Heavy Metal Biosorption Ability of EPS Obtained from Cultures of Fusarium culmorum Strains with Different Effects on Cereals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains
2.2. Growth of Strains on a Culture Medium with the Addition of Heavy Metals
2.3. EPS Isolation and Chemical Characterisation
2.4. Estimation of the Sugar Polymer Masses by Gel-Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.5. Binding of Metal Ions
R = 100% × [(Ci − Cf)/Ci]
R—percentage of ion binding
Ci—initial concentration
Cf—final concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Chemical Characterisation of F. culmorum EPS Preparations
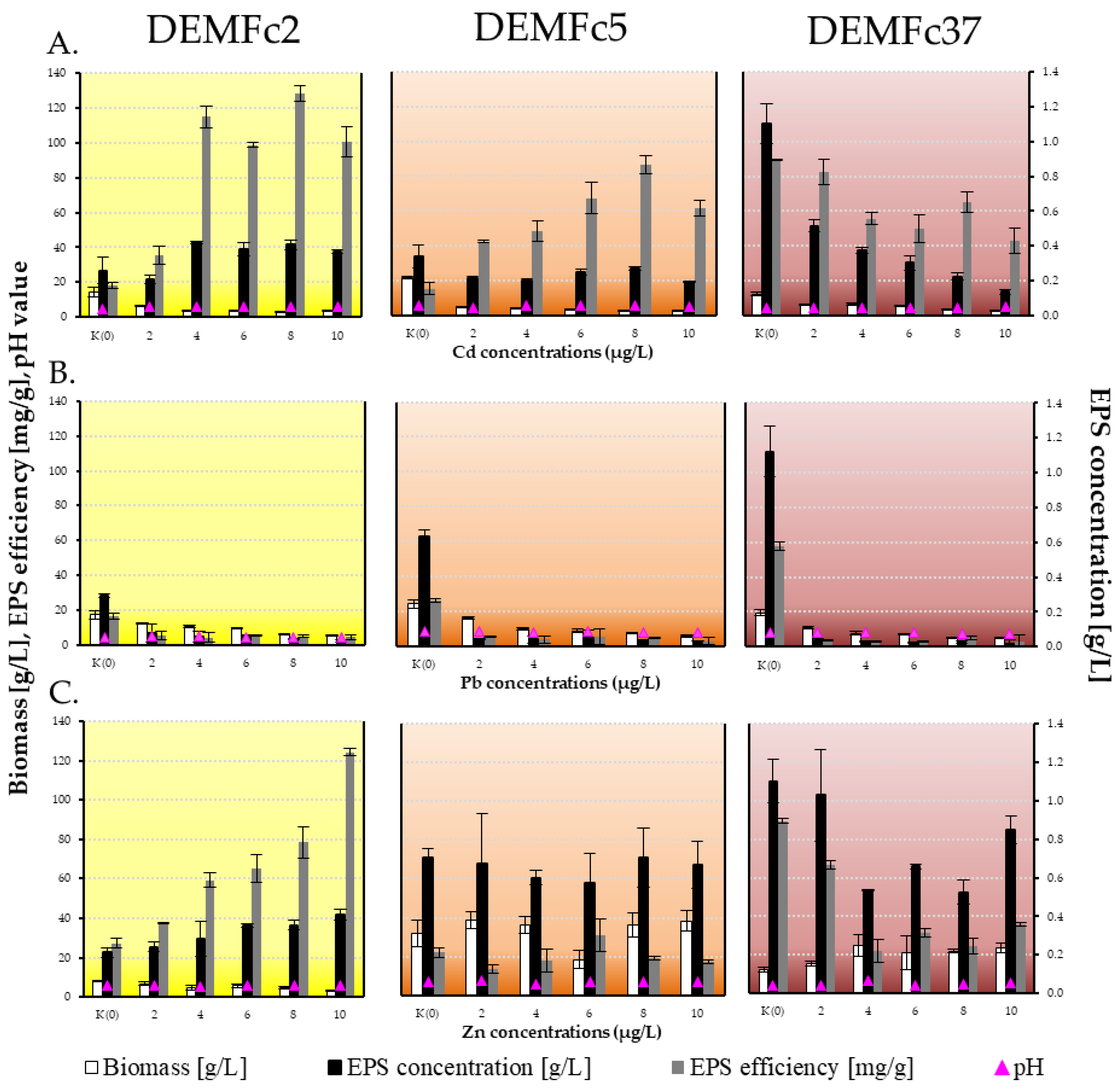
3.2. F. culmorum Strains’ Growth and EPS Synthesis on a Media Free of Heavy Metals and with the Addition of Heavy Metals
3.2.1. Growth of the Fungal Strains
3.2.2. EPS Synthesis by F. culmorum Strains
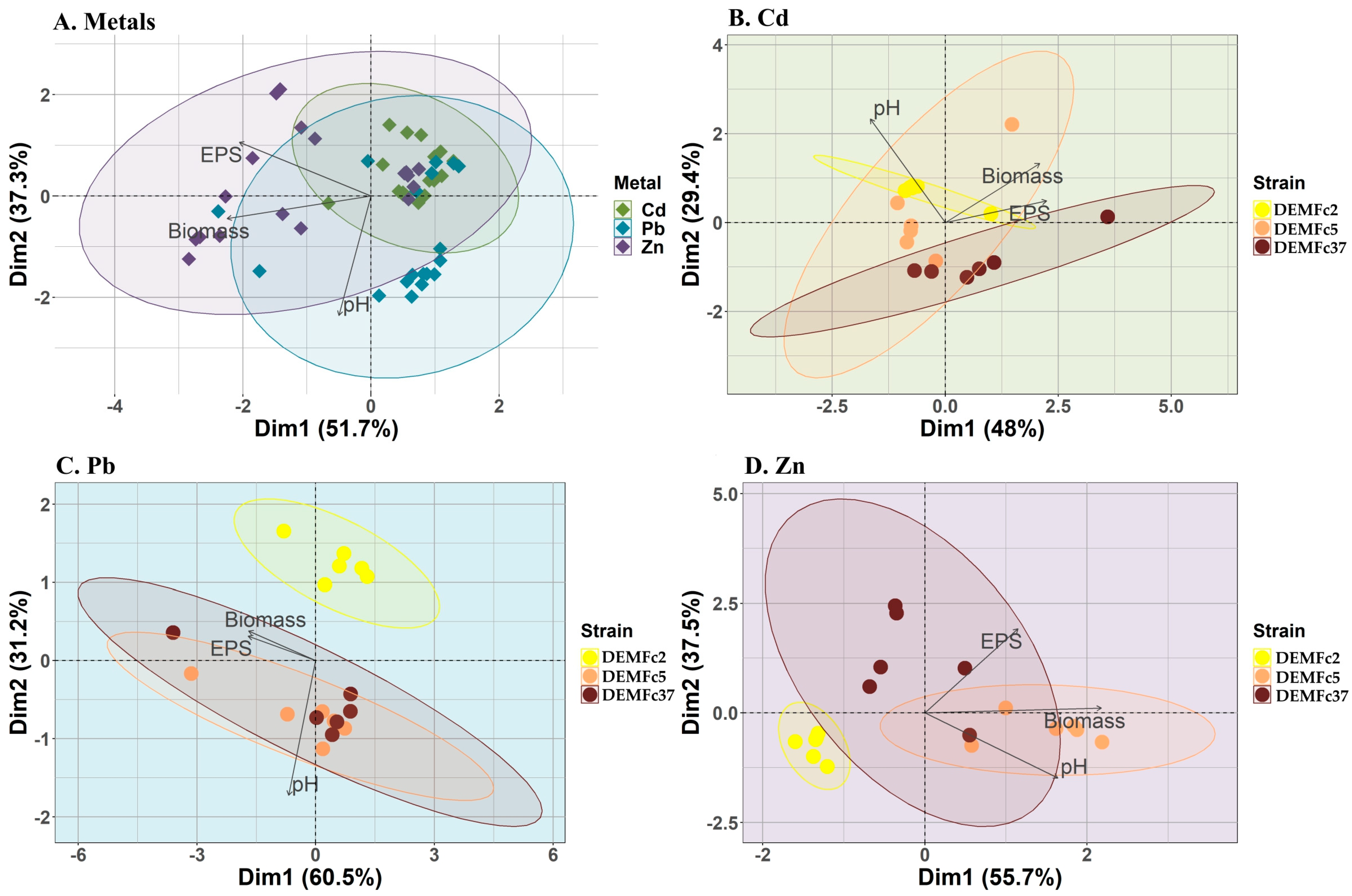
3.3. Binding of Metal Ions—Chelating Properties of F. culmorum EPS
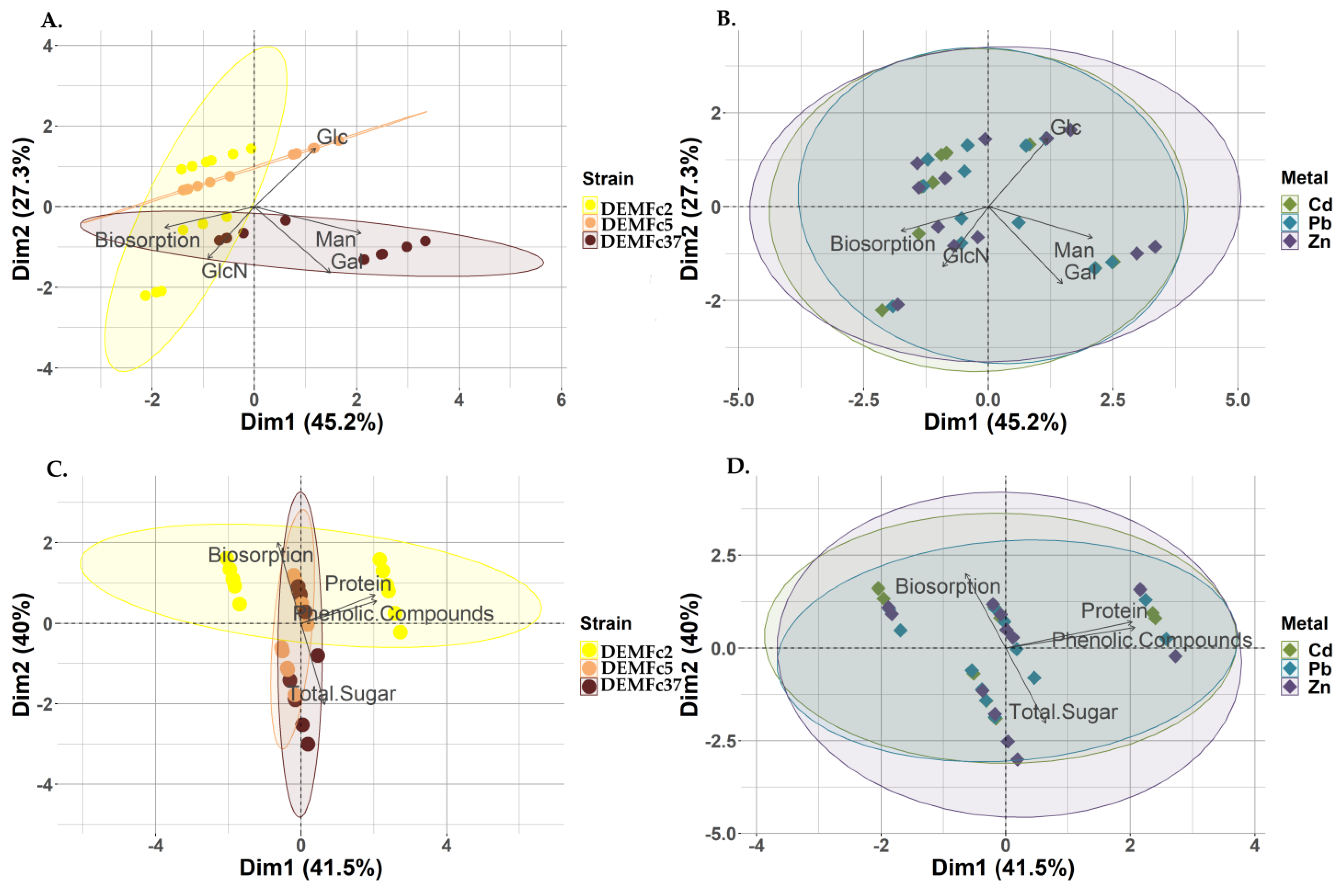
3.4. Relationship Between Metal Biosorption and Type and Composition of EPS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awasthi, S.; Srivastava, P.; Mishra, P.K. Application of EPS in agriculture: An important natural resource for crop improvement. Agric. Res. Technol. Open Access J. 2017, 8, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, M.C.S.; Vespermann, K.A.C.; Pelissari, F.M.; Molina, G. Current status of biotechnological production and applications of microbial exopolysaccharides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: Ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, J.; Floryszak-Wieczorek, J.; Sobieszczuk-Nowicka, E.; Mattoo, A.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M. Fungal and oomycete pathogens and heavy metals: An inglorious couple in the environment. IMA Fungus 2022, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, A.; Chaudhary, A. Effects of biocontrol agents and heavy metals in controlling soil-borne phytopathogens. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2019, 7, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.R.; Isikhuemhen, O.S.; Anike, F.N. Fungal–metal interactions: A review of toxicity and homeostasis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre, L.; de Siloniz, M.I.; Valderrama, M.J.; Benito, T.; Larrea, M.T.; Peinado, J.M. Occurence of yeast in municipal wastes and their behavior in presence of cadmium, copper and zinc. J. Basic Microbiol. 2003, 43, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzouhri, L.; Castro, E.; Moya, M.; Espinola, F.; Lairini, K. Heavy metal tolerance of filamentous fungi isolated from polluted sites in Tangier, Morocco. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 3, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Falandysz, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Saba, M.; Krasinska, G.; Wiejak, A.; Li, T. Evaluation of mercury contamination in fungi Boletus species from latosols, lateritic red earths, and red and yellow earths in the circum-Pacific mercuriferous belt of southwestern China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choma, A.; Nowak, K.; Komaniecka, I.; Waśko, A.; Pleszczyńska, M.; Siwulski, M.; Wiater, A. Chemical characterization of alkali-soluble polysaccharides isolated from a Boletus edulis (Bull.) fruiting body and their potential for heavy metal biosorption. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Širić, I.; Humar, M.; Kasap, A.; Kos, I.; Mioč, B.; Pohleven, F. Heavy metal bioaccumulation by wild edible saprophytic and ectomycorrhizal mushrooms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18239–18252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundy, S.D.; Payne, R.J.; Giles, K.R.; Garrill, A. Heavy metals have different effects on mycelial morphology of Achlya bisexualis as determined by fractal geometry. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 201, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Osińska-Jaroszuk, M.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Szałapata, K.; Nowak, A.; Jaszek, M.; Ozimek, E.; Majewska, M. Extracellular polysaccharides from Ascomycota and Basidiomycota: Production Conditions, Biochemical Characteristics, and Biological Properties. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1823–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.-H.; Luo, B.; Zhou, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-H. Generalized solutions for advection–dispersion transport equations subject to time- and space-dependent internal and boundary sources. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 178, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, M.; Gadd, G.M. Biosorption: Current perspectives on concept, definition and application. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption and me. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.H.; Ismail, I.M.; Mostafa, T.M.; Sulaymon, A.H. Biosorption of heavy metals: A review. J. Chem. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Quan, S.; Li, L.; Lei, G.; Li, S.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W. Endophytic bacteria improve bio- and phytoremediation of heavy metals. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, V.; Pandit, S. Advanced omics approach and sustainable strategies for heavy metal microbial remediation in contaminated environments. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakarkumar, Y.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Gujjula, K.R.; Vasu, V.; Balamurugan, P.; Murali, G. Fungal bioremediation: An overview of the mechanisms, applications and future perspectives. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 6, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Kutyła, M.; Kaczmarek, J.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Jędryczka, M. Differences in the production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and other metabolites of Plenodomus (Leptosphaeria) infecting winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Metabolites 2023, 13, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Kurek, E.; Winiarczyk, K.; Baturo, A.; Łukanowski, A. Colonization of root tissues and protection against Fusarium wilt of rye (Secale cereale) by nonpathogenic rhizosphere strains of Fusarium culmorum. Biol. Control 2008, 45, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Kurek, E.; Rodzik, B.; Winiarczyk, K. Interactions Between rye (Secale cereale) root border cells (RBCs) and pathogenic and nonpathogenic rhizosphere strains of Fusarium culmorum. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Nowak, A.; Komaniecka, I.; Choma, A.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Osińska-Jaroszuk, M.; Tyśkiewicz, R.; Wiater, A.; Rogalski, J. Differences in production, composition, and antioxidant activities of exopolymeric substances (EPS) obtained from cultures of endophytic Fusarium culmorum strains with different effects on cereals. Molecules 2020, 25, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Kurek, E. Hydrolysis of fungal and plant cell walls by enzymatic complexes from cultures of Fusarium isolates with different aggressiveness to Rye (Secale cereale). Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Kurek, E.; Trytek, M. Efficiency of indoleacetic acid, gibberellic acid and ethylene synthesized in vitro by Fusarium culmorum strains with different effects on cereal growth. Biologia 2014, 69, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, E.; Machowicz, Z.; Kulpa, D.; Slomka, A. The microorganisms of rye [Secale cereal L.] rhizosphere. Acta Microbiol. Pol. 1994, 2, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Czapek, F. Untersuchungen über die Stickstoffgewinnung und Eiweifsbildung der Pflanzen. Hofmeisters Beiträge Zur Chem. Phys. U. Pathol. Bd. Ii 1902, 1, 559. [Google Scholar]
- Dox, A.W. The Intracellular Enzymes of Penicillium and Aspergillus: With Special Reference to Those of Penicillium camemberti; US Department of Agriculture, Bureau of Animal Industry: Washington, DC, USA, 1910; Volume 111. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folin, O.; Ciocalteu, V. On tyrosine and tryptophane determinations in proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1927, 73, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawardeker, J.S.; Sloneker, J.H.; Jeanes, A. Quantitative determination of monosaccharides as their alditol acetates by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1602–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S. A Rapid Permethylation of glycolipid, and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Gutiérrez, D.; Gómez-Gil, L.; Guarro, J.; Roncero, M.I.G.; Fernández-Bravo, A.; Capilla, J.; López-Fernández, L. Role of the Fusarium oxysporum metallothionein Mt1 in resistance to metal toxicity and virulence. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocek-Płóciniak, A. Wpływ metali ciężkich na mikroorganizmy oraz aktywność enzymatyczną gleby. Rocz. Glebozn. 2011, 4, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Golubović-Ćurguz, V.; Tabaković-Tošić, M.; Veselinović, M.; Rajković, S. The influence of heavy metals on the growth of pathogenic fungi. For. Ideas 2010, 16, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewska, J.; Azzahra, N.A.; Bingöl, Ö.A.; Izbiańska-Jankowska, K.; Jelonek, T.; Deckert, J.; Floryszak-Wieczorek, J.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M. Cadmium stress reprograms ROS/RNS homeostasis in Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gallego, T.; Molina-Luzón, M.J.; Conéjéro, G.; Berthomieu, P.; Ferrol, N. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis uses the copper exporting ATPase RiCRD1 as a major strategy for copper detoxification. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, S.; Rovina, K.; Al Azad, S.; Naher, L.; Suryani, S.; Chaikaew, P. Heavy metal contaminants removal from wastewater using the potential filamentous fungi biomass: A review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.J.; de Rezende Pinto, F.; do Amaral, L.A.; Garcia-Cruz, C.H. Biosorption of cadmium (II) and lead (II) from aqueous solution using exopolysaccharide and biomass produced by Colletotrichum sp. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 7878–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimalnath, S.; Subramanian, S. Studies on the biosorption of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution using extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paria, K.; Pyne, S.; Chakraborty, S.K. Optimization of heavy metal (lead) remedial activities of fungi Aspergillus penicillioides (F12) through extracellular polymeric substances. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.H.; Park, C.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y. Il Biosorption isotherms of Pb (II) and Zn (II) on pestan, an extracellular polysaccharide of Pestalotiopsis sp. KCTC 8637P. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.S.; Hamed, H.A.; Mouafi, F.E.; Gad, A.S. Acidic pH-shock induces the production of an exopolysaccharide by the fungus Mucor rouxii: Utilization of beet-molasses. N. Y. Sci. J. 2012, 5, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- George, B.; Kumar, J.I.N.; Kumar, R.N.; Sajish, P.R. Biosorption potentiality of living Aspergillus niger Tiegh in removing heavy metal from aqueous solution. Bioremediation J. 2012, 16, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. State of the art for the biosorption process—a review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1389–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.; Abbas, L.; Coutinho, O.; Opara, S.; Najaf, H.; Kasperek, D.; Pokhrel, K.; Li, X.; Tiquia-Arashiro, S. Applications of Fourier Transform-Infrared spectroscopy in microbial cell biology and environmental microbiology: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1304081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Nurgul, R.; Dong, M. Isolation and identification of an exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacterium strain from chinese paocai and biosorption of Pb(II) by its exopolysaccharide. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, T111–T117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, M.D.; Cvetković, O.G.; Nikolić, S.D.; Dordević, D.S.; Jakovljević, D.M.; Vrvić, M.M. Simultaneous production of pullulan and biosorption of metals by Aureobasidium pullulans strain CH-1 on peat hydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6673–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.; Stoll, A.; Starke, L.; Duncan, J. Chemical and enzymatic extraction of heavy metal binding polymers from isolated cell walls of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 44, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Du, H.; Cai, P.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Zhou, D.M. Influence of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances on the sorption of Zn on γ-alumina: A combination of FTIR and EXAFS studies. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nell, R.M.; Fein, J.B. Influence of sulfhydryl sites on metal binding by bacteria. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 199, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strain | DEMFc2 | DEMFc5 | DEMFc37 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Composition of water fraction of EPS (µg/mg) | |||||
| C | P | C | P | C | P | |
| Proteins | 2.3 | 0 | 1.2 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 |
| Phenolic compounds | 31.6 | 14.4 | 26.9 | 20.7 | 27.7 | 20.5 |
| Total sugars | 143.7 | 52.4 | 103.9 | 200.8 | 147.1 | 260.2 |
| Strain | DEMFc2 | DEMFc5 | DEMFc37 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Sugar composition [μg/mg] ± SD * | |||||
| C | P | C | P | C | P | |
| Mannose (Man) | 6.97 (SD = 1.670) | 12.40 (SD = 0.552) | 29.22 (SD = 3.466) | 58.39 (SD = 3.828) | 37.39 (SD = 4.957) | 128.99 (SD = 19.94) |
| Glucose (Glc) | 36.14 (SD = 4.230) | 12.69 (SD = 1.419) | 18.18 (SD = 3.200) | 75.48 (SD = 9.038) | 15.18 (SD = 3.760) | 34.04 (SD = 5.726) |
| Galactose (Gal) | 3.12 (SD = 1.290) | 8.01 (SD = 0.329) | 2.80 (SD = 0.129) | 6.09 (SD = 0.531) | 9.41 (SD = 1.299) | 13.59 (SD = 1.574) |
| Glucosamine (GlcN) | - | 1.09 (SD = 0.155) | - | - | - | - |
| Fraction ** | Molecular weights [kDa] | |||||
| P | P | P | ||||
| HMW | 1000–735 | - | 1000–735 | |||
| MMW | 15.8 | 73.5–34.1 | 18.5 | |||
| LMW | - | 5.4 | ||||
| Type of linkage | Glycosidic bonds [%] | |||||
| P | P | P | ||||
| tHex I (Man (1→) | 18.3 | 31.6 | 46.9 | |||
| tHex III (Gal (1→) | 13.4 | Tr. | Tr. | |||
| →2) Hex (1→ | 24.5 | 20.3 | 22.8 | |||
| →3) Hex (1→ | Tr. | 1.8 | Tr. | |||
| →4) Hex (1→ | 20.9 | 15.6 | 5.1 | |||
| →6) Hex (1→ | - | Tr. | 6.7 | |||
| →3,4) Hex (1→ | 13.8 | - | Tr. | |||
| →3,6) Hex (1→ | 9.1 | - | 11.6 | |||
| →2,3,4,6) Hex (1→ | - | 30.7 | 6.9 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J.; Nowak, A.; Pac-Sosińska, M.; Kołodyńska, D.; Komaniecka, I. Heavy Metal Biosorption Ability of EPS Obtained from Cultures of Fusarium culmorum Strains with Different Effects on Cereals. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083744
Jaroszuk-Ściseł J, Nowak A, Pac-Sosińska M, Kołodyńska D, Komaniecka I. Heavy Metal Biosorption Ability of EPS Obtained from Cultures of Fusarium culmorum Strains with Different Effects on Cereals. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083744
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaroszuk-Ściseł, Jolanta, Artur Nowak, Małgorzata Pac-Sosińska, Dorota Kołodyńska, and Iwona Komaniecka. 2025. "Heavy Metal Biosorption Ability of EPS Obtained from Cultures of Fusarium culmorum Strains with Different Effects on Cereals" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083744
APA StyleJaroszuk-Ściseł, J., Nowak, A., Pac-Sosińska, M., Kołodyńska, D., & Komaniecka, I. (2025). Heavy Metal Biosorption Ability of EPS Obtained from Cultures of Fusarium culmorum Strains with Different Effects on Cereals. Sustainability, 17(8), 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083744







