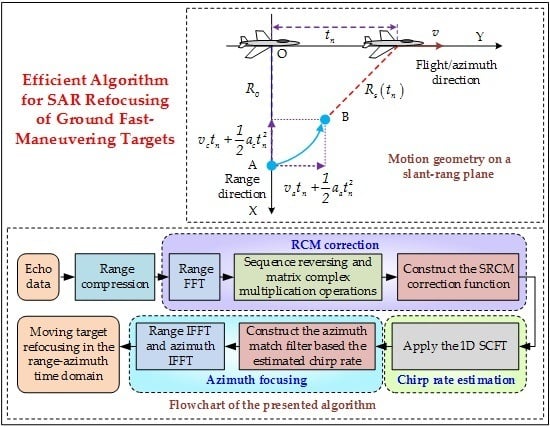
Efficient Algorithm for SAR Refocusing of Ground Fast-Maneuvering Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
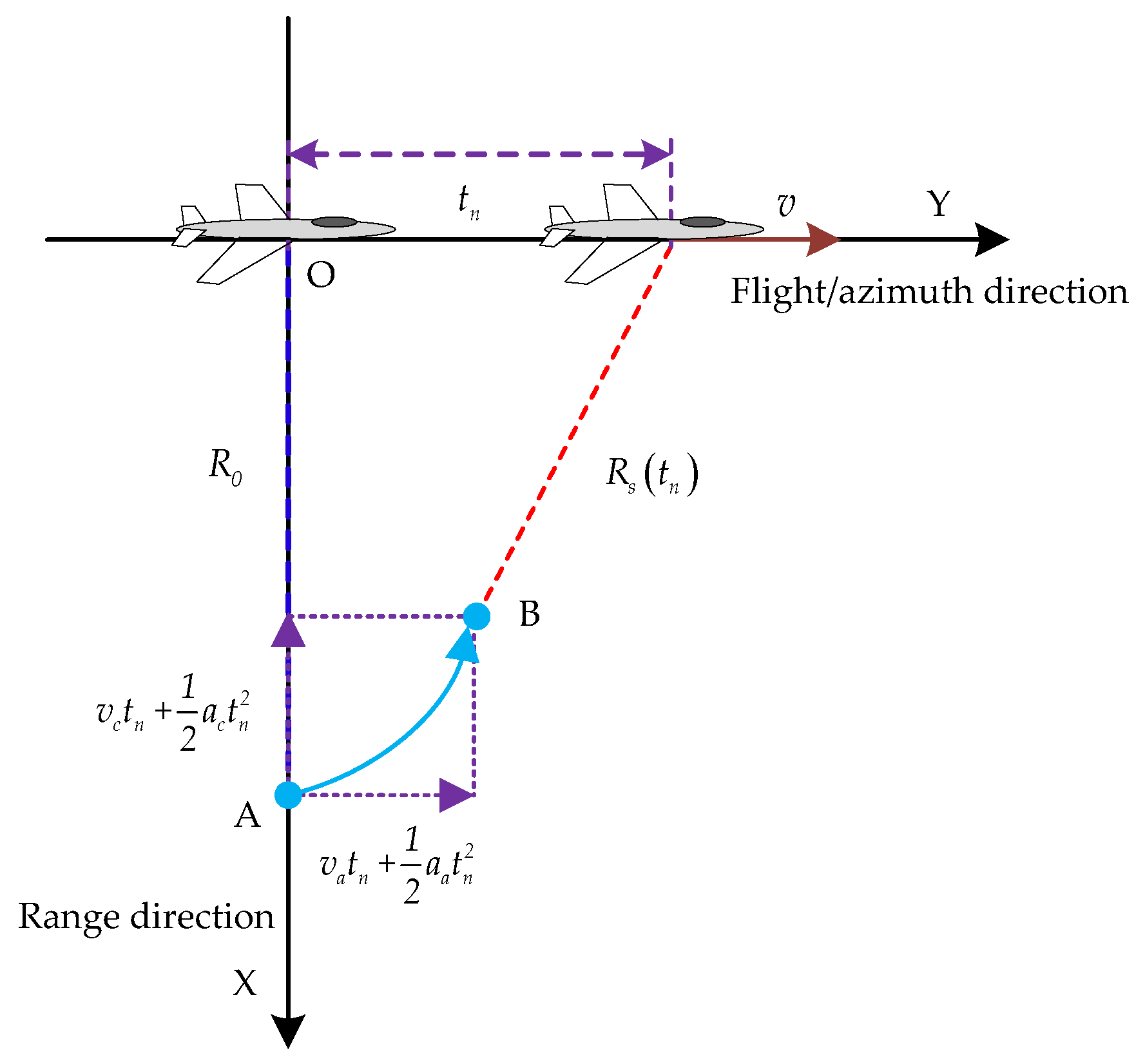
2. Signal Model and Characteristics
2.1. Signal Model
2.2. Signal Characteristics
3. Proposed Algorithm Description
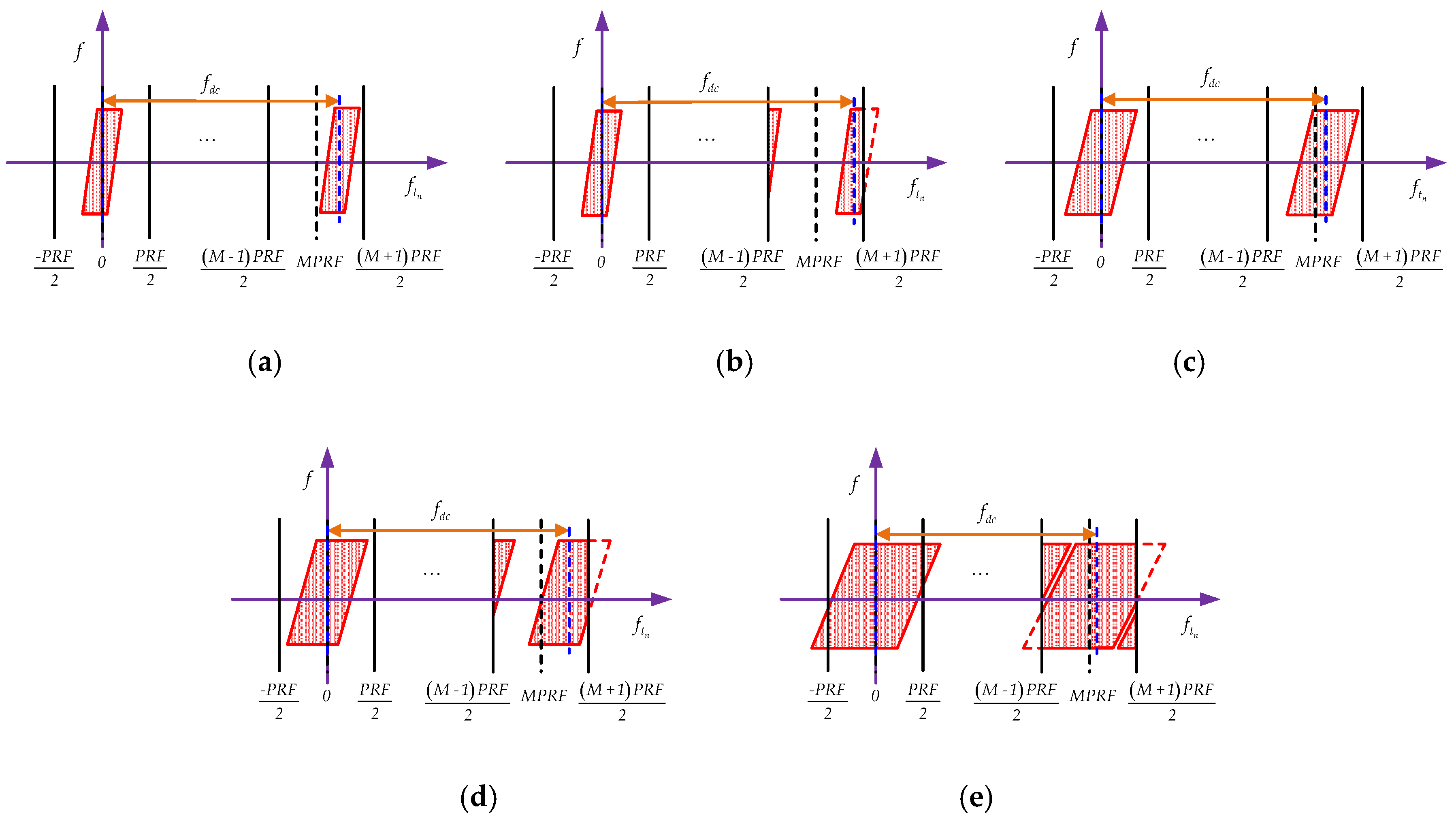
3.1. RCM, Doppler Centre Shift and QDFM Compensation
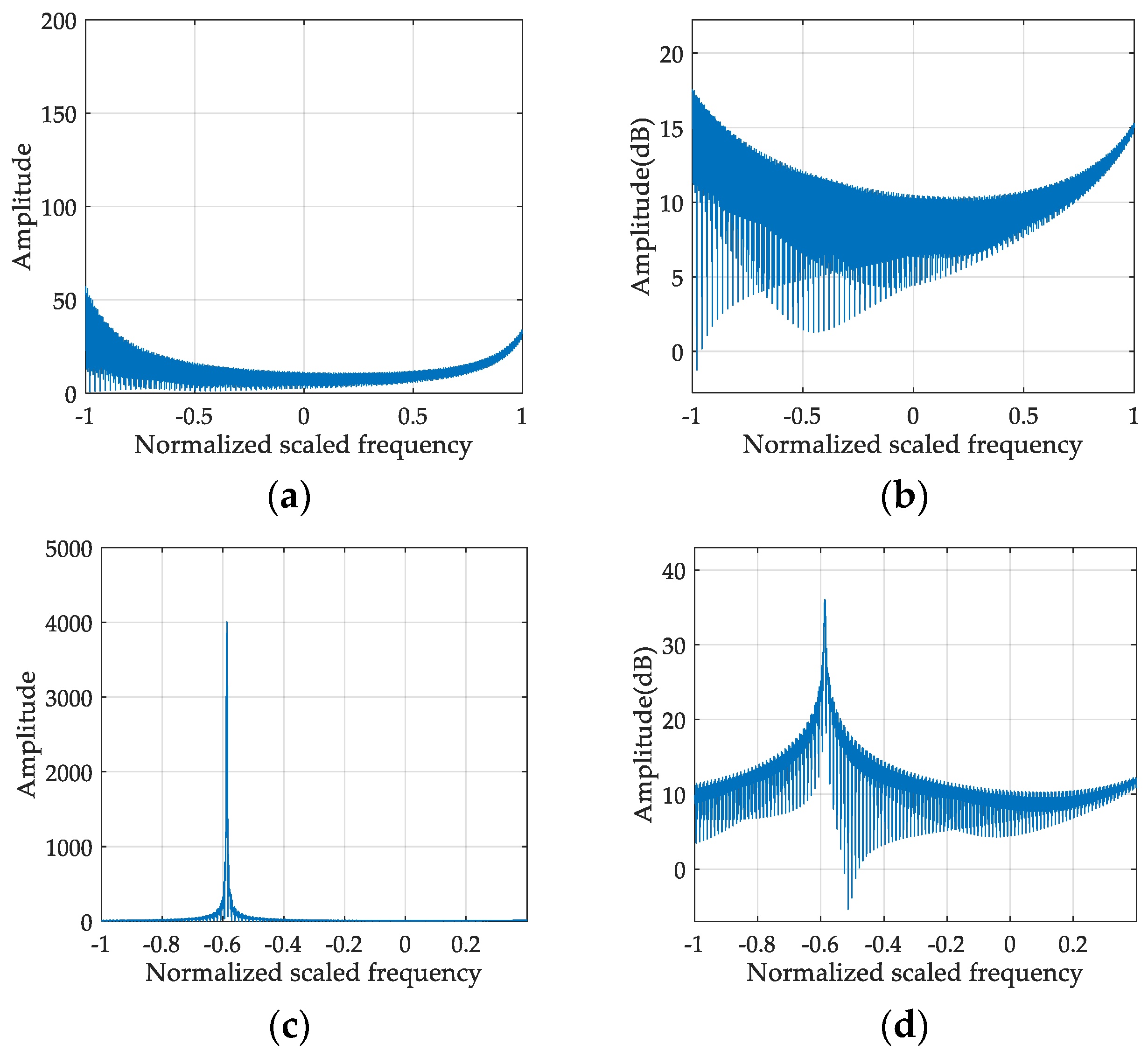
3.2. Estimation of Chirp Rate by 1D SCFT
3.3. Azimuth Focusing by Matched Filter Based on Estimated Chirp Rate
- (1)
- RCM correction
- (1.1)
- Apply the range FFT to the range compressed signal , and obtain .
- (1.2)
- Perform the sequence reversing operation to , and calculate Equation (9) to obtain .
- (1.3)
- Construct the SRCM correction function , and calculate Equation (12) to obtain .
- (2)
- Estimate the chirp rate by using the 1D SCFT, and obtain .
- (3)
- Azimuth focusing
- (3.1)
- Construct the azimuth match filter , and multiply Equation (16) by to obtain .
- (3.2)
- Perform 2D IFFT to , and obtain the final focused result ,
4. Analysis Related to the Proposed Algorithm
4.1. Analysis of the SRCM Correction Function Mismatch
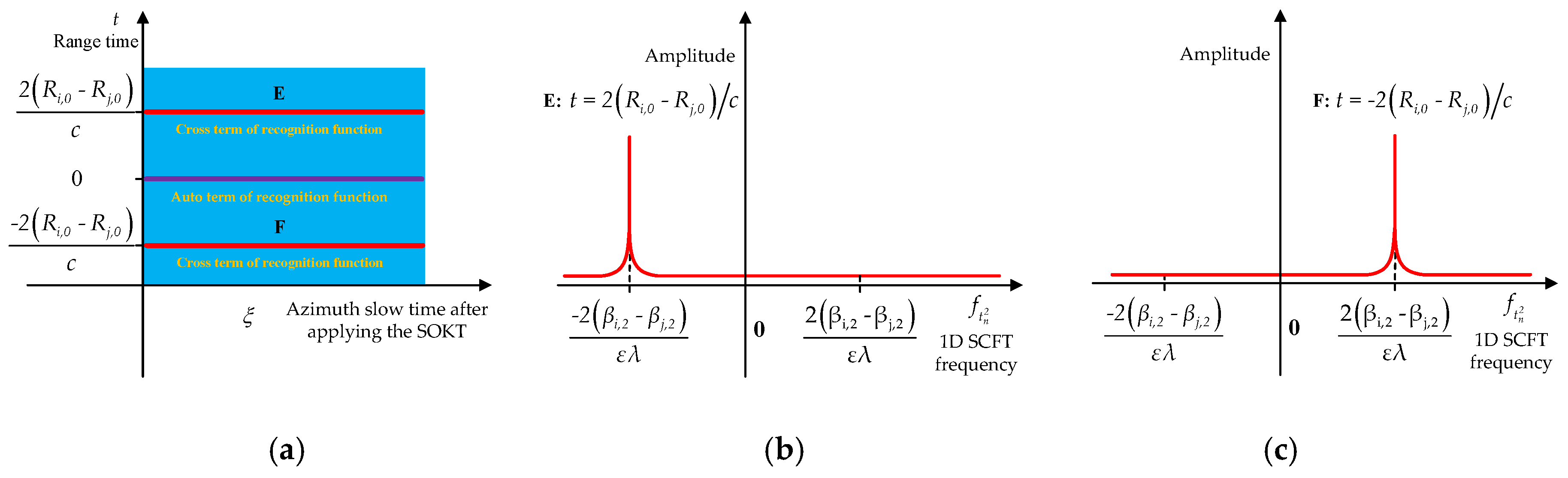
4.2. Analysis of Multiple Target Focusing
5. Experimental Results
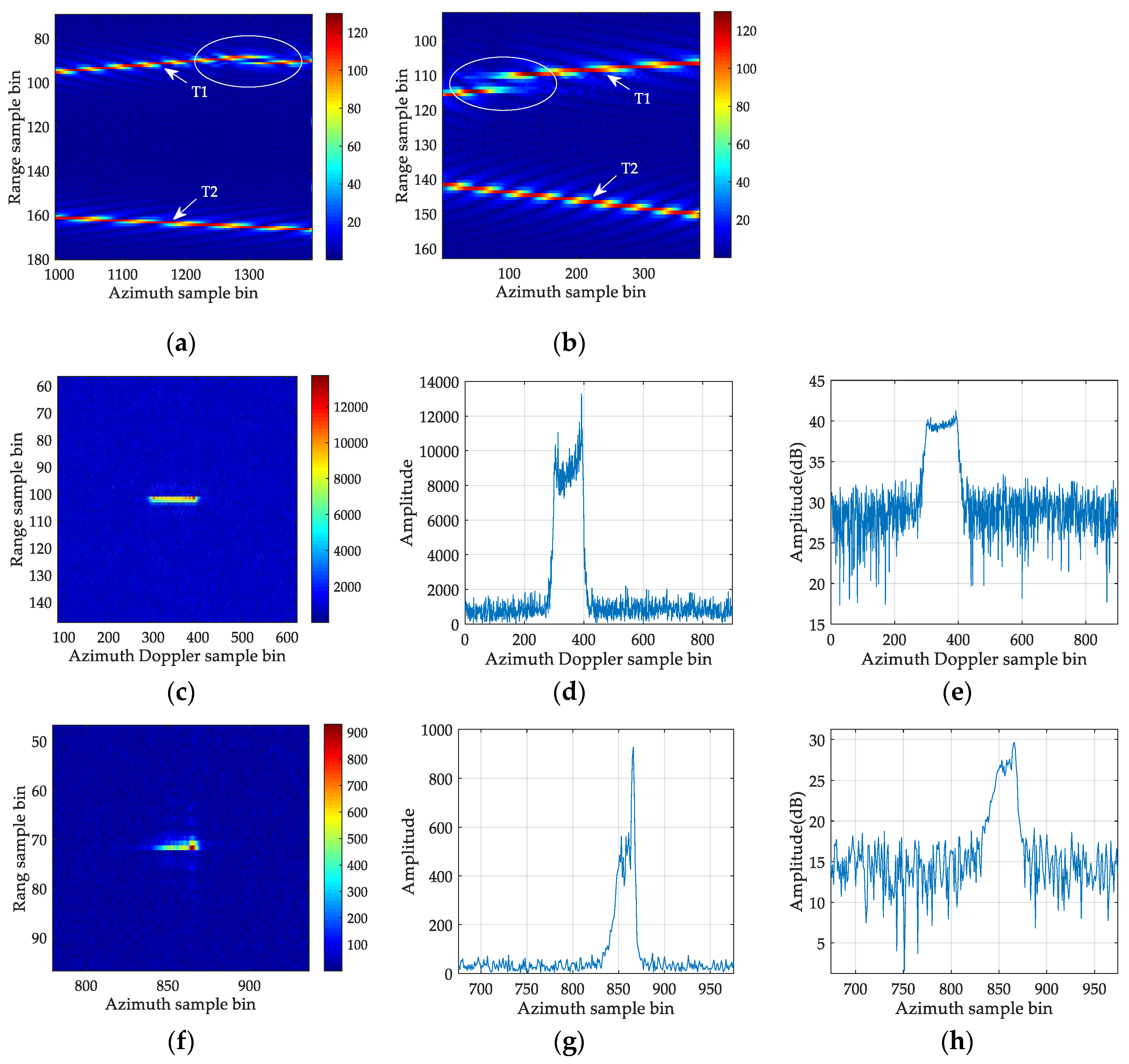
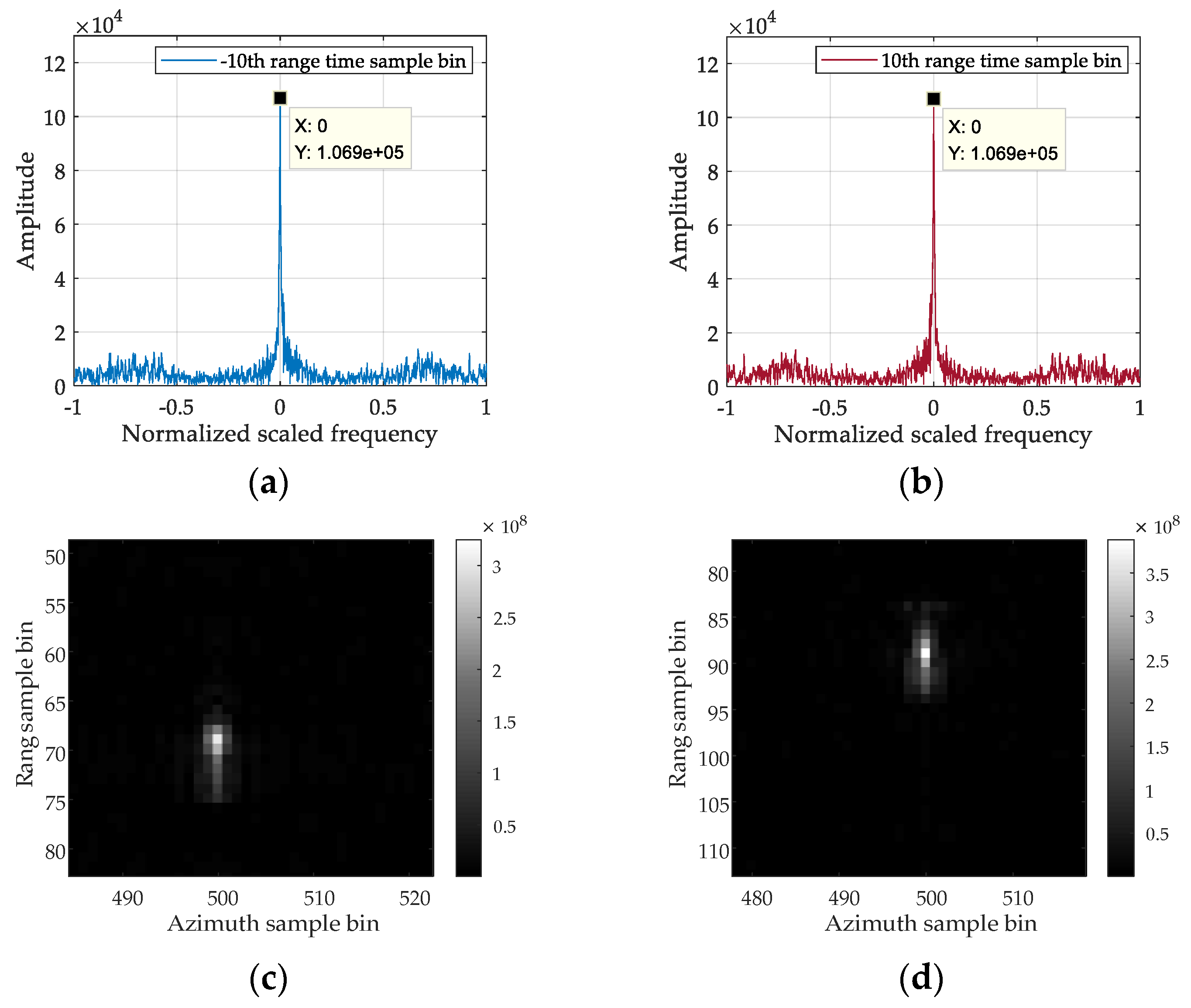
5.1. Simulation Experimental Result Analysis
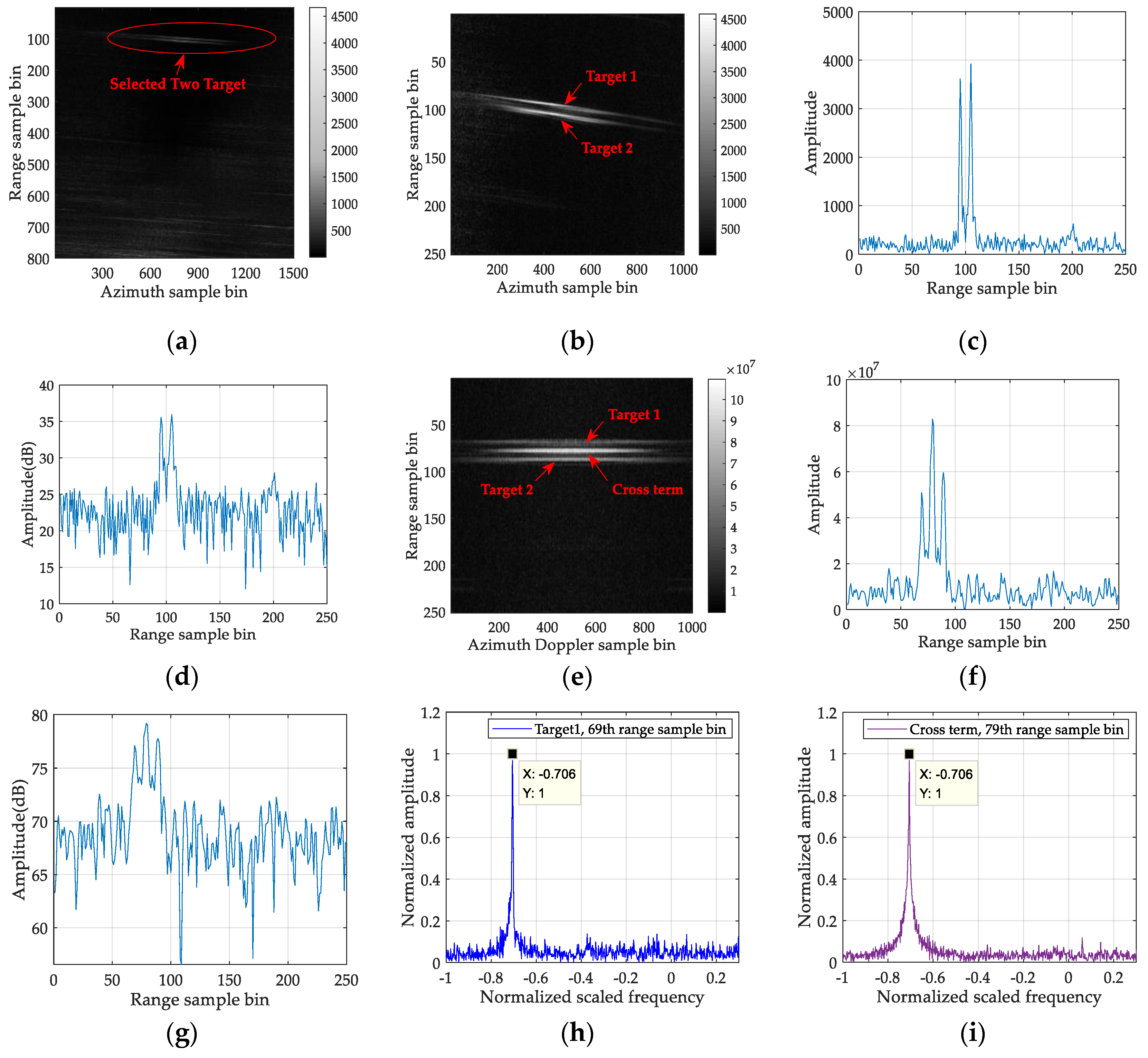
5.2. Real Data Processing Result Analysis
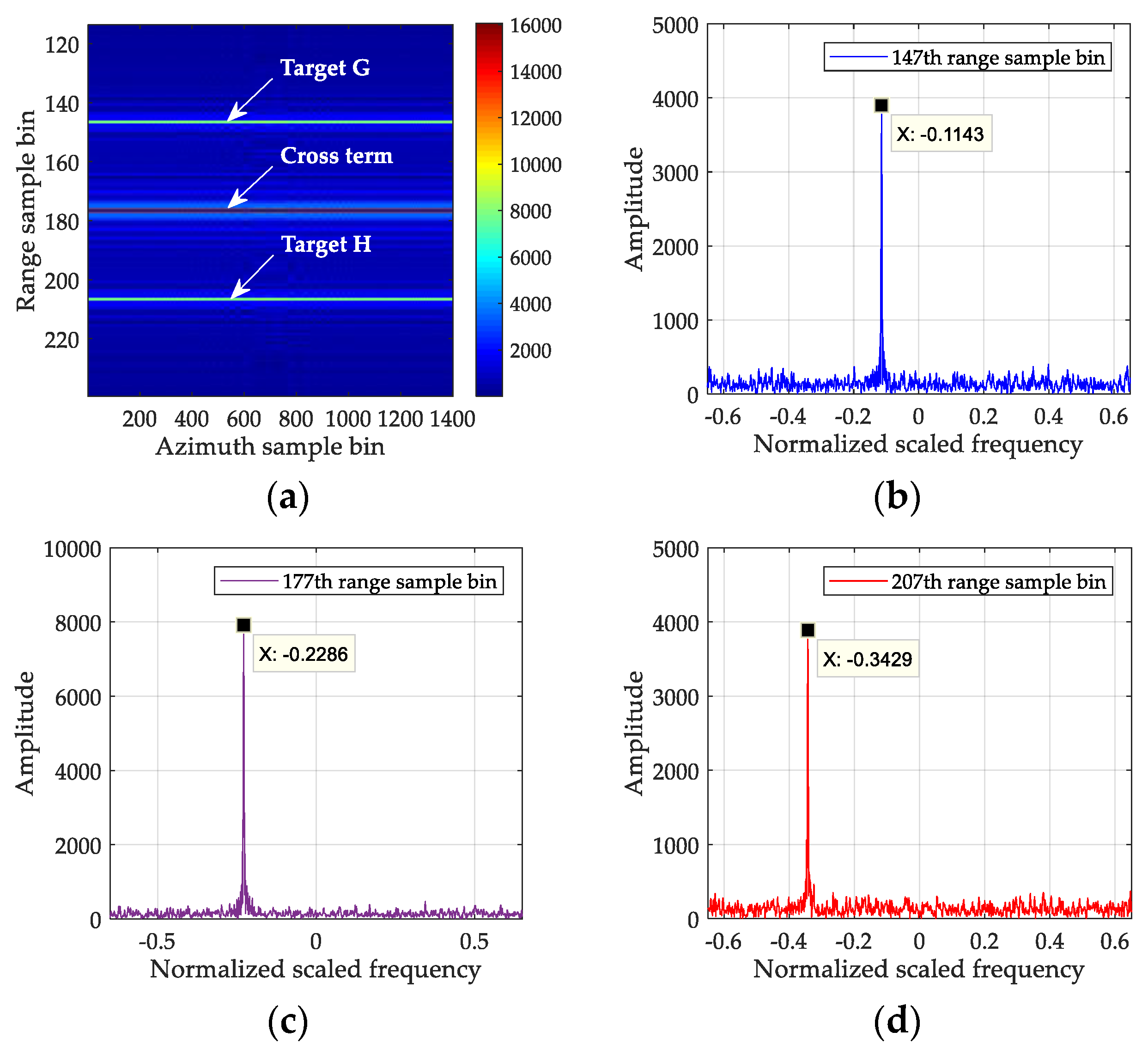
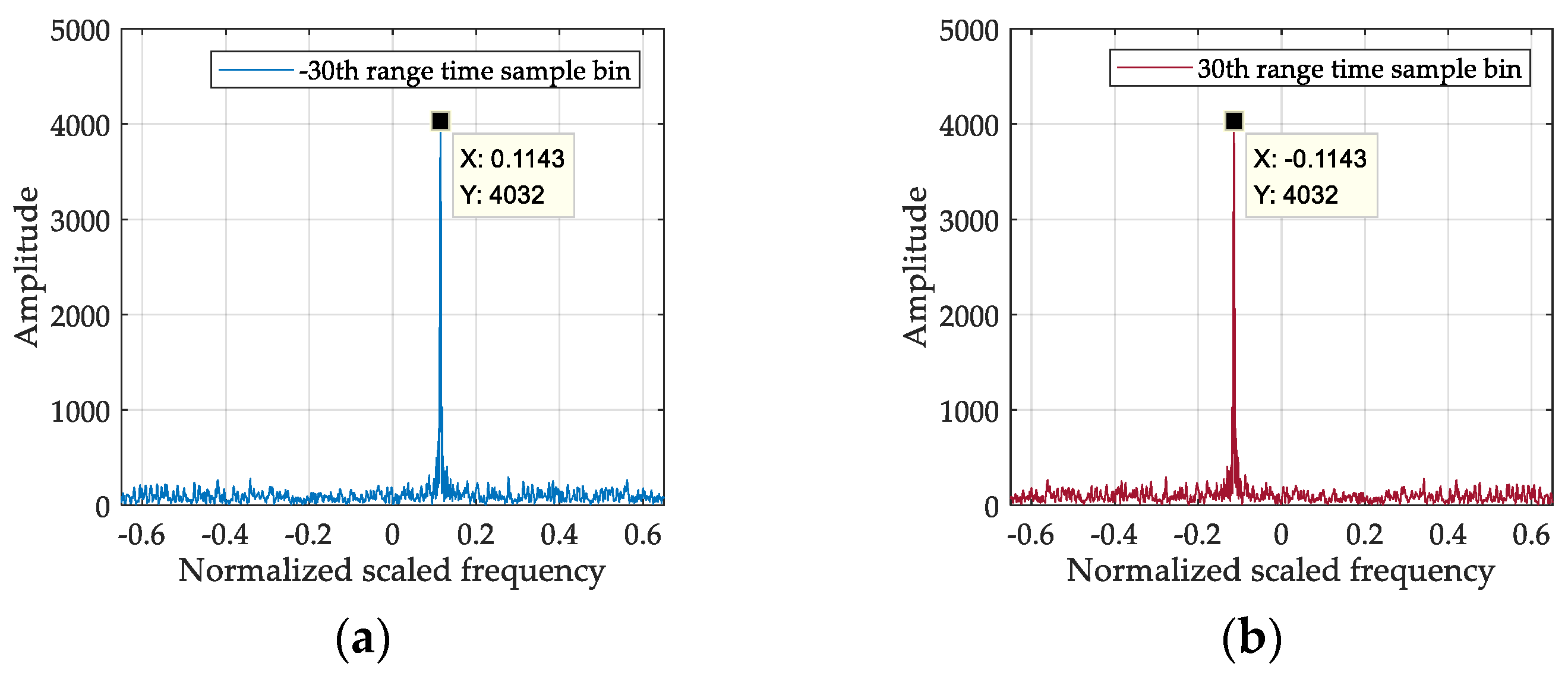
5.2.1. Processing Result of a Single Target
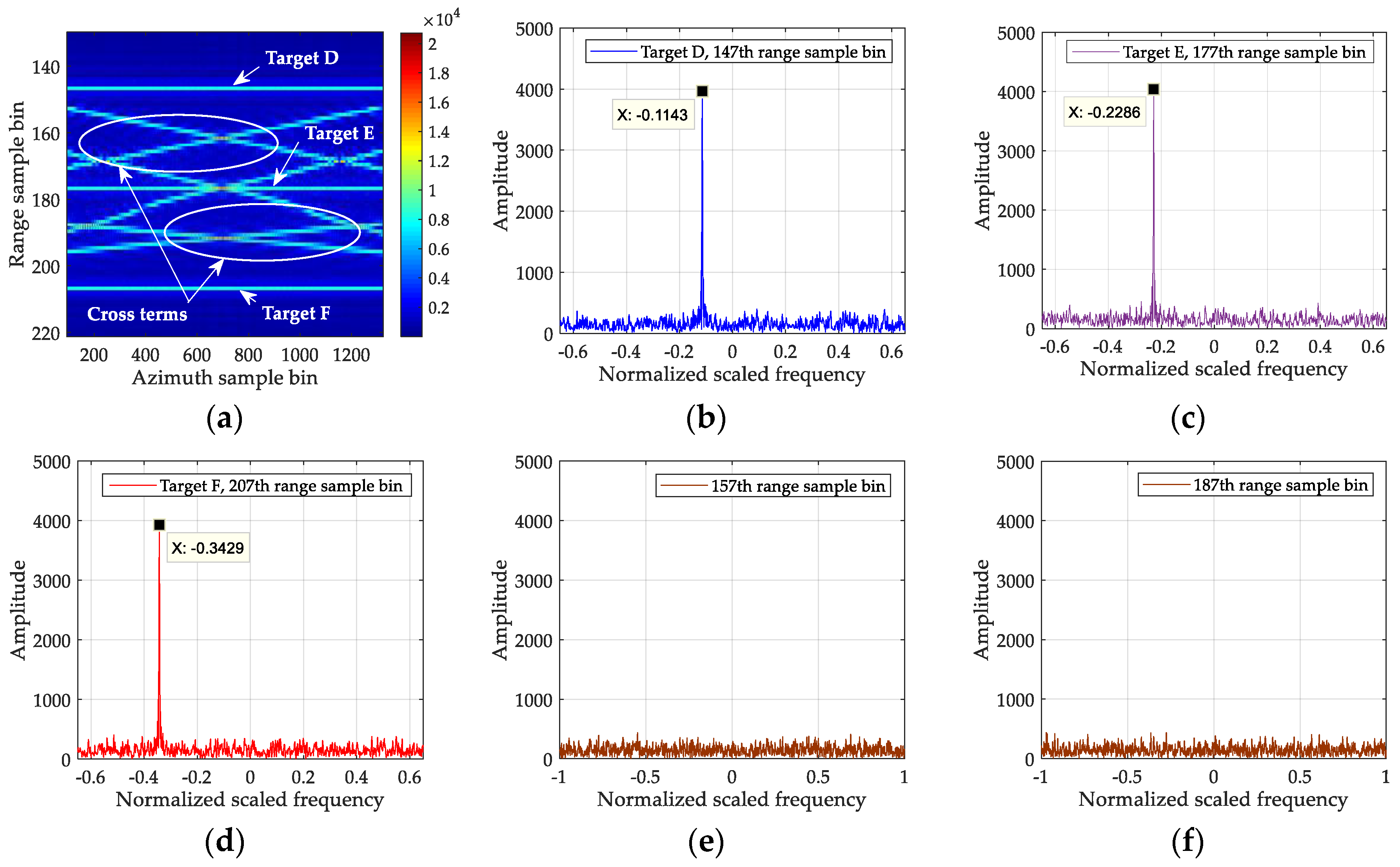
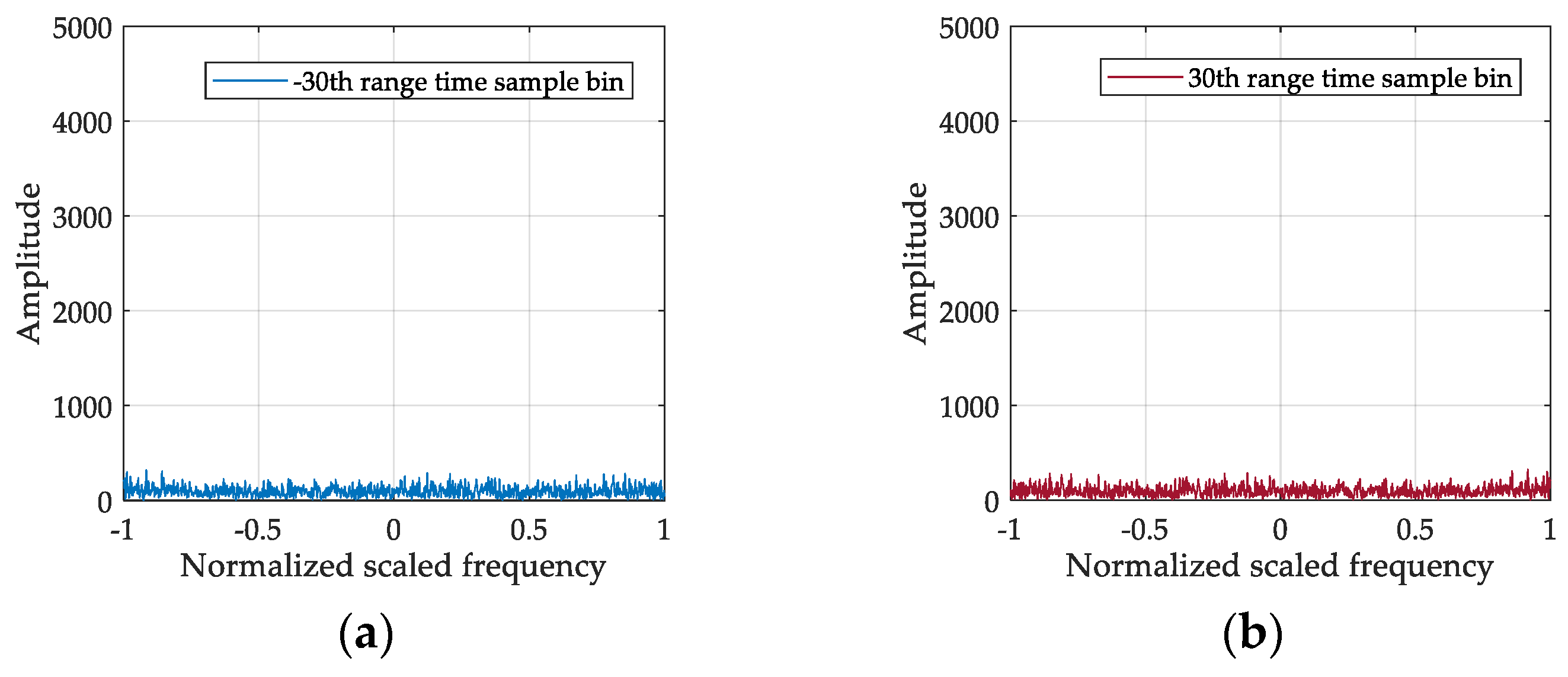
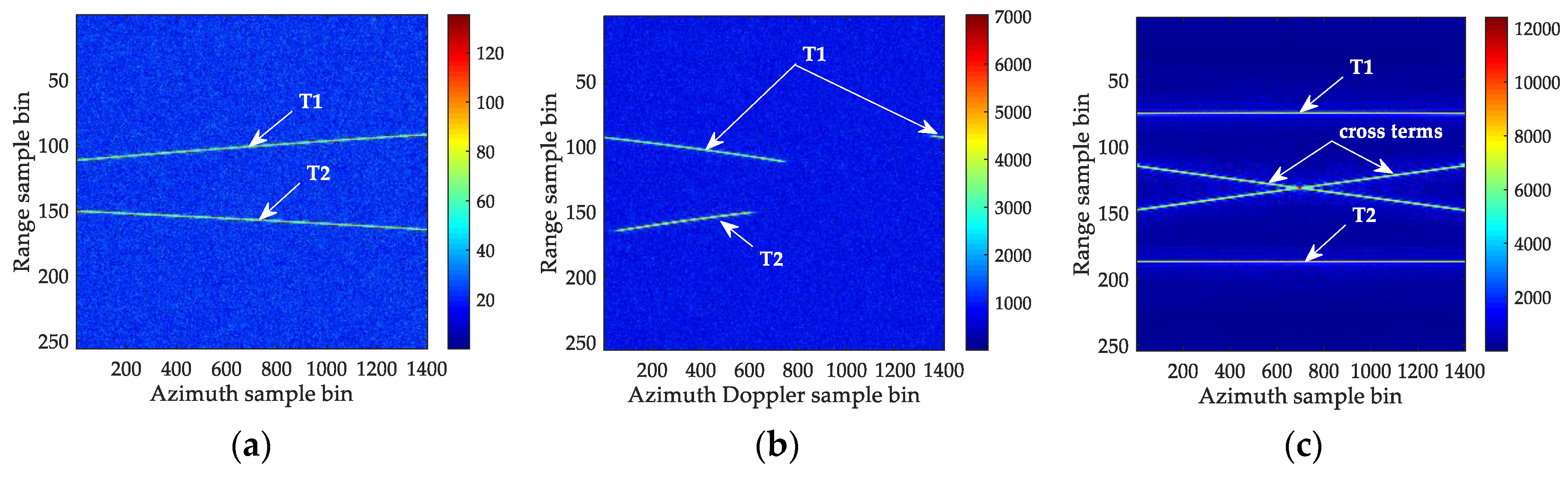
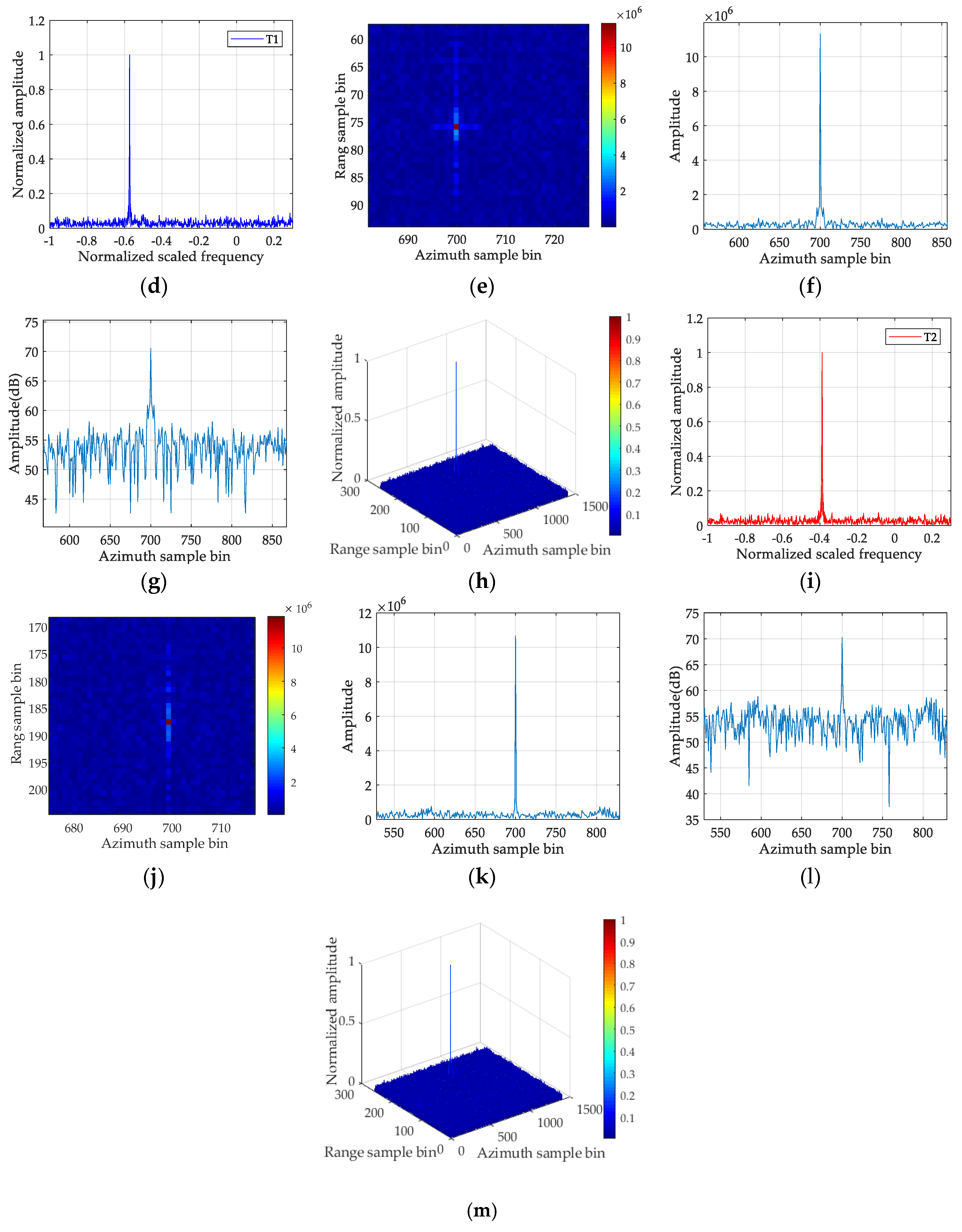
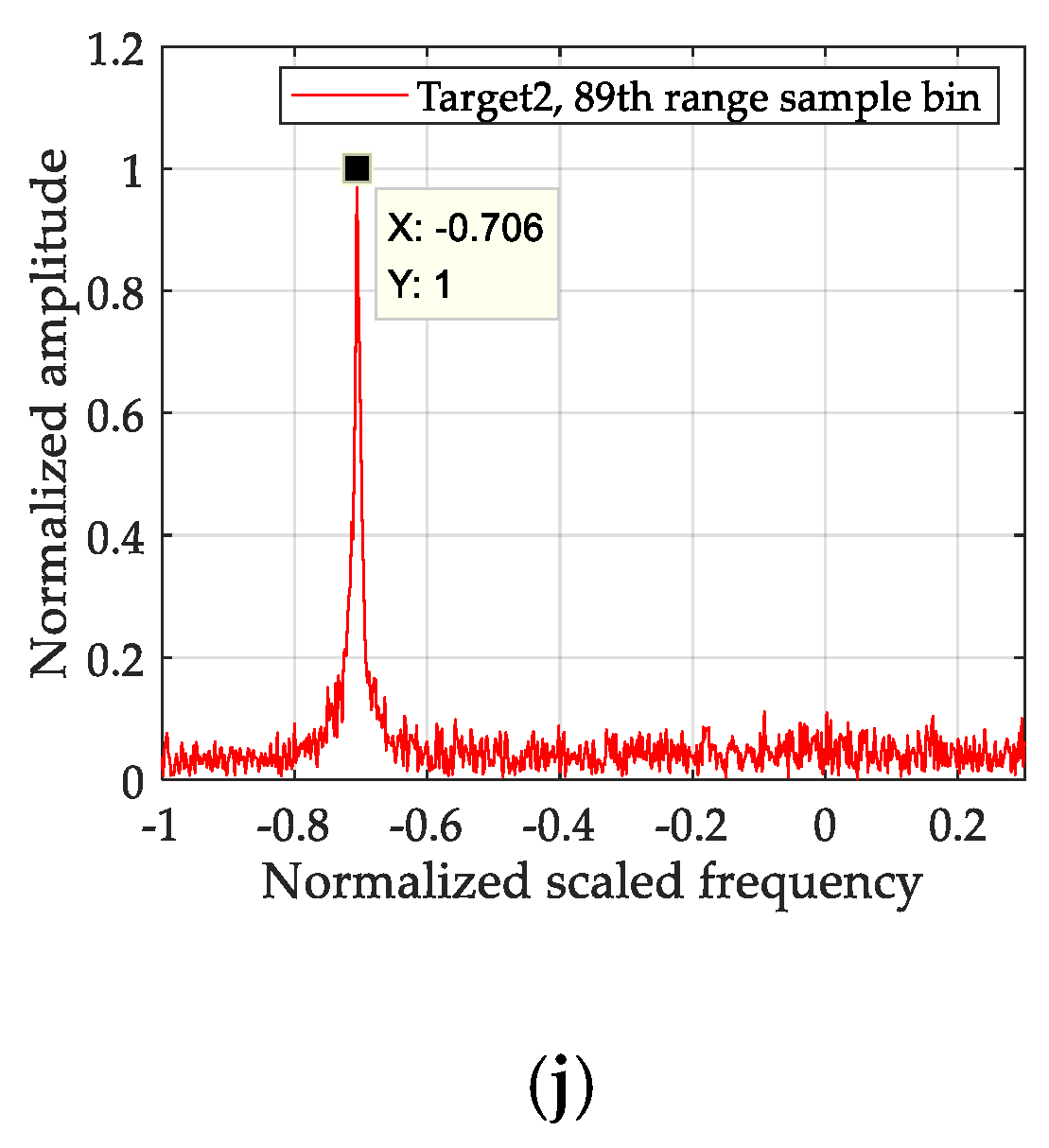
5.2.2. Processing Result of Two Targets
6. Discussion
6.1. Computational Complexity
6.2. Some Remarks
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithm and Implementation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.; Iraola, P.P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomba, G.; Parizzi, A.; Zan, F.D.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Toward operational compensation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms: The split-spectrum method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Giacovazzo, V.M.; Refice, A.; Veneziani, N. Multichromatic analysis of InSAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4790–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Derauw, D.; Rana, F.M.; Barbier, C.; Refice, A.; Veneziani, N.; Vitulli, R. Multi-chromatic analysis of SAR images for coherent target detection. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8822–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippo, B. COSMO-SkyMed staring spotlight SAR data for micro-motion and inclination angle estimation of ships by pixel tracking and convex optimization. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippo, B.; Pia, A.; Danilo, O.; Carmine, C. Micro-motion estimation of maritime targets using pixel tracking in Cosmo-Skymed synthetic aperture radar data-an operative assessment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1637. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, R.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Mallorqui, J.J.; López-Martínez, C.; Gili, J.A.; Corominas, J. Atmospheric phase screen compensation in ground-based SAR with a multiple-regression model over mountainous regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Li, D.; Tang, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Xu, L. A fast high-resolution imaging algorithm for helicopter-borne rotating array SAR based on 2-D chirp-z transform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; So, H.C. Focusing high-resolution highly-squinted airborne SAR data with maneuvers. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, S.V.; Krieger, G. Simultaneous high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging and ground moving target indication: Processing approaches and system concepts. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5015–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Lin, C.; Liu, N.; Wan, J. General range model for multi-channel SAR/GMTI with curvilinear flight trajectory. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Yang, D. GMTI and parameter estimation for MIMO SAR system via fast interferometry RPCA method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 1774–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanizadeh, A.; Amini, J. An integrated method for simulation of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) raw data in moving target detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, C.; Tang, S.; Wan, J. A non-adaptive space-time clutter canceller for multi-channel synthetic aperture radar. IET Signal Process. 2019, 13, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Ma, J. An approach for refocusing of ground fast-moving target and high-order motion parameter estimation using Radon-high-order time-chirp rate transform. Digit. Signal Process. 2016, 48, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhan, C.; Ma, H.; Liu, H.; Su, J.; Liu, Q. An efficient SAR ground moving target refocusing method based on PPFFT and coherently integrated CPF. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 114102–114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveis, A.H.; Sebt, M.A. Coherent method for ground-moving target indication and velocity estimation using Hough transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, W.; Liu, W. 2-D coherent integration processing and detecting of aircrafts using GNSS-based passive radar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.P.; DiPietro, R.C.; Fante, R.L. SAR imaging of moving targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Keystone transform without interpolation for SAR ground moving-target imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, R.; Xing, M. Approach for single channel SAR ground moving target imaging and motion parameter estimation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2007, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, D. Imaging moving targets using the second-order keystone transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.G.; Peng, Y. Doppler keystone transform: An approach suitable for parallel implementation of SAR moving target imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.G.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Z. Robust ground moving-target imaging using deramp-keystone processing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cui, W.; Xia, X.G.; Wu, S. Parameter estimation of ground moving targets based on SKT-DLVT processing. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2016, 2, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liao, G.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X. Ground moving targets imaging algorithm for synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liao, G.; Yang, D.; Tao, H. A new method for radar high-speed maneuvering weak target detection and imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Xia, X.G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liao, G.; Jiang, X. Ground moving target refocusing in SAR imagery based on RFRT-FrFT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5476–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. Ground moving target focusing and motion parameter estimation method via MSOKT for synthetic aperture radar. IET Signal Process. 2019, 13, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tao, H.; Xie, J.; Rao, X.; Guo, X. Imaging and Doppler parameter estimation for maneuvering target using axis mapping based coherently integrated cubic phase function. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 62, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Xia, X.G.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J. Ground maneuvering target imaging and high-order motion parameter estimation based on second-order keystone and generalized Hough-HAF transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Su, W.; Gu, H. Ground moving target motion parameter estimation using radon modified lv’s distribution. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 69, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, S. Ground moving target imaging and analysis for near-space hypersonic vehicle-borne synthetic aperture radar system with squint angle. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. A Doppler ambiguity tolerated method for radar sensor maneuvering target focusing and detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6691–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; So, H.C.; Liu, H. Subspace-based algorithm for parameter estimation of polynomial phase signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 4977–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Shu, Y.; Du, W. Approach for space-based radar maneuvering target detection and high-order motion parameter estimation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2015, 9, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. Imaging and parameter estimation of fast-moving targets with single-antenna SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, G.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J. Geometry-information-aided efficient motion parameter estimation for moving-target imaging and location. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.G. Discrete Chirp-Fourier transform and its application to chirp rate estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 3122–3133. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, L.B. The fractional Fourier transform and time–frequency representations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 3084–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Bi, G.A.; Wan, C.; Xing, M. Lv’s distribution: Principle, implementation, properties, and performance. IEEE Trans on Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3576–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Nguyen, N. An accurate algorithm for nonuniform fast Fourier transforms (NUFFT’s). IEEE Microw. Guided Wave Lett. 1998, 8, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Liu, Q.H.; Torrione, P.; Collins, L. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional NUFFT migration method for landmine detection using ground-penetrating radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J. Radar high-speed maneuvering target detection based on joint second-order keystone transform and modified integrated cubic phase function. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiurewicz, J.; Kulpa, K.S.; Czekala, Z.; Filipek, T.A. Radar detection of helicopters with application of CNEAN method. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 3525–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, L.; Cui, G.; Yi, W. CLEAN-based coherent integration method for high-speed multi-targets detection. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maori, D.C.; Sikaneta, I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemn, R. Introduction to space-time adaptive processing. Electron. Commun. Eng. J. 1999, 11, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, R.C. Extended factored space-time processing for airborne radar systems. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 26–28 October 1992; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar]




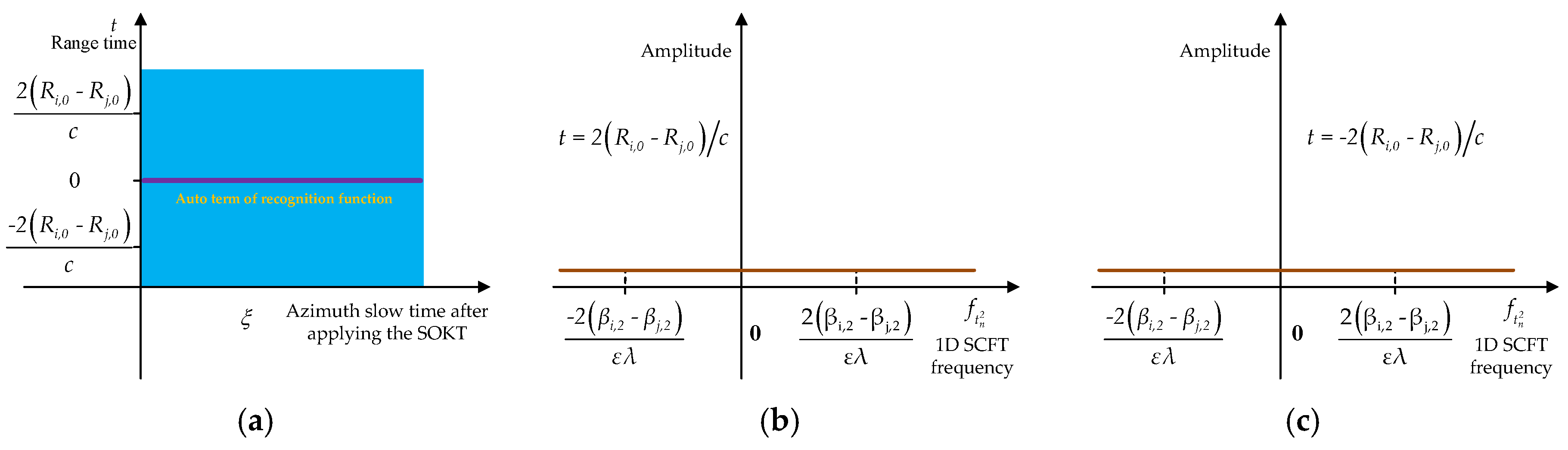


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 10 GHz |
| Range bandwidth | 80 MHz |
| Pulse duration time | 1 μs |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 1400 Hz |
| Radar platform velocity | 250 m/s |
| Nearest slant range | 6000 m |
| Dwell time | 1 s |
| Cross-Track Velocity (m/s) | Cross-Track Acceleration (m/s2) | Along-Track Velocity (m/s) | Along-Track Acceleration (m/s2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 36.8 | −3.6 | 25.2 | −4.5 |
| T2 | −26.5 | 1.6 | 5.9 | 0.6 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 5.3 GHz |
| Range bandwidth | 30.116 MHz |
| Pulse duration time | 41.74 μs |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 1256.98 Hz |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H. Efficient Algorithm for SAR Refocusing of Ground Fast-Maneuvering Targets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192214
Wan J, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Chen Z, Yu H. Efficient Algorithm for SAR Refocusing of Ground Fast-Maneuvering Targets. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(19):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192214
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Jun, Yu Zhou, Linrang Zhang, Zhanye Chen, and Hengli Yu. 2019. "Efficient Algorithm for SAR Refocusing of Ground Fast-Maneuvering Targets" Remote Sensing 11, no. 19: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192214
APA StyleWan, J., Zhou, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, Z., & Yu, H. (2019). Efficient Algorithm for SAR Refocusing of Ground Fast-Maneuvering Targets. Remote Sensing, 11(19), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192214