Using GMDH Neural Networks to Model the Power and Torque of a Stirling Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles of Modeling Using GMDH Types of Artificial Neural Networks


3. Results and Discussion
| (°C) | (bar) | () | Output Power (W) | Torque (N.m) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | (600–900) | (4.14–12.41) | (2.5–7.8) | - | - | [35,36] |
| Output | - | - | - | (36–500) | (0.19–3.7) | [35,36] |
| Statistical Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9518 |
| MAPE | 0.0007 |
| RMSE | 0.1718 |
| Statistical Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9737 |
| MAPE | 0.0005 |
| RMSE | 0.1838 |


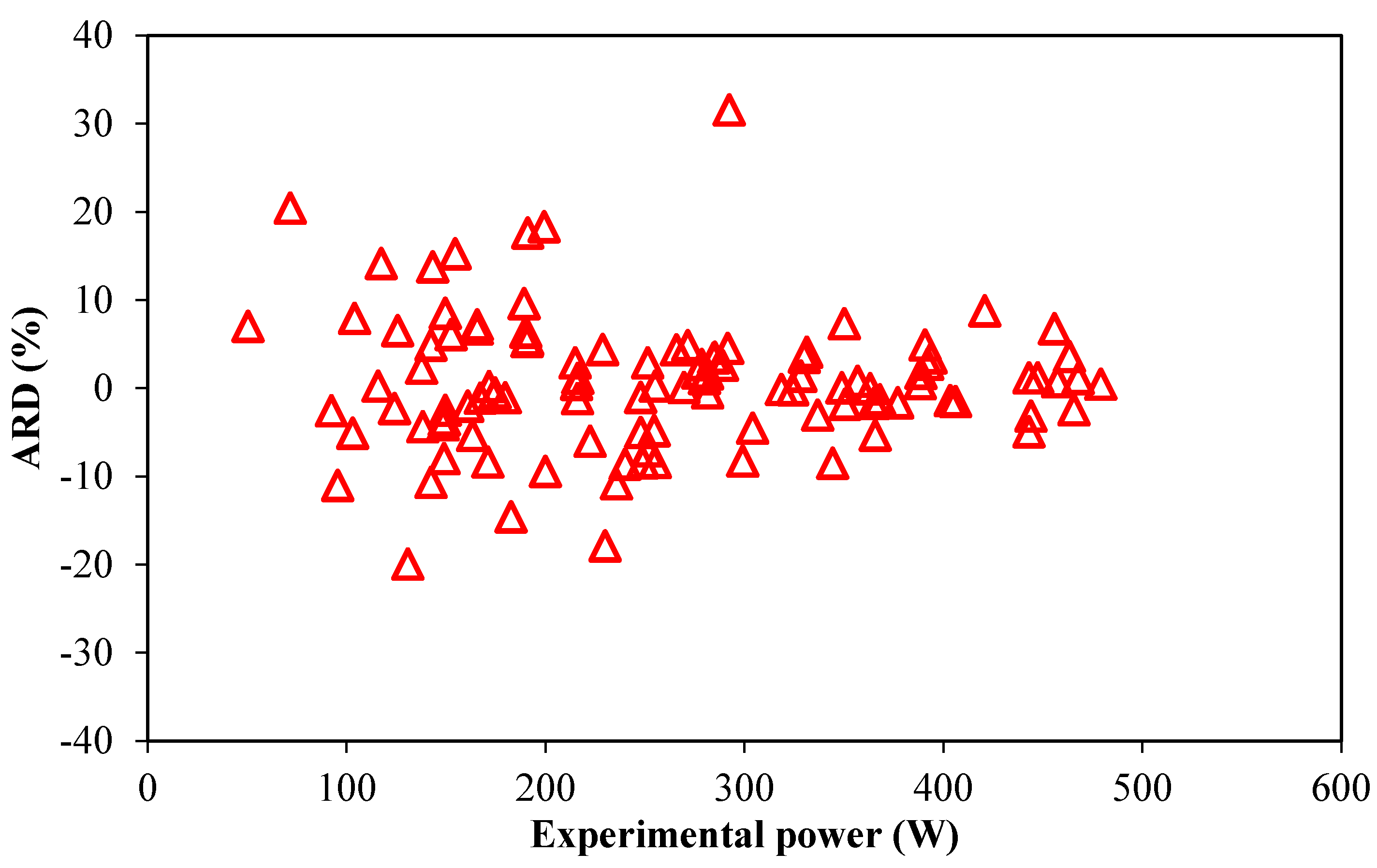

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shendage, D.J.; Kedare, S.B.; Bapat, S.L. An analysis of a beta type Stirling engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, D.G.; Verma, S.K. Technological development in the Stirling cycle engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, H.; Yucesu, H.S.; Cinar, C. Nodal analysis of a Stirling engine with concentric piston and displacer. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, H.; Yucesu, H.S.; Cinar, C.; Aksoy, F. An experimental study on the development of a b-type Stirling engine for low and moderate temperature heat sources. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodesser, E. Electricity production in rural villages with biomass Stirling engines. Renew. Energy 1999, 16, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripakagorn, A.; Srikam, C. Design and performance of a moderate temperature difference Stirling engine. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, H.; Cinar, C.; Ozturk, E.; Yucesu, H.S. Torque and power characteristics of a helium charged Stirling engine with a lever controlled displacer driving mechanism. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Yu, Y.J. Numerical model for predicting thermodynamic cycle and thermal efficiency of a beta-type Stirling engine with rhombic-drive mechanism. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2590–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Wong, K.L.; Po, L.W. A numerical analysis on the performance of a pressurized twin power piston gamma-type Stirling engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 62, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formosa, F.; Despesse, G. Analytical model for Stirling cycle machine design. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Pourkiaei, S.M. Optimisation of the thermodynamic performance of the Stirling engine. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Dehghani, S. Evaluation of the maximized power of a regenerative endoreversible Stirling cycle using the thermodynamic analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 76, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghyani, S.; Kasaeian, A.; Ahmadi, M.H. Multi-objective optimization of Stirling engine using non-ideal adiabatic method. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Ghare Aghaj, S.S.; Nazeri, A. Prediction of power in solar Stirling heat engine by using neural network based on hybrid genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 22, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Hosseinzade, H.; Sayyaadi, H.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Kimiaghalam, F. Application of the multi-objective optimization method for designing a powered Stirling heat engine: Design with maximized power, thermal efficiency and minimized pressure loss. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Sayyaadi, H.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Barranco-Jimenez, M.A. Thermo-economic multi-objective optimization of solar dish-Stirling engine by implementing evolutionary algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 73, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Sayyaadi, H.; Dehghani, S.; Hosseinzade, H. Designing a solar powered Stirling heat engine based on multiple criteria: Maximized thermal efficiency and power. Energy Convers. Manage. 2013, 75, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.; Shibata, T.; Zadeh, L. Genetic Algorithms and Fuzzy Logic Systems: Soft Computing Perspectives; World Scientific Publishing: River Edge, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kristinson, K.; Dumont, G. System identification and control using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1992, 22, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koza, J. Genetic Programming: On the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Ahmadi, M.A.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Feidt, M.; Pourkiaei, S.M. Multi-objective optimization of an irreversible Stirling cryogenic refrigerator cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 82, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Ahmadi, M.A.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Mehrpooya, M.; Feidt, M. Thermodynamic optimization of Stirling heat pump based on multiple criteria. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Dehghani, S.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Feidt, M.; Barranco-Jimenez, M.A. Optimal design of a solar driven heat engine based on thermal and thermo-economic criteria. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 75, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vazquez, K. Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms in Non-Linear System Identification. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ivakhnenko, A.C. Polynomial theory of complex systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1971, 1, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farlow, S.J. Self-Organizing Method in Modelling: GMDH Type Algorithm; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, J.A.; Lemke, F. Self-Organizing Data Mining; Libri: Hamburg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nariman-zadeh, N.; Darvizeh, A.; Felezi, M.E.; Gharababei, H. Polynomial modelling of explosive compaction process of metallic powders using GMDH-type neural networks and singular value decomposition. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2002, 10, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.M.; Fleming, P.J. Nonlinear system identification with multi-objective genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 13th World Congress of the International Federation of Automatic Control, San Francisco, CA, USA, 30 June–5 July 1996; Pergamon: San Francisco, CA; USA, 1996; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.P.; Kadirkamanathan, V. Multi-objective criteria for neural network structure selection and identification of nonlinear systems using genetic algorithms. IEE Proc. Control Theory Appl. 1999, 146, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariman-Zadeh, N.; Darvizeh, A.; Ahmad-Zadeh, R. Hybrid Genetic Design of GMDH-Type Neural Networks Using Singular Value Decomposition for Modelling and Prediction of the Explosive Cutting Process. Proc. Inst. Mech. E Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2003, 217, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, V.W. Evolutionary computation approaches to solving problems in neural computation. In Handbook of Evolutionary Computation; Back, T., Fogel, D.B., Michalewicz, Z., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X. Evolving artificial neural networks. IEEE Proc. 1999, 87, 1423–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasechkina, E.F.; Yarin, V.D. Evolving polynomial neural network by means of genetic algorithm: Some application examples. Complex Int. 2001, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, G.L. Performance Characteristics of the Stirling Engine. Master’s Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, J.I.; Gonzaalez, M.A.; Gonzaalez, C.; Fano, J. A new equation representing the performance of kinematic Stirling engines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2000, 214, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariman-zadeh, N.; Atashkari, K.; Jamali, A.; Pilechi, A.; Yao, X. Inverse modelling of multi-objective thermodynamically optimized turbojet engines using GMDH-type neural networks and evolutionary algorithms. J. Eng. Optim. 2005, 37, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.A.; Golshadi, M. Neural Network Based Swarm Concept for Prediction Asphaltene Precipitation due Natural Depletion. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 98–99, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashkari, K.; Nariman-Zadeh, N.; Jamali, A.; Pilechi, A. Thermodynamic Pareto optimization of turbojet using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2005, 44, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashkari, K.; Nariman-Zadeh, N.; Golcu, M.; Khalkhali, A.; Jamali, A. Modelling and multi-objective optimization of a variable valve-timing spark-ignition engine using polynomial neural networks and evolutionary algorithms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Nariman-zadeh, N.; Darvizeh, A.; Masoumi, A.; Hamrang, S. Multi-objective evolutionary optimization of polynomial neural networks for modelling and prediction of explosive cutting process. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2009, 22, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.I.E.; Cheng, C.T.; Chau, K.W. Using support vector machines for long-term discharge prediction. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sanchez, A.; Frausto-Solis, J.; Ojeda-Bustamante, W. Attribute Selection Impact on Linear and Nonlinear Regression Models for Crop Yield Prediction. Sci. World J. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçiçek, H.; Akdoğan, E.; Karagöz, S. The Use of Artificial Neural Network for Prediction of Dissolution Kinetics. Sci. World J. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Ersin, O. Modeling Markov Switching ARMA-GARCH Neural Networks Models and an Application to Forecasting Stock Returns. Sci. World J. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmadi, M.H.; Ahmadi, M.-A.; Mehrpooya, M.; Rosen, M.A. Using GMDH Neural Networks to Model the Power and Torque of a Stirling Engine. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2243-2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022243
Ahmadi MH, Ahmadi M-A, Mehrpooya M, Rosen MA. Using GMDH Neural Networks to Model the Power and Torque of a Stirling Engine. Sustainability. 2015; 7(2):2243-2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022243
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmadi, Mohammad Hossein, Mohammad-Ali Ahmadi, Mehdi Mehrpooya, and Marc A. Rosen. 2015. "Using GMDH Neural Networks to Model the Power and Torque of a Stirling Engine" Sustainability 7, no. 2: 2243-2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022243
APA StyleAhmadi, M. H., Ahmadi, M.-A., Mehrpooya, M., & Rosen, M. A. (2015). Using GMDH Neural Networks to Model the Power and Torque of a Stirling Engine. Sustainability, 7(2), 2243-2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7022243








