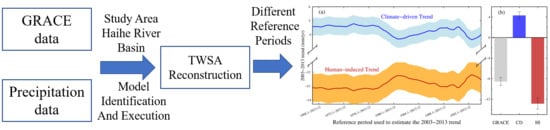
Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Contributions to Water Storage Variations in the Haihe River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. GRACE Data
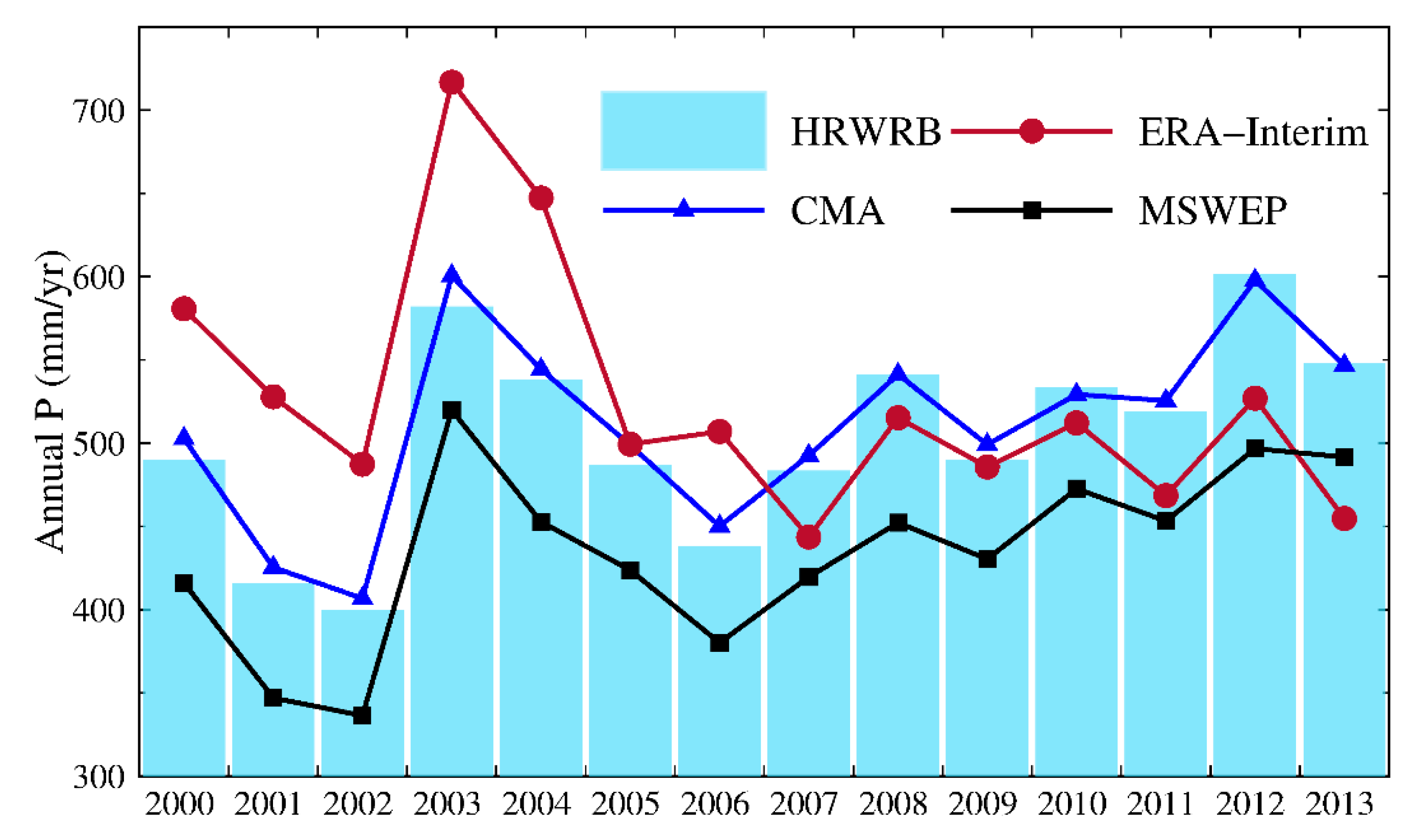
2.3. Precipitation Data
2.4. Land Surface Models
2.5. Climate-Driven Water Storage Variability
2.6. Quantifying the Contributions of Climate-Driven and Human-Induced TWSA Trends
2.7. Error Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Trend of Climate-driven and Human-Induced TWSA
3.2. Interannual Variations of TWSA
4. Discussion
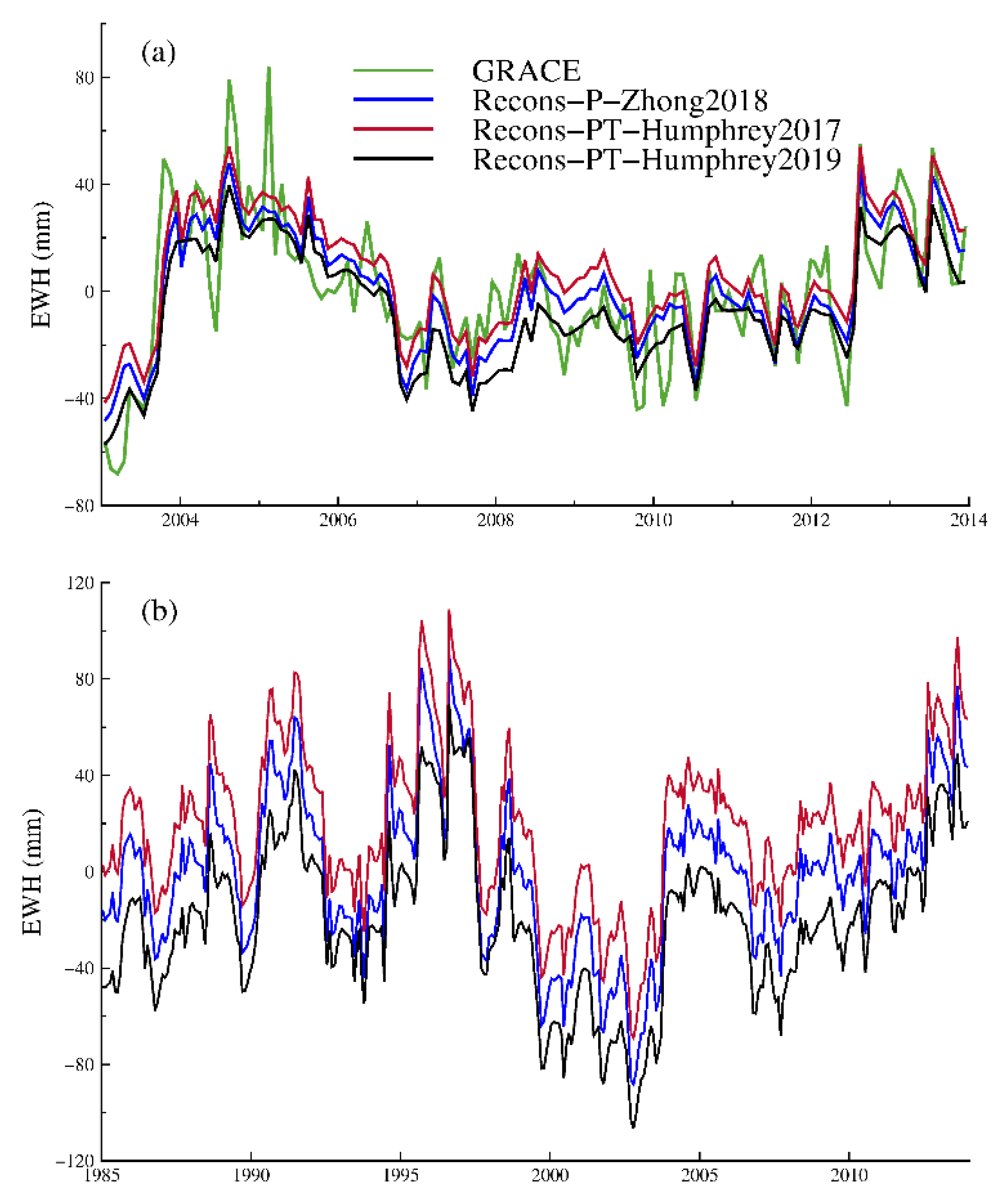
4.1. Comparison of Different GRACE Solutions and Methods
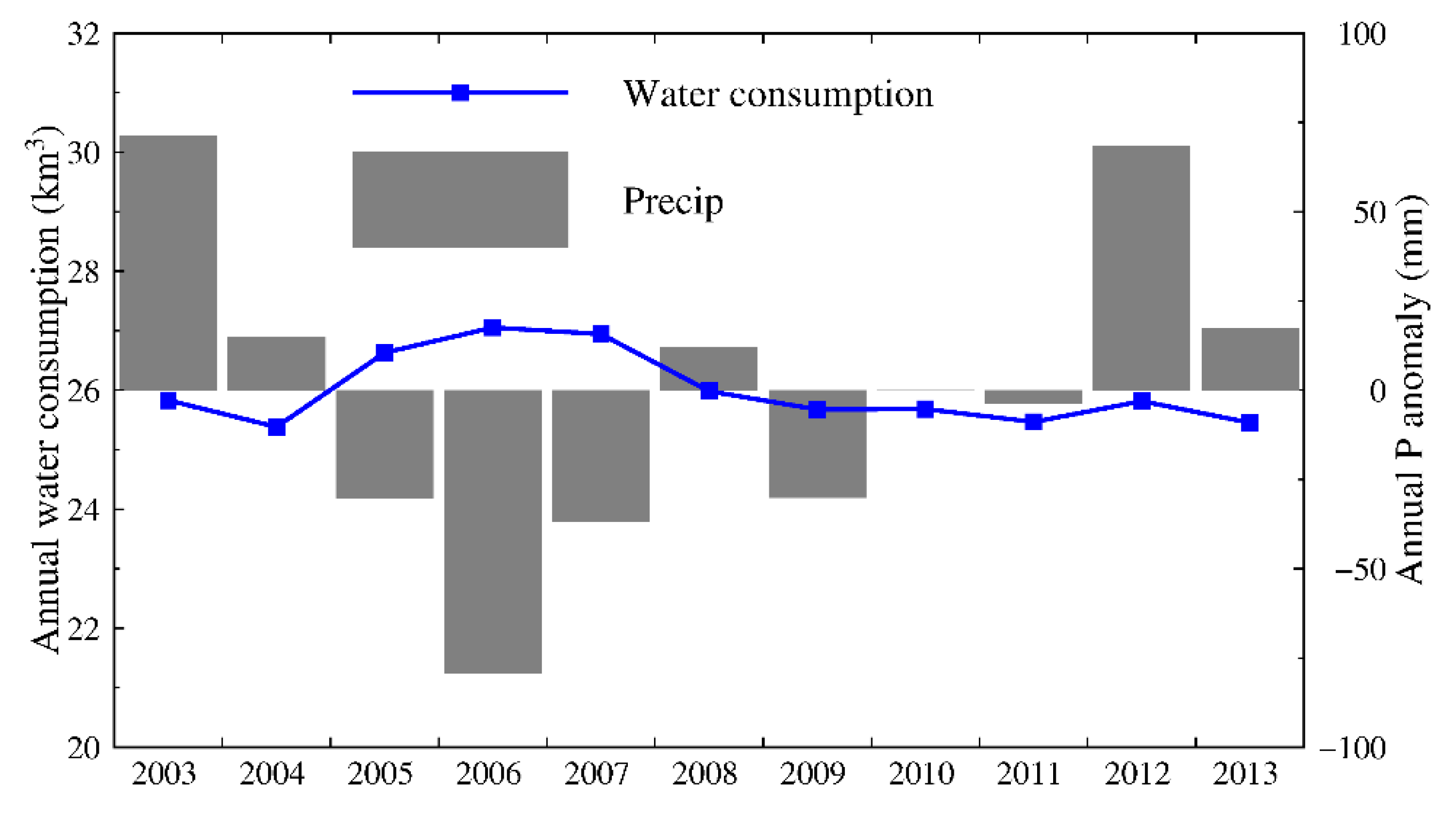
4.2. Impact of Annual Precipitation Trend
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



| Method | R | MBE (mm) | RMSE (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMA | 0.99 | 6.67 | 9.24 |
| ERA-Interim | 0.37 | 21.85 | 76.86 |
| MSWEP | 0.97 | −69.63 | 70.92 |
| Method | NSE | RMSE (mm) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| This study | 0.41 | 16.34 | 0.79 |
| Humphrey et al. [54] | 0.40 | 16.38 | 0.79 |
| Humphrey and Gudmundsson [56] | 0.45 | 16.09 | 0.80 |
| Method | NSE | RMSE (mm) | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| This study vs Humphrey et al. [54] | 1.00 | 1.24 | 1.00 |
| This study vs Humphrey and Gudmundsson [56] | 0.96 | 6.50 | 0.98 |
| Humphrey et al. [54] vs Humphrey and Gudmundsson [56] | 0.95 | 7.03 | 0.98 |
References
- Syed, T.H.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Rodell, M.; Chen, J.; Wilson, C.R. Analysis of terrestrial water storage changes from GRACE and GLDAS. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.J.F.; Swenson, S.C.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Rodell, M. Remote sensing of groundwater storage changes in Illinois using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE). Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassberg, G.; Scanlon, B.R.; Chambers, D. Evaluation of groundwater storage monitoring with the GRACE satellite: Case study of the High Plains aquifer, central United States. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Famiglietti, J.S. Remote Sensing of Terrestrial Water Storage, Soil Moisture and Surface Waters. In The State of the Planet: Frontiers and Challenges in Geophysics; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, A.; Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Brambilla, D.; Ivanov, V.I. Generation of a Design Flood-Event Scenario for a Mountain River with Intense Sediment Transport. Water 2016, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albano, R.; Mancusi, L.; Abbate, A. Improving flood risk analysis for effectively supporting the implementation of flood risk management plans: The case study of “Serio” Valley. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 75, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Shum, C.K.; Zhong, M.; Pan, Y. Groundwater Storage Changes in China from Satellite Gravity: An Overview. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Wilson, C.R.; Tapley, B.D.; Yang, Z.L.; Niu, G.Y. 2005 drought event in the Amazon River basin as measured by GRACE and estimated by climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J.L. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.C.; Thompson, P.F.; Watkins, M.M. GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 2004, 305, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felfelani, F.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Pokhrel, Y.N. Natural and human-induced terrestrial water storage change: A global analysis using hydrological models and GRACE. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Salama, M.S.; Krol, M.S.; Su, Z.B.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.X. Estimation of human-induced changes in terrestrial water storage through integration of GRACE satellite detection and hydrological modeling: A case study of the Yangtze River basin. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8494–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Wiese, D.N.; Reager, J.T.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Landerer, F.W.; Lo, M.H. Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature 2018, 557, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.; van Beek, L.P. Water balance of global aquifers revealed by groundwater footprint. Nature 2012, 488, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Sun, A.Y.; Muller Schmied, H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Wiese, D.N.; Wada, Y.; Long, D.; Reedy, R.C.; et al. Global models underestimate large decadal declining and rising water storage trends relative to GRACE satellite data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1080–E1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapley, B.D.; Watkins, M.M.; Flechtner, F.; Reigber, C.; Bettadpur, S.; Rodell, M.; Sasgen, I.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Landerer, F.W.; Chambers, D.P.; et al. Contributions of GRACE to understanding climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.Q.; Chang, L.L.; Gupta, H.; Niu, G.Y. Climatic forcing for recent significant terrestrial drying and wetting. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 133, 103425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.X.; Liu, X.G. Analysis of permafrost region coherence variation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau with a high-resolution TerraSAR-X image. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Stepaniak, D.P. Indices of El Nino evolution. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasullo, J.T.; Boening, C.; Landerer, F.W.; Nerem, R.S. Australia’s unique influence on global sea level in 2010–2011. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4368–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.; Nerem, R.S.; Fox-Kemper, B.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Rajagopalan, B. The influence of ENSO on global terrestrial water storage using GRACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, S.N.; Chen, J.L.; Wilson, C.R.; Li, J.; Hu, X.G.; Fu, R. Global Terrestrial Water Storage Changes and Connections to ENSO Events. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyah, R.O.; Forootan, E.; Awange, J.L.; Khaki, M. Understanding linkages between global climate indices and terrestrial water storage changes over Africa using GRACE products. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.L.; Luo, Z.C.; Wang, H.H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, H. GRACE-Derived Terrestrial Water Storage Changes in the Inter-Basin Region and Its Possible Influencing Factors: A Case Study of the Sichuan Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doll, P.; Müller Schmied, H.; Schuh, C.; Portmann, F.T.; Eicker, A. Global-scale assessment of groundwater depletion and related groundwater abstractions: Combining hydrological modeling with information from well observations and GRACE satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5698–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, H.H.G.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; van der Zaag, P. Evolving water science in the Anthropocene. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Reedy, R.C.; Pool, D.R.; Save, H.; Long, D.; Chen, J.L.; Wolock, D.M.; Conway, B.D.; Winester, D. Hydrologic implications of GRACE satellite data in the Colorado River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 9891–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.L.; Zhong, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Shen, Y.C.; Wu, D.C. Groundwater Depletion in the West Liaohe River Basin, China and Its Implications Revealed by GRACE and In Situ Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhanja, S.N.; Mukherjee, A. In situ and satellite-based estimates of usable groundwater storage across India: Implications for drinking water supply and food security. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 126, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kaban, M.K.; Thomas, M.; Chen, C.; Ma, X. The Challenge of Spatial Resolutions for GRACE-Based Estimates Volume Changes of Larger Man-Made Lake: The Case of China’s Three Gorges Reservoir in the Yangtze River. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, B.F.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, Y.S. Impact of artificial reservoir water impoundment on global sea level. Science 2008, 320, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, M.X.; Ma, Z.G.; Li, M.X.; Zheng, Z.Y. Quantitative Analysis of Terrestrial Water Storage Changes Under the Grain for Green Program in the Yellow River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1336–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasullo, J.T.; Lawrence, D.M.; Swenson, S.C. Are GRACE-era Terrestrial Water Trends Driven by Anthropogenic Climate Change? Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 4830603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, S.; Sun, W.K.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.L. Anthropogenic and climate-driven water depletion in Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9061–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, Y.J. Quantifying water and energy budgets and the impacts of climatic and human factors in the Haihe River Basin, China: 1. Model and validation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MWR). River Sediment Bulletin of China; Ministry of Water Resour. of the PRC, Ed.; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2013; p. 85.
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation-a global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, H.L.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.Q.; Li, X.J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, H.G.; Zhou, C.F. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.L.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Li, X.J.; Zhou, D.M.; Zhao, W.J. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by GRACE for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Tang, Y. Anthropogenic impacts on mass change in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3924–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiwo, J.P.; Tao, F.L.; Lu, W.X. Analysis of satellite-based and in situ hydro-climatic data depicts water storage depletion in North China Region. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. Drought analysis of the Haihe river basin based on GRACE terrestrial water storage. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 578372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.B.; Wu, W.W.; Meng, G.J.; Chen, Q. Geodetic and hydrological measurements reveal the recent acceleration of groundwater depletion in North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Shi, L.S.; Zeng, J.C.; Yang, J.Z.; Zha, Y.Y.; Yao, Y.J.; Cao, G.L. Estimation of actual irrigation amount and its impact on groundwater depletion: A case study in the Hebei Plain, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, H.; Bettadpur, S.; Tapley, B.D. High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7547–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Watkins, M.M. Quantifying and reducing leakage errors in the JPL RL05M GRACE mascon solution. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7490–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthcke, S.B.; Sabaka, T.J.; Loomis, B.D.; Arendt, A.A.; McCarthy, J.J.; Camp, J. Antarctica, Greenland and Gulf of Alaska land-ice evolution from an iterated GRACE global mascon solution. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L.; Seneviratne, S.I. A global reconstruction of climate-driven subdecadal water storage variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zhu, J. Assessing Quality of Grid Daily Precipitation Datasets in China in Recent 50 Years. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L. GRACE-REC: A reconstruction of climate-driven water storage changes over the last century. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gong, H.L.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Shen, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.Y.; Li, X.J. Detection of human-induced evapotranspiration using GRACE satellite observations in the Haihe River basin of China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; van den Dool, H. Climate Prediction Center global monthly soil moisture data set at 0.5° resolution for 1948 to present. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, V.; Gudmundsson, L.; Seneviratne, S.I. Assessing Global Water Storage Variability from GRACE: Trends, Seasonal Cycle, Subseasonal Anomalies and Extremes. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 357–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Ni, S.N. Long-term groundwater variations in Northwest India from satellite gravity measurements. Global. Planet. Chang. 2014, 116, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, J.; Ditmar, P.; Klees, R.; Farahani, H.H. Statistically optimal estimation of Greenland Ice Sheet mass variations from GRACE monthly solutions using an improved mascon approach. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, M.; Duan, J.B.; Xu, H.Z.; Peng, P.; Yan, H.M.; Zhu, Y.Z. Trend of China land water storage redistribution at medi- and large-spatial scales in recent five years by satellite gravity observations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balsamo, G.; Albergel, C.; Beljaars, A.; Boussetta, S.; Brun, E.; Cloke, H.; Dee, D.; Dutra, E.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Pappenberger, F.; et al. ERA-Interim/Land: A global land surface reanalysis data set. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, H.E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; de Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25 degrees global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.W.; Shen, H.F.; Zhang, L.P.; Zheng, X.W.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, Q.Q. High-quality seamless DEM generation blending SRTM-1, ASTER GDEM v2 and ICESat/GLAS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 123, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Number i | Reference Period | Trend |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1967.01–2013.12 | 4.56 ± 0.63 () |
| 2 | 1967.02–2013.12 | 4.56 ± 0.63 () |
| … | … | … |
| 157 | 1980.01–2013.12 | 3.82 ± 0.63 () |
| … | … | … |
| 324 | 1993.12–2013.12 | 3.97 ± 0.63 () |
| Mean | 4.31 ± 0.72 () |
| GRACE-Derived TWSA Trend | Climate-Driven TWSA Trend | Human-Induced TWSA Trend | Description (GRACE Solution, Method) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 4.31 ± 0.72 | −12.87 ± 1.07 | CSR-M, reconstruction |
| −9.86 ± 0.69 | 3.35 ± 0.66 | −13.21 ± 0.96 | GSFC-M, reconstruction |
| −14.20 ± 0.99 | 5.66 ± 0.95 | −19.86 ± 1.37 | JPL-M, reconstruction |
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 1.09 ± 0.70 | −9.65 ± 1.06 | CSR-M, climate-driven TWSA from Noah |
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 2.48 ± 0.69 | −11.04 ± 1.05 | CSR-M, climate-driven TWSA from CPC |
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 2.49 ± 2.58 | −11.05 ± 2.46 | CSR-M, linear regression (Yi et al. 2016) |
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 4.33 ± 0.63 | −12.89 ± 1.01 | CSR-M, reconstruction and linear regression |
| −8.56 ± 0.79 | 4.31 ± 0.71 | −12.87 ± 1.07 | CSR-M, reconstruction (detrended annual precipitation used) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Feng, W.; Humphrey, V.; Zhong, M. Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Contributions to Water Storage Variations in the Haihe River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243050
Zhong Y, Feng W, Humphrey V, Zhong M. Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Contributions to Water Storage Variations in the Haihe River Basin, China. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(24):3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243050
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yulong, Wei Feng, Vincent Humphrey, and Min Zhong. 2019. "Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Contributions to Water Storage Variations in the Haihe River Basin, China" Remote Sensing 11, no. 24: 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243050
APA StyleZhong, Y., Feng, W., Humphrey, V., & Zhong, M. (2019). Human-Induced and Climate-Driven Contributions to Water Storage Variations in the Haihe River Basin, China. Remote Sensing, 11(24), 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243050