Screening and Identification of SOB and Its Effect on the Reduction in H2S in Dairy Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Screening Method of Strain
2.2.2. Strain Identification
2.2.3. Genome Analysis of Halomonas sp. AEB2
2.2.4. Carbon and Nitrogen Sources and Dosage Optimization of the AEB2 Strain
2.2.5. Effect of Different Environmental Conditions on the S2− Removal Rate and OD Value
2.2.6. S2− Product Analysis
2.3. Determination Methods
2.4. Statistical Methods for Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Strain Screening
3.2. AEB2 Strain Identification
3.2.1. Morphological Identification of AEB2 Strain
3.2.2. Physiological and Biochemical Identification of the AEB2 Strain
3.3. The Genome and Comparative Genome Studies of Halomonas Sp. AEB2
3.3.1. Genetic Identification of AEB2 Strain
3.3.2. Genomic Characteristics
3.3.3. Comparative Genomic Results
3.4. Conditions Optimization and Application of AEB2
3.4.1. Carbon and Nitrogen Source Optimizations of AEB2
3.4.2. Operation Factors Optimization of AEB2
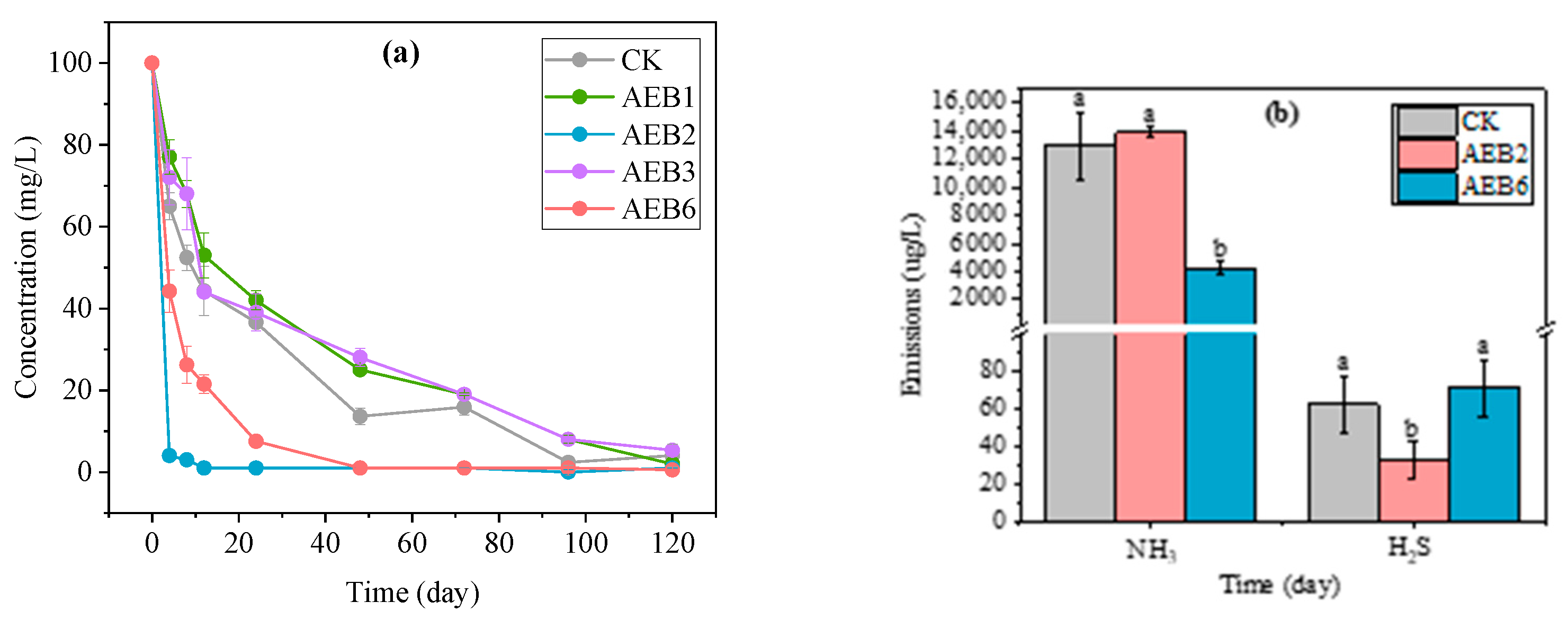
3.4.3. Application of AEB2
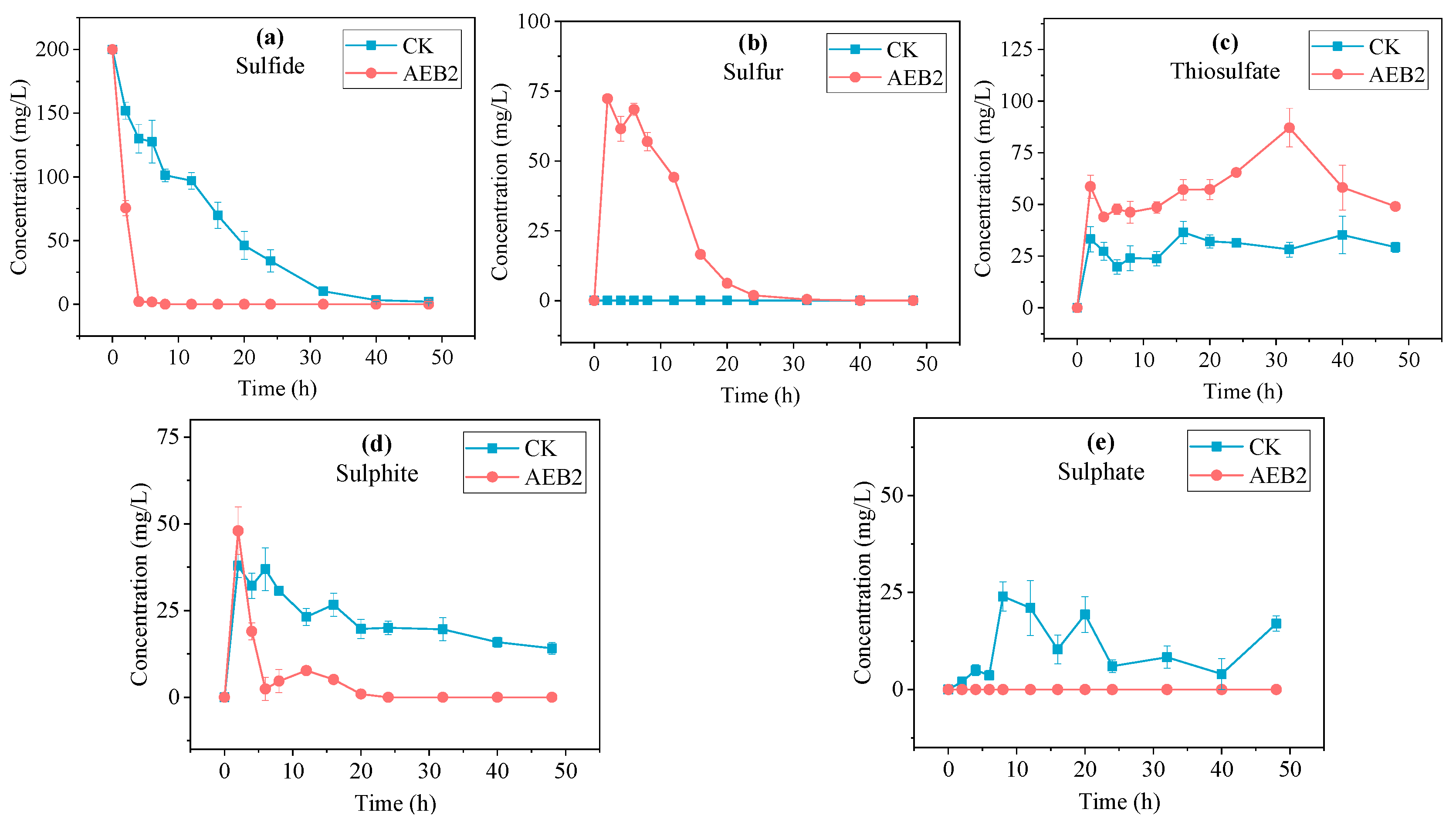
3.5. Products Analysis
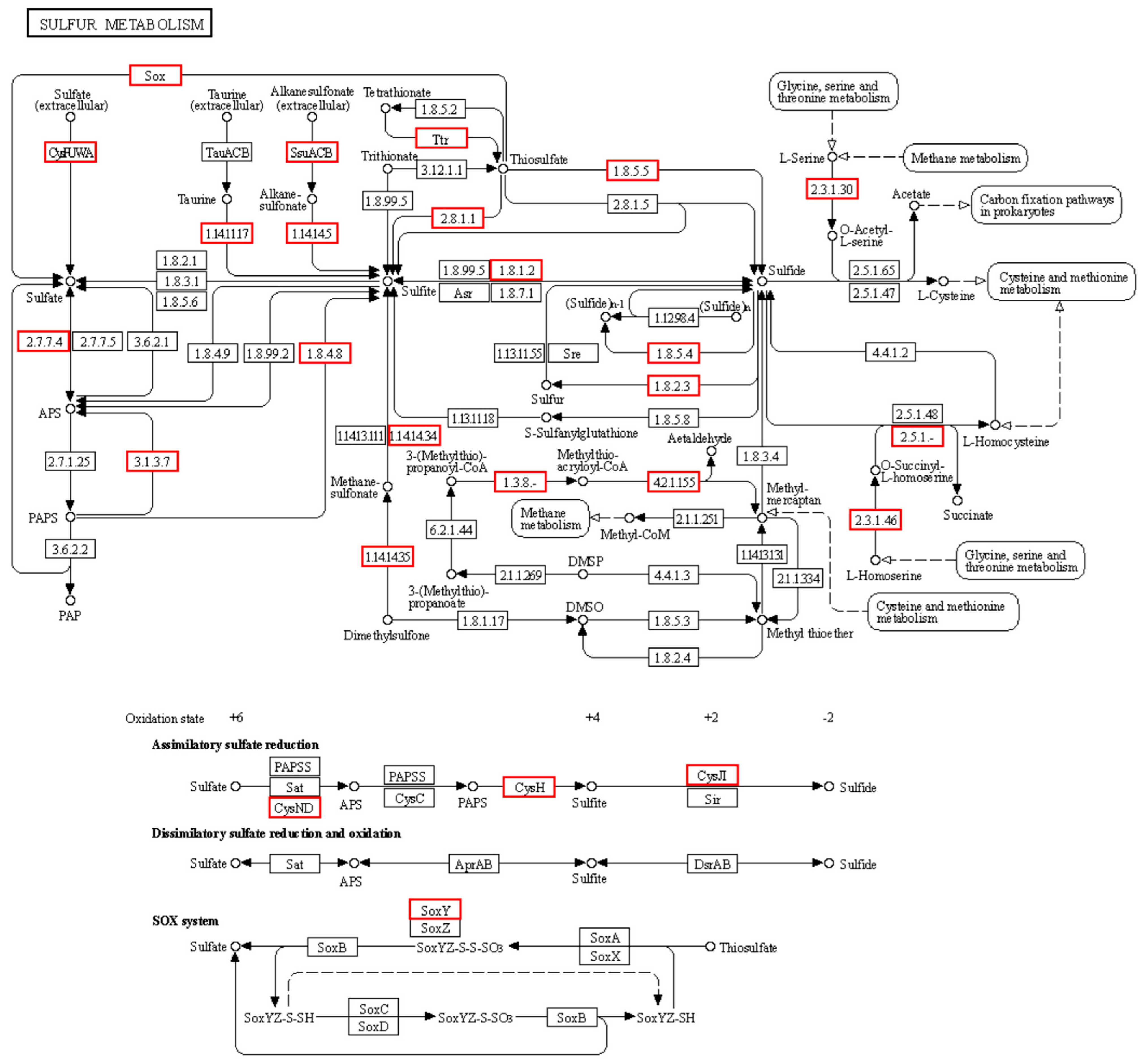
3.6. Degradation Pathway Analysis
- (1)
- Sulfide oxidation to elemental sulfur (S0).
- Q: ubiquinone (electron acceptor);
- QH2: reduced panquinone (enters the electron transport chain to produce ATP).
- (2)
- Sulfide is oxidized to thiosulfate (S2O32−).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Penttinen, P.; Wang, Q.; Ling, J.; Lan, T.; Ou, D.; Li, Y. Analysis on Coupling Coordination Degree for Cropland and Livestock from 2000 to 2020 in China. Agriculture 2020, 13, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Deng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F. Livestock greenhouse gas emission and mitigation potential in China. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 348, 119494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Jo, S.H.; Son, J.; Yu, S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, T.H. Removal of livestock odor gas ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol by electron beam in a continuous flow system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y. Changes in non-CO2 greenhouse gas emissions from livestock production, meat consumption and trade in China. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2023, 42, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Han, M.F.; Jia, T.P.; Hu, X.R.; Zhu, H.Q.; Tong, Z.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Liu, D.Z.; Peng, Y.Z.; et al. Emissions, measurement, and control of odor in livestock farms: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabue, S.L.; Kerr, B.J.; Scoggin, K.D. Swine diets impact manure characteristics and gas emissions: Part I sulfur level. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Minh, N.; Sivret, E.C.; Shammay, A.; Stuetz, R.M. Factors affecting the adsorption of gaseous environmental odors by activated carbon: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Tec. 2018, 48, 341–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, S.B.; Adhoum, N.; Monser, L. Chemical oxidation of a malodorous compound, indole, using iron entrapped in calcium alginate beads. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 301, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, W.; Mao, C.; Mi, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. A low-cost deodorizing spray net device for the removal of ammonia emissions in livestock houses. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 318, 128516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, F.; Franz, B.; Dahl, C. Regulation of Dissimilatory Sulfur Oxidation in the Purple Sulfur Bacterium Allochromatium Vinosum. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, H.; Ogawa, T.; Shiga, M.; Inoue, K. Inorganic sulfur oxidizing system in green sulfur bacteria. Photosynth. Res. 2010, 104, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikromvarasiri, N.; Pisutpaisal, N. Hydrogen sulfide removal in biotrickling filter system by Halothiobacillus neapolitanus. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashun, E.; Toor, U.A.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.R.; Park, S.J.; Hong, S.; Oh, S.E. A direct contact bioassay using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) for toxicity assessment of contaminated field soils. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Su, P.; Lin, Z. A review of sulfate-reducing bacteria: Metabolism, influencing factors and application in wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, F.; Liu, H.; Xun, L. Recombinant Escherichia coli with sulfide: Quinone oxidoreductase and persulfide dioxygenase rapidly oxidises sulfide to sulfite and thiosulfate via a new pathway. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5123–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Pang, B.; Xi, J.; Hu, H.Y. Screening and characterization of mixotrophic sulfide oxidizing bacteria for odorous surface water bioremediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, L. Isolation and application of a mixotrophic sulfide-oxidizing Cohnella thermotolerans LYH-2 strain to sewage sludge composting for hydrogen sulfide odor control. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, D.F.; Singhal, N.; Elefsiniotis, P. Effect of feed characteristics and operational conditions on treatment of dairy farm wastewater in a coupled anoxic-upflow and aerobic system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 133, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, S.K.; Sun, J.Q. Halomonas alkalisoli sp. nov., a novel haloalkalophilic species from saline-alkaline soil, and reclassification of Halomonas daqingensis Wu et al. 2008 as a later heterotypic synonym of Halomonas desiderata Berendes et al. 1996. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 45, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lai, Y.X.; Li, L.; Tan, H.L.; Wang, J.L.; Li, Y.; Tang, T.T.; Qin, L. Bacterial inhibition potential of 3D rapid-prototyped magnesium-based porous composite scaffolds-an in vitro efficacy study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltyanskaya, Y.V.; Kevbrin, V.V.; Lysenko, A.M.; Kolganova, T.V.; Tourova, T.P.; Osipov, G.A.; Zhilina, T.N. Halomonas mongoliensis sp. nov. and Halomonas kenyensis sp. nov., new haloalkaliphilic denitrifiers capable of N 2 O reduction, isolated from soda lakes. Microbiology 2007, 76, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaff, M.; Klok, J.B.; Bijmans, M.F.; Muyzer, G.; Janssen, A.J. Application of a 2-step process for the biological treatment of sulfidic spent caustics. Water Res. 2012, 46, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorna, D.; Zabranska, J. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in environmental technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Baskaran, V.; Nemati, M. Bacteria of the sulphur cycle: An overview of microbiology, biokinetics and their role in petroleum and mining industries. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 44, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, P.L.; Sorokin, D.Y.; Buisman, C.J.; Janssen, A.J. The effect of pH on thiosulfate formation in a biotechnological process for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burschel, S.; Kreuzer, D.D.; Nuber, F.; Stiller, M.; Hofmann, M.; Zupok, A.; Siemiatkowska, B.; Gorka, M.; Leimkühler, S.; Friedrich, T. Iron-sulfur cluster carrier proteins involved in the assembly of Escherichia coli NADH: Ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Lü, C.; Hou, N.; Xin, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Xun, L. Sulfide production and oxidation by heterotrophic bacteria under aerobic conditions. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2754–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcia, M.; Ermler, U.; Peng, G.; Michel, H. A new structure-based classification of sulfide: Quinone oxidoreductases. Proteins 2010, 78, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strains | Accession Number | G + C (mol%) | ANI (%) | dDDH (Formula 1%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halomonas sp. AEB2 | - | 67.46 | 95.8 | 63.3 |
| H. mongoliensis Z-7009T | Un-uploaded data | 67.58 | 95.8 | 63.3 |
| H. alkalicola 56-L4-10aEnT | GCA_003182195.1 | 67.6 | 89.63 | 52.6 |
| H. shengliensis CGMCC 1.6444T | GCA_000475415.1 | 68.6 | 87.22 | 42.3 |
| H. campaniensis 5AGT | GCA_014193375.1 | 67.73 | 88.33 | 49.1 |
| H. ventosae CECT 5797T | GCA_004363555.1 | 67.4 | 86.26 | 36.3 |
| H. denitrificans DSM 18045T | GCA_003056305.1 | 68.7 | 86.17 | 35.3 |
| H. nitroreducens 11ST | GCA_003966155.1 | 67.5 | 85.56 | 28.5 |
| H. pacifica NBRC 102220T | GCA_007989625.1 | 67.2 | 85.94 | 29.4 |
| H. gudaonensis CGMCC 1.6133T | GCA_900100195.1 | 64.9 | 85.52 | 27.1 |
| H. heilongjiangensis 9-2T | GCA_003202165.1 | 66.1 | 86.26 | 30.7 |
| H. halophila NBRC 102604T | GCA_007989465.1 | 68.1 | 85.50 | 28.1 |
| H. daqiaonensis CGMCC 1.9150T | GCA_900109725.1 | 63.15 | 85.35 | 29.2 |
| H. daqingensis CGMCC 1.6443T | GCA_900108215.1 | 64.8 | 85.69 | 26.9 |
| H. smyrnensis AAD6T | GCA_000265245.2 | 67.9 | 86.22 | 28.4 |
| KO ID | KO Name | KO Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gene2638 | fccA | Flavocytochrome cytochrome sulfide dehydrogenase (big subunit) |
| Gene2639 | fccB | Flavocytochrome cytochrome sulfide dehydrogenase (small subunit) |
| Gene2641 | SoxY | Sulfur oxidizing protein |
| Gene2687 | sqr | Sulfide quinone oxidoreductase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Phyu, K.; Zhi, S.; Liang, J. Screening and Identification of SOB and Its Effect on the Reduction in H2S in Dairy Farms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083551
Cao Y, Yu S, Zhang K, Xu X, Phyu K, Zhi S, Liang J. Screening and Identification of SOB and Its Effect on the Reduction in H2S in Dairy Farms. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083551
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yuang, Shuhao Yu, Keqiang Zhang, Xiaoyu Xu, Khinkhin Phyu, Suli Zhi, and Junfeng Liang. 2025. "Screening and Identification of SOB and Its Effect on the Reduction in H2S in Dairy Farms" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083551
APA StyleCao, Y., Yu, S., Zhang, K., Xu, X., Phyu, K., Zhi, S., & Liang, J. (2025). Screening and Identification of SOB and Its Effect on the Reduction in H2S in Dairy Farms. Sustainability, 17(8), 3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083551







