Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag as Aggregate for Sustainable Road Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Asphalt Mixture Design
2.3. Leaching Tests
2.3.1. Analytical Methods
2.3.2. Reporting of the Dynamic Surface Leaching Test Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compliance Leaching Test EN 12457-4 on Granular EAF Slag
3.2. Compliance Leaching Test EN 12457-4 on Loose Asphalt Mixtures
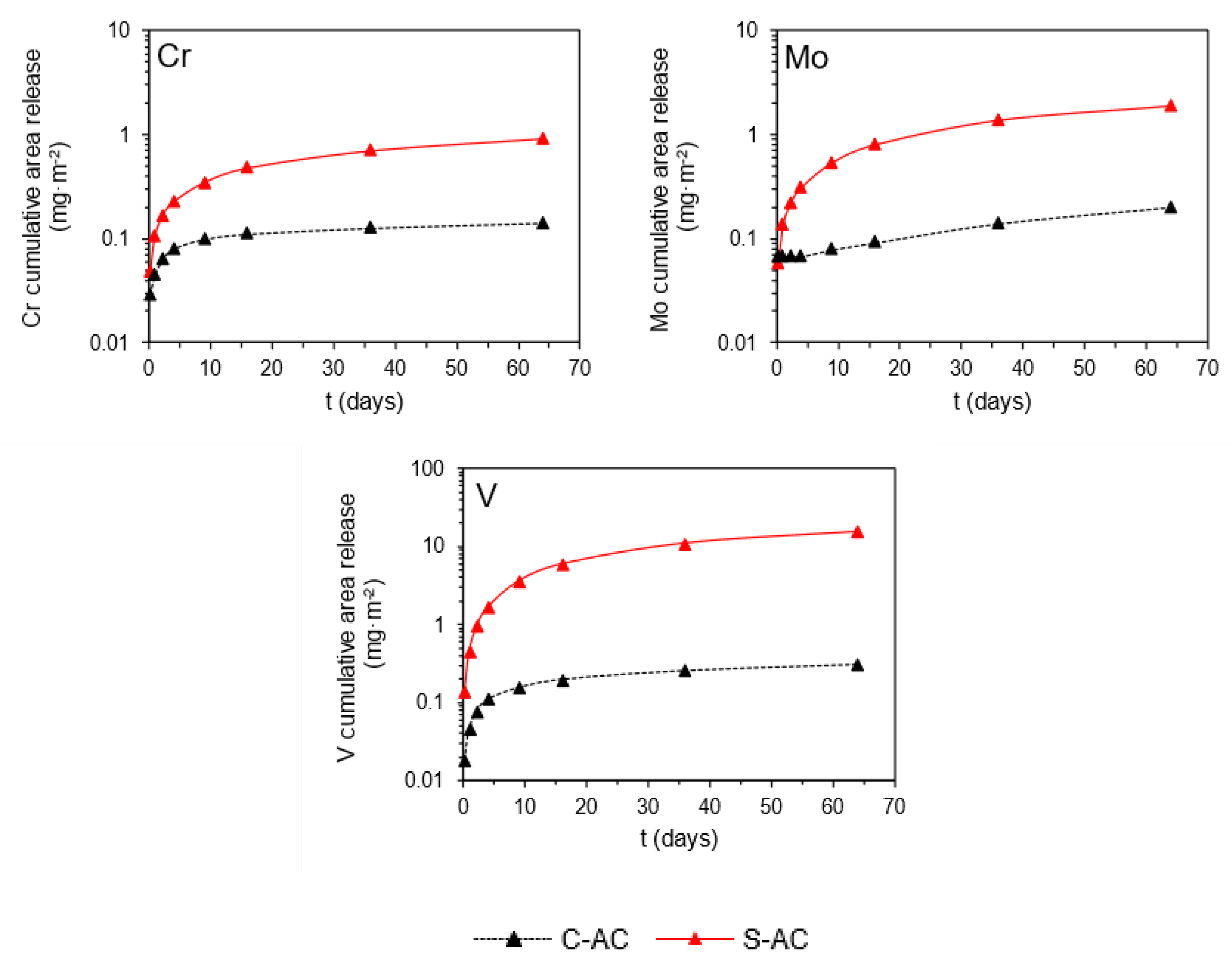
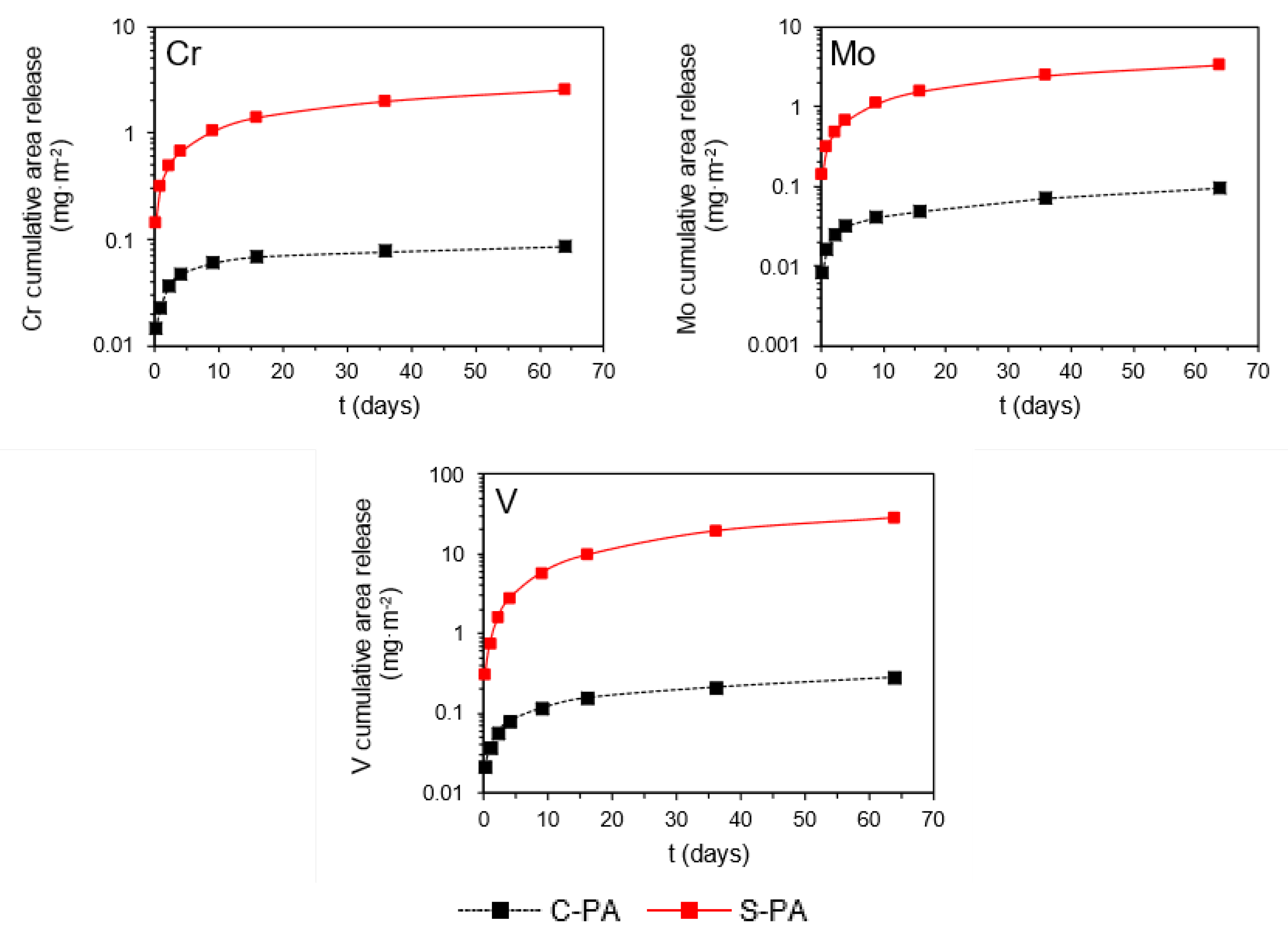
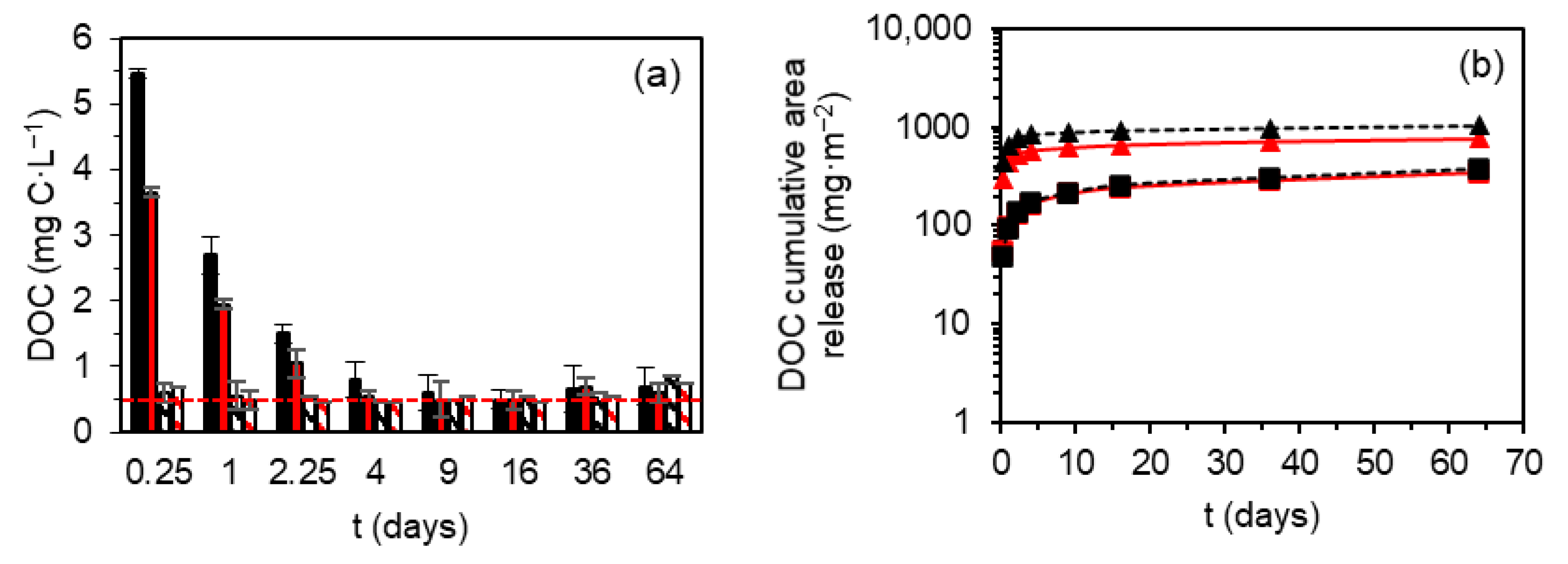
3.3. Dynamic Surface Leaching Test (CEN/TS 16637-2) on Monolithic Asphalt Mixtures
3.4. Release Mechanisms of Cr, Mo, V, and DOC from Monolithic Asphalt Mixtures
3.5. Long-Term Environmental Impact of the Use of EAF Slag in Asphalt Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basilico, A.; Botta, M.; Galli, G.; Gargani, F.; Gori, V.; Melfi, L.; Napoli, M.; Stefanucci, S. Assessment of the Unit Costs of Capital Expenditure for Investment Projects in Road Transport. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/e87de0f3-9e83-11eb-b85c-01aa75ed71a1/language-en/format-PDF/source-281549759 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- International Resource Panel. Resource Efficiency for a Low-Carbon Future. Available online: https://www.resourcepanel.org/file/1966/download?token=dNgPqfZE (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- European Asphalt Pavement Association (EAPA). The Use of Secondary Materials, by-Products and Waste in Asphalt Mixtures; European Asphalt Pavement Association (EAPA): Bruxelles, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UEPG (European Aggregates Association). Annual Review 2016–2017; UEPG (European Aggregates Association): Bruxelles, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Poulikakos, L.D.; Papadaskalopoulou, C.; Hofko, B.; Gschösser, F.; Cannone Falchetto, A.; Bueno, M.; Arraigada, M.; Sousa, J.; Ruiz, R.; Petit, C.; et al. Harvesting the Unexplored Potential of European Waste Materials for Road Construction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 116, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euroslag. Statistics on Slag Production in Europe. Available online: https://www.euroslag.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Statistics-2018.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Loureiro, C.D.A.; Moura, C.F.N.; Rodrigues, M.; Martinho, F.C.G.; Silva, H.M.R.D.; Oliveira, J.R.M. Steel Slag and Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Replacing Quarries to Supply Sustainable Materials for the Asphalt Paving Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yu, B. Steel Slag for Roadway Construction: A Review of Material Characteristics and Application Mechanisms. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 03122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, M.; Manso, J.M.; Aragón, Á.; Fuente-alonso, J.A. EAF Slag in Asphalt Mixes: A Brief Review of Its Possible Re-Use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Ahmadi, A. Recycling of RAP and Steel Slag Aggregates into the Warm Mix Asphalt: A Performance Evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Slag Association Iron and Steel Slags-Non Hazards. Available online: https://nationalslag.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/nsa_194-5_slag_a_non-hazard-1.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Saveyn, H.; Eder, P.; Garbarino, E.; Hjelmar, O.; Van Der Sloot, H.; Van Zomeren, A.; Hyks, J. Study on Methodological Aspects Regarding Limit Values for Pollutants in Aggregates in the Context of the Possible Development of End-of-Waste Criteria Under the EU Waste Framework Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014; ISBN 9789279395390. [Google Scholar]
- Maghool, F.; Arulrajah, A.; Du, Y.J.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijniwat, A. Environmental Impacts of Utilizing Waste Steel Slag Aggregates as Recycled Road Construction Materials. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Harvey, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, D.; Liu, L. Environmental Impact of Solid Waste Filler in Porous Asphalt Mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandow, N.; Gartiser, S.; Ilvonen, O.; Schoknecht, U. Evaluation of the Impact of Construction Products on the Environment by Leaching of Possibly Hazardous Substances. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Regulation No 305/2011 of the European Parliament and the Council of 9 March 2011 Laying down Harmonised Conditions for the Marketing of Construction Products and Repealing Council Directive 89/106/EEC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L88, 5–43.
- CEN (2014). CEN/TS 16637-2; Construction Products—Assessment of Release of Dangerous Substances—Part 2: Horizontal Dynamic Surface Leaching Test. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Weiler, L.; Pfingsten, J.; Eickhoff, H.; Geist, I.; Hilbig, H.; Hornig, U.; Kalbe, U.; Krause, K.; Kautetzky, D.; Linnemann, V.; et al. Improving Consistency at Testing Cementitious Materials in the Dynamic Surface Leaching Test on the Basis of the European Technical Specification CEN/TS 16637–2—Results of a Round Robin Test. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 114959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maherzi, W.; Ennahal, I.; Bouaich, F.Z.; Benzerzour, M.; Rais, Z.; Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Abriak, N.E. Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Monolithic Polymer Mortars Comprised of Wastes. Materials 2023, 16, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makoundou, C.; Fathollahi, A.; Kleiven, S.; Coupe, S.J.; Sangiorgi, C. Mechanical and Leaching Characterisation of Impact-Absorbing Rubberised Asphalts for Urban Pavements. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constructions 2023, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadgoleh, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.M.; Ghodrati, A.; Sharifi, S.S.; Palizban, S.M.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Vahidi, E.; Ayar, P. Characterization of Contaminant Leaching from Asphalt Pavements: A Critical Review of Measurement Methods, Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement, Porous Asphalt, and Waste-Modified Asphalt Mixtures. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, D. Study of Toxicity Assessment of Heavy Metals from Steel Slag and Its Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2020, 13, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahpour, A.; Alipour, S.; Khodadadi, M.; Khodaii, A.; Absi, J. Leaching and Mechanical Performance of Rubberized Warm Mix Asphalt Modified through the Chemical Treatment of Hazardous Waste Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milačič, R.; Zuliani, T.; Oblak, T.; Mladenovič, A.; Ančar, J.Š. Environmental Impacts of Asphalt Mixes with Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, S.; Ye, Q. Investigation of the Physic-Chemical Properties and Toxic Potential of Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag (BOF) in Asphalt Pavement Constructed after 15 Years. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, H.; Schick, J.; Poirier, J.E. Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Monolithic Surface Road Materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadri, A.A.; Pérez-Moreno, S.; Altamar, C.L.; Navarro, F.J.; Bolívar, J.P. Phosphogypsum as Additive for Foamed Bitumen Manufacturing Used in Asphalt Paving. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi, A.; Makoundou, C.; Coupe, S.J.; Sangiorgi, C. Leaching of PAHs from Rubber Modified Asphalt Pavements. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizasoain-Arteaga, E.; Lastra-González, P.; Indacoechea-vega, I.; Flintsch, G. Comprehensive Analysis of the Environmental Impact of Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag on Asphalt Mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, D.; Mapelli, C.; Barella, S.; Di Cecca, C.; Le Saout, G.; Garcia-Diaz, E. The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Leaching Behaviour of Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Carbon Steel Slag during a Standard Leaching Test. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhold, S.; van Zomeren, A.; Dijkstra, J.J.; van der Sloot, H.A.; Drissen, P.; Algermissen, D.; Mudersbach, D.; Schüler, S.; Griessacher, T.; Raith, J.G.; et al. Investigation of Possible Leaching Control Mechanisms for Chromium and Vanadium in Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Slags Using Combined Experimental and Modeling Approaches. Minerals 2019, 9, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-González, P.; Calzada-Pérez, M.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Indacoechea-Vega, I. Porous Asphalt Mixture with Alternative Aggregates and Crumb-Rubber Modified Binder at Reduced Temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-González, P.; Calzada-Pérez, M.A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Indacoechea-Vega, I. Asphalt Mixtures with High Rates of Recycled Aggregates and Modified Bitumen with Rubber at Reduced Temperature. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN (2003) EN 12457-4; Characterisation of Waste—Leaching—Compliance Test for Leaching of Granular Waste Materials and Sludges—Part 4: One Stage Batch Test at a Liquid to Solid Ratio of 10 L/Kg for Materials with Particle Size below 10 Mm (Without or with Size). European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Soil Quality Decree. Available online: https://wetten.overheid.nl/BWBR0023085/2020-06-09 (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Van Zomeren, A. On the Nature of Organic Matter from Natural and Contaminated Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sorlini, S.; Sanzeni, A.; Rondi, L. Reuse of Steel Slag in Bituminous Paving Mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, D.; Gruttadauria, A.; Barella, S.; Mapelli, C. The Influence of Slag Tapping Method on the Efficiency of Stabilization Treatment of Electric Arc Furnace Carbon Steel Slag (EAF-C). Minerals 2019, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecnalia End of Waste Criteria Protocol for Waste Used as Aggregates. Available online: https://www.cinderela.eu/The-project/Reports/D5.5-End-of-waste-criteria-protocol-for-waste-used-as-aggregates (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Xue, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y. Evaluation of Dissolved Organic Carbon Released from Aged Asphalt Binder in Aqueous Solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sloot, H.A.; Dijkstra, J.J. Development of Horizontally Standardized Leaching Tests for Construction Materials: A Material Leaching Mechanisms for Different Materials? Identical Leaching Mechanisms for Different Materials. Available online: https://publications.tno.nl/publication/34628440/P1kb20/c04060.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Lizasoain-Arteaga, E.; Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Alonso, B.; Castro-Fresno, D. Influence of Traffic Delay Produced during Maintenance Activities on the Life Cycle Assessment of a Road. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 120050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizasoain-Arteaga, E.; Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Castro-Fresno, D. Environmental Impact Assessment of Induction-Healed Asphalt Mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Properties | Standard | Ophite Coarse | EAF Slag Coarse/Fine | Limestone Fine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific weight (g·cm−3) | EN 1097-6:2022 | 2.937 | 3.943 | 2.725 |
| Los Angeles coefficient | EN 1097-2:2020 | 16 | 18 | 25 |
| Flakiness index | EN 933-3: 2012 | 8 | 2 | - |
| Water absorption (%) | EN 1097-6:2012 | 0.6 | 1.1 | - |
| Crushed surfaces (%) | EN 933-5:2022 | 100 | 100 | - |
| Polished stone value (BPN) | EN 1097-8:2020 | 57 | 56 | - |
| Sand equivalent | EN 933-8:2012 +A12015 | - | - | 78 |
| Major Elements | % wt. | Trace Elements | mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 10.18 ± 0.47 | As | <2 |
| Al2O3 | 5.98 ± 0.09 | Ba | 872.5 ± 20.5 |
| Fe2O3 | 45.92 ± 1.24 | Cd | <0.5 |
| MnO | 6.28 ± 0.27 | Cr | 17,700 ± 1414 |
| MgO | 6.67 ± 0.22 | Cu | 104.5 ± 2.12 |
| CaO | 22.47 ± 1.48 | Hg | <1 |
| Na2O | 0.055 ± 0.01 | Mo | 147 ± 9.89 |
| TiO2 | 0.41 ± 0.002 | Ni | 17.5 ± 2.12 |
| P2O5 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | Pb | 17 ± 1.41 |
| S | 0.077 | Sb | 0.4 |
| LOI * | −1.85 | Se | <3 |
| V | 1092.5 ± 78.49 | ||
| Zn | 197.5 ± 0.71 |
| Properties | Standard | Bitumen B 50/70 | Polymer Modified Bitumen 45/80-65 |
| Specific weight (g·cm−3) | EN 15326:2007 | 1.035 | 1.028 |
| Penetration (25 °C, dmm) | EN 1426:2015 | 57 | 55 |
| Softening point (°C) | EN 1427:2015 | 51.6 | 74.1 |
| Fraass brittle point (°C) | EN 15326:2007 | −11 | −13 |
| Elastic recovery (25 °C, %) | EN 13398:2017 | - | 92 |
| Materials (Particle Size, mm) | % wt. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-AC | S-AC | C-PA | S-PA | |
| EAF Slag (8/16) | - | 33.4 | - | 63.1 |
| EAF Slag (4/8) | - | 24 | - | 9.7 |
| EAF Slag (0/4) | - | 20.5 | - | 20.4 |
| Ophite (8/16) | 31.9 | - | 43.5 | - |
| Ophite (4/8) | 21.2 | - | 33.9 | - |
| Ophite (2/4) | 10.3 | - | 4.5 | - |
| Limestone (0/2) | 31.7 | 17.2 | 10.8 | - |
| Limestone filler | 0.6 | 0.6 | 2.8 | 2.6 |
| Bitumen | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.2 |
| Type of bitumen | B 50/70 | PMB 45/80-65 | ||
| Property | C-AC | S-AC | Limit | C-PA | S-PA | Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voids test (EN 12697-8:2003) | ||||||
| Density (g·cm−3) | 2.453 | 3.09 | - | 1.992 | 2.691 | - |
| Voids (%) | 5.1 | 5.3 | 4–6 | 23.1 | 22.6 | ≥20 |
| Voids in aggregates (%) | 15.3 | 17.9 | ≥15 | 16.1 | 16.6 | - |
| Marshall test (EN 12697-34:2020) | ||||||
| Stability (kN) | 15.7 | 16.3 | >15 (*) | - | - | - |
| Strain (mm) | 3.8 | 3.2 | 2–3.5 (*) | - | - | - |
| Cantabro particle loss test (EN 12697-17:2017) | ||||||
| Particle loss (%) | - | - | - | 7.1 | 11.1 | ≤20 |
| Water sensitivity test (EN 12697-12:2018) | ||||||
| ITS Dry (kPa) | 1745.7 | 1844.4 | - | 1074.2 | 923.6 | - |
| ITS Wet (kPa) | 1610 | 1719.6 | - | 1034.3 | 859.3 | - |
| ITSR (%) | 92 | 93 | ≥85 | 96 | 93 | ≥85 |
| Wheel tracking test (EN 12697-22:2020) | ||||||
| Slope (mm/1000 cycles) | 0.08 | 0.08 | ≤0.10 | - | - | - |
| Rut (mm) | 3.1 | 3.2 | - | - | - | - |
| Binder drainage test (EN 12697-18:2017) | ||||||
| Binder drainage (%) | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | ≤0.3 |
| Substances (mg·kg−1) | EAF Slag | Limit Values * | C-AC | S-AC | C-PA | S-PA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 11.46 ± 0.05 | - | 9.68 ± 0.07 | 10.38 ± 0.03 | 10.02 ± 0.05 | 10.76 |
| Conductivity (µS·cm−1) | 305.67 ± 15.5 | - | 48.53 ± 1.39 | 100.55 ± 1.85 | 58.03 | 178.27 |
| Arsenic (As) | 0.002 ± 0.00005 | 0.5 | 0.001 ± 0.0004 | 0.002 ± 0.0002 | 0.001 ± 0.0007 | 0.001 |
| Barium (Ba) | 1.040 ± 0.016 | 20 | 0.029 ± 0.005 | 0.645 ± 0.079 | 0.026 ± 0.0029 | 0.615 ± 0.026 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.00028 ± 0.00006 | 0.04 | <0.00015 | <0.00015 | <0.00015 | <0.00015 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.343 ± 0.064 | 0.5 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 0.061 ± 0.005 | 0.022 ± 0.006 | 0.051 ± 0.0002 |
| Copper (Cu) | <0.0015 | 2 | <0.0015 | <0.0015 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.001 |
| Mercury (Hg) | 0.011 ± 0.00051 | 0.01 | <0.0003 | 0.0005 ± 0.00007 | <0.0003 | 0.0005 ± 0.00007 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.778 ± 0.08 | 0.5 | 0.018 ± 0.0002 | 0.106 ± 0.019 | 0.016 ± 0.005 | 0.081 ± 0.016 |
| Nickel (Ni) | <0.0003 | 0.4 | 0.001 ± 0.0004 | 0.0012 ± 0.001 | 0.003 ± 0.0004 | 0.001 ± 0.0002 |
| Lead (Pb) | <0.0007 | 0.5 | <0.0007 | <0.0007 | <0.0007 | <0.0007 |
| Antimony (Sb) | 0.002 ± 0.0002 | 0.06 | 0.0004 ± 0.0003 | 0.0007 ± 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0007 ± 0.0003 |
| Selenium (Se) | 0.144 ± 0.0058 | 0.1 | 0.0036 ± 0.001 | 0.019 ± 0.0016 | 0.007 ± 0.0004 | 0.009 ± 0.005 |
| Vanadium (V) | 3.661 ± 0.043 | 1.5 ** | 0.009 ± 0.0008 | 0.616 ± 0.060 | 0.0036 ± 0.006 | 0.591 ± 0.012 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.019 ± 0.0027 | 4 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.001 ± 0.0006 |
| Chloride (Cl−) | 5.15 ± 2.188 | 800 | <2.5 | <2.5 | <2.5 | <2.5 |
| Fluoride (F−) | 3.947 ± 0.102 | 10 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Sulphate ([SO4]2−) | 230 ± 14.142 | 1000 | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 |
| Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | <5 | 500 | 9.0 ± 0.283 | 8.5 ± 0.353 | 12.5 ± 0.71 | 9.0 |
| Element (mg·m−2) | C-AC | S-AC | C-PA | S-PA | SQD Limit Values * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.14 | 0.92 | 0.09 | 2.54 | 120 |
| Mo | 0.20 | 1.86 | 0.05 | 3.29 | 144 |
| V | 0.31 | 15.39 | 0.28 | 28.67 | 320 |
| Release Mechanism | C-AC | S-AC | C-PA | S-PA | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Mo | V | DOC | Cr | Mo | V | DOC | Cr | Mo | V | DOC | Cr | Mo | V | DOC | |
| M1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| M1.1 | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M2 | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| M2.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M2.2 | - | - | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M4 | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M4.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| M4.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Determined mechanism | M4 | M4 | M2.2 | M1.1 | M2 | M2.2 | M2.2 | M1.1 | M1 | M1 | M2 | M1 | M2 | M2 | M2 | M1 |
| Long-term release prediction * (mg·m−2) | 1.32 | 1.85 | 2.02 | - | 8.47 | 18.58 | 163.23 | - | - | - | 2.12 | - | 19.19 | 24.87 | 216.49 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salas, I.; Cifrian, E.; Lastra-González, P.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Andrés, A. Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag as Aggregate for Sustainable Road Construction. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083737
Salas I, Cifrian E, Lastra-González P, Castro-Fresno D, Andrés A. Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag as Aggregate for Sustainable Road Construction. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083737
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalas, Iván, Eva Cifrian, Pedro Lastra-González, Daniel Castro-Fresno, and Ana Andrés. 2025. "Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag as Aggregate for Sustainable Road Construction" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083737
APA StyleSalas, I., Cifrian, E., Lastra-González, P., Castro-Fresno, D., & Andrés, A. (2025). Assessment of Dynamic Surface Leaching of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag as Aggregate for Sustainable Road Construction. Sustainability, 17(8), 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083737








