Assessment of the Lifespan of a Site Drilling Machine in Saudi Arabia and India Using Correspondence Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Overview of Factors Influencing Drilling Machine Lifespan
2.2. Correspondence Analysis (CA) Method
2.3. Gap in Knowledge
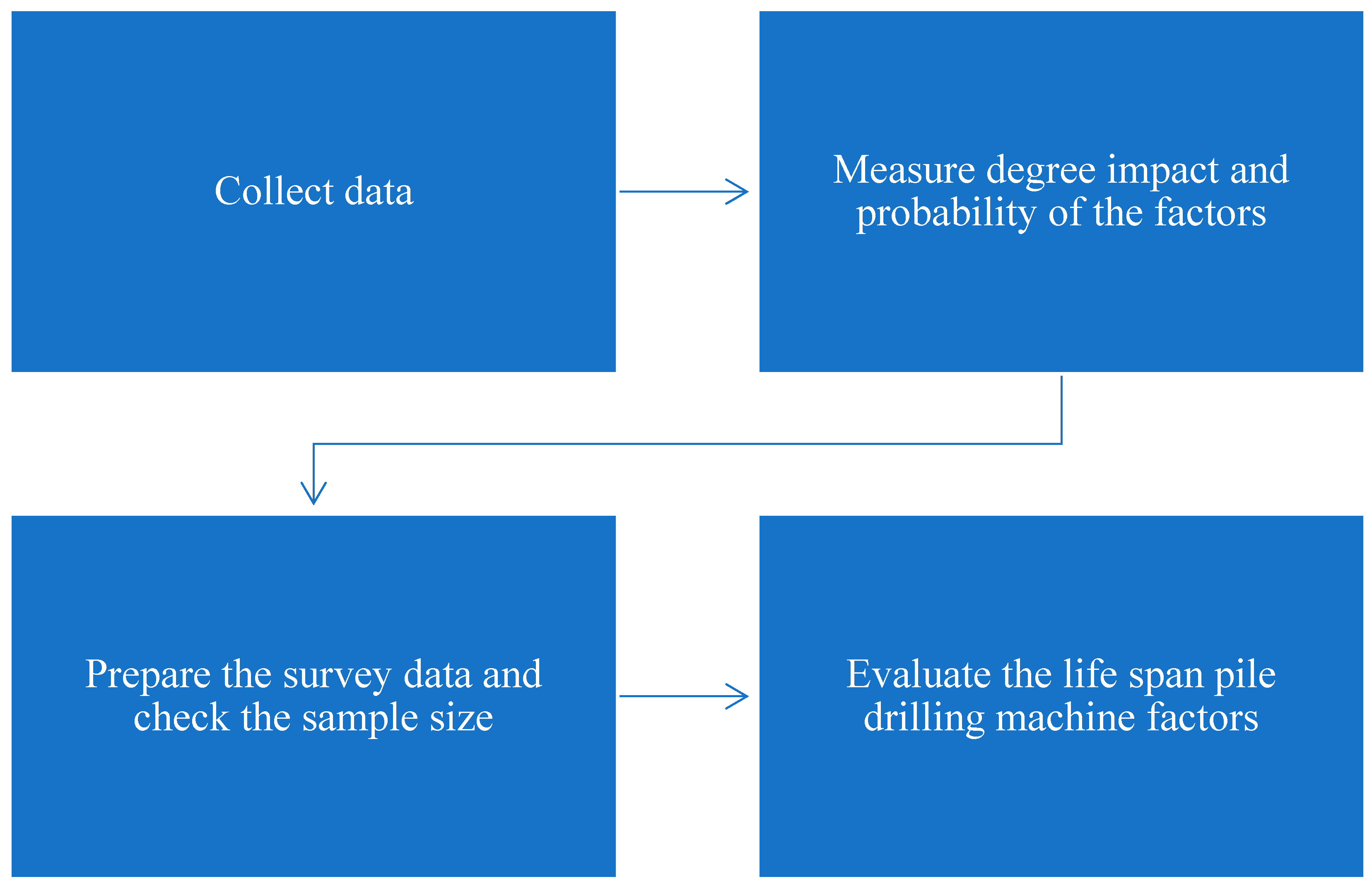
3. Methodology
3.1. Collect Data
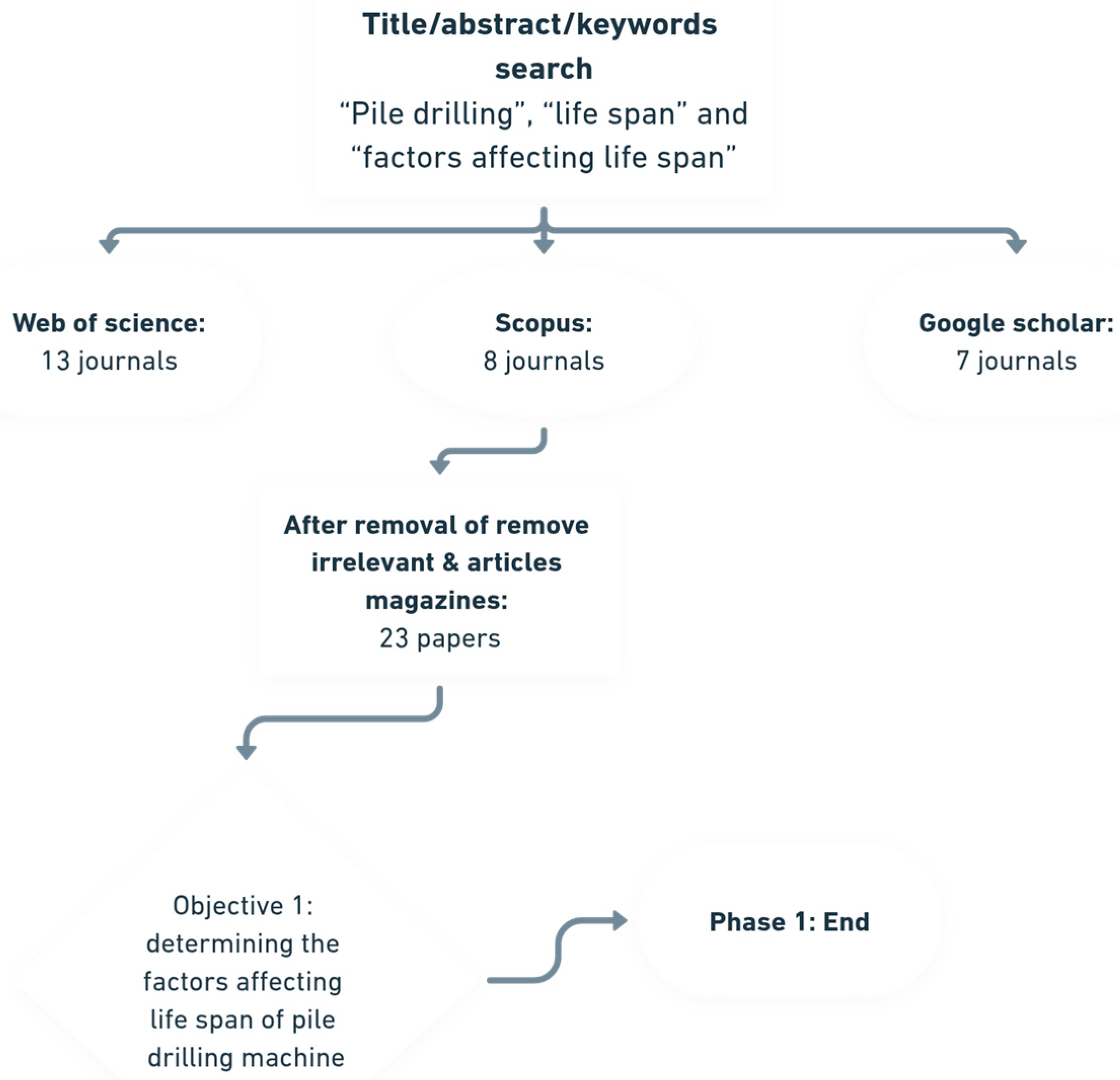
3.1.1. Determining the Factors
3.1.2. Extracting the Factors
3.2. Measure the Degree of Impact and Probability of the Factors
- The probability of the factor risk.
- The degree of impact of the factor.
Quantitative Measurement
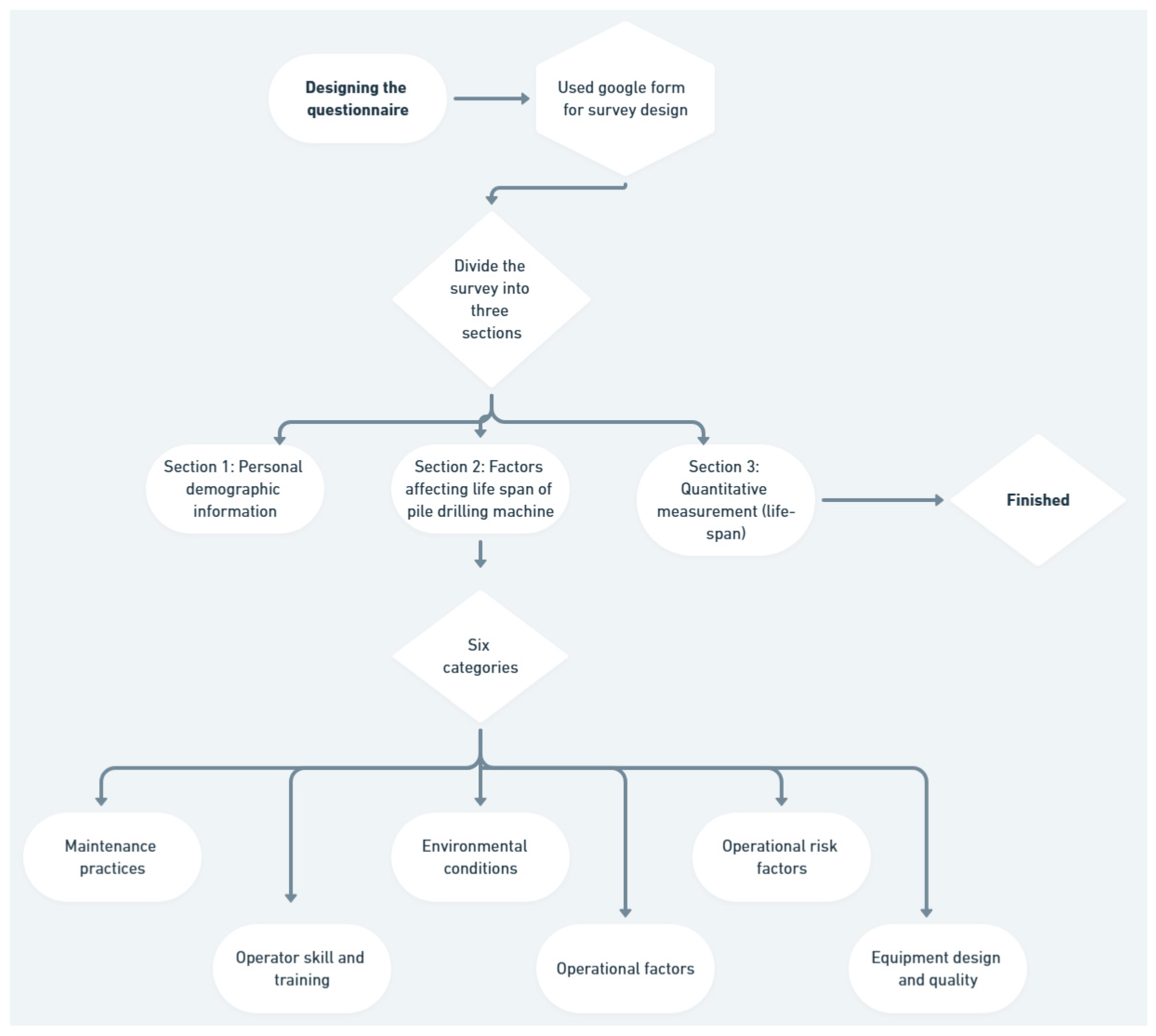
3.3. Prepare the Survey Data and Check the Sample Size
3.4. Evaluate the Site Drilling Machine’s Lifespan Factors
3.4.1. Compute the Contribution of Impact and Probability of the Factors Using CA
Compute the Grand Total, Row Totals, and Column Totals
Compute the Relative Matrix
Calculate Expected Frequencies
Compute the Matrix of Deviations (Standardized Residuals)
Perform Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Compute Contributions of Factors
3.4.2. Evaluate Factors Using the Matrix Assessment Method
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Information
4.2. Contribution of Impact and Probability Factors
4.3. Risk Assessment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Enhancing operator proficiency (addressing OF5) by investing in and mandating standardized, comprehensive operator training programs beyond basic operation to include machine limitations.
- Managing operational intensity (addressing OF1, OF2, and OR1) by developing realistic project schedules for equipment capacity and necessary maintenance downtime.
- Mitigating environmental risks (addressing EC3, India; EC4, Saudi Arabia; EC1, global) by mandating thorough pre-drilling geotechnical investigations to understand soil conditions (EC3) and selecting drilling methods and support systems (e.g., casing) appropriate for the identified ground types.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assaf, S.A.; Al-Hejji, S. Causes of delay in large construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2006, 24, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, R.D. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge; Project Management Institute: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, P.X.W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. Understanding the key risks in construction projects in China. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2007, 25, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud El-Gohary, K.; Fayek Aziz, R. Factors Influencing Construction Labor Productivity in Egypt. J. Manag. Eng. 2014, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, R.K. An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.P.C.; Chan, D.W.M.; Ho, K.S.K. An empirical study of the benefits of construction partnering in Hong Kong. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2003, 21, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, R. Applications of maintenance optimization models: A review and analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1996, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.P.; Han, Y.M.; Jin, J. An Optimum Design of Piling Machine Column with FEM. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 668, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanova, S.; Vinogradova, N. Analysis of the requirements of normative and technical documentation for piling equipment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 911, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Narang, H.K.; Sahu, A.K.; Sahu, N.K. Machine economic life estimation based on depreciation-replacement model. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1249225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 31000: 2018; Risk Management—Guidelines. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Ford, D.N.; Sterman, J.D. Dynamic modeling of product development processes. Syst. Dyn. Rev. J. Syst. Dyn. Soc. 1998, 14, 31–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J. System dynamics at sixty: The path forward. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2018, 34, 5–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, A.B.; Langarudi, S.P.; Clancy, T. What is System Dynamics? Defining Characteristics and the Opportunities they Create. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimani, S.; van der Veen, J.; Sobek, D.K.; Gulyaz, E.; Venugopal, V. On the application of Lean principles and practices to innovation management: A systematic review. TQM J. 2019, 31, 1064–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Saeed, S. Monitoring and predicting land use and land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS techniques—A case study of a hilly area, Jiangle, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakano, M. System dynamics to design an educational game for improving interpersonal skills to manage conflict. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2019, 13, JAMDSM0040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youzuan. Tips for Maintaining and Extending the Lifespan of Rotary Drilling Rigs in Pile Foundation Operations; Drillmaster Engineering Technology: Changsha, China. Available online: https://www.drillmastergroup.com/tips-for-maintaining-and-extending-the-lifespan-of-rotary-drilling-rigs-in-pile-foundation-operations/#:~:text=Routine%20visual%20inspections%20of%20the,could%20accelerate%20wear%20and%20corrosion (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Ehsani, M.; Ehsani, M. Pile Repair Methods; PileMedic: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Daryaei, R.; Bakroon, M.; Aubram, D.; Rackwitz, F. Numerical evaluation of the soil behavior during pipe-pile installation using impact and vibratory driving in sand. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 134, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Alharbi, T.; Al Hawas, R.; Rikan, N. Geographic Information System and Multivariate Analysis Approach for Mapping Soil Contamination and Environmental Risk Assessment in Arid Regions. Land 2025, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, P. Analysis of Soil Response during High-Frequency Vibratory Steel Pipe Pile Driving in Soft Soil. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2024, 2024, 4223470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, P. How to Repair and Maintain Steel Pipe Piling; Pile Buck Magazine: Vero Beach, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Erumban, A.A. Lifetimes of machinery and equipment: Evidence from Dutch manufacturing. Rev. Income Wealth 2008, 54, 237–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Schunnesson, H.; Kumar, U. Evaluation of operating life length of rotary tricone bits using Measurement While Drilling data. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 83, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, M.; Peng, Q.; Wang, C. Analysis of Foundation Pit Support Selection and Design Problems in Deep Soft Soil Area. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2024, 2024, 2779898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Tateishi, R. Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.L.; Franke, G.R. Correspondence Analysis: Graphical Representation of Categorical Data in Marketing Research. J. Mark. Res. 1986, 23, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M. Correspondence Analysis in Practice; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Doey, L.; Kurta, J. Correspondence Analysis applied to psychological research. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2011, 7, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F. Correspondence Analysis and Data Coding with JAVA and R; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2005; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.1201/9781420034943/correspondence-analysis-data-coding-java-fionn-murtagh (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Anton, H.; Rorres, C. Elementary Linear Algebra; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge; Project Management Institute: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 1987, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Frontmatter. In Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessions, J.; Berry, M.; Han, H.S. Machine rate estimates and equipment utilization—A modified approach. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2021, 42, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumeanu, A.C. Considerations regarding determination of optimal preventive maintenance periodicity for subsurface sucker rod pumps. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulychev, V.; Golubina, S.; Semenov, M.; Korzhikov, A. Predicting the Intensity of Abrasive Wear Based on the Fatigue Hypothesis. MATEC Web Conf. 2021, 346, 03069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linins, O.; Jansons, E.; Leitans, A.; Boiko, I.; Lungevics, J. Estimation of service life of mechanical engineering components. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 27, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breesam, H.K.; Jawad, Z.A. Factors affecting maintenance procedures for public buildings. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1090, 012120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Techniques, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, M. A hybrid approach for a cost estimate of residential buildings in Egypt at the early stage. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Muñiz, B.; Montes-Peón, J.M.; Vázquez-Ordás, C.J. Occupational accidents and the economic cycle in Spain 1994–2014. Saf. Sci. 2018, 106, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyland, A.; Rausand, M. System Reliability Theory: Models and Statistical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vision 2030 Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Dhillon, B.S. Engineering Maintenance: A Modern Approach; CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Achelpohl, E.R. The Effect of Overloading on Reliability of Wheel Loader Structur Eliability of Wheel Loader Structural Components. Ph.D. Thesis, Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, MO, USA, 2018. Available online: https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/doctoral_dissertations/2655 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Alharbi, B.H. Airborne Dust in Saudi Arabia: Source Areas, Entrainment, Simulation and Composition. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Clayton VIC, Australia, 2008. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=ar&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Airborne+Dust+in+Saudi+Arabia%3A+Source+Areas%2C+Entrainment%2C+Simulation+and+Composition&btnG= (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- ISO 7243; Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment—Assessment of Heat Stress Using the WBGT (Wet Bulb Globe Temperature) Index. International Organization Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: www.iso.orgiTehSTANDARDPREVIEW (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- ISO 3834-2-2021; Quality Requirements for Fusion Welding of Metallic Materials—Part 2: Comprehensive Quality Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 3834-1:2021; Quality Requirements for Fusion Welding of Metallic Materials—Part 1: Criteria for the Selection of the Appropriate Level of Quality Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.






| Category | Risk Factor | Code | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Factors | Frequency of use | OF1 | [18] |
| Duration of operation per session | OF2 | [36] | |
| Workload intensity | OF3 | [36] | |
| Maintenance schedule | OF4 | [37] | |
| Operator training | OF5 | [18] | |
| Environmental Conditions | Climate | EC1 | [33] |
| Exposure to elements | EC2 | ||
| Soil conditions | EC3 | [20] | |
| Presence of abrasive materials | EC4 | [38] | |
| Air quality | EC5 | ||
| Equipment Design and Quality | Material quality | EDQ1 | [19] |
| Structural integrity | EDQ2 | [16] | |
| Component compatibility | EDQ3 | [10] | |
| Engineering standards | EDQ4 | [39] | |
| Manufacturing quality control | EDQ5 | [40] | |
| Maintenance Practices | Regularity of inspections | MP1 | [15] |
| Timeliness of repairs | MP2 | ||
| Lubrication schedule | MP3 | [18] | |
| Replacement of worn parts | MP4 | [15] | |
| Cleaning procedures | MP5 | ||
| Operator Skill and Training | Knowledge of equipment | OST1 | [18] |
| Maintenance procedures | OST2 | ||
| Ability to detect problems | OST3 | ||
| Safe operating practices | OST4 | ||
| Availability of skilled technician | OST5 | ||
| Operational Risk Factors | Collisions or external impacts during operation | OR1 | [40] |
| Emergency shutdowns | OR2 | ||
| Transportation conditions | OR3 | ||
| Equipment age | OR4 | ||
| Overloading | OR5 |
| Global | India | Saudi Arabia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | I | Factor | P | Factor | I | Factor | P | Factor | I | Factor | P |
| OF5 | 0.042 | OF5 | 0.042 | OF5 | 0.043 | OF5 | 0.043 | OF5 | 0.040 | OF5 | 0.041 |
| OF2 | 0.039 | OF1 | 0.039 | OF2 | 0.042 | OF1 | 0.043 | OR1 | 0.039 | OR1 | 0.041 |
| OF1 | 0.038 | OF2 | 0.039 | OF1 | 0.042 | OF2 | 0.042 | OR7 | 0.039 | OR7 | 0.038 |
| OR7 | 0.037 | OR7 | 0.037 | EC3 | 0.041 | EC3 | 0.041 | OF2 | 0.036 | OF1 | 0.037 |
| EC3 | 0.037 | EC3 | 0.037 | OF3 | 0.037 | OF3 | 0.038 | OR4 | 0.036 | OR4 | 0.036 |
| OR1 | 0.035 | OR1 | 0.036 | OF4 | 0.036 | OR7 | 0.037 | OF1 | 0.034 | OF2 | 0.036 |
| OF3 | 0.033 | OF3 | 0.033 | OR7 | 0.036 | OF4 | 0.037 | MP1 | 0.033 | EC3 | 0.034 |
| OF4 | 0.033 | OF4 | 0.033 | EC1 | 0.034 | EC1 | 0.034 | EC4 | 0.033 | OST1 | 0.034 |
| EC4 | 0.033 | OR4 | 0.033 | EC2 | 0.033 | EC2 | 0.033 | EC3 | 0.033 | EC4 | 0.033 |
| OR4 | 0.033 | EC4 | 0.032 | EC4 | 0.032 | EC4 | 0.032 | OST1 | 0.033 | OST4 | 0.032 |
| EC1 | 0.032 | OST1 | 0.032 | OR1 | 0.031 | OR1 | 0.030 | OR2 | 0.033 | OR5 | 0.032 |
| OST1 | 0.031 | EC2 | 0.031 | EC5 | 0.030 | OST1 | 0.030 | OST4 | 0.032 | OR3 | 0.032 |
| MP1 | 0.031 | OR5 | 0.031 | OST1 | 0.030 | OR4 | 0.029 | OR5 | 0.032 | EDQ5 | 0.032 |
| EC2 | 0.031 | OST4 | 0.031 | EDQ1 | 0.030 | EDQ1 | 0.029 | OST5 | 0.031 | OST3 | 0.032 |
| OR2 | 0.031 | OR3 | 0.031 | EDQ3 | 0.030 | OR3 | 0.029 | OR3 | 0.031 | OF4 | 0.031 |
| OST4 | 0.030 | EDQ5 | 0.030 | OR6 | 0.029 | MP3 | 0.029 | OF4 | 0.031 | OR6 | 0.030 |
| OR5 | 0.030 | EC1 | 0.030 | OR4 | 0.029 | OR6 | 0.029 | EDQ5 | 0.030 | EC5 | 0.030 |
| OR3 | 0.030 | OST3 | 0.030 | OR5 | 0.029 | EDQ3 | 0.029 | OR6 | 0.030 | OST5 | 0.030 |
| OR6 | 0.030 | OR6 | 0.030 | OST4 | 0.029 | EC5 | 0.029 | EC1 | 0.030 | MP1 | 0.030 |
| EDQ5 | 0.030 | EC5 | 0.030 | MP3 | 0.029 | OST4 | 0.029 | OF3 | 0.030 | OR2 | 0.030 |
| EC5 | 0.030 | EDQ1 | 0.029 | OR3 | 0.029 | OR5 | 0.029 | OST3 | 0.030 | MP4 | 0.030 |
| EDQ1 | 0.029 | MP1 | 0.029 | EDQ5 | 0.029 | OR2 | 0.028 | EC2 | 0.029 | OF3 | 0.029 |
| OST3 | 0.029 | OR2 | 0.029 | MP1 | 0.028 | MP1 | 0.028 | OST2 | 0.029 | EC2 | 0.029 |
| MP3 | 0.029 | MP2 | 0.029 | OST3 | 0.028 | EDQ5 | 0.028 | EC5 | 0.029 | MP2 | 0.029 |
| OST5 | 0.029 | EDQ3 | 0.028 | EDQ2 | 0.028 | OST3 | 0.028 | MP3 | 0.029 | EDQ1 | 0.029 |
| OST2 | 0.029 | MP3 | 0.028 | OR2 | 0.028 | EDQ2 | 0.028 | MP2 | 0.028 | EDQ3 | 0.028 |
| EDQ3 | 0.028 | OST5 | 0.028 | OST2 | 0.028 | MP2 | 0.028 | EDQ1 | 0.028 | MP3 | 0.028 |
| MP2 | 0.028 | MP4 | 0.027 | MP2 | 0.027 | OST2 | 0.028 | MP4 | 0.028 | EC1 | 0.027 |
| EDQ4 | 0.027 | OST2 | 0.027 | EDQ4 | 0.027 | EDQ4 | 0.027 | EDQ3 | 0.027 | OST2 | 0.027 |
| EDQ2 | 0.026 | EDQ4 | 0.027 | MP5 | 0.026 | MP5 | 0.026 | EDQ4 | 0.027 | EDQ4 | 0.026 |
| MP4 | 0.026 | EDQ2 | 0.026 | OST5 | 0.026 | OST5 | 0.026 | EDQ2 | 0.025 | MP5 | 0.026 |
| MP5 | 0.025 | MP5 | 0.026 | MP4 | 0.025 | MP4 | 0.024 | MP5 | 0.025 | EDQ2 | 0.025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhtar, S.; Al-Otaibi, S.M.; Algaraawi, W.S.; Alsanabani, N.M.; Al-Gahtani, K.S.; Fnais, A. Assessment of the Lifespan of a Site Drilling Machine in Saudi Arabia and India Using Correspondence Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093865
Akhtar S, Al-Otaibi SM, Algaraawi WS, Alsanabani NM, Al-Gahtani KS, Fnais A. Assessment of the Lifespan of a Site Drilling Machine in Saudi Arabia and India Using Correspondence Analysis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093865
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhtar, Salman, Saad M. Al-Otaibi, Waleed S. Algaraawi, Naif M. Alsanabani, Khalid S. Al-Gahtani, and Abdulrahman Fnais. 2025. "Assessment of the Lifespan of a Site Drilling Machine in Saudi Arabia and India Using Correspondence Analysis" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093865
APA StyleAkhtar, S., Al-Otaibi, S. M., Algaraawi, W. S., Alsanabani, N. M., Al-Gahtani, K. S., & Fnais, A. (2025). Assessment of the Lifespan of a Site Drilling Machine in Saudi Arabia and India Using Correspondence Analysis. Sustainability, 17(9), 3865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093865







