Advancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Bumblebee Pollination: Bibliometric Insights and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bumblebee Biological Characteristics
2.1. Behavior and Pollination Characteristics
2.1.1. Floral Visitation Behavior and Preferences
2.1.2. Pollen Collection and Buzz Pollination
2.2. Ecological Characteristics of Bumblebees
2.2.1. Co-Evolution with Plants
2.2.2. Population Dynamics and Environmental Impacts
2.2.3. Contribution to Ecosystem Services
3. Application of Bumblebees in Agriculture
3.1. Applications in Greenhouse and Open-Field Crops
3.1.1. Greenhouse Crops
3.1.2. Open-Field Crops
3.2. Applications in Crops Requiring Vibration Pollination
3.3. Bumblebee Rearing and Commercial Applications
3.4. The Role of Bumblebees in Sustainable Agriculture
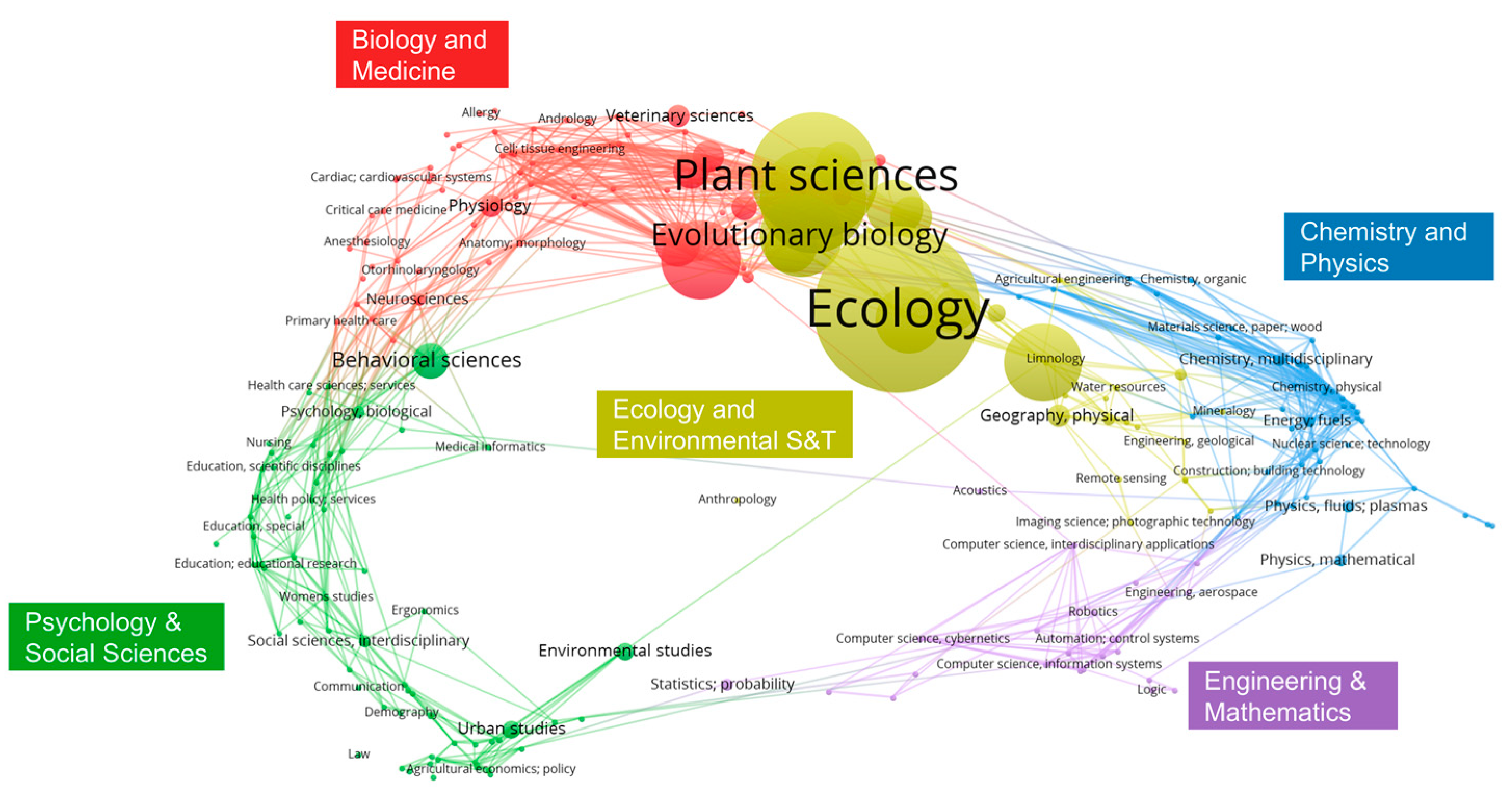
4. Bibliometric Analysis in Bumblebee Pollination Research
4.1. Methodology
4.2. Result
4.2.1. Overview of Research
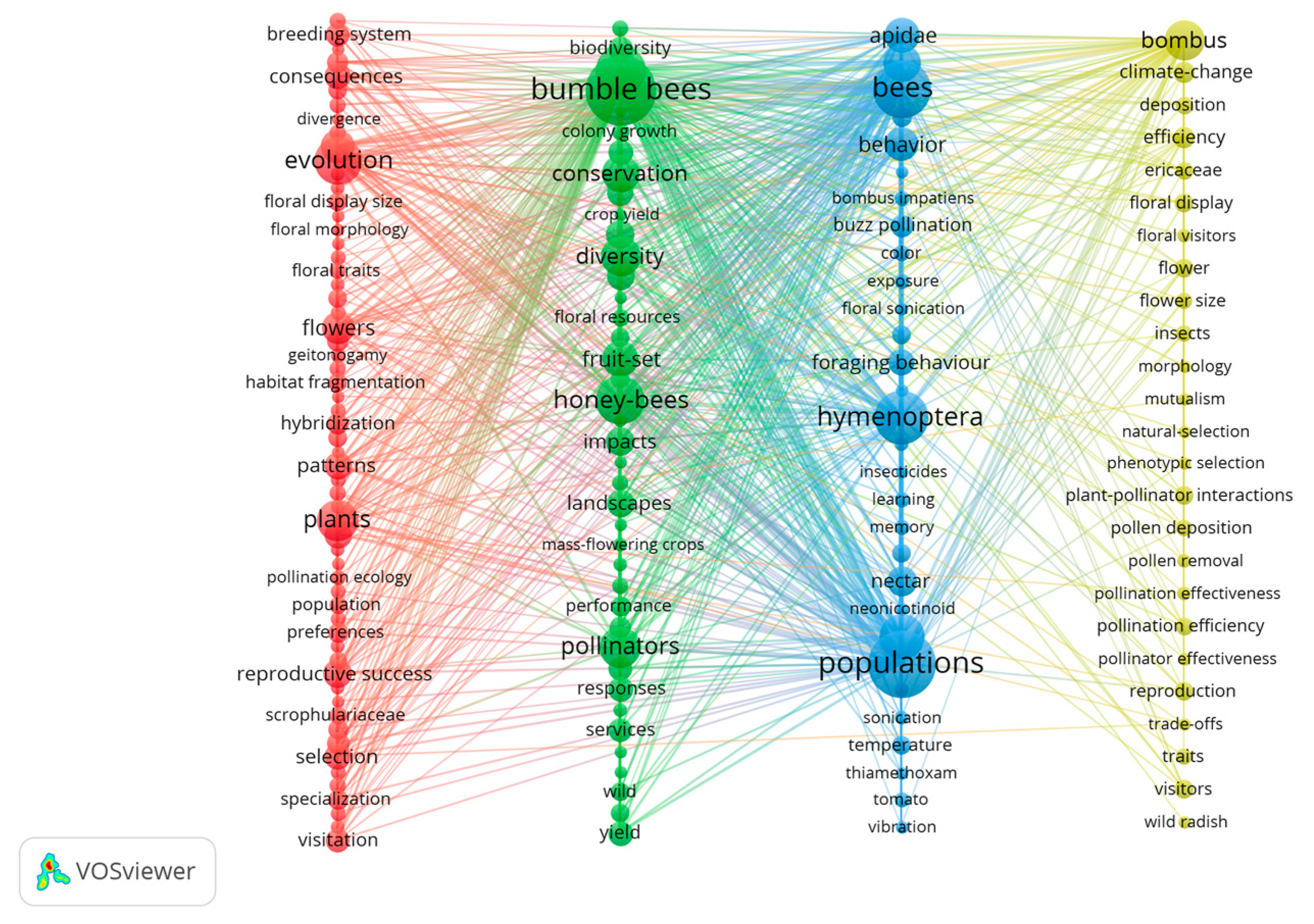
4.2.2. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
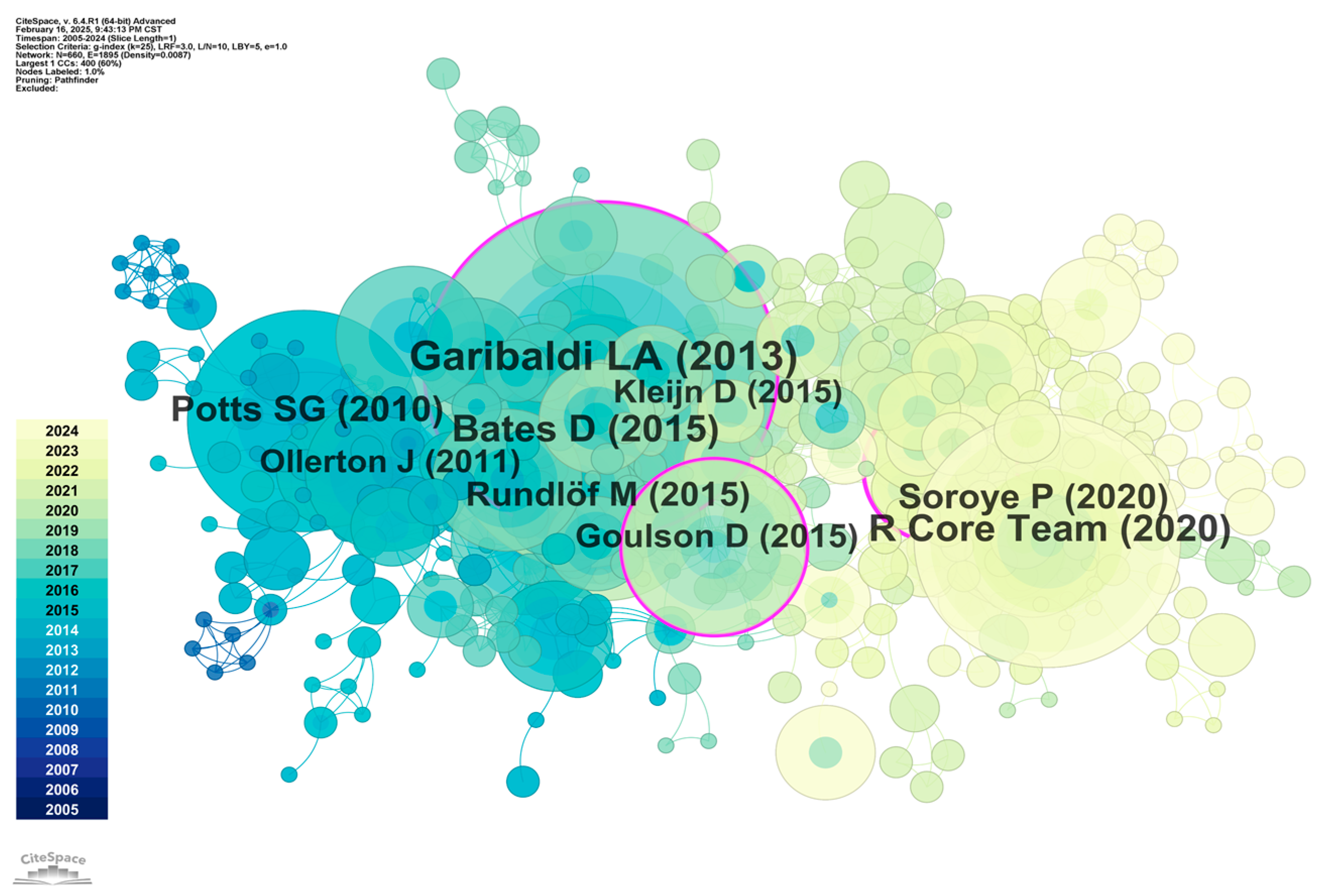
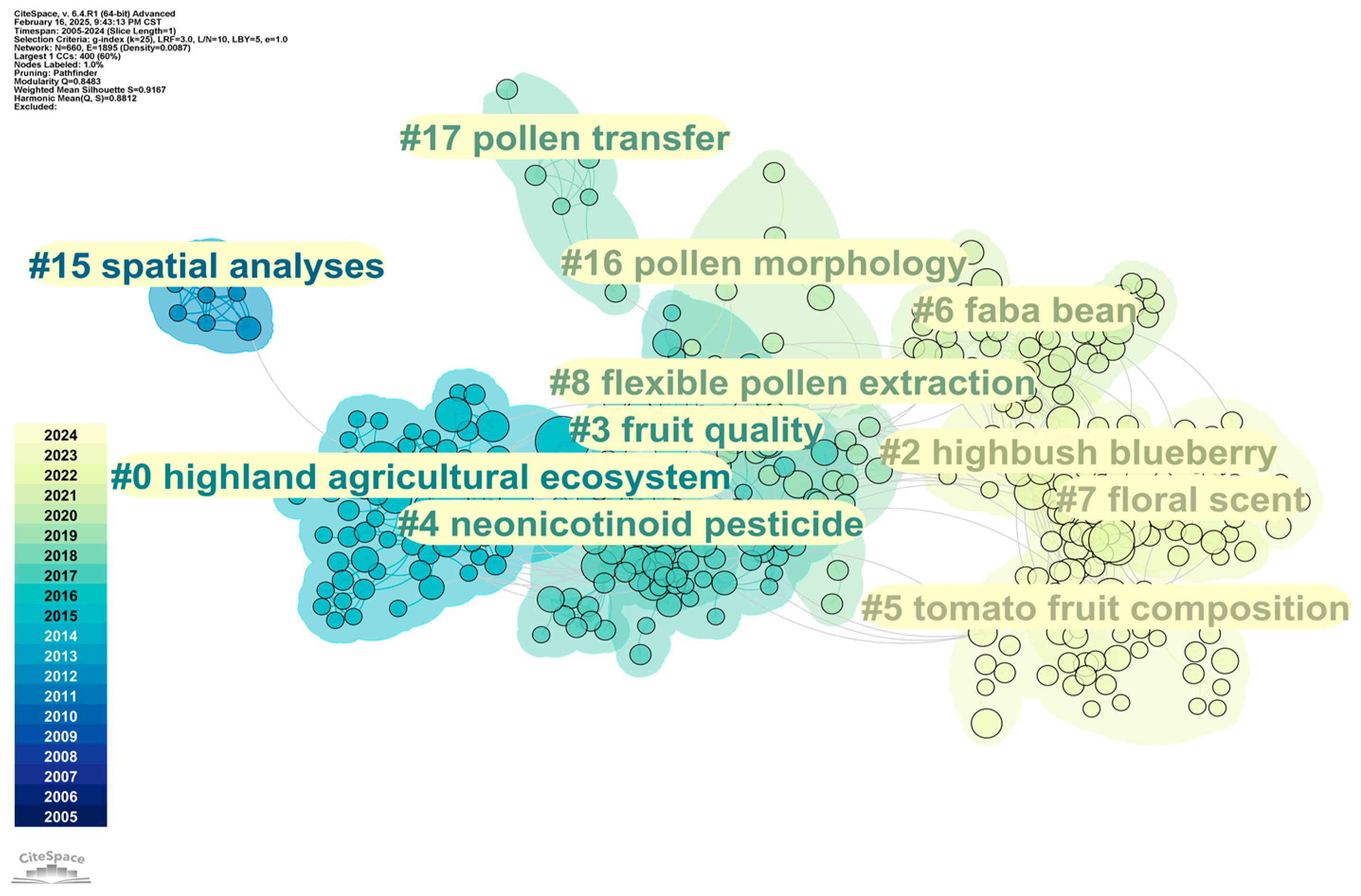
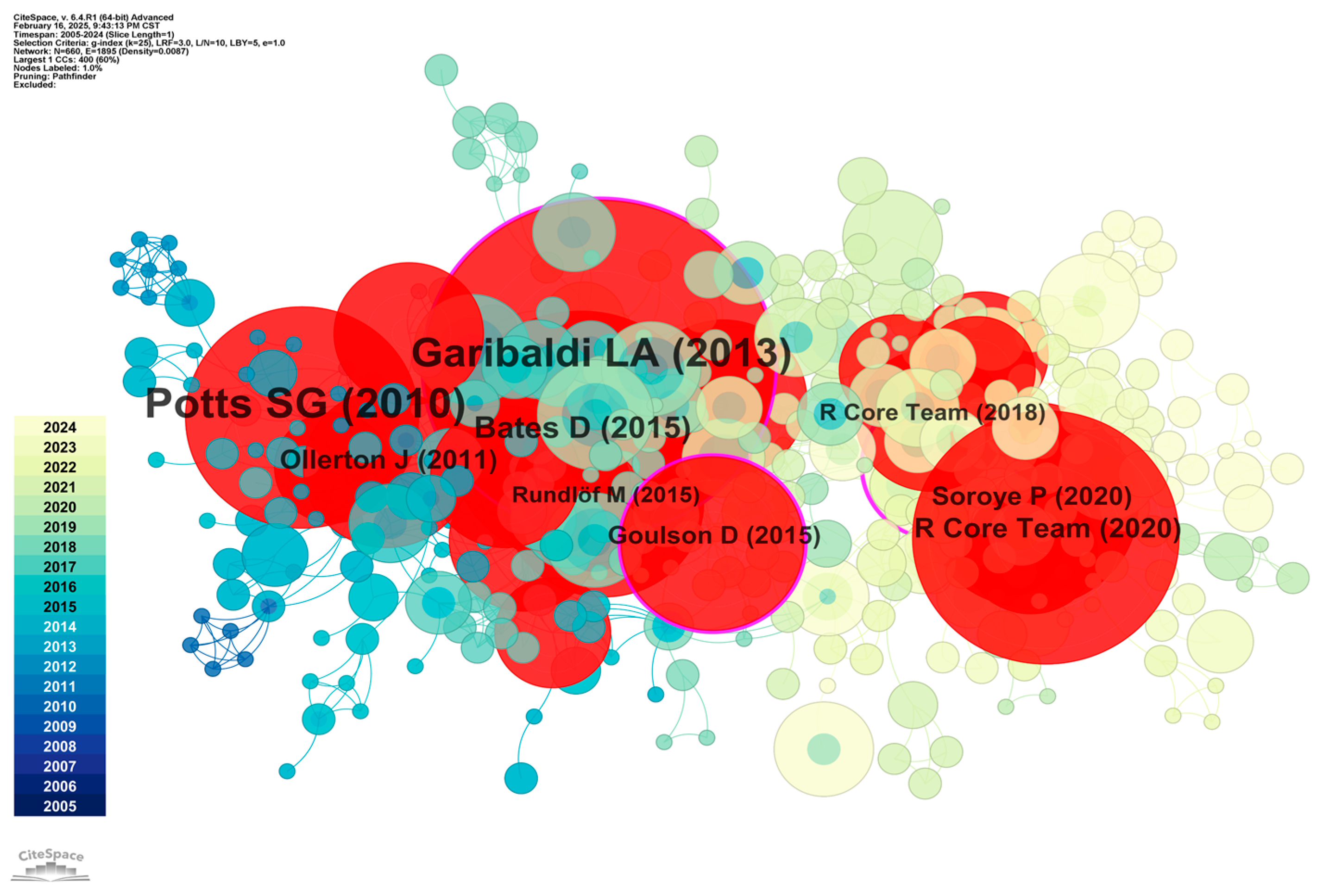
4.2.3. Co-Citation Analysis
5. Future Research Directions and Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; An, J. Species diversity, pollination application and strategy for conservation of the bumblebees of China. Biodivers. Sci. 2018, 26, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.R.; Guerra-Sanz, J.M. Quality fruit improvement in sweet pepper culture by bumblebee pollination. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.A.; Bussiere, L.F.; Souto-Vilaros, D.; Goulson, D.; Mason, A.C.; Vallejo-Marín, M. Variability in bumblebee pollination buzzes affects the quantity of pollen released from flowers. Oecologia 2013, 172, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhiya, V.C.; Kanani, M.K.; Dodiya, T.P.; Pastagia, J.J. Utilization of Bumblebee in Crop Pollination. Asian Res. J. Agric. 2024, 17, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahengbam, J.; Raut, A.M.; Satinder Pal, S.P.; Banu, A.N. Role of bumble bee in pollination. Ann. Biol. 2019, 35, 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Becher, M.A.; Twiston-Davies, G.; Penny, T.D.; Goulson, D.; Rotheray, E.L.; Osborne, J.L. Bumble-BEEHAVE: A systems model for exploring multifactorial causes of bumblebee decline at individual, colony, population and community level. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2790–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisbain, G.; Ghisbain, G.; Thiery, W.; Thiery, W.; Massonnet, F.; Massonnet, F.; Erazo, D.; Erazo, D.; Rasmont, P.; Rasmont, P.; et al. Projected decline in European bumblebee populations in the twenty-first century. Nature 2023, 628, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroye, P.; Newbold, T.; Kerr, J. Climate change contributes to widespread declines among bumble bees across continents. Science 2020, 367, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrey, A.H.; Raina, R.H.; Saddam, B.; Pathak, P.; Kumar, S.; Uniyal, V.; Gupta, D.; Khan, S.A. Role of bumblebees (hymenoptera: Apidae) in pollination of high land ecosystems: A review. Agric. Rev. 2021, 43, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D.; Lye, G.C.; Darvill, B. Decline and conservation of bumble bees. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2008, 53, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Morandin, L.A.; Richardson, L.L.; Guzman, L.M.; M’gonigle, L.K. Climate change winners and losers among North American bumblebees. Biol. Lett. 2022, 18, 20210551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Gargi, B.; Semwal, P.; Tripathi, V. Global trends, research progress and knowledge mapping of plant–pollinator interactions through bibliometric analysis (1984 to 2023). Biodiversity 2023, 24, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Wang, Z.; Massaro, C.F.; Ekundayo, T.C. Global Trends on the Research of Plant Resin Use by Stingless Bees (1985–2022) and Apis mellifera (1967–2022): A Bibliometric Analysis. In Stingless Bee Nest Cerumen and Propolis, Volume 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 45–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, R.; Ahmi, A.; Ahmad, A.H.; Othman, Z.; Azman, K.F.; Ab Aziz, C.B.; Ismail, C.A.N.; Shafin, N. Visualising and mapping a decade of literature on honey research: A bibliometric analysis from 2011 to 2020. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoto, K. Bumblebee visits to Impatiens spp.: Pattern and efficiency. Oecologia 1988, 76, 364–370. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, T.; Whitehorn, P.; Lye, G.C.; Vallejo-Marín, M. Floral sonication is an innate behaviour in bumblebees that can be fine-tuned with experience in manipulating flowers. J. Insect Behav. 2016, 29, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.J.; Vallejo-Marín, M. Floral vibrations by buzz-pollinating bees achieve higher frequency, velocity and acceleration than flight and defence vibrations. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb220541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.W.; Mountjoy, C.; Faulkner, B.E.; Roberts, M.V.; Macnair, M.R. Bumble bee selection of Mimulus guttatus flowers: The effects of pollen quality and reward depletion. Ecology 1999, 80, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithson, A.; Macnair, M.R. Frequency-dependent selection by pollinators: Mechanisms and consequences with regard to behaviour of bumblebees Bombus terrestris (L.)(Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Evol. Biol. 1996, 9, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macior, L.W. Foraging behavior of Bombus (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in relation to Aquilegia pollination. Am. J. Bot. 1966, 53, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, X.-L.; Li, R.-X.; Wang, S.; Tian, L.-X. Ultrastructure and distribution of antennal sensilla of Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Zool. Anz. 2022, 302, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, C.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Tscharntke, T. Mass flowering oilseed rape improves early colony growth but not sexual reproduction of bumblebees. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gironés, M.A.; Llandres, A.L. Resource Competition triggers the co-evolution of long tongues and deep corolla tubes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.J.; Nigel, E.R. Changes in learning and foraging behaviour within developing bumble bee (Bombus terrestris) colonies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, P.A.; Vallejo-Marín, M. What’s the ‘buzz’ about? The ecology and evolutionary significance of buzz-pollination. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Marín, M. Buzz pollination: Studying bee vibrations on flowers. New Phytol. 2018, 224, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, H.; Vallejo-Marín, M. Buzz-pollinated crops: A global review and meta-analysis of the effects of supplemental bee pollination in tomato. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingley, A.; Anwar, S.; Kristiansen, P.; Warwick, N.W.M.; Wang, C.-H.; Sindel, B.M.; Cazzonelli, C.I. Precision pollination strategies for advancing horticultural tomato crop production. Agronomy 2022, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, H.M.; Hendrix, S.D. Bumble bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) diversity and abundance in tallgrass prairie patches: Effects of local and landscape floral resources. Environ. Èntomol. 2005, 34, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, H.H.W.; Van Doorn, A. A century of advances in bumblebee domestication and the economic and environmental aspects of its commercialization for pollination. Apidologie 2006, 37, 421–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D. Bumblebees: Behaviour, Ecology, and Conservation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, B. Bumblebee Economics; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmont, P.; Franzen, M.; Lecocq, T.; Harpke, A.; Roberts, S.; Biesmeijer, K.; Castro, L.; Cederberg, B.; Dvorak, L.; Fitzpatrick, U.; et al. Climatic risk and distribution atlas of European bumblebees. BioRisk 2015, 10, 1–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuell, J.K.; Isaacs, R. Weather during bloom affects pollination and yield of highbush blueberry. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2010, 103, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gegear, R.J.; Laverty, T.M. Flower constancy in bumblebees: A test of the trait variability hypothesis. Anim. Behav. 2005, 69, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunau, K.; Fieselmann, G.; Heuschen, B.; van de Loo, A. Visual targeting of components of floral colour patterns in flower-naïve bumblebees (Bombus terrestris; Apidae). Sci. Nat. 2006, 93, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobbs, L.W.; Greig, N. First report of bumblebee (Bombus impatiens cresson) transmission of Pepino mosaic virus between tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and perennial climbing nightshade (Solanum dulcamara L.). Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 36, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.D.; Goodell, K. Pollen removal and deposition by honeybee and bumblebee visitors to apple and almond flowers. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmott, J.; Waser, N.M.; Price, M.V. Tolerance of pollination networks to species extinctions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Kozak, K.H.; Fine, P.V.A.; Kembel, S.W. The merging of community ecology and phylogenetic biology. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 693–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.-M.; Vaissière, B.E.; Cane, J.H.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Tscharntke, T. Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 274, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elshafiey, E.H.; Shetaia, A.A.; El-Wahed, A.A.A.; Algethami, A.F.; Musharraf, S.G.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Zhao, C.; Masry, S.H.D.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; et al. Overview of bee pollination and its economic value for crop production. Insects 2021, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Rafferty, N.E.; Ren, Z.X.; Zhong, L.; Li, H.D.; Li, D.Z.; Wang, H. Evolutionary and ecological factors structure a plant–bumblebee network in a biodiversity hotspot, the Himalaya–Hengduan Mountains. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 2523–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D.; Nicholls, E.; Botías, C.; Rotheray, E.L. Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 2015, 347, 1255957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, B.A.; Bullock, J.M.; Shore, R.F.; Heard, M.S.; Pereira, M.G.; Redhead, J.W.; Ridding, L.; Dean, H.; Sleep, D.; Henrys, P.A.; et al. Country-specific effects of neonicotinoid pesticides on honey bees and wild bees. Science 2017, 356, 1393–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winfree, R.; Aguilar, R.; Vázquez, D.P.; LeBuhn, G.; Aizen, M.A. A meta-analysis of bees’ responses to anthropogenic disturbance. Ecology 2009, 90, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, B.; Dellicour, S.; Ghisbain, G.; Przybyla, K.; Zambra, E.; Lecocq, T.; Boustani, M.; Baghirov, R.; Michez, D.; Rasmont, P. Global effects of extreme temperatures on wild bumblebees. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 35, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.; Lu, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, Y.-L. Elevated temperature affects energy metabolism and behavior of bumblebees. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 155, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbassioon, A.; Yearlsey, J.; Dirilgen, T.; Hodge, S.; Stout, J.C.; Stanley, D.A. Responses in honeybee and bumblebee activity to changes in weather conditions. Oecologia 2023, 201, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, L.A.; Jarvis, E.M.; Lawson, D.A.; Rands, S.A. The behavioural responses of bumblebees Bombus terrestris to simulated rain. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 231882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvell, C.; Meek, W.R.; Pywell, R.F.; Goulson, D.; Nowakowski, M. Comparing the efficacy of agri-environment schemes to enhance bumble bee abundance and diversity on arable field margins. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 44, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L.A.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Leonhardt, S.D.; Aizen, M.A.; Blaauw, B.R.; Isaacs, R.; Kuhlmann, M.; Kleijn, D.; Klein, A.M.; Kremen, C.; et al. From research to action: Enhancing crop yield through wild pollinators. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 12, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascompte, J.; Jordano, P. Plant-animal mutualistic networks: The architecture of biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 38, 567–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L.A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Winfree, R.; Aizen, M.A.; Bommarco, R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Harder, L.D.; Afik, O.; et al. Wild pollinators enhance fruit set of crops regardless of honey bee abundance. Science 2013, 339, 1608–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Kremen, C. Resource diversity and landscape-level homogeneity drive native bee foraging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Han, C.; Breeze, T.D.; Li, M.; Mashilingi, S.K.; Hua, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; An, J. Bumblebee pollination enhances yield and flavor of tomato in gobi desert greenhouses. Agriculture 2022, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.D.; Fountain, M.T.; Brown, M.J. Varietal and seasonal differences in the effects of commercial bumblebees on fruit quality in strawberry crops. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 281, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, T.D.; Gratton, C. A consistent positive association between landscape simplification and insecticide use across the Midwestern US from 1997 through 2012. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmer, P.G.; Stone, G.N. Behavioral, ecological, and physiological determinants of the activity patterns of bees. Adv. Study Behav. 2004, 34, 347–466. [Google Scholar]
- Rader, R.; Edwards, W.; Westcott, D.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Howlett, B.G. Diurnal effectiveness of pollination by bees and flies in agricultural Brassica rapa: Implications for ecosystem resilience. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2013, 14, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.P.; Riaño-Jimenez, D.; Hakim, J.R.C. Pollination efficiency and foraging behavior of Bombus pauloensis (Hymenoptera: Apidae) on two highbush blueberry cultivars (Vaccinium corymbosum). Sociobiology 2024, 71, e9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Differences in Pollination Efficiency Among Three Bee Species in a Greenhouse and Their Effects on Yield and Fruit Quality of Northern Highbush ‘Bluecrop’ Blueberry. HortScience 2021, 56, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Kaushal, B.; Sharma, H.K.; Kumar, P.; Thakur, M. Impact of Bumble Bee Pollination on Strawberry Production under Protected Conditions. Indian J. Èntomol. 2023, 85, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.K.; Rana, K.; Bairwa, V.K.; Singh, P.; Bharthi, V.D. A review on role of bumblebee pollination in fruits and vegetables. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Marín, M. How and why do bees buzz? Implications for buzz pollination. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 73, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straw, E.A.; Cini, E.; Gold, H.; Linguadoca, A.; Mayne, C.; Rockx, J.; Brown, M.J.F.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Potts, S.G.; Senapathi, D. Neither sulfoxaflor, Crithidia bombi, nor their combination impact bumble bee colony development or field bean pollination. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rivas, B.; Monzón, V.H.; Rego, J.O.; Mesquita-Neto, J.N. Pollination by native bees achieves high fruit quantity and quality of highbush blueberry: A sustainable alternative to managed pollinators. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1142623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streinzer, M.; Chakravorty, J.; Neumayer, J.; Megu, K.; Narah, J.; Schmitt, T.; Bharti, H.; Spaethe, J.; Brockmann, A. Species composition and elevational distribution of bumble bees (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Bombus Latreille) in the east Himalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, India. ZooKeys 2019, 851, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Bodlah, I.; Mehmood, K.; Sheikh UA, A.; Aziz, M.A. Pollination and foraging potential of European bumblebee, Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae) on tomato crop under greenhouse system. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Lei, X.; Zhao, S.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, B.; Wang, M. Research progress on efficient pollination technology of crops. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigs, J.T.; Holzhauer, S.I.; Huang, S.; Brunet, J.; Diekmann, M.; Hedwall, P.O.; Kramp, K.; Naaf, T. Pollinator movement activity influences genetic diversity and differentiation of spatially isolated populations of clonal forest herbs. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 908258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pywell, R.; Warman, E.; Carvell, C.; Sparks, T.; Dicks, L.; Bennett, D.; Wright, A.; Critchley, C.; Sherwood, A. Providing foraging resources for bumblebees in intensively farmed landscapes. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 121, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A. Effects of Landscape Context on Populations of Bumblebees. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marja, R.; Viik, E.; Mänd, M.; Phillips, J.; Klein, A.; Batáry, P. Crop rotation and agri-environment schemes determine bumblebee communities via flower resources. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, A.; Strange, J.P.; Koch, J.B. Foraging economics of the hunt bumble bee, a viable pollinator for commercial agriculture. Environ. Èntomol. 2019, 48, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamo, T.; Nikkeshi, A.; Tawaratsumida, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Kishi, S. Pollination efficiency of bumblebee, honeybee, and hawkmoth in kabocha squash, Cucurbita maxima, production in Kagoshima, Japan. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2022, 57, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, L.S.; Barber, N.A.; Biller, O.M.; Irwin, R.E. Flowering plant composition shapes pathogen infection intensity and reproduction in bumble bee colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11559–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, S.H. Bumble bee ecophysiology: Integrating the changing environment and the organism. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 22, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsalem, E.; Grozinger, C.M.; Padilla, M.; Hefetz, A. The physiological and genomic bases of bumble bee social behaviour. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 48, pp. 37–93. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.A.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Wickens, J.B.; Wickens, V.J.; Potts, S.G.; Raine, N.E. Neonicotinoid pesticide exposure impairs crop pollination services provided by bumblebees. Nature 2015, 528, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.J.; Raine, N.E. Chronic impairment of bumblebee natural foraging behaviour induced by sublethal pesticide exposure. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, D.D.L.; Schiestl, F.P. Real-time divergent evolution in plants driven by pollinators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, N.; Colombo, B.; Pioltelli, E.; Biella, P.; Casiraghi, M.; Galimberti, A. Urban habitat fragmentation and floral resources shape the occurrence of gut parasites in two bum-blebee species. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, N.D.; Colla, S.R.; Wagner, D.L.; Gall, L.F.; Kerr, J.T. Do pathogen spillover, pesticide use, or habitat loss explain recent North American bumblebee declines? Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, T.A.; Janousek, W.M.; Gaulke, S.M.; Nicholas, A.C.; Keinath, D.A.; Bell, C.M.; Cannings, S.; Hatfield, R.G.; Heron, J.M.; Koch, J.B.; et al. Western bumble bee: Declines in the continental United States and range-wide information gaps. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.J.; Holland, J.M.; Hughes, W.O.H.; Goulson, D. Targeted agri-environment schemes significantly improve the population size of common farmland bumblebee species. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1668–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, H.E.; Mazer, S.J.; Seltmann, K.C. Native bee habitat restoration: Key ecological considerations from recent North American literature. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1358621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekière, A.; Michez, D.; Vanderplanck, M. Bumble bee breeding on artificial pollen substitutes. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2022, 115, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.E.; O’neill, M.A. Technological advances in field studies of pollinator ecology and the future of e-ecology. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 38, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasamy, V.; Sundaraguru, R.; Amala, U. Emerging vistas of remote sensing tools in pollination studies. Sociobiology 2019, 66, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, D.; Meeus, I.; Eeraerts, M.; Pisman, M.; Smagghe, G. Linking remote sensing data to the estimation of pollination services in agroecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, B.K.; Robson, A.J.; Howlett, B.G.; Rader, R. Toward an integrated approach to crop production and pollination ecology through the application of remote sensing. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, D.; Hempel de Ibarra, N.; Anderson, K. Remote sensing of floral resources for pollinators–new horizons from satellites to drones. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 869751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Szczesna, N. Assessment of the flying activity of the buff-tailed bumblebee (Bombus terrestris L.) on greenhouse-grown tomatoes. J. Apic. Sci. 2008, 52, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Peat, J.; Goulson, D. Effects of experience and weather on foraging rate and pollen versus nectar collection in the bumblebee, Bombus terrestris. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2005, 58, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, M.; García, D. Complementary contribution of wild bumblebees and managed honeybee to the polli-nation niche of an introduced blueberry crop. Insects 2021, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharnhorst, V.S.; Thierolf, K.; Neumayer, J.; Becsi, B.; Formayer, H.; Lanner, J.; Ockermüller, E.; Mirwald, A.; König, B.; Kriechbaum, M.; et al. Changes in community composition and functional traits of bumblebees in an alpine ecosystem relate to climate warming. Biology 2023, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heraghty, S.D.; Jackson, J.M.; Lozier, J.D. Whole genome analyses reveal weak signatures of population structure and environmentally associated local adaptation in an important North American pollinator, the bumble bee Bombus vosnesenskii. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 5479–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.L.; Martin, A.P.; Carreck, N.L.; Swain, J.L.; Knight, M.E.; Goulson, D.; Hale, R.J.; Sanderson, R.A. Bumblebee flight distances in relation to the forage landscape. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 77, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, E.; Breeze, T.D.; Clough, Y.; Smith, H.G.; Baldock, K.C.R.; Campbell, A.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Gillespie, M.A.K.; Kunin, W.E.; McKerchar, M.; et al. Reliably predicting pollinator abundance: Challenges of calibrating process-based ecological models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, B.; Federsel, L.M. Bumblebees in the city: Abundance, species richness and diversity in two urban habitats. J. Insect Conserv. 2014, 18, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baude, M.; Danchin, É.; Mugabo, M.; Dajoz, I. Conspecifics as informers and competitors: An experimental study in foraging bumble-bees. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Méndez, N.; Andersson, G.K.S.; Requier, F.; Hipólito, J.; Aizen, M.A.; Morales, C.L.; García, N.; Gennari, G.P.; Garibaldi, L.A. The economic cost of losing native pollinator species for orchard production. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Crop | Indicator | Bumblebee Performance | Honeybee Performance | References | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato | Yield | Bumblebee pollination increases yield by 20–30% (greenhouse). | Honeybee pollination shows weaker yield increase (no vibration pollination capability). | [27,56,69] | Bumblebees excel at buzz pollination. |
| Fruit Quality | Brix value increases by 8–10%, more uniform fruits. | No significant increase in Brix value. | [56] | Greenhouse environment experiment. | |
| Sweet Pepper | Yield | Individual fruit weight increases by 15%, misshapen fruits decrease by 40%. | [2] | Bumblebee pollination is highly efficient. | |
| Pollination Rate | Pollen deposition significantly higher than honeybees. | Pollen deposition lower than bumblebees. | [2] | ||
| Blueberry | Yield | Bumblebee pollination results in fruit ripening 5–7 days earlier, individual plant yield increases by 25%. | Honeybee pollination increases yield by 15%. | [34,67] | Open-field environment. |
| Fruit Quality | Fruit diameter increases by 10%, better sugar-acid ratio. | No significant improvement in fruit quality. | [67] | ||
| Strawberry | Yield | Bumblebee pollination increases fruit weight by 12–18%. | Honeybee pollination increases fruit weight by 5–8%. | [57] | Commercial hive comparison experiment. |
| Misshapen Rate | Misshapen fruit rate decreases by 30%. | Misshapen fruit rate decreases by 15%. | [57] | ||
| Apple | Pollination Efficiency | Fewer flower visits, but high pollen deposition. | More frequent flower visits, but lower pollen transfer efficiency. | [38] | Honeybees more reliant on frequent visits. |
| Pumpkin | Pollination Rate | Bumblebee pollination success rate is 85%. | Honeybee pollination success rate is 70%. | [76] | Open-field environment (Japan). |
| Highbush Blueberry | Economic Value | Bumblebee pollination increases market value of fruit by 20%. | [67] | Sustainable alternative to managed hives. | |
| Canola | Pollination Efficiency | Bumblebees are more active under low temperatures. | Honeybees are limited in activity under low temperatures. | [49] | Weather dependency differences. |
| Keywords | Year | Strength | Begin | End | 2005–2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| seed set | 2006 | 6.23 | 2006 | 2013 | ▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| reproductive success | 2007 | 3.54 | 2007 | 2016 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| bombus-terrestris | 2006 | 3.57 | 2008 | 2010 | ▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| floral display size | 2011 | 3.13 | 2011 | 2013 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| pollen | 2008 | 3.49 | 2014 | 2017 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| ecology | 2005 | 3.08 | 2016 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| honey bee | 2017 | 3.5 | 2017 | 2021 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| bees hymenoptera | 2006 | 3.11 | 2020 | 2021 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂ |
| pollinators | 2021 | 5.6 | 2021 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ |
| responses | 2022 | 3.48 | 2022 | 2024 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bie, M.; Song, K.; Dong, H.; Zhao, W.; Lin, H.; Shi, D.; Liu, D. Advancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Bumblebee Pollination: Bibliometric Insights and Future Directions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052177
Bie M, Song K, Dong H, Zhao W, Lin H, Shi D, Liu D. Advancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Bumblebee Pollination: Bibliometric Insights and Future Directions. Sustainability. 2025; 17(5):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052177
Chicago/Turabian StyleBie, Mei, Kai Song, He Dong, Wanru Zhao, Hongze Lin, Dongfang Shi, and Duo Liu. 2025. "Advancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Bumblebee Pollination: Bibliometric Insights and Future Directions" Sustainability 17, no. 5: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052177
APA StyleBie, M., Song, K., Dong, H., Zhao, W., Lin, H., Shi, D., & Liu, D. (2025). Advancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Bumblebee Pollination: Bibliometric Insights and Future Directions. Sustainability, 17(5), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052177






