On Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Plastic Pollution in Natural Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radiative Transfer Theory
2.2. Global Temperatures of Seawater and the Temperature Above
3. Results
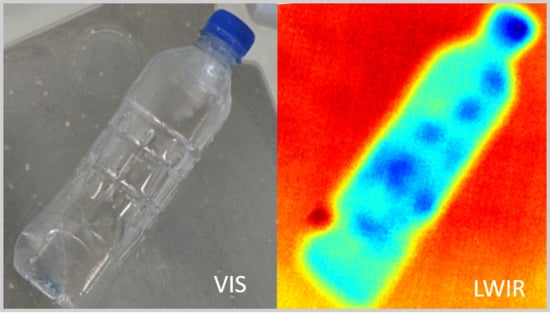
3.1. Plastic Targets in the Aegean Sea
3.2. Global Maps of Monthly Average Air–Sea Temperature Differences
3.2.1. The Month June
3.2.2. The Months December, March and September
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.A.; Hardesty, B.D.; van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Lavender Law, K. A global inventory of small floating plastic debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddijn-Murphy, L.M.; Dufaur, J. Proof of concept for a model of light reflectance of plastics floating on natural waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topouzelis, K.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Garaba, S.P. Detection of floating plastics from satellite and unmanned aerial systems (Plastic Litter Project 2018). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 79, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaba, S.P.; Aitken, J.; Slat, B.; Dierssen, H.M.; Lebreton, L.; Zielinski, O.; Reisser, J. Sensing Ocean Plastics with an Airborne Hyperspectral Shortwave Infrared Imager. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11699–11707. [Google Scholar]
- Maximenko, N.; Corrad, P.; Law, K.L.; Van Sebille, E.; Garaba, S.P.; Lampitt, R.S.; Galgani, F.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Goddijn-Murphy, L.; Veiga, J.M.; et al. Toward the integrated marine debris observing system. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Dech, S. Theoretical background of thermal infrared remote sensing. In Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing: Sensors, Methods, Applications; Kuenzer, C., Dech, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 17, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Peckham, J.; O’Young, S.; Jacobs, J.T. Comparison of medium and long wave infrared imaging for ocean based sensing. J. Ocean Technol. 2015, 10, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, L.; Qin, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Geng, J.; Zhao, S. Identifying the lambertian property of ground surfaces in the thermal infrared region via field experiments. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardon, R. The emissivity of transparent materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1956, 39, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, C. Thermal remote sensing of sea surface temperature. In Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing: Sensors, Methods, Applications; Kuenzer, C., Dech, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 17, pp. 287–313. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, S.M.; Smith, J.A.; Glew, M.D.; Rogers, S.M.; Taylor, J.P. Temperature and salinity dependence of sea surface emissivity in the thermal infrared. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2539–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Aoki, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Motoyoshi, H.; Hachikubo, A.; Sugiura, K.; Yasunari, T.J.; Eide, H.; Storvold, R.; Nakajima, Y.; et al. In-situ measured spectral directional emissivity of snow and ice in the 8–14 Am atmospheric window. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optotherm Emissivity Table. Available online: https://www.optotherm.com/emiss-table.htm (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Thermoworks Emissivity Table. Available online: https://www.thermoworks.com/emissivity_table (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Minkina, W.; Klecha, D. Atmospheric transmission coefficient modelling in the infrared for thermovision measurements. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2016, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1979 to Present. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=form (accessed on 23 July 2019).
- Hirahara, S.; Balmaseda, A.M.; de Boisseson, E.; Hersbach, H. Sea surface temperature and sea ice concentration for ERA5. ERA Report Series, 26; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts: Berkshire, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Donlon, C.J.; Minnett, P.J.; Gentemann, C.; Nightingale, T.J.; Barton, I.J.; Ward, B.; Murray, M.J. Toward improved validation of satellite sea surface skin temperature measurements for climate research. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedger, A.G.J.; Dürr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; Van Cappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Grate Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, A.L.D.F.; Rodrigues, L.D.S.; van Sebille, E.; Rodrigues, F.L.; Ribeiro, L.; Secchi, E.R.; Kessler, F.; Proietti, M.C. Plastics in sea surface waters around the Antarctic Peninsula. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that the great pacific garbage patch is rapidly accumulating plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donlon, C.J.; Martin, M.; Stark, J.; Roberts-Jones, J.; Fiedler, E.; Wimmer, W. The operational sea surface temperature and sea ice analysis (OSTIA) system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 116, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Emissivity | Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | 0.75–0.85 | thermal | [15] |
| Polyethylene | 0.10 | thermal | [15] |
| Styrofoam, insulating | 0.60 | thermal | [16] |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | 0.91–0.93 | thermal | [16] |
| Water | 0.98 | 8–14 µm | [8] |
| Ice | 0.97–0.98 | 8–14 µm | [8] |
| Ice | 0.95–0.99 | 10.5–12.5 µm | [14] |
| Snow | 0.97–1.00 | 10.5–12.5 µm | [14] |
| Sea surface | 0.96–0.99 | thermal remote sensing | [12] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goddijn-Murphy, L.; Williamson, B. On Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Plastic Pollution in Natural Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11182159
Goddijn-Murphy L, Williamson B. On Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Plastic Pollution in Natural Waters. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(18):2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11182159
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoddijn-Murphy, Lonneke, and Benjamin Williamson. 2019. "On Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Plastic Pollution in Natural Waters" Remote Sensing 11, no. 18: 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11182159
APA StyleGoddijn-Murphy, L., & Williamson, B. (2019). On Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Plastic Pollution in Natural Waters. Remote Sensing, 11(18), 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11182159