The Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Trends, and Climate Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
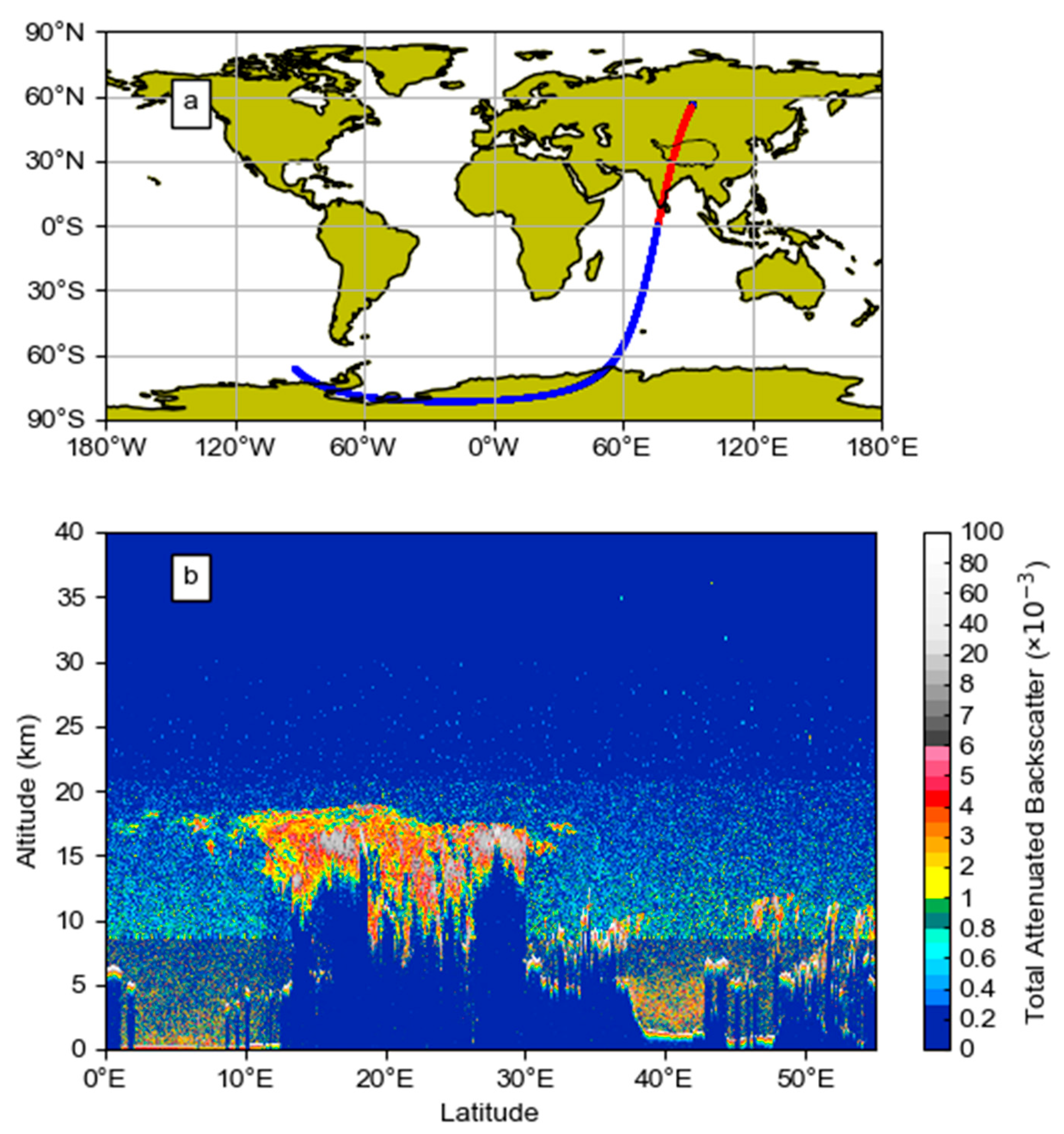
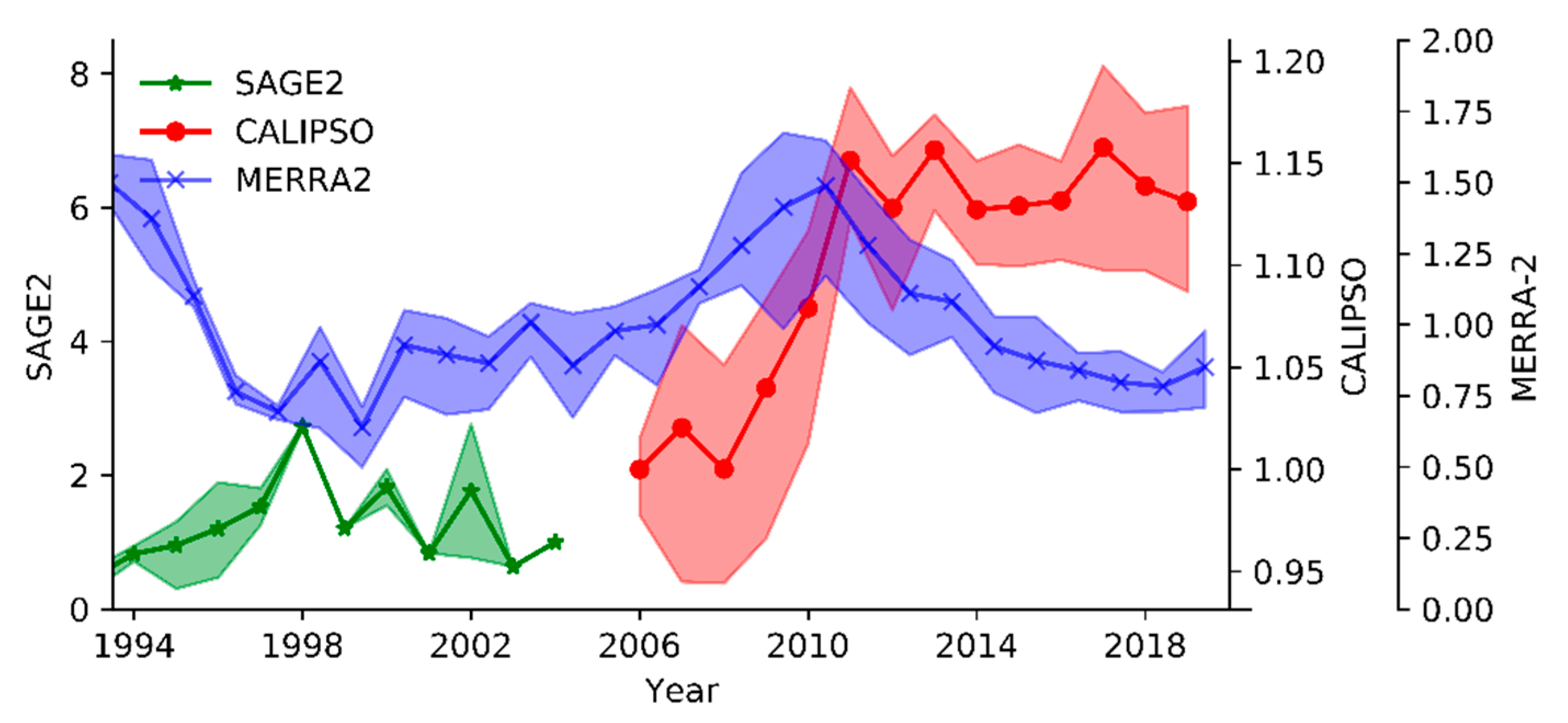
2. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics and Components of ATAL
3. Formation Mechanism and Sources of ATAL
4. Climate Effects of the ATAL
5. Conclusions and Discussion
6. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucci, S.; Legras, B.; Sellitto, P.; d’Amato, F.; Viciani, S.; Montori, A.; Chiarugi, A.; Ravegnani, F.; Ulanovsky, A.; Cairo, F. Deep-convective influence on the upper troposphere–lower stratosphere composition in the Asian monsoon anticyclone region: 2017 StratoClim campaign results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12193–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Akimoto, H.; Kurokawa, J.; Horii, N.; Yamaji, K.; Yan, X.; Hayasaka, T. An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4419–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghan, S.J.; Zaveri, R.A. Parameterization of optical properties for hydrated internally mixed aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mokgobu, M.I.; Mukhola, M.S.; Hunter, R.P. Health outcomes of exposure to biological and chemical components of inhalable and respirable particulate matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Kang, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Paudyal, R. Vertical distribution of the Asian tropopause aerosols detected by CALIPSO. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Agrawal, M. Acid rain and its ecological consequences. J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 29, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lau, W.M.; Ramanathan, V.; Wu, G.; Ding, Y.; Manoj, M.; Liu, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T. Aerosol and monsoon climate interactions over Asia. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 866–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M.C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Gong, D.; Huang, J.; Jiang, M. East Asian study of tropospheric aerosols and their impact on regional clouds, precipitation, and climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13026–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Luo, Y. Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 2002, 297, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Gong, D.; Fan, J.; Leung, L.R.; Bennartz, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, W. Heavy pollution suppresses light rain in China: Observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, D. Advances in studying interactions between aerosols and monsoon in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.E. The whitehouse effect—Shortwave radiative forcing of climate by anthropogenic aerosols: An overview. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 27, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.; Vignati, E.; van Dingenen, R.; Amann, M.; Klimont, Z.; Anenberg, S.C.; Muller, N.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Raes, F. Simultaneously mitigating near-term climate change and improving human health and food security. Science 2012, 335, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, C.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Du, W.; Huang, J. Linking atmospheric pollution to cryospheric change in the Third Pole region: Current progress and future prospects. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Gao, T.; Sprenger, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Black Carbon Size in Snow of Chinese Altai Mountain in Central Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, R.; Ma, J. Spatiotemporal and Vertical Distribution of Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer Using Long-Term Multi-Source Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquila, V.; Oman, L.D.; Stolarski, R.S.; Colarco, P.R.; Newman, P.A. Dispersion of the volcanic sulfate cloud from a Mount Pinatubo–like eruption. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Moorthy, K.K.; Manchanda, R.K.; Sinha, P.R.; Satheesh, S.; Vajja, D.P.; Srinivasan, S.; Kumar, V.A. Free tropospheric black carbon aerosol measurements using high altitude balloon: Do BC layers build “their own homes” up in the atmosphere? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Sellitto, P.; Legras, B.; Vernier, J.P.; Jegou, F.; Venkat Ratnam, M.; Suneel Kumar, B.; Lakshmi Madhavan, B.; Berthet, G. Impact of the 2018 Ambae eruption on the global stratospheric aerosol layer and climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Ramachandran, S.; Bhavani Kumar, Y.; Narayana Rao, D.; Krishnaiah, M. Features of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere aerosols observed by lidar over Gadanki, a tropical Indian station. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitari, G.; Cionni, I.; Di Genova, G.; Visioni, D.; Gandolfi, I.; Mancini, E. Impact of stratospheric volcanic aerosols on age-of-air and transport of long-lived species. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobo, Y.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ohashi, T.; Tamura, K.; Zhang, D. Balloon-borne observations of high aerosol concentrations near the summertime tropopause over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Park, M.; Emmons, L.; Kinnison, D.; Bernath, P.; Walker, K.A.; Boone, C.; Pumphrey, H. Asian monsoon transport of pollution to the stratosphere. Science 2010, 328, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Diamond, J. China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 2005, 435, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Habib, G.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Miguel, A.; Friedlander, S. Residential biofuels in South Asia: Carbonaceous aerosol emissions and climate impacts. Science 2005, 307, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, P. Study on the sensitivity of summer ozone density to the enhanced aerosol loading over the tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, P. Weather and climate effects of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Duan, A.; Jin, F.-F. Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, D.; Bai, Z.; Li, Q.; Lyu, D.; Zhou, X. Transport of Asian surface pollutants to the global stratosphere from the Tibetan Plateau region during the Asian summer monsoon. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Honomichl, S.B.; Kinnison, D.E.; Abalos, M.; Randel, W.J.; Bergman, J.W.; Bian, J. Transport of chemical tracers from the boundary layer to stratosphere associated with the dynamics of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 14159–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.P.; Thomason, L.W.; Pommereau, J.P.; Bourassa, A.; Pelon, J.; Garnier, A.; Hauchecorne, A.; Blanot, L.; Trepte, C.; Degenstein, D. Major influence of tropical volcanic eruptions on the stratospheric aerosol layer during the last decade. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodion, J.; Fussen, D.; Vanhellemont, F.; Bingen, C.; Mateshvili, N.; Gilbert, K.; Skelton, R.; Turnbull, D.; McLeod, S.; Boone, C. Aerosols and clouds in the upper troposphere–lower stratosphere region detected by GOMOS and ACE: Intercomparison and analysis of the years 2004 and 2005. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 42, 1730–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckendorn, P.; Weisenstein, D.; Fueglistaler, S.; Luo, B.P.; Rozanov, E.; Schraner, M.; Thomason, L.W.; Peter, T. The impact of geoengineering aerosols on stratospheric temperature and ozone. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, B.; Robock, A.; Shindell, D.T.; Miller, M.A. Sensitivity of stratospheric geoengineering with black carbon to aerosol size and altitude of injection. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaini, R.; Chipperfield, M.; Montzka, S.; Rap, A.; Dhomse, S.; Feng, W. Efficiency of short-lived halogens at influencing climate through depletion of stratospheric ozone. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, J.W.; Fierli, F.; Jensen, E.J.; Honomichl, S.; Pan, L.L. Boundary layer sources for the Asian anticyclone: Regional contributions to a vertical conduit. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2560–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Randel, W.J.; Gettelman, A.; Massie, S.T.; Jiang, J.H. Transport above the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone inferred from Aura Microwave Limb Sounder tracers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzella, A.; Legras, B. A Lagrangian view of convective sources for transport of air across the Tropical Tropopause Layer: Distribution, times and the radiative influence of clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12517–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, V.N.; Madhavan, B.L.; Akhil Raj, S.T.; Ratnam, M.V.; Vernier, J.-P.; Wienhold, F.G. Shortwave Radiative Impacts of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL) using Balloon-borne In-situ measurements at three distinct locations in India. EGUsphere 2024, 2024, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, M.; Weigel, R.; Weinbruch, S.; Schneider, L.; Kandler, K.; Lauterbach, S.; Köllner, F.; Plöger, F.; Günther, G.; Vogel, B. Characterization of refractory aerosol particles collected in the tropical upper troposphere–lower stratosphere (UTLS) within the Asian tropopause aerosol layer (ATAL). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 4771–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Bossolasco, A.; Thomason, L.; Legras, B.; Berthet, G.; Jegou, F.; Fadnavis, S.; Sellitto, P. Reconsidering the existence of a trend in the Asian tropopause aerosol layer (ATAL) from 1979 to 2017. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD039784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Yu, S.M. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of aerosols in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau region and numerical simulation of their radiative forcing and climate effects. Chin. Sci. (Vol. D Earth Sci.) 2001, 31, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Shibata, T.; Iwasaka, Y.; Shi, G.; Zhou, X.; Tamura, K.; Ohashi, T. Enhancement of aerosols near the cold tropopause in summer over Tibetan Plateau: Lidar and balloonborne measurements in 1999 at Lhasa, Tibet, China. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Industry and Environment Monitoring III, Hangzhou, China, 24–25 October 2002; pp. 496–503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Bi, Y.; Yi, M. Distribution characteristics of aerosol content in the air over the Qinghai Tibet Plateau and its relationship with ozone. Plateau Meteorol. 2008, 27, 500–508. [Google Scholar]
- Vernier, J.P.; Fairlie, T.; Natarajan, M.; Wienhold, F.; Bian, J.; Martinsson, B.; Crumeyrolle, S.; Thomason, L.; Bedka, K. Increase in upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric aerosol levels and its potential connection with Asian pollution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, L.; Vernier, J.-P. Improved SAGE II cloud/aerosol categorization and observations of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer: 1989–2005. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4605–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Fairlie, T.; Deshler, T.; Venkat Ratnam, M.; Gadhavi, H.; Kumar, B.; Natarajan, M.; Pandit, A.; Akhil Raj, S.; Hemanth Kumar, A. BATAL: The balloon measurement campaigns of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 955–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Liu, S.; Telg, H.; Thornberry, T.D.; Rollins, A.W.; Portmann, R.W.; Bai, Z.; Ray, E.A.; Duan, Y. Efficient transport of tropospheric aerosol into the stratosphere via the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6972–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shi, T.; Niu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ji, M.; Wang, X. Seasonal to sub-seasonal variations of the Asian Tropopause Aerosols Layer affected by the deep convection, surface pollutants and precipitation. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Toon, O.B.; Neely, R.R.; Martinsson, B.G.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A. Composition and physical properties of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer and the North American tropospheric aerosol layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, T.D.; Liu, H.; Vernier, J.P.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; Jo, D.S.; Zhang, B.; Natarajan, M.; Avery, M.A.; Huey, G. Estimates of regional source contributions to the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer using a chemical transport model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liao, H.; Bian, J. Summertime nitrate aerosol in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere over the Tibetan Plateau and the South Asian summer monsoon region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6641–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Kalita, G.; Kumar, K.R.; Gasparini, B.; Li, J.-L.F. Potential impact of carbonaceous aerosol on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) and precipitation during Asian summer monsoon in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11637–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Brühl, C.; He, Q.; Steil, B.; Karydis, V.A.; Klingmüller, K.; Tost, H.; Chen, B.; Jin, Y.; Liu, N. Modeling the aerosol chemical composition of the tropopause over the Tibetan Plateau during the Asian summer monsoon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11587–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Bai, Z.; Xia, X.; Chen, B.; Zong, X.; Bian, J. In situ measurements and backward-trajectory analysis of high-concentration, fine-mode aerosols in the UTLS over the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossolasco, A.; Jegou, F.; Sellitto, P.; Berthet, G.; Kloss, C.; Legras, B. Global modeling studies of composition and decadal trends of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettelman, A.; Kinnison, D.E.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Brasseur, G.P. Impact of monsoon circulations on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Randel, W.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Livesey, N.J. Transport pathways of carbon monoxide in the Asian summer monsoon diagnosed from Model of Ozone and Related Tracers (MOZART). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, W.; Schofield, R.; Hoor, P.; Kunkel, D.; Ravegnani, F.; Ulanovsky, A.; Viciani, S.; D’Amato, F.; Lane, T.P. The impact of overshooting deep convection on local transport and mixing in the tropical upper troposphere/lower stratosphere (UTLS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6467–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z. Origin, maintenance and variability of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): The roles of monsoon dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Lau, W.K.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Relationship between Asian monsoon strength and transport of surface aerosols to the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): Interannual variability and decadal changes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Semeniuk, K.; Pozzoli, L.; Schultz, M.; Ghude, S.; Das, S.; Kakatkar, R. Transport of aerosols into the UTLS and their impact on the Asian monsoon region as seen in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8771–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely III, R.; Yu, P.; Rosenlof, K.; Toon, O.; Daniel, J.; Solomon, S.; Miller, H. The contribution of anthropogenic SO2 emissions to the Asian tropopause aerosol layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Günther, G.; Müller, R.; Grooß, J.-U.; Riese, M. Impact of different Asian source regions on the composition of the Asian monsoon anticyclone and of the extratropical lowermost stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13699–13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legras, B.; Bucci, S. Confinement of air in the Asian monsoon anticyclone and pathways of convective air to the stratosphere during the summer season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11045–11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissier, A.-S.; Legras, B. Convective sources of trajectories traversing the tropical tropopause layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3383–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, J.W.; Jensen, E.J.; Pfister, L.; Yang, Q. Seasonal differences of vertical-transport efficiency in the tropical tropopause layer: On the interplay between tropical deep convection, large-scale vertical ascent, and horizontal circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, T. Water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric aerosols along the transport pathway of Asian dust: Optical properties, chemical compositions, and potential sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Collins, W.; Haywood, J.; Lean, J.; Mahowald, N.; Myhre, G.; Naik, V.; Shine, K.P.; Soden, B.; Stenchikov, G. Radiative forcing of climate: The historical evolution of the radiative forcing concept, the forcing agents and their quantification, and applications. Meteorol. Monogr. 2019, 59, 14.1–14.101. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wright, J.S. Aerosol Effects on Clear-Sky Shortwave Heating in the Asian Monsoon Tropopause Layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD036956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Duan, A.; Chen, D.; Wu, G. Surface energy budget diagnosis reveals possible mechanism for the different warming rate among Earth’s three poles in recent decades. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.-Y.; Hayasaka, T.; Ohmura, A.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Che, H.-Z.; Xu, L. Data quality assessment and the long-term trend of ground solar radiation in China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kaiser, D.P.; Leung, L.R.; Xu, M. More frequent cloud-free sky and less surface solar radiation in China from 1955 to 2000. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Haywood, J.; Hawcroft, M. Are changes in atmospheric circulation important for black carbon aerosol impacts on clouds, precipitation, and radiation? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7930–7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, K.M. Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall, and circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volten, H.; Munoz, O.; Rol, E.; De Haan, J.; Vassen, W.; Hovenier, J.; Muinonen, K.; Nousiainen, T. Scattering matrices of mineral aerosol particles at 441.6 nm and 632.8 nm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 17375–17401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, K.T. The physical characteristics of sulfur aerosols. In Sulfur in the Atmosphere; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 135–159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. Overview of the impact of aerosols on weather, climate, and environment in China. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Kreidenweis, S.M.; Petters, M.; Lohmann, U. 100 years of progress in cloud physics, aerosols, and aerosol chemistry research. Meteorol. Monogr. 2019, 59, 11.1–11.72. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-K.; Lau, W.K.; Chin, M.; Kim, K.-M.; Sud, Y.; Walker, G.K. Atmospheric teleconnection over Eurasia induced by aerosol radiative forcing during boreal spring. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4700–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Ramaswamy, V.; Chen, G. A model investigation of aerosol-induced changes in boreal winter extratropical circulation. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 6077–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Chung, C.; Kim, D.; Bettge, T.; Buja, L.; Kiehl, J.T.; Washington, W.M.; Fu, Q.; Sikka, D.R.; Wild, M. Atmospheric brown clouds: Impacts on South Asian climate and hydrological cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5326–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, T.D.; Zhang, J.; Campbell, J.R.; Reid, J.S.; Vaughan, M.A. Temporal variability of aerosol optical thickness vertical distribution observed from CALIOP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9117–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-O.; Chung, C.E. Sensitivity of aerosol direct radiative forcing to aerosol vertical profile. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 24376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cziczo, D.; Abbatt, J. Ice nucleation in NH4HSO4, NH4NO3, and H2SO4 aqueous particles: Implications for cirrus cloud formation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Jiang, J.H.; Liu, X.; Penner, J.E.; Read, W.G.; Massie, S.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Colarco, P.; Livesey, N.J.; Santee, M.L. Observed increase of TTL temperature and water vapor in polluted clouds over Asia. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2728–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Portmann, R.W.; Daniel, J.S.; Davis, S.M.; Sanford, T.J.; Plattner, G.-K. Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science 2010, 327, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ma, J. The Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Trends, and Climate Effects. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083381
Liu H, Ma J. The Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Trends, and Climate Effects. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083381
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongchao, and Junjie Ma. 2025. "The Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Trends, and Climate Effects" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083381
APA StyleLiu, H., & Ma, J. (2025). The Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Trends, and Climate Effects. Sustainability, 17(8), 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083381




