Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Plastic Bags Used as Improvised Food Cooking Covers: A Case Study from the Mozambican Community
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Sample Overview
2.2. Sample Preparation for Density Determination
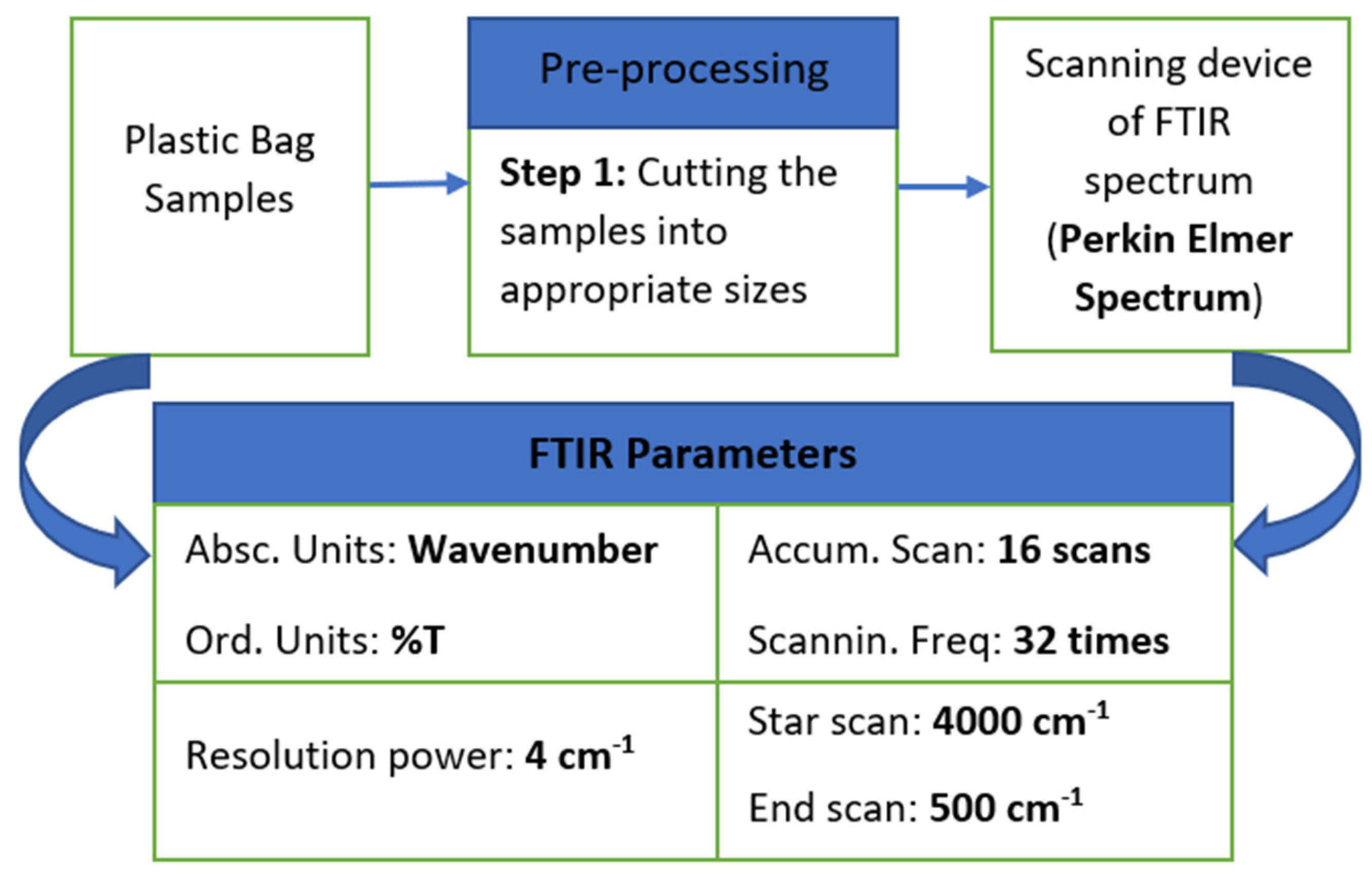
2.3. Plastic Bags’ Characterization Based on Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Sample Preparation for FTIR Analysis
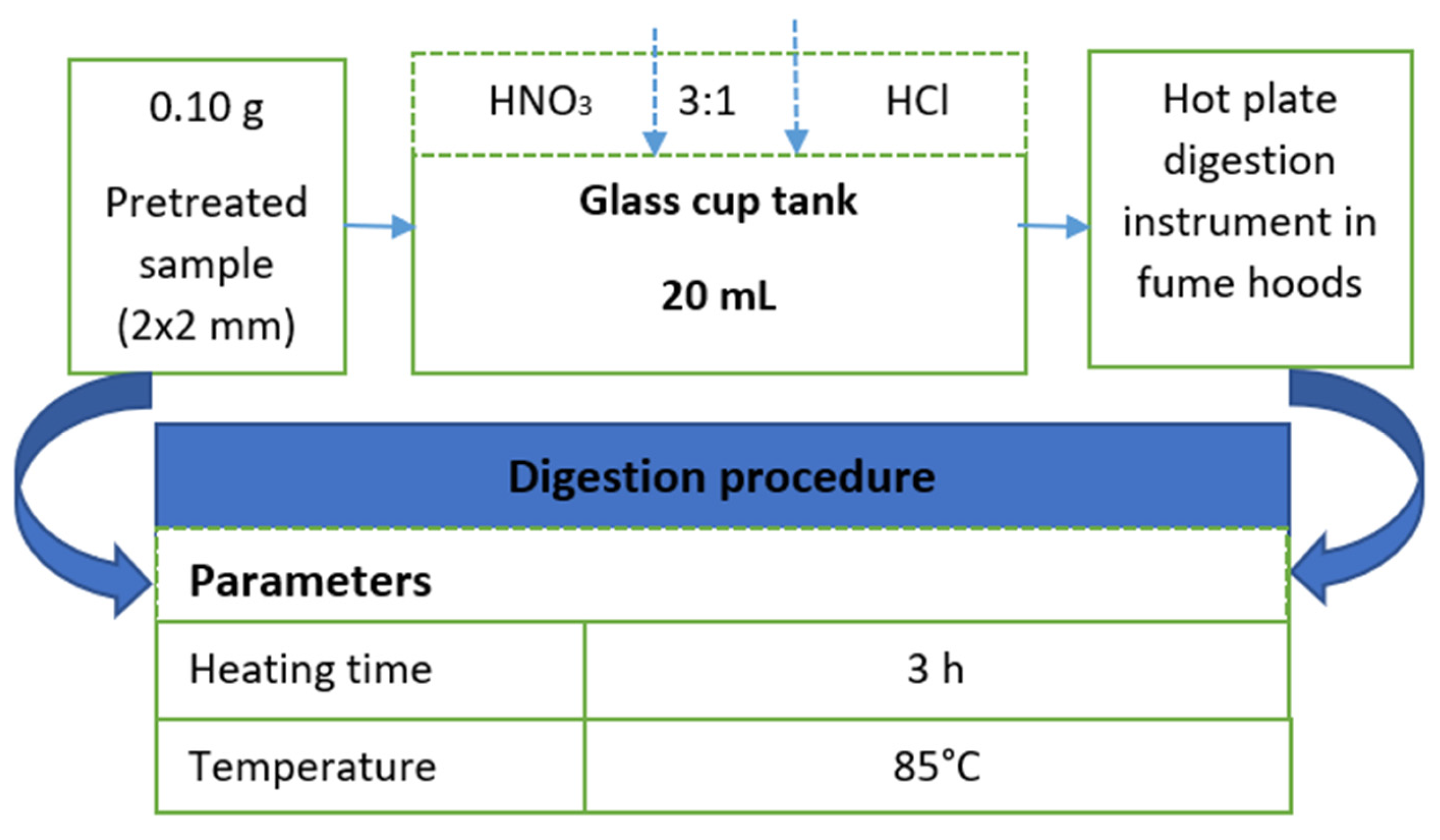
2.4. Plastic Bags’ Characterization Based on Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
2.4.1. Sample Preparation for AAS Analysis
2.4.2. Reagents
2.4.3. Conversion of Instrument Data into mg/kg Concentration
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the Density
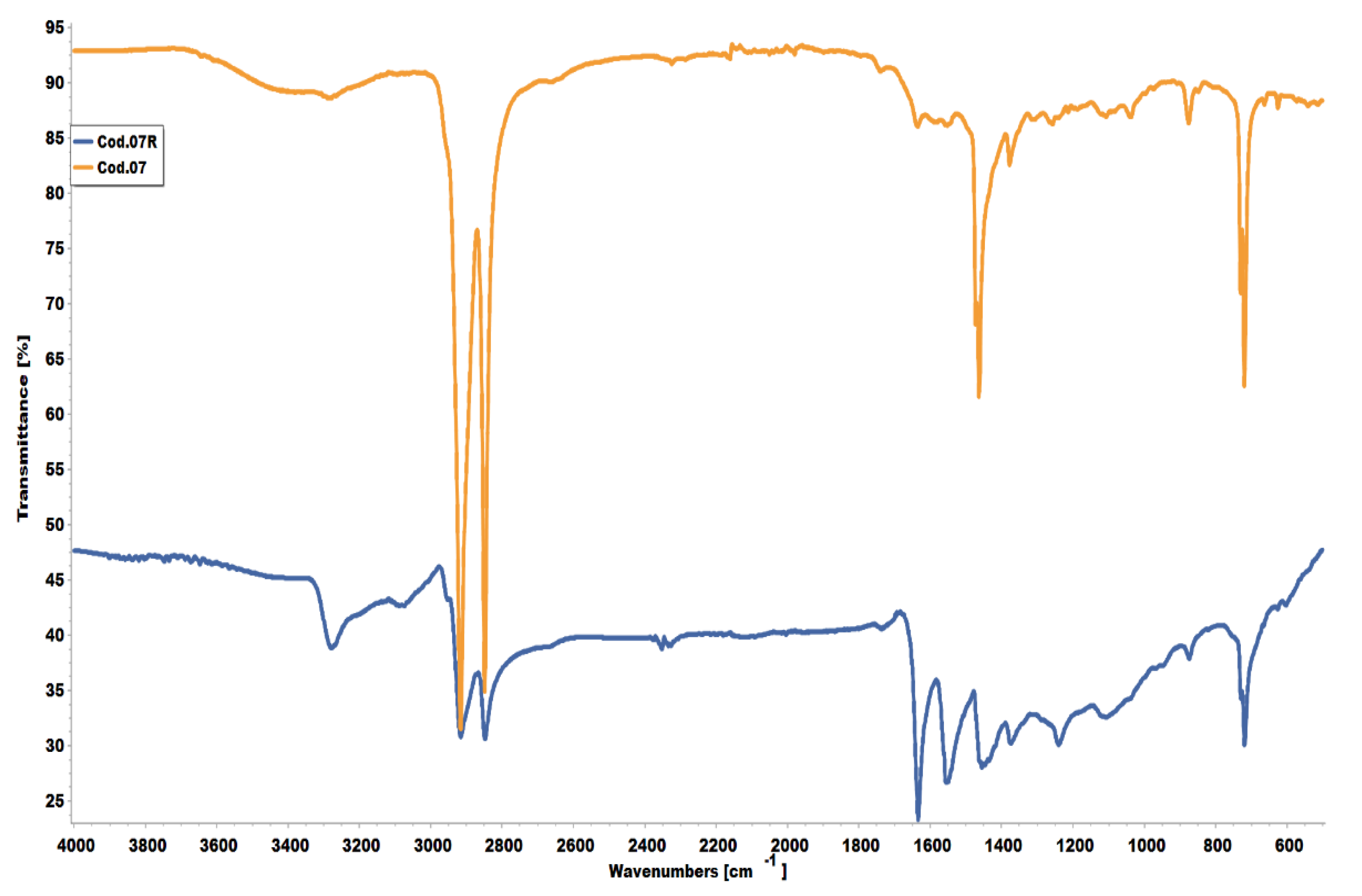
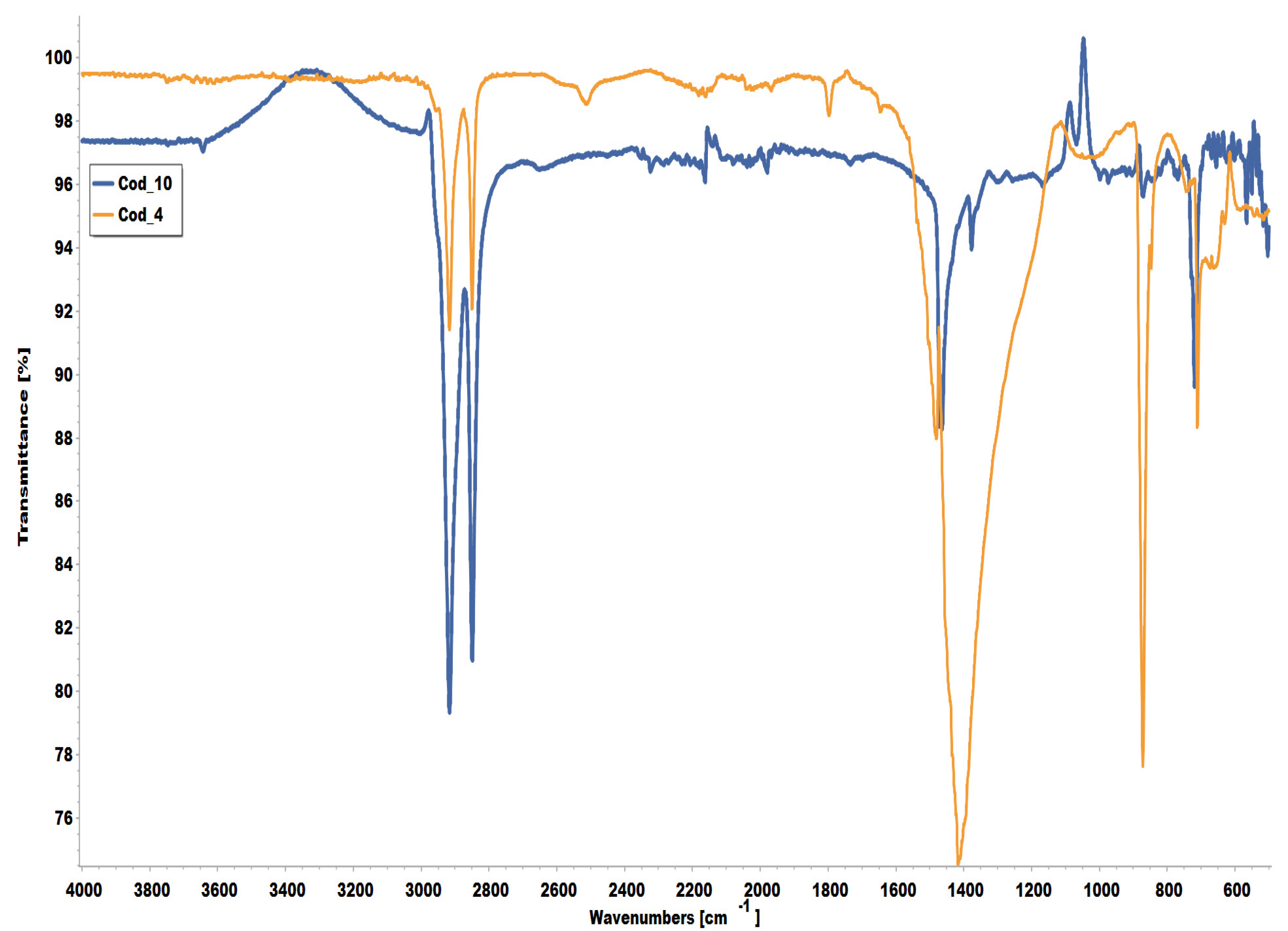
3.2. Characterization of the Plastic Bags by FTIR
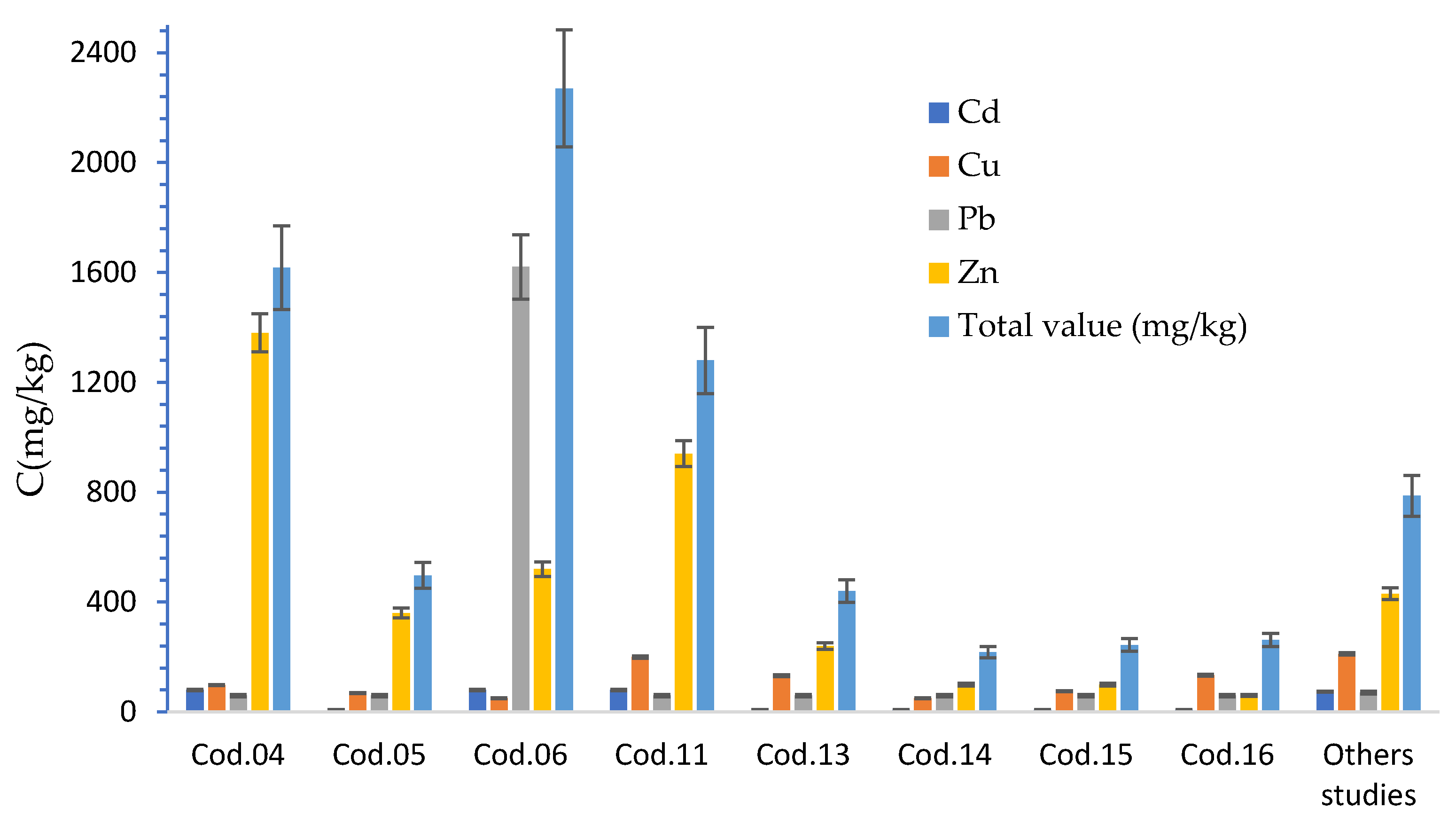
3.3. Quantification of Heavy Metals in the Plastic Bags by AAS
4. Limitations of the Study and Suggestions for Safe Practices for Food Cooking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alabi, O.A.; Ologbunjaye, K.I.; Awosohe, O.; Alalade, O.E. Public and environmental health effects waste disposal: A review. J. Toxical Risk Assess 2019, 5, 021. [Google Scholar]
- Vedolin, M.C. Study of the Distribution of Metals in Plastics on the Coast of São Paulo: Pollution Assessment Through Pellet Analysis; Desert presented to the Oceanography Institute of the University of São Paulo; Oceanography Institute of the University of São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Son, G.; Zhang, H. Material identification and heavy metals characterization of plastic packaging bags used in Chinese express delivery. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1253108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, F.J.; Sharff, P.A. Buldings: Plastics and Composites. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Simpson Gumpertz & Heger, Inc.: Arlington, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 833–841. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J. Comparing Thermoplastic elastomers and Thermoset Rubber. In Plastics Engineering; The Madison Group: Madison, WI, USA, 2016; pp. 36–38. Available online: www.plasticsengineering.org (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Amin, S.; Amin, M. Thermoplastic Elastomeric (TPE) materials and their use in outdoor electrical isulation. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2011, 29, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Le, V.G.; Nguyen, M.; Nguyen, H.L.; Lin, C.; Hadi, M.; Hung, N.T.Q.; Hoang, H.G.; Nguyen, K.N.; Tran, H.T.; How, D.; et al. A comprehensive review of micro and nanoplastics in the atmosphere: Occurrence, fate, toxicity and strategies for risk reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 904, 166649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.I.; Sarkingobir, Y.; Dikko, M. Spectro-analytical research of selected heavy metals (Cu, Cd, Cr and Pb) in four different single-use plastics commonly in contact with food from Sokoto, Nigeria. J. Teknokes 2022, 15, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred-Ahmadu, O.H.; Ayejuyo, O.O.; Tenebe, I.T.; Benson, N.V. Occurrence and distribuition of micro (meso) plastic sorbed heavy metals and metalloids in sediments, Gulf of Gunea coast (SE Atlantic). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, O.; Wang, S.; Lu, W. Heavy metals dispersion during thermal treatment of plastic bags and its recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sall, L.M.; Diaw, D.K.A.; Gningue-Sall, D.; Aaron, E.S.; Aaron, J. Toxic heavy metals: Impact on the environmental and human health and treatment with conducting organic polymers, a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29927–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metals Toxicity and Environment. Natl. Inst. Health 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Okpara, C.E.; Fayemi, E.O.; Wojuola, B.O.; Onwudiwe, C.D.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical detection of selected heavy metals in water: A case study of African experiences. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2022, 2, 26319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.; Raina, A.; Mohineesh; Dogra, D.T. Direct determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead, Copper metals in tap water of Delhi (India) by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Technique. EDP Sci. 2013, 1, 09009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylak, M.; Aydin, A. Determination of some heavy metals in food an environmental sample by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after coprecipitation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 124–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, K.M.; Pivnenko, K.; Olsson, M.E.; Astrup, F.M. Contamination in plastic recycling: Influence of metals on the quality of reprocessed plastic. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, H.; Schiller, M.; Maier, R. Plastics Additives Handbook, 6th ed.; Hanser Gardner: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2009; p. 1248. ISBN 1569904308/9781569904305. [Google Scholar]
- Peltzer, M.A.; Simoneau, C. Report an Interlaboratory Comparison from the European Reference Laboratory of Food Contact Materials: ILC002 2023-Identification of Polymeric Materials; JRC valideted methods, Reference Methods and Measurements reports; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alin, J. Migration from Plastic Food Packaging During Microwave Heating; KTH. Chemical Science and Engineering: Stockholm, Sweden, 2012; ISBN 978-7501-363-3. [Google Scholar]
- Eti, S.A.; Islam, M.S.; Shourove, J.H.; Saha, B.; Ray, S.K.; Sultana, S.; Shaik, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Assessment of heavy metals migrated from food contact plastic packaging: Bangladesh perspective. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, A.R. Migration levels of toxic heavy metals in locally made food packaging containers. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopffer, M.; Flanconneche, B. Transport properdines of gases in polymer, bibliographic review. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 56, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Kotsanopoulos, K.V. Migration phenomenon in food packaging. Food-package interactions, mechanisms, types of migrants, testing and relative legislation; A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parlament and Council Directive 94/62/EC of 20 December 1994: On Packaging and Packaging Waste. (OJL 365 31.12.1994, p.10). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/1994/62/oj (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Netherland Institute for Sustainable packaging. Fact Sheet-Heavy metals in packaging. In Part of the Dossier on Food Safety; Netherland Institute for Sustainable packaging: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Small Organoarsenic Species in Food; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Manoel, G.F. Physico-Chemical Characterization and Rheological Study of Asphaly Modified by HDPE, LDPE and LLDPE Polymers and Contribuition to the Aging Study of Petroleum Asphalt Cement. Ph.D. Thesis, Minas Gerais Federal University, Minas Gerais, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (Arsenic (As), Cadimium (Cd), Chromium (Cr (VI)), Mercury (Hg) and Lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environ. Moni. Assess 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Biswas, C.; Banerjee, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Pramanick, K. Interaction of plastic particles with heavy metals and the resulting toxicological impacts: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60291–60307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Yesmin, M.; Jeba, F.; Hoque, M.S.; Jamee, R.A.; Salam, A. Risk assessment and evaluation of heavy metals concentrations in blood samples of plastic industry workes in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 81243: 2020; Safety of Toys-Migration of Certain Elements. International Standard (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Traistaru, E.; Rivis, A.; Moldovan, C.R.; Menelaou, A.; Georgescu, C. Modelling migration from plastic packaging materials used in food industry. J. Agroaliment. Process Technol. 2013, 19, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Akhyar, F.M. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy; Intech Open: London, UK, 2012; p. 270. ISBN 978-953-307-817-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussoke, L.; Banadda, N.; Sempala, C.; Kigozi, J. Migration of chemical contaminants from polyethylene bags into food during cooking. Open Food Sci. J. 2015, 9, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN-EA-Quantis. National Guidance for Access Points and Plastic Pollution Modeling Actions: Results from Mozambique; IUCN-EA-Quantis: Maputo, Mozambique, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, M.S.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, L.; Khan, A.; Mateen, A.; Jahan, S.; Ullah, U.; AlMasoud, N.; Alomar, T.S.; Rauf, A.; et al. Quantification of toxic heavy metals, trace elements and essential minerals contents in traditional herbal medicines commonly utilized in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malook, K.; Ul-Haque, I. Evaluation of essential and non-essential elemental composition of commonly used medicinal plants from district Peshwar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64337–64344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; He, H.; Chen, R. In Situ Density Determination of Polyethylene in Multilayer Polymer Films Using Raman Microscopy; Thermo Fisher Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neves dos Santos, L.R. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Separation of Plastics from Municipal Solid Waste by Selective Dissolution Methods. Master’s Thesis, School of Engineering, University of Minho, Braga, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.C. The Infrared spectra of polymers II: Polyethylene. Spectroscopy 2021, 36, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, M.J. Engineering Plastics Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, O.; Yang, L.; Yanchun, X. Determination of the selected heavy metals and metalloid contents in various types of plastics bags. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC 17025; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Standards Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iasonline.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/ISO-IEC-17025-2017-IAS.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- GB/T16606.3-2018; Packing for Express Service—Part 3: Packing Bag. Standardization Administration of China SAC: Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://www.gbstandards.org/GB_Search.asp?word=packaging (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Shivasharana, C.; Kesti, S.S. Physical and Chemical of low density polyethylene and high density polyethylene. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Switzerland. Verordnung zur Reduktion von RIsiken Beim Umgang mit Bestimmten Stoffer; Zubereitungen und Gegenstanden (Chemikalien-Risiko Redktions-Verordnung [chenRRV], Draft. 2002. Available online: https://www.newsd.admin.ch/newsd/message/attachments/90961.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Germany. Regulations on the Packaging and Processing of Packaging Materials (BRD 1998): 13 Contraton of Energy. 1998. Available online: https://zoek.officielebekendmakingen.nl/stcrt-1997-125-p14-SC9815.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2024).

| Code | Photography | Origin | Color | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | Supermarket No. 1 | Orange, Red | Recycled material 30%; Thickness 30 µm |
| 2 |  | Intermoda | White, Black | 60 µm; LDPE |
| 3 |  | Fashion Moda | Black, Brown | LDPE |
| 4 |  | Pep | Yellow, Blue, and White | Recycled material 30%; Thickness 30 µm; HDPE; 38 L |
| 5 |  | SPAR VIP Manica Shopping | Green, White, and Red | 100% Pure material; Thickness 30 µm; HDPE; 24 L |
| 6 |  | Shoprite | Yellow, Red | Recycled material 30%; Thickness 30 µm; HDPE; 24 L |
| 7 |  | Common Flexible Plastic | Red, Black | Recycled material 40%; Thickness 30 µm |
| 8 |  | Common Flexible Plastic | Blue | Recycled material 40%; Thickness 30 µm |
| 9 |  | Fang Zhene | Black | Recycled material 40%; Thickness 30 µm |
| 10 |  | Common Plastic | Golden 60% | |
| 11 |  | Recheio_Cash & Carry | Blue, White, and Red | 100% Pure material; Thickness 30 µm; HDPE; 24 L |
| 12 |  | Hope Plastic_Unipersonal Society | Blue, Black | |
| 13 |  | Beira Hardware | Green, White | 30 µm, 60% Pure matter |
| 14 |  | Lucky International | Yellow, Black | |
| 15 |  | Jasmine Garden Supermarket | Golden 40%, Black | HDPE |
| 16 |  | Carfimpex_Cash & Carry | White, Black, Red, Green, and Yellow | 100% Pure material; thickness 30 µm; HDPE; 24 L |
| 17 |  | Hope Plastic_Unipersonal Society | Red, Black |
| Reagents | Chemical Formula | Purity (%) | Brand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid | HNO3 | ≥65 | PronaLAB® |
| Hydrochloridric Acid | HCl | ≥37.0 | VWR® Chemicals |
| Samples | Average Mass (g) | Average Thickness (mm) | Thickness of the Bag (µm) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cod.01 | 0.02359 | 0.1236 | 30 | 0.0763 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.02 | 0.0388 | 0.2614 | 60 | 0.0593 ± 0.0004 |
| Cod.03 | 0.03109 | 0.1864 | --- | 0.0667 ± 0.0003 |
| Cod.04 | 0.03615 | 0.1902 | 30 | 0.0760 ± 0.0004 |
| Cod.05 | 0.01636 | 0.0824 | 30 | 0.0794 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.06 | 0.01900 | 0.1092 | 30 | 0.0695 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.07 | 0.03079 | 0.1778 | 30 | 0.0692 ± 0.0003 |
| Cod.08 | 0.01899 | 0.1196 | 30 | 0.0635 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.09 | 0.01864 | 0.1480 | 30 | 0.0503 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.10 | 0.00968 | 0.0950 | --- | 0.04075 ± 0.00001 |
| Cod.11 | 0.01748 | 0.1228 | 30 | 0.0569 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.12 | 0.01694 | 0.1378 | --- | 0.0491 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.13 | 0.02502 | 0.1414 | 30 | 0.0707 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.14 | 0.02082 | 0.1432 | --- | 0.0581 ± 0.0002 |
| Cod.15 | 0.01416 | 0.1010 | --- | 0.0560 ± 0.0001 |
| Cod.16 | 0.01558 | 0.1072 | 30 | 0.0581 ± 0.0001 |
| Cod.17 | 0.01196 | 0.1068 | --- | 0.0447 ± 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nhanga, M.C.; Geraldo, D.; Nhapulo, S.L.; João, A.F.; Carneiro, J.; Costa, M.F.M. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Plastic Bags Used as Improvised Food Cooking Covers: A Case Study from the Mozambican Community. Sustainability 2025, 17, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030964
Nhanga MC, Geraldo D, Nhapulo SL, João AF, Carneiro J, Costa MFM. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Plastic Bags Used as Improvised Food Cooking Covers: A Case Study from the Mozambican Community. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030964
Chicago/Turabian StyleNhanga, Manença Cristiano, Dulce Geraldo, Sérgio Leonardo Nhapulo, Afonso Filipe João, Joaquim Carneiro, and Manuel F. M. Costa. 2025. "Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Plastic Bags Used as Improvised Food Cooking Covers: A Case Study from the Mozambican Community" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030964
APA StyleNhanga, M. C., Geraldo, D., Nhapulo, S. L., João, A. F., Carneiro, J., & Costa, M. F. M. (2025). Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Plastic Bags Used as Improvised Food Cooking Covers: A Case Study from the Mozambican Community. Sustainability, 17(3), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030964









