The Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall in Shenzhen City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Definition of Extreme Precipitation
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Wavelet Analysis
2.4.2. Mann–Kendall Mutation Test Method
2.4.3. Hurst Index Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Evolutionary Characterization and Mutability Analysis
3.1.1. Characterization of the Intraannual Evolution of Extreme Rainfall and Analysis of Sudden Variability
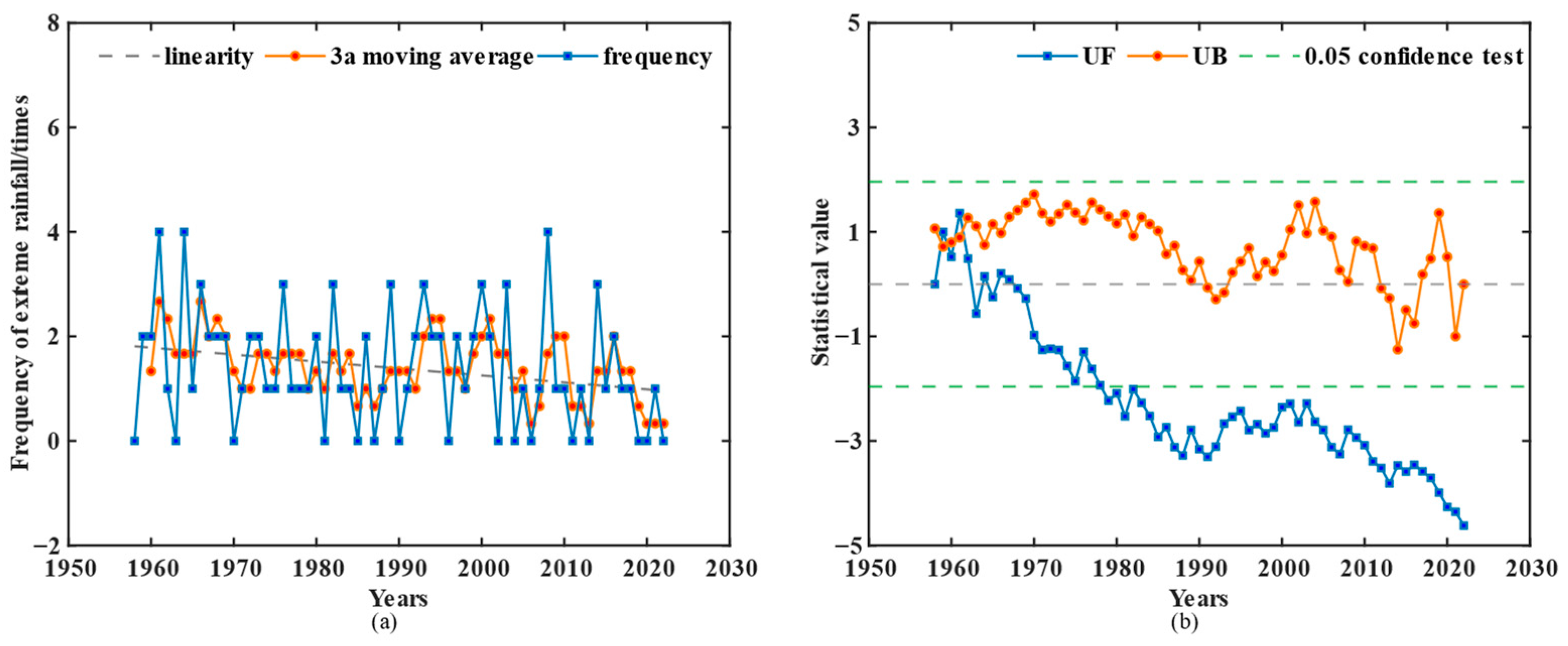
3.1.2. Characterization of the Intraannual Evolution of Extreme Rainfall Frequency and Analysis of Sudden Variability
3.2. Cycle Analysis
3.2.1. Cycle Analysis of Rainfall
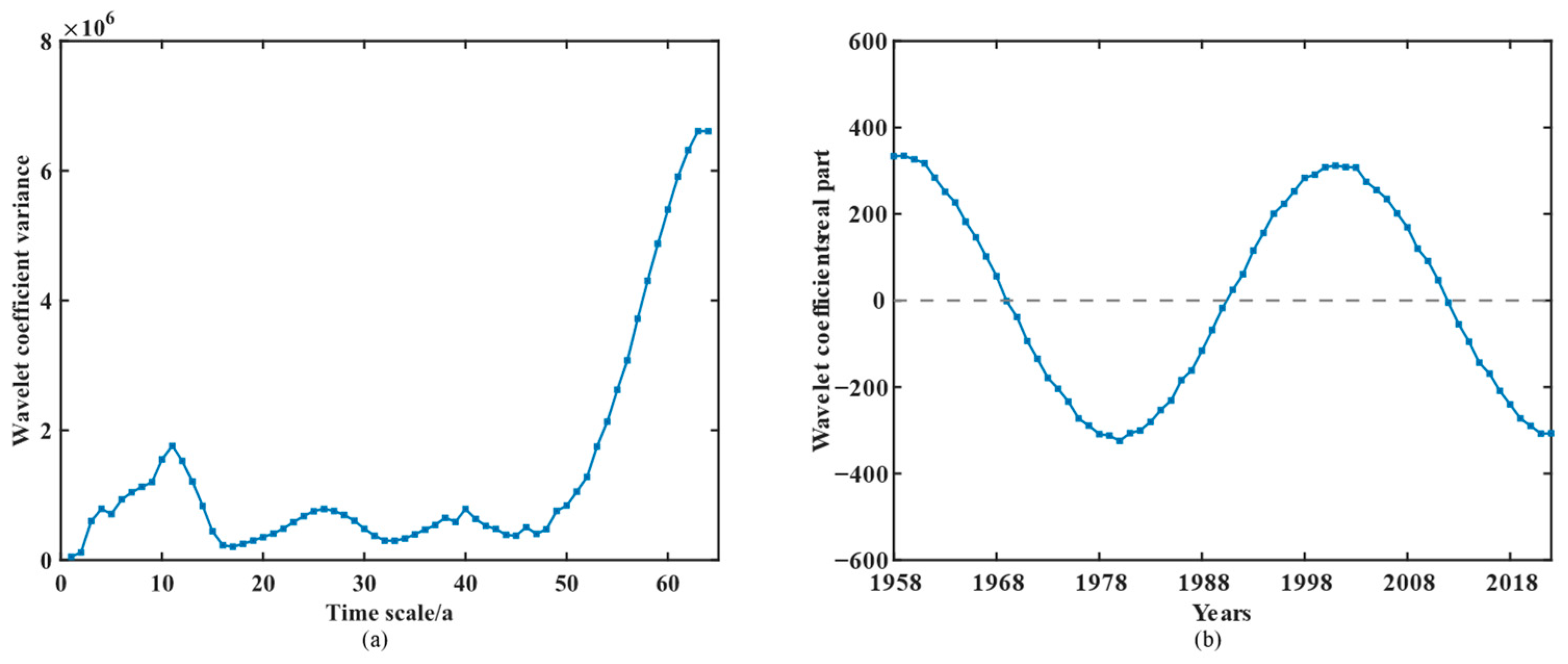
3.2.2. Cycle Analysis of Extreme Rainfall
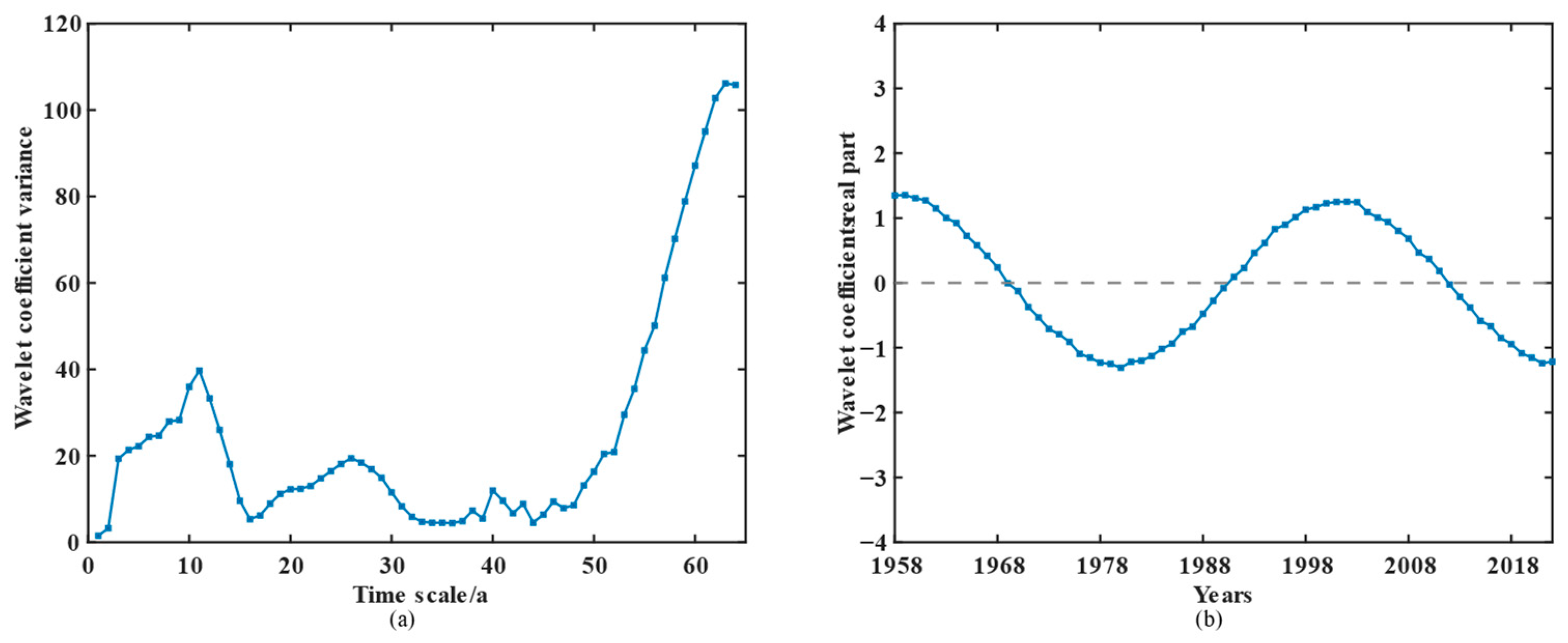
3.2.3. Cycle Analysis of Extreme Rainfall Frequency
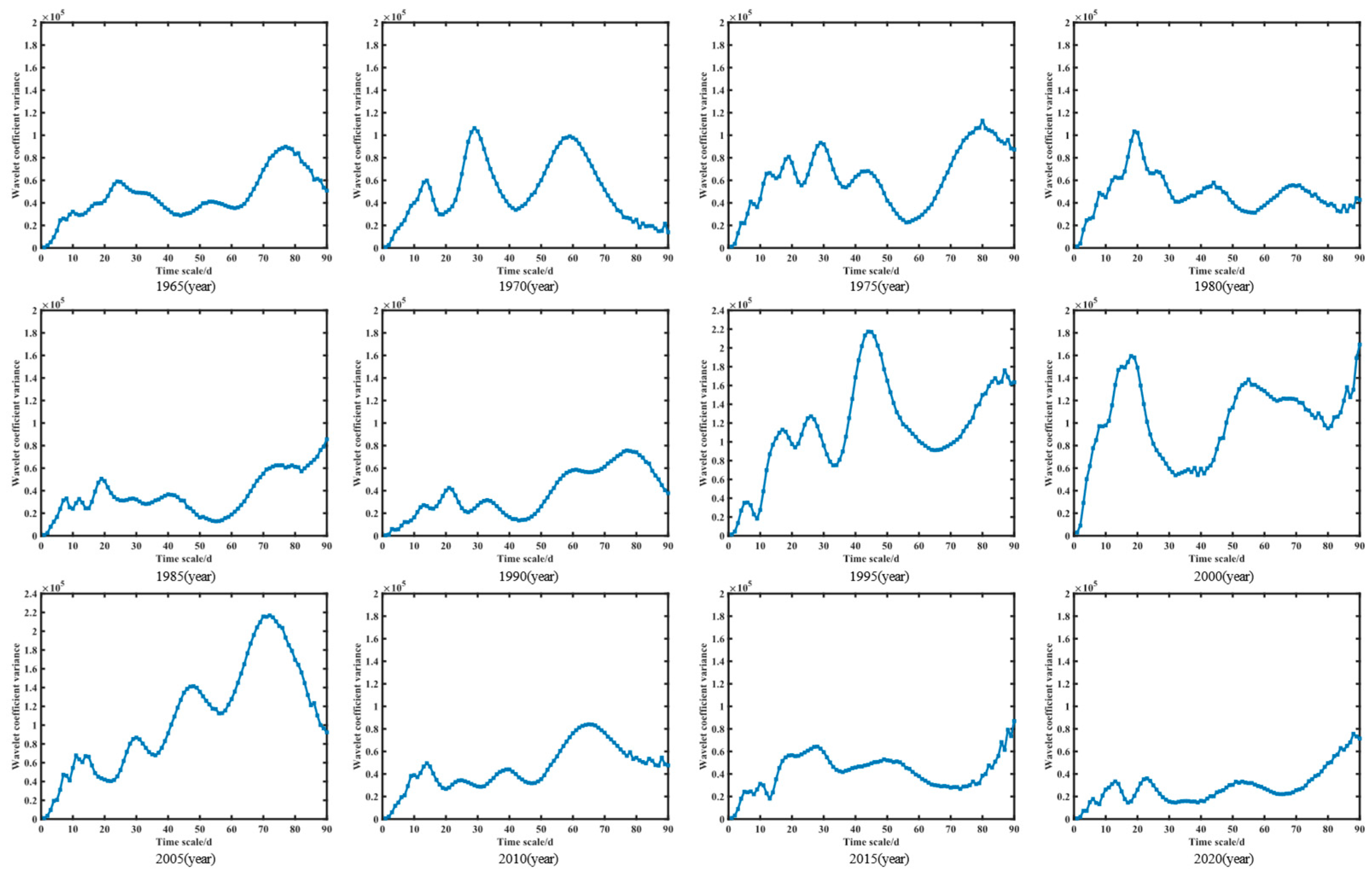
3.3. Characteristics of Main Cycle Evolution in Shenzhen Based on Daily Rainfall Wavelet Variance
3.4. Projections of Future Trends in Extreme Rainfall Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, Z.; Li, N.; Lu, M.; Xu, L. Change characteristics of extreme precipitation events in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2017. Water Resour. Hydropower Technol. 2019, 50, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Yu, Q.; Li, N. Characteristics of flood risk evolution and urban resilience enhancement strategies in changing environments. J. Water Resour. 2022, 53, 757–768+778. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Karmakar, S.; PaiMazumder, D.; Ghosh, S.; Niyogi, D. Urbanization Alters Rainfall Extremes over the Contiguous United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, P.K.; Mall, R.K.; Srivastava, P.K. Changes in extremes rainfall events in present and future climate scenarios over the teesta river basin, India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, J. Regional Landslide Susceptibility Assessment and Model Adaptability Research. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, F. Stability and support analysis of coverage rock-soil aggregate of Longhuguan landslide. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Permeability of particle soils under soil pressure. Transp. Porous Media 2018, 123, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Sun, J. Monitoring Ground Deformation in Beijing and Analysis of Influencing Factors. Int. J. Ground Sediment Water 2025, 21, 1557–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, G. Research on underground water pollution caused by geological fault through radioactive stratum. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 297, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Ground sediment transport model and numerical simulation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Survey and research frame for ground sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18960–18965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumei, X. Analysis of spatial and temporal distribution of extreme rainfall in Hebei Province and accuracy test of prediction model. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2023, 9, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Ganguly, A.R.; Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Changes in observed climate extremes in global urban areas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Z. Characteristics of spatial and temporal variability of extreme precipitation and its response to temperature changes in Xinjiang. J. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Cui, S.; Fang, X. Spatial and temporal dynamics of the “7.20” flood disaster in Henan Province. Disaster Sci. 2022, 37, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Narimani, R.; Jun, C.; Saedi, A.; Bateni, S.M.; Oh, J. A multivariate decomposition–ensemble model for estimating long-term rainfall dynamics. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 1625–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Li, T. Countermeasures and suggestions for urban storm water disaster defense in changing environments. Proc. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 37, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Meehl, G.A. Extreme weather and climate events with ecological relevance: A review. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liao, W.; Wang, h. Efficient Urban Flooding Management: A Multi-Physical-Process-Oriented Flood Modelling and Analysis Method. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenzhen Municipal Bureau of Statistics; Survey Team of Shenzhen, National Bureau of Statistics. 2023 Statistical Bulletin of Shenzhen’s National Economic and Social Development. Shenzhen Special Zone Daily, 28 April 2024.
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Tan, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Analysis of spatial and temporal evolution patterns of precipitation characteristics in Shenzhen. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 55, 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Prein, A.F.; Westra, S.; Allan, R.P.; Ban, N.; Barbero, R.; Berg, P.; Blenkinsop, S.; Do, H.X.; et al. Anthropogenic intensification of short-duration rainfall extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, M.; Adounkpe, J.; Larbi, I.; Hounkpe, J.; Koubodana, H.D.; Toure, A.; Bokar, H.; Dotse, S.-Q.; Limantol, A.M. Urban Flash Flood and Extreme Rainfall Events Trend Analysis in Bamako, Mali. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Xia, J.; Shao, Q.; Yu, E.; Zhao, T.; She, D.; Sun, J.; Yu, J.; Pan, X.; et al. Regional patterns of extreme precipitation and urban signatures in metropolitan areas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 641–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; He, Y.; Lei, X.; Cheng, H.; Mei, X. Analysis of spatial and temporal variations of rainfall in Shenzhen from 1960 to 2009. China Rural Water Conserv. Hydropower 2013, 15, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Hua, P.; Gao, Y. Trend analysis of precipitation changes in Shenzhen from 1961 to 2011. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2017, 28, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Xian, Z. Analysis of changes in extreme weather events in Shenzhen from 1953 to 2012. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2014, 25, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shi, H. Characterization of spatial and temporal evolution of extreme precipitation in Shenzhen. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Hydropower (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Che, R.; Lin, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, W.; Zeng, F.; Mao, B.; Shi, L.; Huang, Z. Analysis of the impact of continuous extreme rainfall on water quality in the Dongjiang River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4440–4449. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Han, L.; Zhou, W. Evolution of air quality and its regulation in typical cities in China—A case study of Shenzhen City from 2000 to 2017. J. Ecol. 2020, 40, 5894–5903. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, H.; Zhai, Y. Dynamic change law of evaporation strength of permeable paving and analysis of influencing factors. J. Peking Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 55, 934–940. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Xie, H. Changing roles of urban river landscape in the context of high-quality development—An example of upgrading river landscape planning in Dameisha, Shenzhen. In Proceedings of the Spatial Governance for High Quality Development—Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Urban Planning in China 2020 (12 Landscape and Environmental Planning), Chengdu, China, 25 September 2021; Volume 6, pp. 483–496. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J. System comprehensive risk assessment of urban rainstorm–induced flood-water pollution disasters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 59826–59843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Wang, G. A new method for estimation of spatially distributed rainfall through merging satellite observations, raingauge records, and terrain digital elevation model data. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2020, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gong, Y.; Xiang, N. Characteristics of 60-year changes in diurnal rainfall days at different levels over the Tibetan Plateau and Southwest China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2023, 28, 367–384. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Jian, S. Definition of extreme rainfall events and design of rainfall based on the copula function. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 3759–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. A comparative study of methods for determining extreme precipitation thresholds in China. Disaster Sci. 2015, 30, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, T.; Feng, J.; Li, L.; Xing, L.; Huang, G. Trend analysis of the evolution of extreme rainfall events in Haikou City. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2016, 27, 6–10+17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Analysis of temporal evolution characteristics of precipitation in Beijing. Int. J. Ground Sediment Water 2023, 30, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W. Trend analysis of runoff from three sources in the upper Tarim River Basin. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2010, 21, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Guo, C.; Peng, G. Morlet wavelet analysis of precipitation in Henan Province from 1951 to 2012. People’s Yellow River 2015, 37, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.-S.; Wang, X.-J. Trends analysis of rainfall and rainfall extremes in Sarawak, Malaysia using modified Mann–Kendall test. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 131, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, E.B.I.; Ugbor, D.O.; Agbo, J.U.; Alfa, A. Analyzing Rainfall Trend and Drought Occurrences in Sudan Savanna of Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2023, 20, e01670. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.; He, R. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrology in the Yellow River Source Region, China. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Swayne, D.A.; Obimbo, C. Trend analysis and change point techniques: A survey. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimer, S.M.; Kumar, N.; Bouanani, A.; Tischbein, B.; Borgemeister, C. Homogenization of daily time series climatological data in the Eastern Nile basin, Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 143, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hou, J.; Chai, J.; Bai, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, B. Characterization of temporal evolution of extreme rainfall in Xi’an. Environ. Eng. 2022, 40, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, J. Linear and Nonlinear Characteristics of Long-Term NDVI Using Trend Analysis: A Case Study of Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Ruan, M. Research on Temporal and Spatial Resolution and the Driving Forces of Ecological Environment Quality in Coal Mining Areas Considering Topographic Correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, B.; Dang, S. Characterization of precipitation and trend prediction in Hangzhou in the last 63 years. Hydropower 2015, 41, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wallis, J.R. Robustness of the rescaled range R/S in the measurement of noncyclic long run statistical dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Dong, X.; Dong, L.; Wu, H.; Ouyang, X. Characterization of precipitation and its future trend in REOF sub-district of Yalong River Basin. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 29, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y. Changing characteristics of extreme precipitation events in Guangdong Province. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2016, 36, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Ma, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Pan, X. Application of Matlab in teaching meteorology majors M-K test mutation analysis of meteorological elements. Lab. Res. Explor. 2019, 38, 48–51+107. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Wang, S. ENSO events and their intensities in the past century. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 3, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, H. The major meteorological disaster events affecting Shenzhen in 2008. Shenzhen Business Daily, 17 February 2009; A08. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, B.; Liu, M. Dry-wet evolution characteristics and response to ENSO events in the Minjiang River basin from 1962 to 2021. South--North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 545–556. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X. Extreme precipitation changes in Shenzhen from 1961 to 2019. J. Nat. Disasters 2021, 30, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Pan, W. The great floods in Shenzhen in 2008. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2010, 30, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Research on the Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Hourly Precipitation over South China During the Warm Season and Its Possible Causes; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Sun, J. The Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall in Shenzhen City, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083512
Wang X, Sun J. The Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall in Shenzhen City, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083512
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaorong, and Jichao Sun. 2025. "The Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall in Shenzhen City, China" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083512
APA StyleWang, X., & Sun, J. (2025). The Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall in Shenzhen City, China. Sustainability, 17(8), 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083512





