Sustainable Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Contaminated Soils Using Iron–Phosphorus–Thiol-Functionalized Trachycarpus fortunei Hydrochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydrothermal Carbon (HTC) Preparation
2.2. Hydrothermal Carbon Activation Modification
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
2.5.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
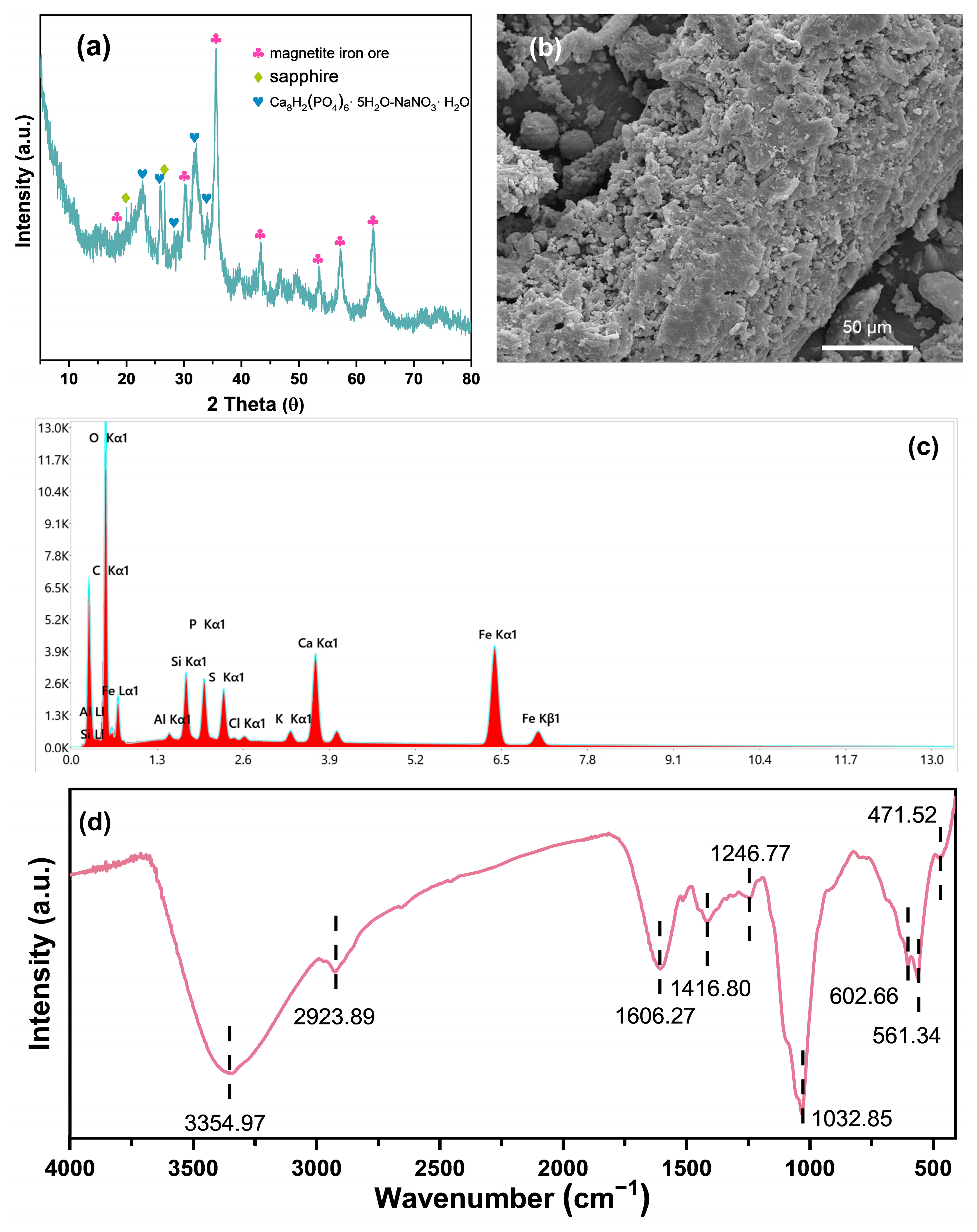
3.1. Characterization of Biochar
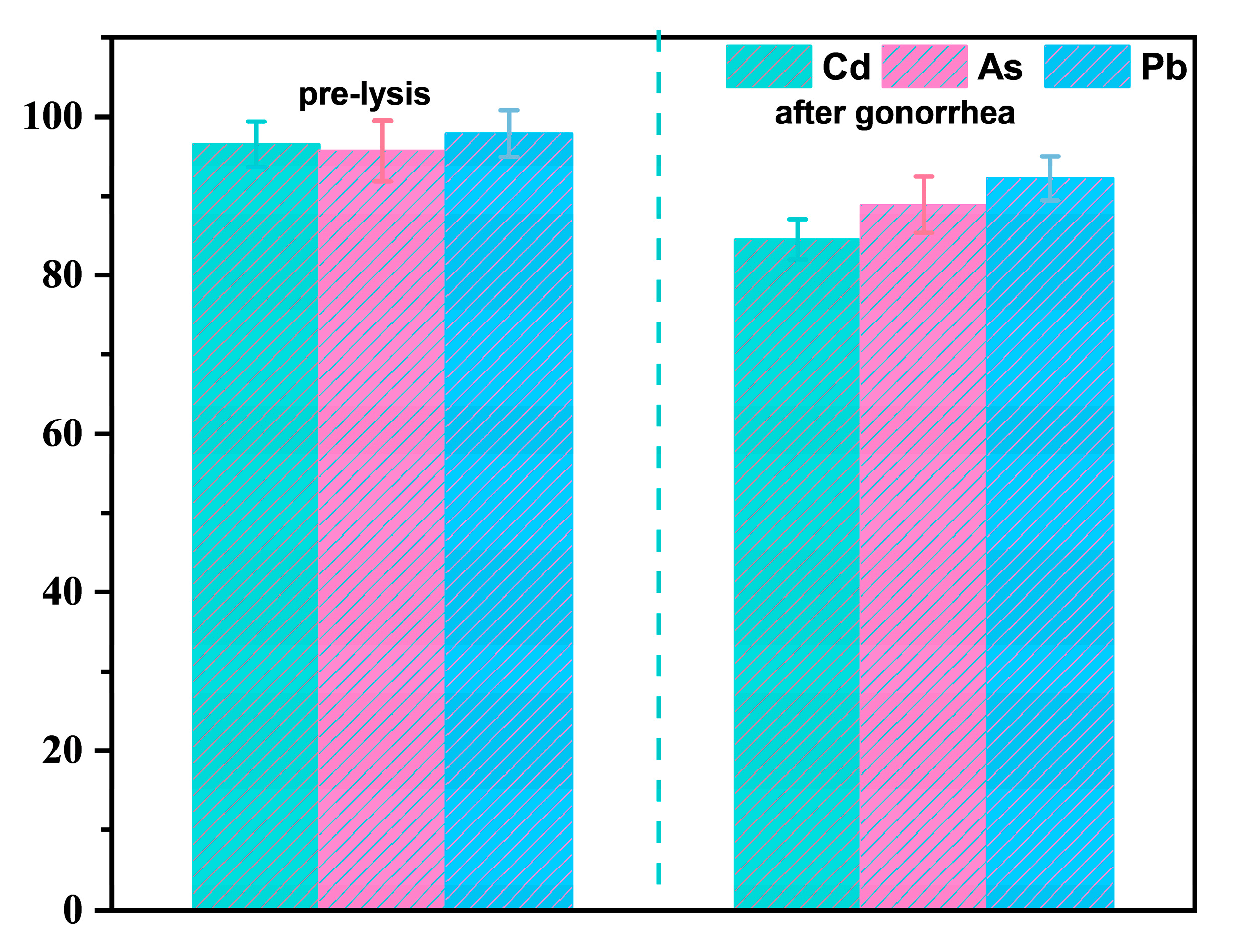
3.2. Stabilization Effects of Biochar on Heavy Metals
3.2.1. Stabilization Effects of Hydrochars from Different Raw Materials on Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic
3.2.2. Stabilization Effects of Hydrochars Modified by Different Methods on Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic
3.2.3. Stabilization Effect of Composite-Modified Hydrochars on Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic
3.3. Mechanism of Heavy Metal Stabilization
3.3.1. Changes in the Metal Speciation of Polluted Soils
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Optimization of Cadmium–Arsenic–Lead Stabilization Composite Materials
3.4.1. Study on the Proportions of Cadmium-Arsenic-Lead Stabilization Composite Materials
3.4.2. Stabilization Effect of Cadmium–Arsenic–Lead Stabilization Composite Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, J. Biomass-Based Hydrothermal Carbons for the Contaminants Removal of Wastewater: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Q.; Gui, X.; Fan, X.; Wei, C.; Jiang, F.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.; Li, F.; et al. Effect of hydrothermal temperature on the optical properties of hydrochar-derived dissolved organic matter and their interactions with copper (II). Biochar 2024, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, E.; Cruz, T.L.D.; Chen, X.W.; Wong, M.H. Ecological consequences of biochar and hydrochar amendments in soil: Assessing environmental impacts and influences. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 42614–42639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, N.M.; Reta, N.; Dalal, H.; Ellis, A.V.; Shapter, J.; Voelcker, N.H. Enhanced adsorption of mercury ions on thiol derivatized single wall carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, C.; Giannis, A.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, R. Transformation behaviors and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals during resource recovery from Sedum plumbizincicola via hydrothermal liquefaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, B.; Cui, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. Clay-hydrochar composites return to cadmium contaminated paddy soil: Reduced Cd accumulation in rice seed and affected soil microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155542. [Google Scholar]
- Genli, N.; Kutluay, S.; Baytar, O.; Şahin, Ö. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from hydrochar by hydrothermal carbonization of chickpea stem: An application in methylene blue removal by RSM optimization. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2022, 24, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.C.; Ouyang, L.; Yuan, S. Single-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Biochar from H3PO4-Activated Lettuce Waste for Efficient Adsorption of Cd(II) in Aqueous Solution. Molecule 2022, 27, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; She, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Ji, R.; Bian, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y.; et al. Comparison of the performance of hydrochar, raw biomass, and pyrochar as precursors to prepare porous biochar for the efficient sorption of phthalate esters. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ji, R.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xue, J.; et al. Hierarchical porous biochars with controlled pore structures derived from co-pyrolysis of potassium/calcium carbonate with cotton straw for efficient sorption of diethyl phthalate from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Shen, B.; Wu, C. Review of biochar for the management of contaminated soil: Preparation, application and prospect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, Z.; Moja, N.T.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; De Kock, L.-A. Utilization of biochar for remediation of heavy metals in aqueous environments: A review and bibliometric analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.R.; Patel, A.K.; Jaisi, D.P.; Adhikari, S.; Lu, H.; Khanal, S.K. Environmental application of biochar: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Xia, L.; Gao, J.; Tang, L.; Jia, Y. KOH-modified hydrochar produced from Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum Alfredii Hance for aqueous Cd (II) removal: Behavior and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.-Y.; Du, Y.-J.; Li, F.-S.; Li, C.-P.; Yan, X.-L.; Arulrajah, A.; Wang, F.; Song, D.-J. In-situ solidification/stabilization of heavy metals contaminated site soil using a dry jet mixing method and new hydroxyapatite based binder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.; Tu, S. Review on Rice Husk Biochar as an Adsorbent for Soil and Water Remediation. Plants 2023, 12, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathy, A.; Pokharel, P.; Chen, X.; Balasubramanian, P.; Chang, S.X. Activation methods increase biochar’s potential for heavy-metal adsorption and environmental remediation: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, C.; Ning, P.; He, M.; Bao, S.; Sun, X.; Li, K. One-step synthesis of magnetic catalysts containing Mn3O4-Fe3O4 from manganese slag for degradation of enrofloxacin by activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156505. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for groundwater quality. Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Gao, R.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Xing, Z.; Ali, U.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu contaminated soil by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate: Speciation transformation, risk evaluation and mechanism inquiry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Lang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Peng, N.; Gai, C. Effect of hydrothermal carbonization on migration and environmental risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge during pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Han, R.; Chen, Q.; Shen, D.; Shentu, J. Soil heterogeneity influence on the distribution of heavy metals in soil during acid rain infiltration: Experimental and numerical modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Zhu, L. Paving the way toward soil safety and health: Current status, challenges, and potential solutions. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reagent Naming | Stabilization Agent |
|---|---|
| ST-1 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 2 mL TMT102 |
| ST-2 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 3 mL TMT102 |
| ST-4 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T + 2 mL TMT + 0.5 g sodium sulfide |
| ST-5 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T + 2 mL TMT + 1 g zeolite |
| T-6 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 3 mL TMT + 2 g zeolite |
| T-7 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 2 mL TMT102 + 1 g CaO |
| T-8 | 1 g zeolite + 0.5 g sodium sulfide + 1 g ferric chloride + 1 g CaO |
| T-9 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 3 mL TMT + 0.5 g sodium sulfide |
| Stabilization Agent | |
|---|---|
| +ST-1 | 1 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 3 mL TMT102 |
| +ST-2 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 2.5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 3 mL TMT102 |
| +ST-3 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 3 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 3 mL TMT102 |
| +ST-4 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 3 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 4 mL TMT102 |
| +ST-5 | 2 g polyferric sulfate + 5 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T hydrochar + 6 mL TMT102 |
| Reagent Naming | Stabilization Agent |
|---|---|
| H-PAL-Fe2-P-T | 2 g Polymeric Ferric Sulfate + 4 g H-PAL-Fe2-P-T Hydrochar + 3 mL TMT102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, K.; Li, K.; Tang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; You, P.; Zhou, R.; Ning, P.; Bao, S. Sustainable Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Contaminated Soils Using Iron–Phosphorus–Thiol-Functionalized Trachycarpus fortunei Hydrochar. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062759
Ouyang K, Li K, Tang Y, Yang H, Chen X, Li Q, You P, Zhou R, Ning P, Bao S. Sustainable Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Contaminated Soils Using Iron–Phosphorus–Thiol-Functionalized Trachycarpus fortunei Hydrochar. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062759
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Kun, Kai Li, Yigui Tang, Haodi Yang, Xuanren Chen, Qian Li, Ping You, Rui Zhou, Ping Ning, and Shuangyou Bao. 2025. "Sustainable Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Contaminated Soils Using Iron–Phosphorus–Thiol-Functionalized Trachycarpus fortunei Hydrochar" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062759
APA StyleOuyang, K., Li, K., Tang, Y., Yang, H., Chen, X., Li, Q., You, P., Zhou, R., Ning, P., & Bao, S. (2025). Sustainable Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Contaminated Soils Using Iron–Phosphorus–Thiol-Functionalized Trachycarpus fortunei Hydrochar. Sustainability, 17(6), 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062759







