The Addition of Degradable Activators Enhances Sedum alfredii Phytoremediation Efficiency in Cd-Contaminated Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, Soil Properties, and Field Profile
2.2. Field Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection, Preparation, and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cadmium Removal
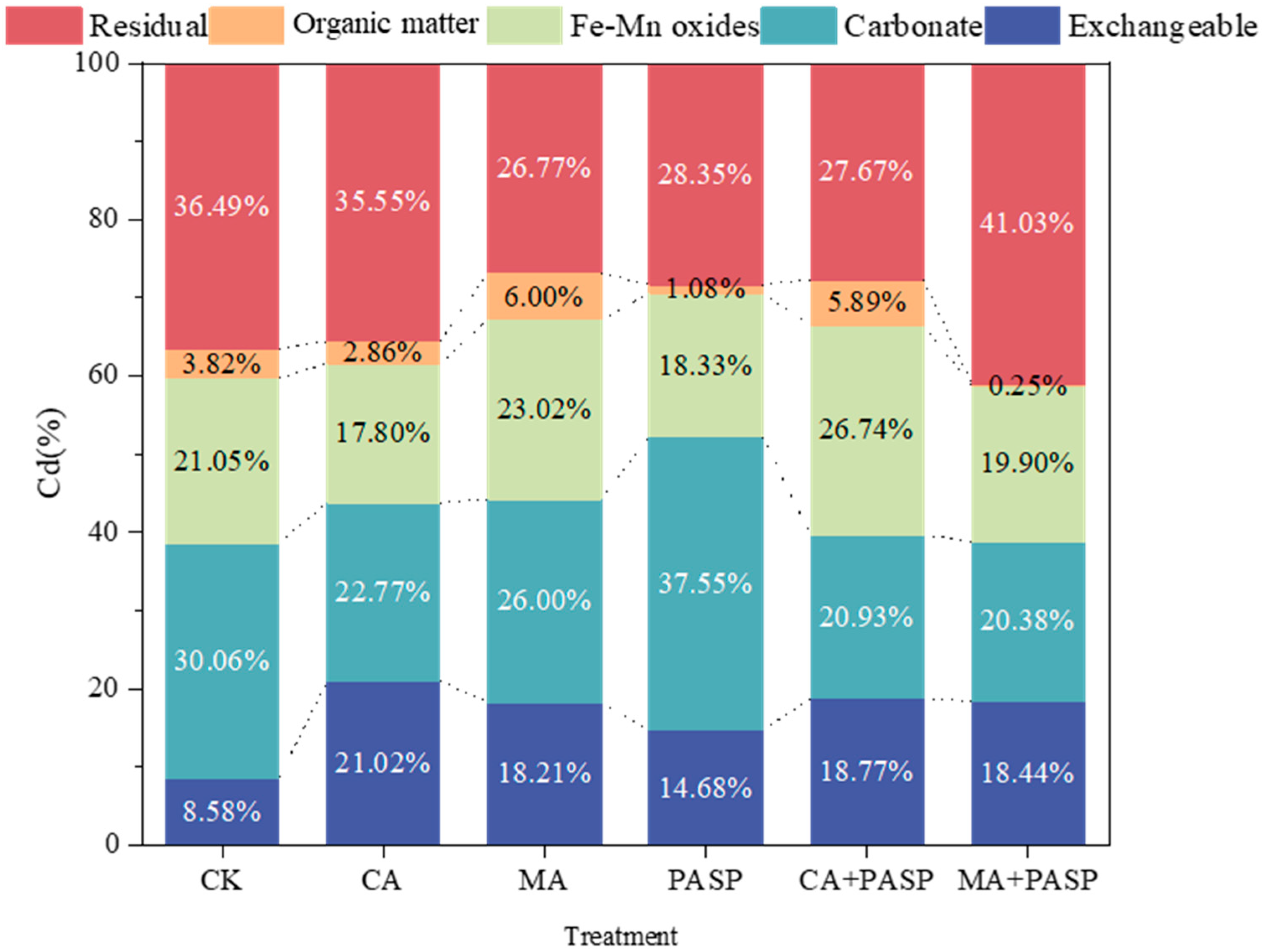
3.2. Activation of Cd in Soil
3.3. Absorption and Remediation Effect of Sedum Alfredii on Cd
3.4. Biomass of Sedum alfredii
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, T.; Zhu, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Chang, M.; Wang, L. Biochelator Assisted Phytoremediation for Cadmium (Cd) Pollution in Paddy Field. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Guo, N.; Chen, X. Intercropping with Brassica juncea L. enhances maize yield and promotes phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by changing rhizosphere properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Ali, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Qi, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. Sedum alfredii Hance: A cadmium and zinc hyperaccumulating plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Rao, S.; Fang, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, A.; Ye, Z.; Fu, W. Organic Materials Could Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Soil Potentially Hazardous Metal by Sedum alfredii Hance. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 91, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Rhodococcus qingshengii facilitates the phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, Ni, and Pb from soils by Sedum alfredii Hance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Gong, X.S.; Wei, S.H. Research progress on technologies of phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 3261–3270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Recent advances in phyto-combined remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 72, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Reyes, J.G.; Valenzuela-Amaro, H.M.; Pizana-Aranda, J.J.P.; Ramirez-Gamboa, D.; Melendez-Sanchez, E.R.; Lopez-Arellanes, M.E.; Castaneda-Antonio, M.D.; Coronado-Apodaca, K.G.; Araujo, R.G.; Sosa-Hernandez, J.E.; et al. Microalgae-Based Biotechnology as Alternative Biofertilizers for Soil Enhancement and Carbon Footprint Reduction: Advantages and Implications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsum, P.G.P.S.; Khanam, R.; Das, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Tack, F.M.G.; Meers, E.; Vithanage, M.; Shahid, M.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on cadmium uptake, toxicity, and tolerance in rice: From physiological response to remediation process. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shourie, A.; Mazahar, S.; Singh, A. Biotechnological approaches for enhancement of heavy metal phytoremediation capacity of plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjana, S.; Jazeel, K.; Janeeshma, E.; Nair, S.G.; Shackira, A.M. Synergistic interactions of assorted ameliorating agents to enhance the potential of heavy metal phytoremediation. Stress Biol. 2024, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Sung, K. Effects of chelates on soil microbial properties, plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in plants. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaier, H.; Ghnaya, T.; Ben Rejeb, K.; Lakhdar, A.; Rejeb, S.; Jemal, F. Effects of EDTA on phytoextraction of heavy metals (Zn, Mn and Pb) from sludge-amended soil with Brassica napus. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3978–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrutia, O.; Garbisu, C.; Hernandez-Allica, J.; Ignacio Garcia-Plazaola, J.; Maria Becerril, J. Differences in EDTA-assisted metal phytoextraction between metallicolous and non-metallicolous accessions of Rumex acetosa L. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Wu, Q.; Qian, T. Mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid as washing agent effectively remove Cd, Zn, Pb, and Cu from soils. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jez, E.; Lestan, D. EDTA retention and emissions from remediated soil. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.G.; Xie, J.T.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Y.Z.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Y.X.; Yin, S.M.; Wu, X.T. Role and Mechanism of Low Molecular-Weight-Organic Acids in Enhanced Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4669–4678. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, C.; Pepe, M.K.; Cutright, T.J. The effect of EDTA and citric acid on phytoremediation of Cd, Cr, and Ni from soil using Helianthus annuus. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 131, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alozie, N.; Heaney, N.; Lin, C. Biochar immobilizes soil-borne arsenic but not cationic metals in the presence of low-molecular-weight organic acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Juanjuan, Z.; Tanchun, X.; Xiaolin, W.; Ying, Y. Effects of citric acid on the bioavailability of Cd-pyrene contamination in soil-willow system. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2021, 57, 375–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, H.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Polyaspartic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in rapeseed leaves by affecting cadmium translocation and cell wall fixation of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.F.; Zheng, Y.F.; Tang, N.; Cai, L.K. Removal of heavy metals from contaminated soil with biodegradable chelating agents-polyaspartic acid. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 17, 237–240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, G.; Qiu, R. Polyaspartic acid assisted-phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated farmland: Phytoextraction efficiency, soil quality, and rhizosphere microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, L.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, G.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J. Polyaspartic acid enhances the Cd phytoextraction efficiency of Bidens pilosa by remolding the rhizospheric environment and reprogramming plant metabolism. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Pt 3, 136068, Erratum in Chemosphere 2023, 312 Pt 1, 137242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Asghar, N.; Ali, A.; Ameer, A.; Shehzad, M.A.; Nawaz, F.; Mehmood, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Iqbal, U.; Kaleem, M.; et al. Optimization of Citric Acid and EDTA Levels Under Ni Stress Using Rapeseed Brassica napus L. for Phytoremediation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, W.; Ren, J.; Chen, S.; Shen, K.; Long, Z. Enhanced Phytoextraction for Co-contaminated Soil with Cd and Pb by Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Abbas, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Mehmood, M.A.; Abbasi, G.H. Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11679–11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, N.; Maletic, S.; Beljin, J.; Dukanovic, N.; Kiprovski, B.; Zeremski, T. Enhancing Phytoextraction Potential of Brassica napus for Contaminated Dredged Sediment Using Nitrogen Fertilizers and Organic Acids. Plants 2024, 13, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Bao, Q.; Wei, X.; Tie, B.; Zhang, S.; Han, E.; Huang, Y. Effects of chelating agents and organic acids on remediation of cadmium and arsenic complex contaminated farmland by Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 1936–1944. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.268-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Multi-elements in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 17141-1997; Soil Quality—Determination of Lead and Cadmium—Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Chen, L.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, J.; Chao, S.L.; Wei, Q. Comparative study on speciation of Cu, Pb and Zn from mining tailingsvia Tessier 5-step sequential extraction and improved BCR method. J. Saf. Environ. 2020, 20, 735–740. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Liu, Q.; Hu, J. Application test of Sedum alfredii Hance in the remediation of Cd contaminated farmland soil. J. Geol. 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nevel, L.V.; Mertens, J.; Oorts, K.; Verheyen, K. Phytoextraction of metals from soils: How far from practice? Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S.; Khan, N.A.; Tuteja, N. Differential cadmium stress tolerance in five indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars: An evaluation of the role of antioxidant machinery. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Ma, R.; Huang, W.; Yang, D.; Cui, X. Exogenous organic acids protect changbai larch (Larix olgensis) seedlings against cadmium toxicity. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 3460–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Islam, E.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; Jin, X.; Mahmood, Q. Comparison of synthetic chelators and low molecular weight organic acids in enhancing phytoextraction of heavy metals by two ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-b.; Zhou, Q.-x.; An, J.; Liu, W.-t.; Liu, R. Chelator-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil irrigated by industrial wastewater with the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii Hance). Geoderma 2009, 150, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Dai, H.; Wei, S.; Hu, Y.; Skuza, L. Effects of Some Chelators and Surfactants on Hyperacculator Sedum alfredii Hance Remediating Contaminated Soil. Soil Sediment Contam. 2019, 28, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Peng, C.; Zeng, P.; Xiao, X.; Xian, Z. Removal of cadmium, lead, and zinc from multi-metal-contaminated soil using chelate-assisted Sedum alfredii Hance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28319–28327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.X.; Zhu, J.; Li, K.L.; Liu, W.G.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K. Exploring a library of water-soluble polymers as abiotic phytoremediation agents for treating (Pseudo)metal ion-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jiang, P.; Fu, X.; Liu, J.; Sunahara, G.I.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, H.; Lin, F.; Wang, X. Phytoextraction of cadmium-contaminated soil by Celosia argentea Linn.: A long-term field study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, M.; Bai, Z.; Zhao, Z. Advances on the study of chelate-enhanced phytoremediation for heavy metal contaminated soils. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2008, 1, 6–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xia, Y.; He, X.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; He, C.; Xia, K. Research Progress of Cd Form Transformation and the Effective Environmental Factors in Soil Based on Tessier Analysis. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 1505–1512. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, C.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, Z. The addition of degradable chelating agents enhances maize phytoremediation efficiency in Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Wen, D.; Xia, X.; Zhang, W.; Gu, Y. Electrokinetic remediation of chromium (Cr)-contaminated soil with citric acid (CA) and polyaspartic acid (PASP) as electrolytes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Q.; Wu, J.L.; Chen, Z. Effects of natural organic acids on cadmium uptake by Sedum plumbizincicola from the soil. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 2413–2422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Effect of malic acid and citric acid addition on Cd transfor mations in soil and Cd uptake in amaranth. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2008, 14, 1132–1138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; He, D.; He, X.; Yan, Y.; Wu, K.; Wei, H. Effects of Exogenous Organic Acids on Cd Tolerance Mechanism of Salix variegata Franch. Under Cd Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 594352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, Q.; Saeed, R.; Nasir, T.; Abbasi, G.H.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Bukhari, S.A.H.; et al. Phyto-management of chromium contaminated soils through sunflower under exogenously applied 5-aminolevulinic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhuang, J.J. Effect of Exogenous Citric Acid Addition on Remediation of Pb Contaminated Soil by Three Ornamental Plants. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 34, 137–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, F.; Li, Y.; Niu, W.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, K. Comparative analysis of the seed germination of pakchoi and its phytoremediation efficacy combined with chemical amendment in four polluted soils. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Austruy, A.; Echevarria, G.; Arshad, M.; Sanaullah, M.; Aslam, M.; Nadeem, M.; Nasim, W.; Dumat, C. EDTA-Enhanced Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals: A Review. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Kang, C.Y.; Ma, E.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Shi, L.; Qin, S.L.; Gao, L.D. Enhanced phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil with Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. by polyaspartic acid. J. Qiqihar Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 39, 68–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, W.B.; Yang, L.; Jin, L.; Song, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qin, L. Transport pathways of cadmium (Cd) and its regulatory mechanisms in plant. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 7921–7929. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, A.; Guan, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zou, L. Phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils by Solanum nigrum L. enhanced with biodegradable chelating agents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 56750–56759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Sun, C.; Deng, X.; Qian, M.; Hu, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; et al. Polyaspartate and liquid amino acid fertilizer are appropriate alternatives for promoting the phytoextraction of cadmium and lead in Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrylak-Nowak, B.; Dresler, S.; Matraszek, R. Exogenous malic and acetic acids reduce cadmium phytotoxicity and enhance cadmium accumulation in roots of sunflower plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Shakoor, M.B.; Gill, R.A.; Najeeb, U.; Iqbal, N.; Ahmad, R. Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, S.; Concheri, G.; Pizzeghello, D.; Sturaro, A.; Rella, R.; Parvoli, G. Soil organic matter mobilization by root exudates. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, H. Biodegradable PASP can effectively inhibit nitrification, moderate NH3 emission, and promote crop yield. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-m.; Dou, Q.-h.; Cui, X.-m.; Lou, Y.-h.; Zhuge, Y.-p. Polyaspartic acid mediates the absorption and translocation of mineral elements in tomato seedlings under combined copper and cadmium stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, X.; Sun, H.; Lv, J.; Wei, G. EDTA and EDDS Enhanced Remediation of Cd and Pb Contaminated Soil by Ramie (Boehmeria nivea). J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 293–1300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Xie, Y.; Dai, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y. Effect of Soil pH and Total Cadmium Concentration of Soil on the Remediation Efficiency of Sedum plumbizincicola. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1604–1612. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Reference | [24] | [38] | [40] | [41] | [39] | [24] | [42] | [43] | [34] | |
| Cd removal (%) | 0.08 | 0.04 | 3.91 | 8.3 | 5.8 | 39.72% | 26.68 | 13.0% | 14.63 | |
| Concentration (mg/kg) | Root | 0.07 | 15.6 | 4.23 | 872 | 5.6 | 1.436 | 1400 | 27.8 | 89.1 |
| Shoot | 1.72 | 12.6 | 21.7 | 2032 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 41.47 | 87.8 | 61.6 | |
| Biomass (g/plant) | Root | 0.68 | 0.7 | 41.47 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 31.15 t/hm2 | 0.2 | 1.69 t/hm2 | 0.18 kg/m2 |
| Shoot | 5.8 | 0.8 g | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 | ||||
| Activator | CA | CA | CA | CA | CA | PASP | PASP | CA | None | |
| Initial Cd (mg/kg) | 3.91 | 20.09 | 0.85 | 10.4 | 3.03 | 0.94 | 8.62 | 3.68 | 0.41 | |
| Plants | Sedum plumbizincicola | NHE Sedum alfredii | Sedum alfredii | Sedum alfredii | Sedum alfredii | Pennisetum sinese R. | Sedum alfredii | Celosia argentea L. | Sedum alfredii | |
| Treatment | BCF | TF | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoots | Roots | Shoots | |
| CK | 8.77 ± 2.8 | 14.53 ± 6.56 | 0.6 ± 0.04 |
| CA | 11.95 ± 3.57 | 16.21 ± 1.43 | 0.73 ± 0.14 |
| MA | 9.44 ± 2.27 | 16.21 ± 2.03 | 0.6 ± 0.18 |
| PASP | 7.43 ± 0.79 | 9.4 ± 1.14 | 0.8 ± 0.14 |
| CA + PASP | 9.2 ± 0.39 | 17.23 ± 3.76 | 0.6 ± 0.08 |
| MA + PASP | 9.14 ± 0.87 | 15.44 ± 4.91 | 0.66 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wei, H.; Sun, M.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Q. The Addition of Degradable Activators Enhances Sedum alfredii Phytoremediation Efficiency in Cd-Contaminated Soils. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073207
Li H, Huang L, Chen Z, Wei H, Sun M, Huang X, Li H, Liu Q. The Addition of Degradable Activators Enhances Sedum alfredii Phytoremediation Efficiency in Cd-Contaminated Soils. Sustainability. 2025; 17(7):3207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073207
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Honggang, Ling Huang, Zhiliang Chen, Hang Wei, Mengqiang Sun, Xiaoqing Huang, Haochao Li, and Qianjun Liu. 2025. "The Addition of Degradable Activators Enhances Sedum alfredii Phytoremediation Efficiency in Cd-Contaminated Soils" Sustainability 17, no. 7: 3207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073207
APA StyleLi, H., Huang, L., Chen, Z., Wei, H., Sun, M., Huang, X., Li, H., & Liu, Q. (2025). The Addition of Degradable Activators Enhances Sedum alfredii Phytoremediation Efficiency in Cd-Contaminated Soils. Sustainability, 17(7), 3207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073207






