Greater Sustainability in the Future of Hanjiang River Under Climate Change: The Case of Nitrogen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Geographical Detector
2.4. Downscaling
2.5. SWAT Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Performance of SWAT Model
3.2. Characteristics of TN Emissions
3.3. Distribution of Nitrogen in Different Forms
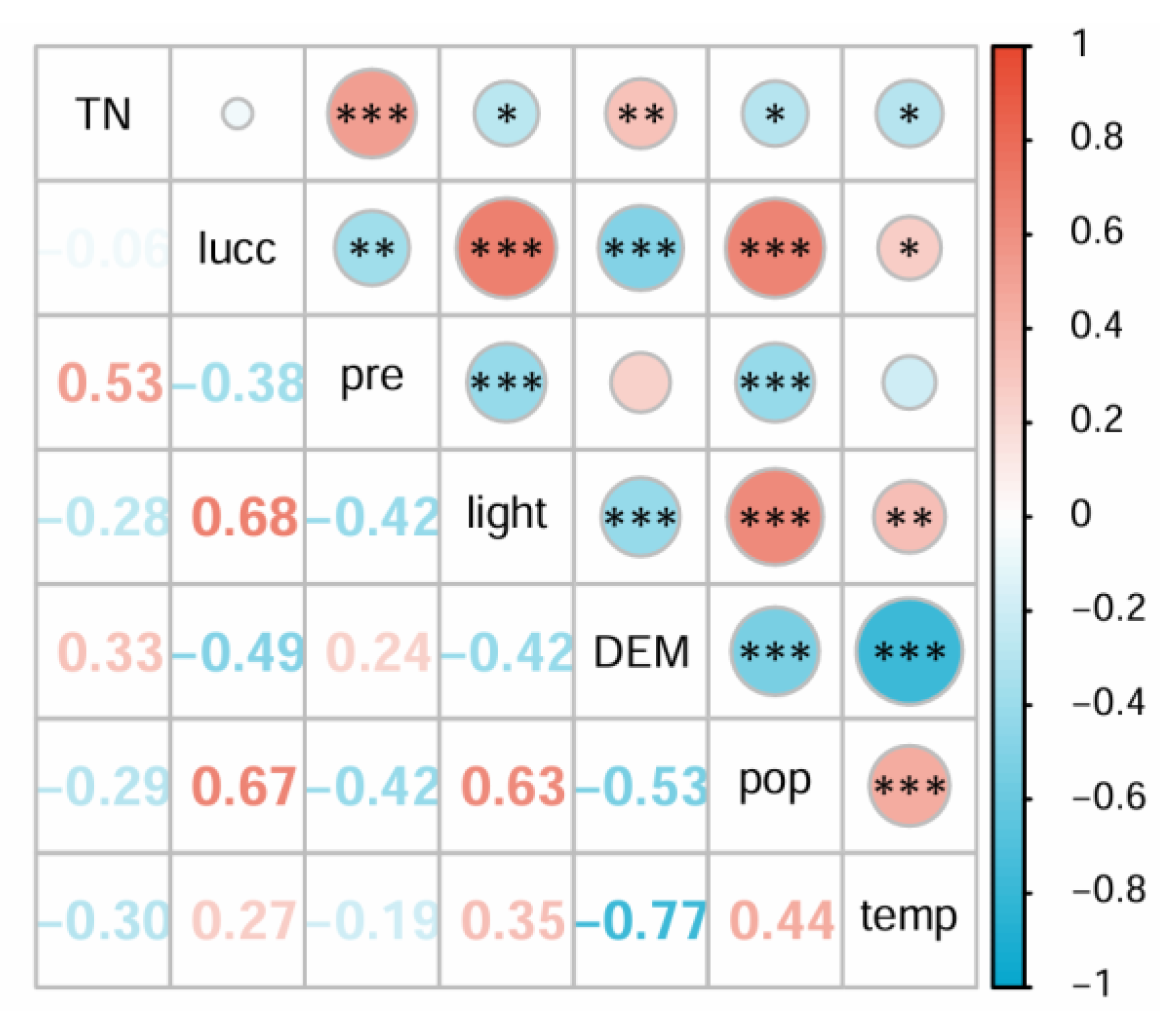
3.4. Driving Factors of TN Spatial Heterogeneity
3.5. Sustainability Change Under Climate Change
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TN | total nitrogen |
| –N | nitrate nitrogen |
| –N | nitrite nitrogen |
| –N | ammonia nitrogen |
| DON | dissolved organic nitrogen |
| SWAT | soil and water assessment tool |
| SSP | shared socioeconomic pathways |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| GCM | general circulation models |
| r | correlation coefficient |
| NRMSE | normalized root mean square error |
| R2 | coefficient of determination |
| NSE | Nash efficiency coefficient |
References
- UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2018: Nature-Based Solutions for Water; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Partnership Water Partnership. Towards Water Security: A Framework for Action; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden; London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2024: Water for Prosperity and Peace; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Li, J.X.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.Y.; Song, Y.H. Recycling of reclaimed water in china: Current situation, development trend, and countermeasures. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 7031–7040. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, H.G.; Lin, C.; Chiang, C.F.; Bui, X.T.; Lukkhasorn, W.; Bui, T.P.T.; Tran, H.T.; Vo, T.D.H.; Le, V.G.; Nghiem, L.D. The individual and synergistic indexes for assessments of heavy metal contamination in global rivers and risk: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Manna, C.; Jain, M. Abundance, interaction, ingestion, ecological concerns, and mitigation policies of microplastic pollution in riverine ecosystem: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Gao, J. Characterizing the river water quality in china: Recent progress and on-going challenges. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Secretary-General, World Commission on Environment and Development. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Note/by the Secretary-General. 1987. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/139811?v=pdf&ln=en (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Xu, C.D.; Liu, W.; Yin, Q. Prediction of nitrogen emission in the upper reaches of the huai river basin under climate change scenarios. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 24, 1558–1574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santy, S.; Mujumdar, P.; Bala, G. Increased risk of water quality deterioration under climate change in ganga river. Front. Water 2022, 4, 971623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Liu, W.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q. Water quality in relation to land use and land cover in the upper han river basin, china. Catena 2008, 75, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Song, C.; Dannenberg, M.P.; Li, J.; Liu, N.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, L. Vegetation greening weakened the capacity of water supply to china’s south-to-north water diversion project. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 5623–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Hanjiang River Ecological Economic Belt Development Plan. China 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2018-12/31/content_5434959.htm (accessed on 15 July 2024). (In Chinese)
- Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Deng, C. The effects of land-use and climatic changes on the hydrological environment in the qinling mountains of shaanxi province. Forests 2022, 13, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.Y.; Deng, Y.; Ni, F.Q.; Kang, W.D.; Xiang, J.; Wu, M.Y.; Jiang, N. Change of runoff volume in the middle and upper reaches of han river basin under future climate scenarios. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2024, 45, 715–728. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, K.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of multiple spatial scale characterization of land use on water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 7106–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Ren, K.; Yan, K.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y. The relationship between mountain wetland health and water quality: A case study of the upper hanjiang river basin, china. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate and planting structure changes on watershed runoff and nitrogen and phosphorus loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 134489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J. Simulation of non-point source pollution in watershed above ankang section of the han river based on hype model. Water Resour. Prot. 2024, 40, 140–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Hao, G.; Li, Y. Evaluation of best management practices for non-point source pollution based on the swat model in the hanjiang river basin, china. Water Supply 2021, 21, 4563–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yu, J.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S. Efficiency analysis of best management practices under climate change conditions in the so-okcheon watershed, south korea. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1297289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, R.D.; Yan, C.Z.; Wu, S.X. CNLUCC Resources and Environment Science Data Registration and Publication System. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn/DOI (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the heshun region, china. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Fu, B.J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y. Influences of population pressure change on vegetation greenness in china’s mountainous areas. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 9041–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Kuang, T.; Tao, S. Quantifying influences of natural factors on vegetation ndvi changes based on geographical detector in sichuan, western china. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to ndvi variations in the middle reaches of the heihe river basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Racines, C.; Tarapues, J.; Thornton, P.; Jarvis, A.; Ramirez-Villegas, J. High-resolution and bias-corrected cmip5 projections for climate change impact assessments. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, V.; Oinam, B.; Wieprecht, S. Synergistic impact of climate and land use land cover change dynamics on the hydrological regime of loktak lake catchment under cmip6 scenarios. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Buishand, A.; van Deursen, W. Estimates of future discharges of the river rhine using two scenario methodologies: Direct versus delta approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosi, A.S.; Doulabian, S.; Ghasemi Tousi, E.; Calbimonte, G.H.; Alaghmand, S. Large-scale flood hazard assessment under climate change: A case study. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 147, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for swat modeling in alpine catchment: A case study in the adige river basin (italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W. Modeling the hydrological impacts of land use/land cover changes in the andassa watershed, blue nile basin, ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Yin, Q. Assessing the response of non-point source nitrogen pollution to land use change based on swat model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Evaluation and application of a swat model to assess the climate change impact on the hydrology of the himalayan river basin. Catena 2019, 181, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghsaei, H.; Dinan, N.M.; Moridi, A.; Asadolahi, Z.; Delavar, M.; Fohrer, N.; Wagner, P.D. Effects of dynamic land use/land cover change on water resources and sediment yield in the anzali wetland catchment, gilan, iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Gosain, A.K.; Khosa, R.; Srinivasan, R. Regional scale hydrologic modeling for prediction of water balance, analysis of trends in streamflow and variations in streamflow: The case study of the ganga river basin. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2018, 16, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Parajuli, P.B.; Ouyang, Y.; Dash, P.; Siegert, C. Assessing land use change impact on stream discharge and stream water quality in an agricultural watershed. Catena 2021, 198, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.; Zhuguo, M.; Zheng, Z.; Saleem, F. Natural and anthropogenic influences on the recent droughts in yellow river basin, china. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.P.; Fu, B.J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.B.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, J.F.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.G.; Wang, H. Sustainable development in the yellow river basin: Issues and strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonisławska, M.; Nędzarek, A.; Rybczyk, A.; Tański, A. The influence of anthropogenic pollution on the physicochemical conditions of the waters of the lower section of the sąpólna river. Water 2023, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.K.; Wang, J. Water quality management of a cold climate region watershed in changing climate. J. Environ. Inform. 2019, 35, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, T.W.; Hemingway, J.D.; Kurek, M.R.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Brown, K.A.; Holmes, R.M.; Galy, V.; Moura, J.M.S.; Mitsuya, M.; Wassenaar, L.I.; et al. The pulse of the amazon: Fluxes of dissolved organic carbon, nutrients, and ions from the world’s largest river. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, 35, e2020GB006895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafta, H.; Opp, C. Understanding the combined effects of land cover, precipitation and catchment size on nitrogen and discharge—A case study of the mississippi river basin. Water 2022, 14, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Anjinho, P.; Barbosa, M.A.G.A.; Neves, G.L.; dos Santos, A.R.; Mauad, F.F. Integrated empirical models to assess nutrient concentration in water resources: Case study of a small basin in southeastern brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23349–23367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Hu, W. Air temperature effects on nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in lake chaohu and adjacent inflowing rivers. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 84, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ouyang, W.; Zhu, J.; Lin, C.; He, M. Discharge dynamics of agricultural diffuse pollution under different rainfall patterns in the middle yangtze river. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, F.; Tian, Q.; Badreldin, N.; Zhao, J. Analysis and estimation of nonpoint source pollution under different land use in anjiagou watershed, gansu, china. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 77428–77447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, N.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Ji, X. Sources and transformations of riverine nitrogen across a coastal-plain river network of eastern china: New insights from multiple stable isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Tang, C.; Cao, Y. Sources and transformation mechanisms of inorganic nitrogen: Evidence from multi-isotopes in a rural-urban river area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Peng, H.; Xin, J.; Wang, S. Analysis of urea nitrogen leaching under high-intensity rainfall using hydrus-1d. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, K.J.; Basu, N.B.; Veenstra, J.J.; Burras, C.L. The nitrogen legacy: Emerging evidence of nitrogen accumulation in anthropogenic landscapes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Beusen, A.H.W.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Wang, J.; van Hoek, W.J.; Ran, X.; Mogollón, J.M.; Bouwman, A.F. Impact of groundwater nitrogen legacy on water quality. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Ministry of Agriculture. Circular of the Chinese Ministry of Agriculture on Printing and Distributing the Action Plan for Zero Growth in the Application of Fertilizer by 2020 and the Action Plan for Zero Growth in the Application of Pesticide by 2020. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2015/san/201711/t20171129_5923401.htm (accessed on 2 January 2025). (In Chinese)
- Hu, K.; Zhao, Q.L.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Han, F.; Shen, X.H. Appropriate technologies for upgrading wastewater treatment plants: Methods review and case studies in china. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 53, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.; Dovi, R.; Yoder, R.; Dias, F.; Warden, B. Determination by ion chromatography and spectrophotometry of the effects of preservation on nitrite and nitrate. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 546, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktavia, M.; Indah, S.; Helard, D. Spatial variability of ammonium, nitrite and nitrate concentrations in water of batang arau river, west sumatera, indonesia. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Minareci, O.; Koruk, M. Assessment of the surface water quality in the kucuk menderes river, tÜrkİye. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2024, 22, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Abegunrin, T.P.; Guo, H.; Huang, Z.; Are, K.S.; Wang, H.; Gu, M.; Wei, L. Variation of dissolved nutrient exports by surface runoff from sugarcane watershed is controlled by fertilizer application and ground cover. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the taizi river basin, china. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorite-Herrera, M.; Hiscock, K.; Jiménez-Espinosa, R. Distribution of dissolved inorganic and organic nitrogen in river water and groundwater in an agriculturally-dominated catchment, south-east spain. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2009, 198, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, E.S.A. Spatio-temporal variability of dissolved organic nitrogen (don), carbon (doc), and nutrients in the nile river, egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.L.; Rowntree, K.M.; Roux, J.J.L. An interrogation of research on the influence of rainfall on gully erosion. Catena 2021, 206, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, D.J.; Yue, Z. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on soil erosion, nitrogen and potassium loss on loess slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 85–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Xie, D.; Ni, J.; Chen, L.; Ni, C.; Ye, W.; Zhao, G.; Shao, J.; Chen, F. Output characteristics and driving factors of non-point source nitrogen (n) and phosphorus (p) in the three gorges reservoir area (tgra) based on migration process: 1995–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Xiao, J.; Oliver, D.M.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, F. Spatio-temporal characteristics and determinants of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs in an ecologically fragile karst basin: Environmental responses and management strategies. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 133, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, A.; Ramasamy, S.; Sankar, G. Assessment of climate change impact on hydrological components of ponnaiyar river basin, tamil nadu using cmip6 models. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Chen, Y. Runoff change simulation and future trend projection in the source area of the yellow river. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 1292–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Huo, J. Response of runoff and its components to climate change and its future trend in the source region of the yangtze river. Hydrol. Process 2024, 38, e15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigabu, T.B.; Wagner, P.D.; Hörmann, G.; Kiesel, J.; Fohrer, N. Climate change impacts on the water and groundwater resources of the lake tana basin, ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 1544–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, F. Simulation and prediction of the impact of climate change scenarios on runoff of typical watersheds in changbai mountains, china. Water 2022, 14, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, L.; Andersen, H.E.; Beklioğlu, M.; Bucak, T.; Couture, R.M.; Cremona, F.; Ferreira, M.T.; Hutchins, M.G.; Mischke, U.; Molina-Navarro, E.; et al. The future depends on what we do today—Projecting europe’s surface water quality into three different future scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
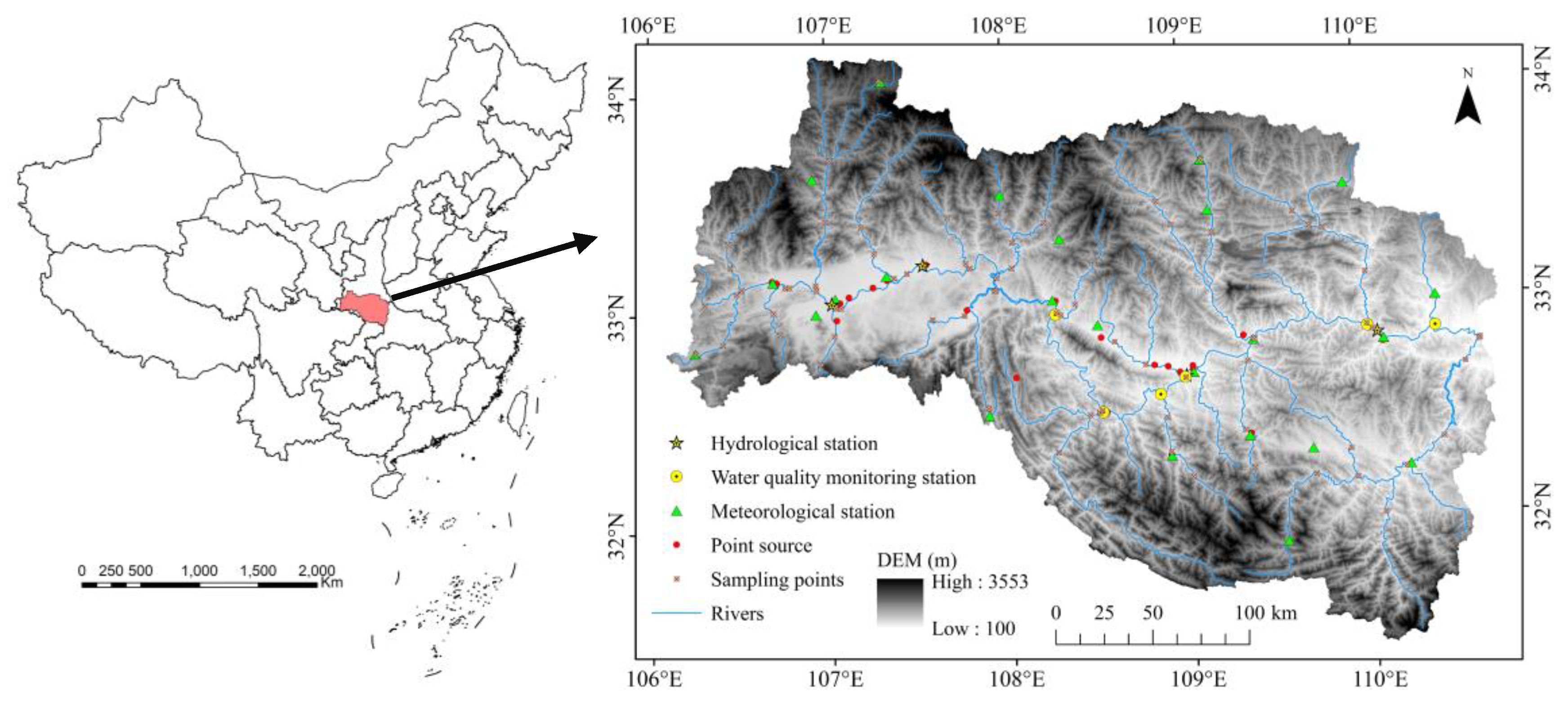



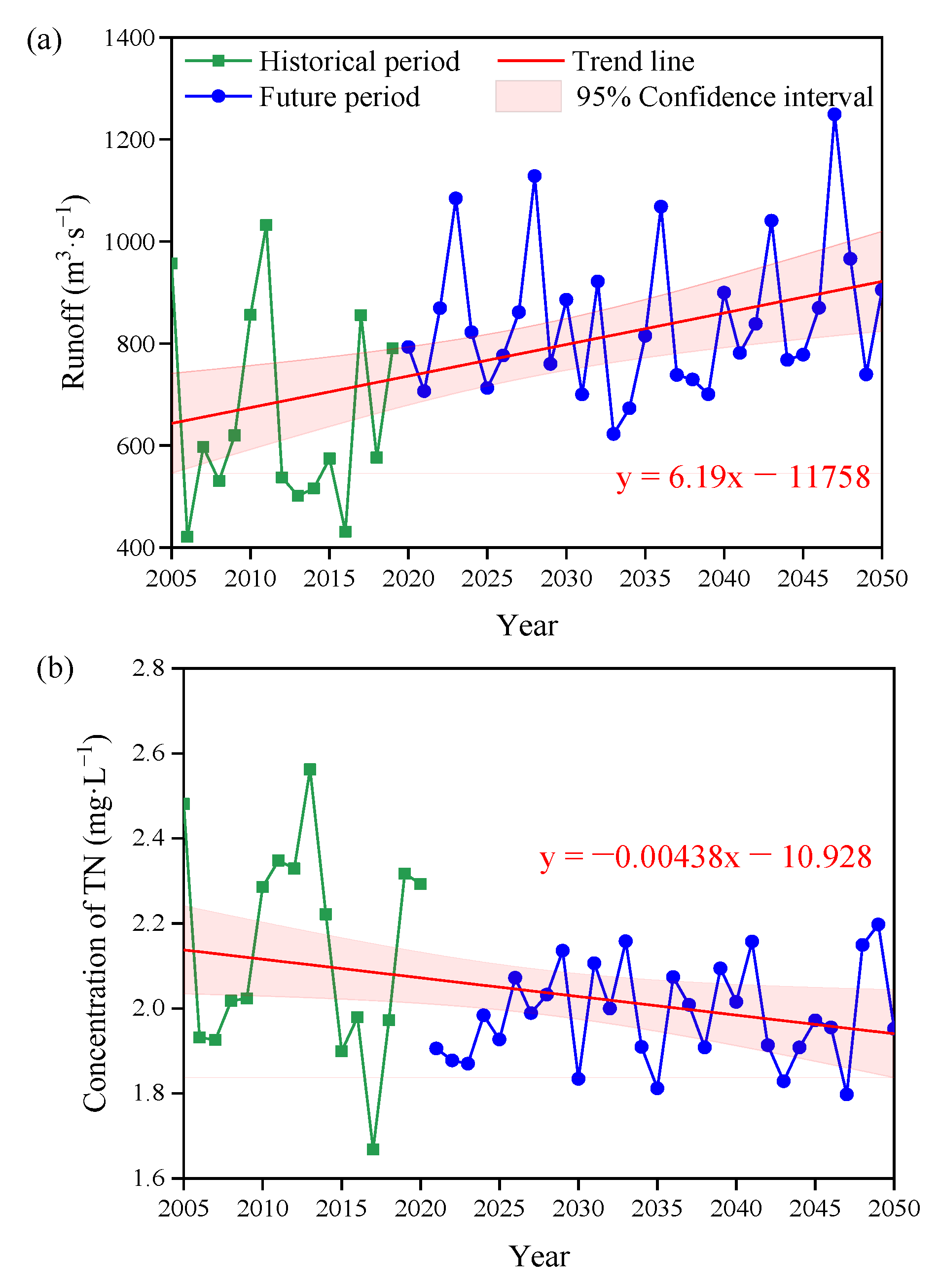
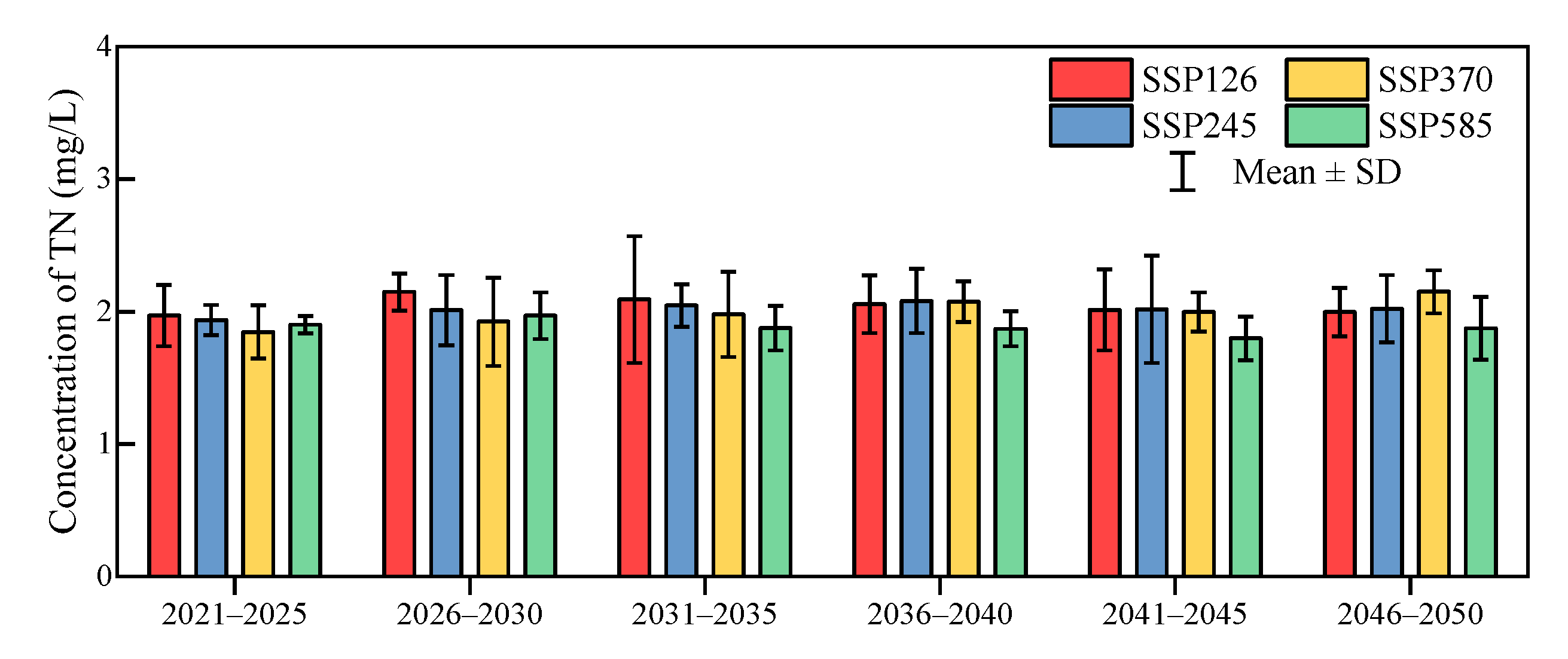

| Study Area | Study Period | Description | TN Concentration(mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| This research | 2005~2020 | The basin area is approximately 74,000 km2, with a vegetation cover of 76% | 2.161 ± 1.087 |
| Amazon basin [46] | 2011~2013 | Basin area exceeds 6 million km2, mainly consisting of tropical forests, snow-capped mountains, and savannas, with an annual precipitation of about 2000 mm. | 0.363 ± 0.085 |
| Mississippi River, United States [47] | 2013~2017 | An important agricultural area, the basin area is about 278,000 km², with an average annual precipitation of 950 mm. | 3.438 ± 2.299 |
| Lobo Stream, Brazil [48] | 2018 | The watershed, spanning 220 km2, receives about 1500 mm of annual rainfall and is a water source conservation area. | 0.55~1.45 |
| Sąpólna River, Poland [44] | 2021–2022 | 87.7 km2, a biological reserve with an annual precipitation of about 625 mm. | 3.194 |
| Athabasca River, Canada [45] | 1983~2013 | 160,000 km2, dominated by forests, with an annual precipitation of about 510 mm. | 0.502 ± 0.228 |
| Nanfei River, Tangxi River, and Pai River in China [49] | 2014~2017 | Subtropical monsoon climate, with an annual average rainfall of 1003.4 mm, 70% of the land is used for agriculture. | 9.137 ± 3.550 |
| Zijiang River, China [50] | 2020~2021 | 28,000 km2, an important rice-growing area with an average annual precipitation of 1200 to 1800 mm. | 1.604~3.574 |
| Anjiagou watershed, China [51] | 2006~2014 | Agricultural basin | 4.17 ± 1.027 |
| Downstream of the Yellow River, China [43] | 2018 | North China Plain agricultural irrigation area. | 7.889 ± 0.795 |
| Study Area | Study Period | –N | –N | –N | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia’s Batang Arau River [60] | 2014 | 0.182–0.510 | 0.0–0.148 | 0.739–1.942 | 172 km2, the upstream area is dominated by forest cover, while the downstream area is densely populated with cities. |
| Mexico’s El Fuerte River [45] | 2017 | 0.012–0.34 | 0–0.012 | 0.002–0.875 | 36,000 km2, the upstream land is mostly forested, the downstream area is agricultural, and the annual precipitation ranges from 311 to 1200 mm. |
| Turkey’s Küçük Menderes River [61] | 2017~2018 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 1.73 | 7 km2, mainly characterized by wetlands. |
| This study | 2023~2024 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 1.66 | 74,000 km², with about 76% covered by forests and grasslands and about 22.7% by arable land. |
| Factor | Explanatory Power (q-Value) | Significance (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | 0.614 | <0.001 |
| Temperature | 0.301 | 0.071 |
| DEM | 0.297 | 0.003 |
| Nighttime lights | 0.230 | 0.005 |
| Population density | 0.205 | 0.100 |
| Land use intensity | 0.142 | 0.096 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y. Greater Sustainability in the Future of Hanjiang River Under Climate Change: The Case of Nitrogen. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041523
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Chen Y. Greater Sustainability in the Future of Hanjiang River Under Climate Change: The Case of Nitrogen. Sustainability. 2025; 17(4):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041523
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuchen, Yan Zhao, and Yiping Chen. 2025. "Greater Sustainability in the Future of Hanjiang River Under Climate Change: The Case of Nitrogen" Sustainability 17, no. 4: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041523
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Greater Sustainability in the Future of Hanjiang River Under Climate Change: The Case of Nitrogen. Sustainability, 17(4), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041523







