 360, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehelin, J.; Hoigne, J. Decomposition of Ozone in Water: Rate of Initiation by Hydroxide Ions and Hydrogen Peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Karimi, M.; Ebrahimi, H.; Fallah, N. Sequencing Batch Reactor/Nanofiltration Hybrid Method for Water Recovery from Textile Wastewater Contained Phthalocyanine Dye and Anionic Surfactant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouni, I.; Marrot, B.; Amar, R. Ben Treatment of Reconstituted Textile Wastewater Containing a Reactive Dye in an Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor Using a Novel Bacterial Consortium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 87, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.; Moreira, I.; Moreira, P.; Pintado, M.; Castro, P. Bioaugmentation of Aerobic Granular Sludge with Dye-Decolorizing Yeast for Textile Industrial Wastewater. Processes 2023, 11, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, N.D.; Novais, J.M.; Pinheiro, H.M. Effect of Some Operational Parameters on Textile Dye Biodegradation in a Sequential Batch Reactor. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 89, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuid, M.; Aris, A.; Krishnen, R.; Chelliapan, S.; Muda, K. Pineapple Wastewater as Co-Substrate in Treating Real Alkaline, Non-Biodegradable Textile Wastewater Using Biogranulation Technology. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 344, 118501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Huang, C. Electrodialysis-based Separation Technologies: A Critical Review. AIChE J. 2008, 54, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Huang, J.; Ricard, B.; Baltaru, M.-C.; Greydanus, B.; Balta, S.; Shen, J.; Vlad, M.; Sotto, A.; et al. Toward Resource Recovery from Textile Wastewater: Dye Extraction, Water and Base/Acid Regeneration Using a Hybrid NF-BMED Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakachaka, V.; Tshangana, C.; Mahlangu, O.; Mamba, B.; Muleja, A. Interdependence of Kinetics and Fluid Dynamics in the Design of Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors. Membranes 2022, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bhawna; Sharma, R.; Gupta, A.; Dubey, K.K.; Khan, A.M.; Singhal, R.; Kumar, R.; Bharti, A.; Singh, P.; et al. TiO2 Based Photocatalysis Membranes: An Efficient Strategy for Pharmaceutical Mineralization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohaprapanon, S.; Matahum, J.; Tayo, L.; You, S.-J. Photodegradation of Reactive Black 5 in a ZnO/UV Slurry Membrane Reactor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, B.; Birhanlı, E.; Ulu, A.; Boran, F.; Yeşilada, Ö.; Ateş, B. Immobilization of Trametes Trogii Laccase on Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biocatalytic Degradation of Textile Dyes. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goei, R.; Lim, T.-T. Ag-Decorated TiO2 Photocatalytic Membrane with Hierarchical Architecture: Photocatalytic and Anti-Bacterial Activities. Water Res. 2014, 59, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Yang, W.; Hussain, M. Recent Developments in Alumina Supported Hydrodesulfurization Catalysts for the Production of Sulfur-Free Refinery Products: A Technical Review. Catal. Rev. 2022, 64, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Ishaq, M.; Yang, W.; Hussain, M. Recent Breakthroughs in Deep Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Refinery Products. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 125731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Hussain, M.; Shafique, S.; Rashid, R.; Akhter, P.; Ahmed, A.; Jeon, J.-K.; Park, Y.-K. Oxidative Desulfurization of Refinery Diesel Pool Fractions Using LaVO4 Photocatalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, K.; Yang, P.; Yang, S.; Lu, C.; Song, Y.; Dong, S.; Sun, J.; Sun, J. One-Pot Facile Synthesis of Bi2S3/SnS2/Bi2O3 Ternary Heterojunction as Advanced Double Z-Scheme Photocatalytic System for Efficient Dye Removal under Sunlight Irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Ji, Y. Synergistic Adsorption-Photocatalysis for Dyes Removal by a Novel Biochar–Based Z-Scheme Heterojunction BC/2ZIS/WO3: Mechanistic Investigation and Degradation Pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) Photocatalytic Nanomaterials: Applications for Fuels and Environmental Management. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 254, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Xiong, T.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; et al. Covalent Organic Framework Photocatalysts: Structures and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4135–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liang, R.; Zhou, C.; Yan, G.; Wu, L. Carbon Quantum Dots (CQDs)/Noble Metal Co-Decorated MIL-53(Fe) as Difunctional Photocatalysts for the Simultaneous Removal of Cr(VI) and Dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, M.; Yasin, M.; Hussain, M.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Nizami, A.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Park, Y.-K. A Review on Recent Advances in the Treatment of Dye-Polluted Wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasse, K.; Baumann, W. Environmental Considerations for Textile Processes and Chemicals. In Textile Chemicals; Lacasse, K., Baumann, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 484–647. ISBN 978-3-642-18898-5. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, K.; Rizwan, M.; Shahid, M.J.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, R.; Rizvi, H. Textile Wastewater Treatment Options: A Critical Review. In Enhancing Cleanup of Environmental Pollutants; Anjum, N.A., Gill, S.S., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 183–207. ISBN 9783319554235. [Google Scholar]
- Amuda, O.S.; Deng, A.; Alade, A.O.; Hung, Y.-T. Conversion of Sewage Sludge to Biosolids. In Biosolids Engineering and Management; Wang, L.K., Shammas, N.K., Hung, Y.-T., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 7, pp. 65–119. ISBN 978-1-59745-174-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Garg, V.K. Industrial Wastes and Sludges Management by Vermicomposting. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, S.K.; Kumar, A. Hydrolytic Enzyme Protease in Sludge: Recovery and Its Application. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2015, 20, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Du, P.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Cheng, X.; Chang, B.; Wang, Z. Advances in Microbial Fuel Cells for Wastewater Treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, C.; Jing, Y.; Li, J. Effect of Energy Grass on Methane Production and Heavy Metal Fractionation during Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; McDonald, J.; Khan, S.J.; Nghiem, L.D. Occurrence of Trace Organic Contaminants in Wastewater Sludge and Their Removals by Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. A Roadmap for Achieving Energy-Positive Sewage Treatment Based on Sludge Treatment Using Free Ammonia. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9630–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Khan, M.D.; Sabir, S.; Gani, K.M.; Oves, M.; Khan, M.Z. Bio-Electro Degradation of Azo-Dye in a Combined Anaerobic–Aerobic Process along with Energy Recovery. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 9461–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurđević, D.; Blecich, P.; Jurić, Ž. Energy Recovery from Sewage Sludge: The Case Study of Croatia. Energies 2019, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinvoh, R.J.; Osadolor, O.A.; Sárvári Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Cost Effective Dry Anaerobic Digestion in Textile Bioreactors: Experimental and Economic Evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, S.; Ciggin, A.S. A Simple Kinetic Modeling Approach for Aerobic Stabilization of Real Waste Activated Sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonai, G.G.; de Souza, S.M.A.G.U.; de Oliveira, D.; de Souza, A.A.U. The Application of Textile Sludge Adsorbents for the Removal of Reactive Red 2 Dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 168, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, C.; Ananthasubramanian, M.; Kandhavadivu, P.; Vigneswaran, C.; Ananthasubramanian, M.; Kandhavadivu, P. 5–Enzymes in Textile Effluents. In Bioprocessing of Textiles; Vigneswaran, C., Ananthasubramanian, M., Kandhavadivu, P.B.T.-B.T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 251–298. ISBN 9789380308425. [Google Scholar]
- Faubert, P.; Barnabé, S.; Bouchard, S.; Côté, R.; Villeneuve, C. Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge Management Practices: What Are the Challenges to Assess the Impacts on Greenhouse Gas Emissions? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 108, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volmajer Valh, J.; Majcen Le Marechal, A.; Vajnhandl, S.; Jerič, T.; Šimon, E. 4.20—Water in the Textile Industry. In Treatise on Water Science; Wilderer, P.B.T.-T.W.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 685–706. ISBN 9780444531995. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, N.; Tahmid, M.; Shoronika, A.Z.; Fariha, A.; Roy, H.; Pervez, M.N.; Cai, Y.; Naddeo, V.; Islam, M.S. A Comprehensive Review on the Sustainable Treatment of Textile Wastewater: Zero Liquid Discharge and Resource Recovery Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Canbolat, Ç.B.; Lin, J.; Luis, P. The Potential of Membrane Technology for Treatment of Textile Wastewater; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun Kabir, S.M.; Mahmud, H.; Schӧenberger, H. Recovery of Dyes and Salts from Highly Concentrated (Dye and Salt) Mixed Water Using Nano-Filtration Ceramic Membranes. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuchiwal, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Malik, A. Treatment of Textile Effluent Using an Anaerobic Reactor Integrated with Activated Carbon and Ultrafiltration Unit (AN-ACF-UF Process) Targeting Salt Recovery and Its Reusability Potential in the Pad-Batch Process. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, R.; Eskikaya, O.; Keskinler, B.; Karagunduz, A.; Dizge, N.; Balakrishnan, D. Fabric Dyeing Wastewater Treatment and Salt Recovery Using a Pilot Scale System Consisted of Graphite Electrodes Based on Electrooxidation and Nanofiltration. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration Membrane Processes for Water Recycling, Reuse and Product Recovery within Various Industries: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska-Nowak, K.M. Application of Ceramic Membranes for the Separation of Dye Particles. Desalination 2010, 254, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, T.; Sarko, A. Mercerization of Cellulose. II. Alkali–Cellulose Intermediates and a Possible Mercerization Mechanism. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Sarko, A. Mercerization of Cellulose. III. Changes in Crystallite Sizes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 33, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y. Recovery of Caustic Soda in Textile Mercerization by Combined Membrane Filtration. In Technical Proceedings of the 2007 Cleantech Conference and Trade Show; CRC Press: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barredo-Damas, S.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Bes-Piá, A.; Iborra-Clar, M.I.; Iborra-Clar, A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Ceramic Membrane Behavior in Textile Wastewater Ultrafiltration. Desalination 2010, 250, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, N.; Jedidi, I.; Cerneaux, S.; Cretin, M.; Ben Amar, R. Development of an Asymmetric Carbon Microfiltration Membrane: Application to the Treatment of Industrial Textile Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Karki, S.; Ingole, P.G. Current Advances and Opportunities in the Development of Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes in the Area of Wastewater Treatment, Water Desalination, Biotechnological and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Chmiel, H.; Mavrov, V. Characteristics and Application of New Ceramic Nanofiltration Membranes. Desalination 2003, 157, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Ren, S.; Gao, Y.; Sun, W.; Gao, Z. Electrocoagulation: A Promising Method to Treat and Reuse Mineral Processing Wastewater with High COD. Water 2020, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, A.; White, M. Sustainable Dyeing Technologies. In Sustainable Apparel: Production, Processing and Recycling; Blackburn, R., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 135–160. ISBN 9781782423577. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Natural Dyeing of Cellulose Fibers Using Syzygium Cumini Fruit Extracts and a Bio-Mordant: A Step toward Sustainable Dyeing. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 33, e00472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, M.; Nawaz, M.S.; Khan, S.J.; Ghaffour, N.; Khan, M.Z. Recovering and Reuse of Textile Dyes from Dyebath Effluent Using Surfactant Driven Forward Osmosis to Achieve Zero Hazardous Chemical Discharge. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andooz, A.; Eqbalpour, M.; Kowsari, E.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ansari Cheshmeh, Z. A Comprehensive Review on Pyrolysis from the Circular Economy Point of View and Its Environmental and Social Effects. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 136021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Militky, J. Denim and Consumers’ Phase of Life Cycle. In Sustainability in Denim; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Wiener, J.; Militky, J. Life-Cycle Assessment of Denim. In Sustainability in Denim; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Duraisamy, G. Carbon Footprint on Denim Manufacturing. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-3-319-48281-1. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Life Cycle Assessment of Denim: A Review. Colourage 2019, 66, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Militky, J. Sustainability in Regenerated Textile Fibers. In Sustainability in the Textile and Apparel Industries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 63–95. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, H.; Periyasamy, A.P. Eco-Fibers in the Textile Industry. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 1413–1433. ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Venkatesan, H. Eco-Materials in Textile Finishing. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 1461–1482. ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Vikova, M.; Vik, M. A Review of Photochromism in Textiles and Its Measurement. Text. Prog. 2017, 49, 53–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikova, M.; Sakurai, S.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Yasunaga, H.; Pechočiaková, M.; Ujhelyiová, A. Differential Scanning Calorimetry/Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Analysis of Ultraviolet Sensible Polypropylene Filaments. Text. Res. J. 2021, 92, 3142–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Vikova, M.; Vik, M. Photochromic Polypropylene Filaments: Impacts of Mechanical Properties on Kinetic Behaviour. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2019, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viková, M.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Vik, M.; Ujhelyiová, A. Effect of Drawing Ratio on Difference in Optical Density and Mechanical Properties of Mass Colored Photochromic Polypropylene Filaments. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Xu, D.; Li, M.; Agbo, C.; Fu, S. Dope Dyeing of Lyocell Fiber with NMMO-Based Carbon Black Dispersion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.-Y.; Min, S.-K.; Cha, I.-H.; Choi, Y.-L.; Cho, Y.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-C. Decolorization of Triphenylmethane and Azo Dyes by Citrobacter Sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Dey, A. P-Nitrophenol -Bioremediation Using Potent Pseudomonas Strain from the Textile Dye Industry Effluent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.M.; Weatherley, L.R. Prediction of Bisolute Dye Adsorption Isotherms on Activated Carbon. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2000, 78, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, A.S.; Colton, J. Decolorisation of the Polymeric Dye Poly R by Streptomyces Viridosporus T7A. J. Basic Microbiol. 1996, 36, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.S. Utilization of Fermentation Waste (Corynebacterium glutamicum) for Biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionysiou, D.D.; Balasubramanian, G.; Suidan, M.T.; Khodadoust, A.P.; Baudin, I.; Laîné, J.M. Rotating Disk Photocatalytic Reactor: Development, Characterization, and Evaluation for the Destruction of Organic Pollutants in Water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2927–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Sofranko, A.C.; Dionysiou, D.D. Nanocrystalline TiO2 Photocatalytic Membranes with a Hierarchical Mesoporous Multilayer Structure: Synthesis, Characterization, and Multifunction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.F.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.W.; Cheng, W.P.; Kao, M.C. Possible Control Approaches of the Electro-Fenton Process for Textile Wastewater Treatment Using on-Line Monitoring of DO and ORP. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; Longo, M.A.; Sanromán, M.A. Electro-Fenton Decoloration of Dyes in a Continuous Reactor: A Promising Technology in Colored Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S. Effects of an Electric Field and Zero Valent Iron on Anaerobic Treatment of Azo Dye Wastewater and Microbial Community Structures. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Gao, D.W.; Fu, Y.; Wu, W.M.; Ren, N.Q. Impact of Reactor Configuration on Anammox Process Start-up: MBR versus SBR. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Sanmartín, I.; Gómez, P. Homogeneous Sonophotolysis of Food Processing Industry Wastewater: Study of Synergistic Effects, Mineralization and Toxicity Removal. Ultrason. Sonochem 2013, 20, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




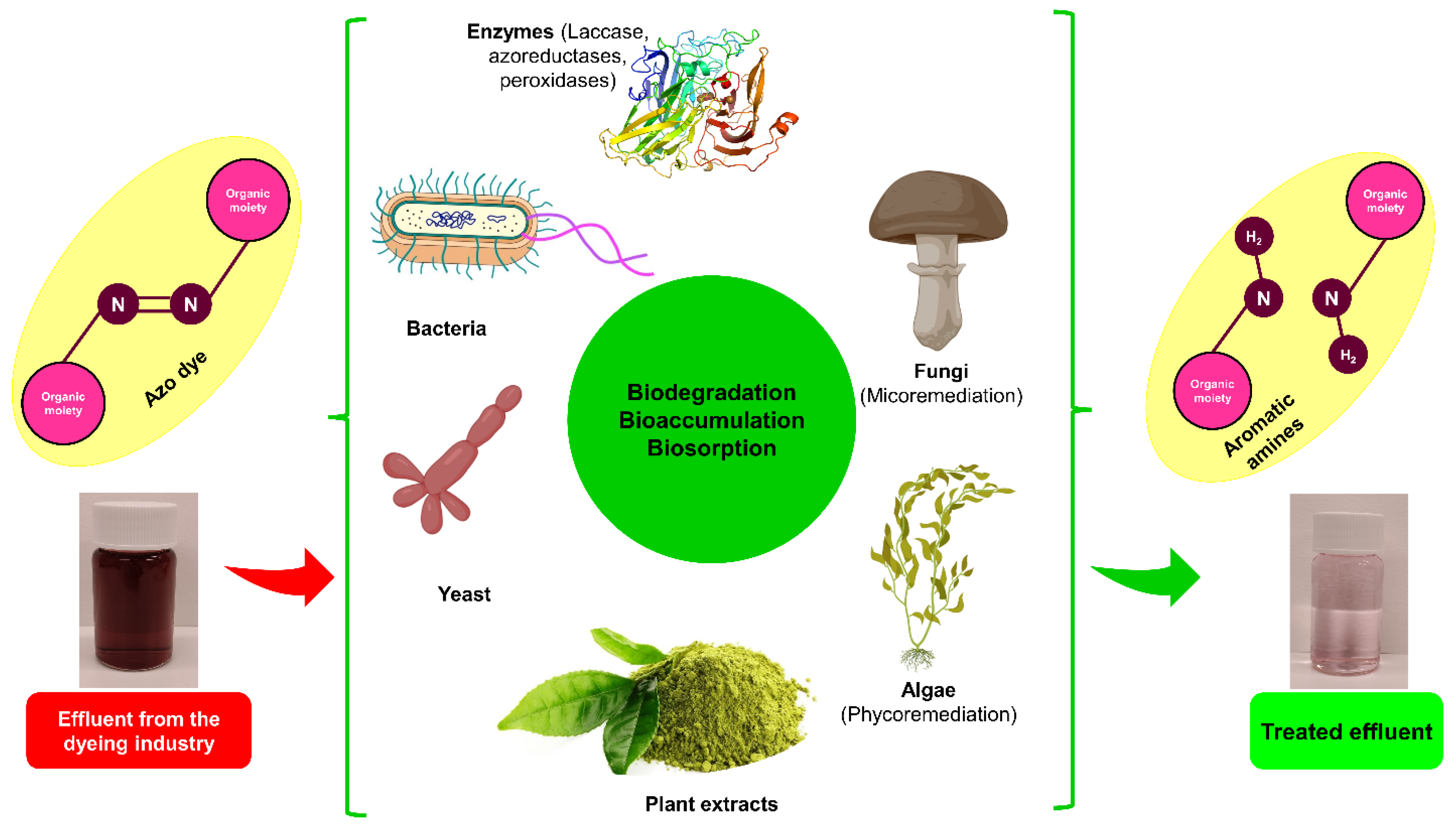








| Type | Treatment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Oxidation | Rapid and effective for both organics and inorganics Can be used for both soluble and insoluble dyes No need to use microorganisms | Formation of by products High energy consumption and running costs | [33,34,35] |
| Ozonation | No alternation in the sample volume | Short half-life and need pretreatment | [33,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | |
| Chemical precipitation | Low investment and simple process | High maintenance and required to dispose the sludge | [43,44] | |
| Electro kinetic coagulation | Economic process | High sludge generation | [45] | |
| Electrochemical treatment | Moderate metal selectivity Rapid breakdown | Formation of by products Require high energy | [46] | |
| Advanced oxidation with Fenton reagents as catalyst | No energy input required Effective for both insoluble and soluble dyes, for wide variety of wastes treatment | Sludge formation Expensive process | [47,48,49,50,51,52,53] | |
| NaOCL | Accelerated azo bond cleavage | Toxic aromatic amine release | [53] | |
| Photochemical degradation (based on catalyst) | Effective oxidation and lab scale applicability No sludge generation | Formation of by products Excessive dissolved O2 is required | [37] | |
| Coagulation-Flocculation/Sedimentation | Variety of coagulants-flocculants | Expensive chemicals and no recycling | [54,55] | |
| Biological method | Single cell organisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae and yeasts | Generally, these are more economical than chemical and physical methods. For any dye industry and as a preparatory step for removal Acceptable efficiency for low concentrations and volumes Highly effective for specific dye species | Requires large land area, less flexible in operation and design and partially to totally non-degrading to dyes | [56,57,58] |
| Aerobic (presence of free DO) | Facile COD removal | Longer detention times | [59,60,61] | |
| Anaerobic (absence of DO) | Resistance to wide variety of dyes Steam generation via the produced biogas | Longer acclimatization phase | [60,61] | |
| Physical | Membrane (ultrafiltration, microfiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis) | Removes all types of dyes | Inapplicable for wastewater treatment due to the large pore size | [62,63,64,65] |
| Adsorption | For all dye industry Regeneration of adsorbent with low loss | Only soluble dyes High energy consumption | [66] | |
| Ion exchange | For specific applications | [67,68] | ||
| Irradiation | Wide range of colorants Efficient even for low volumes | High dissolved oxygen requirement Light-resistant colorants cannot be degraded | [69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Periyasamy, A.P. Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020495
Periyasamy AP. Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability. 2024; 16(2):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020495
Chicago/Turabian StylePeriyasamy, Aravin Prince. 2024. "Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment" Sustainability 16, no. 2: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020495
APA StylePeriyasamy, A. P. (2024). Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 16(2), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020495






