Abstract
Geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) has a long integration time and a large imaging scene. Therefore, various nonideal factors are easily accumulated, introducing phase errors and degrading the imaging quality. Within the long integration time, tropospheric status changes with time and space, which will result in image shifts and defocusing. According to the characteristics of GEO SAR, the modeling, and quantitative analysis of background troposphere and turbulence are conducted. For background troposphere, the accurate GEO SAR signal spectrum, which takes into account the time-varying troposphere, is deduced. The influences of different rates of changing (ROC) of troposphere with time are analyzed. Finally, results are verified using the refractive index profile data from Fengyun (FY) 3C satellite and the tropospheric zenith delays data from international GNSS service (IGS). The time–space changes of troposphere can cause image shifts which only depend on the satellite beam-foot velocity and the linear ROC of troposphere. The image defocusing is related to the wavelength, resolution requirement, and the second and higher orders of ROC. The short-wavelength GEO SAR systems are more susceptible to impacts, while L-band GEO SAR will be affected when the integration time becomes longer. Tropospheric turbulence will cause the amplitude and phase random fluctuations resulting in image defocusing. However, in the natural environment, radio waves are very weakly affected by turbulence, and the medium-inclined GEO SAR of L- to C-band will not be affected, while the X-band will be influenced slightly.
1. Introduction
Troposphere is nondispersive and it affects the amplitude and phase of the radio waves passing through it. It can be divided into two parts: the background troposphere and the turbulence. The background troposphere mainly refers to the slowly changing part due to the large-scale component and corresponds to the input region []. Radio wave propagation in the troposphere can be characterized by refractive index. When the signal passes through the troposphere, the propagation velocity slows down because the refractive index is greater than 1, which introduces delay errors. Generally, different atmospheric conditions can cause different delay errors. Besides, because the meteorological elements such as atmospheric temperature, pressure, and humidity change with the height and spatial distribution of the refractive index, it is inhomogeneous, causing the propagation path to bend and introducing the bending errors. The tropospheric turbulence refers to the dramatic changing part due to the small-scale vortices and corresponds to the inertial region. The meteorological elements change intensely and cause rapid fluctuations on the refractive index under some extreme weather conditions, resulting in random fluctuations on the amplitude and phase of signal.
Errors introduced by troposphere can affect the coherence of SAR signals, deteriorating the imaging quality. Quegan et al. studied effects of ionosphere and troposphere on low Earth orbit SAR (LEO SAR) imaging, and pointed out that the effects of the ionosphere on spaceborne SAR need to be considered and the effects of the troposphere can be ignored for low-frequency system []. Using Hopfield’s tropospheric model and ray tracing methods, Sun and Zhang et al. studied the influence of troposphere on spaceborne SAR imaging. They concluded that the higher the resolution was and the larger the incident angle was, the more serious the influence was [,]. Tropospheric disturbances will reduce the accuracy of interferometry and differential interferometry phases [], which will seriously reduce the accuracy of elevation information and deformation retrieval [,].
The tropospheric turbulence will also affect the radio waves propagation. Many studies have analyzed the phase fluctuation caused by the tropospheric turbulence and the corresponding errors on the spaceborne SAR imaging based on the Tatarskii theory [,]. From 2004 to 2007, Sandia National Laboratory systematically studied impacts of turbulence on SAR imaging and analyzed image shifts and defocusing caused by low-layer atmospheric disturbances through simulations and the airborne SAR data in the Ku band from Sandia National Laboratory [,,]. Abnormal brightness in SAR images was observed, which were attributed to atmospheric refractive index perturbations. They found that tropospheric disturbances had negligible effects on radio waves propagation below 10 GHz and had the most obvious impacts on a 22–60 GHz system [].
Relevant studies have shown that the troposphere has less effects on the current spaceborne SAR focusing than the ionosphere. However, with the increasing of integration time, the impact of the troposphere will also become serious. GEO SAR operates at a height of 36,000 km and the integration time can be from 100 s to several hours [,,,] depending on the orbit configuration. Compared to LEO SAR, GEO SAR’s integration time increases by several orders of magnitude [,,]. Therefore, the impact of the troposphere cannot be ignored. Hobbs et al. analyzed the GEO SAR system design and pointed out that the influence of the ionosphere and troposphere on focusing cannot be ignored []. The refractive index during radio wave propagation mainly changes due to water vapor in the troposphere [,]. Li et al. [] analyzed the influences of troposphere and random turbulence on GEO SAR imaging based on Saastamoinen model and the Askne model for background troposphere, and Matern-based power spectrum and the random walk model for turbulence. These analyses are mainly focused on the meteorological model.
Then Hobbs and Monti-Guarnieri et al. studied the tropospheric effects in the near-zero inclination and high-frequency GEO SAR [,,,]. Atmospheric errors can accumulate over several hours, seriously affecting high-resolution imaging performance. Meantime, the method of atmospheric phase screen (APS) retrieval and compensation using interferometry approaches are given and gradually developed to bistatic [] and distributed configurations [], which improves the timeliness and performance of monitoring. Ruiz Rodon and Broquetas et al. studied the water vapor retrieval algorithm in detail [,]. They received echoes from permanent scatters (PS) and divided subapertures in azimuth to achieve the water vapor content estimation and subsequent imaging focusing. Monti-Guarnieri et al. quantitatively evaluated effects of turbulence on GEO SAR and proposed a new focusing method by integrating the estimation and compensation of APS []. The proposed method is most suitable for C-band signals.
Kou et al. analyzed the effects of troposphere on imaging of L-band circular GEO SAR (GEOCAR) whose integration time is 24 h based on the measured data of the troposphere. A slight defocusing occurred with range offset which depends on the vertical variation of the refractive index, satellite-target geometry, and wavelength [,].
Different from the near-zero inclination GEO SAR and GEOCSAR, the integration time of the medium inclination GEO SAR can be hundreds to thousands of seconds. Most studies focus on ionospheric effects on the L-band system, including ionospheric modeling [], quantitative analysis [], compensation algorithms [], and experimental verification []. The troposphere causes less influence in L-band and the relevant research is relatively less. However, the impact of the troposphere has also become more serious with the increase of operating frequency.
Considering the characteristics of GEO SAR, this paper completes the modeling of the background troposphere using the polynomial expansion of delay errors against azimuth time, and turbulence considering a modified Kolmogorov power law spectrum and phase screen theory. The tropospheric influences are quantitatively analyzed using the simulated and measured data. The accurate GEO SAR signal spectrum considering the time-varying troposphere is derived and the influence of different tropospheric rates of changing with time (ROC) is analyzed, along with the thresholds of tropospheric errors causing image shifts and defocusing. Since the impacts depend not only on the tropospheric status, but also on the GEO SAR system parameters, in this paper, the effects of different GEO SAR orbital configurations are comparatively analyzed. In addition, influences of different integration times and wavelengths are also compared and summarized. These results are verified with the refractive index profile data from Fengyun (FY) 3C satellite and tropospheric zenith delay data from international GNSS service (IGS). As for the tropospheric turbulence, the random amplitude and phase errors caused by turbulence are analyzed based on the theory of phase screen, which is verified by simulation; its influences through the spectrum analysis method, which can build the relationship between the imaging performance indicators (e.g., PSLR and ISLR). Finally, taking the real natural turbulence status into account, we conclude that there is no effect of the turbulence on the medium inclination and high-inclination GEO SAR focusing except the slight defocusing for X-band and even shorter wavelength systems.
The structure of this paper is as follows. In Section 2, the phase errors introduced by troposphere are modeled and analyzed. Next, the GEO SAR signal affected by troposphere is proposed and the tropospheric effects are discussed in Section 3. In Section 4, some simulations and measured data of troposphere are used to verify our analysis. Finally, conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Modeling of Tropospheric Phase Errors
2.1. Modeling of Background Tropospheric Errors
2.1.1. The Radio Refractivity
Background troposphere will introduce delay errors and bending errors, mainly caused by the change of refractive index with height. Therefore, the influence of the troposphere on radio wave propagation is usually expressed by the refractive index n, which is between 1.00026 and 1.00046. For convenience, the radio refractivity N is used in the paper:
Radio refractivity N is categorized into dry item and wet item []. N can be expressed as
where , and represent the temperature, the pressure, and the humidity, respectively, of the atmosphere at different heights. It is noted that the electrons effects are not considered here and the refractivity is not affected by the ionosphere because we only study the tropospheric effects in this paper.
2.1.2. Modeling of Propagation Errors
The GEO SAR geometry is shown in Figure 1, where is the geocentric center and is the Earth’s radius. Target is at a height of from ground, and the curve from GEO SAR passing through the point and to target represents the actual propagation path which passes through the heterogeneous troposphere. The straight line from GEO SAR to is the straight path of the signal. The point is the intersection of the GEO SAR signal propagation path and the tropopause. The point represents any point on the actual path of the signal. is the elevation angle at the target . is the elevation angle at any point on the signal propagation path. is the height of and is the height of the tropopause.
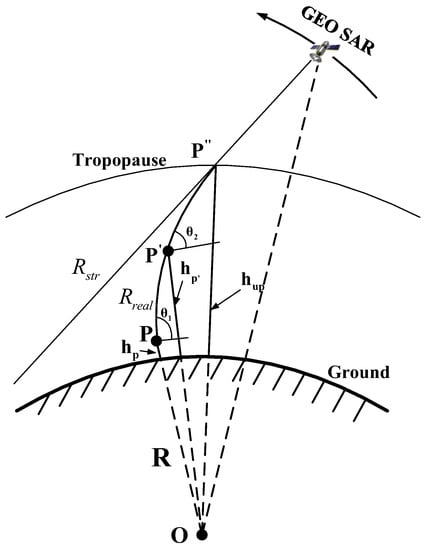
Figure 1.
Sketch map of geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) signal propagation in the troposphere.
Ray tracing methods [,] can be used to calculate the propagation errors in the troposphere. According to the geometric relation of Figure 1, the actual propagation distance of GEO SAR signal in the troposphere is
where and are respectively the distances from and to , , . When the GEO SAR signal passes through the troposphere, the error caused by propagation path is:
where represents the path length when the GEO SAR signal propagates straightly in the ideal case. The first term on the right side of the equation represents the delay error caused by the slowing down of the signal propagating velocity and the second term represents the bending error due to the bending of the signal propagation path. It can be seen that the troposphere is a nondispersive medium and the resulting signal delay is independent of wavelength.
According to the analysis of massive Global Positioning System (GPS) data, the total tropospheric error can reach meters, but the proportion of bending error is very small, generally no more than 0.1 m []. Moreover, the change in this curved path contribution as a function of refractive index change due to variation in its wet part is usually negligible. So the bending errors can be treated as being constant.
Therefore, in the following analysis, we neglect the effects of bending errors, and only consider the delay error, that is, the elevation angle is assumed to remain unchanged in the integration path. At this time, the tropospheric propagation error can be simplified as
It can be seen that the delay error introduced by the troposphere in GEO SAR is mainly determined by the integral of the refractivity along the propagation path. At this point, the tropospheric phase error introduced into GEO SAR is
which can be calculated from the tropospheric refractivity parameters and the GEO SAR signal propagating geometry.
Actually, during the long aperture time and within large observation swath of GEO SAR, the phase error will change, mainly including (1) during the synthetic aperture time, the propagation path of the signal in the troposphere changes. The length of the propagation path corresponding to different PRT moments is different, introducing different delay errors. (2) Due to the long synthetic aperture time, the tropospheric state may change with time, resulting in time-varying delay errors. (3) Due to the large swath, the refractive index of different propagation paths vary inhomogeneously during the signal passing through the troposphere, causing that the refractive index along different propagation paths are different, resulting in different delay errors.
The time-varying, the gradient change of the spatial distribution of troposphere, and the change of the signal propagation path all cause the delay errors. However, all these phase errors will appear as a time-varying pattern in GEO SAR signals from pulse to pulse, but differ from various positions of target. Therefore, in this paper, these three effect types all can be modeled as a series expansion form with slow time, and used to establish the analytical expression and quantitative analysis of the influence of troposphere on imaging and give the threshold under the different parameters of GEO SAR systems. But the effects of the three categories were not separately analyzed and compared. The comparison of these three kinds of influences will be studied in future work. The phase errors can be expressed as
where is the ith temporal ROC in the error and P denotes the different locations.
2.2. Modeling of Turbulence Random Errors
2.2.1. Power Spectrum Model of Tropospheric Turbulence
Tropospheric turbulence will cause the random fluctuations of refractivity. A common model describing turbulence is atmospheric general circulation model (GCM) [], which is an atmospheric dynamics model that simulates global and large area climate change processes. It is used for weather forecasting, understanding the climate, and forecasting climate change. It may be not suitable for our research because we only study the tropospheric effects on GEO SAR for specific short period of time and relatively small scale, i.e., the synthetic aperture time and length. So in our paper, we choose the power spectrum density (PSD) obeying the power law distribution []:
where is the spatial wave number; , is inner scale, is outer scale; , , is the tropospheric refractivity structure constant which can express the turbulence intensity.
Compared to the Kolmogorov spectrum [] that only applies to the inertial zone and to the Tatarskii spectrum [] that applies to the inertial and dissipation zone, the Kolmogorov-von Karman spectrum can be used to describe the distribution of the tropospheric turbulence in the entire wave number domain []. Besides, the modified turbulence power spectrum is proposed which can describe the PSD of turbulence in all wave number domains:
where .
However, the turbulence is not static. There exists a movement of turbulence along with wind which will cause the temporal variation on turbulence PSD. Similar to the analysis from Pratsiraola et al. [], we analyze the time-varying characteristics by considering the drift velocity in the phase screen model. Firstly, starting from the autocorrelation function of refractivity and considering the drift velocity of turbulence, the PSD model affected by the drift velocity is obtained.
Assuming that the drift velocity is and the tropospheric penetrate point velocity is , then the status of the tropospheric irregularity located at at time after the time corresponds to the status of the tropospheric irregularity at time located at . This relationship can be expressed as refractivity autocorrelation function :
Therefore, considering the drift velocity, the autocorrelation function can be modified as
where is the velocity scale conversion rate and is relative velocity.
According to Wiener–Sinqin’s theorem, the refractivity autocorrelation function and its PSD are an Fourier transform pair (i.e., ). Therefore, the turbulence PSD considering time-varying can be obtained by scaling the original PSD:
It can be seen that will have effect on amplitude and cutoff frequency of PSD.
2.2.2. Turbulence Energy
The turbulence level in the troposphere is determined by the turbulence energy which is expressed as the variance of the refractive index . It can be obtained by integrating the refractivity structure spectrum in the inertial region. Taking (9) as an example, can be expressed as
where and .
Here we can define the factor G which represents the integral of the normalized shape of the PSD as
The value of G depends on the shape of the selected power spectrum. When different power spectra are chosen, G is different. So the relationship between and can be expressed as
2.2.3. Multiple Phase Screen Model
The amplitude and phase fluctuations caused by the tropospheric turbulence can be simulated using the phase screen theory similarly to the ionospheric scintillation. In this theory, the phase of the signal will be disturbed randomly when it traverses the turbulence (i.e., modeled as thin phase screens). Then the signal propagates in the free space after passing through the phase screen, the disturbing phase makes the wave fronts of the signal interfere with each other, causing the amplitude and phase fluctuations.
The ionospheric scintillation can be modeled as a thin screen at a height of ~350 km above the ground. The signal passes through the phase screen and propagates in the free space. The troposphere is different. The troposphere distributes from the ground to the height of ~10 km and there is no part of the signal that propagates in free space. The intensity of tropospheric turbulence (includes vortices caused by convection or wind shear) is related to altitude. It will reach maximum as it approaches the ground. However, if we divide the entire troposphere into multiple phase screens along the vertical height, the thinner the thickness of each subphase screen and the greater the total number of phase screens, the closer to the actual tropospheric distribution.
In this paper, we employ a multiphase screen theory to model turbulence as multiple thin screens, integrating the energy of each layer separately onto different thin screens. For simplicity, here we only consider the spatial coherence accumulation of each layer, regardless of the coherence between layers.
The disturbing phase introduced by the tropospheric turbulence can be described by the power spectrum . Assuming that the thickness of each layer is , the relationship of the phase power spectrum of the ith layer and the 2D power spectrum of the refractive index can be expressed as []
where . If is the total thickness of turbulence, we can divide the turbulence into layers. Equation (16) shows that the turbulence energy of each layer with a thickness of is integrated together to form a screen and radio waves continue to propagate in free space after passing it. So, phase screen theory can be used to analyze the impact of turbulence for each layer.
In the simulation, firstly, the PSD function is used to construct the phase random fluctuations:
where is the zero mean and unit variance Hermitian complex Gaussian random variable.
The signal propagating in turbulence can be modeled by parabolic wave function and solved through the multiple phase screen theory [,]. The amplitude fluctuations and phase fluctuations of the signal can be obtained by calculating the tropospheric transfer function .
where u is horizontal space position. Equation (18) is obtained using parabolic equation approximation []. It is noted that the Rytov approximation is also a theory to solve the random turbulence and the amplitude and phase fluctuations can be obtained by Rytov transform, which is seemly similar with (18). But the Rytov approximation can only solve the weak fluctuation problem, which is the limitation compared with the parabolic equation approximation. Therefore, in order to analyze the effects of turbulent strength on GEO SAR imaging in the subsequent content, we choose the parabolic equation approximation for phase screen theory in our paper.
Therefore, the total tropospheric transfer function is
As the GEO SAR orbit height is ~36,000 km, the heights of the ionosphere and troposphere relative to GEO SAR orbit are not much different. Therefore, the ionospheric transfer function (ITF) of ionospheric scintillation and tropospheric turbulence have similar pattern in GEO SAR cases.
3. GEO SAR Signal Modeling and Tropospheric Effect Analysis
According to the above analysis in Section 2, the phase errors introduced by the troposphere to the signal passing through it can be expressed as
where is the target in the different position and is the azimuth slow time. is the phase error introduced by the background troposphere, as shown in (7); is the random phase error introduced by tropospheric turbulence, as shown in (17).
Because the troposphere is a nondispersive medium, the effects of different frequency components are the same. Taking the background troposphere and turbulence into account, the accurate echo signals of the GEO SAR can be expressed as
where is the fast time, and are the envelope function in range and azimuth, respectively, is the range frequency modulation rate, is wavelength, is azimuthal slow time, and and are amplitude and phase errors introduced by turbulence, respectively.
3.1. Background Troposphere Effects Analysis
3.1.1. Theoretical Analysis
The troposphere is a nondispersive medium that has the same effect on different frequency signals and it cannot affect the imaging in range. Here we only consider GEO SAR azimuth signal influenced by troposphere. Time-varying tropospheric status and different propagation path’s lengths between the different pulses lead to different delay errors which will affect azimuth imaging. These influences are modeled as a series expansion form varying with slow time. The GEO SAR azimuth signal considering background troposphere is analyzed here which can be written as
where is azimuth slow time, is the integration time, is azimuth frequency modulation rate, is wavelength, and is the ith order rate of change of tropospheric delay error. Through the series inversion theory and the Fourier transform method [], the derived azimuth signal spectrum is
where is azimuth frequency, is the GEO SAR frequency-domain signal that is not affected by the troposphere, and is the phase error caused by . The delay introduced by is , so the azimuth image offset can be written as [,,]
where is the beam-foot velocity, which is defined as the speed of the radar beam center on the ground. Here, is employed because GEO SAR operates in ‘pseudo-spotlight’ mode [] which is caused by the ultrahigh orbit height and Earth rotation. It is noted that the beam-foot velocity and motion velocity are not approximately equal for GEO SAR due to the high-orbital characteristics, which are different from the LEO SAR and airborne SAR.
Since is inversely proportional to , the azimuthal offset is only related to when the acquisition geometry of GEO SAR or is fixed. Therefore, the azimuth shift does not depend on wavelength for GEO SAR.
The quadratic phase error of azimuth will cause the main lobe widening and sidelobes increasing. Taking the relationship of , and into account, substituting into and considering the largest error at edge of the aperture (i.e., ), the maximum second-order phase error of tropospheric delay can be obtained as
It can be seen that depends on , and .
The azimuthal third-order phase error produces the asymmetric sidelobes and may cause azimuthal defocusing. Similarly, the maximum of can be expressed as
It can be seen that depends on , and .
3.1.2. Analysis and Discussion on Impacts of Different GEO SAR Configurations
From the theoretical analysis in the previous section, the effects of the troposphere are not only related to the changes of the troposphere but also the GEO SAR system parameters (i.e., the configuration of the GEO SAR such as high inclination, low inclination, and near-zero inclination). The image shift caused by the troposphere mainly depends on the linear ROC of the troposphere. The tropospheric linear ROC is related to not only the status of the troposphere but also the propagation path. When the GEO SAR operates at a large squint angle or a large look angle, the ROC of the propagation path increases and the tropospheric impact is more serious. At this time, the linear ROC of the troposphere also increases and the image shift becomes more serious too. Besides, the look angles and the squint angles corresponding to the different targets in the scene are also different, resulting in the different offsets of different pixels in the image and causing image distortion.
According to the relationship between integration time, frequency modulation rate, and azimuth resolution, the maximum second-order phase error relating to the azimuth resolution can be obtained by substituting into (23). Equation (25) can be written as
where is azimuthal resolution and is the beam-foot velocity. When the geometric configuration and are fixed, the higher the resolution is, the more serious the quadratic phase error will be. When the wavelength and are fixed and the orbit configuration is unfixed, is related to and (and ). Therefore, the smaller is, the larger the quadratic phase error and the serious defocus will be. Generally, the smaller the orbital inclination is, the smaller will be and the more serious defocus will be. For the same orbital configuration (except the near-zero inclination), the perigee or apogee is the smallest, while the velocity is the largest near the equator. As a result, the levels of deterioration of different orbital positions are not same.
When only considering the impact of and the fixed size antenna, the shorter the wavelength is, the smaller the integration time is because of . Therefore, assuming the geometrical configurations are same, is proportional to the integration time.
When only considering the impact of , (27) can be written as
where is the slant range of zero-Doppler and is the azimuthal bandwidth. When the resolution is fixed, the larger the wavelength is, the more serious the impact will be. This can be also explained that much greater integration time is needed for longer wavelength when the resolution is fixed.
The third-order phase error introduced by the troposphere is only related to the integration time. The longer the integration time is, the more serious the impacts will be. However, for different configurations of GEO SAR, the small inclination GEO SAR needs longer integration time to achieve a certain resolution. Therefore, under the same resolution requirement, the smaller the orbital inclination is, the severer the tropospheric effect will be.
3.2. Tropospheric Turbulence Effect Analysis
GEO SAR azimuthal signal affected by turbulence can be written as
In order to investigate the degree of the fluctuation, is defined as the normalized amplitude standard deviation of , which describes the amplitude fluctuation strength; is the phase standard deviation of , which describes the phase fluctuation strength:
As and become greater, the turbulence will be more serious.
4. Simulations and Verifications
4.1. Background Troposphere
In this section, we will mainly use measured data (refractive index profile data from FY-3C and tropospheric zenith delay data from IGS), which changes slowly with time to complete the analysis of impacts on GEO SAR imaging. For the IGS data, the slant delay can be mapped from troposphere zenith delay data by mapping function to analyze the background tropospheric effects []. It is verified that these two methods can get the almost same conclusions because the first and second order rate of change (ROC) of tropospheric slant path delay is the same level, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Tropospheric delay of each order of time ROC in GEO SAR signal.
The atmospheric refractive index profile data was acquired from the FY-3C satellite [], released by China National Satellite Meteorological Center. The time interval is usually 2 to 5 min, including atmospheric refraction index, data time (year/month/day/hour/minute/second) and satellite position coordinates. The data from 18:28 to 18:40 on May 27, 2015 are selected for analysis and the data interval is 2 min. There are six sets of data in 10 min. Using the ray tracing method, the signal delay corresponding to the six sets of refractive index data is obtained, as shown by the red “+” in Figure 2. We calculate the amount of tropospheric delay per second by Lagrange interpolation [,], as shown in Figure 2a. Similarly, we also get the 12 min troposphere zenith path delay data from IGS BJFS site (Beijing) from 18:28 to 18:40 on May 27, 2015 [], where the data interval is 5 min. The slant path delay can be obtained by mapping function as shown in Figure 2b.
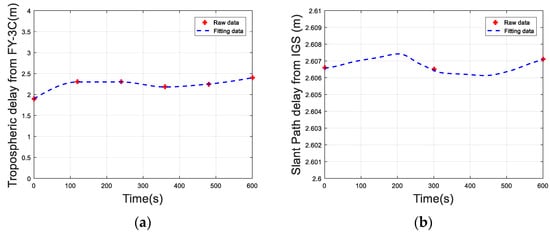
Figure 2.
Tropospheric signal delay based on measured data: (a) atmospheric refractive index profile data from FY-3C and (b) tropospheric zenith delay data from IGS.
Since FY-3C is a LEO satellite, the signal delay here is not fully equivalent to the effects of the troposphere on the GEO SAR signal. Therefore, equivalent treatment [] based on the GEO SAR and FY-3C satellite orbital parameters is required to calculate the tropospheric delay data on the GEO SAR signal propagation path. Every order ROCs can be obtained as shown in Table 1. We can find the first and second order ROC of FY-3C satellite and IGS are at same level. In the following, we mainly used FY-3C satellite data for more detailed analysis.
It is noted that the measured data is not representative for the atmospheric status in China. The main work of this paper is to establish a GEO SAR signal model considering the influence of the troposphere, and theoretically analyze the influence of the troposphere. The measured data here are only used to verify the correctness of the tropospheric model, but are not employed to give any conclusion of tropospheric effects in China or a region based on a large number of measured data.
The effects of background troposphere on GEO SAR imaging are related to the integration time except the azimuth shift. Although the troposphere is a nondispersive medium and does not affect imaging in slant range, the phase errors of GEO SAR at different wavelengths are different in the azimuthal imaging. The phase delay errors introduced by troposphere in different bands can be calculated by atmospheric refractive index profile data from FY-3C refractive index profile data, and is same for different bands since the troposphere is nondispersive medium. can be obtained by interpolation and fitting the raw refractive index profile data. According to the parameters in Table 1 and Table 2, the azimuth signals in different bands (L, S, C, and X) and different integration times can be determined and peak sidelobe ratio (PSLR) and integral sidelobe ratio (ISLR) can be obtained after pulse compression processing. The azimuthal PSLR and ISLR of L, S, C, and X bands are simulated based on (22). The evaluation results are shown in Figure 3. Tropospheric errors can cause image defocusing for long integration time. The smaller the wavelength is, the greater the impact will be. The changes of the troposphere can also result in azimuthal image shifts that are independent of the wavelength and integration time. Instead, it only depends on the linear ROC in the troposphere.

Table 2.
System and orbit parameters of GEO SAR.
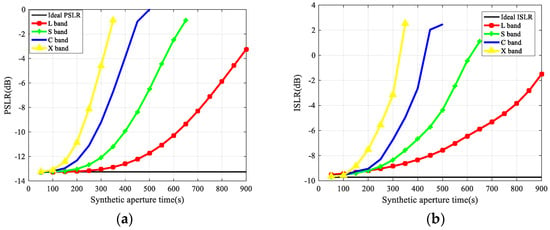
Figure 3.
Assessment of impacts on GEO SAR imaging of troposphere at different wavelengths and integration times (Red: L-band; green: S band; blue: C band; black: X band). (a) Peak sidelobe ratio (PSLR). (b) Integral sidelobe ratio (ISLR).
However, for the same integration time, GEO SAR with different wavelengths can reach different resolutions. The smaller the wavelength is, the higher the resolution will be. The following will analyze effects of various geometries configuration and wavelengths of GEO SAR on the troposphere for the same resolution. Table 3 shows the assessment of GEO SAR imaging of point target at different orbital positions for the L-band and X-band with low-inclination orbit and high-inclination orbit. The resolution is set as 10 m (other parameters are shown in Table 2). The image offset caused by troposphere is only related to the geometric configuration instead of the wavelength. However, due to the short wavelength of the X-band GEO SAR, less time is required to reach the same resolution of 10 m. Therefore, the X-band GEO SAR is less affected by the troposphere when the same resolution is required, and defocus occurs only in case of GEO SAR with low inclination. Under the same geometric configuration, the integration time of L-band system is nearly 2000 s, and the azimuth will be defocused due to the tropospheric influences. The point target azimuthal envelopes of L-band and X-band system in this case are shown in Figure 4.

Table 3.
Evaluations of point target imaging of GEO SAR with different orbital configurations at different wavelengths (P: perigee; E: equator; H: high-inclination; L: low-inclination).
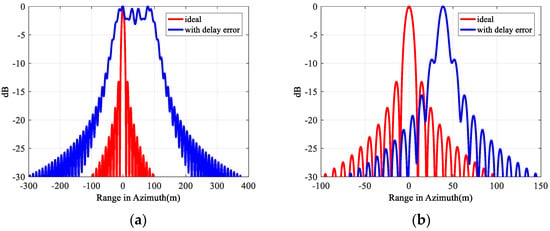
Figure 4.
The azimuthal profiles of point target imaging of low-inclination GEO SAR at perigee. (a) L-band. (b) X-band.
4.2. Tropospheric Turbulence
4.2.1. Simulations of Turbulent Energy
In this section, the effects of turbulence on GEO SAR imaging are analyzed by evaluating the azimuthal PSLR and ISLR. The amplitude and phase errors caused by turbulence are weak in nature and coupled with the random error of the system, making it difficult to accurately extract and reproduce. However, this random process can be described by spatial PSD and its energy. The effects of turbulence on imaging can be obtained by semiphysical simulation based on the turbulent energy and PSD shape.
Firstly, we simulate the PSD mentioned in Section 2 to choose an appropriate PSD for our analysis. Assuming that , , the surface temperature is 20.85 °C, the ground relative humidity is 76.8%, the inner scale is 5 cm, the outer scale is 100 m, and the thickness of turbulence is 500 m. The distributions of aforementioned four PSD are shown in Figure 5. It can be found that the modified turbulence PSD has the obvious input zone, inertial zone, and dissipative zone, which is more in line with the actually observed turbulence distribution. Different regions of PSD represent different status of troposphere []. The background troposphere mainly refers to the slowly changing part due to the large-scale variation and corresponds to the input region. The tropospheric turbulence refers to the dramatic changing part due to the small-scale vortices and corresponds to the inertial region. Therefore, the modified PSD shown as (14) is used in the following analysis and only the inertial zone is considered.
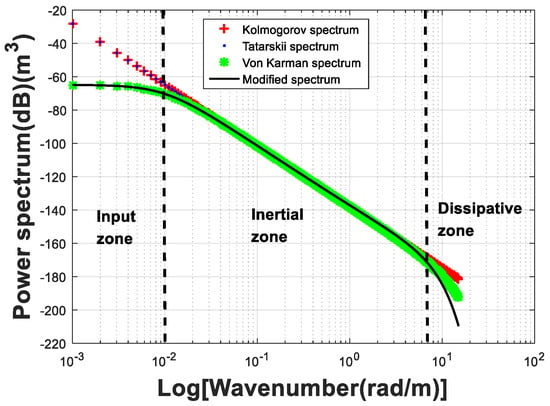
Figure 5.
The refractivity structure spectrum .
.
In nature, the intensity of the tropospheric turbulence is related to the atmospheric status. The turbulence intensity is represented by the refractivity structure constant , which is a function of altitude. Taking into account the changes of atmospheric humidity and water vapor content, can be expressed as []
where, , is the height of troposphere, is the RMS value of the wind speed along the vertical path, and the typical value is 21 m/s []. can be written as
where is the ground temperature and is the ground refractive rate.
We assume that the turbulent thickness is 1000 m. If the troposphere is divided into five layers, then
At this time, the distribution of and the percentage of energy in each layer are shown in Figure 6.
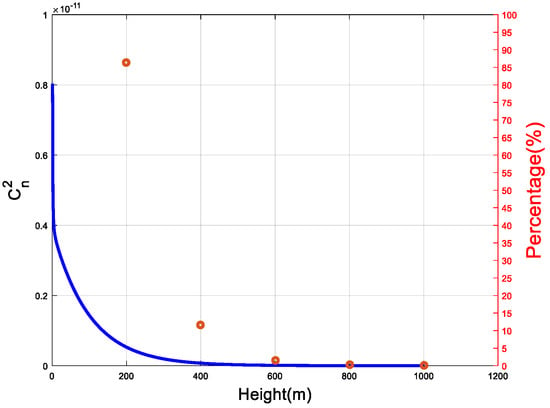
Figure 6.
The distribution of and the percentage of energy in each layer.
The percentage of turbulent energy at the height of 200 m from the ground is above 85%. Therefore, the following analysis is about the impact of only one layer of turbulence.
The intensity of tropospheric turbulence can be expressed as the refractive index variance , whose unit is []. Figure 7 shows the random phase power spectra for and on the L-band and the amplitude and phase fluctuations produced by the phase screen method.
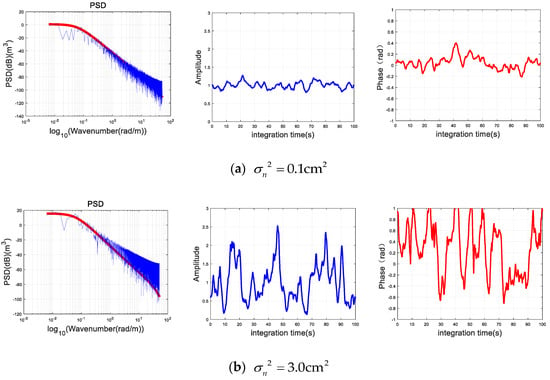
Figure 7.
The power spectrum density, the amplitude and phase fluctuations at different turbulence intensities. (a) ; (b) . (Top: the power spectrum; bottom: amplitude and phase fluctuations.)
We can find that the amplitude and phase fluctuations become more obvious when increases. In the simulation, we assume equals to , , , and , respectively. The corresponding values of , and can be obtained by (31) and (30). Then the Monte Carlo simulation is carried out that the fluctuations are generated and measured by and . The results are shown in Figure 8. increases with the increase of , which indicates the change of turbulence intensity. Meanwhile, the and increase with the increase of turbulence intensity, indicating that the amplitude and phase fluctuations of signal become serious with the increase of tropospheric turbulence.
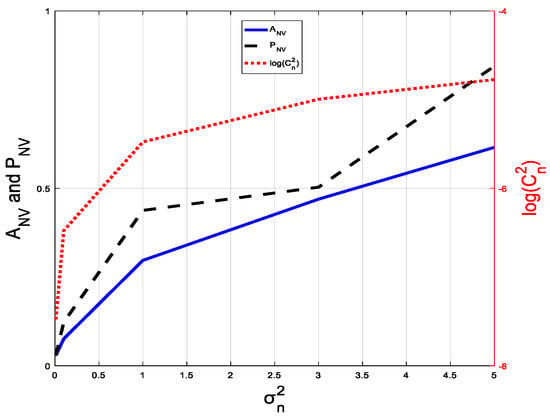
Figure 8.
Changes of , and with . (blue: ; black: ; red: ).
4.2.2. Simulation of Point Target
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the tropospheric turbulence may cause the amplitude and phase of the signal to fluctuate, resulting in the deterioration of GEO SAR imaging quality. Therefore, for different integration time and wavelengths, impacts of tropospheric turbulence on imaging are analyzed by evaluating point target imaging. The system parameters of GEO SAR are shown in Table 2. Actually, in nature, the typical values of are generally between (weak turbulence) and (strong turbulence). Assuming that , which is the value in extreme unstable atmospheric conditions, the amplitude fluctuations and phase fluctuations , which have effects on imaging, can be obtained by phase screen theory. The averages of PSLR and ISLR with Monte Carlo simulation of the L-, C-, and X-band point target imaging for different integration time are analyzed in Table 4. We found that tropospheric turbulence has little effect on the L/C band in the inertial region, while has a slight effect for X-band.

Table 4.
The imaging results in extreme unstable atmospheric conditions for different bands and integration time.
Since the turbulence of the inertial region in nature is not great enough to cause serious influence, in order to analyze the influence of different turbulent energy, wavelength and integration time, needs to enlarged artificially. We give the results in Appendix A. Table A1 presents the averages of PSLR and ISLR with Monte Carlo simulation of the L-, C-, and X-band point target imaging. Table A2 shows the Monte Carlo simulation results of target imaging at 100 s, 150 s, and 300 s with different wavelengths when .
According to Table A1, it can be seen that the larger the turbulence intensity is, the more severe the PSLR and ISLR will be. However, for the L-band, the PSLR does not change much. For the same turbulence intensity, the higher the signal frequency is, the worse the PSLR and ISLR will be.
Figure 9 shows the azimuthal profiles of different for L-band. The red line represents the azimuthal profiles without tropospheric turbulence.
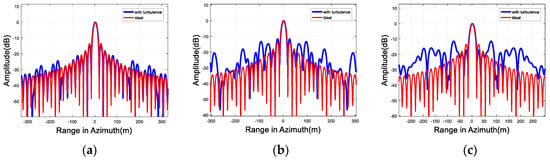
Figure 9.
Azimuthal profiles for L-band. (a) ; (b) ; (c) .
It can be seen that, for the L-band, with the increase of , the PSLR has a slight deterioration while the ISLR has a significant deterioration, which is consistent with the experimental data.
4.2.3. Discussion
From the previous analysis we can see that the order of magnitude of is and the fluctuations are not obvious when . It is 5 to 9 orders of magnitude greater than the turbulence in nature, whose lies between (weak) and (strong turbulence). In the extreme unstable atmospheric conditions, can only achieve up to magnitude [], but still much less than .
Therefore, the tropospheric turbulence of inertial subrange basically has no effect on the imaging in nature, only has slightly effect on X-band as shown in Table 4. It is noted that the atmospheric turbulence is dependent on the hour of the day, with low relative disturbances at night hours and maximum turbulence around noon. We use which is ~ in nature to indicate turbulent energy. Therefore, it has included all-day turbulence distribution. Since the strongest turbulence has no obvious effect on GEO SAR according to the subsequent analysis, no analysis is performed for specific time interval.
In fact, the azimuthal SAR signal impacted by turbulence is
Considering the turbulence is very weak in microwave band, only the phase fluctuation need to be considered. The SAR signal can be rewritten using Taylor expansion as
Then it can be transformed into the frequency domain [] to complete the analysis of turbulence effects:
where, is spectral convolution, is the power spectrum density of the random phase, and is the azimuthal frequency. Due to the long integration time of GEO SAR (generally above 100 s), the main lobe of is within 0.01 Hz. Considering the relationship of azimuthal frequency and spatial frequency, we can write as []
where, is the beam-foot velocity.
As the tropospheric turbulence occurs mainly near the surface, where the speed is generally below 30 m/s. The sum velocity of wind speed and is still at the level of (as shown in Figure 10). Here we employ the value of for analysis. We can get the expression of in the inertial zone:
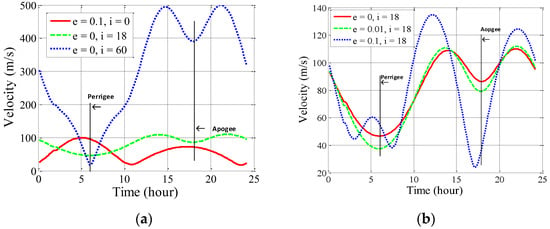
Figure 10.
Beam-foot velocity variations of GEO SAR with different orbital configurations. (a) Different orbital inclinations and (b) different eccentricity in case of 18° inclination.
So cutoff frequency of the power spectrum is . When the integration time is above 100 s, we can get . Combined with (40), the turbulence only affects the side lobe rather than the main lobe and the degree of influence depends on the turbulent energy.
When , we can get the and in nature:
So the ISLR can be expressed as
where is the ideal ISLR. In the natural, and are too much smaller, as shown in (41), and are sure to be ignored.
As mentioned above, the turbulence energy in nature is very small and the influence on GEO SAR in low-frequency bands can be ignored.
Here, it is noted that variations of the tropospheric measures can reach a standard deviation of 0.3–0.5 cm [,] which cannot be ignored in X-band systems. This conclusion seems to be mismatched with the one here, but actually it is just a verification of our research from another aspect. In the measurement, the tropospheric variations consist of both the slow-varying tropospheric component and the fast-varying turbulent component. However, in this section, the standard deviation of the path delay is only related to the tropospheric turbulence. But when considering the slow-varying troposphere together, i.e., background troposphere, the total path delay standard deviation caused by troposphere reaches 0.843 cm (considering the slow-varying component in Table 1 and fast-varying turbulence by Figure 6 and (13)). Thus, the varying troposphere will be sure to affect the X-band signal. Besides, it is calculated that the total path delay standard deviation from IGS zenith delay data can also reach 0.56 cm, which can also verify our conclusions.
5. Conclusions
GEO SAR has the characteristics of long synthetic aperture time and large observation range, and the atmosphere changes more severely with time and space. In this paper, we model and analyze the tropospheric influences on GEO SAR, including background troposphere and turbulence.
For the background tropospheric influences, the changing troposphere causes the GEO SAR image to shift and the offset is only related to the first-order ROC instead of the orbital configuration and the wavelength. The high order of phase error will accumulate within the long integration time, which results in image defocusing. Through the theoretical analysis and the verification of FY-3C satellite data and IGS data, we can get two important conclusions. Firstly, the shorter wavelength is, the greater tropospheric ROCs will be and the higher azimuth resolution will be required, which will result in more serious deterioration on GEO SAR image. Secondly, when the azimuthal resolution is fixed, the smaller the beam-foot velocity is and the longer the integration time is, the more serious the deterioration will be.
For the tropospheric turbulence, it will produce the random amplitude and phase fluctuations which results in the image defocusing. We mainly analyze the effects of turbulence on GEO SAR imaging by phase screen theory and simulation verification. We find that the short wavelength signals are more susceptible to the turbulence. Besides, we also find that in nature the tropospheric turbulence of inertial subrange has a negligible effect on the GEO SAR imaging in nature, and only slightly influences the X-band. The tropospheric effects could affect the GEO SAR interferometry and differential interferometry performance, which can be studied in future work.
Author Contributions
Data Curation, Y.L. and Y.T.; Formal Analysis, X.D.; Investigation, Y.L.; Methodology, X.D. and J.H.; Supervision, T.L.; Writing—Original Draft, X.D. and J.H.; Writing—Review & Editing, C.H.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61827901, 61501032, and 61471038; the Chang Jiang Scholars Program (T2012122); the 111 project of China under Grant B14010; the Beijing Natural Science Foundation under Grant 4162052; and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2017QNRC001).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Satellite Meteorological Centre for FY-3C refractive index profile data and International GNSS Service for troposphere zenith path delay data. The refractive index profile data are downloaded from: http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/portalsite/StaticContent/Load_Profile/FY_3C/Instrument/gnos.aspx?currentculture=en-US. The troposphere zenith path delay data is downloaded from: ftp://cddis.nasa.gov/gnss/products/troposphere/zpd/.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Influences of Different Wavelengths and Turbulent Energies
Given the values of , can be calculated by (15) and the amplitude fluctuations and phase fluctuations which have effects on imaging can be obtained by phase screen theory.
When the integration time is 100 s, the averages of PSLR and ISLR with Monte Carlo simulation of the L, C, and X-band point target imaging are analyzed in Appendix, where the refractive index variance are assumed as , , and , respectively.

Table A1.
Evaluations of azimuth profiles of point target under L-, C-, and X-bands (integration time is 100 s).
Table A1.
Evaluations of azimuth profiles of point target under L-, C-, and X-bands (integration time is 100 s).
| Band | PSLR (dB) (Average Value) | ISLR (dB) (Average Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 0.1 | −13.41 | −9.19 |
| 1.0 | −12.45 | −5.91 | |
| 3.0 | −11.45 | −2.66 | |
| C | 0.1 | −10.49 | −1.21 |
| 1.0 | −7.01 | 1.76 | |
| 3.0 | −5.49 | 4.48 | |
| X | 0.1 | −9.17 | −0.21 |
| 1.0 | −5.55 | 5.71 | |
| 3.0 | −2.03 | 6.96 |
Appendix B. Influence of Different Integration Time
Table A2 shows the Monte Carlo simulation results of target imaging at 100 s, 150 s, and 300 s for different wavelengths when .

Table A2.
Evaluations of point target imaging for different bands and different integration time.
Table A2.
Evaluations of point target imaging for different bands and different integration time.
| Band | Integration Time(s) | PSLR (dB) (Average Value) | ISLR (dB) (Average Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 100 | −13.41 | −9.11 |
| 150 | −13.58 | −8.68 | |
| 300 | −12.57 | −6.63 | |
| C | 100 | −12.71 | −3.52 |
| 150 | −9.47 | −0.98 | |
| 300 | −7.06 | 2.27 | |
| X | 100 | −8.39 | −0.34 |
| 150 | −6.96 | 2.21 | |
| 300 | −3.77 | 4.01 |
References
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Local structure of turbulence in an incompressible viscous fluid at very high reynolds numbers. Phys. Uspekhi 1968, 10, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quegan, S.; Lamont, J. Ionospheric and tropospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, W. High resolution SAR performance limitation by the change of tropospheric refractivity. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 24–27 October 2011; Volume 2, pp. 1448–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Hu, W. Multiband Microwave Imaging Analysis of Ionosphere and Troposphere Refraction for Spaceborne SAR. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 913056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, R.M.; Uson, M.F.; Ibars, A.B. Interferometric orbit determination for geostationary satellites. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, R.; Cui, C. Optimal 3D deformation measuring in inclined geosynchronous orbit SAR differential interferometry. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcello, L.J. Turbulence-Induced Phase Errors in Synthetic-Aperture Radars. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1970, AES-6, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fante, R.L. Turbulence-induced distortion of synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, F.M.; DeLaurentis, J.M.; Doerry, A.W. A SAR imaging model for large-scale atmospheric inhomogeneities. In Proc. SPIE 5410, Radar Sensor Technology VIII and Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technology VII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2004; Volume 5410, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Muschinski, A.; Dickey, F.M.; Doerry, A.W. Possible effects of clear-air refractive-index perturbations on SAR images. In Proc. SPIE 5788, Radar Sensor Technology IX; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5788, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, F.M.; Doerry, A.W.; Romero, L.A. Degrading effects of the lower atmosphere on long-range airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging. IET Radarsonar Navig. 2007, 1, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danklmayer, A.; Doring, B.; Schwerdt, M.; Chandra, M. Assessment of Atmospheric Propagation Effects in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3507–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.Z.C.; Dong, X.; Li, Y. Geosynchronous SAR Tomography: Theory and First Experimental Verification using Beidou IGSO Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Ding, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y. Beam scan mode analysis and design for geosynchronous SAR. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Hu, C.; Ding, Z.; Dong, X.; Tian, W.; Zeng, T. Geosynchronous SAR: System and Signal Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Hu, C.; Rocca, F. Performance and Requirements of GEO SAR Systems in the Presence of Radio Frequency Interferences. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Xiao, F.; Xie, Y.; Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Long, T. A Modified Fixed-Point Chirp Scaling Algorithm Based on Updating Phase Factors Regionally for Spaceborne SAR Real-Time Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7436–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Dong, X.; Hu, C.; Sun, Y. GRFT-Based Moving Ship Target Detection and Imaging in Geosynchronous SAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ye, T.; Dong, X.; Rui, W.; Teng, L. Computerized Ionospheric Tomography Based on Geosynchronous SAR: CIT based on geosynchronous SAR. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 2686–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Potential of geosynchronous SAR interferometric measurements in estimating three-dimensional surface displacements. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.; Mitchell, C.N.; Forte, B.; Holley, R.; Snapir, B.; Whittaker, P. System Design for Geosynchronous Synthetic Aperture Radar Missions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 7750–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Hobbs, S.E. Radar Imaging From Geosynchronous Orbit: Temporal Decorrelation Aspects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rodriguezcassola, M.; Pratsiraola, P.; Dong, Z.; Wu, M.; Moreira, A. Modelling of tropospheric delays in geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Wadge, G.; Schulz, D. GeoSTARe initial mission design. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F.; Ibars, A.B. Impact of atmospheric water vapor on the design of a Ku band geosynchronous SAR system. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. II-945–II-948. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F. Options for continuous radar Earth observations. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.; Sanchez, J.P. Laplace plane and low inclination geosynchronous radar mission design. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGuarnieri, M.; Tebaldini, S.; Rocca, F.; Broquetas, A. GEMINI: Geosynchronous SAR for Earth Monitoring by Interferometry and Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Broquetas, A.; Recchia, A.; Rocca, F.; Ruiz-Rodon, J. Advanced Radar Geosynchronous Observation System: ARGOS. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JRodon, R.; Broquetas, A.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F. Geosynchronous SAR Focusing With Atmospheric Phase Screen Retrieval and Compensation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4397–4404. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Rodon, J.; Broquetas, A.; Makhoul, E.; Guarnieri, A.M.; Rocca, F. Nearly Zero Inclination Geosynchronous SAR Mission Analysis With Long Integration Time for Earth Observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, A.M.; Leanza, A.; Recchia, A.; Tebaldini, S.; Venuti, G. Atmospheric Phase Screen in GEO-SAR: Estimation and Compensation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.-L.; Wang, X.-Q.; Xiang, M.-S.; Chong, J.-S.; Zhu, M.-H. Effect of orbital errors on the geosynchronous circular synthetic aperture radar imaging and interferometric processing. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2011, 12, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Xiang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M. Tropospheric effects on L-band geosynchronous circular SAR imaging. IET Radarsonar Navig. 2013, 7, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Cheng, H.; Xichao, D.; Tao, Z.; Teng, L.; Kuan, L.; Xinyu, Z. Theoretical Analysis and Verification of Time Variation of Background Ionosphere on Geosynchronous SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 721–725. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, R.; Ao, D. Performance Analysis of L-Band Geosynchronous SAR Imaging in the Presence of Ionospheric Scintillation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Hobbs, S.E.; Tian, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, L. Joint Amplitude-Phase Compensation for Ionospheric Scintillation in GEO SAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3454–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Hu, C.; Tian, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, Y.; Long, T. Experimental Study of Ionospheric Impacts on Geosynchronous SAR Using GPS Signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofsted, D.H. Turbulence Simulation: Outer Scale Effects on the Refractive Index Spectrum; Army Research Laboratory: Adelphi, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, L.; Nievinski, F.G.; Santos, M.C. Ray-traced slant factors for mitigating the tropospheric delay at the observation level. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, D.; Macmillan, D.S.; Gipson, J. Tropospheric delay ray tracing applied in VLBI analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 9156–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, B.W.; Axelrad, P.; Enge, P. Global Positioning System Theory and Applications; AAIA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Wikipedia: General Circulation Model. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/General_circulation_model (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Von Karman, T. Progress in the Statistical Theory of Turbulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1948, 34, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The Local Structure of Turbulence in Incompressible Viscous Fluid for Very Large Reynolds Numbers. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1991, 434, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, A. Temporal frequency spectra of multifrequency waves in turbulent atmosphere. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1972, 20, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, L.C. An Analytical Model for the Refractive Index Power Spectrum and Its Application to Optical Scintillations in the Atmosphere. J. Mod. Opt. 1992, 39, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratsiraola, P.; Lopezdekker, P.; de Zan, F.; Yaguemartinez, N.; Zonno, M.; Rodriguezcassola, M. Performance of 3-D Surface Deformation Estimation for Simultaneous Squinted SAR Acquisitions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, V.; Feral, L. Comparison of 2D and 3D Electromagnetic Approaches to Predict Tropospheric Turbulence Effects in Clear Sky Conditions. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 4398–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, C.S.; Groves, K.M.; Caton, R.G. Simulating the impacts of ionospheric scintillation on L band SAR image formation. Radio Sci. 2012, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging degradations imposed by ionospheric irregularities. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 060308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontovich, M.; Fock, V. Solution of the problem of propagation of electromagnetic waves along the earth’s surface by the method of parabolic equation. J. Phys. USSR 1946, 10, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Tian, Y.; Yang, X.; Zeng, T.; Long, T.; Dong, X. Background Ionosphere Effects on Geosynchronous SAR Focusing: Theoretical Analysis and Verification Based on the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.J. Performance Requirements for Ionospheric Correction of Low-Frequency SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3694–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Yin, W.; Ding, Z.; Long, T. Motion and Doppler Characteristics Analysis Based on Circular Motion Model in Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FY-3C Global Navigation Satellite System Occultation Sounder (GNOS). Available online: http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/portalsite/StaticContent/Load_Profile/FY_3C/Instrument/gnos.aspx?currentculture=en-US (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Berrut, J.; Trefethen, L.N. Barycentric Lagrange Interpolation. SIAM Rev. 2004, 46, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetken, G. A new approach for the design of digital interpolating filters. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speechand Signal Process. 1979, 27, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International GNSS Service (IGS) Troposphere Zenith Delay Data. Available online: ftp://cddis.nasa.gov/gnss/products/troposphere/zpd/ (accessed on 26 March 2019).
- International Telecommunications Union. Recommendation ITU-R S.484-3, Station-Keeping in Longitude of Geostationary Satellites in the Fixed-Satellite Service; International Telecommunications Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jinping, S.; Yuekai, B.; Xiao, H.; Yanping, W. Turbulence effects on high resolution airborne SAR performance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics Communications and Control, Ningbo, China, 9–11 September 2011; pp. 1190–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Tunick, A.; Army Research Laboratory (Eds.) The Refractive Index Structure Parameter/Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Model:CN2; Army Research Laboratory: Adelphi, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fremouw, E.J.; Leadabrand, R.L.; Livingston, R.C.; Cousins, M.D.; Rino, C.L.; Fair, B.C.; Long, R.A. Early results from the DNA Wideband satellite experiment—Complex-signal scintillation. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keihm, S.J. Water Vapor Radiometer Measurements of the Tropospheric Delay Fluctuations at Goldstone Over a Full Year; TDA Progress Report; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Realini, E.; Tsuda, T.; Sato, K.; Oigawa, M.; Iwaki, Y. Analysis of the Temporal and Spatial Variability of the Wet Troposphere at a Local Scale by High-rate PPP Using a Dense GNSS Network. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2012), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–22 September 2012; pp. 3406–3412. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).