Study on the Sand Reduction Effect of Slope Vegetation Combination in Loess Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
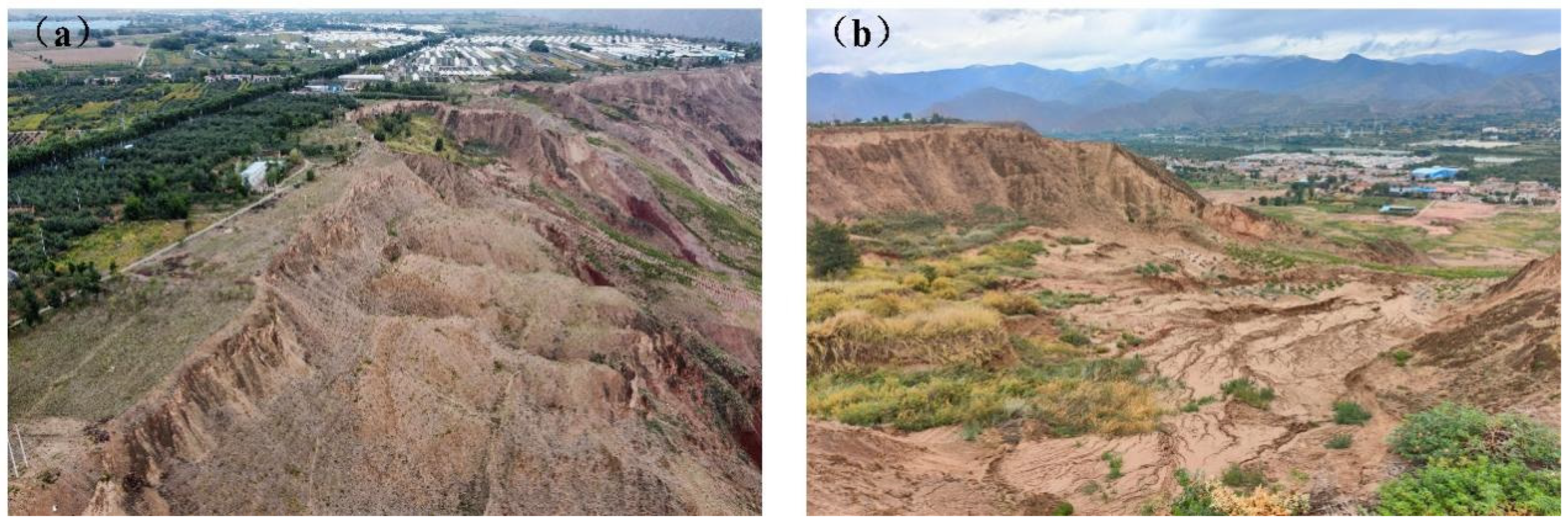
2.1. Research Area Overview
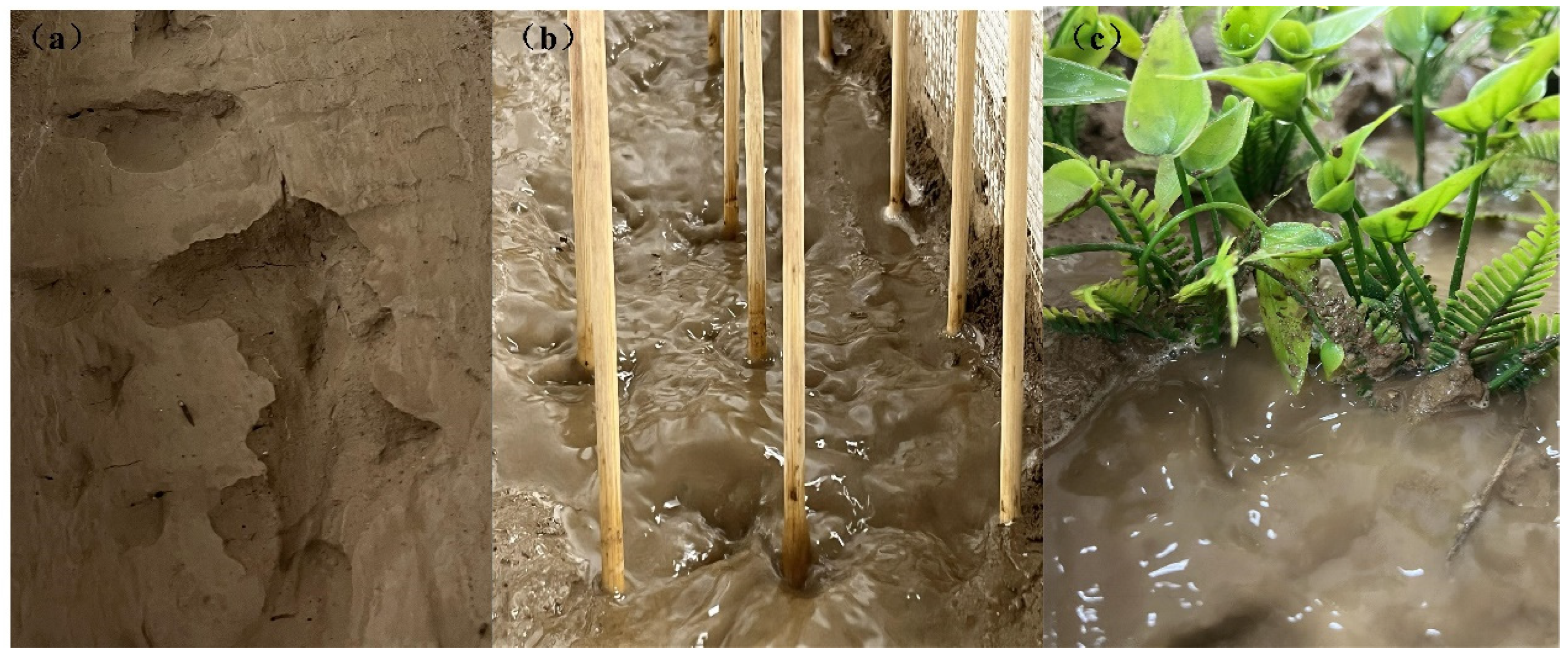
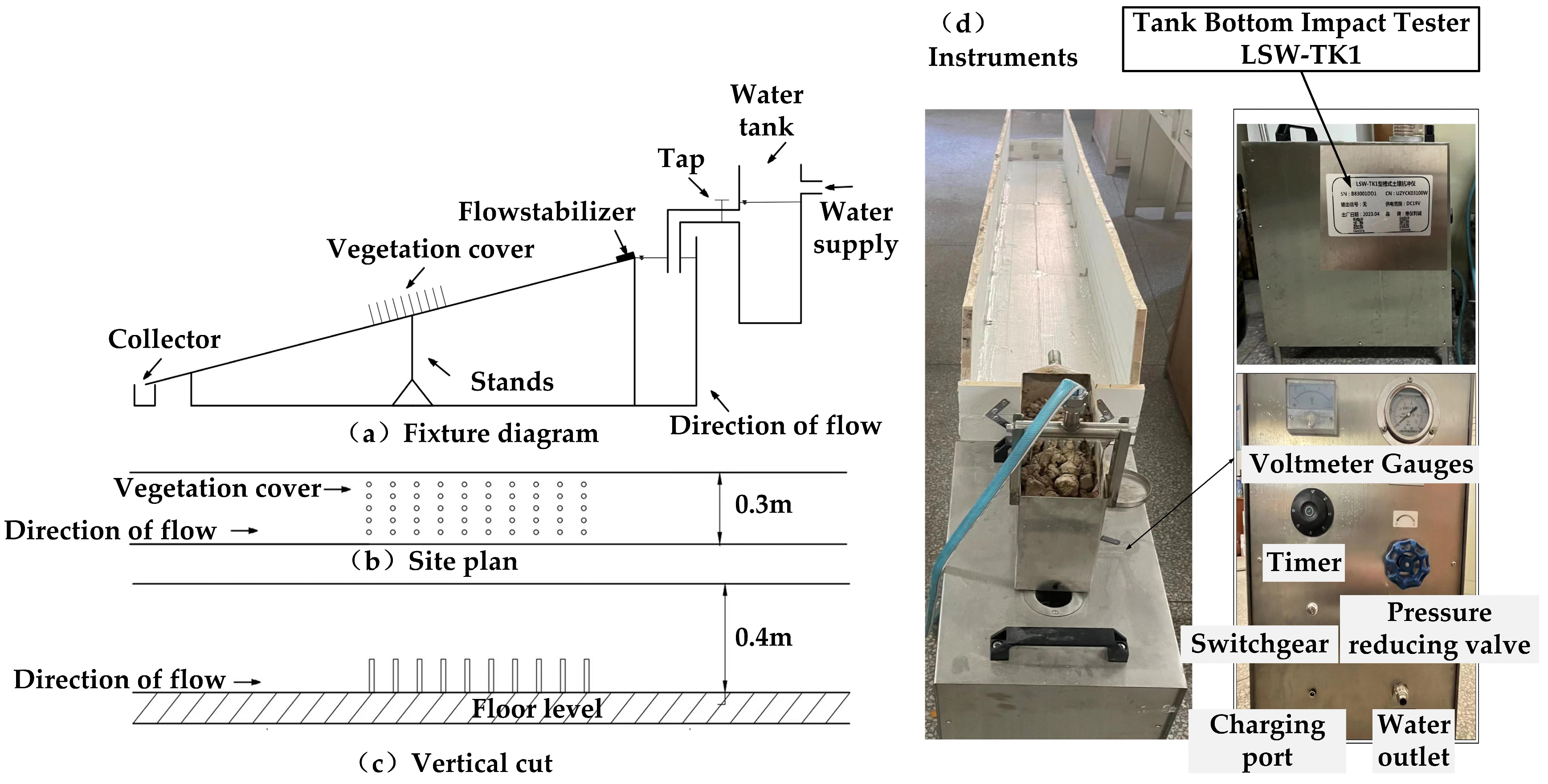
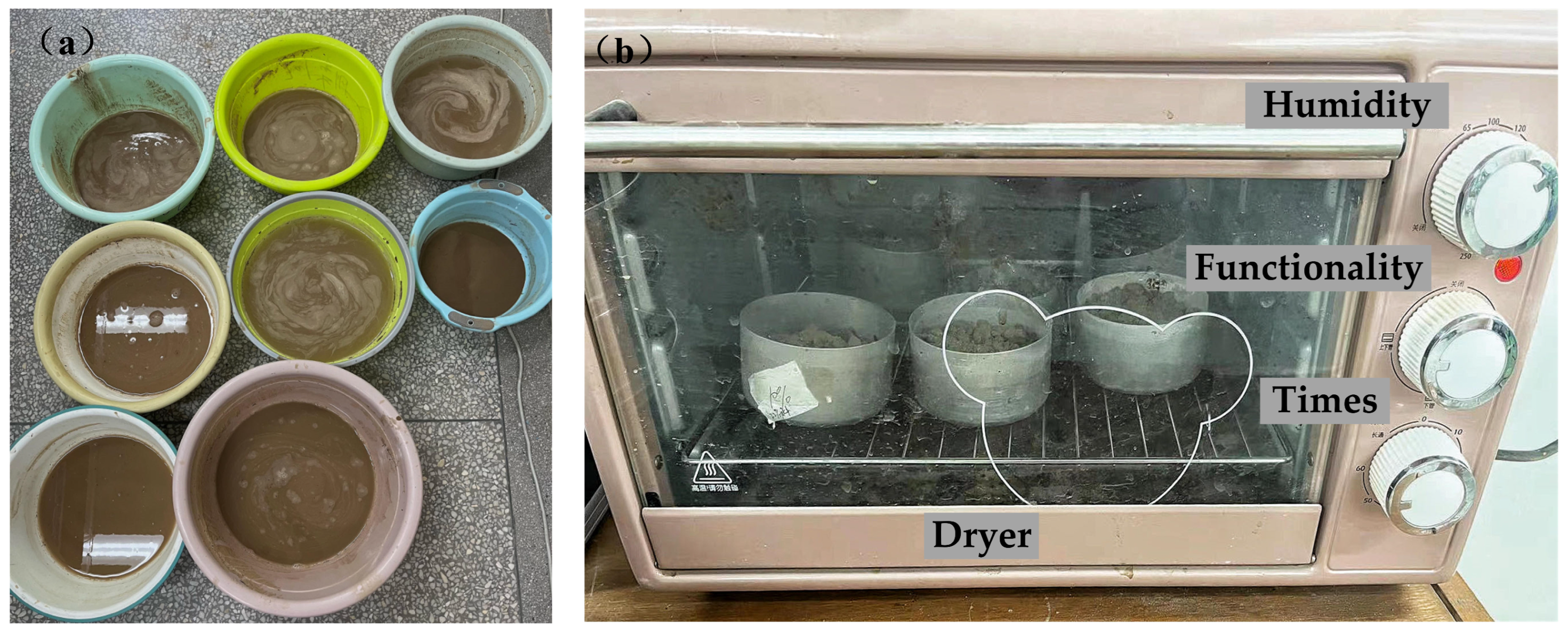
2.2. Design and Methodology
3. Theoretical Analyses
3.1. Slope Runoff Sand Production Analysis
3.2. Data Calculation
4. Analysis of Results
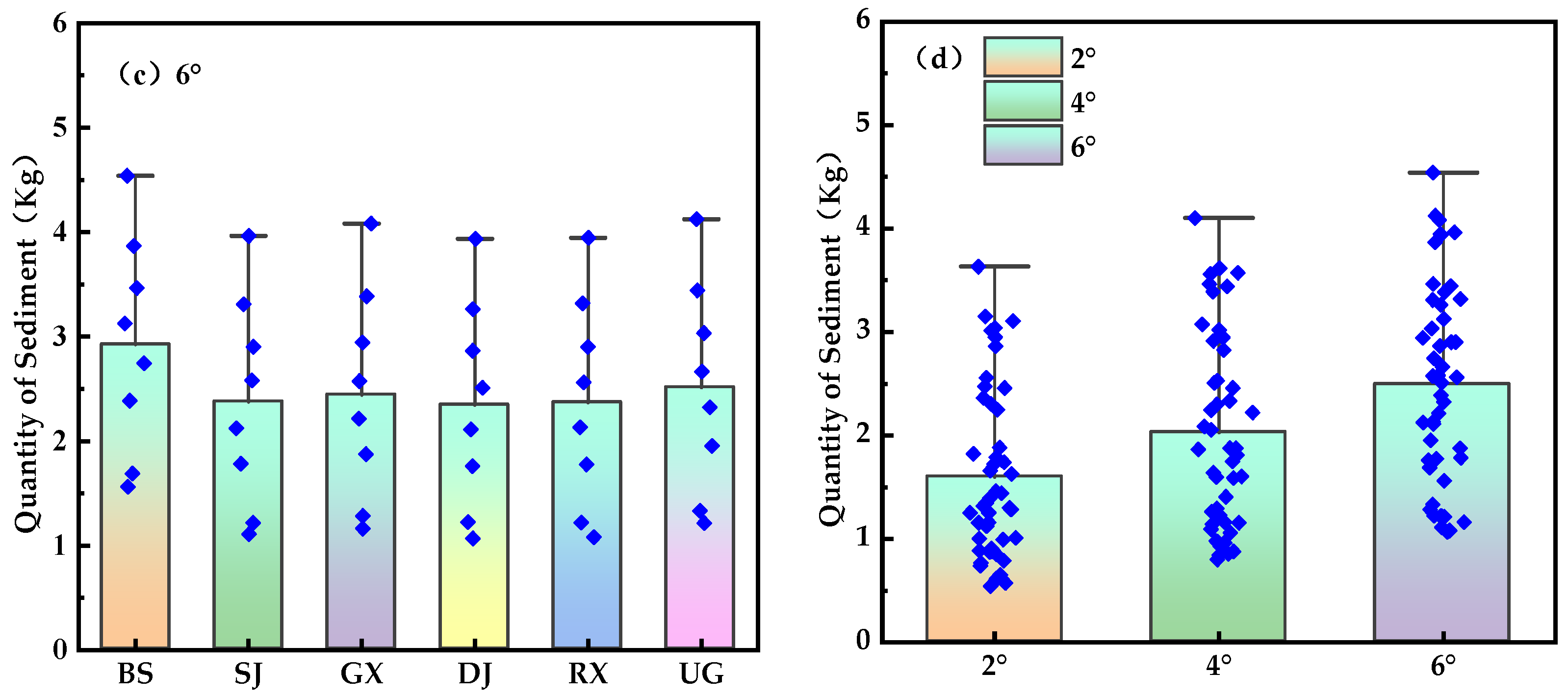
4.1. Characteristics of Changes in Slope Erosion Sand Production
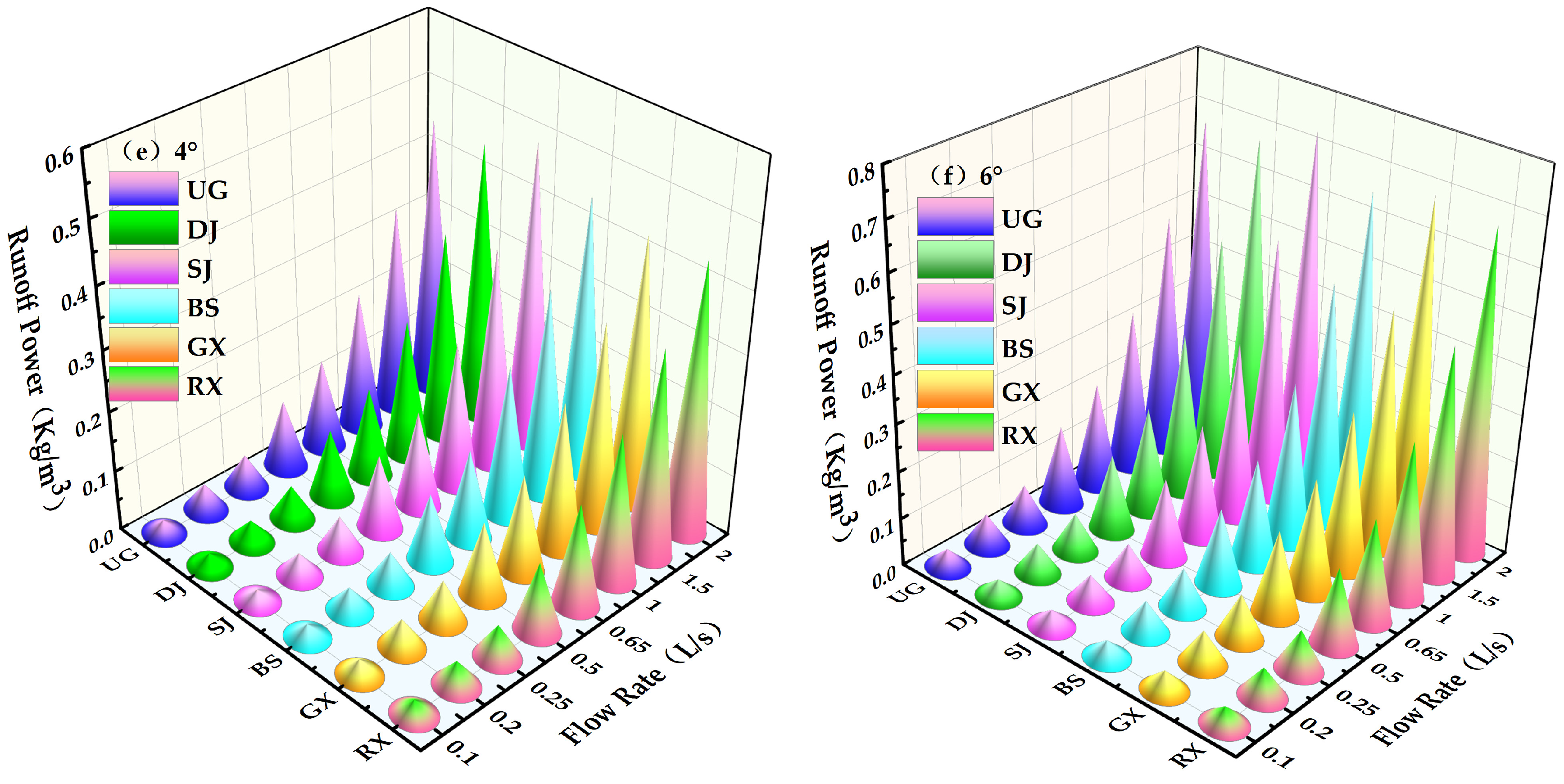
4.2. Hydrodynamic Parameters
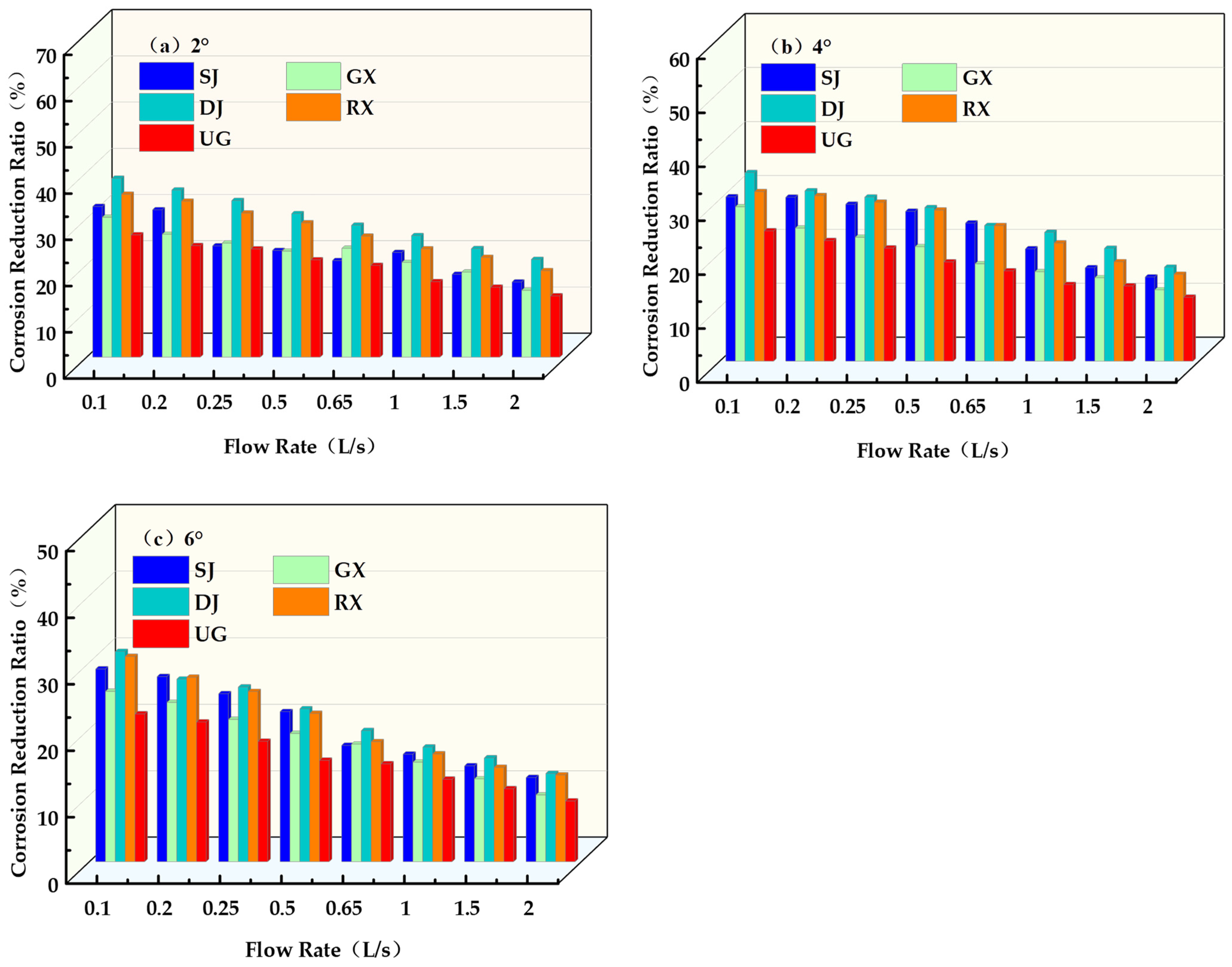
4.3. Characteristics of Runoff Shear Change
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Shangguan, Z.; Yao, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Dang, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, B. Ecological Effects of Soil Conservation in Loess Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H. Scale characters analysis for gully structure in the watersheds of loess landforms based on digital elevation models. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Cao, W.; Guo, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yin, Z. Review of the effects of vegetation patterns on soil erosion and sediment yield. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 4905–4912. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Rubinato, M.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, J. Impact of Multiple Vegetation Covers on Surface Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Small Basin of Nverzhai, Hunan Province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lin, Q.; Wu, F. Comparative Study of the Impacts of Maize and Soybean on Soil and Water Conservation Benefits during Different Growth Stages in the Loess Plateau Region. Land 2024, 13, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of farmland vegetation row direction on overland flow hydraulic characteristics. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M. Effects of Vegetation Stems on Hydraulics of Overland Flow Under Varying Water Discharges. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.; Keesstra, S.D.; Stroosnijder, L.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Maroulis, J. Soil conservation through sediment trapping: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Luo, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y. Runoff- and erosion-reducing effects of vegetation on the loess hillslopes of China under concentrated flow. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.; Kavian, A.; Roushan, M.H.; Jafarian, Z. The efficiency of vegetative buffer strips in runoff quality and quantity control. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Cui, J.; Cheng, H. Influence of Load Mode on Particle Crushing Characteristics of Silica Sand at High Stresses. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04019194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T. Sediment deposition and overland flow hydraulics in simulated vegetative filter strips under varying vegetation covers. Hydrol Process. 2016, 30, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Flanagan, D.C.; Engel, B.A. Estimating sediment transport capacity for overland flow. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 123985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Pan, C.; Peng, J.; Wang, L. Characteristics of the Sediment Transport Process in Vegetation Hillslopes under Different Flow Rates. Water 2023, 15, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L. Effectiveness of typical plant communities in controlling runoff and soil erosion on steep gully slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Bi, H.; Huo, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, W. Determining the optimal vegetation coverage for controlling soil erosion in Cynodon dactylon grassland in North China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yoshimoto, N.; Wen, L. Correlation of Critical State Strength Properties with Particle Shape and Surface Fractal Dimension of Clinker Ash. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervroëdan, L.; Armand, R.; Saunier, M.; Faucon, M. Effects of plant traits and their divergence on runoff and sediment retention in herbaceous vegetation. Plant Soil. 2019, 441, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G. Quantifying the Binding and Bonding Effects of Plant Roots on Soil Detachment by Overland Flow in 10 Typical Grasslands on the Loess Plateau. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z. The Contribution of Astragalus adsurgens Roots and Canopy to Water Erosion Control in the Water–Wind Crisscrossed Erosion Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.X. Assessment of fabric characteristics with the development of sand liquefaction in cyclic triaxial tests: A DEM study. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 176, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Mu, H.; Liu, B.; Yu, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y. Effects on the plant stem arrangement onsediment transport capacity of croplands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Deng, J.; Gu, C.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Gao, J. Effect of shrub-grass vegetation coverage and slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Z. Calibration of an elastoplastic model of sand liquefaction using the swarm intelligence with a multi-objective function. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 15, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, Z.; Ding, S. Inhibiting Effects of Vegetation on the Characteristics of Runoff and Sediment Yield on Riparian Slope along the Lower Yellow River. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Lan, M.; Wainwright, J.; Shangguan, Z. Overland flow resistances on varying slope gradients and partitioning on grassed slopes under simulated rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2490–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Yu, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H. Effects of Pinus tabulaeformis litter cover on the sediment transport capacity of overland flow. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Yu, X.; Fu, S.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G. Effect of stem cover on hydraulic parameters of overland flow. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Huang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Xie, W.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y. Effect of complex-grain-size curves on shear modulus degradation of calcareous sand. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, C.; Zheng, H. Importance of grass stolons in mitigating runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainstorms. Catena 2022, 213, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, C. The relative importance of different grass components in controlling runoff and erosion on a hillslope under simulated rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Li, Z.B.; Yu, G.Q.; Li, C. Effects of precipitation and different distributions of grass strips on runoff and sediment in the loess convex hillslope. Catena 2018, 162, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, G.Q.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P. Experimental study on slope runoff, erosion and sediment under different vegetation types. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2415–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, Z. Development of a Large Shaking Table Test for Sand Liquefaction Analysis. Lithosphere 2024, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Meng, X.; Ye, Z. Impacts of Grass Coverage and Arrangement Patterns on Runoff and Sediment Yield in Slope-Gully System of the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2023, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Effects of slope vegetation patterns on erosion sediment yield and hydraulic parameters in slope-gully system. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jing, H.; Song, Y.; Li, C. Experimental study on flow characteristics in a flume with flexible vegetation. Yangtze River 2018, 49, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Lei, S.; Gong, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, G. Study on erosion and stability of the ecological slope. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1071231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Yao, W.; Wang, G. Effects of soil shear strength and runoff erosivity on slopes with different vegetation cover. Adv. Water Sci. 2016, 27, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, Y.; Liang, D.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Zou, S. Hydrodynamic performance of shallow-water waveguides subject to nonlinear waves. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 047108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M. Flow and Transport in Regions with Aquatic Vegetation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 44, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assessment of the impact of different vegetation patterns on soil erosion processes on semiarid loess slopes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1860–1870. [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Wang, F.; Shi, X.; Bu, S.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xiong, L. Research on the Impact of Using a Combination of Rigid and Flexible Vegetation on Slope Hydrological Properties in Loess Regions. Water 2024, 16, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, N.; Liu, J. Response of soil detachment rate by raindrop-affected sediment-laden sheet flow to sediment load and hydraulic parameters within a detachment-limited sheet erosion system on steep slopes on Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 185, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Fu, X. Research on relationships between sediment yield and hydraulics parameters on slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Shi, D.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Runoff erosion process on different underlying surfaces from disturbed soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lü, N.; Wang, S. Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau. Catena 2015, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, H.; Mouzai, L.; Bouhadef, M. Plants Cover Effects on Overland Flow and on Soil Erosion under Simulated Rainfall Intensity. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 7, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y. Experimental Study of Overland Flow through Rigid Emergent Vegetation with Different Densities and Location Arrangements. Water 2018, 10, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.Q.; Yao, W.Y.; Shen, Z.Z.; Yang, C.X. Experimental study on erosion process and hydrodynamics mechanism of alfalfa grassland. Shuili Xuebao 2011, 42, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, J. Effects of patchy distributed Artemisia capillaris on overland flow hydrodynamic characteristics. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Zhu, B. Experimental Study on Impact of Vegetation Patterns on Sediment Yield of Slope. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Shen, M. Effects of Grass Belt Distribution on runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, G. Effects of long-term vegetation coverage on runoff and sediment reducing ability of purple soil slope. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Jia, C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wu, G. Effects of mosaic-pattern shrub patches on runoff and sediment yield in a wind-water erosion crisscross region. Catena 2019, 174, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y. Experiment of the sediment transport pattern and resistance mechanism for sand beaing flow in vegetation patches. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural. Engineering 2023, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.C.; Wei, W.; Duan, X.W. Response of the runoff and sediment process on loess slope to the vertical structure changes of three shrub and grass vegetations under simulated rainfall. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 8602–8611. [Google Scholar]









| Natural Moisture Content (%) | Dry Density (g/cm3) | Relative Particle Density | Plastic Limit (%) | Liquid Limit (%) | Soil Particle Size <0.005 mm (%) | Soil Particle Size 0.005~0.05 mm (%) | Soil Particle Size >0.05 mm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2 | 1.29 | 2.63 | 17.8 | 23.7 | 16 | 60 | 24 |
| Slope (°) | Layout Average | Sand Production (kg) | Average Erosion Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2° | SJ | 1.54 | 23.67 |
| GX | 1.56 | 22.66 | |
| DJ | 1.43 | 29.89 | |
| RX | 1.47 | 27.39 | |
| UG | 1.61 | 19.96 | |
| 4° | SJ | 1.90 | 24.64 |
| GX | 2.01 | 20.09 | |
| DJ | 1.85 | 26.60 | |
| RX | 1.89 | 25.15 | |
| UG | 2.06 | 17.84 | |
| 6° | SJ | 2.37 | 20.69 |
| GX | 2.44 | 18.18 | |
| DJ | 2.34 | 21.78 | |
| RX | 2.36 | 21.00 | |
| UG | 2.51 | 15.49 |
| Slope | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2° | h = 1.466Q0.642 | 0.993 |
| 4° | h = 1.500Q0.672 | 0.986 |
| 6° | h = 1.465Q0.634 | 0.993 |
| Slope | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2° | v = 0.076ln(Q + 0.364) + 0.213 | 0.976 |
| 4° | v = 0.345ln(Q + 3.9) − 0.327 | 0.994 |
| 6° | v = 0.093ln(Q + 0.334) + 0.255 | 0.993 |
| Slope | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2° | 0.992 | |
| 4° | 0.987 | |
| 6° | 0.993 |
| Slope | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2° | Φ = 2.24 + 0.11V | 0.99 |
| 4° | Φ = −4.85 + 0.23V | 0.99 |
| 6° | Φ = 0.002 + 0.34V | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Tao, H.; Shi, X.; Bu, S.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, D. Study on the Sand Reduction Effect of Slope Vegetation Combination in Loess Areas. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9132. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209132
Wang F, Tao H, Shi X, Bu S, Bao Z, Zhang D. Study on the Sand Reduction Effect of Slope Vegetation Combination in Loess Areas. Sustainability. 2024; 16(20):9132. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209132
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fucui, Hu Tao, Xi Shi, Shilong Bu, Ziming Bao, and Dezhi Zhang. 2024. "Study on the Sand Reduction Effect of Slope Vegetation Combination in Loess Areas" Sustainability 16, no. 20: 9132. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209132
APA StyleWang, F., Tao, H., Shi, X., Bu, S., Bao, Z., & Zhang, D. (2024). Study on the Sand Reduction Effect of Slope Vegetation Combination in Loess Areas. Sustainability, 16(20), 9132. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209132






