Abstract
Herein, targeting arsenic-containing acidic wastewater generated from washing arsenic-containing flue gas with concentrated sulfuric acid, the arsenic removal efficiency using H2S was investigated. The effects of H2S concentration, the gas flow rate, H2SO4 concentration, temperature, and Cl−/F− ions on arsenic removal were studied. Results indicate that H2S concentration is the primary factor. Arsenic was precipitated as amorphous As2S3, reducing residual arsenic to 0.28 mg/L. Cl− enhanced arsenic removal, yielding a residual concentration of 0.68 mg/L, while F− exhibited a dual effect: the inhibition at low concentrations and promotion at high concentrations. At 100 g/L F−, the residual arsenic was 29.59 mg/L. These effects are attributed to Cl−/F− altering the surface electrochemical properties of As2S3 particles. Additionally, both ions improved As2S3 hydrophobicity. This study provides insights for purifying arsenic-containing sulfuric acid.
1. Introduction
As-containing acidic wastewater, a typical inorganic hazardous waste, is produced by copper smelting flue gas contacts with washing liquid in a washing tower [1]. It contains high H2SO4 concentration (5–20 wt.%), high As concentration (0.5–20 g/L) [2,3,4], and anions (such as Cl− and F−) [5]. The characteristics of corrosiveness and toxicity make it hard to treat worldwide and pose a serious risk to human health and the environment [6,7]. In addition, As-containing waste has been listed as the highest-priority contaminant, and an environmental protection tax must be paid for it in China [8]. Hence, the handling and mitigation of As contaminations from copper smelting operations are thus critical for sustainable development and environmental protection.
Several methods [9], such as the lime ferric salt method, ion exchange method, membrane technology [10], adsorption [11], biotechnology [12], and electrolysis method [13], have treated the contamination efficiently in recent years. However, these methods produce large amounts of As-containing hazardous wastes and cause secondary pollution although they remove As efficiently. Based on the above thoughts, the sulfide precipitation method stabilized As by forming As2S3 to lower the As concentration. Moreover, the generated As2S3 can be utilized as a resource in photosensitive materials, thermoelectric materials, and other applications [14,15]. Yong Kuili et al. used natural pyrite to remove arsenic from copper smelting wastewater, achieving a removal efficiency of over 99.4% [16]. Pieter Ostermeyer et al. added NaHS at a S:As molar ratio of 2.5 to arsenic-containing acid at pH = 2, achieving an arsenic removal rate of 99% [17]. Although these vulcanizing agents exhibit high arsenic removal efficiency, they introduce new impurity ions and prevent the recycling of valuable acid solutions. To address this, H2S has recently gained attention for removing heavy metals through vulcanization. Qian Liang et al. reported that the performance of As precipitated by H2S fluctuated greatly during the actual treatment. An excess of HS− and S2− in the solution will alter the surface properties of the precipitate, causing As2S3 to dissolve again [18]. However, excessive H2S cannot be completely absorbed by the waste acid, and the discharged low-concentration H2S gas not only pollutes the surrounding environment but also wastes resources. The additional amount of the vulcanizing agent is very important to the final As removal rate. Additionally, the particles formed during metal sulfide precipitation are typically micron- to nano-sized [19]. This poses a challenge in separating and removing them from the solution.
To address these issues, Yunxi Copper and China Enfei have proposed a new treatment procedure after extensive exploration: washing the flue gas with a high concentration of H2SO4. Due to its limited solubility in concentrated H2SO4, As2O3 will precipitate and separate from the washing water [2]. Previous studies in our research group have shown that, when the H2SO4 concentration reaches 52 wt.%, the solubility of As2O3 is significantly reduced. However, the arsenic-containing high-acid wastewater (AHAW) after As2O3 separation still requires further treatment via vulcanization. Therefore, the sulfide precipitation method remains necessary for arsenic removal. Liu Haidi et al. demonstrated that H2S can theoretically precipitate arsenic in 55 wt.% H2SO4 [20]. In addition, the effects of Cl and F are rarely noticed. Feng Zhu et al. evaluated the effects of CO32−, SiO32−, PO43−, Cl−, SO42−, and NH4+ under alkaline conditions. Except for the fact that CO32− has a weak inhibitory effect, the influence of other anions can be ignored [21]. Xu et al. found the complex influence of Cl− concentration on the desulfurization removal of As(III) and As(V) but did not explain the mechanism [22].
Although there has been basic research on the application of vulcanization in a high concentration H2SO4 environment, there is still a lack of discussion on the system’s working conditions. The mechanism of anion (Cl− and F−) influence still needs further study. In this paper, the effects of H2S gas concentration, gas flow rate, H2SO4 concentration, and temperature on As removal were studied. Simultaneously, this study investigates the impact of Cl− and F− in AHAW on the efficiency of As precipitation. The mechanism is explained by solid phase characterization and DFT theoretical calculation. This research provides recommendations for arsenic removal in the copper smelting industry, aiming to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve resource utilization efficiency. The findings offer both economic benefits and positive environmental impacts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4, AR), hydrochloric acid (HCl, AR), and hydrofluoric acid (HF, AR) were procured from Chengdu Cologne Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH, AR) was obtained from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co. (Shanghai, China). H2S gas in cylinders (1000 ppm, nitrogen as carrier gas, Dalian Dart Gas Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) and nitrogen in cylinders (99.99%, Kunming Guangruida Gas Co., Ltd., Kunming, China) were utilized to generate H2S gas at desired concentrations in the experiments. As2O3 was provided by an enterprise in East China with purity of 99.47%.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
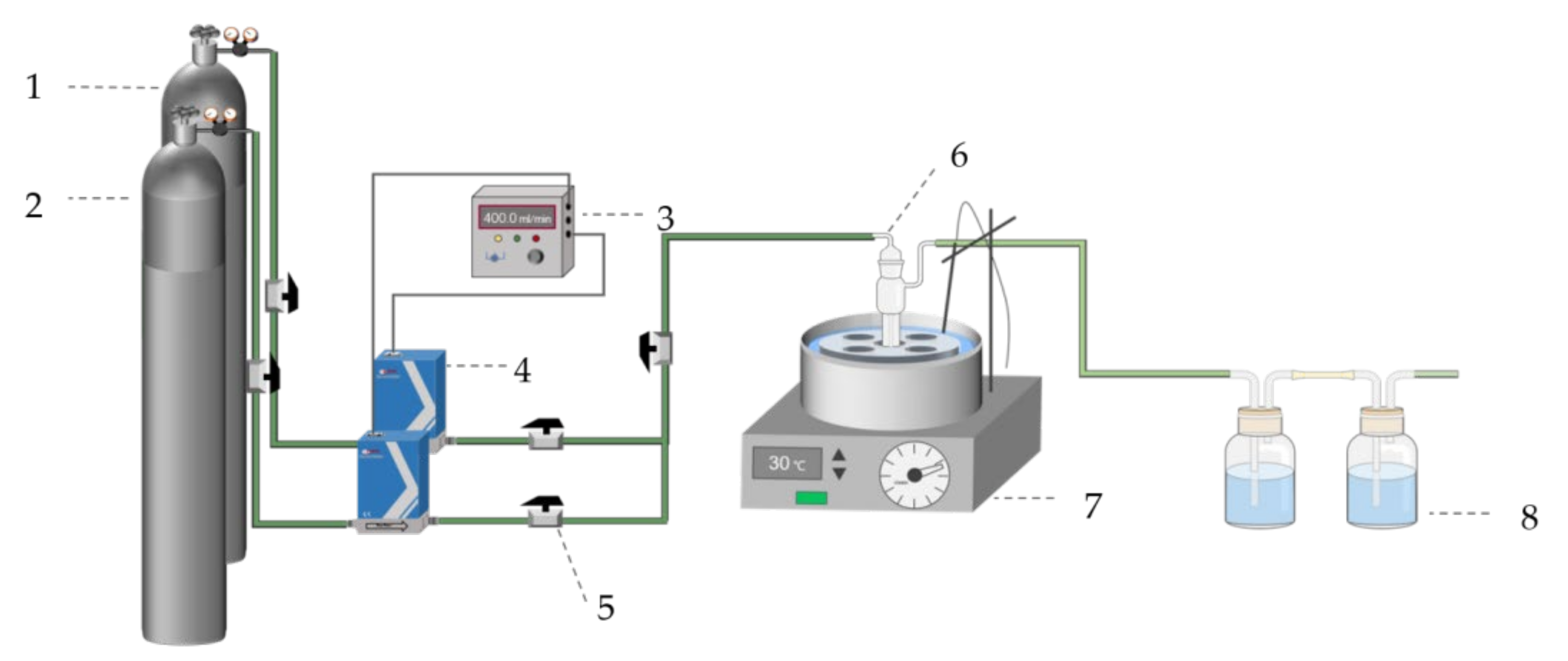
The As removal experimental apparatus is depicted in Figure 1 and as follows: The As removal test was carried out in a bubble absorption bottle, using H2S gas to react with AHAW to form As2S3 at 30 °C. H2S from the gas cylinder was diluted with N2 (99.9%) to the desired concentrations at the flow rate of 400 mL/min. And, then, the gas passed through the prepared 30 mL of AHAW into bubble absorption bottle at 3 h. The bubble absorption bottle kept temperature in thermostat water bath. After reacting, tail gas that passed through in the experiment was absorbed by a solution of sodium hydroxide. In addition, the blue copper sulfate solution connected at the rear was utilized to display the operational condition of the absorption bottle. The solution passed through a filter with a particle size of 0.45 μm to obtain samples, and, then, the samples were washed three times with DI water. All experiments were repeated three times, and the As removal efficiency (η) was used to assess the effectiveness of As removal and calculated by Equation (1). Given the very corrosive nature of hydrogen sulfide gas, the experiment utilized predominantly stainless steel tubes, with the remaining connections made using PTFE pipes.
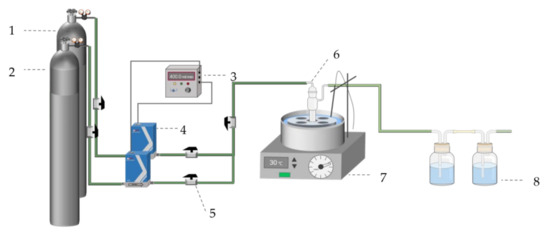
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of experimental apparatus (1—N2 cylinder gas (99.99%); 2—H2S cylinder gas (1000 ppm); 3—digital display; 4—mass flowmeter; 5—stop valve; 6—bubble absorption tube; 7—thermostat water bath; and 8—tail gas absorption device (1 mol/L of NaOH and 1 mol/L of CuSO4)).
Removal efficiency is based on the next test calculation:
where C0 and Ct are the initial and transient concentrations of As (mg/L).
2.3. Analysis and Characterization
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Agilent 5110, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to determine the concentration of As in the solution. The crystal structures of samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Anton Paar XRD Dynamic500, Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) with scan speed of 10°/min at 10–80°. The surface morphology and elemental composition were analyzed by SEM and EDS (ZEISS Sigma 300, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Scientific ESCALAB Xi+, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with Al Kα X-ray was used to detect valence state of elements and calibrate C 1s peak at 284.8 eV. The surface properties of precipitated solids under different conditions were analyzed by using a Zeta potential analyzer (Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90, Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK).
2.4. Computational Method
In this work, spin-polarized density functionary calculations were used by Dmol3 program in Materials Studio software (2017 version) [23,24]. The composition of As sulfide clusters were selected according to the most stable cluster structures as predicted by previous theoretical studies and used GGA/PBE functional method with DNP basis [23,25]. DFT-D3 method includes dispersion energy correction by atomic pair with Becke–Johnson damping function [24]. To simulate the liquid phase situation, the implicit solvation model COSMO was considered [26]. The core electrons of H, O, Cl, F and S were treated with all electron methods, while semi-core pseudopotential method was used for the core electrons of As. The tolerance of the energy, max force, and displacement convergence was 1.0 × 10−5 Hartree (Ha), 2.0 × 10−3 Ha/Å and 5.0 × 10−3 Å, respectively. Absorption energies for A-B systems were computed as follows:
where EAB corresponds to the total energy of the AB system, and EA and EB are the energies of the isolated fragments A and B, respectively. In this framework, the more negative the Eabs values, the more stable the AB system is.
Eabs = EAB − (EA + EB)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis of As Sulfide Precipitation
The dissolution of As2O3 in water has been documented to produce arsenious acid (H3AsO3) [27]. Hence, H3AsO3 is the chemical composition of elemental As when it is dissolved in the H2SO4 solution. H3AsO3 undergoes decomposition to make As2S3 precipitate by reaction with HS− and S2− generated from the decomposition of H2S. As2S3 has a strong tendency to form a solid when the circumstances are acidic, and its solubility product constant (Ksp = 2.1 × 10−22) is extremely low. The chemical equation that represents the whole reaction process is as follows [18]:
As2O3 + 3H2O = 2H3AsO3 K = 8.29 × 10−3
2H3AsO3 + 3H2S = 2As2S3 + 3H2O K = 9.29 × 1027
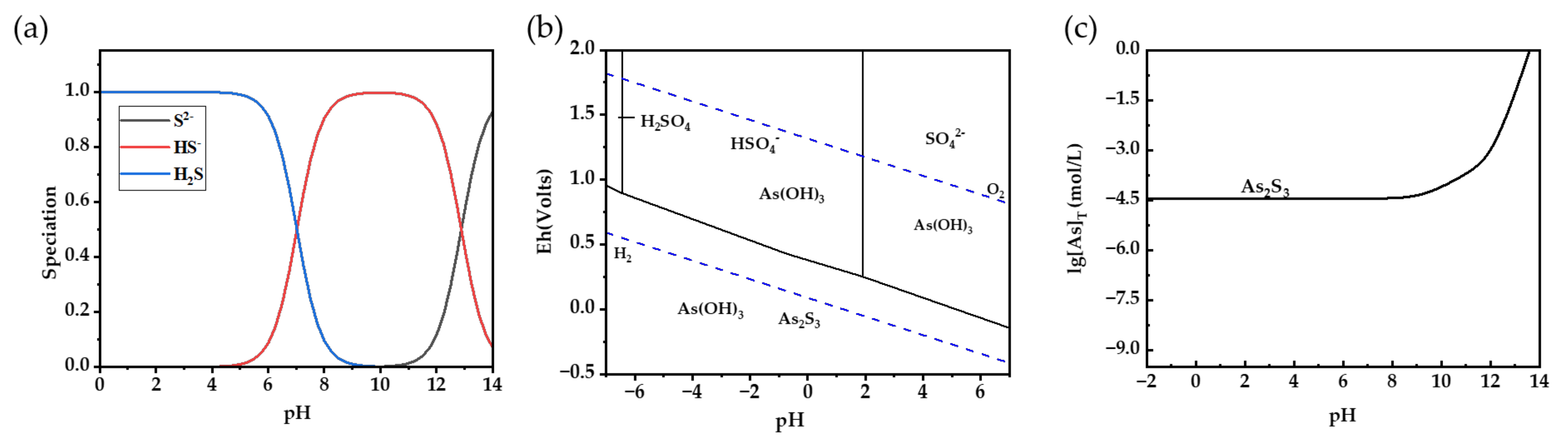
However, when the pH drops below 2, the bulk of H2S exists in the solution as molecules, as seen in Figure 2a. The H2SO4 solution reaches a pH as low as −0.86 at a concentration of 52 wt.%. The high concentration of H+ in the solution will impede the process of ionization for H2S and H3AsO3. In order to conduct a more detailed examination of the reaction process, an Eh-pH diagram of the As-S-H2O system was generated using HSC software (6.0 version). The experiment was conducted at a constant air pressure of 1 bar, a temperature of 25 °C, and with the concentration of the As element set at 6.67 mM (500 mg/L).
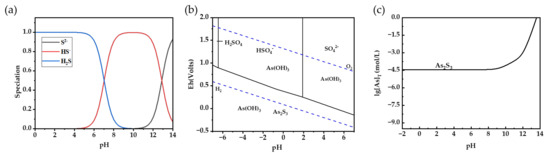
Figure 2.
Species distribution of H2S (a) and arsenite (b) from acidic to alkaline conditions under one bar pressure and 25 °C. (c) Dissolution curve of As trisulfide at different pH values.
As shown in Figure 2b, the results suggest that As(III) is present in the solution as both As2S3 and H3AsO3, depending on the redox potential rather than the pH value. The reason for this is because H3AsO3 exhibits resistance to breakdown in acidic circumstances, allowing it to maintain stability throughout a broad spectrum of environments. As2S3 exhibits greater stability in an environment characterized by a low redox potential. The maximum concentration of H2SO4 in the AHAW is 7.50 mol/L. Within this specific range of concentration, H2SO4 will not undergo ionization in the subsequent phase and will mostly exist as HSO4−. Furthermore, based on the dissolution curve of As2S3 in relation to the variation in pH (Figure 2c), the concentration of free As in the solution is around 10−4.4 mol/L [28]. As2S3 demonstrates excellent stability in acidic conditions, maintaining a consistent solubility independent of the acidity level.
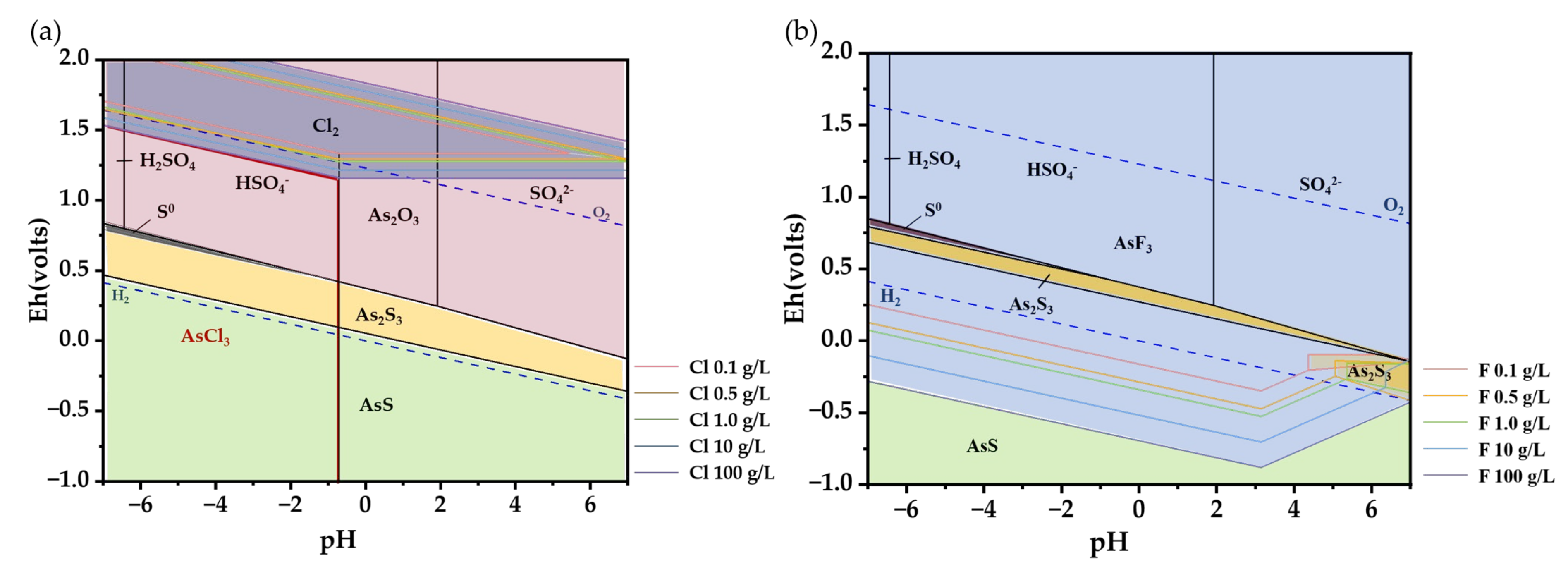
Upon introducing HCl and HF into the system, the circumstances undergo a noticeable change. Shown in Figure 3a, the introduction of Cl− causes the valence state of the As element to transition to a lower valence state, resulting in the formation of As(II)-S complexes, such as AsS. In areas with a high redox potential, As predominantly exists as an oxide rather than H3AsO3, as indicated by the pink range in the picture. As the amount of Cl element in the system increases, the likelihood of Cl2 forming also increases, even in the presence of a specific oxidizing environment. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid any interaction between the reactants and oxygen throughout the experiment and implement appropriate safety precautions. At a Cl− concentration of 100 g/L, a new species called AsCl3 emerges, in the area enclosed by red lines in the lower left corner of Figure 3a. The subsequent reactions will transpire during the process of conjecture [29]:
H3AsO3 + 3HCl = AsCl3 + 3H2O K = 2.52 × 10−11
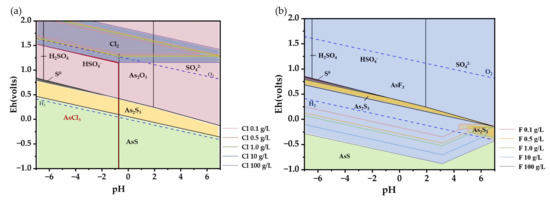
Figure 3.
E-pH diagram of different systems at 25 °C, 1 bar: (a) As-S-Cl-O; (b) As-S-F-O (The pink area is As2O3, the yellow is As2S3, the green is AsS, and the blue is AsF3).
Owing to the reversible nature of the reaction, a certain quantity of products will be obtained when there is a enough amount of the reactant HCl. The reaction has limited spontaneity at a normal temperature, and the resulting product AsCl3 demonstrates solubility in liquid, hence precluding the formation of any by-product AsCl3.
The use of HF increases the stringency of the conditions required for the generation of As2S3 precipitate (Figure 3b). As the concentration of HF increases, As has a tendency to react with F to produce AsF3. Simultaneously, the development of AsS is highly improbable due to the inability of genuine experimental circumstances to achieve the necessary level of reduction for its creation. Usually, F− and OH− are regarded as having analogous molecular orbitals [30]. So, the OH− of H3AsO3 in a solution is more readily substituted by F−. Unfortunately, there are little data available on the solubility product constant of AsF3. It is estimated using the equilibrium constant of the decomposition process of AsF3 (K = 4.72 × 10−17).
AsF3(l) + 3H2O(l) = As(OH)3(a) + 3HF(a) K = 4.72 × 10−17
As2S3 is usually determined to have a lower solubility. It is not feasible to determine the perpetual existence of AsF3 as a by-product only based on its theoretical worth. Additional experimental investigation is required to determine if the presence of HF will have an impact on the ultimate creation of As2S3.
3.2. Adaptability of H2S Sulfidation for As Removal
3.2.1. Effect of H2S Concentration
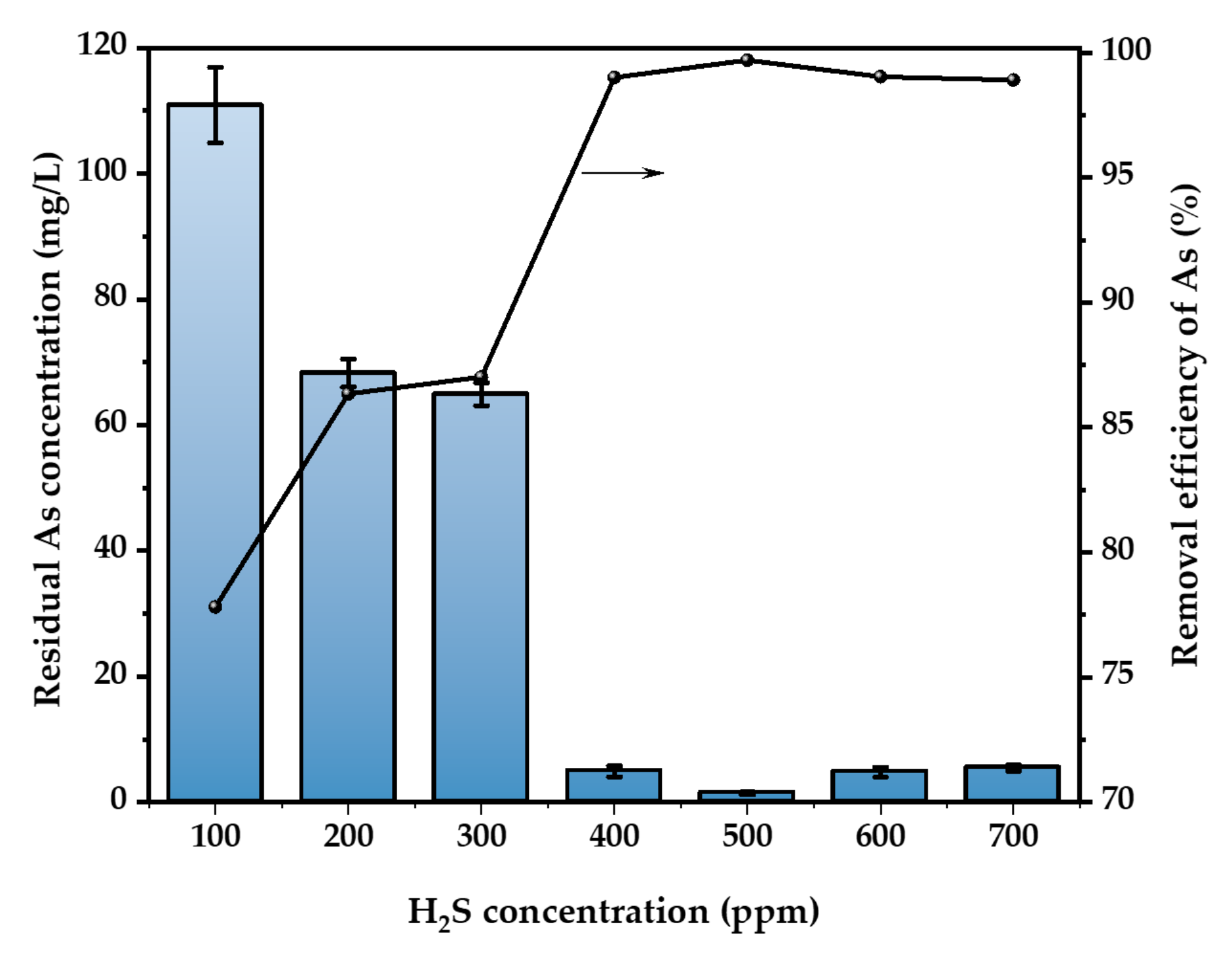
Figure 4 illustrates the effect of gas concentration on the removal of As. At a temperature of 30 °C and with a H2SO4 concentration of 52 wt.%, H2S gas at concentrations of 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, and 700 ppm was continuously added to the acidic waste liquid containing 500 mg/L of As. The flow rate of the waste liquid was maintained at 400 mL/min for a duration of 3 h for each concentration of H2S gas. After the concentration of H2S increased from 100 ppm to 700 ppm, the efficiency of As removal increased from 33.9% to 99.04%. The best rate of elimination occurs when the concentration of H2S hits 500 ppm. When the gas concentration surpasses 500 ppm, the concentration of As in the solution increases by 3.2% to 3.4% compared to the optimum circumstances. Optimizing the gas concentration within a certain range enhances the occurrence of effective collisions throughout the reaction, hence promoting a more favorable forward direction of the reaction. However, if a large amount of H2S is passed through, it might increase the supersaturation of the solution, which is not ideal for the formation of the products [31]. Additionally, the surplus of the S element might react with the generated As2S3 to create H2As3S6−, leading to a reduction in the rate of As removal [32]. Consequently, the optimal concentration of H2S gas was found to be 500 ppm, and this concentration was used for further investigations.
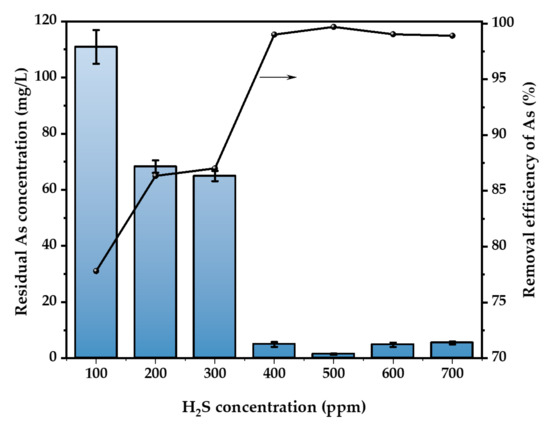
Figure 4.
Effect of H2S concentration (T = 30 °C, H2SO4 concentration = 52 wt.%, H2S flow rate = 400 mL/min, t = 3 h. The arrow indicates the axis corresponding to the curve).
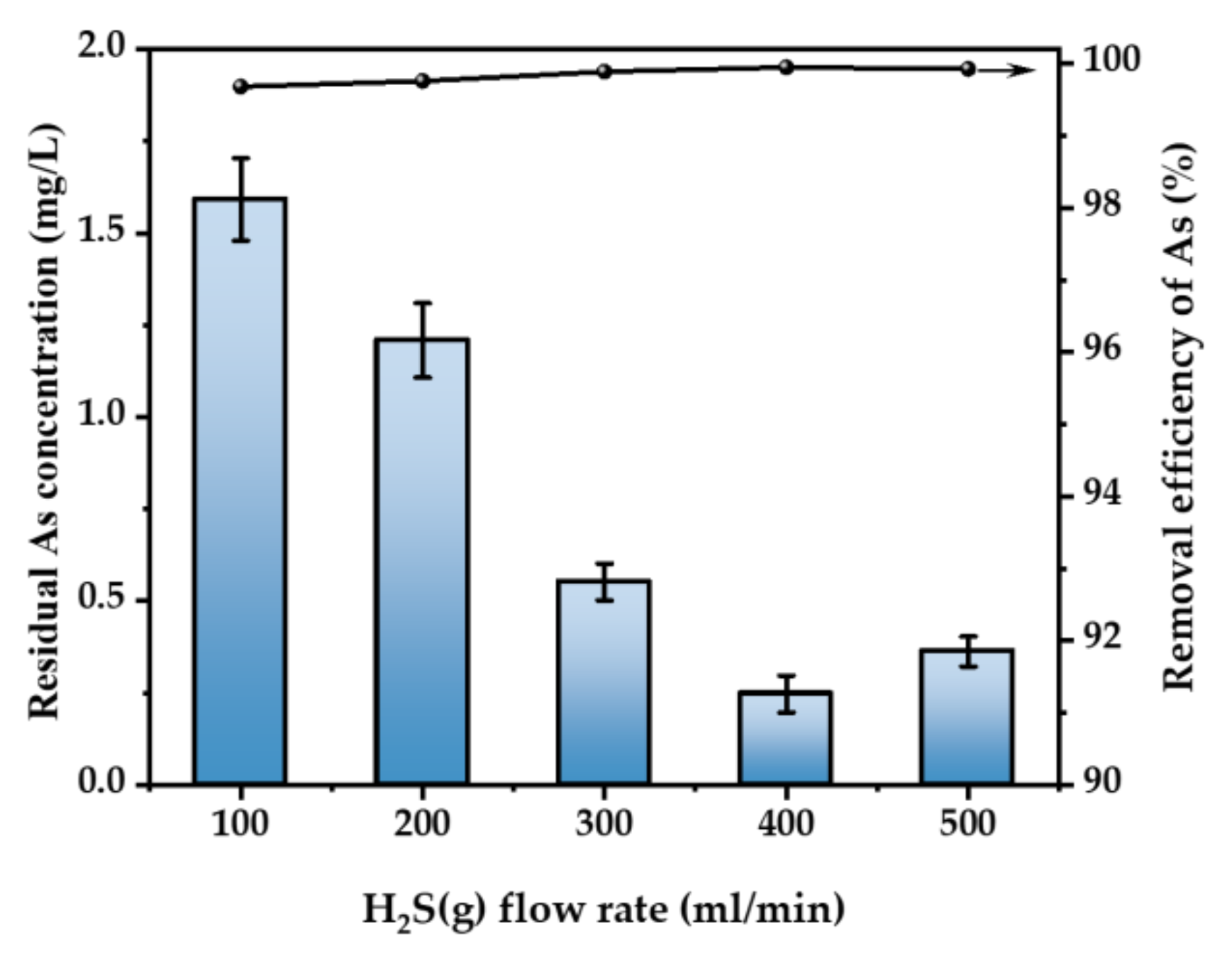
3.2.2. Effect of H2S Flow Rate
Figure 5 illustrates the impact of the gas flow rate on the elimination of As. Under the conditions of H2SO4 concentration of 52 wt.% and 30 °C, 500 ppm of H2S gas was introduced into the acidic As-containing waste liquid with an As concentration of 500 mg/L at the flow rate of 100–500 mL/min for 3 h. Typically, an increase in the gas flow rate leads to a corresponding increase in the rate of As removal [28]. The efficacy of As removal was seen at five different flow rates: 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 mL/min, resulting in a clearance rate above 99%. Following purification, the concentration of As ranged from 0.22 to 1.23 mg/L. The highest As removal rate was achieved at a flow rate of 400 mL/min, at a rate of 99.87%. On the premise that the gas concentration is guaranteed, the effect of the flow rate on As removal can be ignored, but, in order to deal with the As-containing waste liquid with higher energy concentration, we choose the flow rate of 400 mL/min for the experiments below.
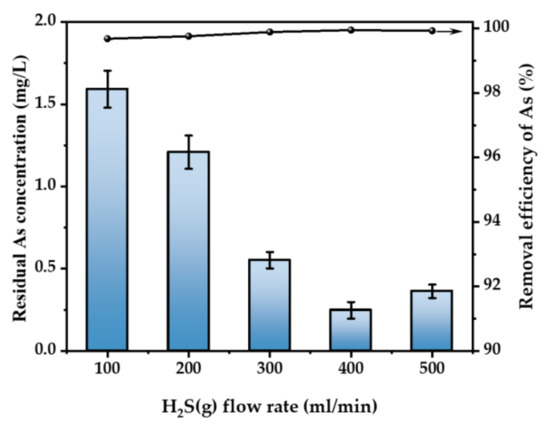
Figure 5.
Effect of H2S flow rate (T = 30 °C, H2SO4 concentration = 52 wt.%, H2S concentration = 500 ppm, t = 3 h. The arrow indicates the axis corresponding to the curve).
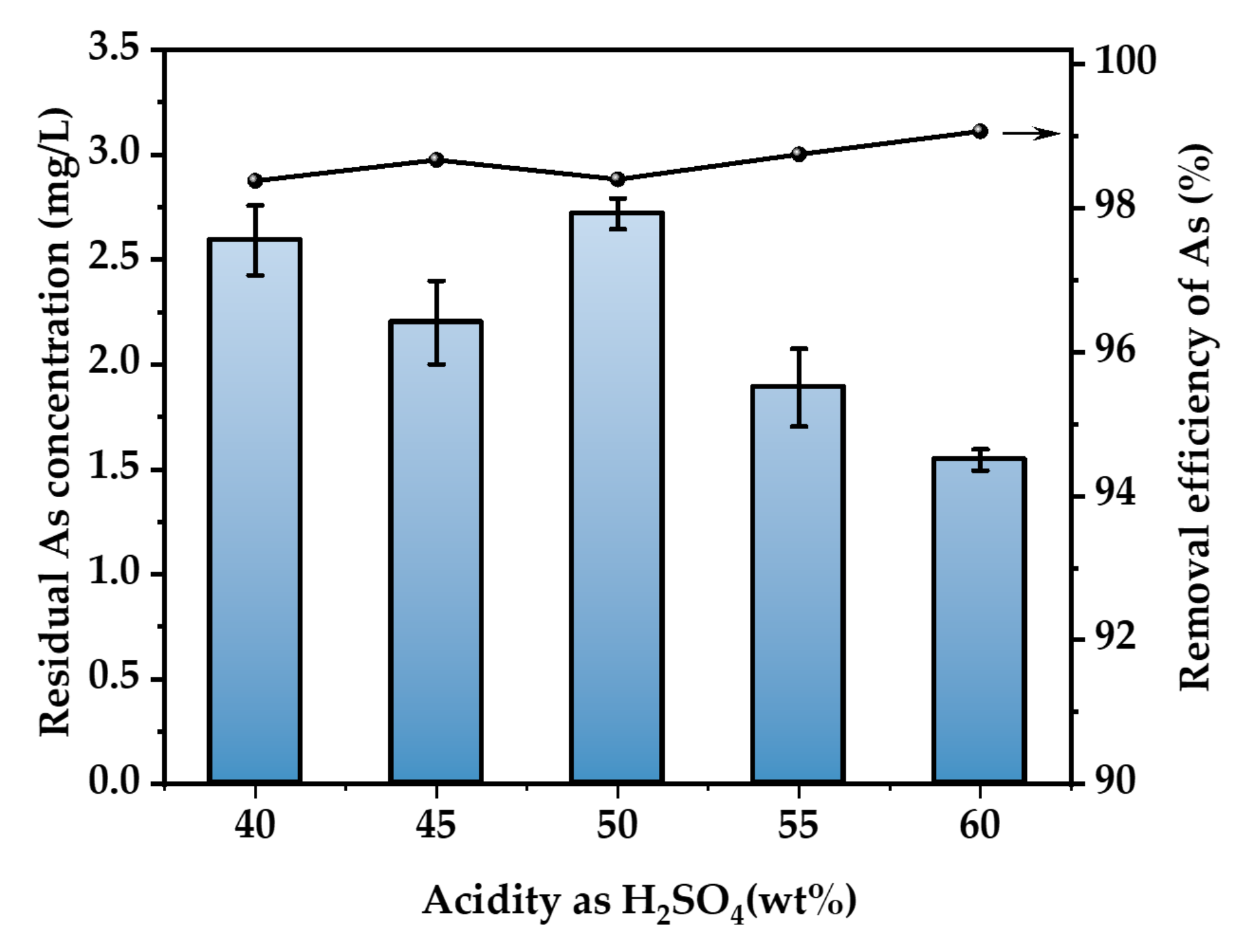
3.2.3. Effect of H2SO4 Concentration
At an As concentration of 500 mg/L, a reaction temperature of 30 °C, and a reaction time of 3 h, a flow rate of 400 mL/min of 500 ppm of H2S gas was passed to investigate the impact of H2SO4 concentration on the removal of As. The calculation result is shown in Figure 6. As in the range of 40% to 60% H2SO4 concentration has a high removal effect. The greatest concentration of As after purification is 2.68 mg/L, while the lowest is 1.54 mg/L. The removal rate of As exceeds 97.6%. The As removal effect was not significantly affected by H2SO4 concentrations ranging from 40 to 60 wt.%. Considering the continuity of operating conditions in practical application, we selected the data of the previous section and determined the sulfuric acid concentration as 52 wt.% [2]. In this way, the flue gas is washed with 52 wt.% sulfuric acid solution, and As2O3 is recovered to the greatest extent. The AHAW produced in this process can be directly sulfided to remove arsenic without adjusting the concentration of sulfuric acid.
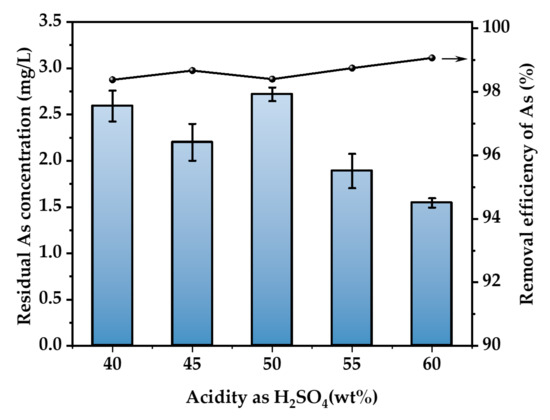
Figure 6.
Effect of H2SO4 concentration (T = 30 °C, H2S concentration = 500 ppm, H2S flow rate = 400 mL/min, t = 3 h. The arrow indicates the axis corresponding to the curve).
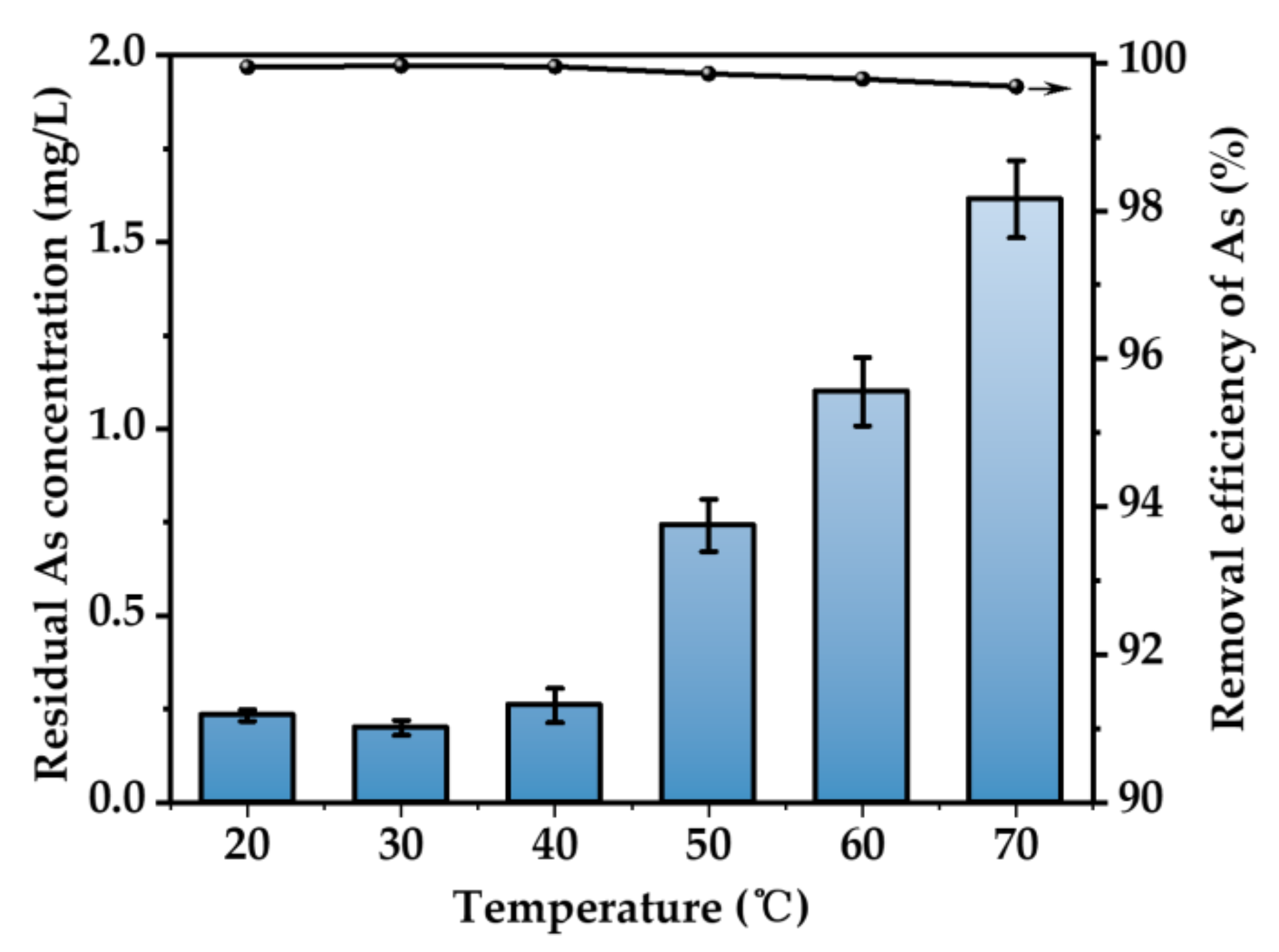
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
Figure 7 illustrates the As removal rate at different temperatures. It can be seen that the temperature has a limited effect on the removal rate of As. In the temperature range of 20~70 °C, the removal efficiency of As is above 99%. The best efficiency is obtained at 30 °C. The ionization of H2S in solution is an endothermic reaction. Increasing the temperature in a certain range is beneficial to the ionization of H2S and increases the concentration of S2− in solution [33]. However, with the increasing temperature, the dissolution of hydrogen sulfide in aqueous solution will be inhibited. Therefore, the optimum temperature for removing As is fixed at 30 °C. The concentration of As in waste solution can be as low as 0.21 mg/L.
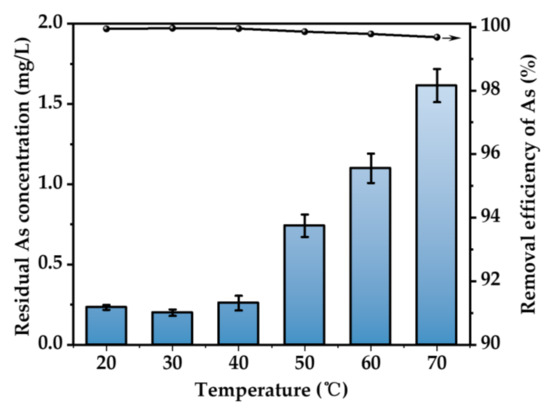
Figure 7.
Effect of temperature (H2SO4 concentration = 52 wt.%, H2S concentration = 500 ppm, H2S flow rate = 400 mL/min, t = 3 h. The arrow indicates the axis corresponding to the curve).
In conclusion, we achieved optimal precipitation conditions for the removal of As from H2SO4. When 500 ppm of H2S gas is supplied into the system at a flow rate of 400 mL/min at a temperature of 30 °C for a duration of 3 h, the removal rate of As achieves 99.87%. The remaining concentration of As in the solution is 0.22 mg/L, which is lower than the theoretical value of 2.99 mg/L specified in Section 3.1. H2S gas at low concentrations has effective As removal capabilities when used with high concentrations of H2SO4. The treated sulfuric acid solution meets the requirements of preparing industrial sulfuric acid [34].
3.2.5. Characterization of Reaction Products
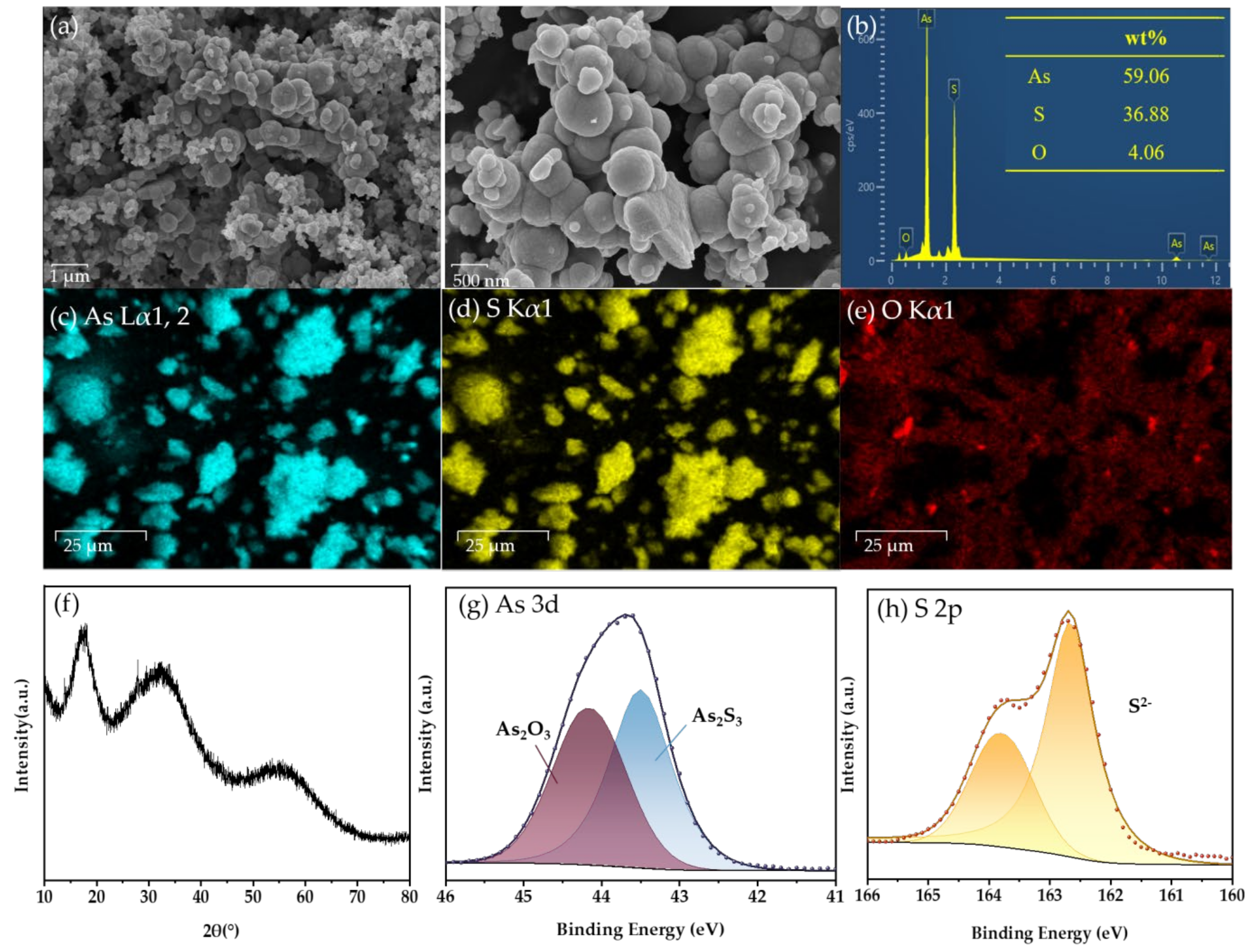
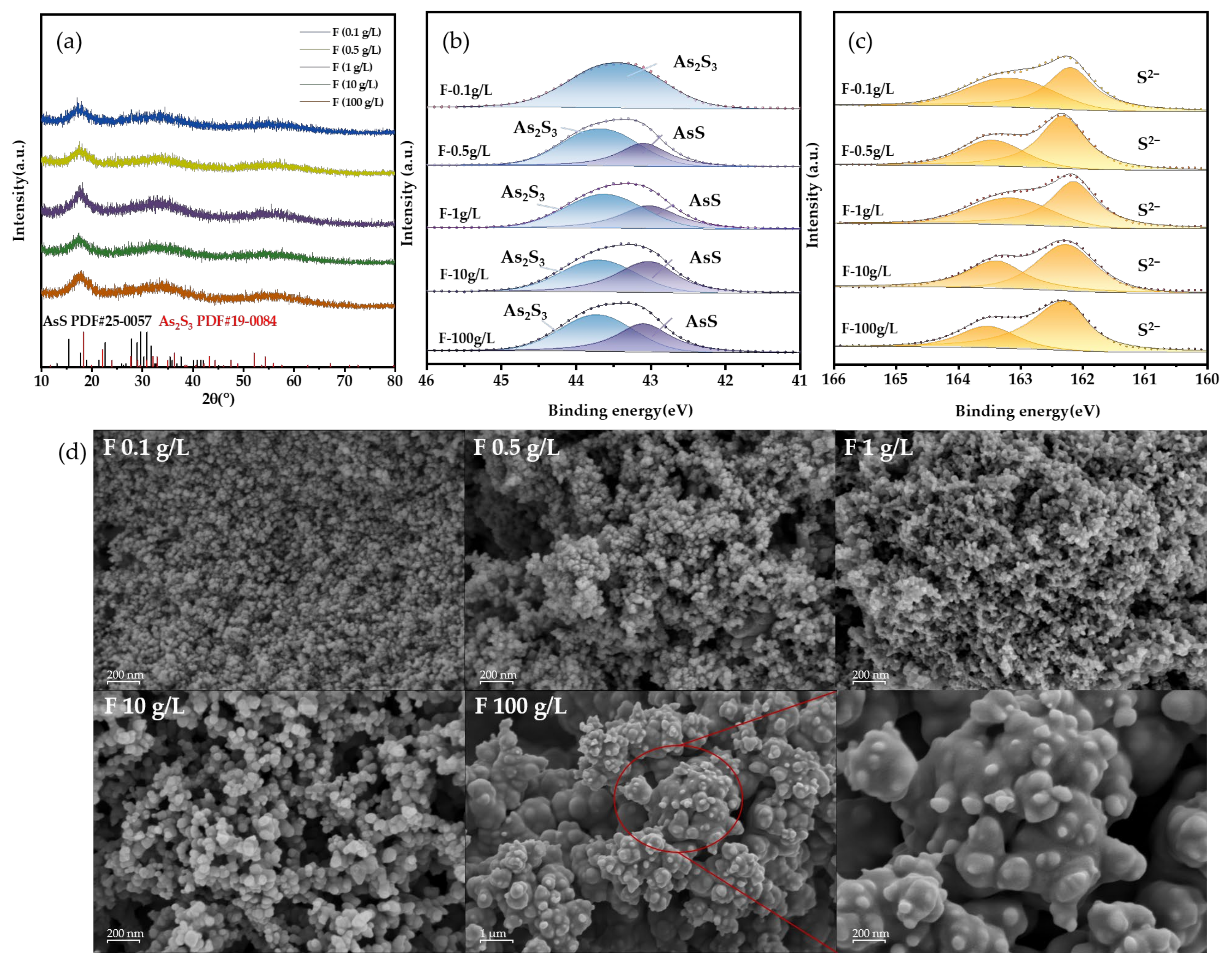
In order to further analyze the products after the reaction, As(III)-S precipitates were collected under the optimum conditions (30 °C, 400 mL/min, 500 ppm, 52 wt.%, 3 h) and characterized by SEM-EDS, XRD and XPS spectra.
The SEM examination image in Figure 8a shows that the precipitate comprises spherical particles with a particle size of about 500 nm. In order to analyze the composition of the solid particle, the scanned images of the elements As, S, and O are displayed in Figure 8c–e, respectively.
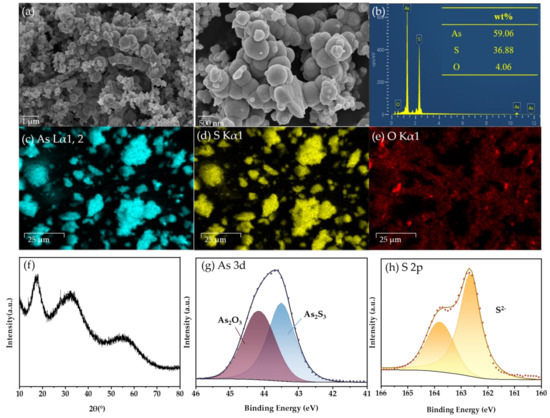
Figure 8.
Characterization of precipitates: (a) SEM images; (b) Elemental mapping; EDS spectra of (c) As, (d) S, and (e) O; (f) XRD pattern; XPS spectra of (g) As 3d and (h) S 2p.
Based on the aforementioned findings, it is evident that the distribution of As and S elements is uniform throughout all sections of the particles, whereas oxygen components are mostly localized near the periphery of the particles. Thus, it may be inferred that As-S is the chemical present in the sample, and the concentration of As2O3 is exceedingly little. The molar ratio of As to S determined by energy spectrum scanning is 1:1.46, which is slightly more than the molar ratio of pure As2S3, which is 1:1.5. There is a small amount of As2O3 on the surface of the sediment, which increases the As element that does not belong to As2S3. So the overall nAs:nS is larger than the theoretical value. Furthermore, it is impossible to prevent the sample from coming into contact with air during the preparation and detection procedure, which makes a small amount of As combine with O to form As2O3. Simultaneously, due to the stochastic nature of the elements acquired by EDX analysis, it remains unfeasible to ascertain the chemical bonding mode and existing state of As and S in the sample. However, it can be concluded that the sample is a compound mostly composed of As and S.
The XRD analysis of the As-S precipitate (Figure 8f) reveals three distinct peaks at about 18°, 32°, and 55°, indicating the presence of amorphous As2S3, which is typical of the precipitate [32].
In addition, XPS analysis was employed to investigate the surface chemical composition of the sulfide precipitate. The peaks seen at 43.5 eV in the fitted data were attributed to As (III), whereas the peaks at 44.15 eV were attributed to As (III)-O. The identified peaks for S 2p at 163.78 and 162.66 eV were attributed to S2−. The main constituent of the precipitates was identified as As2S3 (Figure 8g,h) [35,36,37].
3.3. Mechanism of the Multi-Roles of Anions (Cl− and F−) for As Removal
To enhance the experimental study’s resemblance to real-industry conditions, the starting concentration of As was elevated to 3 g/L. Other circumstances were set to the ideal parameters reported in Section 3.2.
3.3.1. Effects of Cl−
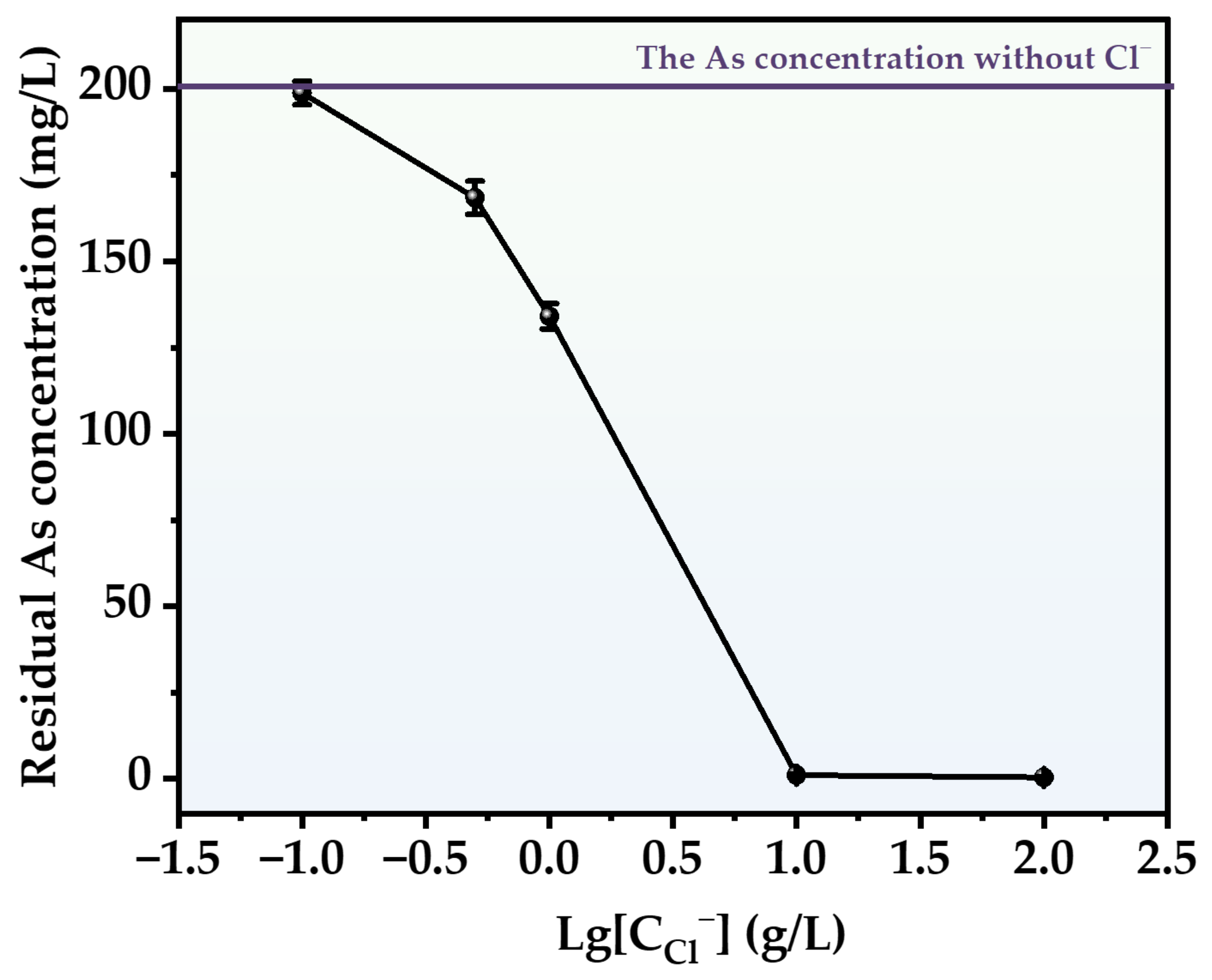
In order to cover the concentration range of Cl− in actual sewage, the removal efficiency of As at five concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 1, 10 and 100 g/L) was studied. The experimental results are shown in Figure 9. The use of HCl facilitated the conversion of As in the liquid to produce a solid precipitate. As the concentration of HCl increased, the amount of residual As in the solution reduced progressively. The highest degree of As removal occurred when the HCl concentration was 100 g/L. Following a 3 h reaction, the concentration of As in the solution was reduced to 0.68 mg/L, which is three orders of magnitude lower compared to the concentration in the absence of HCl. This might be due to the fact that the presence of HCl facilitates the conversion of arsenious acid in the solution into AsCl3 (Equation (5)), and AsCl3 is capable of dissolving in water [38]. The dissolution of AsCl3 expedited the exposure of As atoms, hence enhancing the precipitation of As-S. At high concentrations of HCl, we noticed an intriguing experimental phenomenon: the particles that formed became smaller in size and gained the capacity to separate from the solution. During the reaction, the freshly formed particles will be carried out of the reactor by the airflow and adhere to the gas pipeline at the conclusion of the process, appearing as a vivid orange hue similar to orpiment.
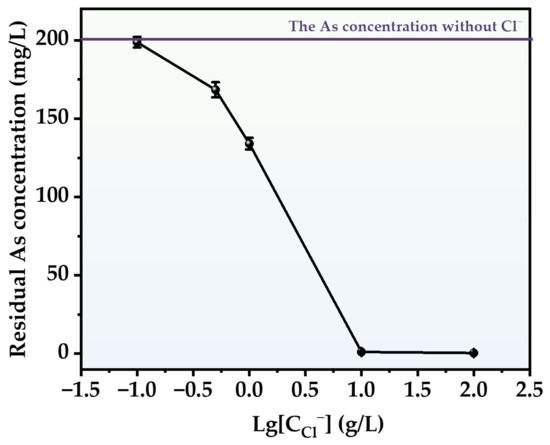
Figure 9.
Effect of different chlorine concentrations on As removal.
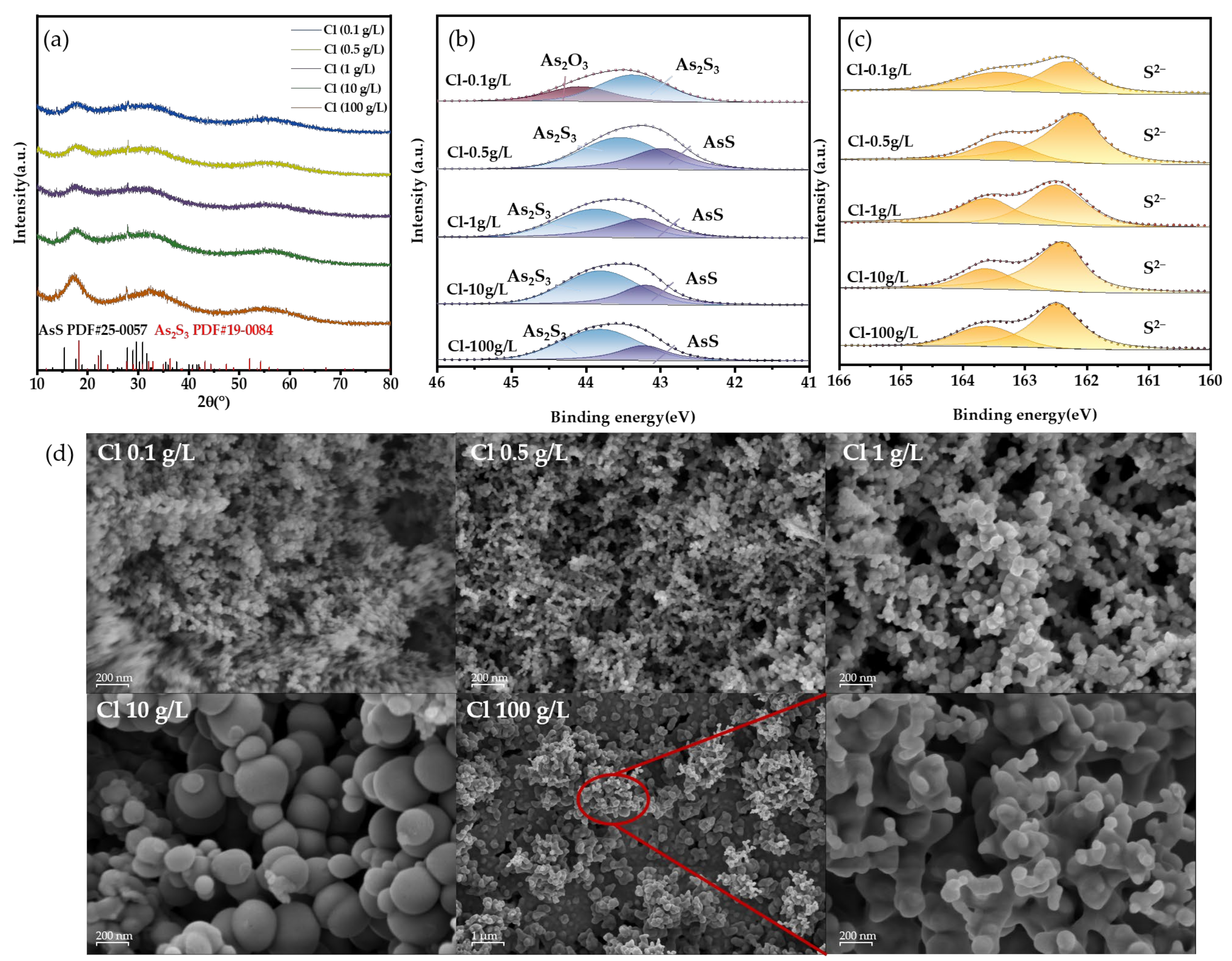
To provide a more detailed explanation of the effect mechanism, we analyzed the As-S precipitates formed in the solid phase under varying Cl− concentrations. The XRD patterns of the precipitates show broad peaks, suggesting poor crystallinity (Figure 10a). Besides the characteristic peaks of amorphous As2S3 at 18°, 32°, and 55°, the AsS phase was detected, matching the reference pattern (JCPDS No. 25-0057). XPS results further confirmed the presence of AsS (Figure 10b). The binding energy of 43.1 eV corresponds to As(II), while 43.5–43.8 eV is attributed to As(III) in As2S3, consistent with previous reports [35,36,39,40]. The SEM images display contrasting outcomes. As seen in Figure 10c, the dimensions of the precipitate particles are significantly lower compared to those of the direct precipitate particles. The addition of HCl will promote the transformation of H3AsO3 into AsCl3, which is more easily decomposed. Atoms are exposed faster, which means that the activity of As increases, and the supersaturation of As in solution increases. This situation will instantly form a large number of fine particles [41]. However, with the increase in Cl− concentration, the precipitation particle size obviously increased, especially at 10 g/L. This may be due to the adsorption of Cl− on the particle surface, which inhibits the contact of S2− and indirectly reduces the supersaturation of the S element, so that the particles can grow. When the concentration of Cl− is 100 g/L, the particles become smaller again. This is because the particles have strong hydrophobicity at this time, and the generated particles will be blown into the back-end gas path and cannot continue to grow, so the particle size is small. Moreover, the ratio of nS to nAs in the sediment ranges from 1.3 to 1.45, which is marginally lower compared to the sediment lacking Cl− (1.46). This indicates that the presence of the Cl− facilitates the conversion of As(III) to the higher valence state As(II). This shows that not only the precipitation reaction but also oxidation–reduction occurred in the solution. AsS may be caused by excessive H2S reduction [42]:
As2S3 + H2S = AsS(s) + H2S2
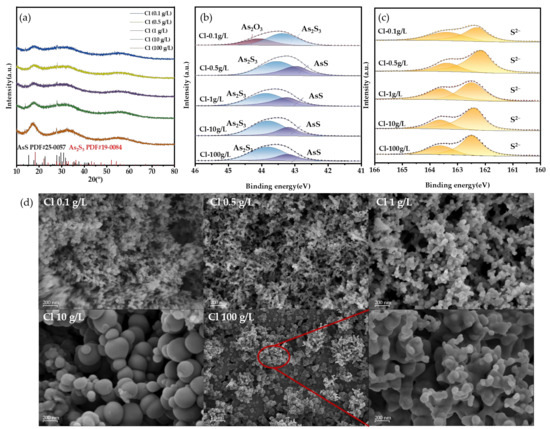
Figure 10.
(a) XRD results, (b,c) XPS results, and (d) SEM results at different chlorine concentrations.
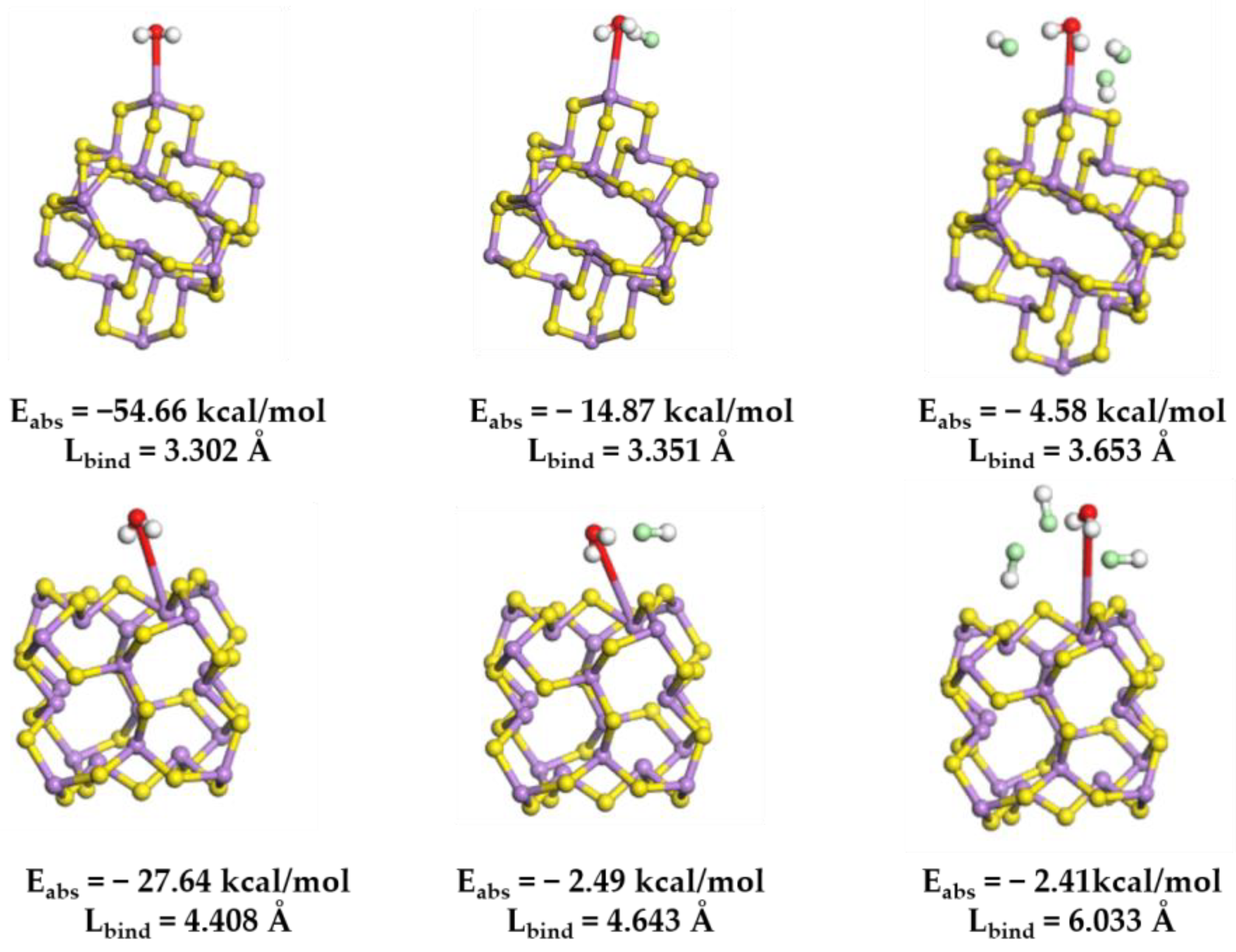
Furthermore, in a chlorine-rich environment, the interaction between arsenic–sulfur (As-S) precipitates and water molecules is significantly more susceptible to degradation. To elucidate this experimental observation, a model of the cluster configuration (As2S3)10 was developed [19,43]. This model enabled the calculation and simulation of the interaction between a H2O molecule and the arsenic atoms located on the surface of the cluster, utilizing DFT. The findings indicate that the bond length between the oxygen atom and the arsenic atom in the H2O molecule measures 3.20 Å, which is typically classified as a weak interaction at this scale [44]. This observation aligns with the known fact that the As2S3 precipitate exhibits insolubility in water. Hydrochloric acid molecules are introduced at a proximity of 3 Å around the H2O molecules. The data presented in Figure 11 indicate that, as the concentration of HCl molecules rises, the interspacing between H2O molecules and As atoms on the cluster surface progressively enlarges. It is important to highlight that, as the molecular weight of HCl increases, the adsorption energy determined at both adsorption sites shows a continuous and notable enhancement. The addition of HCl enhances the hydrophobicity of the produced As2S3 precipitate, facilitating its expulsion from the solution and simplifying the separation and recovery of arsenic sulfide by-products.
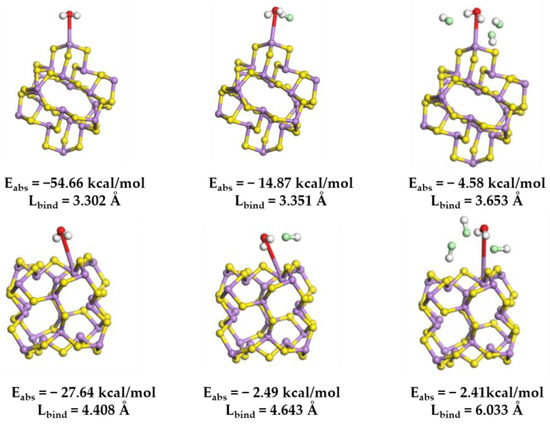
Figure 11.
The optimized molecular structure of H2O onto (As2S3)10 clusters at different chlorine concentrations, and the Coulomb absorption energy (Eabs) and binding length (Lbind) associated with the interaction. Color code: H (white); O (red); S (yellow); As (purple); and Cl (green).
3.3.2. Effects of F−
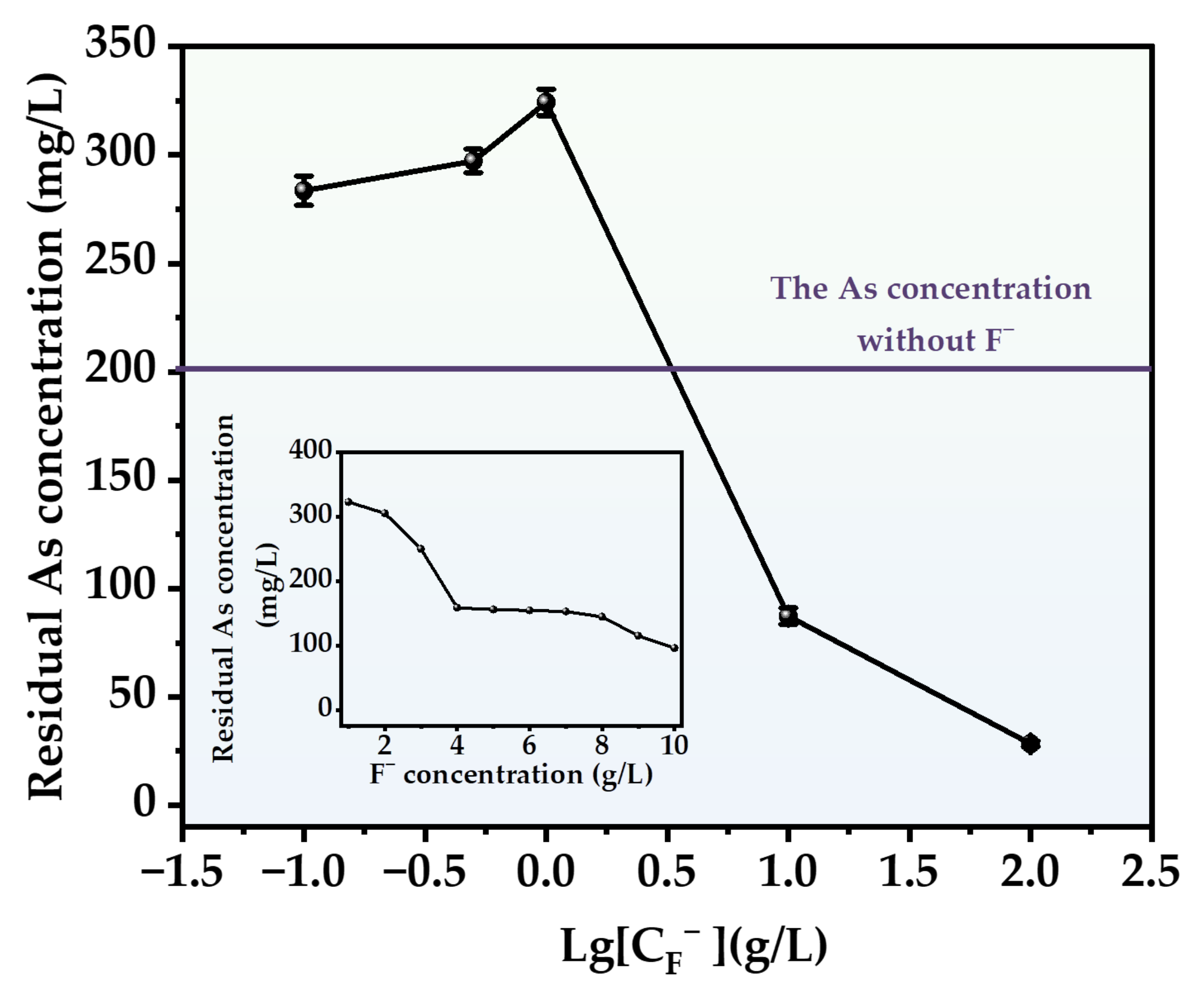
The impact of the F− addition on the arsenic precipitation process in the presence of H2S displays a clear segmentation into two distinct regions based on its concentration levels (Figure 12). At low concentrations (<4 g/L), the incorporation of F− exerts an inhibitory effect on the arsenic removal process, with the most pronounced inhibition occurring at a concentration of 1 g/L. Following the identical reaction duration, the residual arsenic level in the solution exceeds double that of the control group. However, as the concentration of F− surpasses 2 g/L, the inhibitory effect progressively diminishes, ultimately transitioning to a promotional effect. Nevertheless, when compared to the promotional effect of Cl− at equivalent concentrations, the efficacy of F− in arsenic remediation is significantly less pronounced. At elevated concentrations, sediment particles are also displaced from the solution, a phenomenon more pronounced than with Cl−, particularly at high concentrations (100 g/L), where nearly no visible particles remain in the solution post-reaction.
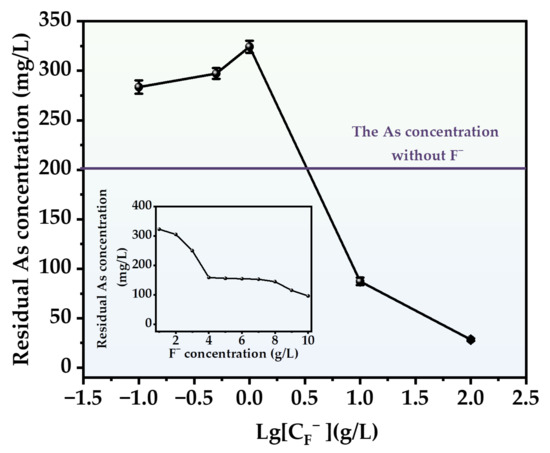
Figure 12.
Effect of different F− concentrations on arsenic removal.
Despite the addition of a sufficient amount of F−, the effectiveness of total arsenic removal remains insufficient. In particular, when F− concentration is held constant at 100 g/L, the final effluent yields an arsenic concentration of 29.59 mg/L. In addition, XRD and the XPS analysis image (Figure 13a,b) also show that the precipitate is amorphous As2S3 and AsS. The SEM results are similar to those under the influence of Cl−, but the precipitation particles formed by F− are finer (Figure 13c). This should be related to the surface properties of particles.
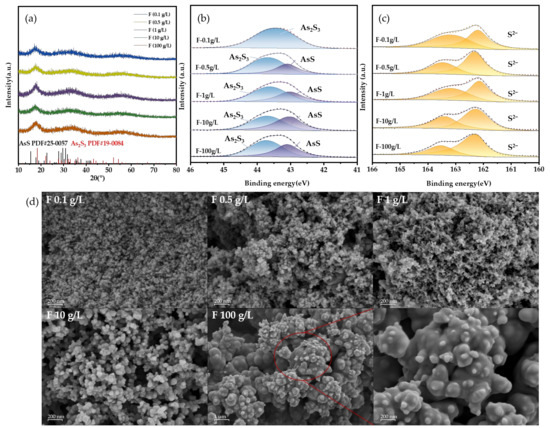
Figure 13.
(a) XRD results, (b,c) XPS results, and (d) SEM results at different F− concentrations.
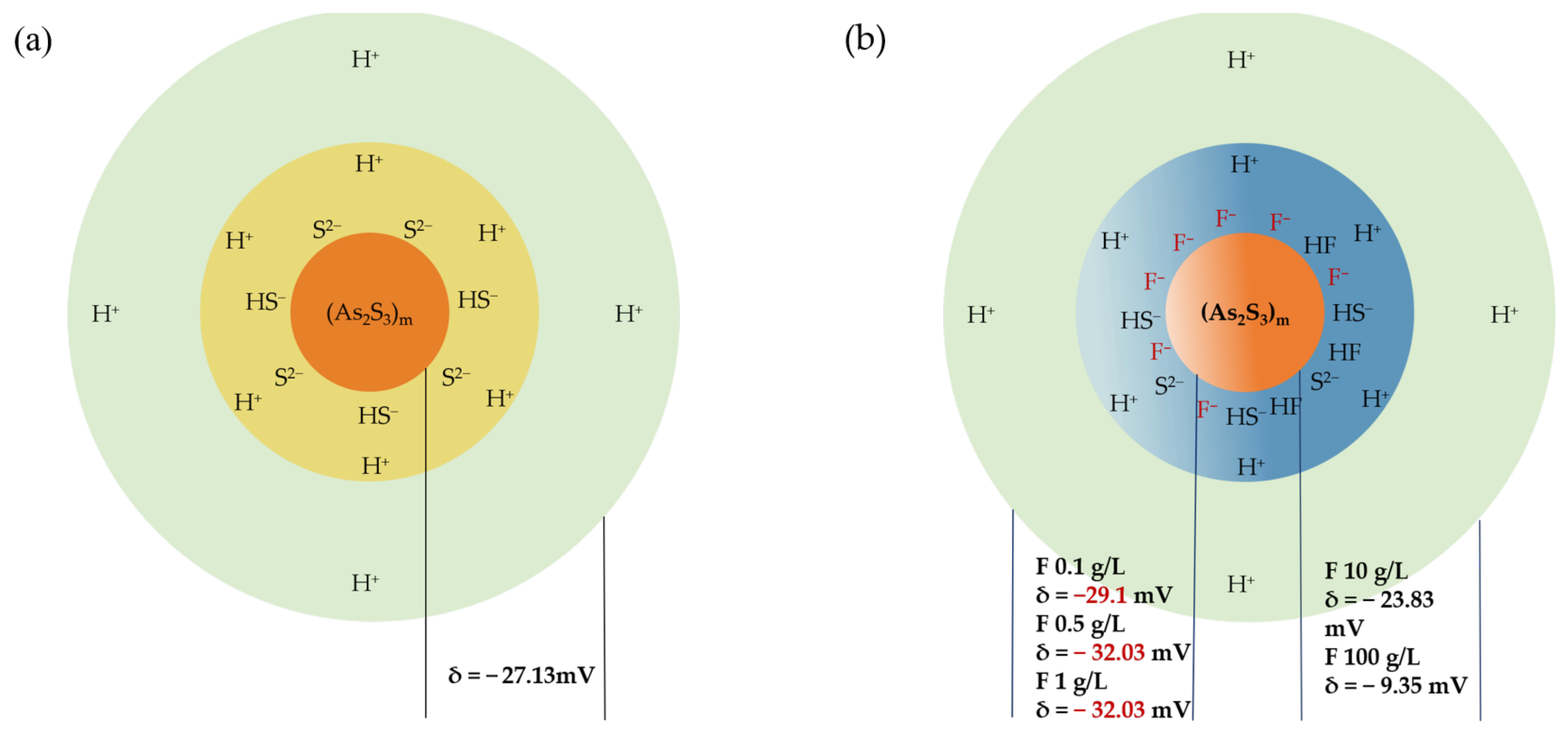
The Zeta potential measurement reflects the intensity of interactions among colloidal particles, significantly influencing the sedimentation rate of these particles [45]. The findings regarding Zeta potential effectively elucidate the dual role of F− in facilitating arsenic removal at elevated concentrations while concurrently inhibiting it at lower concentrations (Figure 14). The addition of a small quantity of F− results in a notable increase in the negative charge on the particle surface, particularly in contrast to the −27.13 mV observed for the precipitate formed under optimal conditions. At dosages of 500 mg/L and 1 g/L, the Zeta potential of the precipitate particles drops to below −30 mV, indicating that the electrostatic forces present on the colloidal surface effectively repel other particles. This repulsion also extends to S2− involved in the reaction, thereby hindering the arsenic precipitation process and ultimately reducing the efficacy of arsenic removal. In contrast, at elevated F− concentrations, there is a reduction in the surface electrification of the colloidal system. The Zeta potential measurements are recorded at −23.83 mV and −9.35 mV for F− concentrations of 10 g/L and 100 g/L, respectively. Because HF is a weak acid, most F elements exist in the form of HF at high concentrations. Zeta potential results show that the precipitated particles are more stable in the solution containing high concentrations of HF. Less negatively charged particles are adsorbed on the particle surface. This means that the repulsive force between particles and reactant S2− decreases, which is beneficial to the arsenic removal reaction. The decrease in repulsive force between particles promotes the aggregation of colloidal particles, thus forming larger particles.
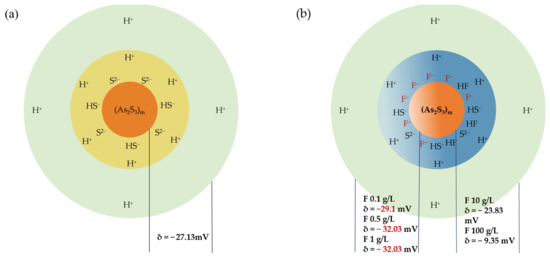
Figure 14.
Images of the microscopic structure of As2S3 micelle at (a) optimum conditions and (b) different F− concentrations.
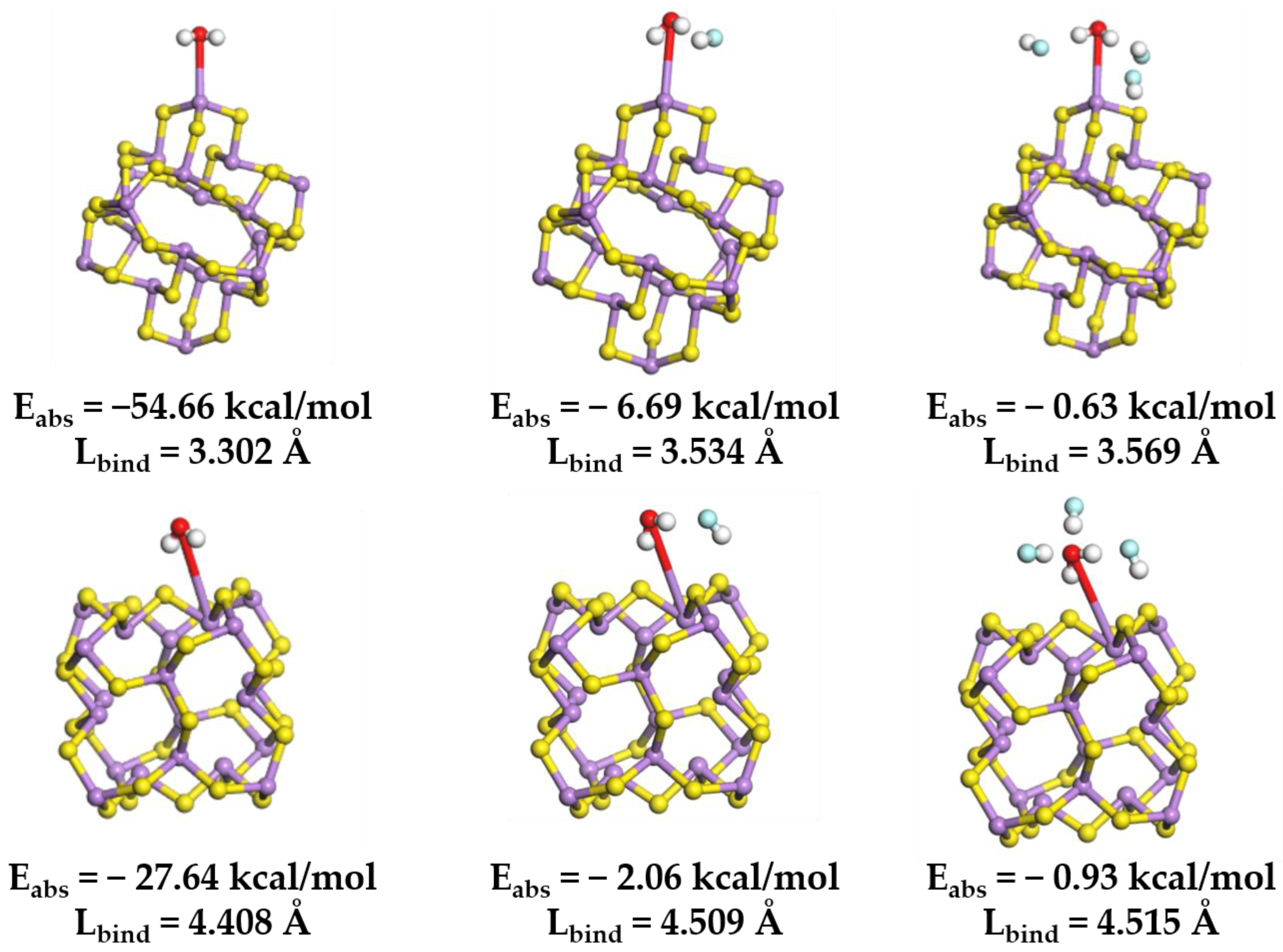
The variation in binding energy between clusters and water molecules (Figure 15) indicates that the introduction of F− enhances the separation capacity between particles and water molecules. Upon the addition of an HF molecule, the absorption energy between the cluster surface and the H2O molecule rose from −54.66 kcal/mol to −6.69 kcal/mol. Subsequently, with further HF molecule incorporation, the absorption energy increased to 0.63 kcal/mol.
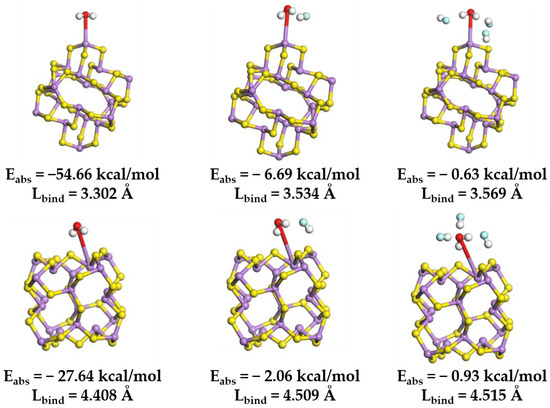
Figure 15.
Optimized molecular structure of H2O onto (As2S3)10 clusters at different F- concentrations, and the Coulomb absorption energy (Eabs) and binding length (Lbind) associated with the interaction. Color code: H (white); O (red); S (yellow); As (purple); and F (blue).
4. Conclusions
In the present work, the sulfidation characteristics of H2S under different working conditions are evaluated. The influences of Cl− and F− were studied, and the mechanism was revealed by XRD, XPS, SEM analysis, Zeta potential measurement, and DFT analysis. The considerable conclusions were summarized as follows:
- The optimal conditions for arsenic extraction were determined: delivering 500 ppm H2S gas at a flow rate of 400 mL/min and maintaining a temperature of 30 °C for a duration of 3 h, resulting in an impressive arsenic removal rate of 99.87%, with a residual concentration of 0.28 mg/L. The treated acid solution can be used to prepare industrial sulfuric acid, which can avoid the waste of acid resources.
- Cl− promoted As removal: Cl− facilitates the decomposition of H3AsO3, thereby accelerating the exposure of reactive sites. The surface properties of the particles have changed, which leads to the formation of arsenic sulfide particles that are more resistant to the adsorption of water molecules and quickly separated from the solution.
- In the presence of F−, As is inclined to form AsF3, a by-product, making As2S3 formation conditions more stringent. However, at sufficiently high F− concentrations, the repulsive forces among sediments gradually diminish, leading to increased hydrophobicity and easier precipitation.
The insights gained from this study highlight the potential for As precipitation via sulfides in concentrated H2SO4 solutions while elucidating the roles of chlorine and F− in this mechanism, thereby offering valuable implications for practical engineering applications.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. carried out the experiments, analyzed the results, performed static DFT calculations, and wrote the manuscript. X.H. confirmed the data and revised the manuscript. X.S., F.W. and K.L. controlled the project and provided experimental resources. L.S. guided the experiments, revised the manuscript, and performed safety supervision. P.N. designed the project. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52260020 and 52204362) and the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant Nos. 202401AT070310 and 202301AU070066).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Due to the ongoing use of the data in further research, the data supporting this study are not publicly available at this time to avoid compromising the research progress. Researchers who require access to the raw data may contact the corresponding author to request it. We will provide the data on a case-by-case basis, ensuring compliance with all relevant regulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shi, J.; Duan, X.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Yan, G.; Wang, H. Removal of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater using zinc slag to synthesize scorodite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D. Removing arsenic from copper smelter gases. JOM 1999, 51, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lu, Q.; Chen, H.; Du, Y.; Du, D. A novel strategy for arsenic removal from dirty acid wastewater via CaCO3-Ca(OH)2-Fe(III) processing. J. Water Process ENG 2016, 12, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Hao, F.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, H. Disposal of high-arsenic waste acid by the stepwise formation of gypsum and scorodite. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Azam, M.; Asubonteng, D.; Ngoie, M.; Lin, S.; Sun, W. Advancements in Removing Fluorine from Copper Concentrate. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Neto, H.F.D.; Pereira, W.V.D.S.; Dias, Y.N.; Souza, E.S.D.; Teixeira, R.A.; Lima, M.W.D.; Ramos, S.J.; Amarante, C.B.D.; Fernandes, A.R. Environmental and human health risks of arsenic in gold mining areas in the eastern Amazon. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Liu, H.-Q.; Guo, X.-P. Current knowledge from heavy metal pollution in Chinese smelter contaminated soils, health risk implications and associated remediation progress in recent decades: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Che, J.; Wen, P.; Xia, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Co-treatment of copper smelting flue dust and arsenic sulfide residue by a pyrometallurgical approach for simultaneous removal and recovery of arsenic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanel, S.R.; Das, T.K.; Varma, R.S.; Kurwadkar, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Joshi, T.P.; Bezbaruah, A.N.; Nadagouda, M.N. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater: Geochemical Basis of Treatment Technologies. ACS Environ. Au 2023, 3, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas Kurz, E.E.; Hellriegel, U.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Bundschuh, J.; Hoinkis, J. Small-scale membrane-based arsenic removal or decentralized applications–Developing a conceptual approach for future utilization. Water Res. 2021, 196, 116978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumari, S.; Parmanand; Sharma, S.K. Constructing the nanomixture of guar gum and Fe3O4 for photocatalytic degradation of dyes and heavy metal. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamood Altowayti, W.A.; Almoalemi, H.; Shahir, S.; Othman, N. Comparison of culture-independent and dependent approaches for identification of native arsenic-resistant bacteria and their potential use for arsenic bioremediation. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, T.; Cao, X.; Liu, X. Recovery of converter steel slag to prepare catalytic H2O2 degradation of dye wastewater as a catalyst. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 24889–24901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soignard, E.; Tsiok, O.B.; Tverjanovich, A.S.; Bytchkov, A.; Sokolov, A.; Brazhkin, V.V.; Benmore, C.J.; Bychkov, E. Pressure-Driven Chemical Disorder in Glassy As2S3 up to 14.7 GPa, Postdensification Effects, and Applications in Materials Design. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Singh, D.; Sonvane, Y.; Thakor, P.B.; Ahuja, R. Bulk and monolayer As2S3 as promising thermoelectric material with high conversion performance. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2020, 183, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Double-pathway arsenic removal and immobilization from high arsenic-bearing wastewater by using nature pyrite as in situ Fe and S donator. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 410, 128303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermeyer, P.; Bonin, L.; Folens, K.; Verbruggen, F.; García-Timermans, C.; Verbeken, K.; Rabaey, K.; Hennebel, T. Effect of speciation and composition on the kinetics and precipitation of arsenic sulfide from industrial metallurgical wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Duan, N.; Xu, F.; He, H. Exploration of the arsenic removal performance fluctuation using H2S from highly acidic wastewater in copper smelting. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gim-Krumm, M.; Quilaqueo, M.; Rojas, V.; Seriche, G.; Ruby-Figueroa, R.; Cortés-Arriagada, D.; Romero, J.; Troncoso, E.; Estay, H. Impact of precipitate characteristics and precipitation conditions on the settling performance of a sulfide precipitation process: An exhaustive characterization of the aggregation behavior. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidi, L.; Bing, C.; Xiaole, M.; Weiman, L.; Yunfa, C.; Yongchun, L. Research on Sulfurizing Sulphuric Acid (55%) with H2S for Arsenic Removal. Nonferr. Metall. Equip. 2023, 37, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Kong, L.; He, M.; Fang, D.; Hu, X.; Peng, X. Effective reduction and recovery of As(III) and As(V) from alkaline wastewater by thiourea dioxide: Efficiency and mechanism. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Ke, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, J.; Yu, L.; Cao, J.; Min, X. Treatment of Acidic Solutions Containing As(III) and As(V) by Sulfide Precipitation: Comparison of Precipitates and Sulfurization Process. Metals 2023, 13, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Song, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Ning, P. Catalytic effect of phosphorus on SO2 oxidation in liquid phase: Experimental and theoretical studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Weng, Q.; Li, D.; Lv, T.; Wang, S.; Zhuo, Y. Effects of O2, SO2, H2O and CO2 on As2O3 adsorption by γ-Al2O3 based on DFT analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Fu, D.; Ni, J.; Sun, C.; Song, S. Adsorption for SO2 gas molecules on B, N, P and Al doped MoS2: The DFT study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 715, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-Q.; Chai, L.-Y.; Li, Q.-Z.; Shu, Y.-D. Redox behavior and chemical species of arsenic in acidic aqueous system. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2017, 27, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Guo, W.; Li, B.; Wei, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Xiao, R. Kinetics and mechanistic aspects of removal of heavy metal through gas-liquid sulfide precipitation: A computational and experimental study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiliang, S.; Qichao, C.; Haodong, S. Arsenic Chemistry and Technology; Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2014; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Lin, H.; Zhu, H.; Mo, W.; Su, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, S.; Feng, J.; Lei, M. Efficient removal of fluorine by carbon fiber supported Mg-Fe binary metal oxide composite adsorbent and mechanism analysis based on DFT. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Peng, X.; Hu, X.; Kong, L. H2S release rate strongly affects particle size and settling performance of metal sulfides in acidic wastewater: The role of homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, T.-Z.; Liu, W.-F.; Zhang, D.-C.; Chen, L. Removal of arsenic from acid wastewater via sulfide precipitation and its hydrothermal mineralization stabilization. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2019, 29, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Demond, A.H.; Gallegos, T.J.; Hayes, K.F. Dependence of particle concentration effect on pH and redox for arsenic removal by FeS-coated sand under anoxic conditions. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 534-2002; Industrial Sulfuric Acid. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Soma, M.; Tanaka, A.; Seyama, H.; Satake, K. Characterization of arsenic in lake sediments by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2743–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Batchelor, B. Macroscopic and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation of interactions of arsenic with synthesized pyrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.S.; Song, J.K.; Batchelor, B.; Abdel-Wahab, A. Removal of arsenite(As(III)) and arsenate(As(V)) by synthetic pyrite (FeS2): Synthesis, effect of contact time, and sorption/desorption envelopes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 392, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Gu, C. Insights into the effect of chlorine on arsenic release during MSW incineration: An on-line analysis and kinetic study. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, M.K.; Woodall, R.O.; Watson, R.L.; Irgolic, K.J. Relaxation during photoemission and LMM Auger decay in arsenic and some of its compounds. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 64, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Demond, A.H.; Hayes, K.F. X-ray absorption and photoelectron spectroscopic study of the association of As(III) with nanoparticulate FeS and FeS-coated sand. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5727–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; van Hille, R. An exploration into the sulphide precipitation method and its effect on metal sulphide removal. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 81, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Qi, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xin, B. Efficient removal of As, Cu and Cd and synthesis of photo-catalyst from Cu-smelting waste acid through sulfide precipitation by biogenic gaseous H2S produced by anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lőrinczi, A.; Sava, F.; Simandan, I.-D.; Velea, A.; Popescu, M. Photoexpansion in amorphous As2S3: A new explanation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 447, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Q.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhong, C.; Min, X.; Zhang, L. Stabilization mechanism of arsenic-sulfide slag by density functional theory calculation of arsenic-sulfide clusters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 410, 124567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokone, T.P.; van Hille, R.P.; Lewis, A.E. Effect of solution chemistry on particle characteristics during metal sulfide precipitation. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).