Abstract
Groundwater is one of the most critical drinking water resources on Earth, and its safety significantly impacts the ecological environment and human health. This study focuses on the pollution characteristics, sources, and health risks of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in the groundwater of the Dongting Lake basin in China. It highlights the concentration distribution and pollution causes of common toxic elements such as manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), iron (Fe), chloride ions (Cl−), and fluoride ions (F−). The results indicate that the Mn concentration reached 28.6 times the background value, followed by Cu at 16.7 times. The groundwater pollution level in the study area reached a severe contamination level, with Zn classified as severely polluted and Mn categorized as moderately to heavily polluted. Approximately 47.05% of the study area was severely contaminated by PTEs. The study further reveals that the primary sources of pollution are anthropogenic activities, including agricultural fertilization, industrial discharges, and urbanization processes, which have significantly elevated PTE concentrations in groundwater. Additionally, natural geochemical processes contribute substantially to the high concentrations of specific elements in certain areas. Health risk assessments indicate that long-term exposure to PTEs in groundwater may pose various potential threats to human health, particularly in terms of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks. Children are identified as the most vulnerable group. This research provides a systematic scientific basis for the management of groundwater pollution in the Dongting Lake basin, emphasizing that the current pollution levels pose serious threats to regional ecosystems and public health. The findings not only offer guidance for groundwater management in the Dongting Lake basin but also serve as a valuable reference for groundwater pollution management in similar regions.
1. Introduction
Groundwater, as a crucial component of global water resources, plays a vital role in sustaining human life and supporting economic development [1]. However, rapid industrialization, mining, and urbanization have released large quantities of potentially toxic elements (PTEs), leading to groundwater contamination, which is now a severe environmental challenge [2,3]. The Dongting Lake is the second-largest freshwater lake in China, located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. It has a dense network of rivers and abundant water resources, with a history of rice cultivation spanning over 8000 years. As an important grain production base, the Dongting Lake region significantly impacts the nation’s rice supply [4]. Beyond its role as a critical water resource, the lake plays a key role in climate regulation, ecological balance, and regional economic development [5,6].
PTEs, which have detrimental effects on ecosystems and human health, have drawn significant attention from researchers globally [7]. Toxic elements such as Cd, Cr, As, and Pb can accumulate in the human body through groundwater exposure and pose severe toxicity even at low concentrations. Notably, Cd, Cr, and As are classified as carcinogenic heavy metals with significant cancer risks [8,9]. Furthermore, essential trace elements like Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn, though necessary for metabolism, can harm human health if their concentrations exceed safe limits [10,11]. Research on groundwater contamination by PTEs has consistently shown that such pollution not only directly affects local ecosystems but also has far-reaching socioeconomic impacts. Understanding the characteristics and sources of PTEs is essential for safeguarding public health and ensuring water security [9,12,13,14,15,16].
Rapid urbanization, industrial activities, and mining in the Dongting Lake Basin have led to varying degrees of PTE pollution in groundwater, soil, and sediments [17]. Research has identified heavy contamination in lake sediments from the Xiangjiang River, with pollutants such as Hg, As, Cd, Zn, Pb, and Mn [18]. In studies on the pollution of Dongting Lake’s water bodies, researchers found that the eastern part of Dongting Lake exhibited higher pollution factors and posed the greatest potential risk to the lake’s water. Cd, Pb, and Mn were identified as the main pollution elements [19]. Zhong and colleagues analyzed paddy soil samples from the Dongting Lake basin and reported moderate to severe anthropogenic Cd pollution. The long-term use of water from the Xiang River as a source for agricultural irrigation was identified as the primary cause of heavy metal accumulation in soils surrounding Dongting Lake [6]. Makokha’s team conducted research on surface water pollution in the Dongting Lake area and found that Zn had the highest average concentration among the heavy metals in surface water. The distribution of most heavy metals was strongly associated with human activities [20]. Further studies by Li et al. indicated that Zn, Pb, Cd, and As in the Dongting Lake region primarily originated from mining and industrial wastewater, while Cu was linked to atypical agricultural pollution sources. The study concluded that the Dongting Lake area is currently facing moderate anthropogenic pollution [5]. Multiple studies have demonstrated that the water, sediments, and soils in the Dongting Lake region are contaminated to varying degrees by heavy metals and toxic elements. Such pollution poses direct risks to human health and the ecological environment through pathways such as the food chain. Therefore, extensive attention should be given to the study of PTEs in the Dongting Lake region [7,11].
Research on PTE pollution in the groundwater of the Dongting Lake basin is essential for understanding the current status of groundwater contamination in the region. Such studies can promote local ecological and environmental protection, reduce the impact of PTEs on human health, and optimize groundwater resource management. Furthermore, this research provides fundamental data and theoretical support for environmental science and water resource management studies. Hence, this study aims to (1) explore the physicochemical properties and contamination status of PTEs in groundwater in the Dongting Lake Basin; (2) identify the spatial distribution patterns and sources of PTE pollution; (3) develop effective prevention and control measures; and (4) assess the health risks associated with PTE contamination in groundwater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
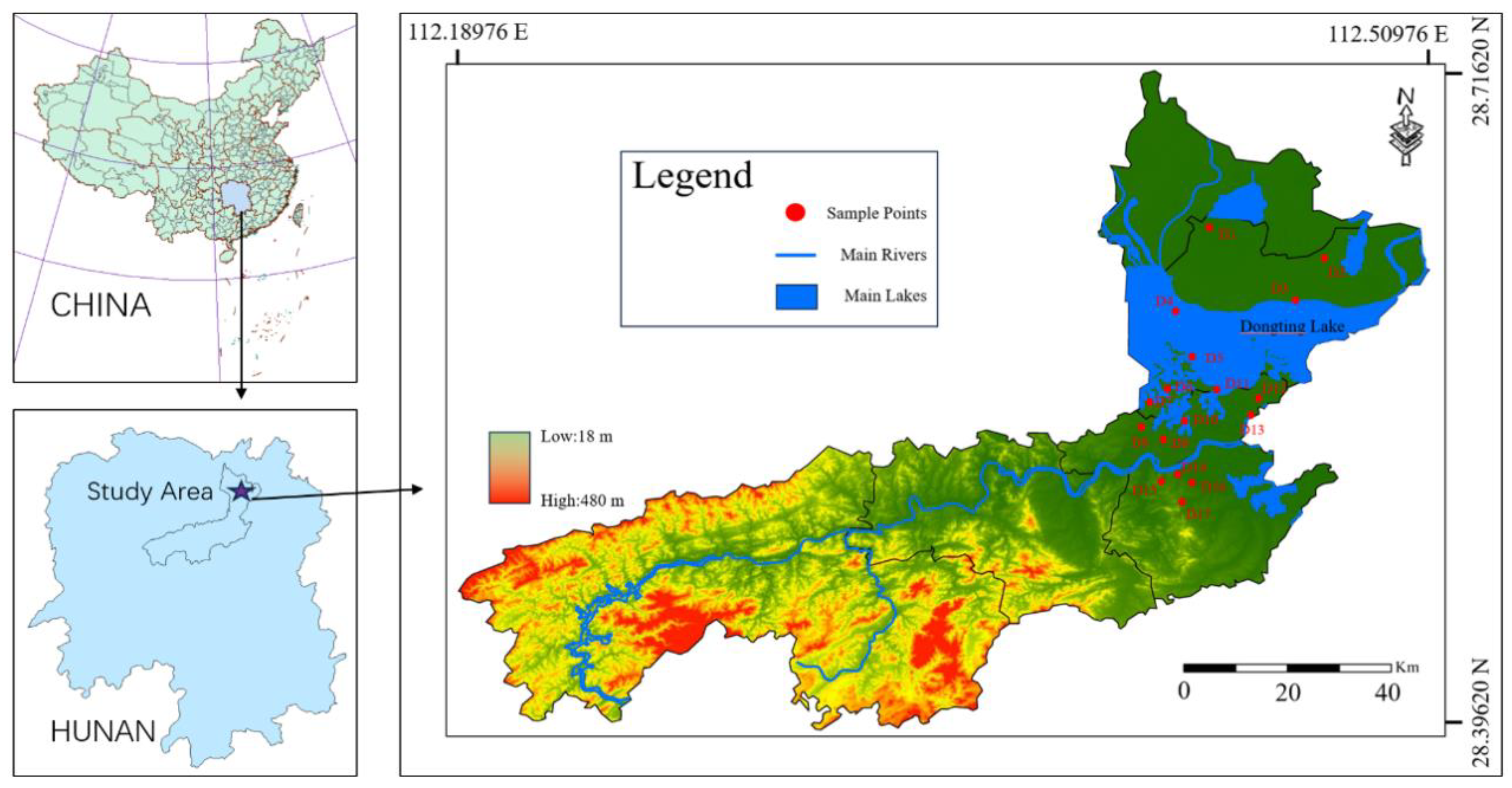
The study area is located in the Dongting Lake region, northern Yiyang City, Hunan Province, China, within the geographical coordinates of 28°44′–29°35′ N and 111°53′–113°05′ E (Figure 1). Yiyang is a typical lakeside city with a total population of approximately 4.75 million. It is one of the core cities in the Dongting Lake Ecological Economic Zone, featuring abundant surface water and groundwater resources. The region has a subtropical continental monsoon climate characterized by four distinct seasons, ample sunlight, plentiful rainfall, significant annual temperature differences, and notable regional variability. The precipitation is concentrated between April and July, with an annual average rainfall of approximately 1107 mm [20,21,22].
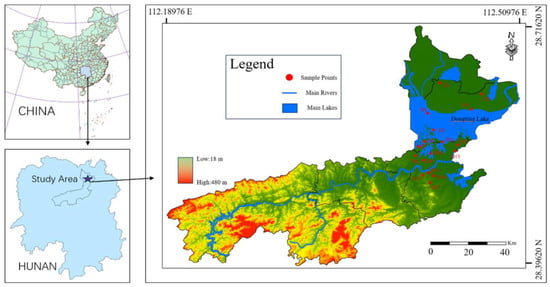
Figure 1.
Overview of Study Area Location and Sample Point Distribution.
The Dongting Lake region is a classic lake–wetland ecosystem. Benefiting from abundant water and fertile soil, the area is known as the “Land of Fish and Rice”. Agriculture and aquaculture are well-developed around the lake; however, the reliance on natural water resources for irrigation, combined with excessive fertilizer and pesticide usage, has led to soil and water pollution, potentially affecting groundwater quality [4]. The aquifer in the study area is primarily composed of sediments and silt, offering good permeability and water storage capacity. Despite the abundance of water resources, groundwater in the region faces pollution risks. Fertilizers and pesticides from agricultural activities infiltrate the groundwater through rainwater percolation, leading to increased concentrations of certain toxic elements. Additionally, the accelerated processes of urbanization and industrialization have resulted in increased industrial wastewater discharge, further exacerbating groundwater pollution [23].
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
In July 2021, 17 groundwater samples were collected from the study area (Figure 1). The depth of groundwater samples is generally between 15 m and 20 m. Before sampling, groundwater samples were tested on-site for pH (using a pH meter: Leici PHSJ-5, China), conductivity (Mettler Toledo SevenExcellence, Switzerland), color (visual comparison with standard color charts), odor (organoleptic assessment following EPA 6040B), taste (for non-toxic samples only), and dissolved oxygen (Hach HQ40d, USA). All instruments were calibrated according to the manufacturers’ protocols Sampling was conducted only after stabilization of all five parameters, defined as three consecutive measurements at 10-min intervals showing variations of less than ±5% for conductivity and dissolved oxygen, and less than ±0.2 units for pH. Color and odor were qualitatively assessed until consistent observations were recorded by two independent technicians. During the sampling process, original samples were collected in 500 mL high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles. Prior to sampling, each bottle was rinsed 2–3 times with the sample water. After parameter stabilization, a single composite sample (500 mL) was collected, and laboratory duplicate samples were analyzed for quality control. The samples were stored at low temperatures using ice packs in insulated coolers to prevent degradation. Special care was taken to avoid contamination from vehicle exhaust and ensure separate reagent storage for sample preservation.
In the laboratory, samples were vacuum-filtered using quartz filter paper preheated at 800 °C for 24 h, then acidified with concentrated HNO3. Concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cl−, F−, As, and Pb were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-Q-MS, PerkinElmer SCIEX ELAN DRC-e) under the following operating conditions: RF power 1500 W, plasma gas flow 15 L/min, auxiliary gas flow 1.2 L/min, nebulizer gas flow 0.98 L/min, dwell time 50 ms per isotope, and 3 replicates per sample. Quality assurance included 10% control group testing and instrument recalibration after every five samples [21]. Recovery experiments were conducted to validate the reliability of groundwater sample analyses. Blank water samples were spiked with standard solutions of Mn, Cu, Zn, Hg, As, Fe, Cl−, and F− at concentrations of 1.5 mg/L. Recovery rates ranged from 98.5% to 100.6%, confirming measurement accuracy.
2.3. Groundwater Pollution Assessment
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) is commonly used to evaluate the accumulation levels of heavy metals in groundwater. The impact of the difference between current concentration and background concentration is often considered for quantitatively assessing the degree of heavy metal pollution [21]. The formula for calculating the geo-accumulation index is as follows:
where Ci represents the concentration of heavy metal ii, and Bi denotes its environmental background level. The constant 1.5 compensates for background value fluctuations under natural conditions. The Igeo index is categorized into seven levels: unpolluted (≤0), slightly polluted (0–1), moderately polluted (1–2), moderately to heavily polluted (2–3), heavily polluted (3–4), heavily to severely polluted (4–5), and severely polluted (≥5) [7].
2.3.2. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
The pollution load index (PLI), introduced by Tomlinson in 1980, evaluates overall pollution levels of trace elements [22]. The PLI provides a comprehensive reflection of the pollution level of individual elements and has been widely used in studies of heavy metal pollution in soil. The formula for calculating PLI is as follows:
where CFi represents the pollution index of element i, Ci is the measured concentration of element i in the soil, and BVi represents the background value of element i. PLI values are classified as low pollution (<1), moderate pollution (1–2), high pollution (2–3), and severe pollution (≥3) [7,23].
2.4. Groundwater Pollution Prediction
2.4.1. Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW)
The inverse distance weighting (IDW) method is commonly used to predict the spatial autocorrelation distribution of heavy metal concentrations. Its principle is to assign weights to sampling points based on their distance to the target point, with closer points having higher weights. This allows for the estimation of heavy metal concentration values across the study area [24,25]. Compared to other spatial interpolation methods, IDW can handle extreme values (outliers) in the dataset and provide comprehensive predictions for unknown areas, yielding more accurate results. The IDW calculation is determined through a linear weighted combination of sample points, and the formula is as follows:
where Z∗ represents the predicted value of heavy metal concentration, Zi is the actual value at the i-th sampling point, λi is the weight coefficient of the observed value point for the predicted interpolation point, and n is the number of sampling points involved in the calculation.
2.4.2. Ordinary Kriging (OK)
The ordinary Kriging (OK) interpolation method is a spatial interpolation technique based on statistical theory, primarily used for interpolating sparse point data and predicting numerical values in observation areas [26]. The OK method establishes a variance function based on observed values and uses relationships among spatial data points—such as distance, angle, and variance—to perform interpolation, ensuring accuracy in the results [1]. The prediction formula for the OK method is as follows:
where Zx represents the predicted heavy metal concentration at an unobserved point, Zk is the observed value at point k, τi is the Kriging weight coefficient at point i, and n is the number of sampling points.
2.4.3. Model Validation
The applicability of the Kriging interpolation method and the inverse distance weighting (IDW) method is validated using the mean absolute error (MAE) in a cross-validation model. MAE represents the average magnitude of errors without being influenced by outliers and is commonly used to measure the error between predicted values (PV) and observed values (OV). A smaller MAE value between PV and OV indicates that the method is more suitable for this study [16]. The formula for calculating MAE is as follows:
where n is the number of samples, X∗ is the predicted value at the sampling point, and X is the observed value at the sampling point.
2.5. Groundwater Source Analysis
2.5.1. Self-Organizing Maps (SOM)
The self-organizing map (SOM) algorithm is an unsupervised computational method first proposed by Kohonen, and, therefore, often referred to as the Kohonen Map [27]. It comprises input and output layers, where each sample element concentration is defined as an N-dimensional input vector. The algorithm computes the Euclidean distance between a neuron and vector X to train the network. After passing through the input layer, the data forms a neural network that outputs a hexagonal arrangement in the output layer [28,29]. The Euclidean distance Di is calculated as:
where Wj represents the weight vector of the j-th neuron in the competitive layer, ωij is the weight between the i-th neuron in the input layer and the j-th neuron in the competitive layer, and n is the number of input vectors. During the computation, there is no established rule for determining the number of neurons in the input layer. In this study, the number of neurons is determined using the formula m = 5 × (n)1/2, where m represents the number of nodes in the self-organizing map.
2.5.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
Principal component analysis (PCA) is commonly used to identify and explore the potential sources of PTE pollution through factor loading [30]. The computation formula is:
where represents the j-th variable in the i-th sample. Then, the matrix Xij is standardized to obtain Zij, and the formula for standardization is as follows:
where represents the mean value, and represents the standard deviation. The standardized correlation matrix is then computed to obtain k eigenvalues and eigenvectors gj. The eigenvalues are arranged in descending order. Next, the principal components Rj are determined using the formula:
When the cumulative contribution rate of the j-th principal component exceeds 85%, the first p principal components R1, R2, …Rp are selected. These p principal components are considered to comprehensively represent the information of the evaluation indicators. Finally, the cumulative variance contribution rate is calculated using Formula (12).
2.6. Health Risk Assessment Model
The health risk assessment model recommended by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) quantifies potential health risks posed by heavy metals in groundwater. Risks are categorized as carcinogenic (CR) or non-carcinogenic (NCR). CR measures the probability of cancer due to exposure, while NCR assesses risks for other health issues. Evaluating both CR and NCR provides a comprehensive understanding of health hazards and helps guide policy measures to mitigate risks.
2.6.1. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
The hazard quotient (HQ) is commonly used to represent non-carcinogenic risk, while the hazard index (HI) evaluates the overall non-carcinogenic risk of all harmful elements. HI is the sum of non-carcinogenic risks through ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact pathways. However, in this study, ingestion is the only pathway considered, as previous research indicates that consuming heavy-metal-contaminated groundwater is the sole pathway through which water pollution affects human health [31]. The formula for calculating the non-carcinogenic risk from ingesting contaminated groundwater is:
where Cwater (mg/L) represents the concentration of PTEs in groundwater. Other parameter indicators are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The formula for calculating HI is:
where RFD (mg/L/day) represents the reference dose, an estimate of the daily intake of a trace element that is unlikely to pose health risks [32]. When HI ≤ 1, the total non-carcinogenic hazard quotient is within an acceptable range, and the risk to human health can be considered negligible.
2.6.2. Carcinogenic Risk
Ingestion of contaminated groundwater can pose carcinogenic risks to human health. The carcinogenic health risk caused by heavy metal elements through oral ingestion is evaluated by multiplying the daily intake of the pollutant by the slope factor (SF) (kg·d/mg). The calculation formula is:
The CRingest represents the carcinogenic risk through the ingestion pathway, and according to the threshold reference for carcinogenic risk, when the cancer risk index (CR) is less than 1 × 10−6, the risk can be considered negligible; when 1 × 10−6 < CR < 1 × 10−4, the risk is deemed acceptable; and when CR > 11 × 10−4, there is a higher cancer risk, requiring appropriate measures to mitigate the risk [33].
2.7. Data Processing
Data processing was performed using Excel 2023 and SPSS 26.0, while MATLAB R2023b was used for SOM analysis. PCA results were analyzed using Origin 2021, and ArcGIS 10.8 facilitated spatial prediction and visualization of heavy metal distribution and pollution potential in the study area.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PTE Pollution Levels in Groundwater
The chemical analysis of 17 groundwater samples revealed that the pH values in the study area ranged from 5.65 to 6.98, with all samples exhibiting acidic properties (pH < 7). The average oxygen consumption rate was 0.845 mg/L, varying between 0.68 and 1.72 mg/L. As shown in Table 1, the average concentrations of all elements exceeded their background levels, with the exception of mercury and F−. Mn was 28.6 times the background level, followed by Cu at 16.7 times. Among the 17 groundwater samples, Cu and Hg exhibited significant point source pollution, with Hg exceeding the concentration limit at a single sample point and Cu exceeding the limit at two sample points, with values of 0.88 mg/L and 0.00356 mg/L, respectively. The severe point source pollution of Cu was the primary reason for the overall increase in its average concentration. The main sources of Hg pollution typically include industrial emissions, coal combustion, electronic products, and metal smelting. However, based on the actual conditions of the study area, none of these pollution sources are present, indicating that Hg in the samples likely originates from natural crustal weathering. Thus, the point source pollution of Cu and Hg does not represent the overall groundwater quality. Consequently, Mn, As, Zn, Cl−, and Fe are identified as the main groundwater pollutants in the study area. The Dongting Lake basin, renowned as the “Land of Fish and Rice”, suggests that the primary cause of PTE accumulation in groundwater is agricultural activities, including pesticide and fertilizer use [34,35].

Table 1.
Descriptive Analysis of PTEs in Groundwater (mg/L).
The coefficient of variation (CV) is commonly used to indicate the variability in heavy metal (HM) concentrations. A CV value of ≤20% indicates low variability; 21% < CV ≤ 50% indicates moderate variability; 51% < CV ≤ 100% indicates high variability; and a CV value of >100% indicates extremely high variability [36]. In this study, only F− exhibited high variability, while all other elements reached extremely high variability levels. Cu showed the highest CV value of 4.07, followed by Zn with a CV of 2.45. Higher CV values indicate that PTEs are more significantly influenced by external factors, demonstrating that the PTE pollution in the study area is primarily caused by human activities [22]. Therefore, the statistical analysis results indicate that Mn, As, Zn, Cl−, and Fe are the key elements of concern in the Yiyang section of the Dongting Lake Basin. However, compared to other groundwater studies in the Dongting Lake Basin, the average concentration of Cl− in this study area is relatively low—yet it still warrants attention [37,38,39,40].
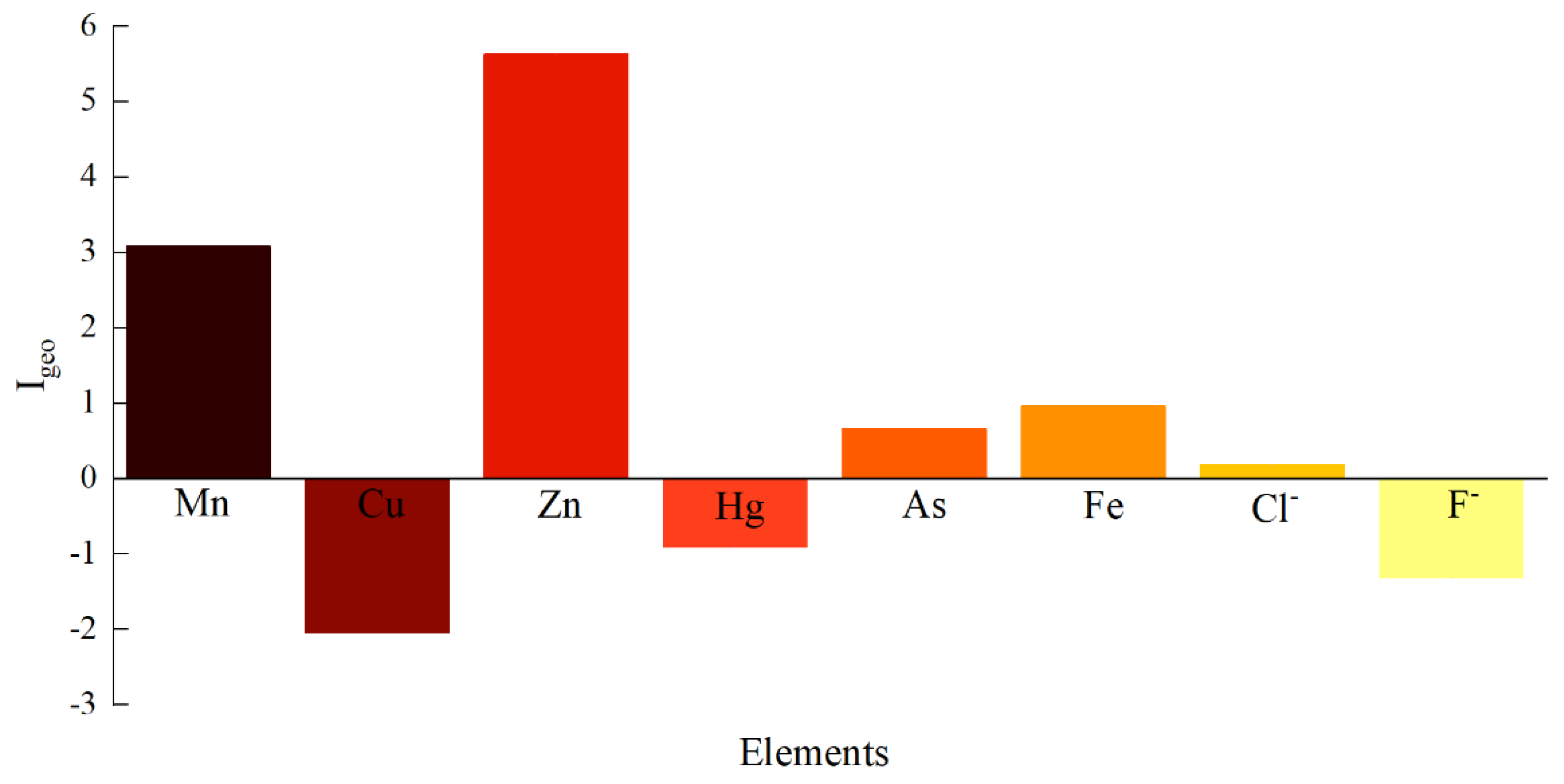
As shown in Figure 2, the average Igeo values of PTEs in the Dongting Lake basin are ranked as follows: Zn (5.63) > Mn (3.08) > Fe (0.97) > As (0.66) > Cl− (0.19) > Hg (−0.91) > F− (−1.31) > Cu (−2.04). Table S2 shows the geo-accumulation index of the sampling point and a single potential pollution element. The average Igeo values of Hg, F−, and Cu are less than 0, categorizing them as “unpolluted”. As, Cl−, and Fe fall within the “slightly polluted” range. Mn is classified as “moderate to severe pollution”, while Zn exhibits the most severe pollution, reaching the “heavily polluted” category. Compared to PTE concentrations in other lake basins, the groundwater pollution in the study area is significantly higher than that in Pakistan, India, and the Yellow River basin of China, warranting attention [34,41,42].
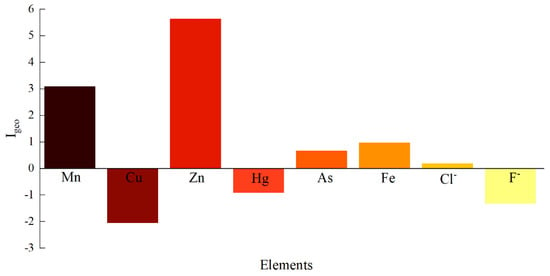
Figure 2.
Geo-Accumulation Index of PTEs.
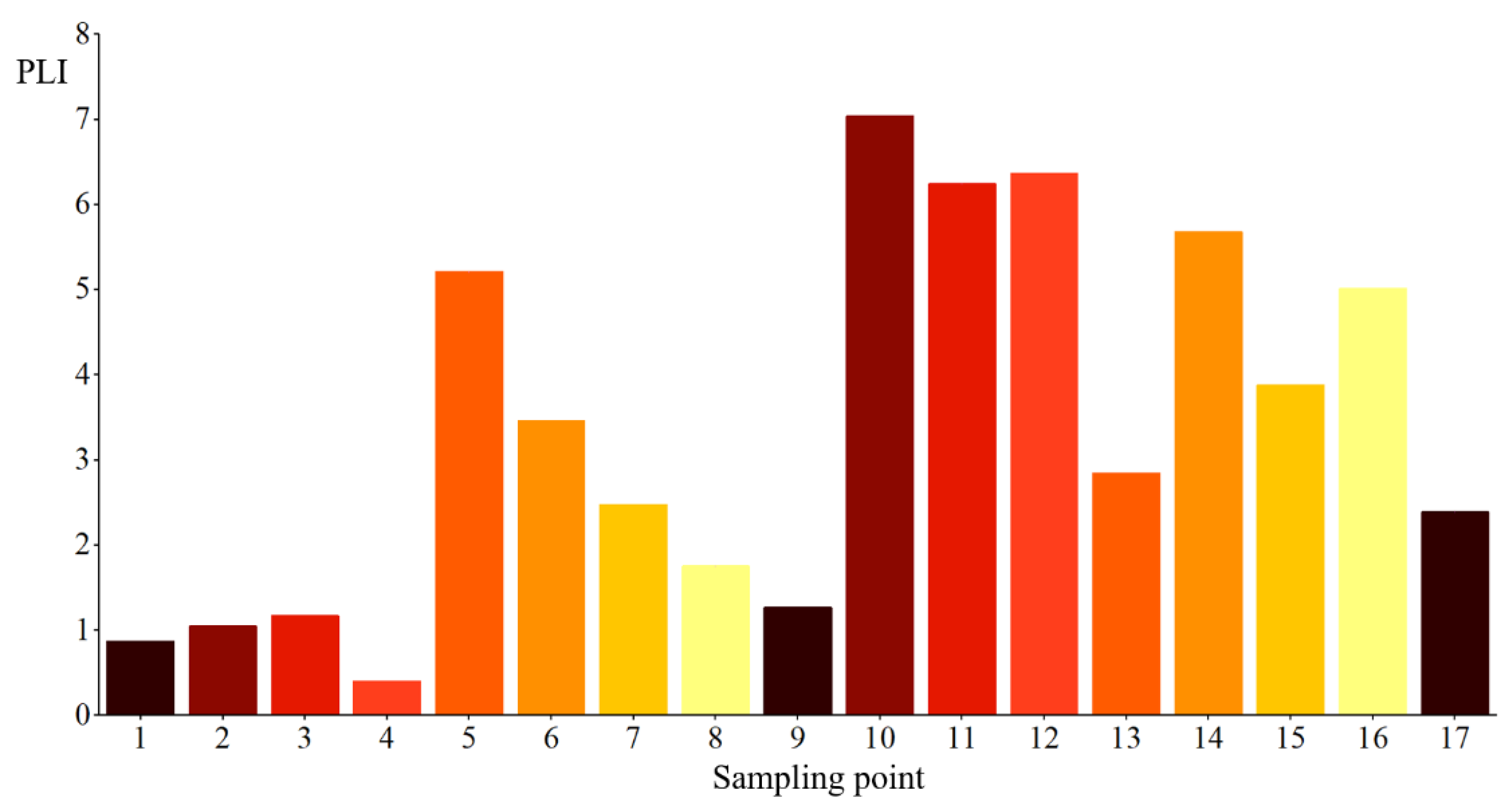
As shown in Figure 3, the PLI values of PTEs in groundwater samples from the Dongting Lake basin range from 0.397 to 7.04, with an average value of 3.36. Among the 17 sampling points, the PLI classification results are as follows: two samples fall under “low pollution”, four under “moderate pollution”, three under “high pollution”, and the remaining eight samples are categorized as “severe pollution”. Based on the representative sampling points, approximately 47.05% of the study area is severely polluted by PTEs. Therefore, the groundwater pollution in the Yiyang section of the Dongting Lake basin is defined as a evere pollution level [38].
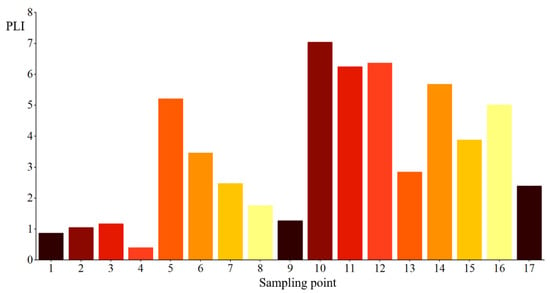
Figure 3.
Pollution Load Index of Sample Points.
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Groundwater PTEs Pollution
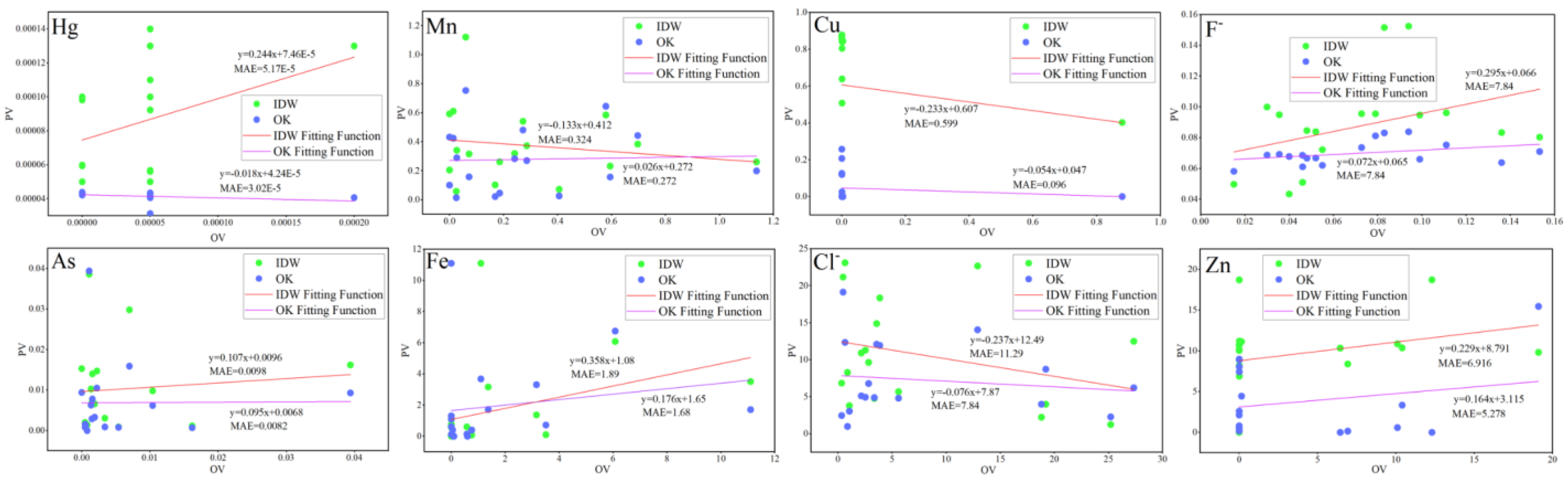
Figure 4 displays the fitting curves of observed (OVs) and predicted values (PVs) for PTEs using IDW and OK methods. For all eight PTEs, the mean absolute error (MAE) of OK interpolation was consistently lower than that of IDW, indicating the higher suitability of OK for this study [43].
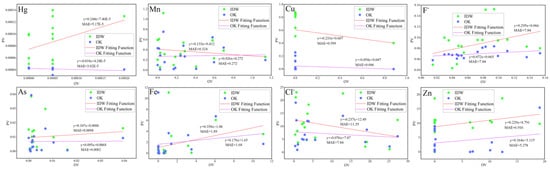
Figure 4.
Fitting Functions of PTEs by IDW and OK Methods.
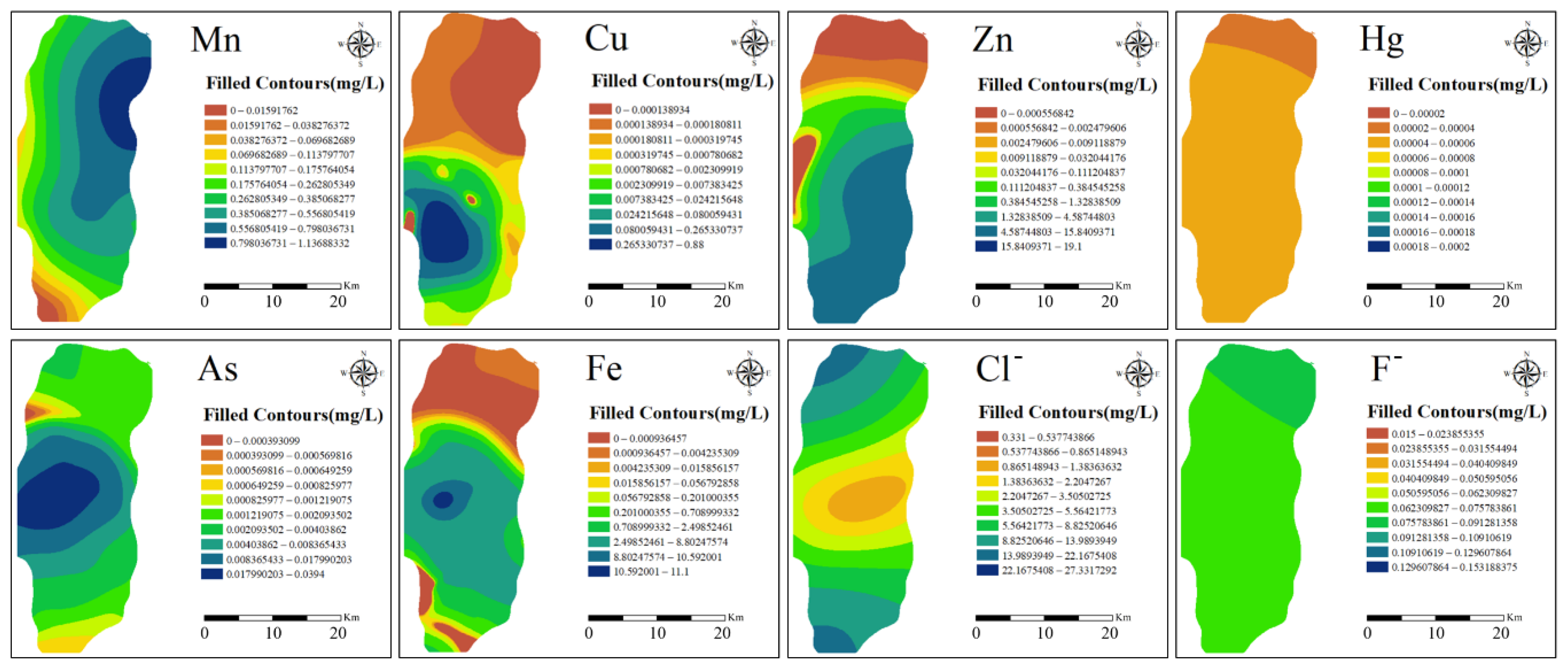
Figure 5 illustrates the spatial distribution of PTE concentrations in groundwater as predicted by OK. The distribution patterns of Hg and F− are similar, with no apparent high-concentration areas, suggesting these elements originate from natural sources. Mn exhibits significant enrichment in the northeastern part of the study area. Cu, As, and Fe share similar distribution patterns, with high concentrations in the southwestern urbanized region. Zn shows high concentrations in the southeastern area, while Cl− exhibits a central low-concentration zone flanked by high concentrations on both sides.
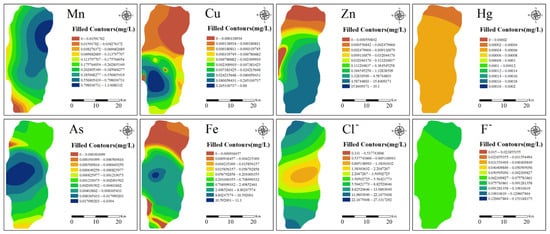
Figure 5.
Spatial Filling Distribution of PTEs.
Based on the spatial distribution results of the study area and field investigations, the following conclusions can be drawn:
(1) Agriculture is the primary economic activity in the Dongting Lake basin and a direct source of PTE pollution in groundwater [38]. Agricultural activities contribute to PTE contamination in both the Yangtze River and the Dongting Lake basin. In the Yangtze River basin, agricultural pollution is primarily associated with surface water irrigation. The use of fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides introduces PTEs into surface water through river runoff and natural leaching, which subsequently infiltrates the groundwater in the Dongting Lake basin. Fertilizer solutions used in agricultural irrigation contribute to the accumulation of PTEs in groundwater, including Mn, As, and chlorides [21]. Known as the “Land of Fish and Rice”, the Dongting Lake basin relies heavily on aquaculture and paddy farming. The extensive use of fishery fertilizers in aquaculture and pesticides in rice cultivation leads to the accumulation of toxic elements such as Cu, Fe, and As, which can permeate into the groundwater [19,23].
(2) Urban industrialization near the Dongting Lake basin has accelerated groundwater pollution. Cu is a representative pollutant from industrial activities in the study area, with high-concentration Cu contamination observed in urban clusters. Industrial wastewater containing Cu from production processes infiltrates the groundwater, resulting in water contamination [5]. Additionally, industrial activities such as smelting, chemical manufacturing, mining, and electroplating produce wastewater rich in Mn, Zn, Fe, and chlorides. Untreated or improperly treated urban sewage and industrial wastewater often lead to the leaching of toxic elements into groundwater [44]. Improper landfill and waste dumping during urbanization generate leachate containing heavy metals and other toxic pollutants, further contributing to groundwater contamination.
(3) The weathering and dissolution of rocks, minerals, and soils in the Dongting Lake basin also contribute to groundwater pollution. Studies indicate that fluoride contamination in the natural environment primarily results from the dissolution of fluoride-rich minerals in the soil. The leaching of Fe is influenced by soil erosion and washing, while chloride contamination mainly originates from leachates in saline-alkali lands. The weathering and dissolution of certain soils and rocks in the Dongting Lake basin introduce PTEs into groundwater, representing a natural source of contamination [19,25].
3.3. Sources of Groundwater PTE Pollution
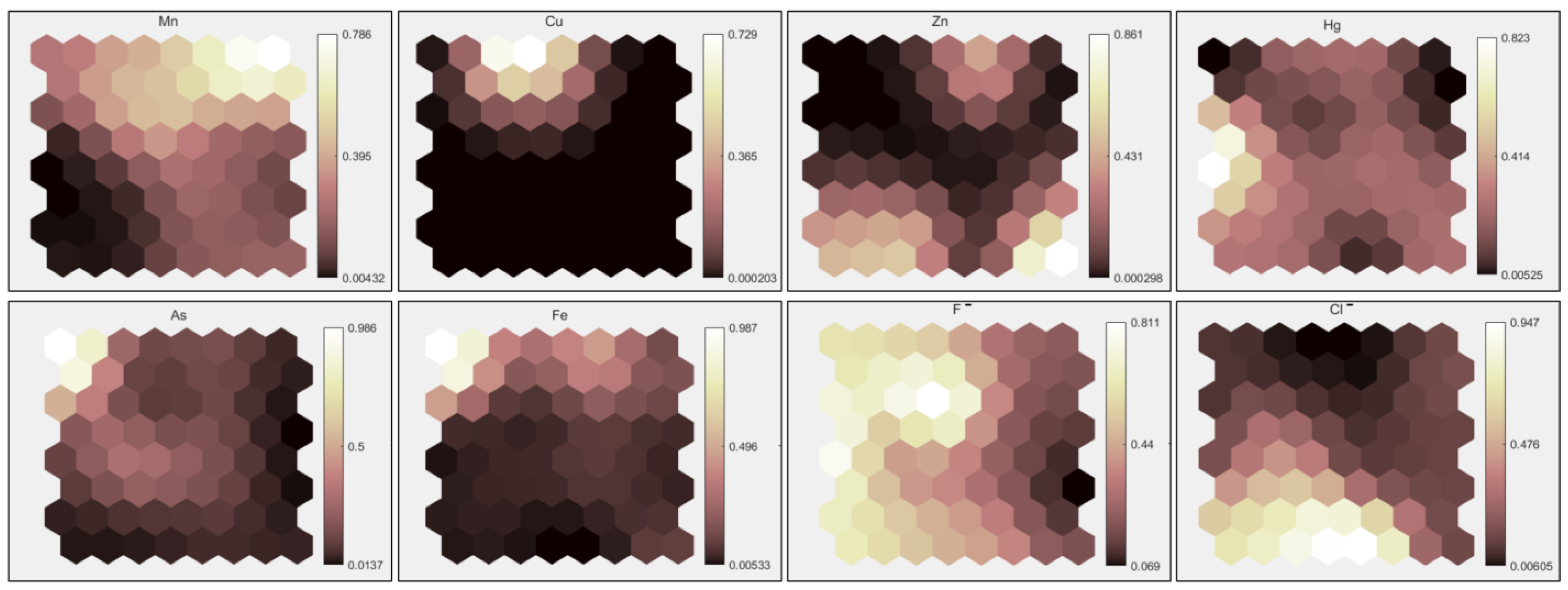
The correlation of PTEs in groundwater within the Dongting Lake basin was analyzed using the SOM method, as shown in the SOM analysis output plane of the study elements. The SOM output plane is categorized by color gradients, where different color levels represent the significance of each variable on the output plane. Each node in the plane represents the reference value of the input vector, ranging from 0 to 1, with yellow indicating low concentrations and white representing high concentrations. Similar or overlapping color distributions between variables on the SOM output plane indicate that the variables share the same distribution patterns [28]. As shown in Figure 6, the high concentrations of Mn, Fe, As, and Cu are primarily concentrated in the upper half of the output plane. Mn tends to be located in the upper-right corner, while As and Fe show similar distributions, with high concentrations in the upper-left corner. High concentrations of fluoride and Hg are clustered on the left plane, whereas chlorides and Zn are concentrated in the lower half of the plane. Based on the SOM output results, the study elements are broadly classified into three groups: Mn, Fe, As, and Cu form the first group, where Mn and Cu show a weak correlation, while As and Fe exhibit a strong correlation. Fluoride and Hg constitute the second group, while chlorides and Zn form the third group, both showing strong internal correlations.
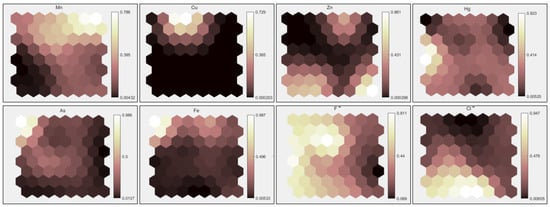
Figure 6.
SOM Competitive Output Network for PTEs.
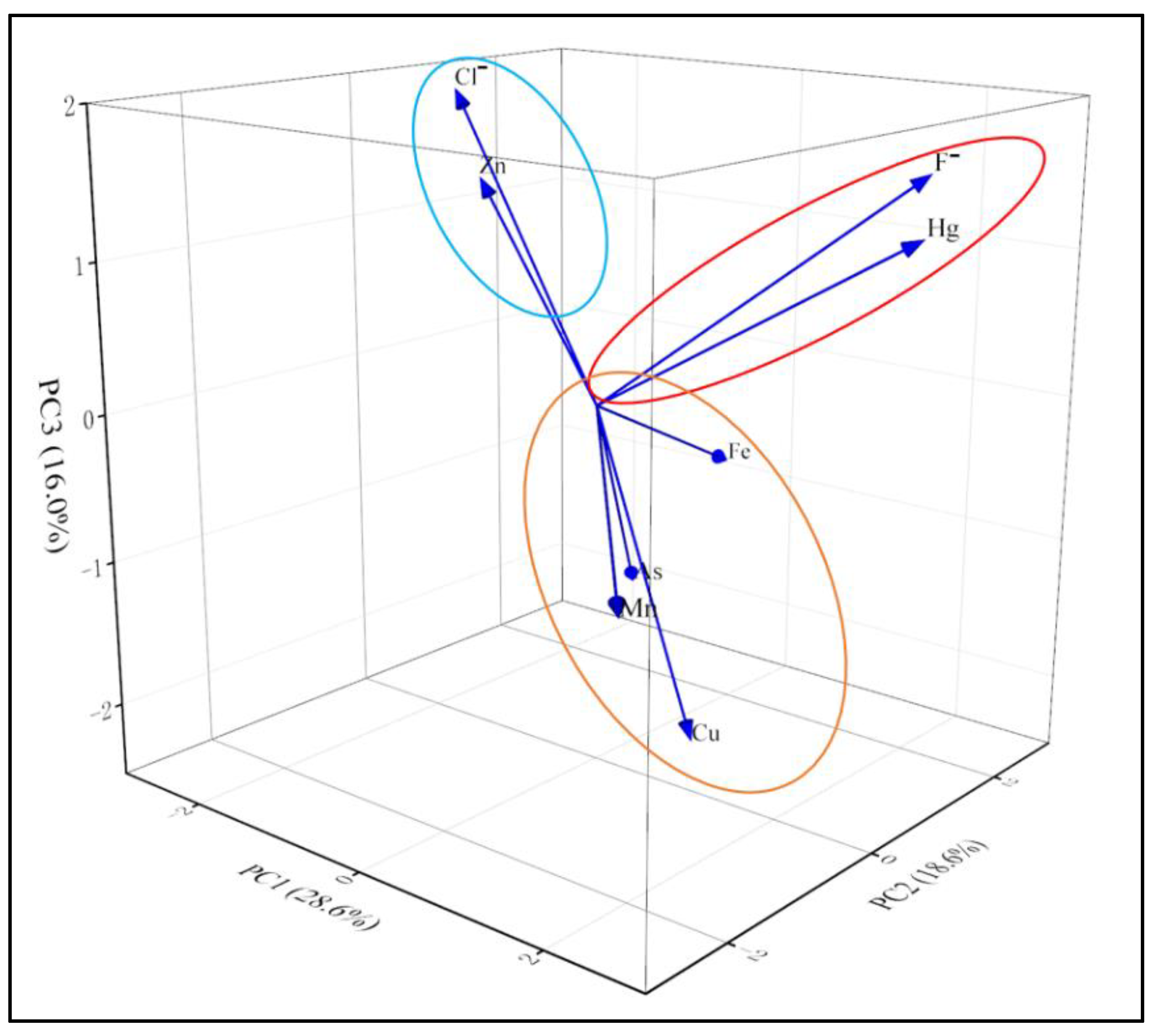
PCA is often used to identify the sources of PTEs in water. Table 2 shows the eigenvalues and cumulative contribution rates of principal components 1, 2, and 3. Figure 7 shows that PC1 has the highest cumulative contribution rate, reaching 28.6%, and is primarily composed of Mn, Cu, As, and Fe. The consistency between the PCA and SOM results suggests that these four elements likely share similar sources. The Dongting Lake basin is known for its extensive agriculture and aquaculture. Fertilizers and pesticides used in these industries are rich in PTEs, and studies indicate that groundwater contamination with Mn and Cu is linked to anthropogenic activities such as agricultural practices and domestic wastewater discharge. Additionally, Cu and Fe are often used as feed additives and preservatives. However, many animals have low absorption efficiency for these PTEs, leading to substantial unabsorbed amounts entering the groundwater system and causing contamination. Among the four elements in PC1, As is commonly used in pesticides and insecticides. Previous studies have shown that the improper use of herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers accelerates the accumulation of As in groundwater [34]. Furthermore, industrial wastewater from sectors such as smelting, chemical production, and electroplating frequently contains toxic elements like Mn, Cu, As, and Fe, which can easily infiltrate groundwater and cause contamination. Thus, PC1 can be defined as a pollution source dominated by anthropogenic activities, primarily driven by agricultural practices, with industrial production also contributing to the process [3,16].

Table 2.
Eigenvalues and Variance Contribution Rates of PCA.
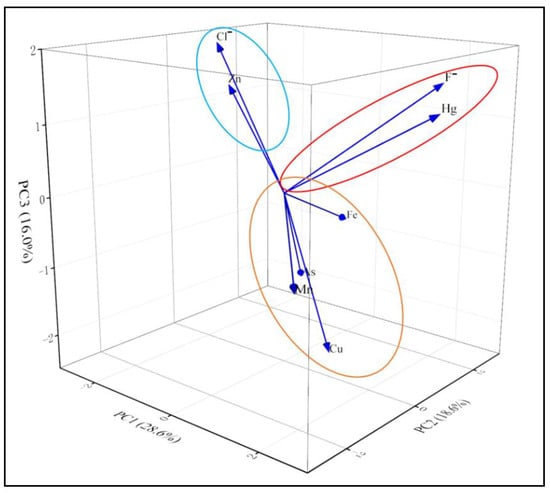
Figure 7.
PCA Analysis of PTEs.
In PC2, F− and Hg show higher contributions, accounting for 18.6%, with a clear correlation observed between them in the SOM results. The average concentrations of F− and Hg in the samples are below the environmental background values, and their spatial distribution is relatively uniform in the analysis. Therefore, PC2 primarily represents the impact of natural weathering on groundwater pollution in the Dongting Lake basin. In PC3, Cl− and Zn are the dominant elements, contributing 16%. Previous studies have indicated that Cl⁻ primarily originates from industrial pollution, including chemical production and salt manufacturing [41,45].
Additionally, studies in the western Dongting Lake basin have identified Zn as an industrial pollutant source, particularly from activities such as electroplating and smelting. Other studies have also shown that the enrichment of Zn and Cl− in groundwater is linked to the overuse of Zn-containing fertilizers and the infiltration of Cl−-rich fertilizers from agricultural practices [22,46]. Thus, PC3 mainly represents industrial pollution sources, with some contributions from agricultural production activities.
In summary, the primary sources of PTE pollution in the groundwater environment of the Dongting Lake basin are anthropogenic. The leading contributor is agricultural production activities, including the use of pesticides, feed additives, herbicides, and preservatives. The second contributor is natural weathering, including rock weathering and soil leaching. The third source is industrial production activities, such as wastewater discharges from chemical production, salt manufacturing, electroplating, and smelting industries. Future research in this area should focus on regulating agricultural practices and implementing appropriate measures to prevent further groundwater quality deterioration.
3.4. Health Risks of Groundwater PTEs Pollution
A health risk assessment of groundwater samples from the Dongting Lake basin was conducted for oral ingestion exposure. Table 3 presents the hazard quotient (HQ) and hazard index (HI) associated with non-carcinogenic risks posed by the studied elements. For adults, the HI values of PTEs are ranked as follows: As > Zn > Fe > Mn > F− > Cu > Cl− > Hg, and the same ranking applies to children. In both groups, As was identified as the element with the highest non-carcinogenic health risk, and the risk of As exposure for children was significantly higher than for adults. Ingesting groundwater with elevated As concentrations can lead to a range of health issues, including skin disorders, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory problems, and reproductive and developmental impacts. Long-term accumulation of As in the human body may also result in neurological and immune system damage [35]. As contamination in groundwater should be a primary focus, and children, as a vulnerable population, require particular attention [47].

Table 3.
Hazard Quotient (HQ) and Hazard Index (HI) for Non-Carcinogenic Risks.
Oral ingestion of groundwater contaminated with PTEs can also pose carcinogenic risks to humans [36]. In this study, aside from As, no other studied elements had reliable carcinogenic slope factor (SF) data or were classified as low-risk non-carcinogenic substances. Therefore, the carcinogenic risk assessment focused solely on the effects of As. The SF value for As through oral ingestion is 1.5, and the calculated results show that As poses a carcinogenic risk of 7.5 × 10−4 for adults and 6.02 × 10−3 for children. In both groups, As presents a significant carcinogenic risk, with children being more susceptible to its effects than adults in the study area [15,36]. Future groundwater pollution and health risk management in the study area should prioritize the control and mitigation of As contamination.
4. Conclusions
This study conducted a systematic analysis of the pollution status of potentially toxic elements in the groundwater of the Dongting Lake basin, aiming to evaluate the safety of regional groundwater resources and their impact on human health. First, the study provided an overview of the geographical features and hydrological environment of the Dongting Lake basin, emphasizing its critical role in the ecosystem and regional economic development. Subsequently, groundwater samples from multiple monitoring points were collected and analyzed to examine the concentration distribution, pollution sources, and health risks of common toxic elements such as Mn, Cu, Zn, As, Hg, Fe, Cl⁻, and F⁻.
The results revealed that groundwater in the Dongting Lake basin generally falls into the severe pollution category. Geo-accumulation index analysis identified Zn as the most severe pollutant, reaching the “heavily polluted” level, while Mn was classified as “moderate to severe pollution”. The primary sources of contamination were anthropogenic activities, including excessive fertilizer and pesticide application, industrial wastewater discharge, and urbanization processes. The prolonged overuse of fertilizers and pesticides in agricultural practices, coupled with inadequate wastewater treatment facilities and the improper operation of certain industrial facilities, has significantly exacerbated the accumulation of PTEs in groundwater. Furthermore, As was identified as the most hazardous element to human health, posing a high carcinogenic risk, particularly to children.
From a sustainable development perspective, controlling toxic element pollution is not only an environmental protection issue but also a critical step in ensuring sustainable water resource utilization and maintaining ecosystem health. Notably, the acidification trend of groundwater may exacerbate heavy metal migration, and this cumulative effect will pose long-term challenges to the sustainable development of the basin. Therefore, establishing an ecologically sensitive groundwater monitoring and early warning system, along with implementing integrated management strategies that combine pollution source control with ecological restoration, is an essential approach to achieving sustainable water resource management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17083554/s1, Table S1. Exposure Factors Used in Estimation of Non-Carcinogenic Risk; Table S2. The Geo-Accumulation Index of the Sampling Point and a Single Potential Pollution Element.
Author Contributions
X.D.: Methodology, Writing—Original, Investigation. H.Z.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft and Editing and Visualization, Investigation. B.R.: Conceptualization, Supervision. J.W.: Investigation. L.C.: Investigation, Resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department, with the support numbers of [41973078] and [2022SK2073] respectively, and APC is supported by [2022SK2073].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
This paper was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 41973078) and the Key R&D Project of Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department (Project No. 2022SK2073).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Zhan, Y. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, A.; Mehra, R.; Kaur, I. Quantitative assessment of exposure of heavy metals in groundwater and soil on human health in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, S.; Azarnivand, A.; Chitsaz, N. Groundwater quality classification derivation using Multi-Criteria-Decision-Making techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Deng, S.; Tan, D.; Long, J.; Lei, M. Heavy metal distribution, translocation, and human health risk assessment in the soil-rice system around Dongting Lake area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17655–17665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Bai, B. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, J. Characterization of heavy metal pollution in the paddy soils of Xiangyin County, Dongting lake drainage basin, central south China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B. Analyzing topsoil heavy metal pollution sources and ecological risks around antimony mine waste sites by a joint methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Bose, J. Evaluation of the heavy metal pollution index for surface and spring water near a limestone mining area of the lower Himalayas. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.N.; Panahande, M.; Yousefi, M.; Asghari, F.B.; Conti, G.O.; Talaee, E.; Mohammadi, A.A. Carcinogenic and Non-carcinogenic Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Groundwater Wells in Neyshabur Plain, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Yin, W.; Xie, Q.; Cai, Z. Potential toxic heavy metals in village rainwater runoff of antimony mining area, China: Distribution, pollution sources, and risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 920, 170702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yin, Y.; Du, W.; Wu, J.; Guo, H. A green sulfidated micro zero-valent iron based-hydrogel for the synergistic removal of heavy metal cations and anions in groundwater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2025, 972, 179096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, A.A.; Ojekunle, Z.O. Concentrations and health risk assessment of industrial heavy metals pollution in groundwater in Ogun state, Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2021, 11, e00666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Shirazi, S.A.; Mazhar, U. Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater Pollution in Kotlakhpat Industrial Complex, Lahore. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, R.; Kulkarni, D.B.; Khanna, D.R.; Gautam, A. Geochemical distribution and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area and its surroundings, Haridwar, India. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, V.M.; Panaskar, D.B.; Mukate, S.V.; Gaikwad, S.K.; Muley, A.A.; Varade, A.M. Health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in groundwater of Kadava River Basin, Nashik, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Li, T. Geographic distribution, source analysis, and ecological risk assessment of PTEs in the topsoil of different land uses around the antimony tailings tank: A case study of Longwangchi tailings pond, Hunan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, W.-Q.; Ren, B.-Z.; Xie, Q.; Cai, Z.-Q.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, J. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment: A study on Linli County soils based on self-organizing map and positive factorization approaches. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 31, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Bao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Gao, P. A statistical approach for determining the environment impact of surface sediments from the Dongting Lake area, central China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2009, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z. Comparison between BCR sequential extraction and geo-accumulation method to evaluate metal mobility in sediments of Dongting Lake, Central China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2008, 26, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makokha, V.A.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. Concentrations, Distribution, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Yin, W.; Xie, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zou, H. Black shale bedrock control of soil heavy metal typical high geological background in China Loushao Basin: Pollution characteristics, source and Influence assessment based on spatial analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Su, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Middleton, B.A.; Lei, T. Correction: Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the West Dongting Lake floodplain, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Liu, H.; Hao, S.; Mao, K. Characterization of heavy metal contamination in groundwater of typical mining area in Hunan Province. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, X. Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: Status, health risks and control measures. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Ren, B.; Shi, X.; Hursthouse, A. Factors on the distribution, migration, and leaching of potential toxic metals in the soil and risk assessment around the zinc smelter. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyankware, M.O.; Akakuru, O.C.; Osisanya, W.O.; Umayah, S.O.; Ukor, K.P. Assessment of heavy metal pollution on groundwater quality in the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goix, S.; Resongles, E.; Point, D.; Oliva, P.; Duprey, J.L.; de la Galvez, E.; Ugarte, L.; Huayta, C.; Prunier, J.; Zouiten, C.; et al. Transplantation of epiphytic bioaccumulators (Tillandsia capillaris) for high spatial resolution biomonitoring of trace elements and point sources deconvolution in a complex mining/smelting urban context. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, K.; Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Dey, P.; Bosu, S.; Datta, D.K.; Rijnaarts, H.H. Spatio-temporal variations in chemical-physical water quality parameters influencing water reuse for irrigated agriculture in tropical urbanized deltas. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 708, 134559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, X.K.; Wang, W.T. Using Kriging with a heterogeneous measurement error to improve the accuracy of extreme precipitation return level estimation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebonye, N.M.; Eze, P.N.; John, K.; Gholizadeh, A.; Dajčl, J.; Drábek, O.; Němeček, K.; Borůvka, L. Self-organizing map artificial neural networks and sequential Gaussian simulation technique for mapping potentially toxic element hotspots in polluted mining soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 222, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, G.; Yang, C.; Liang, K.; Ma, S.; Huang, L. Using self-organizing map for coastal water quality classification: Towards a better understanding of patterns and processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Tao, H.; Gong, X.; Li, Y. Exploring the database of a soil environmental survey using a geo-self-organizing map: A pilot study. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.; Deng, R.; Wang, Z. Distribution, source identification, and ecological-health risks of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in soil of thallium mine area (southwestern Guizhou, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16556–16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, K.; Mor, S. Distribution and health risk assessment of arsenic and selected heavy metals in Groundwater of Chandigarh, India. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaie, A.H.; Aghili, F. Health risk assessment of Pb and Cd in soil, wheat, and barley in Shazand County, central of Iran. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, L.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhu, P.; Fu, S.; Liang, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in contaminated paddy fields—A case study in Xiangtan City, southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Hui, K.; Su, J.; Tan, W. Seasonal variations in health risks associated with nitrates and heavy metals in groundwater: A case study of typical regions along the riverside plain in China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 196, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yin, L.; Wen, X.; Du, C.; Wu, L.; Long, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Microplastics in Sediment and Surface Water of West Dongting Lake and South Dongting Lake: Abundance, Source and Composition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Study on Hydrochemical Characteristics and Interactions between Groundwater and Surface Water in the Dongting Lake Plain. Water 2024, 16, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Taniguchi, M.; Liu, G.; Miyaoka, K.; Onodera, S.-I.; Tokunaga, T.; Fukushima, Y. Nitrate pollution of groundwater in the Yellow River delta, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Batool, S.; Farooqi, A. Chapter 22—Groundwater pollution in Pakistan. In Global Groundwater; Mukherjee, A., Scanlon, B.R., Aureli, A., Langan, S., Guo, H., McKenzie, A.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, M.; Qie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, R.; Li, L.; Lin, A. Health risk assessment based on source identification of heavy metals: A case study of Beiyun River, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B. Trends and risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of river-connected lakes: A case study of Dongting Lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Tang, L.; Xie, Y.; Gao, W.; Tan, X.; Zeng, J. Groundwater heavy metal(loid)s risk prediction based on topsoil contamination and aquifer vulnerability at a zinc smelting site. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.D.; Van Leeuwen, P.; Davis, B.D.; Maddaloni, M.; A Hogan, K.; Marcus, A.H.; Elias, R.W. The conceptual structure of the integrated exposure uptake biokinetic model for lead in children. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 1998, 106, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).